licenses
sequencelengths 1
3
| version
stringclasses 677
values | tree_hash
stringlengths 40
40
| path
stringclasses 1
value | type
stringclasses 2
values | size
stringlengths 2
8
| text
stringlengths 25
67.1M
| package_name
stringlengths 2
41
| repo
stringlengths 33
86
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | code | 1356 | #!/usr/bin/env julia
using Documenter
using HypertextLiteral
# Setup for doctests embedded in docstrings.
DocMeta.setdocmeta!(HypertextLiteral, :DocTestSetup, :(using HypertextLiteral))
# Highlight indented code blocks as Julia code.
using Documenter.Expanders: ExpanderPipeline, Selectors, Markdown, iscode
abstract type DefaultLanguage <: ExpanderPipeline end
Selectors.order(::Type{DefaultLanguage}) = 99.0
Selectors.matcher(::Type{DefaultLanguage}, node, page, doc) =
iscode(node, "")
Selectors.runner(::Type{DefaultLanguage}, node, page, doc) =
page.mapping[node] = Markdown.Code("julia", node.code)
custom_footer = """
Powered by [Documenter.jl](https://github.com/JuliaDocs/Documenter.jl),
[NarrativeTest.jl](https://github.com/MechanicalRabbit/NarrativeTest.jl),
and the [Julia Programming Language](https://julialang.org/).
"""
makedocs(
sitename = "HypertextLiteral.jl",
format = Documenter.HTML(prettyurls=(get(ENV, "CI", nothing) == "true"),
footer=custom_footer),
pages = [
"Overview" => "index.md",
"content.md",
"attribute.md",
"script.md",
"notation.md",
"design.md",
"primitives.md",
"reference.md",
],
modules = [HypertextLiteral])
deploydocs(
repo = "github.com/MechanicalRabbit/HypertextLiteral.jl.git",
)
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | code | 1537 | """
HypertextLiteral
The `HypertextLiteral` module exports the `@htl` macro which implements
interpolation aware of hypertext escape context. It also provides for
escaping of JavaScript within the `<script>` tag.
```jldoctest
julia> v = "<1 Brown \\\"M&M's\\\"!";
julia> @htl "<span>\$v</span>"
<span><1 Brown "M&M's"!</span>
julia> @htl "<script>console.log(\$v)</script>"
<script>console.log("<1 Brown \\\"M&M's\\\"!")</script>
```
This escaping of Julia values to JavaScript values is done with `js`
function, which is not exported by default.
```jldoctest
julia> v = "<1 Brown \\\"M&M's\\\"!";
julia> @htl "<div onclick='alert(\$(HypertextLiteral.js(v)))'>"
<div onclick='alert("<1 Brown \\"M&M's\\"!")'>
```
There is also a non-standard string literal, `@htl_str` that is not
exported. It can be used with dynamically constructed templates.
See also: [`@htl`](@ref), [`HypertextLiteral.@htl_str`](@ref)
"""
module HypertextLiteral
@static if VERSION >= v"1.3"
using Tricks: static_hasmethod
end
export @htl, @htl_str
include("primitives.jl") # Wrap, Unwrap, EscapeProxy
include("macro.jl") # @htl macro and `Result` object
include("convert.jl") # runtime conversion of objects
include("style.jl") # printing of content within a style tag
include("script.jl") # printing of content within a script tag
include("lexer.jl") # interpolate string to macro expression
include("rewrite.jl") # macro optimizations called by interpolate
end
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | code | 6588 | """
print_value(io, value)
This is the default translation of interpolated values within rawtext
tags, such as `<style>` and attribute values.
* The elements of a `Tuple` or `AbstractArray` object are printed,
with a space between each item.
* The `Pair`, `NamedTuple`, and `Dict` objects are treated as if
they are CSS style elements, with a colon between key and value,
each pair delimited by a semi-colon.
* The `Nothing` object is treated as an empty string.
Otherwise, this method simply uses the standard `print` representation
for the given object.
"""
print_value(io::IO, @nospecialize value) =
print(io, value)
print_value(io::IO, ::Nothing) =
nothing
function print_value(io::IO, xs::Union{Tuple, AbstractArray, Base.Generator})
prior = false
for x in xs
if prior
print(io, " ")
end
print_value(io, x)
prior = true
end
end
function print_pairs(io, xs)
prior = false
for (key, value) in xs
name = normalize_attribute_name(key)
if prior
print(io, "; ")
end
print(io, name)
print(io, ": ")
print_value(io, value)
prior = true
end
print(io, ";")
end
print_value(io::IO, pair::Pair) = print_pairs(io, (pair,))
print_value(io::IO, items::Dict) = print_pairs(io, items)
print_value(io::IO, items::NamedTuple) = print_pairs(io, pairs(items))
print_value(io::IO, items::Tuple{Pair, Vararg{Pair}}) = print_pairs(io, items)
"""
attribute_value(x)
This method may be implemented to specify a printed representation
suitable for use within a quoted attribute value.
"""
attribute_value(x::String) = x
attribute_value(x::Number) = x
attribute_value(x::Symbol) = x
mutable struct AttributeValue
content::Any
end
Base.print(ep::EscapeProxy, x::AttributeValue) =
print_value(ep, x.content)
attribute_value(@nospecialize x) = AttributeValue(x)
function content end
@doc """
content(x)
This method may be implemented to specify a printed representation
suitable for `text/html` output. `AbstractString`, `Symbol` and `Number`
(including `Bool`) types are printed, with proper escaping.
A default implementation first looks to see if `typeof(x)` has
implemented a way to show themselves as `text/html`, if so, this is
used. Otherwise, the result is printed within a `<span>` tag, using a
`class` that includes the module and type name. Hence, `missing` is
serialized as: `<span class="Base-Missing">missing</span>`.
""" content
@static if VERSION >= v"1.3"
function content(x::T) where {T}
if static_hasmethod(show, Tuple{IO, MIME{Symbol("text/html")}, T})
return Render(x)
else
mod = parentmodule(T)
cls = string(nameof(T))
if mod == Core || mod == Base || pathof(mod) !== nothing
cls = join(fullname(mod), "-") * "-" * cls
end
span = """<span class="$cls">"""
return reprint(Bypass(span), x, Bypass("</span>"))
end
end
else
@generated function content(x)
if hasmethod(show, Tuple{IO, MIME{Symbol("text/html")}, x})
return :(Render(x))
else
mod = parentmodule(x)
cls = string(nameof(x))
if mod == Core || mod == Base || pathof(mod) !== nothing
cls = join(fullname(mod), "-") * "-" * cls
end
span = """<span class="$cls">"""
return :(reprint(Bypass($span), x, Bypass("</span>")))
end
end
end
function reprint(xs...)
# generated functions cannot contain a closure
Reprint() do io::IO
for x in xs
print(io, x)
end
end
end
content(x::Union{AbstractString, Symbol}) = x
content(x::Nothing) = ""
content(x::Union{AbstractFloat, Bool, Integer}) = x
content(xs...) = content(xs)
function content(xs::Union{Tuple, AbstractArray, Base.Generator})
Reprint() do io::IO
for x in xs
print(io, content(x))
end
end
end
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------
"""
attribute_pair(name, value)
Wrap and escape attribute name and pair within a single-quoted context
so that it is `showable("text/html")`. It's assumed that the attribute
name has already been normalized.
If an attribute value is `Bool` or `Nothing`, then special treatment is
provided. If the value is `false` or `nothing` then the entire pair is
not printed. If the value is `true` than an empty string is produced.
"""
no_content = Reprint(io::IO -> nothing)
function attribute_pair(name, value)
Reprint() do io::IO
print(io, " ")
print(io, name)
print(io, Bypass("='"))
print(io, attribute_value(value))
print(io, Bypass("'"))
end
end
function attribute_pair(name, value::Bool)
if value == false
return no_content
end
Reprint() do io::IO
print(io, " ")
print(io, name)
print(io, Bypass("=''"))
end
end
attribute_pair(name, value::Nothing) = no_content
"""
inside_tag(value)
Convert Julian object into a serialization of attribute pairs,
`showable` via `MIME"text/html"`. The default implementation of this
delegates value construction of each pair to `attribute_pair()`.
"""
function inside_tag(value::Pair)
name = normalize_attribute_name(value.first)
return attribute_pair(name, value.second)
end
function inside_tag(value::Union{AbstractString, Symbol})
name = normalize_attribute_name(value)
return attribute_pair(name, "")
end
function inside_tag(xs::AbstractDict)
Reprint() do io::IO
for (key, value) in xs
name = normalize_attribute_name(key)
print(io, attribute_pair(name, value))
end
end
end
inside_tag(values::NamedTuple) =
inside_tag(pairs(values))
inside_tag(::Nothing) = no_content
"""
tag_name(x)
Tag names need to start with `/[a-z]/i`,
and can't contain any spaces, `>` or `/`.
Although technically all other characters would be valid,
we only allow letters, numbers and hyphens for now.
"""
function tag_name(x::String)
if isempty(x)
throw("A tag name can not be empty")
elseif !occursin(r"^[a-z]"i, x)
throw("A tag name can only start with letters, not `$(x[1])`")
elseif occursin(r"[^a-z0-9-]", x)
throw("Content within a tag name can only contain latin letters, numbers or hyphens (`-`)")
else
x
end
end
tag_name(x::Symbol) = tag_name(string(x))
tag_name(x::Any) = throw("Can't use complex objects as tag name")
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | code | 20469 | @enum HtlParserState STATE_DATA STATE_TAG_OPEN STATE_END_TAG_OPEN STATE_TAG_NAME STATE_BEFORE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME STATE_AFTER_ATTRIBUTE_NAME STATE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME STATE_BEFORE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE STATE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_DOUBLE_QUOTED STATE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_SINGLE_QUOTED STATE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_UNQUOTED STATE_AFTER_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_QUOTED STATE_SELF_CLOSING_START_TAG STATE_COMMENT_START STATE_COMMENT_START_DASH STATE_COMMENT STATE_COMMENT_LESS_THAN_SIGN STATE_COMMENT_LESS_THAN_SIGN_BANG STATE_COMMENT_LESS_THAN_SIGN_BANG_DASH STATE_COMMENT_LESS_THAN_SIGN_BANG_DASH_DASH STATE_COMMENT_END_DASH STATE_COMMENT_END STATE_COMMENT_END_BANG STATE_MARKUP_DECLARATION_OPEN STATE_RAWTEXT STATE_RAWTEXT_LESS_THAN_SIGN STATE_RAWTEXT_END_TAG_OPEN STATE_RAWTEXT_END_TAG_NAME
is_alpha(ch) = 'A' <= ch <= 'Z' || 'a' <= ch <= 'z'
is_space(ch) = ch in ('\t', '\n', '\f', ' ')
normalize(s) = replace(replace(s, "\r\n" => "\n"), "\r" => "\n")
nearby(x,i) = i+10>length(x) ? x[i:end] : x[i:i+8] * "…"
"""
interpolate(args)::Expr
Take an interweaved set of Julia expressions and strings, tokenize the
strings according to the HTML specification [1], wrapping the
expressions with wrappers based upon the escaping context, and returning
an expression that combines the result with an `Result` wrapper.
For these purposes, a `Symbol` is treated as an expression to be
resolved; while a `String` is treated as a literal string that won't be
escaped. Critically, interpolated strings to be escaped are represented
as an `Expr` with `head` of `:string`.
There are tags, "script" and "style" which are rawtext, in these cases
there is no escaping, and instead raise an exception if the appropriate
ending tag is in substituted content.
[1] https://html.spec.whatwg.org/multipage/parsing.html#tokenization
"""
function interpolate(args)
state = STATE_DATA
parts = Union{String,Expr}[]
attribute_start = attribute_end = 0
element_start = element_end = 0
buffer_start = buffer_end = 0
attribute_tag = nothing
element_tag = nothing
state_tag_is_open = false
function choose_tokenizer()
if state_tag_is_open
if element_tag in (:style, :xmp, :iframe, :noembed,
:noframes, :noscript, :script)
return STATE_RAWTEXT
end
end
return STATE_DATA
end
args = [a for a in args if a != ""]
for j in 1:length(args)
input = args[j]
if !isa(input, String)
if state == STATE_DATA || state == STATE_COMMENT
push!(parts, :(content($(esc(input)))))
elseif state == STATE_RAWTEXT
if :script === element_tag
push!(parts, :(ScriptTag($(esc(input)))))
elseif :style === element_tag
push!(parts, :(StyleTag($(esc(input)))))
else
throw(DomainError(element_tag,
"Only script and style rawtext tags are supported."))
end
elseif state == STATE_BEFORE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE
state = STATE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_UNQUOTED
# rewrite previous string to remove ` attname=`
@assert parts[end] isa String
name = parts[end][attribute_start:attribute_end]
parts[end] = parts[end][1:(attribute_start-2)]
attribute = normalize_attribute_name(name)
push!(parts, :(attribute_pair($attribute, $(esc(input)))))
# peek ahead to ensure we have a delimiter
if j < length(args)
next = args[j+1]
if next isa String && !occursin(r"^[\s+\/>]", next)
msg = "$(name)=$(nearby(next,1))"
throw(DomainError(msg, "Unquoted attribute " *
"interpolation is limited to a single component"))
end
end
elseif state == STATE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_UNQUOTED
throw(DomainError(input, "Unquoted attribute " *
"interpolation is limited to a single component"))
elseif state == STATE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_SINGLE_QUOTED ||
state == STATE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_DOUBLE_QUOTED
push!(parts, :(attribute_value($(esc(input)))))
elseif state == STATE_BEFORE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME ||
state == STATE_AFTER_ATTRIBUTE_NAME
# strip space before interpolated element pairs
if parts[end] isa String
if parts[end][end] == ' '
parts[end] = parts[end][1:length(parts[end])-1]
end
end
# ensure a space between this and next attribute
if j < length(args)
next = args[j+1]
if next isa String && !occursin(r"^[\s+\/>]", next)
args[j+1] = " " * next
end
end
append!(parts, rewrite_inside_tag(input))
elseif state == STATE_TAG_OPEN
push!(parts, :(tag_name($(esc(input)))))
# Not setting tag-open so it doesn't try to parse this fetch the element-name later
# (Because we can't get the element name from a binding during macro analysis)
state = STATE_TAG_NAME
elseif state == STATE_END_TAG_OPEN
push!(parts, :(tag_name($(esc(input)))))
state = STATE_TAG_NAME
elseif state === STATE_TAG_NAME
push!(parts, :(tag_name($(esc(input)))))
# It might still be a open tag, but we can't parse it with
# bindings inside anyway, so setting state_tag_is_open to false
state_tag_is_open = false
else
throw("unexpected binding $(state)")
end
else
input = normalize(input)
inputlength = lastindex(input)
i = 1
while i <= inputlength
ch = input[i]
if state == STATE_DATA
if ch === '<'
state = STATE_TAG_OPEN
end
elseif state == STATE_RAWTEXT
if ch === '<'
state = STATE_RAWTEXT_LESS_THAN_SIGN
end
elseif state == STATE_TAG_OPEN
if ch === '!'
state = STATE_MARKUP_DECLARATION_OPEN
elseif ch === '/'
state = STATE_END_TAG_OPEN
elseif is_alpha(ch)
state = STATE_TAG_NAME
state_tag_is_open = true
element_start = i
i = prevind(input, i)
elseif ch === '?'
# this is an XML processing instruction, with
# recovery production called "bogus comment"
throw(DomainError(nearby(input, i-1),
"unexpected question mark instead of tag name"))
else
throw(DomainError(nearby(input, i-1),
"invalid first character of tag name"))
end
elseif state == STATE_END_TAG_OPEN
@assert !state_tag_is_open
if is_alpha(ch)
state = STATE_TAG_NAME
i = prevind(input, i)
elseif ch === '>'
state = STATE_DATA
else
throw(DomainError(nearby(input, i-1),
"invalid first character of tag name"))
end
elseif state == STATE_TAG_NAME
if isspace(ch) || ch === '/' || ch === '>'
if state_tag_is_open
element_tag = Symbol(lowercase(
input[element_start:element_end]))
element_start = element_end = 0
end
if isspace(ch)
state = STATE_BEFORE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME
# subordinate states use state_tag_is_open flag
elseif ch === '/'
state = STATE_SELF_CLOSING_START_TAG
state_tag_is_open = false
elseif ch === '>'
state = choose_tokenizer()
state_tag_is_open = false
end
else
if state_tag_is_open
element_end = i
end
end
elseif state == STATE_BEFORE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME
if is_space(ch)
nothing
elseif ch === '/' || ch === '>'
state = STATE_AFTER_ATTRIBUTE_NAME
i = prevind(input, i)
elseif ch in '='
throw(DomainError(nearby(input, i-1),
"unexpected equals sign before attribute name"))
else
state = STATE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME
attribute_start = i
attribute_end = nothing
i = prevind(input, i)
end
elseif state == STATE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME
if is_space(ch) || ch === '/' || ch === '>'
state = STATE_AFTER_ATTRIBUTE_NAME
i = prevind(input, i)
elseif ch === '='
state = STATE_BEFORE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE
elseif ch in ('"', '\'', '<')
throw(DomainError(nearby(input, i-1),
"unexpected character in attribute name"))
else
attribute_end = i
end
elseif state == STATE_AFTER_ATTRIBUTE_NAME
if is_space(ch)
nothing
elseif ch === '/'
state = STATE_SELF_CLOSING_START_TAG
elseif ch === '='
state = STATE_BEFORE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE
elseif ch === '>'
state = choose_tokenizer()
state_tag_is_open = false
else
state = STATE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME
attribute_start = i
attribute_end = nothing
i = prevind(input, i)
end
elseif state == STATE_BEFORE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE
if is_space(ch)
nothing
elseif ch === '"'
attribute_tag = input[attribute_start:attribute_end]
state = STATE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_DOUBLE_QUOTED
elseif ch === '\''
attribute_tag = input[attribute_start:attribute_end]
state = STATE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_SINGLE_QUOTED
elseif ch === '>'
throw(DomainError(nearby(input, i-1),
"missing attribute value"))
else
state = STATE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_UNQUOTED
i = prevind(input, i)
end
elseif state == STATE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_DOUBLE_QUOTED
if ch === '"'
state = STATE_AFTER_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_QUOTED
attribute_tag = nothing
end
elseif state == STATE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_SINGLE_QUOTED
if ch === '\''
state = STATE_AFTER_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_QUOTED
attribute_tag = nothing
end
elseif state == STATE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_UNQUOTED
if is_space(ch)
state = STATE_BEFORE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME
elseif ch === '>'
state = choose_tokenizer()
state_tag_is_open = false
elseif ch in ('"', '\'', "<", "=", '`')
throw(DomainError(nearby(input, i-1),
"unexpected character in unquoted attribute value"))
end
elseif state == STATE_AFTER_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_QUOTED
if is_space(ch)
state = STATE_BEFORE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME
elseif ch === '/'
state = STATE_SELF_CLOSING_START_TAG
elseif ch === '>'
state = choose_tokenizer()
state_tag_is_open = false
else
throw(DomainError(nearby(input, i-1),
"missing whitespace between attributes"))
end
elseif state == STATE_SELF_CLOSING_START_TAG
if ch === '>'
state = STATE_DATA
# TODO Choose tokenizer here too? User thinks he is self-closing,
# .... but if this is a <script> or <style> the browser will ignore the "self-closing" `/`
# .... or maybe _just_ warn when a self closing script or style is encountered?
state_tag_is_open = false
else
throw(DomainError(nearby(input, i-1),
"unexpected solidus in tag"))
end
elseif state == STATE_MARKUP_DECLARATION_OPEN
if ch === '-' && input[i + 1] == '-'
state = STATE_COMMENT_START
i = nextind(input, i)
elseif startswith(input[i:end], "DOCTYPE")
throw("DOCTYPE not supported")
elseif startswith(input[i:end], "[CDATA[")
throw("CDATA not supported")
else
throw(DomainError(nearby(input, i-1),
"incorrectly opened comment"))
end
elseif state == STATE_COMMENT_START
if ch === '-'
state = STATE_COMMENT_START_DASH
elseif ch === '>'
throw(DomainError(nearby(input, i-1),
"abrupt closing of empty comment"))
else
state = STATE_COMMENT
i = prevind(input, i)
end
elseif state == STATE_COMMENT_START_DASH
if ch === '-'
state = STATE_COMMENT_END
elseif ch === '>'
throw(DomainError(nearby(input, i-1),
"abrupt closing of empty comment"))
else
state = STATE_COMMENT
i = prevind(input, i)
end
elseif state == STATE_COMMENT
if ch === '<'
state = STATE_COMMENT_LESS_THAN_SIGN
elseif ch === '-'
state = STATE_COMMENT_END_DASH
end
elseif state == STATE_COMMENT_LESS_THAN_SIGN
if ch === '!'
state = STATE_COMMENT_LESS_THAN_SIGN_BANG
elseif ch === '<'
nothing
else
state = STATE_COMMENT
i = prevind(input, i)
end
elseif state == STATE_COMMENT_LESS_THAN_SIGN_BANG
if ch == '-'
state = STATE_COMMENT_LESS_THAN_SIGN_BANG_DASH
else
state = STATE_COMMENT
i = prevind(input, i)
end
elseif state == STATE_COMMENT_LESS_THAN_SIGN_BANG_DASH
if ch == '-'
state = STATE_COMMENT_LESS_THAN_SIGN_BANG_DASH_DASH
else
state = STATE_COMMENT_END
i = prevind(input, i)
end
elseif state == STATE_COMMENT_LESS_THAN_SIGN_BANG_DASH_DASH
if ch == '>'
state = STATE_COMMENT_END
i = prevind(input, i)
else
throw(DomainError(nearby(input, i-1),
"nested comment"))
end
elseif state == STATE_COMMENT_END_DASH
if ch === '-'
state = STATE_COMMENT_END
else
state = STATE_COMMENT
i = prevind(input, i)
end
elseif state == STATE_COMMENT_END
if ch === '>'
state = STATE_DATA
elseif ch === '!'
state = STATE_COMMENT_END_BANG
elseif ch === '-'
nothing
else
state = STATE_COMMENT
i = prevind(input, i)
end
elseif state == STATE_COMMENT_END_BANG
if ch === '-'
state = STATE_COMMENT_END_DASH
elseif ch === '>'
throw(DomainError(nearby(input, i-1),
"nested comment"))
else
state = STATE_COMMENT
i = prevind(input, i)
end
elseif state == STATE_RAWTEXT_LESS_THAN_SIGN
if ch === '/'
state = STATE_RAWTEXT_END_TAG_OPEN
elseif ch === '!' && element_tag == :script
# RAWTEXT differs from SCRIPT here
throw("script escape or comment is not implemented")
else
state = STATE_RAWTEXT
# do not "reconsume", even though spec says so
end
elseif state == STATE_RAWTEXT_END_TAG_OPEN
if is_alpha(ch)
state = STATE_RAWTEXT_END_TAG_NAME
buffer_start = i
i = prevind(input, i)
else
state = STATE_RAWTEXT
i = prevind(input, i)
end
elseif state == STATE_RAWTEXT_END_TAG_NAME
if is_alpha(ch)
buffer_end = i
elseif ch in ('/', '>') || is_space(ch)
# test for "appropriate end tag token"
current = input[buffer_start:buffer_end]
if Symbol(lowercase(current)) == element_tag
if ch === '/'
state = STATE_SELF_CLOSING_START_TAG
elseif ch === '>'
state = STATE_DATA
else
state = STATE_BEFORE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME
end
continue
else
state = STATE_RAWTEXT
end
else
state = STATE_RAWTEXT
end
else
throw("unhandled state transition")
end
i = nextind(input, i)
end
push!(parts, input)
end
end
parts = Expr[(x isa String ? :(Bypass($x)) : x) for x in parts]
return Expr(:call, :Result, parts...)
end
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | code | 4166 | """
@htl string-expression
Create a `Result` object with string interpolation (`\$`) that uses
context-sensitive hypertext escaping. Before Julia 1.6, interpolated
string literals, e.g. `\$("Strunk & White")`, are treated as errors
since they cannot be reliably detected (see Julia issue #38501).
