SlimSAM: 0.1% Data Makes Segment Anything Slim

0.1% Data Makes Segment Anything Slim
Zigeng Chen, Gongfan Fang, Xinyin Ma, Xinchao Wang
Learning and Vision Lab, National University of Singapore
Paper: [Arxiv]
Updates
- 🚀 December 11, 2023: Release the training code, inference code and pre-trained models for SlimSAM.
Introduction

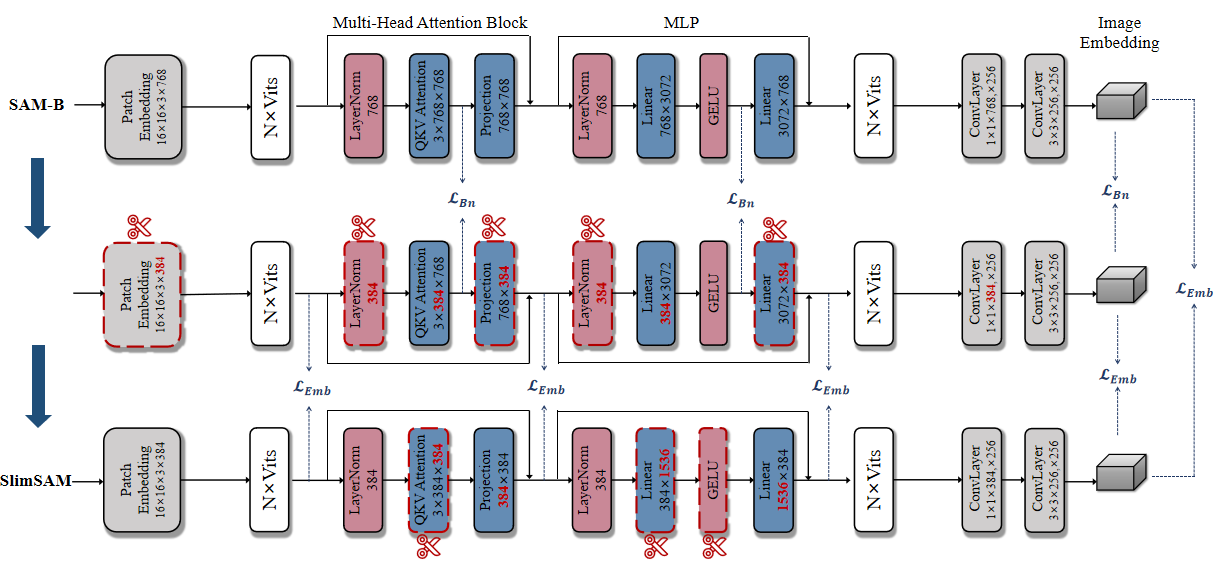
SlimSAM is a novel SAM compression method, which efficiently reuses pre-trained SAMs without the necessity for extensive retraining. This is achieved by the efficient reuse of pre-trained SAMs through a unified pruning-distillation framework. To enhance knowledge inheritance from the original SAM, we employ an innovative alternate slimming strategy that partitions the compression process into a progressive procedure. Diverging from prior pruning techniques, we meticulously prune and distill decoupled model structures in an alternating fashion. Furthermore, a novel label-free pruning criterion is also proposed to align the pruning objective with the optimization target, thereby boosting the post-distillation after pruning.
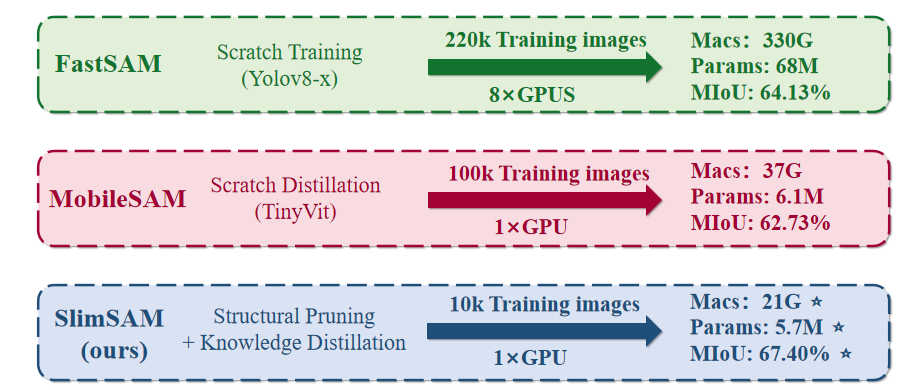
SlimSAM achieves approaching performance while reducing the parameter counts to 0.9% (5.7M), MACs to 0.8% (21G), and requiring mere 0.1% (10k) of the training data when compared to the original SAM-H. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method realize significant superior performance while utilizing over 10 times less training data when compared to other SAM compression methods.
Visualization Results
Qualitative comparison of results obtained using point prompts, box prompts, and segment everything prompts are shown in the following section.
Segment Everything Prompts

