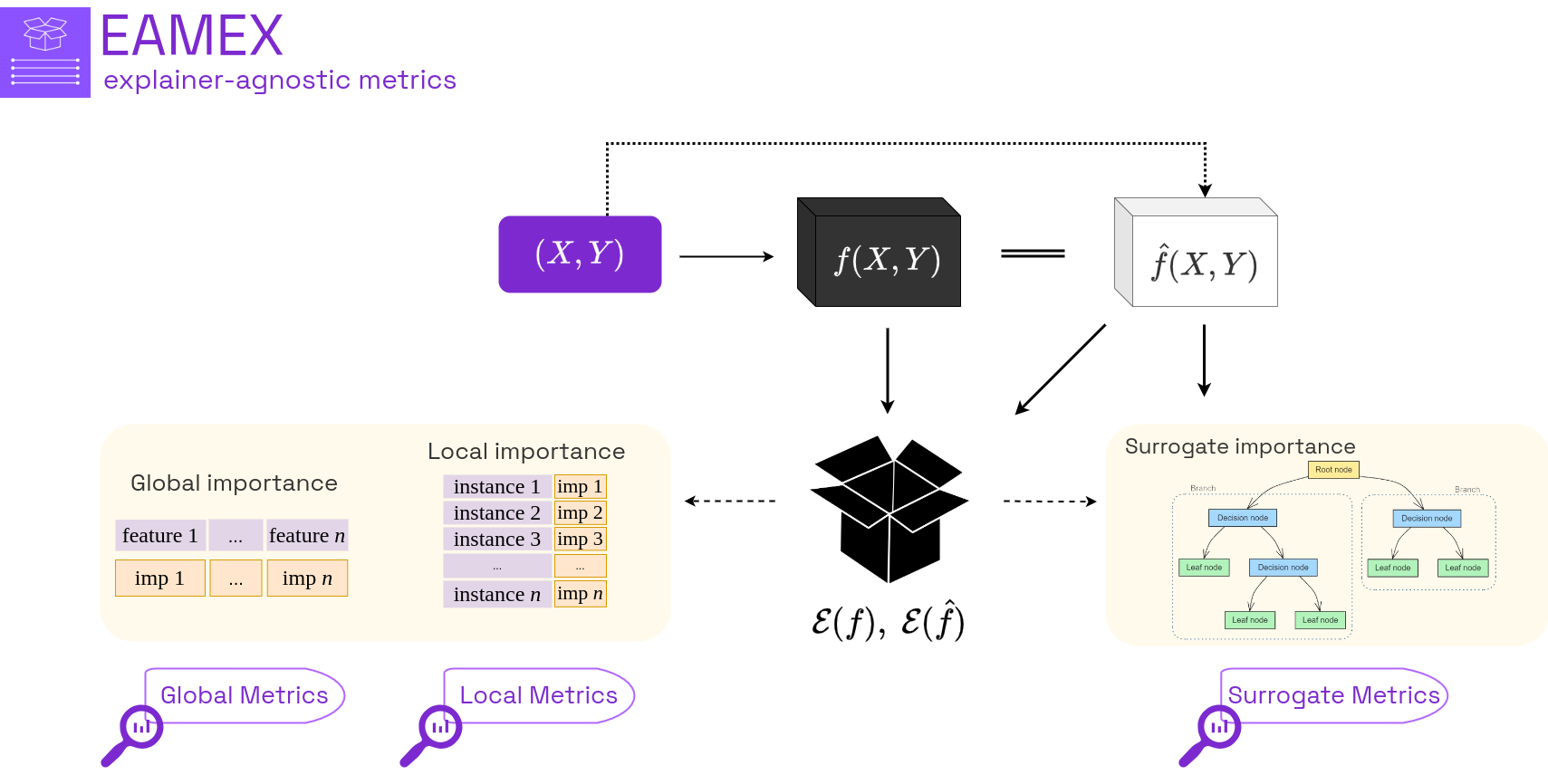








The rapid integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into various industries has introduced new challenges in governance and regulation, particularly regarding the understanding of complex AI systems. A critical demand from decision-makers is the ability to explain the results of machine learning models, which is essential for fostering trust and ensuring ethical AI practices. In this paper, we develop six distinct model-agnostic metrics designed to quantify the extent to which model predictions can be explained. These metrics measure different aspects of model explainability, ranging from local importance, global importance, and surrogate predictions, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of how models generate their outputs. Furthermore, by computing our metrics, we can rank models in terms of explainability criteria such as importance concentration and consistency, prediction fluctuation, and surrogate fidelity and stability, offering a valuable tool for selecting models based not only on accuracy but also on transparency. We demonstrate the practical utility of these metrics on classification and regression tasks, and integrate these metrics into an existing Python package for public use.
@article{dacosta2025bmbench,
author = {Munoz, C., da Costa, K., Modenesi, B., Koshiyama, A.},
title = {Evaluating Explainability in Machine Learning Predictions through Explainer-Agnostic Metrics},
year = {2024},
url = {}
}