"""
macro htl(expr)
if typeof(expr) == String
return interpolate([expr])
end
if !Meta.isexpr(expr, :string)
throw(DomainError(expr, "a string literal is required"))
end
args = expr.args
for part in expr.args
if Meta.isexpr(part, :(=))
throw(DomainError(part,
"assignments are not permitted in an interpolation"))
end
end
if VERSION < v"1.6.0-DEV"
# Find cases where we may have an interpolated string literal and
# raise an exception (till Julia issue #38501 is addressed)
if length(args) == 1 && args[1] isa String
throw("interpolated string literals are not supported")
end
for idx in 2:length(args)
if args[idx] isa String && args[idx-1] isa String
throw("interpolated string literals are not supported")
end
end
end
return interpolate(expr.args)
end
"""
@htl_str -> Result
Create a `Result` object with string interpolation (`\$`) that uses
context-sensitive hypertext escaping. Unlike the `@htl` macro, this
string literal does not include escaping feature [1]. To include `\$`
within user content one must write `$`. Observe that `"` and
any other HTML ampersand escape sequence can be used as appropriate.
In this syntax, interpolation is extended beyond regular Julia strings
to handle three additional cases: tuples, named tuples (for attributes),
and generators. See Julia #38734 for the feature request so that this
could also work within the `@htl` macro syntax.
[1] There are also a few edge cases, see `@raw_str` documentation and
Julia #22926 for more detail.
"""
macro htl_str(expr::String)
# Essentially this is an ad-hoc scanner of the string, splitting
# it by `$` to find interpolated parts and delegating the hard work
# to `Meta.parse`, treating everything else as a literal string.
args = Any[]
start = idx = 1
strlen = lastindex(expr)
while true
idx = findnext(isequal('$'), expr, start)
if idx == nothing
chunk = expr[start:strlen]
push!(args, expr[start:strlen])
break
end
push!(args, expr[start:prevind(expr, idx)])
start = nextind(expr, idx)
if length(expr) >= start && expr[start] == '$'
push!(args, "\$")
start += 1
continue
end
(nest, tail) = Meta.parse(expr, start; greedy=false)
if nest == nothing
throw("missing expression at $idx: $(expr[start:end])")
end
if !(expr[start] == '(' || nest isa Symbol)
throw(DomainError(nest,
"interpolations must be symbols or parenthesized"))
end
if Meta.isexpr(nest, :(=))
throw(DomainError(nest,
"assignments are not permitted in an interpolation"))
end
if nest isa String
# this is an interpolated string literal
nest = Expr(:string, nest)
end
push!(args, nest)
start = tail
end
return interpolate(args)
end
"""
Result(fn)
This object wraps a function produced by the `@htl` macro. This function
prints a the evaluated to the given `io`. This object is also showable
via `"text/html"` so it may be used in an HTML display context.
"""
struct Result
content::Function
Result(fn::Function) = new(fn)
end
Result(ob) = Result(io::IO -> print(io, ob))
function Result(xs...)
Result() do io::IO
for x in xs
print(io, x)
end
end
end
Base.show(io::IO, h::Result) = h.content(EscapeProxy(io))
Base.show(io::IO, m::MIME"text/html", h::Result) = h.content(EscapeProxy(io))
Base.show(io::EscapeProxy, h::Result) = h.content(io)
Base.show(io::EscapeProxy, m::MIME"text/html", h::Result) = h.content(io)
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | code | 3204 | """
Reprint(fn) - apply the lambda function when printed
"""
mutable struct Reprint
content::Function
end
Base.print(io::IO, r::Reprint) = r.content(io)
"""
Render(data) - printed object shows its text/html
"""
struct Render{T}
content::T
end
Base.print(io::IO, r::Render) =
show(io, MIME"text/html"(), r.content)
"""
Bypass(data) - printed object passes though EscapeProxy unescaped
"""
mutable struct Bypass{T}
content::T
end
Base.print(io::IO, x::Bypass) = print(io, x.content)
abstract type IOProxy <: IO end
"""
EscapeProxy(io) - wrap an `io` to perform HTML escaping
This is a transparent proxy that performs HTML escaping so that objects
that are printed are properly converted into valid HTML values. As a
special case, objects wrapped with `Bypass` are not escaped, and
bypass the proxy.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> ep = EscapeProxy(stdout);
julia> print(ep, "A&B")
A&B
julia> print(ep, Bypass("<tag/>"))
<tag/>
```
"""
struct EscapeProxy{T<:IO} <: IOProxy
io::T
end
Base.print(ep::EscapeProxy, h::Reprint) = h.content(ep)
Base.print(ep::EscapeProxy, w::Render) =
show(ep.io, MIME"text/html"(), w.content)
Base.print(ep::EscapeProxy, x::Bypass) = print(ep.io, x)
function Base.write(ep::EscapeProxy, octet::UInt8)
if octet == Int('&')
write(ep.io, "&")
elseif octet == Int('<')
write(ep.io, "<")
elseif octet == Int('"')
write(ep.io, """)
elseif octet == Int('\'')
write(ep.io, "'")
else
write(ep.io, octet)
end
end
function Base.unsafe_write(ep::EscapeProxy, input::Ptr{UInt8}, nbytes::UInt)
written = 0
last = cursor = input
final = input + nbytes
while cursor < final
ch = unsafe_load(cursor)
if ch == Int('&')
written += unsafe_write(ep.io, last, cursor - last)
written += unsafe_write(ep.io, pointer("&"), 5)
cursor += 1
last = cursor
continue
end
if ch == Int('<')
written += unsafe_write(ep.io, last, cursor - last)
written += unsafe_write(ep.io, pointer("<"), 4)
cursor += 1
last = cursor
continue
end
if ch == Int('\'')
written += unsafe_write(ep.io, last, cursor - last)
written += unsafe_write(ep.io, pointer("'"), 6)
cursor += 1
last = cursor
continue
end
if ch == Int('"')
written += unsafe_write(ep.io, last, cursor - last)
written += unsafe_write(ep.io, pointer("""), 6)
cursor += 1
last = cursor
continue
end
cursor += 1
end
if last < final
written += unsafe_write(ep.io, last, final - last)
end
return written
end
# IO passthrough methods:
Base.in(key_value::Pair, io::IOProxy) = in(key_value, io.io)
Base.haskey(io::IOProxy, key) = haskey(io.io, key)
Base.getindex(io::IOProxy, key) = getindex(io.io, key)
Base.get(io::IOProxy, key, default) = get(io.io, key, default)
Base.keys(io::IOProxy) = keys(io.io)
Base.displaysize(io::IOProxy) = displaysize(io.io)
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | code | 2415 | """
normalize_attribute_name(name)
For `String` names, this simply verifies that they pass the attribute
name production, but are otherwise untouched.
For `Symbol` names, this converts `snake_case` Symbol objects to their
`kebab-case` equivalent. So that keywords, such as `for` could be used,
we strip leading underscores.
"""
function normalize_attribute_name(name::Symbol)
name = String(name)
if '_' in name
while length(name) > 0 && name[1] == '_'
name = name[2:end]
end
name = replace(name, "_" => "-")
end
return normalize_attribute_name(name)
end
function normalize_attribute_name(name::AbstractString)
# Attribute names are unquoted and do not have & escaping;
# the &, % and \ characters don't seem to be prevented by the
# specification, but they likely signal a programming error.
for invalid in "/>='<&%\\\"\t\n\f\r\x20\x00"
if invalid in name
throw(DomainError(name, "Invalid character ('$invalid') " *
"found within an attribute name."))
end
end
if isempty(name)
throw("Attribute name must not be empty.")
end
return name
end
"""
rewrite_inside_tag(expr)
Attempt to speed up serialization of inside_tag by exploring the
expression tree at macro expansion time.
"""
function rewrite_inside_tag(expr)::Vector{Expr}
if Meta.isexpr(expr, :tuple)
return [rewrite_attribute(pair) for pair in expr.args]
end
if Meta.isexpr(expr, :call) && expr.args[1] == :Dict
return [rewrite_attribute(pair) for pair in expr.args[2:end]]
end
return [rewrite_attribute(expr)]
end
function rewrite_attribute(expr)::Expr
if expr isa QuoteNode && expr.value isa Symbol
(name, value) = (expr, "")
elseif Meta.isexpr(expr, :(=), 2)
(name, value) = expr.args
elseif Meta.isexpr(expr, :string, 1) && typeof(expr.args[1]) == String
(name, value) = (expr.args[1], "")
elseif Meta.isexpr(expr, :call, 3) && expr.args[1] == :(=>)
(_, name, value) = expr.args
else
return :(inside_tag($(esc(expr))))
end
if name isa QuoteNode && name.value isa Symbol
name = name.value
end
if name isa Expr || name isa QuoteNode
return :(inside_tag($(esc(expr))))
end
attribute = normalize_attribute_name(name)
return :(attribute_pair($attribute, $(esc(value))))
end
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | code | 6761 | """
ScriptTagProxy(io)
This is a transparent proxy that ensures neither `<!--` nor `</script>`
occur in the output stream.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> gp = ScriptTagProxy(stdout);
julia> print(gp, "valid");
valid
julia> print(gp, "</script>")
ERROR: "Content within a script tag must not contain `</script>`"
```
"""
mutable struct ScriptTagProxy{T<:IO} <: IOProxy where {T}
io::T
index::Int
ScriptTagProxy(io::T) where T = new{T}(io::T, 0)
end
"""
ScriptTag(data)
This object prints `data` unescaped within a `<script>` tag, wrapped in
a `ScriptTagProxy` that guards against invalid script content.
"""
struct ScriptTag
content
end
Base.print(ep::EscapeProxy, x::ScriptTag) =
print_script_hook(ScriptTagProxy(ep.io), x.content)
"""
Script(data)
This object renders Javascript `data` escaped within an attribute.
"""
mutable struct Script
content::Any
end
Base.print(io::IO, x::Script) =
print_script_hook(io, x.content)
Base.show(io::IO, ::MIME"text/javascript", sv::Script) =
print(io, sv)
"""
js(x)
This method may be implemented to specify a printed representation
suitable for use within a quoted attribute value starting with `on`.
"""
js(x) = Script(x)
"""
JavaScript(js) - shows `js` as `"text/javascript"`
"""
struct JavaScript
content
end
Base.show(io::IO, ::MIME"text/javascript", js::JavaScript) =
print(io, js.content)
"""
print_script_hook(io, value)
Provides a hook to override `print_script` for custom Javascript
runtimes, such as `Pluto.jl`, to provide their own value marshalling.
"""
print_script_hook(io::IO, value) =
print_script(io, value)
"""
print_script(io, value)
Show `value` as `"text/javascript"` to the given `io`, this provides
some baseline functionality for built-in data types.
- `nothing` becomes `undefined`
- `missing` becomes `null`
- `Bool` values are printed as `true` or `false`
- `AbstractString` and `Symbol` become a double-quoted string
- `AbstractVector` and `Tuple` become an array
- `Dict` and `NamedTuple` become a Javascript object, with
keys converted to string values
- `AbstractFloat` and `Integer` are printed directly, where
`NaN` remains `NaN` but `Inf` is printed as `Infinity`
The fallback behavior of `print_script` is to show the object as
`"text/javascript"`. The `Javascript` wrapper will take any string
and let it be printed in this way.
"""
@static if VERSION > v"1.9.99"
# With the new JuliaSyntax parser, `hasmethod` appears to be invoked before
# other packages are loaded.
print_script(io::IO, value::Any) =
show(io, MIME"text/javascript"(), value)
else
@generated function print_script(io::IO, value)
# workaround for Julia#18221
if hasmethod(show, Tuple{IO, MIME{Symbol("text/javascript")}, value})
return :(show(io, MIME"text/javascript"(), value))
end
throw("$(value) is not showable as text/javascript")
end
end
print_script(io::IO, ::Nothing) =
print(io, "undefined")
print_script(io::IO, ::Missing) =
print(io, "null")
print_script(io::IO, value::Union{Bool, Symbol}) =
print(io, value)
function print_script(io::IO, value::Union{NamedTuple, AbstractDict})
print(io, '{')
first = true
for (k,v) in pairs(value)
if !first
print(io, ", ")
end
print_script(io, string(k))
print(io, ": ")
print_script(io, v)
first = false
end
print(io, '}')
end
function print_script(io::IO, value::Union{Tuple, AbstractVector})
print(io, '[')
first = true
for item in value
if !first
print(io, ", ")
end
print_script(io, item)
first = false
end
print(io, ']')
end
function print_script(io::IO, value::Union{Integer, AbstractFloat})
if isfinite(value) || isnan(value)
print(io, value)
else
if value < 0
print(io, "-")
end
print(io, "Infinity")
end
end
function print_script(io::IO, value::AbstractString)
final = lastindex(value)
i = last = 1
function emit(s::String)
print(io, SubString(value, last, prevind(value, i)))
last = nextind(value, i)
print(io, s)
end
print(io, "\"")
while i <= final
ch = value[i]
if ch === '\n'
emit("\\n")
elseif ch === '\r'
emit("\\r")
elseif ch === '\\'
emit("\\\\")
elseif ch === '\"'
emit("\\\"")
elseif ch === '\u2028'
emit("\\u2028")
elseif ch === '\u2029'
emit("\\u2029")
elseif ch === '<' && i+1 <= final
# escape nested script and comment tags
nc = value[i+1]
if nc in ('s', 'S', '!', '/')
emit("<\\")
end
end
i = nextind(value, i)
end
print(io, SubString(value, last, final))
print(io, "\"")
end
function scan_for_script(index::Int, octet::UInt8)::Int
if 1 == index
return octet == Int('!') ? 12 : octet == Int('/') ? 2 : 0
elseif 2 == index
return (octet == Int('S') || octet == Int('s')) ? 3 : 0
elseif 3 == index
return (octet == Int('C') || octet == Int('c')) ? 4 : 0
elseif 4 == index
return (octet == Int('R') || octet == Int('r')) ? 5 : 0
elseif 5 == index
return (octet == Int('I') || octet == Int('i')) ? 6 : 0
elseif 6 == index
return (octet == Int('P') || octet == Int('p')) ? 7 : 0
elseif 7 == index
return (octet == Int('T') || octet == Int('t')) ? 8 : 0
elseif 8 == index
if octet == Int('>')
throw("Content within a script tag must not contain `</script>`")
end
elseif 12 == index
return octet == Int('-') ? 13 : 0
elseif 13 == index
if octet == Int('-')
throw("Content within a script tag must not contain `<!--`")
end
else
@assert false # unreachable?!
end
return 0
end
function Base.write(sp::ScriptTagProxy, octet::UInt8)
if 0 == sp.index
if octet == Int('<')
sp.index = 1
end
return write(sp.io, octet)
end
sp.index = scan_for_script(sp.index, octet)
return write(sp.io, octet)
end
function Base.unsafe_write(sp::ScriptTagProxy, input::Ptr{UInt8}, nbytes::UInt)
cursor = input
index = sp.index
final = input + nbytes
while cursor < final
octet = unsafe_load(cursor)
if octet == Int('<')
index = 1
elseif 0 != index
index = scan_for_script(index, octet)
end
cursor += 1
end
sp.index = index
return unsafe_write(sp.io, input, nbytes)
end
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | code | 2551 | """
StyleTagProxy(io)
This is a transparent proxy that ensures neither `<!--` nor `</style>`
occur in the output stream.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> gp = StyleTagProxy(stdout);
julia> print(gp, "valid");
valid
julia> print(gp, "</style>")
ERROR: "Content within a style tag must not contain `</style>`"
```
"""
mutable struct StyleTagProxy{T<:IO} <: IOProxy where {T}
io::T
index::Int
StyleTagProxy(io::T) where T = new{T}(io::T, 0)
end
"""
StyleTag(data)
This object prints `data` unescaped within a `<style>` tag, wrapped in a
`StyleTagProxy` that guards against invalid style content. Content is
treated as if it had occurred within an attribute value, only that
amperstand escaping is not used.
"""
struct StyleTag
content
end
Base.print(ep::EscapeProxy, x::StyleTag) =
print_value(StyleTagProxy(ep.io), x.content)
function scan_for_style(index::Int, octet::UInt8)::Int
if 1 == index
return octet == Int('!') ? 12 : octet == Int('/') ? 2 : 0
elseif 2 == index
return (octet == Int('S') || octet == Int('s')) ? 3 : 0
elseif 3 == index
return (octet == Int('T') || octet == Int('t')) ? 4 : 0
elseif 4 == index
return (octet == Int('Y') || octet == Int('y')) ? 5 : 0
elseif 5 == index
return (octet == Int('L') || octet == Int('l')) ? 6 : 0
elseif 6 == index
return (octet == Int('E') || octet == Int('e')) ? 7 : 0
elseif 7 == index
if octet == Int('>')
throw("Content within a style tag must not contain `</style>`")
end
elseif 12 == index
return octet == Int('-') ? 13 : 0
elseif 13 == index
if octet == Int('-')
throw("Content within a style tag must not contain `<!--`")
end
else
@assert false # unreachable?!
end
return 0
end
function Base.write(sp::StyleTagProxy, octet::UInt8)
if 0 == sp.index
if octet == Int('<')
sp.index = 1
end
return write(sp.io, octet)
end
sp.index = scan_for_style(sp.index, octet)
return write(sp.io, octet)
end
function Base.unsafe_write(sp::StyleTagProxy, input::Ptr{UInt8}, nbytes::UInt)
cursor = input
index = sp.index
final = input + nbytes
while cursor < final
octet = unsafe_load(cursor)
if octet == Int('<')
index = 1
elseif 0 != index
index = scan_for_style(index, octet)
end
cursor += 1
end
sp.index = index
return unsafe_write(sp.io, input, nbytes)
end
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | code | 8292 | #!/usr/bin/env julia
using Faker, HypertextLiteral, Hyperscript, BenchmarkTools
using HypertextLiteral: @htl_str
# This is going to simulate a hierarchical report that lists a set of
# companies, and for each company, a list of employees.
Faker.seed(4321)
make_employee() = (
first_name=Faker.first_name(),
last_name=Faker.last_name(),
title=Faker.job(),
main_number=Faker.phone_number(),
email=Faker.email(),
cell_phone=Faker.cell_phone(),
color= Faker.hex_color(),
comments= Faker.paragraphs()
)
make_customer() = (
company=Faker.company(),
url=Faker.url(),
phrase=Faker.catch_phrase(),
active=Faker.date_time_this_decade(before_now=true, after_now=false),
notes= Faker.sentence(number_words=rand(2:9), variable_nb_words=true),
employees=[make_employee() for x in 1:rand(3:18)])
database = [make_customer() for x in 1:13]
htl_database(d) = @htl("
<html>
<head><title>Customers & Employees)</title></head>
<body>
$((map(d) do c; htl_customer(c); end))</body>
</html>
")
htl_customer(c) = @htl("
<dl>
<dt>Company<dd>$(c.company)
<dt>Phrase<dd>$(c.phrase)
<dt>Active Since<dd>$(c.active)
<dt>Employees<dd>
<table>
<tr><th>Last Name<th>First Name<th>Title
<th>E-Mail<th>Office Phone<th>Cell Phone
<th>Comments</tr>
$((map(c.employees) do e; htl_employee(e); end))</table>
</dl>
")
htl_employee(e) = @htl("
<tr><td>$(e.last_name)<td>$(e.first_name)<td>$(e.title)
<td><a href='mailto:$(e.email)'>$(e.email)</a>
<td>$(e.main_number)<td>$(e.cell_phone)
<td>$((@htl("<span>$c</span>") for c in e.comments))
")
htl_test() = begin
io = IOBuffer()
ob = htl_database(database)
show(io, MIME("text/html"), ob)
return io
end
# very silly test using attributes rather than elements...
att_database(d) = @htl("""
<html>
<head title="Customers & Employees"/>
<body>
$(map(d) do c; att_customer(c); end)
</body>
</html>
""")
att_customer(c) = @htl("""
<div>
<form>
<label>Company</label><input value=$(c.company)>
<label>Phrase</label><input value='$(c.phrase)'>
<label>Active Since</label><input value="$(c.active)">
<label>Employees</label>
</form>
$((map(c.employees) do e; att_employee(e); end))
</div>
""")
att_employee(e) = @htl("""
<form>
<label>Last Name</label><input value=$(e.last_name)>
<label>First Name</label><input value="$(e.first_name)">
<label>Title</label><input value='$(e.title)'>
<label>E-Mail</label><input $(:value => e.email)>
<label>Main</label><input $("value" => e.main_number))>
<label>Cell</label><input $((value=e.main_number,))>
$((@htl("<span $((value=x,))/>") for x in e.comments))
""")
att_test() = begin
io = IOBuffer()
ob = att_database(database)
show(io, MIME("text/html"), ob)
return io
end
ee(x) = replace(replace(x, "&" => "&"), "<" => "<")
ea(x) = replace(replace(x, "&" => "&"), "'" => "'")
reg_database(d) = """
<html>
<head><title>Customers & Employees</title></head>
<body>
$(join([reg_customer(c) for c in d]))
</body>
</html>
"""
reg_customer(c) = """
<dl>
<dt>Company<dd>$(ee(c.company))
<dt>Phrase<dd>$(ee(c.phrase))
<dt>Active Since<dd>$(ee(c.active))
<dt>Employees<dd>
<table>
<tr><th>Last Name<th>First Name<th>Title
<th>E-Mail<th>Office Phone<th>Cell Phone
<th>Comments</tr>
$(join([reg_employee(e) for e in c.employees]))
</table>
</dl>
"""
reg_employee(e) = """
<tr><td>$(ee(e.last_name))<td>$(ee(e.first_name))<td>$(e.title)
<td><a href='mailto:$(ea(e.email))'>$(ee(e.email))</a>
<td>$(ee(e.main_number))<td>$(ee(e.cell_phone))
<td>$(join(["<span>$(ee(c))</span>" for c in e.comments]))
"""
reg_test() = begin
io = IOBuffer()
ob = reg_database(database)
show(io, ob)
return io
end
@tags html head body title dl dt dd table tr th td span
hs_database(d) =
html(head(title("Customers & Employees")),
body([hs_customer(c) for c in d]...))
hs_customer(c)=
dl(dt("Company"), dd(c.company),
dt("Phrase"), dd(c.phrase),
dt("Active Since"), dd(c.active),
dt("Employees"), dd(
table(tr(th("Last Name"),th("First Name"),th("Title"),
th("E-Mail"),th("Office Phone"),th("Cell Phone"),
th("Comments")),
[hs_employee(e) for e in c.employees]...)))
hs_employee(e) = tr(td(e.last_name), td(e.first_name), td(e.title),
td(href="mailto:$(e.email)", e.email),
td(e.main_number), td(e.cell_phone),
td([span(c) for c in e.comments]...))
hs_test() = begin
io = IOBuffer()
ob = hs_database(database)
show(io, MIME("text/html"), ob)
return io
end
function H(xs...)
