# 이미지 캡셔닝[[image-captioning]]
[[open-in-colab]]
이미지 캡셔닝(Image captioning)은 주어진 이미지에 대한 캡션을 예측하는 작업입니다.
이미지 캡셔닝은 시각 장애인이 다양한 상황을 탐색하는 데 도움을 줄 수 있도록 시각 장애인을 보조하는 등 실생활에서 흔히 활용됩니다.
따라서 이미지 캡셔닝은 이미지를 설명함으로써 사람들의 콘텐츠 접근성을 개선하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
이 가이드에서는 소개할 내용은 아래와 같습니다:
* 이미지 캡셔닝 모델을 파인튜닝합니다.
* 파인튜닝된 모델을 추론에 사용합니다.
시작하기 전에 필요한 모든 라이브러리가 설치되어 있는지 확인하세요:
```bash
pip install transformers datasets evaluate -q
pip install jiwer -q
```
Hugging Face 계정에 로그인하면 모델을 업로드하고 커뮤니티에 공유할 수 있습니다.
토큰을 입력하여 로그인하세요.
```python
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
notebook_login()
```
## 포켓몬 BLIP 캡션 데이터세트 가져오기[[load-the-pokmon-blip-captions-dataset]]
{이미지-캡션} 쌍으로 구성된 데이터세트를 가져오려면 🤗 Dataset 라이브러리를 사용합니다.
PyTorch에서 자신만의 이미지 캡션 데이터세트를 만들려면 [이 노트북](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/GIT/Fine_tune_GIT_on_an_image_captioning_dataset.ipynb)을 참조하세요.
```python
from datasets import load_dataset
ds = load_dataset("lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions")
ds
```
```bash
DatasetDict({
train: Dataset({
features: ['image', 'text'],
num_rows: 833
})
})
```
이 데이터세트는 `image`와 `text`라는 두 특성을 가지고 있습니다.
많은 이미지 캡션 데이터세트에는 이미지당 여러 개의 캡션이 포함되어 있습니다.
이러한 경우, 일반적으로 학습 중에 사용 가능한 캡션 중에서 무작위로 샘플을 추출합니다.
[~datasets.Dataset.train_test_split] 메소드를 사용하여 데이터세트의 학습 분할을 학습 및 테스트 세트로 나눕니다:
```python
ds = ds["train"].train_test_split(test_size=0.1)
train_ds = ds["train"]
test_ds = ds["test"]
```
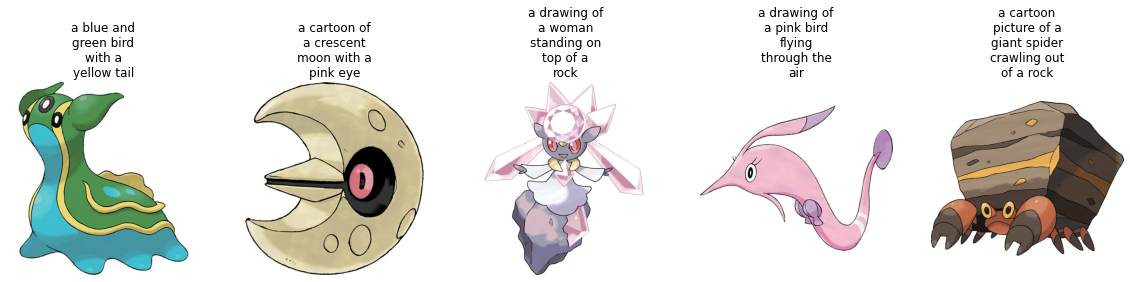
학습 세트의 샘플 몇 개를 시각화해 봅시다.
Let's visualize a couple of samples from the training set.
```python
from textwrap import wrap
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def plot_images(images, captions):
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 20))
for i in range(len(images)):
ax = plt.subplot(1, len(images), i + 1)
caption = captions[i]
caption = "\n".join(wrap(caption, 12))
plt.title(caption)
plt.imshow(images[i])
plt.axis("off")
sample_images_to_visualize = [np.array(train_ds[i]["image"]) for i in range(5)]
sample_captions = [train_ds[i]["text"] for i in range(5)]
plot_images(sample_images_to_visualize, sample_captions)
```
## 데이터세트 전처리[[preprocess-the-dataset]]
데이터세트에는 이미지와 텍스트라는 두 가지 양식이 있기 때문에, 전처리 파이프라인에서 이미지와 캡션을 모두 전처리합니다.
