
Quick Use
import os
import torch
import json
import argparse
from tqdm import tqdm
from collections import defaultdict
import torch.nn.functional as F
from time import time
from easydict import EasyDict as edict
from model.mico import *
def load_from_pretrained_dir(pretrain_dir, video_resolution=224, return_modal="full"):
checkpoint_dir = os.path.join(pretrain_dir,'ckpt')
file_cfg = edict(json.load(open(os.path.join(pretrain_dir,'log','hps.json'))))
model_cfg = file_cfg.model_cfg
checkpoint_ls = [ i for i in os.listdir(checkpoint_dir) if i.startswith('model_step')]
checkpoint_ls = [int(i.split('_')[2].split('.')[0]) for i in checkpoint_ls]
checkpoint_ls.sort()
step = checkpoint_ls[-1]
checkpoint_name = 'model_step_'+str(step)+'.pt'
ckpt_file = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, checkpoint_name)
checkpoint = torch.load(ckpt_file, map_location = 'cpu')
print(f'load_from_pretrained: {ckpt_file}')
new_ckpt = {}
for k,v in checkpoint.items():
if 'video' in k:
new_ckpt[k.replace('video','vision')]=v
elif 'evaclip_model' in k:
new_ckpt[k.replace('evaclip_model','vision_encoder')]=v
elif 'clip_model' in k:
new_ckpt[k.replace('clip_model','vision_encoder')]=v
else:
new_ckpt[k] = v.float()
checkpoint = new_ckpt
if model_cfg.frame_embedding_type == 'adaptive':
if 'vision_frame_embedding' in checkpoint:
pretrain_embed = checkpoint['vision_frame_embedding']
if pretrain_embed.shape[1]!=model_cfg.max_vision_sample_num:
pretrain_embed = F.interpolate(pretrain_embed.permute(0,2,1),model_cfg.max_vision_sample_num,mode='nearest').permute(0,2,1)
checkpoint['vision_frame_embedding'] = pretrain_embed
else:
pretrain_embed = checkpoint['vision_perceiver.vision_frame_embedding']
if pretrain_embed.shape[1]!=model_cfg.max_vision_sample_num:
pretrain_embed = F.interpolate(pretrain_embed.permute(0,2,1),model_cfg.max_vision_sample_num,mode='nearest').permute(0,2,1)
checkpoint['vision_perceiver.vision_frame_embedding'] = pretrain_embed
if 'audio_frame_embedding' in checkpoint:
pretrain_embed_a = checkpoint['audio_frame_embedding']
if pretrain_embed_a.shape[1]!=model_cfg.max_audio_sample_num:
pretrain_embed_a = F.interpolate(pretrain_embed_a.permute(0,2,1),model_cfg.max_audio_sample_num,mode='nearest').permute(0,2,1)
checkpoint['audio_frame_embedding'] = pretrain_embed_a
if model_cfg.vision_encoder_type.startswith('clip'):
vision_width = checkpoint["vision_encoder.visual.positional_embedding"].shape[1]
vision_layers = len([k for k in checkpoint.keys() if k.startswith("visual.") and k.endswith(".attn.in_proj_weight")])
vision_patch_size = checkpoint["vision_encoder.visual.conv1.weight"].shape[-1]
grid_size = round((checkpoint["vision_encoder.visual.positional_embedding"].shape[0] - 1) ** 0.5)
src = checkpoint["vision_encoder.visual.positional_embedding"]
src_cls = src[0:1]
src_oth = src[1:]
new_grid_size = model_cfg.vision_resolution // vision_patch_size
if new_grid_size!=grid_size:
src_oth = F.interpolate(src_oth.reshape(grid_size,grid_size,vision_width).permute(2,0,1).unsqueeze(0),(new_grid_size,new_grid_size),mode='bilinear')
src_oth = src_oth[0].permute(1,2,0).reshape(-1,src.shape[-1])
tgt = torch.cat((src_cls,src_oth),dim=0)
checkpoint["vision_encoder.visual.positional_embedding"] = tgt
elif model_cfg.vision_encoder_type.startswith('evaclip'):
vision_width = checkpoint["vision_encoder.visual.pos_embed"].shape[2]
vision_layers = len([k for k in checkpoint.keys() if k.startswith("visual.") and k.endswith(".attn.in_proj_weight")])
vision_patch_size = checkpoint["vision_encoder.visual.patch_embed.proj.weight"].shape[-1]