HTML() do io
for x in xs
show(io, MIME"text/html"(), x)
end
end
end
function entity(str::AbstractString)
@assert length(str) == 1
entity(str[1])
end
entity(ch::Char) = "&#$(Int(ch));"
HE(x) = HTML(replace(x, r"[<&]" => entity))
HA(x) = HTML(replace(x, r"[<']" => entity))
#HE(x) = HTML(replace(replace(x, "&" => "&"), "<" => "<"))
#HA(x) = HTML(replace(replace(x, "&" => "&"), "\"" => """))
cus_database(d) =
H(HTML("<html><head><title>"), HE("Customers & Employees"),
HTML("</title></head><body>"),
[cus_customer(c) for c in d]...,
HTML("</body></html>"))
cus_customer(c) =
H(HTML("<dl><dt>Company<dd>"), HE(c.company),
HTML("<dt>Phrase<dd>"), HE(c.phrase),
HTML("<dt>Active Siince<dd>"), HE(c.active),
HTML("""
<dt>Employees<dd>
<table>
<tr><th>Last Name<th>First Name<th>Title
<th>E-Mail<th>Office Phone<th>Cell Phone
<th>Comments</tr>"""),
[cus_employee(e) for e in c.employees]...,
HTML("</table></dd></dl>"))
cus_employee(e) =
H(HTML("<tr><td>"), HE(e.last_name),
HTML("<td>"), HE(e.first_name),
HTML("<td>"), HE(e.title),
HTML("<td><a href='mailto:"), HA(e.email),
HTML("'>"), HE(e.email), HTML("</a>"),
HTML("<td>"), HE(e.main_number),
HTML("<td>"), HE(e.cell_phone),
HTML("<td>"),
[H(HTML("<span>"), HE(c), HTML("</span>")) for c in e.comments]...)
cus_test() = begin
io = IOBuffer()
ob = cus_database(database)
show(io, MIME("text/html"), ob)
return io
end
nest_result(d) = @htl("
<html>
<head><title>Customers & Employees)</title></head>
<body>
$((map(d) do c; @htl("
<dl>
<dt>Company<dd>$(c.company)
<dt>Phrase<dd>$(c.phrase)
<dt>Active Since<dd>$(c.active)
<dt>Employees<dd>
<table>
<tr><th>Last Name<th>First Name<th>Title
<th>E-Mail<th>Office Phone<th>Cell Phone
<th>Comments</tr>
$((map(c.employees) do e; @htl("
<tr><td>$(e.last_name)<td>$(e.first_name)<td>$(e.title)
<td><a href='mailto:$(e.email)'>$(e.email)</a>
<td>$(e.main_number)<td>$(e.cell_phone)
<td>$((@htl("<span>$c</span>") for c in e.comments))
"); end))</table>
</dl>"); end))</body>
</html>
")
nest_test() = begin
io = IOBuffer()
ob = nest_result(database)
show(io, MIME("text/html"), ob)
return io
end
BenchmarkTools.DEFAULT_PARAMETERS.seconds = 20
@info("interpolate: ", @benchmark reg_test())
@info("Custom HTML: ", @benchmark cus_test())
@info("Hyperscript: ", @benchmark hs_test())
@info("HypertextLiteral: ", @benchmark htl_test())
@info("HTL (Attributes): ", @benchmark att_test())
@info("Nest Testing: ", @benchmark nest_test())
if false
open("htl.html", "w") do f
ob = htl_database(database)
show(f, MIME("text/html"), ob)
end
open("hs.html", "w") do f
ob = hs_database(database)
show(f, MIME("text/html"), ob)
end
open("reg.html", "w") do f
ob = reg_database(database)
show(f, ob)
end
open("cus.html", "w") do f
ob = cus_database(database)
show(f, MIME("text/html"), ob)
end
end
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | code | 3001 | #!/usr/bin/env julia
using Documenter, Logging, NarrativeTest, Test
using HypertextLiteral
subs = NarrativeTest.common_subs()
# Ignore the difference in the output of `print(Int)` between 32-bit and 64-bit platforms.
push!(subs, r"Int64" => s"Int(32|64)")
# Normalize printing of vector types.
if VERSION < v"1.6.0-DEV"
Base.show_datatype(io::IO, x::Type{Vector{T}}) where {T} = print(io, "Vector{$T}")
end
# Normalize printing of type parameters.
if VERSION < v"1.6.0-DEV"
function Base.show_datatype(io::IO, x::DataType)
istuple = x.name === Tuple.name
if (!isempty(x.parameters) || istuple) && x !== Tuple
n = length(x.parameters)::Int
if istuple && n > 3 && all(i -> (x.parameters[1] === i), x.parameters)
print(io, "NTuple{", n, ", ", x.parameters[1], "}")
else
Base.show_type_name(io, x.name)
print(io, '{')
for (i, p) in enumerate(x.parameters)
show(io, p)
i < n && print(io, ", ")
end
print(io, '}')
end
else
Base.show_type_name(io, x.name)
end
end
end
# Ignore line ending differences for Windows targets.
push!(subs, r"\r\n" => "\n")
# Set the width to 72 so that MD->PDF via pandoc fits the page.
ENV["COLUMNS"] = "72"
package_path(x) = relpath(joinpath(dirname(abspath(PROGRAM_FILE)), "..", x))
default = package_path.(["README.md", "docs/src"])
@testset "HypertextLiteral" begin
if isempty(ARGS) || "doctest" in ARGS
@info "Running doctest..."
DocMeta.setdocmeta!(
HypertextLiteral,
:DocTestSetup,
quote
using HypertextLiteral:
HypertextLiteral, @htl, @htl_str,
Reprint, Render, Bypass, EscapeProxy,
attribute_value, content, attribute_pair,
inside_tag
using Dates
end)
with_logger(Logging.ConsoleLogger(stderr, Logging.Warn)) do
doctest(HypertextLiteral)
end
end
if isempty(ARGS)
@info "Running narrative tests..."
NarrativeTest.testset(; default=default, subs=subs)
else
filter!(!=("doctest"), ARGS)
if !isempty(ARGS)
@info "Running narrative tests..."
NarrativeTest.testset(ARGS; subs=subs)
end
end
end
@static if VERSION >= v"1.3"
struct Foo end
@testset "invalidation" begin
@test HypertextLiteral.content(Foo()) isa HypertextLiteral.Reprint # fallback
# Now define a html printing type
@eval Base.show(io::IO, ::MIME"text/html", ::Foo) = "Foo"
# Previously this would not have worked because content is a generated function depending on hasmethod in the generator
@test repr(Base.invokelatest(HypertextLiteral.content, Foo())) == "HypertextLiteral.Render{Foo}(Foo())"
end
end
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | docs | 1616 | # Release Notes
## v0.9.4
- Pull #27: Make IO Context available inside `<script>`
## v0.9.3
- Pull #18: Interpolating within a paired tags
- Pull #19: Fix bug where <hr /></div> throws error
- Pull #20: Interpolating within self-closing tag
## v0.9.2
- Fix #17: Attribute interpolation bug
## v0.9.1
- Fix #16: Error interpolating unicode into JS
## v0.9.0
- Removing Javscript treatment from `on` attributes
- Exporting `htl` non-standard string literal
- In `htl` literal, doubling of `$` escapes `$`
- Continued review of documentation
## v0.8.0
- Restructructed documentation to improve navigation
- Specialize interpolation within Javascript valued attributes
- Ensure that `@htl` is passed a string literal (Fixed #11)
- Provide better CSS serialization within `<style>` tag
## v0.7.0
- Adding `<span>` as wrapper for default content interpolation
- Support `"text/javascript"` serialization within `<script>` tag (#10)
- Support `"text/css"` serialization within `<style>` tag
- Remove experimental support for nested non-standard string literals
- Documented how `@htl_str` can be used for dynamic templates
# v0.6.0
- Improved documentation
- Fixed lots of edge cases
- Interpolation within comment blocks
# v0.5.0
- Ensured that unicode works for templates
# v0.4.0
- Separate string literal vs macro
- No longer export string literal by default
# v0.3.0
- General refactoring for extensibility
- Converted to use an escape proxy
- Simplify attribute dispatch
# v0.2.0
- Added benchmarking test
- Significant perforamance enhancements
- Implemented via closures rather than objects
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | docs | 4783 | # HypertextLiteral.jl
*HypertextLiteral is a Julia package for generating [HTML][html],
[SVG][svg], and other [SGML][sgml] tagged content. It works similar to
Julia string interpolation, only that it tracks hypertext escaping needs
and provides handy conversions dependent upon context.*
[![Stable Docs][docs-stable-img]][docs-stable-url] [![Dev Docs][docs-dev-img]][docs-dev-url] [![Release Build][release-img]][release-url] [![Code Coverage][codecov-img]][codecov-url] [![Zulip Chat][chat-img]][chat-url] [![ISC License][license-img]][license-url]
> This project is inspired by [Hypertext Literal][htl] by Mike Bostock
> ([@mbostock][@mbostock]) available at [here][observablehq]. This work
> is based upon a port to Julia written by Michiel Dral with significant
> architectural feedback by Kirill Simonov ([@xitology][@xitology]).
This package provides the macro `@htl` which returns an object that can
be rendered to `MIME"text/html"` displays. This macro provides
contextual interpolation sensible to the needs of HTML construction.
```julia
using HypertextLiteral
books = [
(name="Who Gets What & Why", year=2012, authors=["Alvin Roth"]),
(name="Switch", year=2010, authors=["Chip Heath", "Dan Heath"]),
(name="Governing The Commons", year=1990, authors=["Elinor Ostrom"])]
render_row(book) = @htl("""
<tr><td>$(book.name) ($(book.year))<td>$(join(book.authors, " & "))
""")
render_table(list) = @htl("""
<table><caption><h3>Selected Books</h3></caption>
<thead><tr><th>Book<th>Authors<tbody>
$((render_row(b) for b in list))</tbody></table>""")
render_table(books)
#=>
<table><caption><h3>Selected Books</h3></caption>
<thead><tr><th>Book<th>Authors<tbody>
<tr><td>Who Gets What & Why (2012)<td>Alvin Roth
<tr><td>Switch (2010)<td>Chip Heath & Dan Heath
<tr><td>Governing The Commons (1990)<td>Elinor Ostrom
</tbody></table>
=#
```
This library implements many features for working with HTML and
JavaScript data within the Julia language, including:
* Performant escaping of interpolated values
* Handles boolean valued attributes, such as `disabled`, `checked`
* Serialization of `Pair` and `Tuple` objects as attribute pairs
* Conversion of `snake_case` => `kebab-case` for attribute names
* Support for CSS style formatting via `Pair`, `Tuple` and `Dict`
* Translation of Julia values to Javascript within `script` tag
* Direct inclusion of objects (like `HTML`) showable by `MIME"text/html"`
* Extension API for customizing object display in various contexts
For more detail, please see the [documentation][docs-stable-url] and
join us on [Julia's Zulip][chat-url].
[htl]: https://github.com/observablehq/htl
[@mbostock]: https://github.com/mbostock
[@xitology]: https://github.com/xitology
[@mattt]: https://github.com/mattt
[names]: https://github.com/NSHipster/HypertextLiteral
[observablehq]: https://observablehq.com/@observablehq/htl
[xml entities]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_XML_and_HTML_character_entity_references
[named character references]: https://html.spec.whatwg.org/multipage/named-characters.html#named-character-references
[xml]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XML
[sgml]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_Generalized_Markup_Language
[svg]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scalable_Vector_Graphics
[html]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTML
[support-img]: https://img.shields.io/github/issues/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.svg
[support-url]: https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl/issues
[docs-dev-img]: https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl/workflows/docs-dev/badge.svg
[docs-dev-url]: https://juliapluto.github.io/HypertextLiteral.jl/dev/
[docs-stable-img]: https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl/workflows/docs-stable/badge.svg
[docs-stable-url]: https://juliapluto.github.io/HypertextLiteral.jl/stable/
[nightly-img]: https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl/workflows/nightly-ci/badge.svg
[nightly-url]: https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl/actions?query=workflow%3Anightly-ci
[release-img]: https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl/workflows/release-ci/badge.svg
[release-url]: https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl/actions?query=workflow%3Arelease-ci
[chat-img]: https://img.shields.io/badge/chat-julia--zulip-blue
[chat-url]: https://julialang.zulipchat.com/#narrow/stream/243342-pluto.2Ejl
[license-img]: https://img.shields.io/badge/license-ISC-brightgreen.svg
[license-url]: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl/master/LICENSE.md
[codecov-img]: https://codecov.io/gh/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl/branch/master/graph/badge.svg
[codecov-url]: https://codecov.io/gh/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | docs | 11024 | # Attributes & Style
Interpolation within single and double quoted attribute values are
supported. Regardless of context, all four characters, `<`, `&`, `'`,
and `"` are escaped.
using HypertextLiteral
qval = "\"&'"
@htl("""<tag double="$qval" single='$qval' />""")
#-> <tag double=""&'" single='"&'' />
Unquoted or bare attributes are also supported. These are serialized
using the single quoted style so that spaces and other characters do not
need to be escaped.
arg = "book='Strunk & White'"
@htl("<tag bare=$arg />")
#-> <tag bare='book='Strunk & White'' />
In this document, we discuss interpolation within attribute values.
## Boolean Attributes
Within bare attributes, boolean values provide special support for
boolean HTML properties, such as `"disabled"`. When a value is `false`,
the attribute is removed. When the value is `true` then the attribute is
kept, with value being an empty string (`''`).
@htl("<button disabled=$(true)>Disabled</button>")
#-> <button disabled=''>Disabled</button>
@htl("<button disabled=$(false)>Clickable</button>")
#-> <button>Clickable</button>
Within a quoted attribute, boolean values are printed as-is.
@htl("<input type='text' value='$(true)'>")
#-> <input type='text' value='true'>
@htl("<input type='text' value='$(false)'>")
#-> <input type='text' value='false'>
## Nothing
Within bare attributes, `nothing` is treated as `false`, and the
attribute is removed.
@htl("<button disabled=$(nothing)>Clickable</button>")
#-> <button>Clickable</button>
Within quoted attributes, `nothing` is treated as the empty string.
@htl("<input type='text' value='$(nothing)'>")
#-> <input type='text' value=''>
This is designed for consistency with `nothing` within element content.
## Vectors
Vectors and tuples are flattened using the space as a separator.
class = ["text-center", "text-left"]
@htl("<div class=$class>...</div>")
#-> <div class='text-center text-left'>...</div>
@htl("<div class='$class'>...</div>")
#-> <div class='text-center text-left'>...</div>
@htl("<tag att=$([:one, [:two, "three"]])/>")
#-> <tag att='one two three'/>
@htl("<tag att='$((:one, (:two, "three")))'/>")
#-> <tag att='one two three'/>
This behavior supports attributes having name tokens, such as Cascading
Style Sheets' `"class"`.
## Pairs & Dictionaries
Pairs, named tuples, and dictionaries are given treatment to support
attributes such as CSS's `"style"`.
style = Dict(:padding_left => "2em", :width => "20px")
@htl("<div style=$style>...</div>")
#-> <div style='padding-left: 2em; width: 20px;'>...</div>
@htl("<div style='font-size: 25px; $(:padding_left=>"2em")'/>")
#-> <div style='font-size: 25px; padding-left: 2em;'/>
@htl("<div style=$((padding_left="2em", width="20px"))/>")
#-> <div style='padding-left: 2em; width: 20px;'/>
For each pair, keys are separated from their value with a colon (`:`).
Adjacent pairs are delimited by the semi-colon (`;`). Moreover, for
`Symbol` keys, `snake_case` values are converted to `kebab-case`.
## General Case
Beyond these rules for booleans, `nothing`, and collections, values
are reproduced with their `print` representation.
@htl("<div att=$((:a_symbol, "string", 42, 3.1415))/>")
#-> <div att='a_symbol string 42 3.1415'/>
This permits the serialization of all sorts of third party objects.
using Hyperscript
typeof(2em)
#-> Hyperscript.Unit{:em, Int64}
@htl "<div style=$((border=2em,))>...</div>"
#-> <div style='border: 2em;'>...</div>
## Extensions
Often times the default print representation of a custom type isn't
desirable for use inside an attribute value.
struct Custom data::String end
@htl "<tag att=$(Custom("A&B"))/>"
#-> <tag att='Custom("A&B")'/>
This can be sometimes addressed by implementing `Base.print()`.
Base.print(io::IO, c::Custom) = print(io, c.data)
print(@htl "<tag att=$(Custom("A&B"))/>")
#-> <tag att='A&B'/>
However, sometimes this isn't possible or desirable. A tailored
representation specifically for use within an `attribute_value` can be
provided.
HypertextLiteral.attribute_value(x::Custom) = x.data
@htl "<tag att=$(Custom("A&B"))/>"
#-> <tag att='A&B'/>
Like `content` extensions, `Bypass` and `Reprint` work identically.
## Inside a Tag
Attributes may also be provided by any combination of dictionaries,
named tuples, and pairs. Attribute names are normalized, where
`snake_case` becomes `kebab-case`. We do not convert `camelCase` due to
XML (MathML and SVG) attribute case sensitivity. Moreover, `String`
attribute names are passed along as-is.
attributes = Dict(:data_style => :green, "data_value" => 42, )
@htl("<div $attributes/>")
#-> <div data-style='green' data_value='42'/>
@htl("<div $(:data_style=>:green) $(:dataValue=>42)/>")
#-> <div data-style='green' dataValue='42'/>
@htl("<div $((:data_style=>:green, "data_value"=>42))/>")
#-> <div data-style='green' data_value='42'/>
@htl("<div $((data_style=:green, dataValue=42))/>")
#-> <div data-style='green' dataValue='42'/>
A `Pair` inside a tag is treated as an attribute.
@htl "<div $(:data_style => "green")/>"
#-> <div data-style='green'/>
A `Symbol` or `String` inside a tag is an empty attribute.
@htl "<div $(:data_style)/>"
#-> <div data-style=''/>
#? VERSION >= v"1.6.0-DEV"
@htl "<div $("data_style")/>"
#-> <div data_style=''/>
To expand an object into a set of attributes, implement `inside_tag()`.
For example, let's suppose we have an object that represents both a list
of CSS classes and a custom style.
using HypertextLiteral: attribute_pair, Reprint
struct CustomCSS class::Vector{Symbol}; style end
HypertextLiteral.inside_tag(s::CustomCSS) = begin
myclass = join((string(x) for x in s.class), " ")
Reprint() do io::IO
print(io, attribute_pair(:class, myclass))
print(io, attribute_pair(:style, s.style))
end
end
style = CustomCSS([:one, :two], :background_color => "#92a8d1")
print(@htl "<div $style>Hello</div>")
#-> <div class='one two' style='background-color: #92a8d1;'>Hello</div>
## Style Tag
Within a `<style>` tag, Julia values are interpolated using the same
rules as they would be if they were encountered within an attribute
value, only that ampersand escaping is not done.
style = Dict(:padding_left => "2em", :width => "20px")
@htl """<style>span {$style}</style>"""
#-> <style>span {padding-left: 2em; width: 20px;}</style>
In this context, content is validated to ensure it doesn't contain
`"</style>"`.
expr = """<style>span {display: inline;}</style>"""
@htl "<style>$expr</style>"
#-> …ERROR: "Content within a style tag must not contain `</style>`"⋮
## Edge Cases
Attribute names should be non-empty and not in a list of excluded
characters.
@htl "<tag $("" => "value")/>"
#-> ERROR: LoadError: "Attribute name must not be empty."⋮
@htl "<tag $("&att" => "value")/>"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with &att:
Invalid character ('&') found within an attribute name.⋮
=#
We don't permit adjacent unquoted attribute values.
@htl("<tag bare=$(true)$(:invalid)")
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with :invalid:
Unquoted attribute interpolation is limited to a single component⋮
=#
Unquoted interpolation adjacent to a raw string is also an error.
@htl("<tag bare=literal$(:invalid)")
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with :invalid:
Unquoted attribute interpolation is limited to a single component⋮
=#
@htl("<tag bare=$(invalid)literal")
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with bare=literal:
Unquoted attribute interpolation is limited to a single component⋮
=#
Ensure that dictionary style objects are serialized. See issue #7.
let
h = @htl("<div style=$(Dict("color" => "red"))>asdf</div>")
repr(MIME"text/html"(), h)
end
#-> "<div style='color: red;'>asdf</div>"
Let's ensure that attribute values in a dictionary are escaped.
@htl "<tag escaped=$(Dict(:esc=>"'&\"<"))/>"
#-> <tag escaped='esc: '&"<;'/>
When we normalize attribute names, we strip leading underscores.
@htl "<tag $(:__att => :value)/>"
#-> <tag att='value'/>
We don't expand into attributes things that don't look like attributes.
@htl "<tag $(3)/>"
#-> ERROR: MethodError: no method matching inside_tag(::Int64)⋮
One can add additional attributes following a bare name.
@htl "<tag bing $(:att)/>"
#-> <tag bing att=''/>
Inside a tag, tuples can have many kinds of pairs.
a1 = "a1"
@htl "<tag $((a1,:a2,:a3=3,a4=4))/>"
#-> <tag a1='' a2='' a3='3' a4='4'/>
The macro attempts to expand attributes inside a tag. To ensure the
runtime dispatch also works, let's do a few things once indirect.
hello = "Hello"
defer(x) = x
@htl "<tag $(defer(:att => hello))/>"
#-> <tag att='Hello'/>
@htl "<tag $(defer((att=hello,)))/>"
#-> <tag att='Hello'/>
@htl "<tag $(:att => defer(hello))/>"
#-> <tag att='Hello'/>
@htl "<tag $(defer(:att) => hello)/>"
#-> <tag att='Hello'/>
It's a lexing error to have an attribute lacking a name.
@htl "<tag =value/>"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with =value/>:
unexpected equals sign before attribute name⋮
=#
It's a lexing error to have an attribute lacking a value.
@htl "<tag att=>"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with =>:
missing attribute value⋮
=#
Attribute names and values can be spaced out.
@htl "<tag one two = value />"
#-> <tag one two = value />
Invalid attribute names are reported.
@htl "<tag at<ribute='val'/>"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with t<ribute=…
unexpected character in attribute name⋮
=#
@htl "<tag at'ribute='val'/>"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with t'ribute=…
unexpected character in attribute name⋮
=#
@htl """<tag at"ribute='val'/>"""
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with t"ribute=…
unexpected character in attribute name⋮
=#
While assignment operator is permitted in Julia string interpolation, we
exclude it to guard it against accidently forgetting a comma.
@htl "<div $((data_value=42,))/>"
#-> <div data-value='42'/>
@htl("<div $((data_value=42))/>")
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with data_value = 42:
assignments are not permitted in an interpolation⋮
=#
@htl("<div $(data_value=42)/>")
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with data_value = 42:
assignments are not permitted in an interpolation⋮
=#
Interpolation of adjacent values should work.
x = 'X'; y = 'Y';
@htl("<span att='$x$y'/>")
#-> <span att='XY'/>
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | docs | 12684 | # Element Content
Hypertext literal provides interpolation via `$`. Within element
content, the ampersand (`&`), less-than (`<`), single-quote (`'`) and
double-quote (`"`) are escaped.
using HypertextLiteral
book = "Strunk & White"
@htl "<span>Today's Reading: $book</span>"
#-> <span>Today's Reading: Strunk & White</span>
Julia expressions can be interpolated using the `$(expr)` notation.
@htl "2+2 = $(2+2)"
#-> 2+2 = 4
To include `$` in the output, use `\$`. Other escape sequences, such as
`\"` also work.
@htl "They said, \"your total is \$42.50\"."
#-> They said, "your total is $42.50".
Within tripled double-quotes, single double-quoted strings can go
unescaped, however, we still need to escape the dollar sign (`$`).
@htl """They said, "your total is \$42.50"."""
#-> They said, "your total is $42.50".
In this document, we discuss interpolation within regular tagged
content. Interpolation within attribute values and within `<script>` or
`<style>` tags is treated differently.
## Strings & Numbers
Strings, symbols, integers, booleans, and floating point values are
reproduced with their standard `print()` representation. Output produced
in this way is properly escaped.
@htl "<enabled>$(false)</enabled><color>$(:blue)</color>"
#-> <enabled>false</enabled><color>blue</color>
@htl "<int>$(42)</int><float>$(6.02214076e23)</float>"
#-> <int>42</int><float>6.02214076e23</float>
We include `AbstractString` for the performant serialization of
`SubString` and other string-like objects.
