File size: 7,597 Bytes
c78c28e |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 |
# Model Overview
A pre-trained model for 3D segmentation of the spleen organ from CT images using DeepEdit.
DeepEdit is an algorithm that combines the power of two models in one single architecture. It allows the user to perform inference as a standard segmentation method (i.e., UNet) and interactively segment part of an image using clicks [2]. DeepEdit aims to facilitate the user experience and, at the same time, develop new active learning techniques.
The model was trained on 32 images and validated on 9 images.
## Data
The training dataset is the Spleen Task from the Medical Segmentation Decathalon. Users can find more details on the datasets at http://medicaldecathlon.com/.
- Target: Spleen
- Modality: CT
- Size: 61 3D volumes (41 Training + 20 Testing)
- Source: Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
- Challenge: Large-ranging foreground size
## Training configuration
The training as performed with the following:
- GPU: at least 12GB of GPU memory
- Actual Model Input: 128 x 128 x 128
- AMP: True
- Optimizer: Adam
- Learning Rate: 1e-4
- Loss: DiceCELoss
### Input
Three channels
- CT image
- Spleen Segment
- Background Segment
### Output
Two channels
- Label 1: spleen
- Label 0: everything else
## Performance
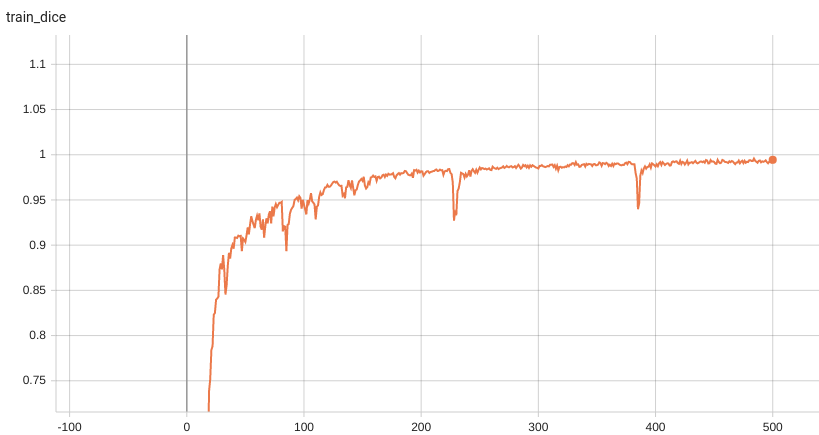
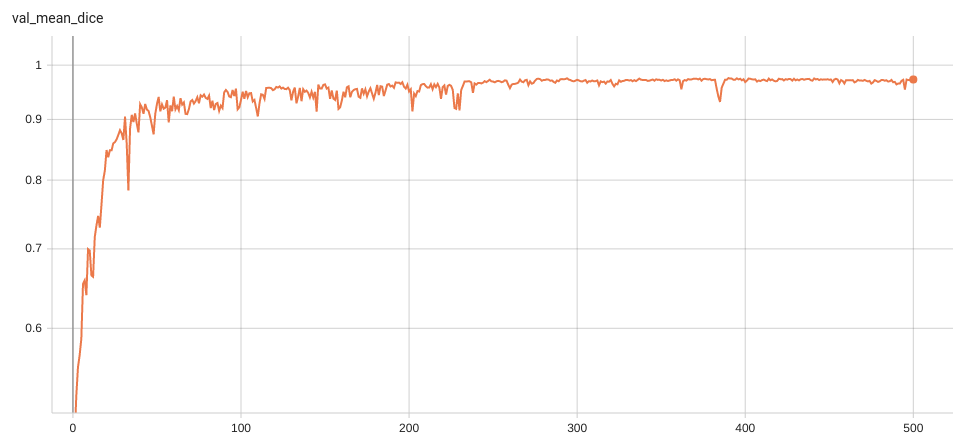
Dice score is used for evaluating the performance of the model. This model achieves a dice score of 0.97, depending on the number of simulated clicks.
#### Training Dice
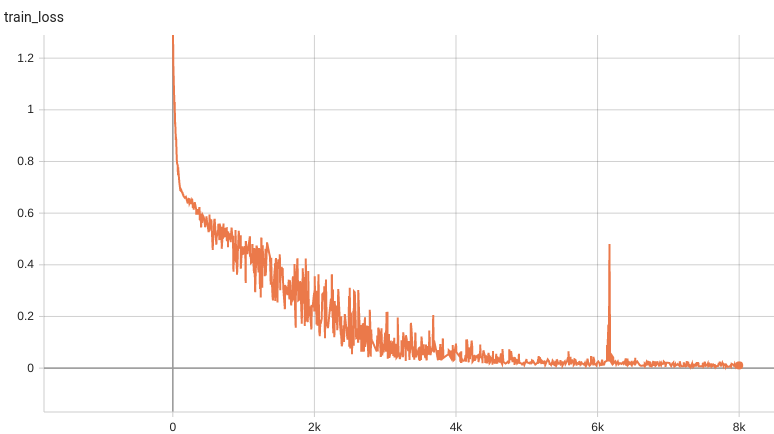
#### Training Loss
#### Validation Dice
#### TensorRT speedup
The `spleen_deepedit_annotation` bundle supports acceleration with TensorRT through the ONNX-TensorRT method. The table below displays the speedup ratios observed on an A100 80G GPU.
