{
"cells": [
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "37f2ea84",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"# Stable Diffusion Text-to-Image Demo\n",
"\n",
"Stable Diffusion is an innovative generative AI technique that allows us to generate and manipulate images in interesting ways, including generating image from text and restoring missing parts of pictures (inpainting)!\n",
"\n",
"Stable Diffusion v2 provides great functionality over previous versions, including being able to use more data, employ more training, and has less restrictive filtering of the dataset. All of these features give us promising results for selecting a wide range of input text prompts!\n",
"\n",
"**Note:** This is a shorter version of the [stable-diffusion-v2-text-to-image](../stable-diffusion-v2/stable-diffusion-v2-text-to-image.ipynb) notebook for demo purposes and to get started quickly. This version does not have the full implementation of the helper utilities needed to convert the models from PyTorch to ONNX to OpenVINO, and the OpenVINO `OVStableDiffusionPipeline` within the notebook directly. If you would like to see the full implementation of stable diffusion for text to image, please visit [stable-diffusion-v2-text-to-image](../stable-diffusion-v2/stable-diffusion-v2-text-to-image.ipynb).\n",
"\n",
"#### Table of contents:\n",
"\n",
"- [Step 0: Install and import prerequisites](#Step-0:-Install-and-import-prerequisites)\n",
"- [Step 1: Stable Diffusion v2 Fundamental components](#Step-1:-Stable-Diffusion-v2-Fundamental-components)\n",
" - [Step 1.1: Retrieve components from HuggingFace](#Step-1.1:-Retrieve-components-from-HuggingFace)\n",
"- [Step 2: Convert the models to OpenVINO](#Step-2:-Convert-the-models-to-OpenVINO)\n",
"- [Step 3: Text-to-Image Generation Inference Pipeline](#Step-3:-Text-to-Image-Generation-Inference-Pipeline)\n",
" - [Step 3.1: Load and Understand Text to Image OpenVINO models](#Step-3.1:-Load-and-Understand-Text-to-Image-OpenVINO-models)\n",
" - [Step 3.2: Select inference device](#Step-3.2:-Select-inference-device)\n",
" - [Step 3.3: Run Text-to-Image generation](#Step-3.3:-Run-Text-to-Image-generation)\n",
"\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "11ed575a-b84a-4306-a09c-1d042c596aff",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Step 0: Install and import prerequisites\n",
"[back to top ⬆️](#Table-of-contents:)\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "cbf65ef4",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"To work with Stable Diffusion v2, we will use Hugging Face's [Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) library. \n",
"\n",
"To experiment with Stable Diffusion models, Diffusers exposes the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation) and `StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline`, similar to the [other Diffusers pipelines](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/overview). "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 2,
"id": "429c97c7-a9f0-481f-bab9-f9fe62d191ca",
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stdout",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"\u001b[33mWARNING: Ignoring invalid distribution -orch (/home/ea/work/ov_venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages)\u001b[0m\u001b[33m\n",
"\u001b[0m\u001b[33mWARNING: Ignoring invalid distribution -orch (/home/ea/work/ov_venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages)\u001b[0m\u001b[33m\n",
"\u001b[0m\u001b[33mWARNING: Ignoring invalid distribution -orch (/home/ea/work/ov_venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages)\u001b[0m\u001b[33m\n",
"\u001b[0m\u001b[33mWARNING: Ignoring invalid distribution -orch (/home/ea/work/ov_venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages)\u001b[0m\u001b[33m\n",
"\u001b[0m\u001b[33mWARNING: Ignoring invalid distribution -orch (/home/ea/work/ov_venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages)\u001b[0m\u001b[33m\n",