Box Prompts and Point Prompts

Quantitative Results
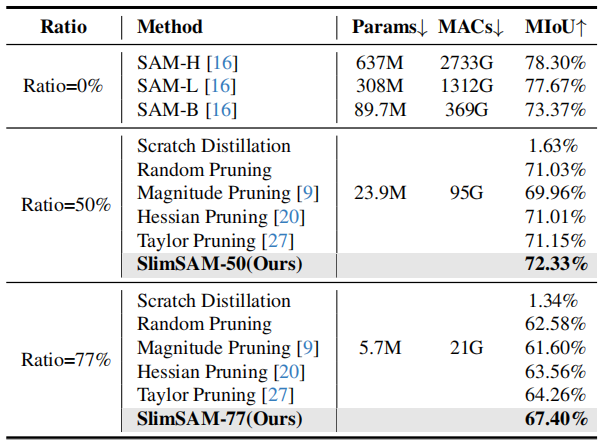
We conducted a comprehensive comparison encompassing performance, efficiency, and training costs with other SAM compression methods and structural pruning methods.
Comparing with other SAM compression methods.

Comparing with other structural pruning methods.
Installation
The code requires python>=3.8, as well as pytorch>=1.7 and torchvision>=0.8. Please follow the instructions here to install both PyTorch and TorchVision dependencies. Installing both PyTorch and TorchVision with CUDA support is strongly recommended.
Install with
pip install -e .
The following optional dependencies are necessary for mask post-processing, saving masks in COCO format.
pip install opencv-python pycocotools matplotlib
Dataset
We use the original SA-1B dataset in our code. See here for an overview of the datastet. The dataset can be downloaded here.
The download dataset should be saved as:
<train_data_root>/
sa_xxxxxxx.jpg
sa_xxxxxxx.json
......
<val_data_root>/
sa_xxxxxxx.jpg
sa_xxxxxxx.json
......
To decode a mask in COCO RLE format into binary:
from pycocotools import mask as mask_utils
mask = mask_utils.decode(annotation["segmentation"])
See here for more instructions to manipulate masks stored in RLE format.
Model Checkpoints
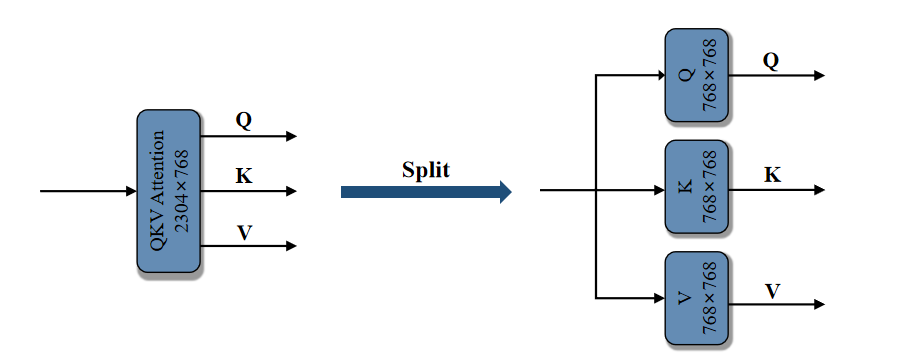
The base model of our method is available. To enhance collaboration with our dependency dectection algorithm, we have split the original image encoder's qkv layer into three distinct linear layers: q, k, and v.
Click the links below to download the checkpoints of orginal SAM-B.
SAM-B: SAM-B model.
The check points of our SlimSAM are avalable. We release two versions, which are SlimSAM-50 (pruning ratio = 50%) and SlimSAM-77 (pruning ratio = 77%).
Click the links below to download the checkpoints for the corresponding pruning ratio.
SlimSAM-50: SlimSAM-50 model.SlimSAM-77: SlimSAM-77 model.
These models can be instantiated by running
import torch
SlimSAM_model = torch.load(<model_path>)
SlimSAM_model.image_encoder = SlimSAM_model.image_encoder.module
def forward(self, x):
x = self.patch_embed(x)
if self.pos_embed is not None:
x = x + self.pos_embed
for blk in self.blocks:
x,qkv_emb,mid_emb,x_emb = blk(x)
x = self.neck(x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2))
return x
import types
funcType = types.MethodType