grid_size = round((checkpoint["vision_encoder.visual.pos_embed"].shape[1] - 1) ** 0.5)
src = checkpoint["vision_encoder.visual.pos_embed"][0]
src_cls = src[0:1]
src_oth = src[1:]
new_grid_size = model_cfg.vision_resolution // vision_patch_size
if new_grid_size!=grid_size:
src_oth = F.interpolate(src_oth.reshape(grid_size,grid_size,vision_width).permute(2,0,1).unsqueeze(0),(new_grid_size,new_grid_size),mode='bilinear')
src_oth = src_oth[0].permute(1,2,0).reshape(-1,src.shape[-1])
tgt = torch.cat((src_cls,src_oth),dim=0)
checkpoint["vision_encoder.visual.pos_embed"] = tgt.unsqueeze(0)
else:
pass
if return_modal=="full":
new_ckpt = checkpoint
elif return_modal=="uni":
new_ckpt = defaultdict()
for k in checkpoint.keys():
if "video_encoder" in k:
new_k = ".".join(k.split(".")[1:])
new_ckpt[new_k] = checkpoint[k]
elif return_modal=="text":
new_ckpt = defaultdict()
for k in checkpoint.keys():
if "multimodal_encoder" in k:
new_k = ".".join(k.split(".")[1:])
new_ckpt[new_k] = checkpoint[k]
else:
pass
return new_ckpt, model_cfg
if __name__ == "__main__":
# import ipdb
# ipdb.set_trace()
device = "cuda"
from model.imageprocessor import ImageProcessor
pretrain_path = 'MiCo-g' # please check your
checkpoint, opts = load_from_pretrained_dir("MiCo-g", video_resolution=224, return_modal="full")
model = MiCo.from_pretrained(opts,checkpoint).to(device)
image_file = "example/test.jpeg"
proc = ImageProcessor(image_resolution=224, image_encoder_type="swin", training=True)
image_input = proc(image_file).to(device)
image_input = image_input.unsqueeze(1) # image as a 1 frame video
video_output = model.forward_vision_encoder(image_input)
video_output_pooled = model.pool_vision_for_contra(video_output)
feat_v = model.contra_head_v(video_output_pooled)
feat_v = F.normalize(feat_v,dim=-1)
texts = ["a man is skiing in a snowy day.", "it's a hot day"]
caption_tokens = model.multimodal_encoder.tokenizer(texts,
padding="max_length",
truncation=True,
max_length=30,
return_tensors="pt")
caption_tokens = caption_tokens.to(torch.device('cuda'))
input_ids = caption_tokens.input_ids
attention_mask = caption_tokens.attention_mask
caption_output = model.forward_multimodal_encoder(input_ids, attention_mask).sequence_output
caption_output_pooled = model.pool_text_for_contra(caption_output)
feat_t = model.contra_head_t(caption_output_pooled)
feat_t = F.normalize(feat_t,dim=-1)
sim_t2v = torch.matmul(feat_t, feat_v.permute(1,0))
print(sim_t2v)
video_input = model.get_multimodal_forward_input_vision(video_output)
slice_output = model.forward_multimodal_encoder(input_ids, attention_mask, video_input).sequence_output
slice_scores = F.softmax(model.itm_head(slice_output[:,0]),dim=1)[:,1]
print(slice_scores)
video_input = model.get_multimodal_forward_input_vision(video_output)
init_input_ids = torch.ones(video_input.size(0), 1).long().cuda().fill_(model.multimodal_encoder.tokenizer.bos_token_id)
init_attention_mask = init_input_ids.new_ones(video_input.size(0), 1, 1)
outputs = model.multimodal_encoder.generate(input_ids=init_input_ids,
attention_mask=init_attention_mask,
encoder_hidden_states=video_input,
max_new_tokens=model.max_caption_len,
num_beams=model.beam_size,
eos_token_id=model.multimodal_encoder.tokenizer.sep_token_id,
pad_token_id=model.multimodal_encoder.tokenizer.pad_token_id,
length_penalty=0.6)
outputs_newgen = outputs[:,1:]
captions = model.multimodal_encoder.tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs_newgen, skip_special_tokens=True)
print(captions)
✨ Inspiration of Multimodal Context: Multimedia Brain Cognition

How the human brain performs coherent multimodal cognition?