"\u001b[0m\u001b[33mWARNING: Ignoring invalid distribution -orch (/home/ea/work/ov_venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages)\u001b[0m\u001b[33m\n",
"\u001b[0m\n",
"\u001b[1m[\u001b[0m\u001b[34;49mnotice\u001b[0m\u001b[1;39;49m]\u001b[0m\u001b[39;49m A new release of pip available: \u001b[0m\u001b[31;49m22.3\u001b[0m\u001b[39;49m -> \u001b[0m\u001b[32;49m23.2.1\u001b[0m\n",
"\u001b[1m[\u001b[0m\u001b[34;49mnotice\u001b[0m\u001b[1;39;49m]\u001b[0m\u001b[39;49m To update, run: \u001b[0m\u001b[32;49mpip install --upgrade pip\u001b[0m\n",
"Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"%pip install -q \"diffusers>=0.14.0\" \"openvino>=2023.1.0\" \"transformers>=4.31\" accelerate \"torch>=2.1\" Pillow opencv-python --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "0c1e8c0b-8e2b-4b39-86a7-9ee12fad7e12",
"metadata": {
"tags": []
},
"source": [
"## Step 1: Stable Diffusion v2 Fundamental components\n",
"[back to top ⬆️](#Table-of-contents:)\n",
"\n",
"Stable Diffusion pipelines for both Text to Image and Inpainting consist of three important parts:\n",
"\n",
"1. A Text Encoder to create conditions: for example, generating an image from a text prompt or performing inpainting to create an infinite zoom effect.\n",
"2. A U-Net for step-by-step denoising of latent image representation.\n",
"3. An Autoencoder (VAE) for decoding the latent space to an image.\n",
"\n",
"Depending on the pipeline, the parameters for these parts can differ, which we'll explore in this demo! \n",
"\n",
"### Step 1.1: Retrieve components from HuggingFace\n",
"[back to top ⬆️](#Table-of-contents:)\n",
"\n",
"Let's start by retrieving these components from HuggingFace!"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "c70762bd",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"The code below demonstrates how to create `StableDiffusionPipeline` using `stable-diffusion-2-1`."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 3,
"id": "94fb75e6-e08f-4082-980e-71b43f87addb",
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stderr",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"2023-09-12 11:59:21.971103: I tensorflow/core/util/port.cc:110] oneDNN custom operations are on. You may see slightly different numerical results due to floating-point round-off errors from different computation orders. To turn them off, set the environment variable `TF_ENABLE_ONEDNN_OPTS=0`.\n",
"2023-09-12 11:59:22.005818: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:182] This TensorFlow binary is optimized to use available CPU instructions in performance-critical operations.\n",
"To enable the following instructions: AVX2 AVX512F AVX512_VNNI FMA, in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.\n",
"2023-09-12 11:59:22.607625: W tensorflow/compiler/tf2tensorrt/utils/py_utils.cc:38] TF-TRT Warning: Could not find TensorRT\n"
]
},
{
"data": {
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
"model_id": "66557a19b9c142849e5dcc2810e80b2f",
"version_major": 2,
"version_minor": 0
},
"text/plain": [
"Loading pipeline components...: 0%| | 0/6 [00:00 Onnx -> OpenVINO\n",
"# 1. Convert the Text Encoder\n",
"txt_encoder_ov_path = txt2img_model_dir / \"text_encoder.xml\"\n",
"convert_encoder(text_encoder, txt_encoder_ov_path)\n",
"# 2. Convert the U-NET\n",
"unet_ov_path = txt2img_model_dir / \"unet.xml\"\n",
"convert_unet(unet, unet_ov_path, num_channels=4, width=96, height=96)\n",
"# 3. Convert the VAE encoder\n",
"vae_encoder_ov_path = txt2img_model_dir / \"vae_encoder.xml\"\n",
"convert_vae_encoder(vae, vae_encoder_ov_path, width=768, height=768)\n",
"# 4. Convert the VAE decoder\n",
"vae_decoder_ov_path = txt2img_model_dir / \"vae_decoder.xml\"\n",
"convert_vae_decoder(vae, vae_decoder_ov_path, width=96, height=96)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "0c0b58ad",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Step 3: Text-to-Image Generation Inference Pipeline\n",
