VisualPRM-8B
[📂 GitHub] [📂 Evaluation Code] [📜 Paper] [🆕 Blog] [🤗 model] [🤗 dataset] [🤗 benchmark]
2025/04/11: We release a new version of VisualPRM (i.e., VisualPRM-8B-v1.1), which greatly enhances the reasoning performance of InternVL3 under Best-of-N settings.
Introduction
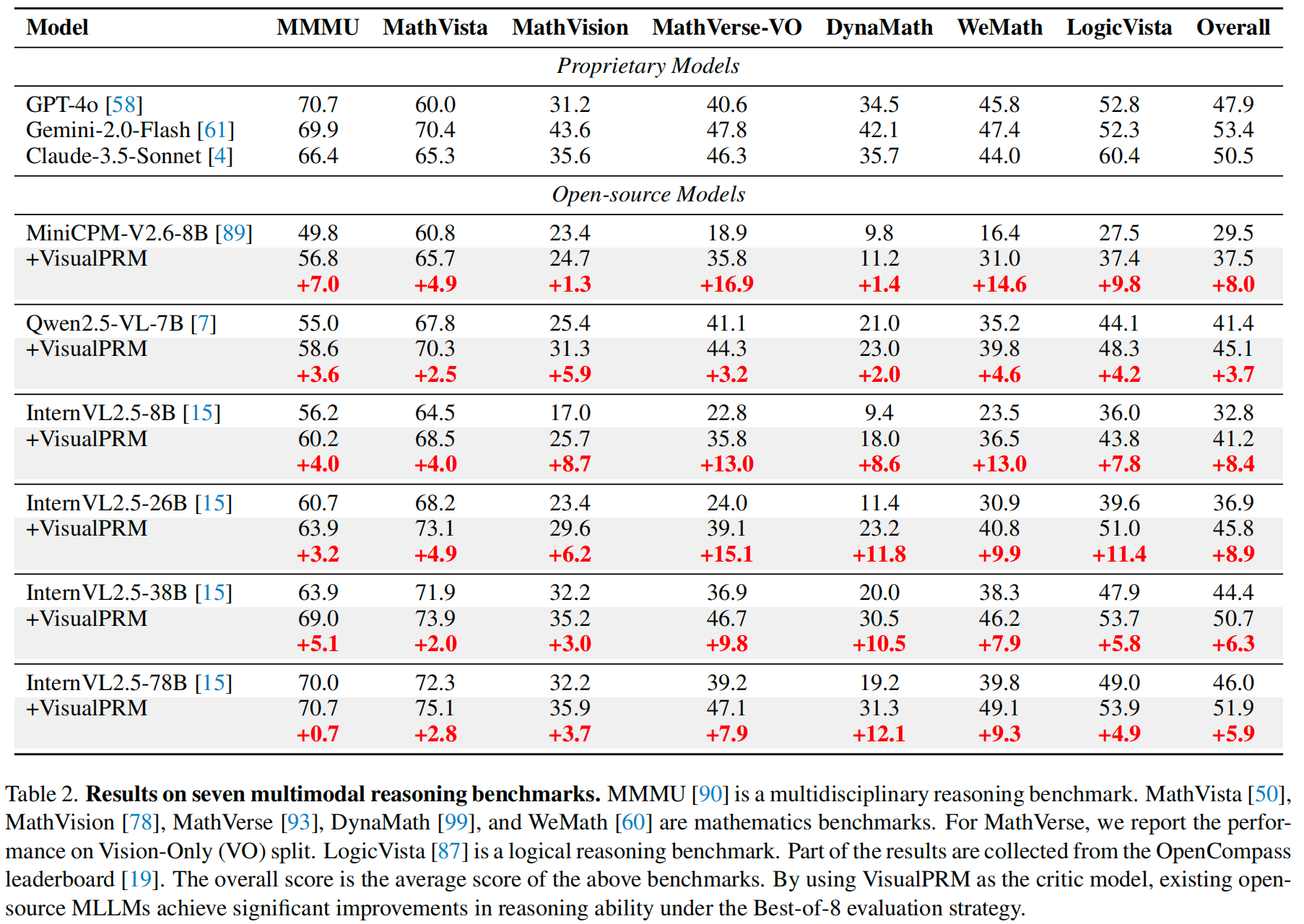
We introduce VisualPRM, an advanced multimodal Process Reward Model (PRM) with 8B parameters, which improves the reasoning abilities of existing Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) across different model scales and families with Best-of-N (BoN) evaluation strategies. Specifically, our model improves the reasoning performance of three types of MLLMs and four different model scales. Even when applied to the highly capable InternVL2.5-78B, it achieves a 5.9-point improvement across seven multimodal reasoning benchmarks. Experimental results show that our model exhibits superior performance compared to Outcome Reward Models and Self-Consistency during BoN evaluation. To facilitate the training of multimodal PRMs, we construct a multimodal process supervision dataset VisualPRM400K using an automated data pipeline. For the evaluation of multimodal PRMs, we propose VisualProcessBench, a benchmark with human-annotated step-wise correctness labels, to measure the abilities of PRMs to detect erroneous steps in multimodal reasoning tasks. We hope that our work can inspire more future research and contribute to the development of MLLMs.