As outlined in Richard Mayer's Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning,our brain processes multimedia signals through two distinct channels—auditory and visual—in sensory memory, as depicted in Figure(a). The sensory memory integrates these signals with prior knowledge through words, transforming new multimedia information into long-term memory. Notably, 1) multimedia signals in the brain share channels, and 2) words function as the reasoning interface in our brain.
Inspired by these insights, we categorize diverse modalities into two types: knowledge modality and interface modality. Knowledge modalities, primarily derived from raw sensors, contribute knowledge in diverse formats. For example, images and depth maps offer visual knowledge, while audio and video provide auditory and spatiotemporal knowledge. The language modality, developed by humans, is inherently more abstract and naturally functions as the interface modality, facilitating learning, reasoning, and the coordination of knowledge. To this end, we design an omni-modal learning architecture, illustrated in Figure (b), with two distinct branches: one for knowledge modalities and one for the interface modality, i.e. natural language. The knowledge and interface modalities are aligned through a novel generative reasoning method.
🚀 MiCo, An omni-modal and scalable pretraining paradigm

We propose collecting large-scale omni-modal paired data, including text, image, video, depth, and normal maps, to learn universal representations.
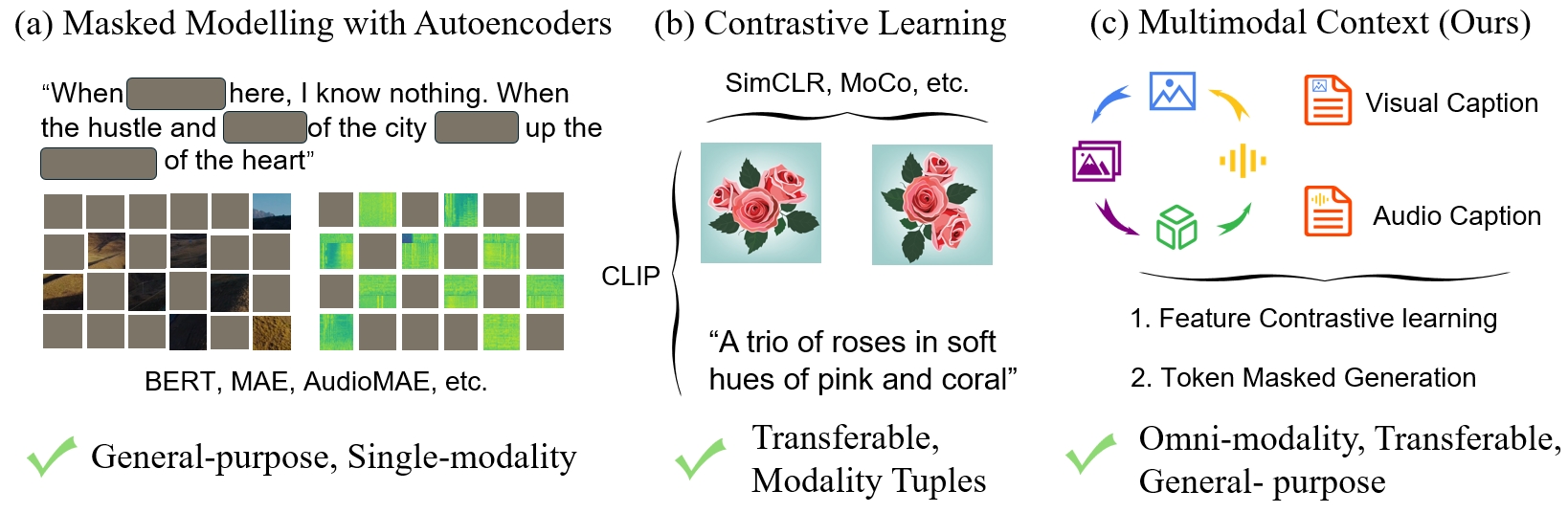
🚀 Evolution of Pretraining Paradigms. Masked modeling (a) has shown great success in single modality, general-purpose understanding. Contrastive learning (b) distinguishes transferable features with modality tuples (such as text-image, text-video, text-audio, etc).