@htl "<slice>$(SubString("12345", 2:4))</slice>"
#-> <slice>234</slice>
All other types, such as `Irrational`, have special treatment. Explicit
conversion to a `String` is a simple way to avoid the remaining rules.
#? VERSION >= v"1.3.0-DEV"
@htl "<value>$(string(π))</value>"
#-> <value>π</value>
## HTML Values
Since values translated by the `@htl` macro are `"text/html"`, they can
be used in a nested manner, permitting us to build template functions.
sq(x) = @htl("<span>$(x*x)</span>")
@htl "<div>3^2 is $(sq(3))</div>"
#-> <div>3^2 is <span>9</span></div>
Values `showable` as `"text/html"` will bypass ampersand escaping.
@htl "<div>$(HTML("<span>unescaped 'literal'</span>"))</div>"
#-> <div><span>unescaped 'literal'</span></div>
Custom datatypes can provide their own representation by implementing
`show` for `"text/html"`.
struct Showable data::String end
function Base.show(io::IO, mime::MIME"text/html", c::Showable)
value = replace(replace(c.data, "&"=>"&"), "<"=>"<")
print(io, "<showable>$(value)</showable>")
end
print(@htl "<span>$(Showable("a&b"))</span>")
#-> <span><showable>a&b</showable></span>
HypertextLiteral trusts that `"text/html"` content is properly escaped.
## Nothing
Within element content, `nothing` is simply omitted.
@htl "<span>$nothing</span>"
#-> <span></span>
Use `something()` to provide an alternative representation.
@htl "<span>$(something(nothing, "N/A"))</span>"
#-> <span>N/A</span>
This design supports template functions that return `nothing`.
choice(x) = x ? @htl("<span>yes</span>") : nothing
@htl "<div>$(choice(true))$(choice(false))</div>"
#-> <div><span>yes</span></div>
Note that `missing` has default treatment, see below.
## Vectors & Tuples
Within element content, vector and tuple elements are concatenated (with no delimiter).
@htl "<tag>$([1,2,3])</tag>"
#-> <tag>123</tag>
@htl "<tag>$((1,2,3))</tag>"
#-> <tag>123</tag>
This interpretation enables nesting of templates.
books = ["Who Gets What & Why", "Switch", "Governing The Commons"]
@htl "<ul>$([@htl("<li>$b") for b in books])</ul>"
#=>
<ul><li>Who Gets What & Why<li>Switch<li>Governing The Commons</ul>
=#
The splat operator (`...`) is supported as a noop.
@htl "$([x for x in 1:3]...)"
#-> 123
Generators are also treated in this manner.
print(@htl "<ul>$((@htl("<li>$b") for b in books))</ul>")
#=>
<ul><li>Who Gets What & Why<li>Switch<li>Governing The Commons</ul>
=#
The `map(container) do item; … ;end` construct works and is performant.
@htl "<ul>$(map(books) do b @htl("<li>$b") end)</ul>"
#=>
<ul><li>Who Gets What & Why<li>Switch<li>Governing The Commons</ul>
=#
## General Case
Within element content, values are wrapped in a `<span>` tag.
@htl """<div>$missing</div>"""
#-> <div><span class="Base-Missing">missing</span></div>
This wrapping lets CSS style output. The following renders `missing` as
`"N/A"`.
```HTML
<style>
span.Base-Missing {visibility: collapse;}
span.Base-Missing::before {content: "N/A"; visibility: visible;}
</style>
```
The `<span>` tag's `class` attribute includes the module and type name.
using Dates
@htl "<div>$(Date("2021-07-28"))</div>"
#-> <div><span class="Dates-Date">2021-07-28</span></div>
This handwork is accomplished with a generated function when an object
is not `showable` as `"text/html"`. If the datatype's module is `Main`
then it is not included in the `class`.
struct Custom data::String; end
Base.print(io::IO, c::Custom) = print(io, c.data)
print(@htl "<div>$(Custom("a&b"))</div>")
#-> <div><span class="Custom">a&b</span></div>
Bypassing `<span>` wrapping can be accomplished with `string()`.
print(@htl "<div>$(string(Custom("a&b")))</div>")
#-> <div>a&b</div>
## Extensions
Sometimes it's useful to extend `@htl` so that it knows how to print
your object without constructing this `<span>` wrapper. This can be done
by implementing a method of the `content()` function.
struct Custom data::String end
HypertextLiteral.content(c::Custom) =
"They said: '$(c.data)'"
@htl "<div>$(Custom("Hello"))</div>"
#-> <div>They said: 'Hello'</div>
You can use `@htl` to produce tagged content.
HypertextLiteral.content(c::Custom) =
@htl("<custom>$(c.data)</custom>")
@htl "<div>$(Custom("a&b"))</div>"
#-> <div><custom>a&b</custom></div>
With our primitives, you could have even more control. If your datatype
builds its own tagged content, you can `Bypass` ampersand escaping.
HypertextLiteral.content(c::Custom) =
HypertextLiteral.Bypass("<custom>$(c.data)</custom>")
@htl "<div>$(Custom("Hello"))</div>"
#-> <div><custom>Hello</custom></div>
Unfortunately, this won't escape the content of your custom object.
@htl "<div>$(Custom("<script>alert('whoops!);"))</div>"
#-> <div><custom><script>alert('whoops!);</custom></div>
The `Reprint` primitive can help with composite templates.
using HypertextLiteral: Bypass, Reprint
HypertextLiteral.content(c::Custom) =
Reprint(io::IO -> begin
print(io, Bypass("<custom>"))
print(io, c.data)
print(io, Bypass("</custom>"))
end)
print(@htl "<div>$(Custom("a&b"))</div>")
#-> <div><custom>a&b</custom></div>
In fact, the `@htl` macro produces exactly this translation.
HypertextLiteral.content(c::Custom) =
@htl("<custom>$(c.data)</custom>")
print(@htl "<div>$(Custom("a&b"))</div>")
#-> <div><custom>a&b</custom></div>
## Tag Names
Interpolation works within tag names, both with symbols and strings.
tagname = "div"
@htl """<$tagname class=active></$tagname>"""
#-> <div class=active></div>
tagname = :div
@htl """<$tagname class=active></$tagname>"""
#-> <div class=active></div>
tagname = "htl-code-block"
@htl """<$tagname class=active></$tagname>"""
#-> <htl-code-block class=active></htl-code-block>
tagname = "my-web-component"
@htl """<$tagname/>"""
#-> <my-web-component/>
tagname = "open-file"
@htl """<icon-$tagname/>"""
#-> <icon-open-file/>
tagname = Symbol("open-file")
@htl """<icon-$tagname/>"""
#-> <icon-open-file/>
tagname = "code"
@htl """<htl-$tagname class=julia>import HypertextLiteral</htl-$tagname>"""
#-> <htl-code class=julia>import HypertextLiteral</htl-code>
prefix = "htl"
@htl """<$prefix-code class=julia>import HypertextLiteral</$prefix-code>"""
#-> <htl-code class=julia>import HypertextLiteral</htl-code>
Because with tags there isn't much fancy interpolation work we can do,
you can't put in any complex object.
complex_prefix = Dict(:class => :julia)
@htl """<$complex_prefix>import HypertextLiteral</$complex_prefix>"""
#-> ERROR: "Can't use complex objects as tag name"
According to the HTML specification, only the first character has to be
`/[a-z]/i`, and the rest can be anything but `/`, `>` and ` ` (space).
We are a bit more restrictive.
contains_space = "import HypertextLiteral"
@htl """<$contains_space></$contains_space>"""
#-> ERROR: "Content within a tag name can only contain latin letters, numbers or hyphens (`-`)"
contains_bigger_than = "a<div>"
@htl """<$contains_bigger_than></$contains_bigger_than>"""
#-> ERROR: "Content within a tag name can only contain latin letters, numbers or hyphens (`-`)"
contains_slash = "files/extra.js"
@htl """<$contains_slash></$contains_slash>"""
#-> ERROR: "Content within a tag name can only contain latin letters, numbers or hyphens (`-`)"
starts_with_hyphen = "-secret-tag-name"
@htl """<$starts_with_hyphen></$starts_with_hyphen>"""
#-> ERROR: "A tag name can only start with letters, not `-`"
empty = ""
@htl """<$empty></$empty>"""
#-> ERROR: "A tag name can not be empty"
empty = ""
@htl """<$empty/>"""
#-> ERROR: "A tag name can not be empty"
technically_valid_but_weird = "Technically⨝ValidTag™"
@htl """<$technically_valid_but_weird></$technically_valid_but_weird>"""
#-> ERROR: "Content within a tag name can only contain latin letters, numbers or hyphens (`-`)"
@htl """<$technically_valid_but_weird/>"""
#-> ERROR: "Content within a tag name can only contain latin letters, numbers or hyphens (`-`)"
technically_valid_starts_with_hyphen = "-secret-tag-name"
@htl """<prefix$technically_valid_starts_with_hyphen/>"""
#-> ERROR: "A tag name can only start with letters, not `-`"
technically_valid_but_empty = ""
@htl """<prefix-$technically_valid_but_empty/>"""
#-> ERROR: "A tag name can not be empty"
## Edge Cases
Within element content, even though it isn't strictly necessary, we
ampersand escape the single and double quotes.
v = "<'\"&"
@htl "<span>$v</span>"
#-> <span><'"&</span>
Symbols are likewise escaped.
v = Symbol("<'\"&")
@htl "<span>$v</span>"
#-> <span><'"&</span>
Interpolation within the `xmp`, `iframe`, `noembed`, `noframes`, and
`noscript` tags are not supported.
@htl "<iframe>$var</iframe>"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with iframe:
Only script and style rawtext tags are supported.⋮
=#
String escaping by `@htl` is handled by Julia itself.
@htl "\"\t\\"
#-> " \
@htl "(\\\")"
#-> (\")
Literal content can contain Unicode values.
x = "Hello"
@htl "⁅$(x)⁆"
#-> ⁅Hello⁆
Escaped content may also contain Unicode.
x = "⁅Hello⁆"
@htl "<tag>$x</tag>"
#-> <tag>⁅Hello⁆</tag>
String interpolation is limited to symbols or parenthesized expressions
(see Julia #37817).
@htl("$[1,2,3]")
#=>
ERROR: syntax: invalid interpolation syntax: "$["⋮
=#
@htl("$(1,2,3)")
#=>
ERROR: syntax: invalid interpolation syntax⋮
=#
Before v1.6, we cannot reliably detect string literals using the `@htl`
macro, so they are errors (when we can detect them).
#? VERSION < v"1.6.0-DEV"
@htl "Look, Ma, $("<i>automatic escaping</i>")!"
#-> ERROR: LoadError: "interpolated string literals are not supported"⋮
#? VERSION < v"1.6.0-DEV"
@htl "$("even if they are the only content")"
#-> ERROR: LoadError: "interpolated string literals are not supported"⋮
However, you can fix by wrapping a value in a `string` function.
@htl "Look, Ma, $(string("<i>automatic escaping</i>"))!"
#-> Look, Ma, <i>automatic escaping</i>!
In particular, before v1.6, there are edge cases where unescaped string
literal is undetectable and content can leak.
x = ""
#? VERSION < v"1.6.0-DEV"
@htl "$x$("<script>alert(\"Hello\")</script>")"
#-> <script>alert("Hello")</script>
Julia #38501 was fixed in v1.6.
#? VERSION >= v"1.6.0-DEV"
@htl "<tag>$("escape&me")</tag>"
#-> <tag>escape&me</tag>
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | docs | 8620 | # Design Rationale
This package is implemented according to several design criteria.
- Operation of interpolated expressions (`$`) should (mostly) mirror
what they would do with regular Julia strings, updated with hypertext
escaping sensibilities including proper escaping.
- Speed of construction is critically important. This library is
intended to be used deep within systems that generate extensive
number of very large reports, interactively or in batch.
- With exception of boolean attributes (which must be removed to be
false), templates are treated as-is and not otherwise modified.
- Within `<script>`, support translation of Julia objects to JavaScript.
Enable this translation to be used within `on` and other contexts via
`HypertextLiteral.js` function.
- Since the `style` and `class` attributes are so important in HTML
construction, interpretations of Julia constructs should support
these CSS attributes.
- There should be a discoverable and well documented extension API that
permits custom data types to provide their own serialization
strategies based upon syntactical context.
- As much processing (e.g. hypertext lexical analysis) should be done
during macro expansion to reduce runtime and to report errors early.
We'll be slightly slower on interactive use to be fast in batch.
- Full coverage of HTML syntax or reporting syntax or semantic errors
within the HTML content is not a goal.
## Specific Design Decisions
Besides implementing `show`, we also provide serialization when printing
to `"text/html"` mime types.
using HypertextLiteral
@htl "<span>Hello World</span>"
#-> <span>Hello World</span>
display("text/html", @htl "<span>Hello World</span>")
#-> <span>Hello World</span>
We wrap `missing` and other data types using a `<span>` tag as they are
printed. This permits customized CSS to control their presentation.
@htl "<tag>$(missing)</tag>"
#-> <tag><span class="Base-Missing">missing</span></tag>
Julia's regular interpolation stringifies everything. Instead, we treat
a `Vector` as a sequence to be concatenated. Within attributes, vectors
are space separated.
@htl "$([x for x in 1:3])"
#-> 123
@htl "<tag att=$([x for x in 1:3])/>"
#-> <tag att='1 2 3'/>
We treat `nothing` as being empty. This is true for both element content
and attribute values.
@htl "<span>$(nothing)</span>"
#-> <span></span>
@htl "<tag att='$(nothing)'/>"
#-> <tag att=''/>
## Notable Features
Attributes assigned a boolean value have specialized support.
@htl "<input type='checkbox' selected=$(false) disabled=$(true)></input>"
#-> <input type='checkbox' disabled=''></input>
Dictionaries are translated to support CSS within attributes and the
`<style>` tag. In this case, `snake_case` symbols become `kebab-case`.
style = Dict(:padding_left => "2em", :width => "20px")
@htl("<div style='font-size: 25px; $style'>...</div>")
#-> <div style='font-size: 25px; padding-left: 2em; width: 20px;'>...</div>
@htl "<style>input {$style}</style>"
#-> <style>input {padding-left: 2em; width: 20px;}</style>
Within a `<script>` tag these macros provide a translation to Javascript.
v = "<1 Brown \"M&M's\"!";
@htl "<script>v = $v</script>"
#-> <script>v = "<1 Brown \"M&M's\"!"</script>
JavaScript translation can be accessed via the `js` function.
using HypertextLiteral: js
@htl "<button onclick='alert($(js("M&M's")))'>"
#-> <button onclick='alert("M&M's")'>
The `@htl_str` form is useful for dynamically constructed templates.
templ = join("<td>\$$x</td>" for x in [:a,:b])
#-> "<td>\$a</td><td>\$b</td>"
(a, b) = (:A, :B);
eval(:(@htl_str($templ)))
#-> <td>A</td><td>B</td>
Within element content, most datatypes are serialized within a `<span>` tag.
using Dates
@htl("<div>$(Date("2021-07-28"))</div>")
#-> <div><span class="Dates-Date">2021-07-28</span></div>
This automatic wrapping permits CSS to be used to style output.
For example, the following style will display `missing` as `"N/A"`.
```HTML
<style>
span.Base-Missing {visibility: collapse;}
span.Base-Missing::before {content: "N/A"; visibility: visible;}
</style>
```
## Lexer Tests
There are several HTML syntax errors that we can detect as part of our
parser. For example, you shouldn't put comments within a script tag.
@htl("<script><!-- comment --></script>")
#-> ERROR: LoadError: "script escape or comment is not implemented"⋮
Our lexer currently doesn't bother with processor instructions or
doctype declarations. You could prepend these before your content.
@htl("<?xml version='1.0'?>")
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with <?xml ver…:
unexpected question mark instead of tag name⋮
=#
@htl("<!DOCTYPE html>")
#-> ERROR: LoadError: "DOCTYPE not supported"⋮
@htl("<![CDATA[No <b>CDATA</b> either.]]>")
#-> ERROR: LoadError: "CDATA not supported"⋮
It's a lexing error to have an attribute lacking a name.
@htl "<tag =value/>"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with =value/>:
unexpected equals sign before attribute name⋮
=#
It's a lexing error to have an attribute lacking a value.
@htl "<tag att=>"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with =>:
missing attribute value⋮
=#
Tags can be ended using SGML ending.
@htl "<tag></>"
#-> <tag></>
We add an extra space to ensure adjacent values parse properly.
@htl "<tag $((:one))two=''/>"
#-> <tag one='' two=''/>
@htl "<tag $((:one))$((:two))/>"
#-> <tag one='' two=''/>
Attribute names and values can be spaced out.
@htl "<tag one two = value />"
#-> <tag one two = value />
Invalid attribute names are reported.
@htl "<tag at<ribute='val'/>"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with t<ribute=…
unexpected character in attribute name⋮
=#
Rawtext has a few interesting lexical cases.
@htl """<style> </s </> </style>"""
#-> <style> </s </> </style>
@htl "<style> </s </style/"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with e/:
unexpected solidus in tag⋮
=#
@htl "<style></style <"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with <:
unexpected character in attribute name⋮
=#
Comments can contain interpolated values.
content = "<!-- a&b -->"
@htl "<!-- $content -->"
#-> <!-- <!-- a&b --> -->
Empty comments are permitted.
@htl "<!---->"
#-> <!---->
Comments should not exist within a script tag.
@htl("<script><!-- comment --></script>")
#-> ERROR: LoadError: "script escape or comment is not implemented"⋮
Comments need to be well formed.
@htl "<!-> "
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with !-> :
incorrectly opened comment⋮
=#
@htl "<!--> "
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with -> :
abrupt closing of empty comment⋮
=#
@htl "<!---> "
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with -> :
abrupt closing of empty comment⋮
=#
Comments cannot contain a nested comment.
@htl "<!-- <!-- nested --> -->"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with - nested …:
nested comment⋮
=#
Comments can contain content that is similar to a comment block, but
the recognition of these valid states is rather involved.
@htl "<!-- <!-->"
#-> <!-- <!-->
@htl "<!--<x-->"
#-> <!--<x-->
@htl "<!--<!x!>-->"
#-> <!--<!x!>-->
@htl "<!--<!-x-->"
#-> <!--<!-x-->
@htl "<!---x-->"
#-> <!---x-->
@htl "<!--<<x-->"
#-> <!--<<x-->
@htl "<!-- - --! --- --!- -->"
#-> <!-- - --! --- --!- -->
Not so sure about this lexical production... perhaps it's a
transcription error from the specification?
@htl "<!----!>"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with !>:
nested comment⋮
=#
Even though actual content may be permitted in these odd spots, we don't
generally permit interpolation.
@htl "<!--<$(:x)"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: "unexpected binding STATE_COMMENT_LESS_THAN_SIGN"⋮
=#
Of course, we could have pure content lacking interpolation, this also
goes though the lexer.
@htl "<div>Hello<b>World</b>!</div>"
#-> <div>Hello<b>World</b>!</div>
However, this macro requires a string literal.
f() = "<div>Hello<b>World</b>!</div>"
@htl f()
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with f():
a string literal is required⋮
=#
Bug that was in the code before, not sure how/where to narrate this.
@htl "<hr /></div>"
#-> <hr /></div>
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | docs | 3344 | # HypertextLiteral Overview
This package provides a Julia macro, `@htl`, that constructs an object
which could be rendered to `MIME"text/html"` displays. This macro
supports string interpolation sensible to the needs of HTML generation.
using HypertextLiteral
v = "<1 Brown \"M&M's\"!";
@htl "<span>$v</span>"
#-> <span><1 Brown "M&M's"!</span>
An equivalent non-standard string literal, `htl`, is also provided.
v = "<1 Brown \"M&M's\"!";
htl"<span>$v</span>"
#-> <span><1 Brown "M&M's"!</span>
Interpolation can use the full expressive power of Julia.
books = ["Who Gets What & Why", "Switch", "Governing The Commons"]
@htl "<ul>$(map(books) do b @htl("<li>$b") end)</ul>"
#=>
<ul><li>Who Gets What & Why<li>Switch<li>Governing The Commons</ul>
=#
## Translation Contexts
How a Julia expression is translated depends upon where it is used.
| | **Native Julia** | **Translation** |
|:------------------- |:-------------------------|:------------------ |
| **Element Content** | `"\"M&M\"'s"` | `M&M's` |
| | `:name` | `name` |
| | `[1, 2]` *or* `(1, 2)` | `12` |
| | `nothing` | *omitted* |
| | `missing` | `<span class="Base-Missing">missing</span>` |
| | `(a = 1, b = 2)` | `<span class="Core-NamedTuple">(a = 1, b = 2)</span>` |
| | `Dict(:a => 1, :b => 2)` | `<span class="Base-Dict">Dict(:a => 1, :b => 2)</span>` |
| **Attribute Value** | `"\"M&M\"'s"` | `M&M's` |
| | `:name` | `name` |
| | `[1, 2]` *or* `(1, 2)` | `1 2` |
| | `nothing` | *omitted* |
| | `missing` | `missing` |
| | `(a = 1, b = 2)` | `a: 1; b: 2;` |
| | `Dict(:a => 1, :b => 2)` | `a: 1; b: 2;` |
| **Script Tag** | `"\"M&M\"'s"` | `"\"M&M\"'s"` |
| | `:name` | `name` |
| | `[1, 2]` *or* `(1, 2)` | `[1, 2]` |
| | `nothing` | `undefined` |
| | `missing` | `null` |
| | `Inf` | `Infinity` |
| | `NaN` | `NaN` |
| | `(a = 1, b = 2)` | `{"a": 1, "b": 2}` |
| | `Dict(:a => 1, :b => 2)` | `{"a": 1, "b": 2}` |
If any of these translations are inconvenient:
* `coalesce()` can be used to provide an alternative for `missing`;
* `something()` provides a substitution for `nothing`;
* `string()` will use the string translation instead; and
* `HTML()` can be used to bypass escaping within element content.
## Table of Contents
```@contents
Pages = ["content.md", "attribute.md", "script.md"]
Depth = 3
```
```@contents
Pages = ["design.md", "notation.md", "primitives.md", "reference.md"]
Depth = 1
```
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | docs | 4274 | # `htl` String Literal
This package additionally provides the `@htl_str` non-standard string
literal.
using HypertextLiteral
name = "World"
htl"<span>Hello $name</span>"
#-> <span>Hello World</span>
@htl_str "<span>Hello \$name</span>"
#-> <span>Hello World</span>
## Notable Differences
Unlike `@htl`, the `htl` string literal uses `@raw_str` escaping rules.
So long as a double-quote character does not come before a slash, the
slash itself need not be escaped.
htl"<span>\some\path</span>"
#-> <span>\some\path</span>
In this notation, `\"` can be used to escape a double quote. However,
other escape sequences are not expanded.
htl"Hello\"\nWorld\""
#-> Hello"\nWorld"
As a special case, the dollar-sign (`$`) can be escaped by doubling.
amount = 42
htl"<span>They paid $$$amount</span>"
#-> <span>They paid $42</span>
Alternatively, one can use the HTML character entity `#&36;`.
htl"<span>They paid $$amount</span>"
#-> <span>They paid $42</span>
Unlike the `@htl` macro, nesting doesn't work.
htl"Hello $(htl"World")"
#-> ERROR: syntax: cannot juxtapose string literal
Triple double-quoted syntax can be used in this case.
htl"""Hello $(htl"World")"""
#-> Hello World
However, this trick works only one level deep. Hence, there are some
significant downsides to using this format, which are explored in detail
at Julia #38948.
## Dynamic Templates
The `@htl_str` macro can be used to dynamically construct templates.
Suppose you have a schema that is provided dynamically. Let's make a
test database with exactly one row.