전처리 작업을 위해, 파인튜닝하려는 모델에 연결된 프로세서 클래스를 가져옵니다.
```python
from transformers import AutoProcessor
checkpoint = "microsoft/git-base"
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
```
프로세서는 내부적으로 크기 조정 및 픽셀 크기 조정을 포함한 이미지 전처리를 수행하고 캡션을 토큰화합니다.
```python
def transforms(example_batch):
images = [x for x in example_batch["image"]]
captions = [x for x in example_batch["text"]]
inputs = processor(images=images, text=captions, padding="max_length")
inputs.update({"labels": inputs["input_ids"]})
return inputs
train_ds.set_transform(transforms)
test_ds.set_transform(transforms)
```
데이터세트가 준비되었으니 이제 파인튜닝을 위해 모델을 설정할 수 있습니다.
## 기본 모델 가져오기[[load-a-base-model]]
["microsoft/git-base"](https://huggingface.co/microsoft/git-base)를 [`AutoModelForCausalLM`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/auto#transformers.AutoModelForCausalLM) 객체로 가져옵니다.
```python
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
```
## 평가[[evaluate]]
이미지 캡션 모델은 일반적으로 [Rouge 점수](https://huggingface.co/spaces/evaluate-metric/rouge) 또는 [단어 오류율(Word Error Rate)](https://huggingface.co/spaces/evaluate-metric/wer)로 평가합니다.
이 가이드에서는 단어 오류율(WER)을 사용합니다.
이를 위해 🤗 Evaluate 라이브러리를 사용합니다.
WER의 잠재적 제한 사항 및 기타 문제점은 [이 가이드](https://huggingface.co/spaces/evaluate-metric/wer)를 참조하세요.
```python
from evaluate import load
import torch
wer = load("wer")
def compute_metrics(eval_pred):
logits, labels = eval_pred
predicted = logits.argmax(-1)
decoded_labels = processor.batch_decode(labels, skip_special_tokens=True)
decoded_predictions = processor.batch_decode(predicted, skip_special_tokens=True)
wer_score = wer.compute(predictions=decoded_predictions, references=decoded_labels)
return {"wer_score": wer_score}
```
## 학습![[train!]]
이제 모델 파인튜닝을 시작할 준비가 되었습니다. 이를 위해 🤗 [`Trainer`]를 사용합니다.
먼저, [`TrainingArguments`]를 사용하여 학습 인수를 정의합니다.
```python
from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer
model_name = checkpoint.split("/")[1]
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir=f"{model_name}-pokemon",
learning_rate=5e-5,
num_train_epochs=50,
fp16=True,
per_device_train_batch_size=32,
per_device_eval_batch_size=32,
gradient_accumulation_steps=2,
save_total_limit=3,
evaluation_strategy="steps",
eval_steps=50,
save_strategy="steps",
save_steps=50,
logging_steps=50,
remove_unused_columns=False,
push_to_hub=True,
label_names=["labels"],
load_best_model_at_end=True,
)
```
학습 인수를 데이터세트, 모델과 함께 🤗 Trainer에 전달합니다.
```python
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=train_ds,
eval_dataset=test_ds,
compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
)
```
학습을 시작하려면 [`Trainer`] 객체에서 [`~Trainer.train`]을 호출하기만 하면 됩니다.
```python
trainer.train()
```
학습이 진행되면서 학습 손실이 원활하게 감소하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
학습이 완료되면 모든 사람이 모델을 사용할 수 있도록 [`~Trainer.push_to_hub`] 메소드를 사용하여 모델을 허브에 공유하세요:
```python
trainer.push_to_hub()
```
## 추론[[inference]]
`test_ds`에서 샘플 이미지를 가져와 모델을 테스트합니다.
```python
from PIL import Image
import requests
url = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/sayakpaul/sample-datasets/resolve/main/pokemon.png"
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
image
```
모델에 사용할 이미지를 준비합니다.
```python
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
pixel_values = inputs.pixel_values
```
[`generate`]를 호출하고 예측을 디코딩합니다.
```python
generated_ids = model.generate(pixel_values=pixel_values, max_length=50)
generated_caption = processor.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
print(generated_caption)
```
```bash
a drawing of a pink and blue pokemon
```
파인튜닝된 모델이 꽤 괜찮은 캡션을 생성한 것 같습니다!