"[back to top ⬆️](#Table-of-contents:)\n",
"\n",
"### Step 3.1: Load and Understand Text to Image OpenVINO models\n",
"[back to top ⬆️](#Table-of-contents:)\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "a51ce1e0-7fb2-4adb-8c0e-7d126d96df6e",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Step 3.2: Select inference device\n",
"[back to top ⬆️](#Table-of-contents:)\n",
"\n",
"select device from dropdown list for running inference using OpenVINO"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 6,
"id": "397f7020-1e01-4d6d-958d-351f98eed101",
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
"model_id": "8ff7de34f6884854958abef754c404b2",
"version_major": 2,
"version_minor": 0
},
"text/plain": [
"Dropdown(description='Device:', index=2, options=('CPU', 'GPU', 'AUTO'), value='AUTO')"
]
},
"execution_count": 6,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"import ipywidgets as widgets\n",
"import openvino as ov\n",
"\n",
"core = ov.Core()\n",
"\n",
"device = widgets.Dropdown(\n",
" options=core.available_devices + [\"AUTO\"],\n",
" value=\"AUTO\",\n",
" description=\"Device:\",\n",
" disabled=False,\n",
")\n",
"\n",
"device"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "1838ff71",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Let's create instances of our OpenVINO Model for Text to Image."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 7,
"id": "ea34cd4a",
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"text_enc = core.compile_model(txt_encoder_ov_path, device.value)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 8,
"id": "0ba07c09-aece-4f6d-9481-061937244efa",
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"unet_model = core.compile_model(unet_ov_path, device.value)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 9,
"id": "b90dfd96-89f7-42c2-a48e-01607c3e0dc1",
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"vae_encoder = core.compile_model(vae_encoder_ov_path, device.value)\n",
"vae_decoder = core.compile_model(vae_decoder_ov_path, device.value)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "1c9216d0",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Next, we will define a few key elements to create the inference pipeline, as depicted in the diagram below:\n",
"\n",
"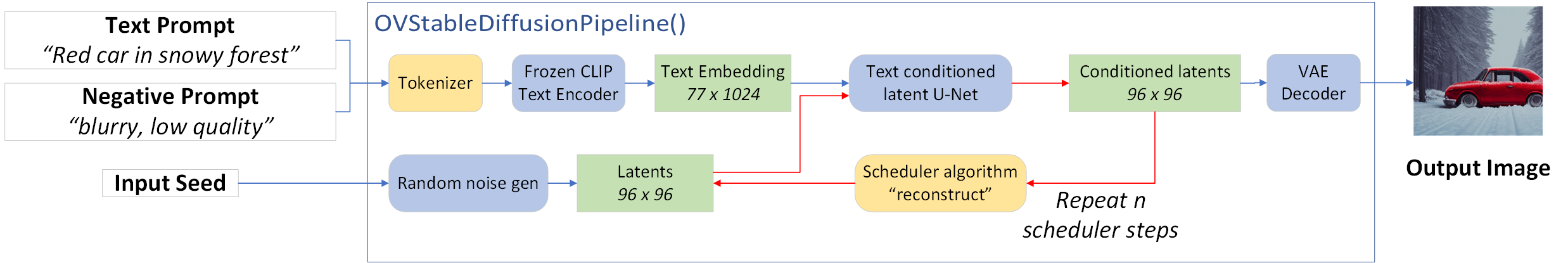\n",
"\n",
"As part of the `OVStableDiffusionPipeline()` class:\n",
"\n",
"1. The stable diffusion pipeline takes both a latent seed and a text prompt as input. The latent seed is used to generate random latent image representations, and the text prompt is provided to OpenAI's CLIP to transform these to text embeddings.\n",
"\n",
"2. Next, the U-Net model iteratively denoises the random latent image representations while being conditioned on the text embeddings. The output of the U-Net, being the noise residual, is used to compute a denoised latent image representation via a scheduler algorithm. In this case we use the `LMSDiscreteScheduler`."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 10,
"id": "fec1c83d",
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "stderr",
"output_type": "stream",
"text": [
"/home/ea/work/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/stable-diffusion-v2/implementation/ov_stable_diffusion_pipeline.py:10: FutureWarning: Importing `DiffusionPipeline` or `ImagePipelineOutput` from diffusers.pipeline_utils is deprecated. Please import from diffusers.pipelines.pipeline_utils instead.\n",
" from diffusers.pipeline_utils import DiffusionPipeline\n"
]
}
],
"source": [
"from diffusers.schedulers import LMSDiscreteScheduler\n",
"from transformers import CLIPTokenizer\n",
"from implementation.ov_stable_diffusion_pipeline import OVStableDiffusionPipeline\n",
"\n",
"scheduler = LMSDiscreteScheduler.from_config(conf)\n",
"tokenizer = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained(\"openai/clip-vit-large-patch14\")\n",