🚀🚀🚀 We aim to achieve general-purpose omni-modal understanding and learn transferable, universal representations in (c).
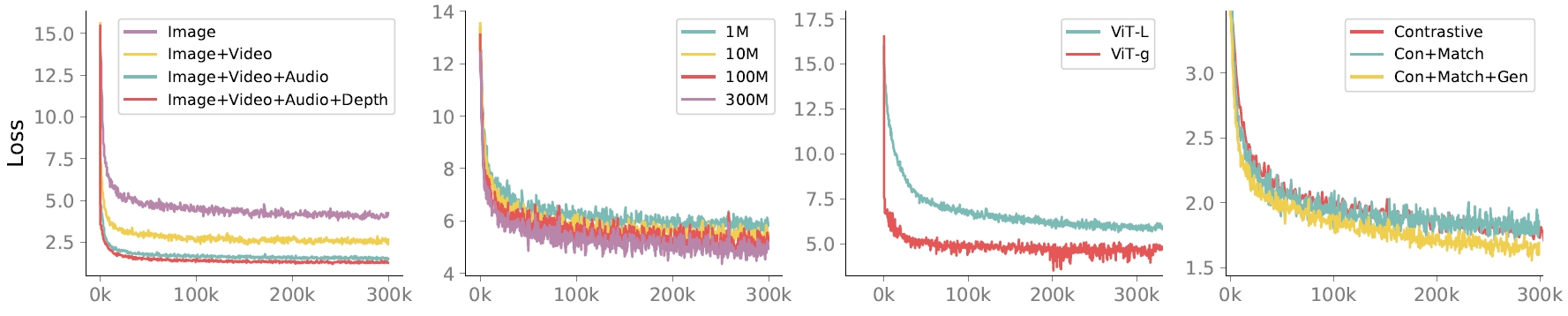
🌟🌟🌟 The Multimodal Scaling Laws with MiCo: Modalities Help Modalies!
🔓 Pretrained Omni-Modal Models
We will continue to update this model zoo including all scales of ViTs and highly-efficient ConvNets with the MiCo pretraining paradigm
🔓 Omni-Modal Dataset Collection
We provdie a detailed doc for preparing the omni-modal dataset step-by-step
⚡ Quick Start
- Download MiCo weights
pip install gdown gdown 1AIQjV1KU8K4OXiO-4gFirxkoxt3twWIq --folder python inference_demo.py
Citation
If the code and paper help your research, please kindly cite:
@article{zhang2024explore,
title={Explore the Limits of Omni-modal Pretraining at Scale},
author={Zhang, Yiyuan and Li, Handong and Liu, Jing and Yue, Xiangyu},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.xxxxx},
year={2024}
}
License
This project is released under the Apache 2.0 license.
Acknowledgement
We appreciate Dr. Xiaohan Ding for the valuable discussion and suggestions.This code is developed based Meta-Transformer, VAST, DPT, and GeoWizard.
Paper
arxiv.org/abs/2406.09412
- Downloads last month
- 18