T = NamedTuple{(:idx, :value), Tuple{Int64, String}};
database = [T((1, "A&B"))];
display(database)
#=>
1-element Vector{NamedTuple{(:idx, :value), …}:
(idx = 1, value = "A&B")
=#
We could construct a table header from this schema.
fields = T.parameters[1]
#-> (:idx, :value)
head = @htl "<tr>$([@htl("<th>$x") for x in fields])"
#-> <tr><th>idx<th>value
Then, we need to compute a template for each row.
row_template = "<tr>$(join(["<td>\$(row[$(repr(x))])" for x in fields]))"
print(row_template)
#-> <tr><td>$(row[:idx])<td>$(row[:value])
Using `eval` with `@htl_str` we could construct our template function.
eval(:(tablerow(row) = @htl_str $row_template))
tablerow(database[1])
#-> <tr><td>1<td>A&B
A template for the entire table could be constructed.
table_template = "<table>$head\$([tablerow(row) for row in data])</table>"
print(table_template)
#-> <table><tr><th>idx…$([tablerow(row) for row in data])</table>
eval(:(print_table(data) = @htl_str $table_template))
Then, finally, this could be used.
print_table(database)
#-> <table><tr><th>idx<th>value<tr><td>1<td>A&B</table>
## Regression Tests & Notes
Due to `@raw_str` escaping, string literal forms are a bit quirky. Use
the triple double-quoted form if your content has a double quote. Avoid
slashes preceding a double quote, instead use the `/` HTML entity.
htl"\"\t\\"
#-> "\t\
htl"(\\\")"
#-> (\")
Even though we could permit interpretation of arrays notation, we stick
with keeping this an error for consistency with the macro form.
htl"$[1,2,3]"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with [1, 2, 3]:
interpolations must be symbols or parenthesized⋮
=#
Let's also not permit top-level assignments.
htl"$(k=value)"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: DomainError with k = value:
assignments are not permitted in an interpolation⋮
=#
Since the implementers of the notation have some control over the
parsing, we can reliably detect string literals (Julia #38501).
htl"""<span>$("A&B")</span>"""
#-> <span>A&B</span>
There is one less round of parenthesis needed for tuples, named tuples
and generators (Julia #38734).
name = "Hello"
htl"<tag $(user=name,)/>"
#-> <tag user='Hello'/>
print(htl"<span>$(n for n in 1:3)</span>")
#-> <span>123</span>
Due to escaping rules, we interpret a dollar sign as beginning an
expression, even if it might otherwise be preceded by a slash.
htl"Hello\$#"
#=>
ERROR: LoadError: "missing expression at 7: #"⋮
=#
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | docs | 2127 | # Escaping Primitives
This is a regression test for components upon which HTL is constructed,
the design centers around `EscapeProxy` which escapes content printed to
it. There are several wrappers which drive special proxy handling.
using HypertextLiteral: EscapeProxy, Bypass, Reprint, Render
## EscapeProxy
This utility class acts wraps an `IO` stream to provide HTML escaping.
io_buffer = IOBuffer()
io = IOContext(io_buffer, :hello => "world")
ep = EscapeProxy(io)
macro echo(expr)
:($expr; print(String(take!(io_buffer))))
end
The result of this proxy is that regular content printed to it is passed
along to the wrapped `IO`, after escaping the ampersand (`&`), less-than
(`<`), single-quote (`'`), and double-quote (`"`).
@echo print(ep, "(&'<\")")
#-> (&'<")
Any [IO context properties](https://docs.julialang.org/en/v1/base/io-network/#Base.IOContext-Tuple{IO,%20Pair}) will be reflected by the `EscapeProxy`:
@echo print(ep, get(ep, :hello, "oops"))
#-> world
## Bypass
This wrapper simply prints its content.
print(Bypass("<tagged/>"))
#-> <tagged/>
Printed content wrapped with `Bypass` is not subject to escaping.
@echo print(ep, Bypass("<span>"), "<A&B>", Bypass("</span>"))
#-> <span><A&B></span>
## Reprint
This wrapper holds a closure that prints to an `io`.
print(Reprint(io::IO -> print(io, "Hello World")))
#-> Hello World
Reprinted content is still subject to escaping.
@echo print(ep, Reprint(io -> print(io, "(&'<\")")))
#-> (&'<")
## Render
This wrapper prints text/html display of an object.
struct Custom
content
end
Base.show(io::IO, m::MIME"text/html", c::Custom) =
print(io, c.content)
print(Render(Custom("<tag/>")))
#-> <tag/>
The printed content is not subject to escaping.
@echo print(ep, Render(Custom("<tag/>")))
#-> <tag/>
It's an error if the wrapped object isn't showable to `"text/html"`.
print(Render("This is an error!"))
#-> ERROR: MethodError: … show(… ::MIME{Symbol("text/html")}⋮
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | docs | 82 | # Package Reference
```@autodocs
Modules = [HypertextLiteral]
Private = true
```
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
] | 0.9.5 | 7134810b1afce04bbc1045ca1985fbe81ce17653 | docs | 5669 | # Script Interpolation
Within a `<script>` tag, Julia values are serialized to their equivalent
Javascript. String literal values are rendered as double-quoted values.
using HypertextLiteral
v = """Brown "M&M's"!""";
@htl "<script>var x = $v</script>"
#-> <script>var x = "Brown \"M&M's\"!"</script>
Julia tuples and vectors are serialized as Javascript array. Integers,
boolean, and floating point values are handled. As special cases,
`nothing` is represented using `undefined` and `missing` using `null`.
v = Any[true, 1, 1.0, nothing, missing]
@htl "<script>var x = $v</script>"
#-> <script>var x = [true, 1, 1.0, undefined, null]</script>
This translation attempts to convert numbers properly.
v = (-Inf, Inf, NaN, 6.02214e23)
@htl "<script>var x = $v</script>"
#-> <script>var x = [-Infinity, Infinity, NaN, 6.02214e23]</script>
Dictionaries are serialized as a Javascript object. Symbols are
converted to string values.
v = Dict(:min=>1, :max=>8)
@htl "<script>var x = $v</script>"
#-> <script>var x = {"max": 8, "min": 1}</script>
Besides dictionary objects, we support named tuples.
v = (min=1, max=8)
@htl "<script>var x = $v</script>"
#-> <script>var x = {"min": 1, "max": 8}</script>
String values are escaped to avoid `<script>`, `</script>`, and `<!--`.
content = """<script>alert("no injection!")</script>"""
@htl "<script>v = $content</script>"
#-> <script>v = "<\script>alert(\"no injection!\")<\/script>"</script>
content = """--><!-- no injection!"""
@htl "<script>v = $content</script>"
#-> <script>v = "--><\!-- no injection!"</script>
## JavaScript
Sometimes you already have content that is valid Javascript. This can be
printed directly, without escaping using a wrapper similar to `HTML`:
using HypertextLiteral: JavaScript
expr = JavaScript("""console.log("Hello World")""")
@htl "<script>$expr</script>"
#-> <script>console.log("Hello World")</script>
The `JavaScript` wrapper indicates the content should be directly
displayed within a `"text/javascript"` context. We try to catch content
which is not properly escaped for use within a `<script>` tag.
expr = """<script>console.log("Hello World")</script>"""
@htl "<script>$(JavaScript(expr))</script>"
#-> …ERROR: "Content within a script tag must not contain `</script>`"⋮
Similarly, a comment sequence is also forbidden.
expr = "<!-- invalid comment -->"
@htl "<script>$(JavaScript(expr))</script>"
#-> …ERROR: "Content within a script tag must not contain `<!--`"⋮
## Script Attributes
Conversion of Julia values to JavaScript can be performed explicitly
within attributes using `js()`, which is not exported by default.
using HypertextLiteral: js
v = """Brown "M&M's"!""";
@htl "<div onclick='alert($(js(v)))'>"
#-> <div onclick='alert("Brown \"M&M's\"!")'>
The `js()` function can be used independently.
msg = "alert($(js(v)))"
@htl "<div onclick=$msg>"
#-> <div onclick='alert("Brown \"M&M's\"!")'>
Although strictly unnecessary, slash escaping to prevent `<\script>`
content is still provided.
v = "<script>nested</script>"
@htl "<div onclick='alert($(js(v)))'>"
#-> <div onclick='alert("<\script>nested<\/script>")'>
## Extensions
If an object is not showable as `"text/javascript"` then you will get
the following exception.
@htl("<script>$(π)</script>")
#-> …ERROR: "Irrational{:π} is not showable as text/javascript"⋮
This can be overcome with a `show()` method for `"text/javascript"`,
struct Log
data
end
function Base.show(io::IO, mime::MIME"text/javascript", c::Log)
print(io, "console.log(", c.data, ")")
end
Like the `HTML` wrapper, you take full control of ensuring this content
is relevant to the context.
print(@htl """<script>$(Log(missing))</script>""")
#-> <script>console.log(missing)</script>
Alternatively, one could implement `print_script`, recursively calling
this function on datatypes which require further translation.
import HypertextLiteral: print_script
function print_script(io::IO, c::Log)
print(io, "console.log(")
print_script(io, c.data)
print(io, ")")
end
print(@htl """<script>$(Log(missing))</script>""")
#-> <script>console.log(null)</script>
This method is how we provide support for datatypes in `Base` without
committing type piracy by implementing `show` for `"text/javascript"`.
## Edge Cases
Within a `<script>` tag, comment start (`<!--`) must also be escaped.
Moreover, capital `<Script>` and permutations are included. We only scan
the first character after the left-than (`<`) symbol, so there may be
strictly unnecessary escaping.
v = "<!-- <Script> <! 3<4 </ <s !>"
@htl "<script>var x = $v</script>"
#-> <script>var x = "<\!-- <\Script> <\! 3<4 <\/ <\s !>"</script>
It's important to handle unicode content properly.
s = "α\n"
@htl("<script>alert($(s))</script>")
#-> <script>alert("α\n")</script>
## Regression tests
Any [IO context properties](https://docs.julialang.org/en/v1/base/io-network/#Base.IOContext-Tuple{IO,%20Pair}) of the renderer can be used, as expected:
struct Hello end
function Base.show(io::IO, ::MIME"text/javascript", ::Hello)
print(io, get(io, :hello, "oops"))
end
h = @htl("""<script>const x = $(Hello())</script>""")
repr(
MIME"text/html"(), h;
context=(:hello => "world")
)
#-> "<script>const x = world</script>"
| HypertextLiteral | https://github.com/JuliaPluto/HypertextLiteral.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 1271 | using Documenter
using StellarSpectraObservationFitting
# DocMeta.setdocmeta!(StellarSpectraObservationFitting, :DocTestSetup, :(using StellarSpectraObservationFitting); recursive=true)
makedocs(
sitename = "StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl",
format = Documenter.HTML(),
modules = [StellarSpectraObservationFitting],
authors = "Christian Gilbertson",
pages = [
"Home" => "index.md",
"Getting started" => "gettingstarted.md",
"User's guide" => [
"Data preparation" => "data.md",
"Creating a SSOF model" => [
"Initialization and model selection" => "init.md",
"Optimization" => "opt.md",
],
"Regularization" => "prior.md",
"Model error estimation" => "error.md",
],
"Various other functions" => [
"Data preprocessing" => "continuum.md",
"(D)EMPCA" => "empca.md",
"Utility functions" => "general.md",
# "Model functions" => "model.md",
"Everything else" => "indices.md",
],
"LICENSE.md",
]
)
deploydocs(
repo = "github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git",
deploy_config = Documenter.GitHubActions(),
) | StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 4862 | module NEIDLSF
import StellarSpectraObservationFitting as SSOF
using FITSIO
using SpecialFunctions
using SparseArrays
# using Interpolations
using DataInterpolations
function conv_gauss_tophat(x::Real, σ::Real, boxhalfwidth::Real; amp::Real=1)
scale = 1 / (sqrt(2) * σ)
arg1 = (boxhalfwidth + x) * scale
arg2 = (boxhalfwidth - x) * scale
return abs(amp * (erf(arg1) + erf(arg2)))
# return abs(amp * (erf(arg1) + erf(arg2)) / (2 * erf(boxhalfwidth * scale))) # used for some visual diagnostic
end
# def conv_gauss_tophat(x, center, amp, sigma, boxhalfwidth):
# '''
# this is an analytical function for the convolution of a gaussian and tophat
# should be a closer approximation to the HPF profile than a simple gaussian
# '''
# arg1 = (2. * center + boxhalfwidth - 2. * x) / (2. * sqrt(2) * sigma)
# arg2 = (-2. * center + boxhalfwidth + 2. * x) / (2. * sqrt(2) * sigma)
# part1 = scipy.special.erf(arg1)
# part2 = scipy.special.erf(arg2)
# out = amp * (part1 + part2)
# return(out)
σs = read(FITS(pkgdir(SSOF) *"/examples/data/sigma_arr.fits")[1])
bhws = read(FITS(pkgdir(SSOF) *"/examples/data/boxhalfwidth_arr.fits")[1]) ./ 2 # Sam's formula has an extra factor of 2
no_lsf_orders = [all(iszero.(view(bhws, :, i))) for i in axes(bhws,2)]
@assert all(no_lsf_orders .== [all(iszero.(view(σs, :, i))) for i in axes(σs,2)])
# function conv_gauss_tophat_integral(σ::Real, bhw::Real, xmμ::Real)
# x1 = xmμ - 0.5
# x2 = xmμ + 0.5
# scale = 1 / (sqrt(2) * σ)
# z1 = (bhw + x1) * scale
# zm1 = (bhw - x1) * scale
# z2 = (bhw + x2) * scale
# zm2 = (bhw - x2) * scale
# return sqrt(2 / π) * σ * (exp(-(zm1^2)) - exp(-(z1^2)) - exp(-(zm2^2)) + exp(-(z2^2))) +
# (bhw - x1) * erf(zm1) - (bhw + x1) * erf(z1) - (bhw - x2) * erf(zm2) + (bhw + x2) * erf(z2)
# end
threeish_sigma(σ::Real, bhw::Real) = 3 * abs(σ) + 0.87 * abs(bhw)
function neid_lsf(order::Int)
@assert 1 <= order <= length(no_lsf_orders)
if no_lsf_orders[order]; return nothing end
n = size(σs, 1)
holder = zeros(n, n)
for i in 1:n
lo = max(1, Int(round(i - threeish_sigma(σs[i, order], bhws[i, order]))))
hi = min(n, Int(round(i + threeish_sigma(σs[i, order], bhws[i, order]))))
holder[i, lo:hi] = conv_gauss_tophat.((lo-i):(hi-i), σs[i, order], bhws[i, order])
# holder[i, lo:hi] = conv_gauss_tophat_integral.(σs[i, order], bhws[i, order], (lo-i):(hi-i))
holder[i, lo:hi] ./= sum(view(holder, i, lo:hi))
end
ans = sparse(holder)
dropzeros!(ans)
return ans
end
function neid_lsf(order::Int, log_λ_neid_order::AbstractVector, log_λ_obs::AbstractVector)
@assert 1 <= order <= length(no_lsf_orders)
if no_lsf_orders[order]; return nothing end
n = length(log_λ_obs)
# need to convert σs, bhws, and threeish_sigma (in units of neid pixels) to units of log_λ_obs pixels
# pixel_separation_log_λ_obs = linear_interpolation(log_λ_obs, SSOF.simple_derivative(log_λ_obs); extrapolation_bc=Line())
pixel_separation_log_λ_obs = DataInterpolations.LinearInterpolation(SSOF.simple_derivative(log_λ_obs), log_λ_obs)
pixel_separation_ratio = SSOF.simple_derivative(log_λ_neid_order) ./ pixel_separation_log_λ_obs.(log_λ_neid_order)
# make the linear_interpolation object and evaluate it
# converter(vals) = linear_interpolation(log_λ_neid_order, pixel_separation_ratio .* vals; extrapolation_bc=Line())(log_λ_obs)
converter(vals) = (DataInterpolations.LinearInterpolation(pixel_separation_ratio .* vals, log_λ_neid_order)).(log_λ_obs)
σs_converted = converter(σs[:, order])
bhws_converted = converter(bhws[:, order])
threeish_sigma_converted = converter(threeish_sigma.(σs[:, order], bhws[:, order]))
holder = zeros(n, n)
for i in 1:n
lo = max(1, Int(round(i - threeish_sigma_converted[i])))
hi = min(n, Int(round(i + threeish_sigma_converted[i])))
holder[i, lo:hi] = conv_gauss_tophat.((lo-i):(hi-i), σs_converted[i], bhws_converted[i])
holder[i, lo:hi] ./= sum(view(holder, i, lo:hi))
end
ans = sparse(holder)
dropzeros!(ans)
return ans
end
end # module
# s = NEID_lsf(100)
# heatmap(Matrix(s[1:100,1:100]))
# heatmap(Matrix(s[end-100:end,end-100:end]))
#
# avg_nz_pix_neighbors = Int(round(length(s.nzval)/s.n/2))
# i = 100
# xx = (i-avg_nz_pix_neighbors-5):(i+avg_nz_pix_neighbors+5)
# plot_subsection = s[i, xx]
# plot(xx, plot_subsection)
# plot!(xx, iszero.(plot_subsection)./10)
# vline!([i])
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 20844 | using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
using Statistics
import StellarSpectraObservationFitting as SSOF
using LaTeXStrings
_plt_dpi = 400
_plt_size = (1920,1080)
_thickness_scaling = 2
_theme = :default
# _theme = :juno
if _theme == :juno
base_color = :white
anti_color = :black
else
base_color = :black
anti_color = :white
end
_plot(; dpi = _plt_dpi, size = _plt_size, thickness_scaling=_thickness_scaling, kwargs...) =
plot(; dpi=dpi, size=size, thickness_scaling=thickness_scaling, kwargs...)
plot_spectrum(; xlabel = "Wavelength (Å)", ylabel = "Continuum Normalized Flux + Const", kwargs...) =
_plot(; xlabel=xlabel, ylabel=ylabel, kwargs...)
plot_rv(; xlabel = "Time (d)", ylabel = "RV (m/s)", kwargs...) =
_plot(; xlabel=xlabel, ylabel=ylabel, kwargs...)
plot_scores(; xlabel = "Time (d)", ylabel = "Scores + Const", kwargs...) =
_plot(; xlabel=xlabel, ylabel=ylabel, kwargs...)
theme(_theme)
_scatter!(plt::Union{Plots.AbstractPlot,Plots.AbstractLayout}, x::AbstractVecOrMat, y::AbstractVecOrMat; markerstrokewidth::Real=0, kwargs...) = scatter!(plt, x, y; markerstrokewidth=markerstrokewidth, kwargs...)
_theme == :default ? plt_colors = palette(_theme).colors.colors : plt_colors = PlotThemes._themes[_theme].defaults[:palette].colors.colors
function rv_legend(label, rvs, times)
intra_night = SSOF.intra_night_std(rvs, times; show_warn=false)
isinf(intra_night) ? appen = "" : appen = ", intra night RMS: $(round(intra_night, digits=3))"
return label * " RVs, RMS: $(round(std(rvs), digits=3))" * appen
end
function plot_model_rvs(times_nu::AbstractVector{T}, model_rvs::AbstractVecOrMat{T}, model_rvs_σ::AbstractVecOrMat{T}, inst_times::AbstractVector{T}, inst_rvs::AbstractVector{T}, inst_rvs_σ::AbstractVector{T}; display_plt::Bool=true, inst_str::String="Instrument", msw::Real=0.5, alpha=0.7, upper_legend=:bottomright, lower_legend=:bottomright, kwargs...) where {T<:Real}
plt = plot_rv(; legend=upper_legend, layout=grid(2, 1, heights=[0.7, 0.3]))
ervs = inst_rvs .- median(inst_rvs)
mrvs = model_rvs .- median(model_rvs)
scatter!(plt[1], inst_times, ervs; yerror=inst_rvs_σ, msc=0.4*plt_colors[1], label=inst_str * " (RMS: $(round(std(ervs), digits=3)), σ: $(round(mean(inst_rvs_σ), digits=3)))", alpha = alpha, msw=msw, kwargs...)
scatter!(plt[1], times_nu, mrvs; yerror=model_rvs_σ, msc=0.4*plt_colors[2], label="SSOF (RMS: $(round(std(mrvs), digits=3)), σ: $(round(mean(model_rvs_σ), digits=3)))", alpha = alpha, msw=msw, kwargs...)
resids = mrvs - ervs
scatter!(plt[2], times_nu, resids; c=:black, ylabel="SSOF - " * inst_str * " (m/s)", yerror=sqrt.(model_rvs_σ .^ 2 + inst_rvs_σ .^ 2), alpha = alpha, msw=msw, label="RMS: $(round(std(resids), digits=3))", legend=lower_legend)
if display_plt; display(plt) end
return plt
end
function plot_model_rvs(times_nu::AbstractVector{T}, model_rvs::AbstractVecOrMat{T}, model_rvs_σ::AbstractVecOrMat{T}, inst_times::AbstractVector{T}, inst_rvs::AbstractVector{T}, inst_rvs_σ::AbstractVector{T}, ccf_rvs::AbstractVector{T}; display_plt::Bool=true, kwargs...) where {T<:Real}
plt = plot_model_rvs(times_nu, model_rvs, model_rvs_σ, inst_times, inst_rvs, inst_rvs_σ)
_scatter!(plt[1], inst_times, ccf_rvs .- median(ccf_rvs); label=rv_legend("CCF", ccf_rvs, inst_times), alpha = 0.7, markerstrokewidth=0.5, kwargs...)
if display_plt; display(plt) end
return plt
end
function plot_stellar_with_lsf!(plt, om::SSOF.OrderModel, y::AbstractVector; d::Union{SSOF.Data, Nothing}=nothing, alpha=1, label="", kwargs...)
if typeof(d) <: SSOF.LSFData
plot!(plt, om.star.λ, y; alpha=alpha/2, label="", kwargs...)
typeof(om) <: SSOF.OrderModelWobble ?
y2 = d.lsf * SSOF.spectra_interp(y, om.rv[1] + om.bary_rvs[1], om.b2o; sih_ind=1) :
y2 = d.lsf * SSOF.spectra_interp(y, om.b2o[1])
plot!(plt, exp.(d.log_λ_star[:, 1]), y2; alpha=alpha, label=label, kwargs...)
else
plot!(plt, om.star.λ, y; alpha=alpha, label=label, kwargs...)
end
end
function plot_telluric_with_lsf!(plt, om::SSOF.OrderModel, y::AbstractVector; d::Union{SSOF.Data, Nothing}=nothing, alpha=1, label="", kwargs...)
if typeof(d) <: SSOF.LSFData
plot!(plt, om.tel.λ, y; alpha=alpha/2, label="", kwargs...)
plot!(plt, exp.(d.log_λ_obs[:, 1]), d.lsf * SSOF.spectra_interp(y, om.t2o[1]); alpha=alpha, label=label, kwargs...)
else
plot!(plt, om.tel.λ, y; alpha=alpha, label=label, kwargs...)
end
end
function plot_telluric_with_lsf!(plt, om::SSOF.OrderModel, y::AbstractMatrix; d::Union{SSOF.Data, Nothing}=nothing, alpha=1, label="", kwargs...)
if typeof(d) <: SSOF.LSFData
plot!(plt, om.tel.λ, vec(time_average(y)); alpha=alpha/2, label="", kwargs...)
plot!(plt, vec(time_average(exp.(d.log_λ_obs))), vec(time_average(d.lsf * SSOF.spectra_interp(y, om.t2o))); alpha=alpha, label=label, kwargs...)
else
plot!(plt, om.tel.λ, vec(time_average(y)); alpha=alpha, label=label, kwargs...)
end
end
function plot_stellar_with_lsf!(plt, om::SSOF.OrderModel, y::AbstractMatrix; d::Union{SSOF.Data, Nothing}=nothing, alpha=1, label="", kwargs...)
if typeof(d) <: SSOF.LSFData
plot!(plt, om.star.λ, vec(time_average(y)); alpha=alpha/2, label="", kwargs...)