"\n",
"ov_pipe = OVStableDiffusionPipeline(\n",
" tokenizer=tokenizer,\n",
" text_encoder=text_enc,\n",
" unet=unet_model,\n",
" vae_encoder=vae_encoder,\n",
" vae_decoder=vae_decoder,\n",
" scheduler=scheduler,\n",
")"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "7fd3ff54",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"### Step 3.3: Run Text-to-Image generation\n",
"[back to top ⬆️](#Table-of-contents:)\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"id": "1c108cae",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"Now, let's define some text prompts for image generation and run our inference pipeline. \n",
"\n",
"We can also change our random generator seed for latent state initialization and number of steps (higher steps = more precise results).\n",
"\n",
"Example prompts:\n",
"\n",
"- \"valley in the Alps at sunset, epic vista, beautiful landscape, 4k, 8k\"\n",
"- \"city filled with cyborgs, modern, industrial, 4k, 8k\n",
"\n",
"To improve image generation quality, we can use negative prompting. While positive prompts steer diffusion toward the images associated with it, negative prompts declares undesired concepts for the generation image, e.g. if we want to have colorful and bright images, a gray scale image will be result which we want to avoid. In this case, a gray scale can be treated as negative prompt. The positive and negative prompt are in equal footing. You can always use one with or without the other. More explanation of how it works can be found in this [article](https://stable-diffusion-art.com/how-negative-prompt-work/)."
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 11,
"id": "ed0aee4f",
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
"model_id": "5020bbf6b49b44ee92ab8d4ad702edf3",
"version_major": 2,
"version_minor": 0
},
"text/plain": [
"VBox(children=(Textarea(value='valley in the Alps at sunset, epic vista, beautiful landscape, 4k, 8k', descrip…"
]
},
"execution_count": 11,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"import ipywidgets as widgets\n",
"\n",
"text_prompt = widgets.Textarea(\n",
" value=\"valley in the Alps at sunset, epic vista, beautiful landscape, 4k, 8k\",\n",
" description=\"positive prompt\",\n",
" layout=widgets.Layout(width=\"auto\"),\n",
")\n",
"negative_prompt = widgets.Textarea(\n",
" value=\"frames, borderline, text, charachter, duplicate, error, out of frame, watermark, low quality, ugly, deformed, blur\",\n",
" description=\"negative prompt\",\n",
" layout=widgets.Layout(width=\"auto\"),\n",
")\n",
"num_steps = widgets.IntSlider(min=1, max=50, value=25, description=\"steps:\")\n",
"seed = widgets.IntSlider(min=0, max=10000000, description=\"seed: \", value=42)\n",
"widgets.VBox([text_prompt, negative_prompt, seed, num_steps])"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": 12,
"id": "87b81c71",
"metadata": {},
"outputs": [
{
"data": {
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
"model_id": "4de038cccf884150aeb943eb0ec004c2",
"version_major": 2,
"version_minor": 0
},
"text/plain": [
" 0%| | 0/25 [00:00"
]
},
"execution_count": 13,
"metadata": {},
"output_type": "execute_result"
}
],
"source": [
"final_image = result[\"sample\"][0]\n",
"final_image.save(\"result.png\")\n",
"final_image"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.8.10"
},
"openvino_notebooks": {
"imageUrl": "https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/blob/latest/notebooks/stable-diffusion-v2/stable-diffusion-v2-optimum-demo.png?raw=true",
"tags": {
"categories": [
"Model Demos",
"AI Trends"
],
"libraries": [],
"other": [
"Stable Diffusion"
],
"tasks": [
"Text-to-Image"
]
}
},
"vscode": {
"interpreter": {
"hash": "cec18e25feb9469b5ff1085a8097bdcd86db6a4ac301d6aeff87d0f3e7ce4ca5"
}
},
"widgets": {
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-state+json": {
"state": {},
"version_major": 2,
"version_minor": 0
}
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 5
}