VARCO-VISION-14B
About the Model
VARCO-VISION-14B is a powerful English-Korean Vision-Language Model (VLM). The training pipeline of VARCO-VISION consists of four stages: Feature Alignment Pre-training, Basic Supervised Fine-tuning, Advanced Supervised Fine-tuning, and Preference Optimization. In both multimodal and text-only benchmarks, VARCO-VISION-14B not only surpasses other models of similar size in performance but also achieves scores comparable to those of proprietary models. The model currently accepts a single image and a text as inputs, generating an output text. It supports grounding, referring as well as OCR (Optical Character Recognition).
- Developed by: NC Research, Multimodal Generation Team
- Technical Report: VARCO-VISION: Expanding Frontiers in Korean Vision-Language Models
- Blog(Korean): VARCO-VISION Technical Report Summary
- Demo Page: The demo page is no longer available.
- Languages: Korean, English
- License: CC BY-NC 4.0
- Architecture: VARCO-VISION-14B follows the architecture of LLaVA-OneVision.
- Base Model:
- Language Model: Qwen/Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct
- Vision Encoder: google/siglip-so400m-patch14-384
- Huggingface Version Model: NCSOFT/VARCO-VISION-14B-HF
- Korean VLM Benchmarks:
- This model is for research purposes only. Commercial use is prohibited.
Uses
Direct Use
To load VARCO-VISION-14B, start by cloning and installing LLaVA-NeXT:
git clone https://github.com/LLaVA-VL/LLaVA-NeXT
cd LLaVA-NeXT
pip install -e ".[train]"
After installing LLaVA-NeXT, you can load VARCO-VISION-14B using the following code:
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from llava.model.language_model.llava_qwen import LlavaQwenForCausalLM
from llava.mm_utils import tokenizer_image_token, process_images
model_name = "NCSOFT/VARCO-VISION-14B"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = LlavaQwenForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
device_map="auto"
)
vision_tower = model.get_vision_tower()
image_processor = vision_tower.image_processor
Prepare an image and a text input. You need to preprocess the image and tokenize the text. Pass the processed inputs to the model to generate predictions.
import requests
from PIL import Image
# Define a chat history and use `apply_chat_template` to get correctly formatted prompt
# Each value in "content" has to be a list of dicts with types ("text", "image")
conversation = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe this image."},
{"type": "image"},
],
},
]
prompt = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True, tokenize=False)
IMAGE_TOKEN_INDEX = -200
EOS_TOKEN = "<|im_end|>"
input_ids = tokenizer_image_token(prompt, tokenizer, IMAGE_TOKEN_INDEX, return_tensors="pt")
input_ids = input_ids.unsqueeze(0).to(model.device)
image_url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
raw_image = Image.open(requests.get(image_url, stream=True).raw)
image_tensors = process_images([raw_image], image_processor, model.config)
image_tensors = [image_tensor.half().to(model.device) for image_tensor in image_tensors]
image_sizes = [raw_image.size]
with torch.inference_mode():
output_ids = model.generate(
input_ids,
images=image_tensors,
image_sizes=image_sizes,
do_sample=False,
max_new_tokens=1024,
use_cache=True,
)
outputs = tokenizer.batch_decode(output_ids)[0]
if outputs.endswith(EOS_TOKEN):
outputs = outputs[: -len(EOS_TOKEN)]
outputs = outputs.strip()
print(outputs)
Specialized Features
If a question is based on bounding boxes or require bounding boxes as an output, please include the special tokens in the input text.
The following special tokens are used to define specific tasks, inputs, and outputs for the model:
<gro>: Indicates that the model's response should include bounding box information.<ocr>: Specifies OCR tasks for recognizing text within an image.<char>and</char>: Used to mark a text phrase.<obj>and</obj>: Used to indicate an object.<bbox>and</bbox>: Used to represent a bounding box.<delim>: Represents multiple location points for a single object or text.