typeof(om) <: SSOF.OrderModelWobble ?
y2 = vec(time_average(d.lsf * SSOF.spectra_interp(y, om.rv + om.bary_rvs, om.b2o))) :
y2 = vec(time_average(d.lsf * SSOF.spectra_interp(y, om.b2o)))
plot!(plt, vec(time_average(exp.(d.log_λ_star))), y2; alpha=alpha, label=label, kwargs...)
else
plot!(plt, om.star.λ, vec(time_average(y)); alpha=alpha, label=label, kwargs...)
end
end
c_ind_f(i) = ((i + 1) % 16) + 1
function plot_model(om::SSOF.OrderModel, airmasses::Vector, times_nu::Vector; display_plt::Bool=true, d::Union{SSOF.Data, Nothing}=nothing, o::Union{SSOF.Output, Nothing}=nothing, incl_χ²::Bool=true, tel_errors::Union{AbstractMatrix, Nothing}=nothing, star_errors::Union{AbstractMatrix, Nothing}=nothing, df_act::Dict=Dict(), return_separate::Bool=false, shift_M::Real=0.2, kwargs...)
plot_stellar = SSOF.is_time_variable(om.star)
plot_telluric = SSOF.is_time_variable(om.tel)
# plot the two templates if there is no time variation
if (!plot_stellar) && (!plot_telluric)
plt = plot_spectrum(; title="Constant Model", legend=:outerright, kwargs...)
plot_telluric_with_lsf!(plt, om, om.tel.lm.μ; d=d, color=plt_colors[1], label=L"\mu_\oplus")
plot_stellar_with_lsf!(plt, om, om.star.lm.μ .- 0.5; d=d, color=plt_colors[2], label=L"\mu_\star")
if display_plt; display(plt) end
return plt
end
n_plots = plot_stellar + plot_telluric
plt = _plot(; layout=grid(2, n_plots), size=(n_plots * _plt_size[1],_plt_size[2]*2), kwargs...)
incl_χ² = incl_χ² && !isnothing(d) && !isnothing(o)
if incl_χ²; χ²_base = SSOF._loss(o, om, d) end
function scaler_string(scaler::Real)
if isapprox(1, scaler); return "" end
return " " * string(round(scaler;digits=2)) * "x scaled"
end
if plot_telluric
inds = axes(om.tel.lm.M, 2)
# basis plot
plot_stellar_with_lsf!(plt[1, 1], om, om.star.lm.μ; d=d, color=base_color, alpha=0.3, label=L"\mu_\star", title="Telluric Model Feature Vectors", legend=:outerright, xlabel = "Wavelength (Å)", ylabel = "Continuum Normalized Flux + Const")
plot_telluric_with_lsf!(plt[1, 1], om, om.tel.lm.μ; d=d, color=plt_colors[1], label=L"\mu_\oplus")
norm_Ms = [norm(view(om.tel.lm.M, :, i)) for i in inds]
s_std = [std(view(om.tel.lm.s, inds[j], :) .* norm_Ms[j]) for j in eachindex(inds)]
max_s_std = maximum(s_std)
shift_s = ceil(10 * max_s_std) / 2
_scatter!(plt[2, 1], times_nu, ((max_s_std / std(airmasses)) .* (airmasses .- mean(airmasses))) .+ shift_s; label="Airmasses (scaled)", color=base_color)
hline!(plt[2, 1], [shift_s]; label="", color=base_color, lw=3, alpha=0.4)
# half_shift_s = ceil(shift_s) / 2
if incl_χ²; holder = copy(om.tel.lm.s) end
# for i in reverse(inds)
for j in eachindex(inds)
i = inds[j]
c_ind = c_ind_f(i - inds[1])
norm_M = norm_Ms[j]
# basis plot
plot_telluric_with_lsf!(plt[1, 1], om, (view(om.tel.lm.M, :, i) ./ norm_M) .- shift_M * (i - 1); d=d, label="Basis $i", color=plt_colors[c_ind])
scaler = max_s_std / std(view(om.tel.lm.s, i, :) .* norm_M)
_label = "Scores $i" * scaler_string(scaler)
# weights plot
if incl_χ²
om.tel.lm.s[i, :] .= 0
Δχ² = 1 - (χ²_base / SSOF._loss(o, om, d; tel=vec(om.tel.lm)))
om.tel.lm.s[i, :] .= view(holder, i, :)
_label *= " (Δχ² = $(round(Δχ²; digits=3)))"
end
isnothing(tel_errors) ? tel_σ = nothing : tel_σ = view(tel_errors, i, :)
scatter!(plt[2, 1], times_nu, (view(om.tel.lm.s, i, :) .* (norm_M * scaler)) .- (shift_s * (i - 1)); yerror=tel_σ, label=_label, color=plt_colors[c_ind], title="Telluric Model Scores", xlabel = "Time (d)", ylabel = "Scores + Const", legend=:outerright, markerstrokewidth=Int(!isnothing(tel_errors))/2, kwargs...)
hline!(plt[2, 1], [-(shift_s * (i - 1))]; label="", color=plt_colors[c_ind], lw=3, alpha=0.4)
end
end
if plot_stellar
plot_telluric ? c_offset = inds[end] - 1 : c_offset = 1
inds = axes(om.star.lm.M, 2)
# basis plot
plot_telluric_with_lsf!(plt[1, n_plots], om, om.tel.lm.μ; d=d, color=base_color, alpha=0.3, label=L"\mu_\oplus", title="Stellar Model Feature Vectors", legend=:outerright, xlabel = "Wavelength (Å)", ylabel = "Continuum Normalized Flux + Const")
plot_stellar_with_lsf!(plt[1, n_plots], om, om.star.lm.μ; d=d, color=plt_colors[1], label=L"\mu_\star")
norm_Ms = [norm(view(om.star.lm.M, :, i)) for i in inds]
s_std = [std(view(om.star.lm.s, inds[j], :) .* norm_Ms[j]) for j in eachindex(inds)]
max_s_std = maximum(s_std)
shift_s = ceil(10 * max_s_std) / 2
_keys = sort([key for key in keys(df_act)])[1:2:end]
for i in reverse(eachindex(_keys))
key = _keys[i]
y = df_act[key]
c = max_s_std / std(y)
scatter!(plt[2, n_plots], times_nu, (c .* (y .- mean(y))) .+ (shift_s*i); label=_keys[i] * " (scaled)", yerror=c.*df_act[key*"_σ"], color=plt_colors[c_ind_f(1 + c_offset)], markerstrokewidth=0.5)
hline!(plt[2, n_plots], [shift_s*i]; label="", color=plt_colors[c_ind_f(1 + c_offset)], lw=3, alpha=0.4)
c_offset += 1
end
if incl_χ²; holder = copy(om.star.lm.s) end
# for i in reverse(inds)
for j in eachindex(inds)
i = inds[j]
c_ind = c_ind_f(i + c_offset)
norm_M = norm_Ms[j]
# basis plot
plot_stellar_with_lsf!(plt[1, n_plots], om, (view(om.star.lm.M, :, i) ./ norm_M) .- shift_M * (i - 1); d=d, label="Basis $i", color=plt_colors[c_ind])
scaler = max_s_std / std(view(om.star.lm.s, i, :) .* norm_M)
_label = "Scores $i" * scaler_string(scaler)
# weights plot
if incl_χ²
om.star.lm.s[i, :] .= 0
Δχ² = 1 - (χ²_base / SSOF._loss(o, om, d; star=vec(om.star.lm)))
om.star.lm.s[i, :] .= view(holder, i, :)
_label *= " (Δχ² = $(round(Δχ²; digits=3)))"
end
isnothing(star_errors) ? star_σ = nothing : star_σ = view(star_errors, i, :)
scatter!(plt[2, n_plots], times_nu, (view(om.star.lm.s, i, :) .* (norm_M * scaler)) .- (shift_s * (i - 1)); yerror=star_σ, label=_label, color=plt_colors[c_ind], title="Stellar Model Scores", xlabel = "Time (d)", ylabel = "Scores + Const", legend=:outerright, markerstrokewidth=Int(!isnothing(star_errors))/2, kwargs...)
hline!(plt[2, n_plots], [-shift_s * (i - 1)]; label="", color=plt_colors[c_ind], lw=3, alpha=0.4)
end
end
if display_plt; display(plt) end
return plt
end
plot_model(mws::SSOF.ModelWorkspace, airmasses::Vector, times_nu::Vector; kwargs...) =
plot_model(mws.om, airmasses, times_nu; d=mws.d, o=mws.o, kwargs...)
function plot_model(lm::SSOF.FullLinearModel; λ=eachindex(lm.μ), times=axes(lm.s, 2), display_plt::Bool=true, shift_M::Real = 0.2, kwargs...)
plt = _plot(; layout=grid(2, 1), size=(_plt_size[1],_plt_size[2]*1.5), kwargs...)
inds = axes(lm.M, 2)
# basis plot
plot!(plt[1, 1], λ, lm.μ; label="μ", title="Model Bases", legend=:outerright, xlabel = "Wavelength (Å)", ylabel = "Continuum Normalized Flux + Const")
shift_s = ceil(10 * maximum([std(lm.s[inds[i], :] .* norm(lm.M[:, inds[i]])) for i in inds])) / 2
for i in reverse(inds)
c_ind = c_ind_f(i - inds[1])
norm_M = norm(view(lm.M, :, i))
# basis plot
plot!(plt[1, 1], λ, (view(lm.M, :, i) ./ norm_M) .- shift_M * (i - 1); label="Basis $i", color=plt_colors[c_ind])
# weights plot
_scatter!(plt[2, 1], times, (view(lm.s, i, :) .* norm_M) .- (shift_s * (i - 1)); label="Scores $i", color=plt_colors[c_ind], title="Model Scores", xlabel = "Time (d)", ylabel = "Scores + Const", legend=:outerright, kwargs...)
hline!(plt[2, 1], [-shift_s * (i - 1)]; label="", color=plt_colors[c_ind], lw=3, alpha=0.4)
end
if display_plt; display(plt) end
return plt
end
function plot_bases(om::SSOF.OrderModel, d::SSOF.Data, stellar::Bool; shift_M::Real=0.2, kwargs...)
plt = _plot(; kwargs...)
if stellar
plot_telluric_with_lsf!(plt, om, om.tel.lm.μ; d=d, color=base_color, alpha=0.3, label=L"\mu_\oplus", title="Stellar Model Feature Vectors", legend=:outerright, xlabel = "Wavelength (Å)", ylabel = "Continuum Normalized Flux + Const")
plot_stellar_with_lsf!(plt, om, om.star.lm.μ; d=d, color=plt_colors[1], label=L"\mu_\star")
lm = om.star.lm
else
plot_stellar_with_lsf!(plt, om, om.star.lm.μ; d=d, color=base_color, alpha=0.3, label=L"\mu_\star", title="Telluric Model Feature Vectors", legend=:outerright, xlabel = "Wavelength (Å)", ylabel = "Continuum Normalized Flux + Const")
plot_telluric_with_lsf!(plt, om, om.tel.lm.μ; d=d, color=plt_colors[1], label=L"\mu_\oplus")
lm = om.tel.lm
end
inds = axes(lm.M, 2)
norm_Ms = [norm(view(lm.M, :, i)) for i in inds]
for j in eachindex(inds)
i = inds[j]
c_ind = c_ind_f(i - inds[1])
norm_M = norm_Ms[j]
# basis plot
if stellar
plot_stellar_with_lsf!(plt, om, (view(lm.M, :, i) ./ norm_M) .- shift_M * (i - 1); d=d, label="Basis $i", color=plt_colors[c_ind])
else
plot_telluric_with_lsf!(plt, om, (view(lm.M, :, i) ./ norm_M) .- shift_M * (i - 1); d=d, label="Basis $i", color=plt_colors[c_ind])
end
end
return plt
end
plot_telluric_bases(om::SSOF.OrderModel, d::SSOF.Data; kwargs...) =
plot_bases(om, d, false; kwargs...)
plot_stellar_bases(om::SSOF.OrderModel, d::SSOF.Data; kwargs...) =
plot_bases(om, d, true; kwargs...)
time_average(a) = mean(a; dims=2)
function status_plot(mws::SSOF.ModelWorkspace; tracker::Int=0, display_plt::Bool=true, include_χ²::Bool=true, kwargs...)
o = mws.o
d = mws.d
obs_mask = vec(all(.!(isinf.(d.var)); dims=2))
obs_λ = exp.(time_average(d.log_λ_obs))
# plot_star_λs = exp.(time_average(d.log_λ_star))
include_χ² ?
plt = plot_spectrum(; legend = :bottomright, layout = grid(3, 1, heights=[0.6, 0.2, 0.2]), ylabel="Flux + Constant Shift", kwargs...) :
plt = plot_spectrum(; legend = :bottomright, layout = grid(2, 1, heights=[0.85, 0.15]), kwargs...)
# TODO: take average after broadening with LSF
tel_model = time_average(mws.om.tel.lm())
plot_telluric_with_lsf!(plt[1], mws.om, vec(tel_model); d=mws.d, label="Mean Telluric Model", color=plt_colors[1])
# tel_model = mws.om.tel.lm()
# plot_telluric_with_lsf!(plt[1], mws.om, tel_model; d=mws.d, label="Mean Telluric Model", color=plt_colors[1])
shift = 1.1 - minimum(tel_model)
star_model = time_average(mws.om.star.lm())
# star_model = mws.om.star.lm()
# typeof(mws.om) <: SSOF.OrderModelWobble ?
# star_model = time_average(mws.om.star()) :
# star_model = time_average(mws.om.star() + mws.om.rv())
plot_stellar_with_lsf!(plt[1], mws.om, vec(star_model .- shift); d=mws.d, label="Mean Stellar Model", color=plt_colors[2])
# plot_stellar_with_lsf!(plt[1], mws.om, star_model .- shift; d=mws.d, label="Mean Stellar Model", color=plt_colors[2])
# shift += 1.1 - minimum(star_model)
# plot!(plt[1], obs_λ, time_average(o.total) .- shift, label="Mean Full Model", color=base_color)
_scatter!(plt[2], obs_λ[obs_mask], time_average(abs.(view(d.flux, obs_mask, :) - view(o.total, obs_mask, :))), ylabel="MAD", label="", alpha=0.5, color=base_color, xlabel="", ms=1.5)
plot!(plt[2], obs_λ, sqrt(2/π) .* mean(sqrt.(d.var); dims=2); label="", c=plt_colors[3], lw=2);
if include_χ²
_scatter!(plt[3], obs_λ, -sum(SSOF._loss_diagnostic(mws); dims=2), ylabel="Remaining χ²", label="", alpha=0.5, color=base_color, xlabel="", ms=1.5)
hline!(plt[3], [-size(d.var, 2)]; label="", c=plt_colors[3], lw=2)
end
if display_plt; display(plt) end
return plt
end
function component_test_plot(ys::Matrix, test_n_comp_tel::AbstractVector, test_n_comp_star::AbstractVector; size=(_plt_size[1],_plt_size[2]*1.5), ylabel="ℓ", xguidefontsize = 16, kwargs...)
plt = _plot(; ylabel=ylabel, layout=grid(2, 1), size=size, xguidefontsize = xguidefontsize, kwargs...)
# lims = [maximum(ys[.!(isinf.(ys))]), minimum(ys[.!(isinf.(ys))])]
lims = Array{Float64}(undef, 2)
lim_inds = ones(Int, 2)
if ylabel=="ℓ"
best = argmax(ys)
if test_n_comp_tel[1:2] == -1:0
lim_inds[1] = min(3, best[1])
end
if test_n_comp_star[1] == 0
lim_inds[2] = min(2, best[2])
end
window = view(ys, lim_inds[1]:length(test_n_comp_tel), lim_inds[2]:length(test_n_comp_star))
lims[1] = minimum(window[isfinite.(window)])
lims[2] = ys[best]
else
best = argmin(ys)
if test_n_comp_tel[1:2] == -1:0
lim_inds[1] = min(3, best[1])
end
if test_n_comp_star[1] == 0
lim_inds[2] = min(2, best[2])
end
lims[1] = ys[best]
window = view(ys, (lim_inds[1]):length(test_n_comp_tel), (lim_inds[2]):length(test_n_comp_star))
lims[2] = maximum(window[isfinite.(window)])
end
buffer = 0.3 * (lims[2] - lims[1])
ylims!(plt, lims[1] - buffer, lims[2] + buffer)
for i in eachindex(test_n_comp_tel)
test_n_comp_tel[i]==-1 ? _label="∅" : _label="$(test_n_comp_tel[i])"
plot!(plt[1], test_n_comp_star, ys[i, :]; label=_label, leg_title=L"K_\oplus", shape=:diamond, msw=0, xlabel=L"K_\star")
end
for i in eachindex(test_n_comp_star)
plot!(plt[2], test_n_comp_tel, ys[:, i]; label="$(test_n_comp_star[i])", leg_title=L"K_\star", shape=:diamond, msw=0, xlabel=L"K_\oplus")
end
# display(plt)
return plt
end
function save_model_plots(mws, airmasses, times_nu, save_path::String; display_plt::Bool=true, incl_χ²::Bool=true, tel_errors::Union{AbstractMatrix, Nothing}=nothing, star_errors::Union{AbstractMatrix, Nothing}=nothing, df_act::Dict=Dict(), kwargs...)
plt = plot_model(mws, airmasses, times_nu; display_plt=display_plt, incl_χ²=incl_χ², tel_errors=tel_errors, star_errors=star_errors, df_act=df_act, kwargs...);
png(plt, save_path * "model.png")
plt = status_plot(mws; display_plt=display_plt, kwargs...);
png(plt, save_path * "status_plot.png")
end
function gated_plot!(plt, plotf!::Function, x::AbstractVector, y::AbstractVector, ylims, c, alpha, label, markersize)
@assert plotf! == scatter! || plotf! == plot!
m1 = y .< ylims[1]
scatter!(x[m1], ones(sum(m1)) .* (ylims[1] + .05); label="", c=c, markershape=:utriangle, markerstrokewidth=0, alpha=alpha, markersize=markersize)
m2 = y .> ylims[2]
scatter!(x[m2], ones(sum(m2)) .* (ylims[2] - .05); label="", c=c, markershape=:dtriangle, markerstrokewidth=0, alpha=alpha, markersize=markersize)
m = SSOF.and.(.!m1, .!m2)
plotf!(x[m], y[m]; label=label, c=c, markerstrokewidth=0, alpha=alpha, markersize=markersize)
end
function data_usage_plot(d::SSOF.Data, bad_inst::Vector, bad_high::Vector, bad_snap::Vector, bad_edge::Vector, bad_isol::Vector, bad_byeye::Vector; save_path::String="", use_var_s::Bool=true)
if use_var_s
ever_used = vec(any(isfinite.(d.var_s); dims=2))
always_used = vec(all(.!(isinf.(d.var_s)); dims=2))
else
ever_used = vec(any(isfinite.(d.var); dims=2))
always_used = vec(all(.!(isinf.(d.var)); dims=2))
end
sometimes_used = xor.(ever_used, always_used)
never_used = .!ever_used
mean_flux = vec(mean(d.flux; dims=2))
pixs = axes(d.flux, 1)
yli = (-.05, 1.5)
plt = _plot(; title="Data Usage", xlabel="Pixel #", ylabel="Normalized Flux", legend=:outerright, ylims=yli)
if sum(always_used) > 0; gated_plot!(plt, scatter!, view(pixs, always_used), view(mean_flux, always_used), yli, base_color, 1, "Always used", 1) end
bads_str = ["Instrumental", "High", "Snappy", "Low SNR", "Isolated", "By Eye"]
bads = [bad_inst, bad_high, bad_snap, bad_edge, bad_isol, bad_byeye]
ss = [3, 3, 3, 2, 2, 2]
for i in eachindex(bads)
bad = bads[i]
bad_str = bads_str[i]
s = ss[i]
if length(bad) > 0; gated_plot!(plt, scatter!, bad, view(mean_flux, bad), yli, plt_colors[i+1], 0.4, bad_str, s) end
end
if sum(sometimes_used) > 0; gated_plot!(plt, scatter!, view(pixs, sometimes_used), view(mean_flux, sometimes_used), yli, plt_colors[1], 0.6, "Sometimes used", 1) end
if sum(never_used) > 0; gated_plot!(plt, scatter!, view(pixs, never_used), view(mean_flux, never_used), yli, :red, 1, "Never used", 1) end
if save_path != ""; png(plt, save_path * "data_usage.png") end
return plt
end
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 5837 | using Pkg
Pkg.activate("examples")
Pkg.instantiate()
import StellarSpectraObservationFitting as SSOF
using JLD2 # importing saved model
using Plots # plotting
using Statistics # mean function
# approximating PDF of saved model scores
using KernelDensity # Bandwidth calculation
using Distributions # Normal distribution
using StatsBase # sample function
include("_plots.jl") # some plotting functions
_plot(; dpi = 100, size = (960, 540), thickness_scaling=1., margin=4Plots.mm, kwargs...) =
plot(; dpi=dpi, size=size, thickness_scaling=thickness_scaling, margin=margin, kwargs...)