SlimSAM_model.image_encoder.forward = funcType(forward, SlimSAM_model.image_encoder)
Inference
First download SlimSAM-50 model or SlimSAM-77 model for inference
We provide detailed instructions in 'inference.py' on how to use a range of prompts, including 'point' and 'box' and 'everything', for inference purposes.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python inference.py
Train
First download a SAM-B model into 'checkpoints/' as the base model.
Step1: Embedding Pruning + Bottleneck Aligning
The model after step1 is saved as 'checkpoints/vit_b_slim_step1_.pth'
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python prune_distill_step1.py --traindata_path <train_data_root> --valdata_path <val_data_root> --prune_ratio <pruning ratio> --epochs <training epochs>
Step2: Bottleneck Pruning + Embedding Aligning
The model after step2 is saved as 'checkpoints/vit_b_slim_step2_.pth'
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python prune_distill_step2.py --traindata_path <train_data_root> --valdata_path <val_data_root> --prune_ratio <pruning ratio> --epochs <training epochs> --model_path 'checkpoints/vit_b_slim_step1_.pth'
You can adjust the training settings to meet your specific requirements. While our method demonstrates impressive performance with just 10,000 training data, incorporating additional training data will further enhance the model's effectiveness
BibTex of our SlimSAM
If you use SlimSAM in your research, please use the following BibTeX entry. Thank you!
@misc{chen202301,
title={0.1% Data Makes Segment Anything Slim},
author={Zigeng Chen and Gongfan Fang and Xinyin Ma and Xinchao Wang},
year={2023},
eprint={2312.05284},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
Acknowledgement
SAM (Segment Anything) [bib]
@article{kirillov2023segany,
title={Segment Anything},
author={Kirillov, Alexander and Mintun, Eric and Ravi, Nikhila and Mao, Hanzi and Rolland, Chloe and Gustafson, Laura and Xiao, Tete and Whitehead, Spencer and Berg, Alexander C. and Lo, Wan-Yen and Doll{\'a}r, Piotr and Girshick, Ross},
journal={arXiv:2304.02643},
year={2023}
}
Torch Pruning (DepGraph: Towards Any Structural Pruning) [bib]
@inproceedings{fang2023depgraph,
title={Depgraph: Towards any structural pruning},
author={Fang, Gongfan and Ma, Xinyin and Song, Mingli and Mi, Michael Bi and Wang, Xinchao},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
pages={16091--16101},
year={2023}
}