| method | torch_fp32(ms) | torch_amp(ms) | trt_fp32(ms) | trt_fp16(ms) | speedup amp | speedup fp32 | speedup fp16 | amp vs fp16|
| :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: |
| model computation | 147.52 | 40.32 | 28.87 | 11.94 | 3.66 | 5.11 | 12.36 | 3.38 |
| end2end |1292.39 | 1204.62 | 1168.09 | 1149.88 | 1.07 | 1.11 | 1.12 | 1.05 |
Where:
- `model computation` means the speedup ratio of model's inference with a random input without preprocessing and postprocessing
- `end2end` means run the bundle end-to-end with the TensorRT based model.
- `torch_fp32` and `torch_amp` are for the PyTorch models with or without `amp` mode.
- `trt_fp32` and `trt_fp16` are for the TensorRT based models converted in corresponding precision.
- `speedup amp`, `speedup fp32` and `speedup fp16` are the speedup ratios of corresponding models versus the PyTorch float32 model
- `amp vs fp16` is the speedup ratio between the PyTorch amp model and the TensorRT float16 based model.
Currently, the only available method to accelerate this model is through ONNX-TensorRT. However, the Torch-TensorRT method is under development and will be available in the near future.
This result is benchmarked under:
- TensorRT: 8.5.3+cuda11.8
- Torch-TensorRT Version: 1.4.0
- CPU Architecture: x86-64
- OS: ubuntu 20.04
- Python version:3.8.10
- CUDA version: 12.0
- GPU models and configuration: A100 80G
### Memory Consumption
- Dataset Manager: CacheDataset
- Data Size: 61 3D Volumes
- Cache Rate: 1.0
- Single GPU - System RAM Usage: 8.2G
### Memory Consumption Warning
If you face memory issues with CacheDataset, you can either switch to a regular Dataset class or lower the caching rate `cache_rate` in the configurations within range [0, 1] to minimize the System RAM requirements.
## MONAI Bundle Commands
In addition to the Pythonic APIs, a few command line interfaces (CLI) are provided to interact with the bundle. The CLI supports flexible use cases, such as overriding configs at runtime and predefining arguments in a file.
For more details usage instructions, visit the [MONAI Bundle Configuration Page](https://docs.monai.io/en/latest/config_syntax.html).
#### Execute training:
```
python -m monai.bundle run --config_file configs/train.json
```
Please note that if the default dataset path is not modified with the actual path in the bundle config files, you can also override it by using `--dataset_dir`:
```
python -m monai.bundle run --config_file configs/train.json --dataset_dir <actual dataset path>
```
#### Override the `train` config to execute multi-GPU training:
```
torchrun --standalone --nnodes=1 --nproc_per_node=2 -m monai.bundle run --config_file "['configs/train.json','configs/multi_gpu_train.json']"
```
Please note that the distributed training-related options depend on the actual running environment; thus, users may need to remove `--standalone`, modify `--nnodes`, or do some other necessary changes according to the machine used. For more details, please refer to [pytorch's official tutorial](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/ddp_tutorial.html).
#### Override the `train` config to execute evaluation with the trained model:
```
python -m monai.bundle run --config_file "['configs/train.json','configs/evaluate.json']"
```
#### Execute inference:
```
python -m monai.bundle run --config_file configs/inference.json
```
Optionally, clicks can be added to the data dictionary that is passed to the preprocessing transforms. The add keys are defined in `label_names` in `configs/inference.json`, and the corresponding values are the point coordinates. The following is an example of a data dictionary:
```
{"image": "example.nii.gz", "background": [], "spleen": [[I1, J1, K1], [I2, J2, K2]]}
```
where **[I1,J1,K1]** and **[I2,J2,K2]** are the point coordinates.
#### Export checkpoint to TensorRT based models with fp32 or fp16 precision:
```bash
python -m monai.bundle trt_export --net_id network_def \
--filepath models/model_trt.ts --ckpt_file models/model.pt \
--meta_file configs/metadata.json --config_file configs/inference.json \
--precision <fp32/fp16> --use_onnx "True" --use_trace "True"
```
#### Execute inference with the TensorRT model:
```
python -m monai.bundle run --config_file "['configs/inference.json', 'configs/inference_trt.json']"
```
# References
[1] Diaz-Pinto, Andres, et al. DeepEdit: Deep Editable Learning for Interactive Segmentation of 3D Medical Images. MICCAI Workshop on Data Augmentation, Labelling, and Imperfections. MICCAI 2022.
[2] Diaz-Pinto, Andres, et al. "MONAI Label: A framework for AI-assisted Interactive Labeling of 3D Medical Images." arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.12362 (2022).
[3] Sakinis, Tomas, et al. "Interactive segmentation of medical images through fully convolutional neural networks." arXiv preprint arXiv:1903.08205 (2019).
# License
Copyright (c) MONAI Consortium
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
|