# load in a prefit SSOF model and the data that it was fit to
@load "examples/data/results.jld2" model
@load "examples/data/data.jld2" data # only used for LSF and blaze function
# how many observations we want
n_simulated_observations = 50
# Adding whatever additional RVs we want
injected_rvs = zeros(n_simulated_observations)
# K = 10 # planet velocity semi-amplitude (m/s)
# P = 60 # planet period (d)
# injected_rvs = K .* sin(times ./ P * 2 * π)
# simulated central pixel SNR
desired_max_snr = 500;
# spread observations evenly across all of 2022 (JD)
times = 2459580 .+ collect(LinRange(365., 0, n_simulated_observations));
# # Barycorrpy version
# using PyCall
# barycorrpy = PyNULL()
# # pyimport_conda("scipy", "scipy")
# # pushfirst!(PyVector(pyimport("sys")."path"), @__DIR__)
# copy!(barycorrpy , pyimport("barycorrpy") )
# barycentric_corrections = barycorrpy.get_BC_vel(JDUTC=times, hip_id=19849, obsname="KPNO", ephemeris="de430")
# barycentric_rvs = barycentric_corrections[1]
# Epicyclic approximation for simplicity (correct within 411 m/s)
year = 365.25
phases = times ./ year * 2 * π
design_matrix = hcat(cos.(phases), sin.(phases), cos.(2 .* phases), sin.(2 .* phases), ones(length(times)))
epicyclic_barycentric_rv_coefficients = [-20906.74122340397, -15770.355782489662, -390.29975114321905, -198.97407208182858, -67.99370656806558]
barycentric_rvs = design_matrix * epicyclic_barycentric_rv_coefficients
# observed wavelengths will just be the same as the original model
# could downsample here
log_λ_obs = model.tel.log_λ * (ones(n_simulated_observations)')
log_λ_stellar = log_λ_obs .+ (SSOF.rv_to_D(barycentric_rvs)')
# getting stellar feature score values that roughly match the original modeled distribution
bandwidth_stellar = KernelDensity.default_bandwidth(vec(model.star.lm.s))
model_scores_stellar = rand.(Normal.(sample(vec(model.star.lm.s), n_simulated_observations; replace=true), bandwidth_stellar))'
model_scores_stellar .-= mean(model_scores_stellar)
# evaluating linear model
_flux_stellar = SSOF._eval_lm(model.star.lm.M, model_scores_stellar, model.star.lm.μ; log_lm=model.star.lm.log) # replace s for custom data
# interpolating stellar flux
b2o = SSOF.StellarInterpolationHelper(model.star.log_λ, injected_rvs + barycentric_rvs, log_λ_obs)
flux_stellar = SSOF.spectra_interp(_flux_stellar, injected_rvs + barycentric_rvs, b2o)
# getting telluric feature score values that roughly match the original modeled distribution
bandwidth_telluric = KernelDensity.default_bandwidth(vec(model.tel.lm.s))
model_scores_telluric = rand.(Normal.(sample(vec(model.tel.lm.s), n_simulated_observations; replace=true), bandwidth_telluric))'
model_scores_telluric .-= mean(model_scores_telluric)
# simulated telluric transmission
flux_tellurics = SSOF._eval_lm(model.tel.lm.M, model_scores_telluric, model.tel.lm.μ; log_lm=model.tel.lm.log)
flux_total = SSOF.total_model(flux_tellurics, flux_stellar)
## getting a realistic LSF
include("_lsf.jl") # defines NEIDLSF.NEID_lsf()
lsf_simulated = NEIDLSF.neid_lsf(81, vec(mean(data.log_λ_obs; dims=2)), vec(mean(log_λ_obs; dims=2)))
flux_total_lsf = lsf_simulated * flux_total
# measured_blaze = data.flux ./ data.var
# _, smooth_blazes = SSOF.calc_continuum(exp.(data.log_λ_obs), measured_blaze, data.var)
# smooth_blaze = vec(mean(smooth_blazes; dims=2))
# # filling in gaps
# lo = Inf
# for i in eachindex(smooth_blaze)
# if isfinite(smooth_blaze[i])
# if isfinite(lo)
# println("$lo, $i")
# smooth_blaze[lo:i] .= smooth_blaze[lo] .+ ((smooth_blaze[i]-smooth_blaze[lo]) * LinRange(0,1,i-lo+1))
# lo = Inf
# end
# elseif !isfinite(lo)
# lo = i-1
# end
# end
# using DataInterpolations
# blaze_function= DataInterpolations.LinearInterpolation(smooth_blaze, vec(mean(data.log_λ_obs; dims=2)))
# @save "examples/data/blaze.jld2" blaze_function
@load "examples/data/blaze.jld2" blaze_function
var_total = flux_total_lsf ./ blaze_function.(log_λ_obs)
# scaling variance to have the desired SNR in the center
cp = Int(round(size(flux_total_lsf,1)/2))
snr_cp = median(flux_total_lsf[(cp-500):(cp+500),:] ./ sqrt.(var_total[(cp-500):(cp+500),:]))
var_total .*= (snr_cp / desired_max_snr)^2
flux_noisy = flux_total_lsf .+ (randn(size(var_total)) .* sqrt.(var_total))
data_simulated = SSOF.LSFData(flux_noisy, var_total, copy(var_total), log_λ_obs, log_λ_stellar, lsf_simulated)
SSOF.mask_bad_edges!(data_simulated);
# getting initial model
star = "26965"
instrument = "SSOF"
order = 81
n_comp = 2 # maximum amount of feature vectors to use for each portion of the model
model_new = SSOF.calculate_initial_model(data_simulated;
instrument=instrument, desired_order=order, star=star, times=times,
max_n_tel=n_comp, max_n_star=n_comp, log_λ_gp_star=1/SSOF.SOAP_gp_params.λ,
log_λ_gp_tel=5.134684755671457e-6,
tel_log_λ=model.tel.log_λ, star_log_λ=model.star.log_λ, oversamp=false)
# setting up model workspace
mws = SSOF.ModelWorkspace(model_new, data_simulated);
SSOF.fit_regularization!(mws)
results = SSOF.improve_model!(mws; iter=500, verbose=true, careful_first_step=true, speed_up=false)
rvs, rvs_σ, tel_s_σ, star_s_σ = SSOF.estimate_σ_curvature(mws)
# rvs, rvs_σ, tel_s_σ, star_s_σ = SSOF.estimate_σ_bootstrap(mws) | StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 5435 | # functions related to computing the Doppler-constrained (EM)PCA for time series spectra
using LinearAlgebra
import ExpectationMaximizationPCA as EMPCA
"""
simple_derivative(x)
Estimate the derivative of `x` with finite differences (assuming unit separation)
"""
function simple_derivative(x::AbstractVector{<:Real})
@assert length(x)>=3
dx = similar(x)
dx[1] = x[2]-x[1]
dx[end] = x[end]-x[end-1]
# faster than dx[2:end-1] .= (x[3:end] - x[1:end-2]) ./ 2
for i in 2:(length(x)-1)
dx[i] = (x[i+1]-x[i-1])/2
end
return dx
end
"""
simple_derivative_AD(x)
Estimate the derivative of `x` with finite differences (assuming unit separation). Autodiff friendly
"""
function simple_derivative_AD(x::Vector{<:Real})
function helper(x::Vector, i::Int)
if i == 1
return x[2]-x[1]
elseif i == length(x)
return x[end]-x[end-1]
else
return (x[i+1]-x[i-1])/2
end
end
@assert length(x)>=3
return [helper(x, i) for i in eachindex(x)]
end
"""
doppler_component(λ, flux)
Estimate the basis vector that encodes the effects of a doppler shift based on Taylor expanding f(λ/(1 + z)) about z=0
doppler_comp = λ * dF/dλ -> units of flux
"""
function doppler_component(λ::AbstractVector{T}, flux::Vector{T}) where {T<:Real}
@assert length(λ) == length(flux)
dλdpix = simple_derivative(λ)
dfluxdpix = simple_derivative(flux)
return dfluxdpix .* (λ ./ dλdpix) # doppler basis
end
doppler_component(λ::AbstractVector{T}, flux::Matrix{T}, kwargs...) where {T<:Real} =
doppler_component(λ, vec(mean(flux, dims=2)), kwargs...)
doppler_component_log(λ::AbstractVector{T}, flux::Vector{T}) where {T<:Real} =
doppler_component(λ, flux) ./ flux
"""
doppler_component_AD(λ, flux)
Estimate the basis vector that encodes the effects of a doppler shift based on Taylor expanding f(λ/(1 + z)) about z=0. Autodiff friendly
doppler_comp = λ * dF/dλ -> units of flux
"""
function doppler_component_AD(λ::Vector{T}, flux::Vector{T}) where {T<:Real}
@assert length(λ) == length(flux)
dλdpix = simple_derivative_AD(λ)
dfluxdpix = simple_derivative_AD(flux)
return dfluxdpix .* (λ ./ dλdpix) # doppler basis
end
doppler_component_AD(λ::Vector{T}, flux::Matrix{T}, kwargs...) where {T<:Real} =
doppler_component_AD(λ, vec(mean(flux, dims=2)), kwargs...)
doppler_component_log_AD(λ::AbstractVector{T}, flux::Vector{T}) where {T<:Real} =
doppler_component_log_AD(λ, flux) ./ flux
"""
project_doppler_comp!(scores, data_temp, doppler_comp, weights)
Finding the optimal `scores` to remove the weighted projection of `doppler_comp` from `data_temp`
"""
function project_doppler_comp!(scores::AbstractVector, data_temp::AbstractMatrix, doppler_comp::AbstractVector, weights::AbstractMatrix)
EMPCA._solve_scores!(doppler_comp, scores, data_temp, weights)
data_temp .-= doppler_comp * scores'
rvs = -light_speed_nu * scores # c * z
return rvs
end
function project_doppler_comp!(M::AbstractMatrix, scores::AbstractVector, data_temp::AbstractMatrix, doppler_comp::AbstractVector, weights::AbstractMatrix)
M[:, 1] = doppler_comp # Force fixed (i.e., Doppler) component to replace first PCA component
return project_doppler_comp!(scores, data_temp, doppler_comp, weights)
end
"""
project_doppler_comp(data_temp, doppler_comp, weights)
Remove the weighted projection of `doppler_comp` from `data_temp`
"""
function project_doppler_comp(data_temp::AbstractMatrix, doppler_comp::AbstractVector, weights::AbstractMatrix)
scores = Array{Float64}(undef, size(weights, 2))
return project_doppler_comp!(scores, data_temp, doppler_comp, weights)
end
"""
DEMPCA!(M, scores, rv_scores, μ, data_temp, weights, doppler_comp; min_flux=0., max_flux=2., save_doppler_in_M1=true, kwargs...)
Perform Doppler-constrained Expectation maximization PCA on `data_temp`
"""
function DEMPCA!(M::AbstractVecOrMat, scores::AbstractVecOrMat, rv_scores::AbstractVector, μ::AbstractVector, data_temp::AbstractMatrix, weights::AbstractMatrix, doppler_comp::Vector{T}; min_flux::Real=_min_flux_default, max_flux::Real=_max_flux_default, save_doppler_in_M1::Bool=true, kwargs...) where {T<:Real}
# remove template
data_temp .-= μ
# take out Doppler projection
if save_doppler_in_M1
rvs = project_doppler_comp!(M, rv_scores, data_temp, doppler_comp, weights)
else
rvs = project_doppler_comp!(rv_scores, data_temp, doppler_comp, weights)
end
# add back template before performing EMPCA
data_temp .+= μ
mask_low_pixels!(data_temp, weights; min_flux=min_flux, using_weights=true)
mask_high_pixels!(data_temp, weights; max_flux=max_flux, using_weights=true)
# perform EMPCA if M exists
if size(M, 2) > 0
EMPCA.EMPCA!(M, scores, μ, data_temp, weights; kwargs...)
end
return rvs
end
DEMPCA!(M::AbstractVecOrMat, scores::AbstractMatrix, μ::AbstractVector, data_temp::AbstractMatrix, weights::AbstractMatrix, doppler_comp::Vector{T}; inds=2:size(M, 2), kwargs...) where {T<:Real} =
DEMPCA!(M, scores, view(scores, 1, :), μ, data_temp, weights, doppler_comp; inds=inds, kwargs...)
DEMPCA!(lm::FullLinearModel, data_temp, weights, doppler_comp; use_log=log_lm(lm), kwargs...) = DEMPCA!(lm.M, lm.s, lm.μ, data_temp, weights, doppler_comp; use_log=use_log, kwargs...)
DEMPCA!(lm::FullLinearModel, rv_scores, data_temp, weights, doppler_comp; use_log=log_lm(lm), kwargs...) = DEMPCA!(lm.M, lm.s, rv_scores, lm.μ, data_temp, weights, doppler_comp; use_log=use_log, kwargs...)
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 431 | ## EMPCA alias
import ExpectationMaximizationPCA as EMPCA
using LinearAlgebra
"""
EMPCA!(lm, data_tmp, weights; kwargs...)
Perform Expectation maximization PCA on `data_temp`. See https://github.com/christiangil/ExpectationMaximizationPCA.jl
"""
EMPCA.EMPCA!(lm::FullLinearModel, data_tmp::AbstractMatrix, weights::AbstractMatrix; kwargs...) =
EMPCA.EMPCA!(lm.M, lm.s, lm.μ, data_tmp, weights; use_log=log_lm(lm), kwargs...)
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 258 | # Adding a function to properly deal with all view inputs
using Nabla
function Nabla.zerod_container(x::Vector{<:SubArray})
y = [copy(θ) for θ in x]
for n in eachindex(y)
@inbounds y[n] = Nabla.zerod_container(y[n])
end
return y
end
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 483 | module StellarSpectraObservationFitting
include("general_functions.jl")
include("model_functions.jl")
include("EMPCA.jl")
include("DPCA_functions.jl")
include("flatten.jl")
include("optimization_functions.jl")
include("regularization_functions.jl")
include("continuum_functions.jl")
include("model_selection_functions.jl")
include("mask_functions.jl")
include("Nabla_extension.jl")
include("prior_gp_functions.jl")
include("rassine.jl")
include("error_estimation.jl")
end # module
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 5599 | using Pkg
Pkg.activate(".")
# Finding reasonable LSF_gp param values from fitting to a lsf broadened line
# Based roughly on the EXPRES LSF at wn = 17000 1/cm (588 nm)
using AbstractGPs
using KernelFunctions
using TemporalGPs
using Optim # Standard optimisation algorithms.
using ParameterHandling # Helper functionality for dealing with model parameters.
using Zygote # Algorithmic Differentiation
import StellarSpectraObservationFitting as SSOF
using Plots
wavenumber_to_Å(wn) = 1e8 ./ wn
_fwhm_2_σ_factor = 1 / (2 * sqrt(2 * log(2)))
fwhm_2_σ(fwhm::Real) = _fwhm_2_σ_factor * fwhm
n = 1000
function matern52_kernel_base(λ::Number, δ::Number)
x = sqrt(5) * abs(δ) / λ
return (1 + x * (1 + x / 3)) * exp(-x)
end
plot_mat_λ!(λ, x) = plot!(x, matern52_kernel_base.((1 / λ), x); label="λ=$λ")
function fits_lsfs(sim_step, sep_test, quiet::Vector, folder::String, lsf_λs::Vector, i::Int, order::Int)
cov_xs = sim_step .* sep_test
# covs = [cor(quiet[1:end-sep], quiet[1+sep:end]) for sep in sep_test]
# covs = [cov(quiet[1:end-sep], quiet[1+sep:end]) for sep in sep_test]
# covs ./= maximum(covs)
covs = [quiet[1:end-sep]'*quiet[1+sep:end] for sep in sep_test] # better covariance function that knows they should be zero mean over long baseline
covs ./= maximum(covs)
plot(cov_xs, covs; label="lsf line", title="How correlated are nearby wavelengths", ylabel="cov", xlabel="log(λ (Å))")
# plot!(cov_xs, covs; label="better cov")
plot_mat_λ!(1e5, cov_xs)
plot_mat_λ!(2e5, cov_xs)
plot_mat_λ!(3e5, cov_xs)
# weights = max.(covs, 0)
# fo(λ) = sum(weights .* ((covs - matern52_kernel_base.((1 / λ[1]), cov_xs)) .^ 2))
fo(λ) = sum((covs - matern52_kernel_base.((1 / λ[1]), cov_xs)) .^ 2)
result = optimize(fo, [2e5], LBFGS(); autodiff = :forward)
lsf_λs[i] = result.minimizer[1]
plot_mat_λ!(round(result.minimizer[1]), cov_xs)
png("figs/lsf/$folder/$(order)_lsf_cor")
end
## EXPRES
using CSV, DataFrames
_eo = CSV.read("EXPRES/expres_psf.txt", DataFrame)
# eo = CSV.read("C:/Users/chris/Downloads/expres_psf.txt", DataFrame)
filter!(:line => ==("LFC"), _eo)
sort!(_eo, ["wavenumber [1/cm]"])
# has orders 37:76, (neid's 50-89), 41-76 is the intersection
lsf_orders = 37:75
lsf_λs = Array{Float64}(undef, length(lsf_orders))
for i in eachindex(lsf_orders)
order = lsf_orders[i]
eo = copy(_eo)
filter!(:order => ==(order), eo)
middle = Int(round(nrow(eo)/2))
central_wn = mean(eo."wavenumber [1/cm]"[middle-10:middle+10])
expres_LSF_FWHM_wn = mean(eo."fwhm [1/cm]"[middle-10:middle+10])
λ_lo, λ_hi = log(wavenumber_to_Å(central_wn+4expres_LSF_FWHM_wn)), log(wavenumber_to_Å(central_wn-4expres_LSF_FWHM_wn))
λs = RegularSpacing(λ_lo, (λ_hi-λ_lo)/n, n)
wns = wavenumber_to_Å.(exp.(λs))
expres_LSF_σ_wn = fwhm_2_σ(expres_LSF_FWHM_wn)
quiet = exp.(-(((wns .- wns[Int(round(n/2))]) ./ expres_LSF_σ_wn) .^ 2)/2)
# quiet .-= mean(quiet)
# plot!(λs .+ mean_λ, quiet)
# how many λs.Δt does it take to contain ~2σ?
n_seps = ((λ_hi + λ_lo) / 2 - log(wavenumber_to_Å(wavenumber_to_Å(exp((λ_hi + λ_lo) / 2)) + 2expres_LSF_σ_wn))) / λs.Δt
sep_test = 0:Int(ceil(n_seps))
sim_step = λs.Δt
fits_lsfs(sim_step, sep_test, quiet, "expres", lsf_λs, i, order)
end
maximum(lsf_λs)
lsf_λs_smooth = Array{Float64}(undef, length(lsf_orders))
f1 = SSOF.ordinary_lst_sq_f(lsf_λs, 2)
lsf_λs_smooth .= f1.(1.:39)
println(lsf_λs_smooth)
plot(lsf_λs)
plot!(lsf_λs_smooth)
## NEID
using JLD2
# Ingesting data (using NEID LSF)
include("../NEID/lsf.jl") # defines NEIDLSF.NEID_lsf()
nlsf = NEIDLSF
npix = 30
@load "order_pixel_spacing.jld2" spacing lsf_orders
lsf_λs = Array{Float64}(undef, length(lsf_orders))
middle = Int(round(size(nlsf.σs,1)/2))
pix = RegularSpacing(-1. * npix, 2npix/n, n)
for i in eachindex(lsf_orders)
# i = 1 # 1:59
order = lsf_orders[i] # has orders 54:112, (expres's 41-99), 54-89 is the intersection (index 1 and 36)
λs = RegularSpacing(-npix * spacing[i], 2*npix*spacing[i]/n, n)
quiet = nlsf.conv_gauss_tophat.(pix, nlsf.σs[middle, order], nlsf.bhws[middle, order])
quiet ./= maximum(quiet)
# how many λs.Δt does it take to contain ~2σ?
tot = 0
# target = sum(quiet)*0.841
# target = sum(quiet)*0.977
# target = sum(quiet)* 0.9938
target = sum(quiet)* (1-3.167e-5)
j = 0
while tot < target
j += 1
tot += quiet[j]
end
sep_test = 0:(j-500+1)
sim_step = λs.Δt
fits_lsfs(sim_step, sep_test, quiet, "neid", lsf_λs, i, order)
end
maximum(lsf_λs)
lsf_λs_smooth = Array{Float64}(undef, length(lsf_orders))
f1 = SSOF.ordinary_lst_sq_f(lsf_λs[1:35], 2)
lsf_λs_smooth[1:35] .= f1.(1.:35)
f2 = SSOF.ordinary_lst_sq_f(lsf_λs[35:59], 2;x=35.:59)
lsf_λs_smooth[36:59] .= f2.(36.:59)
println(lsf_λs_smooth)
plot(lsf_λs)
plot!(lsf_λs_smooth)
## Visual inspection
@load "order_pixel_spacing.jld2" spacing lsf_orders
middle = Int(round(size(nlsf.σs,1)/2))
pix = RegularSpacing(-1. * npix, 2npix/n, n)
i = 1
order = lsf_orders[30] # has orders 54:112, (expres's 41-99), 54-89 is the intersection (index 1 and 36)
λs = RegularSpacing(-npix * spacing[i], 2*npix*spacing[i]/n, n)
quiet = nlsf.conv_gauss_tophat.(pix, nlsf.σs[middle, order], nlsf.bhws[middle, order])
quiet ./= maximum(quiet)
function plt(var_kernel, λ; plot_sample=true)
pt = plot(λs, quiet, label="data")
f = build_gp((var_kernel = var_kernel, λ = λ))
fx = f(λs, 1e-6)
if plot_sample
for i in 1:3
plot!(pt, λs, rand(fx), label="sample")
end
end
f_post2 = posterior(fx, quiet)
y_post2 = marginals(f_post2(λs))
ym2 = mean.(y_post2)
ys2 = std.(y_post2)
plot!(pt, λs, ym2, alpha=0.8, ribbon=(-ys2,ys2), label="posterior")
return pt
end
plt(0.2, 180000.; plot_sample=true)
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 4214 | # Finding reasonable SOAP_gp param values from fitting to a quiet solar spectrum
# downloaded from https://zenodo.org/record/3753254
using HDF5
using AbstractGPs
using KernelFunctions
using TemporalGPs
using Optim # Standard optimisation algorithms.
using ParameterHandling # Helper functionality for dealing with model parameters.
using Zygote # Algorithmic Differentiation
# Ingesting data
# hdf5_loc = "C:/Users/chris/Downloads/res-1000-1years_full_id1.h5"
hdf5_loc = "D:/Christian/Downloads/res-1000-1years_full_id1.h5"
fid = h5open(hdf5_loc, "r")
quiet = fid["quiet"][:]
inds = quiet .!= 0
λs = fid["lambdas"][:]#u"nm"/10
λs = log.(λs[inds])
quiet = quiet[inds]
quiet ./= maximum(quiet)
# std(y)
# using Plots
# plot(λs, quiet)
# Setting up kernel
flat_initial_params, unflatten = value_flatten((
var_kernel = positive(0.1),
λ = positive(4e4),
))
function build_gp(params)
f_naive = GP(params.var_kernel * Matern52Kernel() ∘ ScaleTransform(params.λ))
return to_sde(f_naive, SArrayStorage(Float64))
end
params = unflatten(flat_initial_params)
# Data
x = λs
# y = quiet .- 1
y = quiet .- mean(quiet)
# Changing this changes the results significantly
# ↑var_noise → ↑λ ↓var_kernel
# var_noise = 1e-6 seems to lead to most sensible results i.e. draws from the
# prior of the optimal result look similar to the input spectra
var_noise = 1e-6
function objective(params)
f = build_gp(params)
return -logpdf(f(x, var_noise), y)
end
# Check that the objective function works:
objective(params)
f = objective ∘ unflatten
function g!(G, θ)
G .= only(Zygote.gradient(f, θ))
end
f(flat_initial_params)
G = zeros(length(flat_initial_params))
g!(G, flat_initial_params)
training_results = optimize(f, g!, flat_initial_params,
BFGS(alphaguess = Optim.LineSearches.InitialStatic(scaled=true),linesearch = Optim.LineSearches.BackTracking()),
Optim.Options(show_trace=true))
final_params = unflatten(training_results.minimizer)
println(final_params)
# final_params = (var_kernel = 0.19222435463373258, λ = 26801.464367577082) after taking out mean
# final_params = (var_kernel = 0.2188511770097717, λ = 26063.07237159581)
# f = build_gp(final_params)
# fx = f(x, var_noise)
# f_post = posterior(fx, y)
# # Compute the posterior marginals.
# y_post = marginals(f_post(x))
#
#
# using Plots
# # pli = 101000:102000
# pli = 423471-500:423471+500
# ym = mean.(y_post[pli])
# ys = std.(y_post[pli])
#
# function plt(var_kernel, λ; plot_sample=true)
# pt = plot(x[pli], y[pli], label="data")
# plot!(pt, x[pli], ym, alpha=0.8, ribbon=(-ys,ys), label="fit posterior")
#
# params = (var_kernel = var_kernel,
# λ = λ,)
# f = build_gp(params)
# fx = f(x, var_noise)
# if plot_sample; plot!(pt, x[pli], rand(fx)[pli], label="sample from input") end
# f_post2 = posterior(fx, y)
# y_post2 = marginals(f_post2(x))
# ym2 = mean.(y_post2[pli])
# ys2 = std.(y_post2[pli])
# plot!(pt, x[pli], ym2, alpha=0.8, ribbon=(-ys2,ys2), label="input posterior")
# println(-logpdf(fx, y))
# pt
# end
# plt(final_params.var_kernel/3, final_params.λ)
# n=30
# wavs = LinRange(log(1e3), log(2e5), n)
# vars = LinRange(log(1e-3), log(1e3), n)
# holder = zeros(n, n)
# function ℓ(vars, wavs; y=y)
# params = (var_kernel = exp(vars),
# λ = exp(wavs),)
# f = build_gp(params)
# fx = f(x, 1e-6)
# return -logpdf(fx, y)
# end
# for i in 1:n
# for j in 1:n
# holder[i,j] = ℓ(vars[j], wavs[i])
# end
# end
# ch = copy(holder)
# ch[ch .> 0] .= 0
# # heatmap(ch; xlabel="vars", ylabel="wavs")
# pt = heatmap(exp.(vars), exp.(wavs), ch; xlabel="vars", ylabel="wavs", xscale=:log10, yscale=:log10)
# png(pt, "gp params heatmap")
# ## Comparing LSF line width to SOAP
#
# wavenumber_to_Å(wn) = 1e8 ./ wn
# _fwhm_2_σ_factor = 1 / (2 * sqrt(2 * log(2)))
# fwhm_2_σ(fwhm::Real) = _fwhm_2_σ_factor * fwhm
#
# wns = wavenumber_to_Å.(exp.(λs[pli]))
# # Ingesting data
# expres_LSF_FWHM_wn = 0.14 # 1/cm
# expres_LSF_σ_Å = fwhm_2_σ.(wns[Int(round(n/2))] .* (expres_LSF_FWHM_wn / central_wn))
# quiet2 = 1 .- exp.(-((wns .- wns[Int(round(n/2))]) ./ expres_LSF_σ_Å) .^ 2)
#
# plt(final_params.var_kernel/3, final_params.λ)
# plot!(λs[pli], quiet2 .- 1)
#
# searchsortedfirst(wavenumber_to_Å.(exp.(λs)), 17000; rev=true)
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 16567 | # Heavily inspired (if not blatantly ripped of from) the functions at
# https://github.com/megbedell/wobble/blob/master/wobble/data.py
using LinearAlgebra
using Statistics
import StatsBase: winsor
_high_quantile_default = 0.9
"""
fit_continuum(x, y, σ²; ignore_weights=false, order=6, nsigma=[0.5,3.0], maxniter=50, edge_mask::Int=0)
Fit the continuum of `y` with a polynomial of order `order` using assymetric sigma-clipping, similar to `wobble`
"""
function fit_continuum(x::AbstractVector, y::AbstractVector, σ²::AbstractVector; ignore_weights::Bool=false, order::Int=6, nsigma::Vector{<:Real}=[0.5,3.0], maxniter::Int=50, edge_mask::Int=0)
@assert 0 <= order < length(x)
@assert length(x) == length(y) == length(σ²)
@assert length(nsigma) == 2
A = _vander(x .- mean(x), order) # the constant design matrix
m = fill(true, length(x)) # the sigma-clipped mask
m[y .< 0.5] .= false # mask out the low pixels
m[σ² .== Inf] .= false # mask out the bad pixels
# masking out edge if desired
if edge_mask > 0
# m[edge_pad+1:edge_mask+edge_pad] .= false
# m[end-edge_mask-edge_pad+1:end-edge_pad] .= false
hold_left = y[1:edge_mask]
hold_right = y[end-edge_mask+1:end]
y[1:edge_mask] .= 1
y[end-edge_mask+1:end] .= 1
end
# preallocating arrays
μ = ones(length(x))
w = Array{Float64}(undef, order+1)
# keep fitting polynomial and sigma clipping until the sigma-clipped mask stops changing
for i in 1:maxniter
if ignore_weights
w[:] = general_lst_sq(view(A, m, :), view(y, m))
else
w[:] = general_lst_sq(view(A, m, :), view(y, m), view(σ², m))
end
μ[:] = A * w
resid = y - μ
# sigma = median(abs.(resid))
sigma = std(resid)
m_new = (-nsigma[1]*sigma) .< resid .< (nsigma[2]*sigma)
m_new[y .< 0.5] .= false
m_new[σ² .== Inf] .= false # mask out the bad pixels
if sum(m) == sum(m_new); break end
m = m_new
end
# restoring edge
if edge_mask > 0
y[1:edge_mask] .= hold_left
y[end-edge_mask+1:end] .= hold_right
end
return μ, w
end
"""
continuum_normalize!(d; order=6, kwargs...)