Grounding
Grounding refers to a task where the model needs to identify specific locations within an image to provide an appropriate answer. To perform grounding, prepend the special token <gro> to the question.
conversation = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "<gro>\nDescribe the image in detail."},
{"type": "image"},
],
},
]
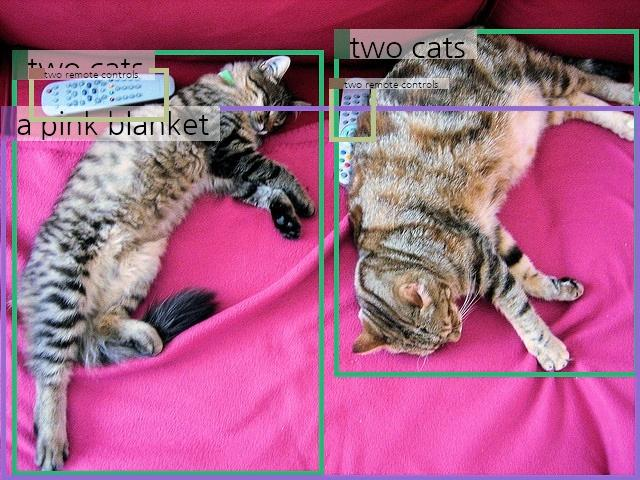
Expected Output Example:
The image shows <obj>two cats</obj><bbox>0.521, 0.049, 0.997, 0.783<delim>0.016, 0.108, 0.512, 0.99</bbox> lying on <obj>a pink blanket</obj><bbox>0.002, 0.231, 0.999, 0.999</bbox>. The cat on the left is lying on its side with its head resting on the blanket and its body stretched out. The cat on the right is lying on its back with its paws stretched out and its head turned to the side. Both cats appear relaxed and comfortable. There are also <obj>two remote controls</obj><bbox>0.039, 0.138, 0.283, 0.257<delim>0.508, 0.166, 0.581, 0.295</bbox> placed near the cats, one on each side of them.

Referring
VARCO-VISION-14B can handle location-specific questions using bounding boxes. To perform referring tasks, make a conversation including the object of interest within <obj> and </obj> tags. You have to specify its location with <bbox> and </bbox> tags. This allows the model to understand the context and focus on the object at the specified location. A bbox is represented in a form of (x1, y1, x2, y2). The first two values indicate the top-left position of a bbox, and the latter two values are the bottom-right position.
conversation = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "<obj>이 물건</obj><bbox>0.039, 0.138, 0.283, 0.257</bbox>은 어떻게 쓰는거야?",
},
{"type": "image"},
],
},
]
Expected Output Example:
**이 물건**은 리모컨으로, 주로 텔레비전이나 다른 전자 기기를 원격으로 조작하는 데 사용됩니다. 버튼을 누르면 채널 변경, 볼륨 조절, 전원 켜기/끄기 등의 기능을 수행할 수 있습니다. 리모컨의 버튼에는 일반적으로 숫자, 메뉴, 설정, 재생/일시정지 등의 기능이 포함되어 있으며, 사용자는 이를 통해 손쉽게 기기를 제어할 수 있습니다.
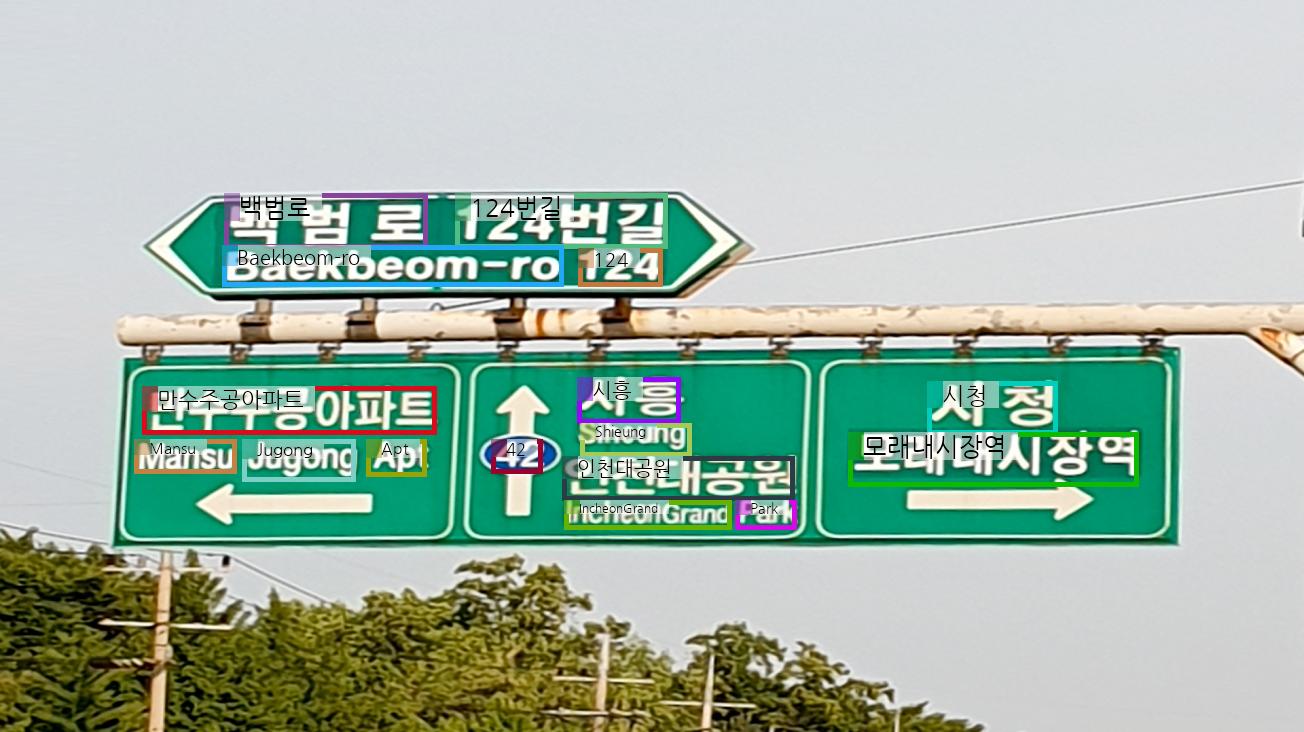
OCR
To perform Optical Character Recognition (OCR), use the <ocr> token.
image_file = "./assets/ocr_1.png"
raw_image = Image.open(image_file)
conversation = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "<ocr>"},
{"type": "image"},
],
},
]
Expected Output Example:
<char>백범로</char><bbox>0.172, 0.265, 0.328, 0.34</bbox>
<char>124번길</char><bbox>0.349, 0.265, 0.512, 0.34</bbox>
<char>Baekbeom-ro</char><bbox>0.171, 0.335, 0.432, 0.391</bbox>
<char>124</char><bbox>0.444, 0.34, 0.508, 0.391</bbox>
<char>만수주공아파트</char><bbox>0.109, 0.528, 0.335, 0.594</bbox>
<char>시흥</char><bbox>0.443, 0.516, 0.522, 0.578</bbox>
<char>시청</char><bbox>0.711, 0.521, 0.811, 0.594</bbox>
<char>Mansu</char><bbox>0.103, 0.601, 0.181, 0.647</bbox>
<char>Jugong</char><bbox>0.186, 0.601, 0.273, 0.658</bbox>
<char>Apt</char><bbox>0.281, 0.601, 0.327, 0.651</bbox>
<char>42</char><bbox>0.377, 0.601, 0.416, 0.647</bbox>
<char>Shieung</char><bbox>0.445, 0.578, 0.53, 0.623</bbox>
<char>인천대공원</char><bbox>0.431, 0.623, 0.609, 0.684</bbox>
<char>모래내시장역</char><bbox>0.651, 0.591, 0.873, 0.664</bbox>
<char>IncheonGrand</char><bbox>0.433, 0.684, 0.561, 0.723</bbox>
<char>Park</char><bbox>0.564, 0.684, 0.611, 0.723</bbox>
Citing the Model
If you use VARCO-VISION-14B in your research, please cite the following:
@misc{ju2024varcovisionexpandingfrontierskorean,
title={VARCO-VISION: Expanding Frontiers in Korean Vision-Language Models},
author={Jeongho Ju and Daeyoung Kim and SunYoung Park and Youngjune Kim},
year={2024},
eprint={2411.19103},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.19103},
}
- Downloads last month
- 941