Performance
Inference with Transformers
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as T
from PIL import Image
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoTokenizer
from torchvision.transforms.functional import InterpolationMode
IMAGENET_MEAN = (0.485, 0.456, 0.406)
IMAGENET_STD = (0.229, 0.224, 0.225)
def build_transform(input_size):
MEAN, STD = IMAGENET_MEAN, IMAGENET_STD
transform = T.Compose([
T.Lambda(lambda img: img.convert('RGB') if img.mode != 'RGB' else img),
T.Resize((input_size, input_size), interpolation=InterpolationMode.BICUBIC),
T.ToTensor(),
T.Normalize(mean=MEAN, std=STD)
])
return transform
def find_closest_aspect_ratio(aspect_ratio, target_ratios, width, height, image_size):
best_ratio_diff = float('inf')
best_ratio = (1, 1)
area = width * height
for ratio in target_ratios:
target_aspect_ratio = ratio[0] / ratio[1]
ratio_diff = abs(aspect_ratio - target_aspect_ratio)
if ratio_diff < best_ratio_diff:
best_ratio_diff = ratio_diff
best_ratio = ratio
elif ratio_diff == best_ratio_diff:
if area > 0.5 * image_size * image_size * ratio[0] * ratio[1]:
best_ratio = ratio
return best_ratio
def dynamic_preprocess(image, min_num=1, max_num=12, image_size=448, use_thumbnail=False):
orig_width, orig_height = image.size
aspect_ratio = orig_width / orig_height
# calculate the existing image aspect ratio
target_ratios = set(
(i, j) for n in range(min_num, max_num + 1) for i in range(1, n + 1) for j in range(1, n + 1) if
i * j <= max_num and i * j >= min_num)
target_ratios = sorted(target_ratios, key=lambda x: x[0] * x[1])
# find the closest aspect ratio to the target
target_aspect_ratio = find_closest_aspect_ratio(
aspect_ratio, target_ratios, orig_width, orig_height, image_size)
# calculate the target width and height
target_width = image_size * target_aspect_ratio[0]
target_height = image_size * target_aspect_ratio[1]
blocks = target_aspect_ratio[0] * target_aspect_ratio[1]
# resize the image
resized_img = image.resize((target_width, target_height))
processed_images = []
for i in range(blocks):
box = (
(i % (target_width // image_size)) * image_size,
(i // (target_width // image_size)) * image_size,
((i % (target_width // image_size)) + 1) * image_size,
((i // (target_width // image_size)) + 1) * image_size
)
# split the image
split_img = resized_img.crop(box)
processed_images.append(split_img)
assert len(processed_images) == blocks
if use_thumbnail and len(processed_images) != 1:
thumbnail_img = image.resize((image_size, image_size))
processed_images.append(thumbnail_img)
return processed_images
def load_image(image, input_size=448, max_num=12):
image = Image.open(image).convert('RGB')
transform = build_transform(input_size=input_size)
images = dynamic_preprocess(image, image_size=input_size, use_thumbnail=True, max_num=max_num)
pixel_values = [transform(image) for image in images]
pixel_values = torch.stack(pixel_values)
return pixel_values
def main():
path = 'OpenGVLab/VisualPRM-8B'
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(path, trust_remote_code=True, use_fast=False)
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(
path,
trust_remote_code=True,
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
).eval().cuda()
question = 'Find m \\angle 3.'
response_a = """
To find the measure of \\angle 3, we need to use the properties of the angles in the given geometric figure.
1. \\angle EDC is a right angle, and it is split into \\angle EDF and \\angle 3.
2. We know that \\angle EDF = 39^\\circ because it is labeled in the diagram.
3. Since \\angle EDC is 90^\\circ, we can set up the equation for \\angle 3: \\angle EDC = \\angle EDF + \\angle 3
4. Substituting the known values, we get: 90^\\circ = 39^\\circ + \\angle 3
5. Solving for \\angle 3: \\angle 3 = 90^\\circ - 39^\\circ
6. Simplifying the equation: \\angle 3 = 51^\\circ
Final answer: 51^\\circ
""".strip()
response_b = """
To find , we need to analyze the given geometric figure carefully.
1. Recognize that is part of triangle . Since is given as 48° and is a right angle (90°), we can use the properties of a right triangle to find .
2. The sum of the angles in any triangle is 180°. Therefore, in triangle : \[ \\angle 1 + \\angle 2 + \\angle 3 = 180° \]
3. Substitute the known values: \[ 48° + 90° + \\angle 3 = 180° \]
4. Solve for : \[ \\angle 3 = 180° - 48° - 90° = 42° \]
Thus, the measure of is 42°.
Final answer: 42
""".strip()
response_list = [
response_a,
response_b,
]
image = 'examples/image.png'
pixel_values = load_image(image).to(torch.bfloat16).cuda()
sorted_response_list = model.select_best_response(
tokenizer=tokenizer,
question=question,
response_list=response_list,
pixel_values=pixel_values,
return_scores=True,
)
print('Best response:', sorted_response_list[0][0])
print('Highest score:', sorted_response_list[0][1])
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
License
This project is released under the MIT License. This project uses the pre-trained internlm2_5-7b-chat as a component, which is licensed under the Apache License 2.0.
Citation
If you find this project useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{wang2025visualprm,
title={VisualPRM: An Effective Process Reward Model for Multimodal Reasoning},
author={Wang, Weiyun and Gao, Zhangwei and Chen, Lianjie and Chen, Zhe and Zhu, Jinguo and Zhao, Xiangyu and Liu, Yangzhou and Cao, Yue and Ye, Shenglong and Zhu, Xizhou and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.10291},
year={2025}
}
- Downloads last month
- 496
Model tree for OpenGVLab/VisualPRM-8B
Base model
OpenGVLab/InternVL2_5-8B