Divide `d.flux` (and `d.var`) by its sigma-clipped polynomial continuum (or its square)
"""
function continuum_normalize!(d::Data; order::Int=6, kwargs...)
continuum = ones(size(d.log_λ_obs, 1))
w = Array{Float64}(undef, order + 1, size(d.flux, 2))
# fit the continuum at each time
for i in axes(d.log_λ_obs, 2)
continuum[:], w[:, i] = fit_continuum(view(d.log_λ_obs, :, i), view(d.flux, :, i), view(d.var, :, i); order=order, kwargs...)
d.flux[:, i] ./= continuum
d.var[:, i] ./= continuum .* continuum
d.var_s[:, i] ./= continuum .* continuum
end
return w
end
_min_flux_default = 0.
_max_flux_default = 2.
or(a::Bool, b::Bool) = a || b
"""
mask_infinite_pixels!(y, σ², log_λ_star, log_λ_star_bounds; padding=0, include_bary_shifts=false, verbose=true, kwargs...)
Mask out pixels whose `y` or `σ²` values are infinite
"""
function mask_infinite_pixels!(y::AbstractMatrix, σ²::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_star::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_star_bounds::AbstractMatrix; padding::Int=0, include_bary_shifts::Bool=false, verbose::Bool=true, kwargs...)
i = findall(vec(all(or.(.!isfinite.(y), .!isfinite.(σ²)); dims=2)))
if length(i) > 0
if verbose; println("Instrumental pipeline already masked out pixels $i at all times") end
if include_bary_shifts
return mask_stellar_pixel!(σ², log_λ_star, log_λ_star_bounds, i; padding=padding, verbose=false)
else
return mask!(σ², i; padding=padding)
end
end
return Int[]
end
function mask_infinite_pixels!(d::Data; kwargs...)
mask_infinite_pixels!(d.flux, d.var_s, d.log_λ_star, d.log_λ_star_bounds; include_bary_shifts=true, kwargs...)
return mask_infinite_pixels!(d.flux, d.var, d.log_λ_star, d.log_λ_star_bounds; include_bary_shifts=false, verbose=false, kwargs...)
end
"""
mask_low_pixels!(bad, y, σ²; padding=0, min_flux=0., padding=2, using_weights=false)
Mask out pixels whose `y` values are below `min_flux`
"""
function mask_low_pixels!(bad::AbstractVector, y::AbstractVector, σ²::AbstractVector; min_flux::Real=_min_flux_default, padding::Int=2, using_weights::Bool=false)
bad[:] = y .< min_flux
# y[bad] .= min_flux
l = length(bad)
for i in findall(bad)
bad[max(1, i - padding):min(i + padding, l)] .= true
end
return mask!(σ², bad; using_weights=using_weights)
end
function mask_low_pixels!(y::AbstractVector, σ²::AbstractVector; kwargs...)
bad = Array{Bool}(undef, length(y))
mask_low_pixels!(bad, y, σ²; kwargs...)
end
function mask_low_pixels!(y::AbstractMatrix, σ²::AbstractMatrix; kwargs...)
affected = Int64[]
bad = Array{Bool}(undef, size(y, 1))
for i in axes(y, 2)
affected2 = mask_low_pixels!(view(y, :, i), view(σ², :, i); kwargs...)
affected_pixels!(affected, affected2)
end
return affected
end
function mask_low_pixels!(d::Data; kwargs...)
mask_low_pixels!(d.flux, d.var_s; kwargs...)
return mask_low_pixels!(d.flux, d.var; kwargs...)
end
"""
mask_high_pixels!(bad, y, σ²; padding=0, max_flux=2., padding=2, using_weights=false)
Mask out pixels whose `y` values are above `max_flux`
"""
function mask_high_pixels!(bad::AbstractVector, y::AbstractVector, σ²::AbstractVector; max_flux::Real=_max_flux_default, padding::Int=2, kwargs...)
bad[:] = y .> max_flux
# y[bad] .= max_flux
l = length(bad)
for i in findall(bad)
bad[max(1, i - padding):min(i + padding, l)] .= true
end
return mask!(σ², bad; kwargs...)
end
function mask_high_pixels!(y::AbstractVector, σ²::AbstractVector; kwargs...)
bad = Array{Bool}(undef, length(y))
mask_high_pixels!(bad, y, σ²; kwargs...)
end
function mask_high_pixels!(y::AbstractMatrix, σ²::AbstractMatrix; kwargs...)
affected = Int64[]
bad = Array{Bool}(undef, size(y, 1))
for i in axes(y, 2)
affected2 = mask_high_pixels!(bad, view(y, :, i), view(σ², :, i); kwargs...)
affected_pixels!(affected, affected2)
end
return affected
end
function mask_high_pixels!(d::Data; kwargs...)
mask_high_pixels!(d.flux, d.var_s; kwargs...)
return mask_high_pixels!(d.flux, d.var; kwargs...)
end
"""
mask_bad_edges!(y, σ², log_λ_star, log_λ_star_bounds; window_width=128, min_snr=8., verbose=true, always_mask_something=false, edges=nothing, kwargs...)
Mask out edges of `y` (either given by `edges` or where `y`/`σ` is on average below `min_snr`)
"""
function mask_bad_edges!(y::AbstractMatrix, σ²::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_star::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_star_bounds::AbstractMatrix; window_width::Int=128, min_snr::Real=8., verbose::Bool=true, always_mask_something::Bool=false, edges=nothing, kwargs...)
# if `edges` isn't given, find how much to mask based on SNR in a sliding window
if isnothing(edges)
n_pix = size(y, 1)
window_start_tot = 0
window_end_tot = n_pix + 1
for i in axes(y, 2)
for window_start in 1:Int(floor(window_width/10)):(n_pix - window_width)
window_end = window_start + window_width
mean_snr = sqrt(mean((y[window_start:window_end, i] .^2) ./ abs.(σ²[window_start:window_end, i])))
if mean_snr > min_snr
window_start_tot = max(window_start_tot, window_start)
break
end
end
end
for i in axes(y,2)
for window_end in n_pix:-Int(floor(window_width/10)):(window_width + 1)
window_start = window_end - window_width
mean_snr = sqrt(mean((y[window_start:window_end] .^2) ./ abs.(σ²[window_start:window_end])))
if mean_snr > min_snr
window_end_tot = min(window_end_tot, window_end)
break
end
end
end
else
window_start_tot, window_end_tot = edges
end
# do the masking
if always_mask_something || window_start_tot > 1
# σ²[1:window_start_tot, :] .= Inf # trim everything to left of window
if verbose; println("masking out low SNR edge from 1:$window_start_tot") end
log_λ_low = maximum(view(log_λ_star_bounds, max(1, window_start_tot), :))
else
log_λ_low = -Inf
end
if always_mask_something || window_end_tot < n_pix
# σ²[window_end_tot:end, :] .= Inf # trim everything to right of window
log_λ_high = minimum(view(log_λ_star_bounds, min(window_end_tot, size(log_λ_star_bounds, 1)), :))
if verbose; println("masking out low SNR edge from $window_end_tot:end") end
else
log_λ_high = Inf
end
if always_mask_something || window_start_tot > 1 || window_end_tot < n_pix
return mask_stellar_feature!(σ², log_λ_star, log_λ_low, log_λ_high; inverse=true, verbose=false, kwargs...), [window_start_tot, window_end_tot]
else
return Int[], [window_start_tot, window_end_tot]
end
end
function mask_bad_edges!(d::Data; kwargs...)
affected, edges = mask_bad_edges!(d.flux, d.var, d.log_λ_star, d.log_λ_star_bounds; kwargs...)
mask_bad_edges!(d.flux, d.var_s, d.log_λ_star, d.log_λ_star_bounds; always_mask_something=true, verbose=false, edges=edges, kwargs...)
return affected
end
"""
flat_normalize!(d; kwargs...)
Divide `d.flux` (and `d.var`) by its `0.9` quantile value (or its square)
"""
function flat_normalize!(d::Data; kwargs...)
for i in axes(d.log_λ_obs, 2)
continuum = quantile(view(d.flux, .!(isnan.(view(d.flux, :, i))), i), _high_quantile_default)
d.flux[:, i] ./= continuum
d.var[:, i] ./= continuum * continuum
d.var_s[:, i] ./= continuum * continuum
end
end
and(a::Bool, b::Bool) = a && b
"""
outlier_mask(v; thres=10, prop=0.2, return_stats=false, only_low::Bool=false)
Mask outliers in `v` that are outside `thres`-σ after winsorizing out the top and bottom `prop` quantiles
"""
function outlier_mask(v::AbstractVecOrMat; thres::Real=10, prop::Real=0.2, return_stats::Bool=false, only_low::Bool=false)
wv = winsor(v; prop=prop)
μ = mean(wv)
σ = stdm(wv, μ)
if only_low
mask = v .> (μ - thres * σ)
if return_stats
return mask, (v .- μ) ./ σ
end
else
mask = and.(v .< (μ + thres * σ), v .> (μ - thres * σ))
end
if return_stats
return mask, abs.((v .- μ) ./ σ)
end
return mask
end
# function recognize_bad_normalization!(d::Data; kwargs...)
# mask = outlier_mask([mean(view(d.var, isfinite.(view(d.var, :, i)), i)) for i in axes(d.var, 2)]; kwargs...) .|| outlier_mask(vec(std(d.flux; dims=1)); kwargs...)
# for i in axes(d.log_λ_obs, 2)
# if !mask[i]
# # d.var[:, i] .= Inf
# println("spectrum $i has a weird continuum normalization, consider removing it from your analysis")
# end
# end
# end
# function recognize_bad_drift!(d::Data; kwargs...)
# mask = outlier_mask(d.log_λ_obs[1, :]; kwargs...)
# for i in axes(d.log_λ_obs, 2)
# if !mask[i]
# # d.var[:, i] .= Inf
# println("spectrum $i has a weird drift, consider removing it from your analysis")
# end
# end
# end
"""
snap(y)
Estimate δ⁴`y`/δ⁴x (a.k.a. the snap) with finite differences. See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Finite_difference#Higher-order_differences
"""
function snap(y::AbstractMatrix)
snp = Array{Float64}(undef, size(y, 1), size(y, 2))
l = size(snp, 1)
snp[1:2, :] .= 0
snp[end-1:end, :] .= 0
snp[3:end-2, :] .= abs.(view(y, 5:l, :) - 4view(y, 4:(l-1), :) + 6view(y, 3:(l-2), :) - 4view(y, 2:(l-3), :) + view(y, 1:(l-4), :))
return snp
end
function snap(y::AbstractMatrix, σ²::AbstractMatrix)
@assert size(y) == size(σ²)
snp = Array{Float64}(undef, size(y, 1), size(y, 2))
m = isfinite.(σ²)
l = size(m, 1)
# snp[1, :] = abs.(view(y, 3, :) - 4view(y, 2, :) + 6view(y, 1, :))
# snp[2, :] = abs.(view(y, 4, :) - 4view(y, 3, :) + 6view(y, 2, :) - 4view(y, 1, :))
# snp[end-1, :] = abs.(-4view(y, l, :) + 6view(y, l-1, :) - 4view(y, l-2, :) + view(y, l-3, :))
# snp[end, :] = abs.(6view(y, l, :) - 4view(y, l-1, :) + view(y, l-2, :))
snp[1:2, :] .= 0
snp[end-1:end, :] .= 0
snp[3:end-2, :] .= abs.(view(y, 5:l, :) - 4view(y, 4:(l-1), :) + 6view(y, 3:(l-2), :) - 4view(y, 2:(l-3), :) + view(y, 1:(l-4), :)) .* view(m, 5:l, :) .* view(m, 4:(l-1), :) .* view(m, 2:(l-3), :) .* view(m, 1:(l-4), :)
# snp[.!m] .= 0
snp[all(.!m; dims=2), :] .= 0
return snp
end
function _snap!(snp::AbstractVector, y::AbstractVector; def_val::Real=1.)
l = length(snp)
@assert length(y) == l
snp[1] = abs.(y[3] - 4y[2] + 6y[1] - 4def_val + def_val)
snp[2] = abs.(y[4] - 4y[3] + 6y[2] - 4y[1] + def_val)
snp[end-1] = abs.(def_val - 4y[l] + 6y[l-1] - 4y[l-2] + y[l-3])
snp[end] = abs.(def_val - 4def_val + 6y[l] - 4y[l-1] + y[l-2])
snp[3:end-2] .= abs.(view(y, 5:l) - 4view(y, 4:(l-1)) + 6view(y, 3:(l-2)) - 4view(y, 2:(l-3)) + view(y, 1:(l-4)))
return snp
end
function _snap(y::AbstractVector; kwargs...)
snp = Array{Float64}(undef, length(y))
_snap!(snp, y; kwargs...)
return snp
end
"""
bad_pixel_flagger(y, σ²; prop=.005, thres=8)
Find anomalous pixels where δ⁴`y`/δ⁴x is high, passing `prop` and `thres` to `outlier_mask()`
"""
function bad_pixel_flagger(y::AbstractMatrix, σ²::AbstractMatrix; prop::Real=.005, thres::Real=8)
snp = snap(y, σ²)
snp = vec(mean(snp; dims=2))
high_snap_pixels = find_modes(snp)
return high_snap_pixels[.!outlier_mask(snp[high_snap_pixels]; prop=prop, thres=thres)]
end
"""
mask_bad_pixel!(y, σ², log_λ_star, log_λ_star_bounds; padding=2, include_bary_shifts=false, verbose=true, bad_pixels=nothing, kwargs...)
Mask anomalous pixels where δ⁴`y`/δ⁴x is high
"""
function mask_bad_pixel!(y::AbstractMatrix, σ²::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_star::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_star_bounds::AbstractMatrix; padding::Int=2, include_bary_shifts::Bool=false, verbose::Bool=true, bad_pixels=nothing, kwargs...)
if isnothing(bad_pixels); bad_pixels = bad_pixel_flagger(y, σ²; kwargs...) end
if length(bad_pixels) > 0
if length(bad_pixels) > 15
if verbose; println("lots of snappy pixels, investigate?") end
else
if verbose; println("masked out high snap pixels $bad_pixels at all times") end
end
if include_bary_shifts
return mask_stellar_pixel!(σ², log_λ_star, log_λ_star_bounds, bad_pixels; padding=padding, verbose=false), bad_pixels
else
return mask!(σ², bad_pixels; padding=padding), bad_pixels
end
end
return Int[], bad_pixels
end
function mask_bad_pixel!(d::Data; kwargs...)
affected, bad_pixels = mask_bad_pixel!(d.flux, d.var, d.log_λ_star, d.log_λ_star_bounds; include_bary_shifts=false, verbose=false, kwargs...)
mask_bad_pixel!(d.flux, d.var_s, d.log_λ_star, d.log_λ_star_bounds; include_bary_shifts=true, bad_pixels=bad_pixels, kwargs...)
return affected
end
"""
mask_isolated_pixels!(σ²; neighbors_required::Int=29, verbose::Bool=true)
Mask between two flagged pixels if there are fewer than `neighbors_required` pixels between them
"""
function mask_isolated_pixels!(σ²::AbstractMatrix; neighbors_required::Int=29, verbose::Bool=true)
affected = Int[]
lo = 1
hi = 1
m = vec(all(isinf.(σ²); dims=2))
l = length(m)
while lo <= l
# if pixel is already flagged, keep going
if m[lo]
lo += 1
# if pixel is not flagged, go until the next flagged pixel is found
# and make sure the distance to it is <`neighbors_required`
else
hi = lo + 1
while hi <= l && !m[hi]
hi += 1
end
hi -= 1
if hi-lo < neighbors_required
σ²[lo:hi, :] .= Inf
if verbose; println("masked isolated pixels $lo:$hi") end
affected_pixels!(affected, lo:hi)
end
lo = hi + 1
end
end
return affected
end
function mask_isolated_pixels!(d::Data; kwargs...)
mask_isolated_pixels!(d.var_s; kwargs...)
return mask_isolated_pixels!(d.var; verbose=false, kwargs...)
end
"""
process!(d; λ_thres=4000., min_snr=8, kwargs...)
Doing all of the data preprocessing, including continuum-fitting and masking of infinite points, anomalously snappy or high pixels, and low SNR edges.
"""
function process!(d; λ_thres::Real=4000., min_snr::Real=8, kwargs...)
flat_normalize!(d)
## masking
# mask_low_pixels_all_times!(d; padding=2)
bad_inst = mask_infinite_pixels!(d; padding=1)
bad_snap = mask_bad_pixel!(d; padding=1) # thres from 4-11 seems good
bad_edge = mask_bad_edges!(d; min_snr=min_snr)
bad_high = mask_high_pixels!(d; padding=1)
bad_isol = mask_isolated_pixels!(d)
## why was each pixel masked
filter_bads(bad) = [i for i in bad if !(i in bad_edge)]
bad_inst = filter_bads(bad_inst)
bad_high = filter_bads(bad_high)
bad_snap = filter_bads(bad_snap)
bad_isol = filter_bads(bad_isol)
## continuum normalizing
# λ_thres = 4000 # is there likely to even be a continuum (neid index order 23+)
# λ_thres = 6200 # where neid blaze correction starts to break down (neid index order 77+)
red_enough = minimum(d.log_λ_obs) > log(λ_thres)
# enough_points = (sum(isinf.(d.var)) / length(d.var)) < 0.5
enough_points = true
if (red_enough && enough_points)
println("normalizing")
w = continuum_normalize!(d; kwargs...)
else
w = nothing
end
return bad_inst, bad_high, bad_snap, bad_edge, bad_isol
end
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 9249 | using Statistics # mean function
using Base.Threads
"""
estimate_σ_curvature_helper(x, ℓ; n=7, use_gradient=false, multithread=nthreads() > 3, print_every=10, kwargs...)
Estimate the uncertainties for the best-fit parameters `x` for ~Gaussian function `ℓ` based on the local curvature
"""
function estimate_σ_curvature_helper(x::AbstractVecOrMat, ℓ::Function; n::Int=7, use_gradient::Bool=false, multithread::Bool=nthreads() > 3, print_every::Int=10, kwargs...)
# intialize arrays
σs = Array{Float64}(undef, length(x))
if !multithread
x_test = Array{Float64}(undef, n)
ℓs = Array{Float64}(undef, n)
end
# use nabla to get autodiff gradient function, if desired (slightly more precise but much slower)
if use_gradient; g = ∇(ℓ) end
# use this to scale size of curvature probe
_std = std(x)
# collect a sample of `ℓ` evaluations around each `x` value and calculate uncertanties
if multithread
nchains = nthreads()
schedule = collect(Iterators.partition(eachindex(x), Int(ceil(length(x)/nchains))))
Threads.@threads for i in 1:nchains
# ThreadsX.foreach(1:nchains) do i
local _todo = copy(schedule[i])
local _σs = Array{Float64}(undef, length(_todo))
local _x = copy(x)
local _x_test = Array{Float64}(undef, n)
local _ℓs = Array{Float64}(undef, n)
for ii in eachindex(_todo)
k = _todo[ii]
_x_test .= _x[k] .+ LinRange(-_std, _std, n)
for j in 1:n
_x[k] = _x_test[j]
if use_gradient
_ℓs[j] = only(g(_x))[k]
else
_ℓs[j] = ℓ(_x)
end
end
estimate_σ_curvature_helper_finalizer!(_σs, _ℓs, _x_test, ii; use_gradient=use_gradient, print_every=100000, kwargs...)
end
σs[_todo] .= _σs
end
else
for i in eachindex(x)
hold = x[i]
# x_test[:] = x[i] .+ LinRange(-_std/1e3, _std/1e3, n)
x_test[:] = x[i] .+ LinRange(-_std, _std, n)
for j in 1:n
x[i] = x_test[j]
if use_gradient
ℓs[j] = only(g(x))[i]
else
ℓs[j] = ℓ(x)
end
end
x[i] = hold
# println("$i: ", ℓs .- ℓs[Int(round(n//2))])
estimate_σ_curvature_helper_finalizer!(σs, ℓs, x_test, i; use_gradient=use_gradient, print_every=print_every, kwargs...)
end
end
return reshape(σs, size(x))
end
"""
estimate_σ_curvature_helper_finalizer!(σs, _ℓs, x_test, i; use_gradient=false, param_str="", print_every=10, verbose=false, show_plots=false)
Calculate uncertanties (filling `σs`) based on the `_ℓs` calculated at `x_test`
"""
function estimate_σ_curvature_helper_finalizer!(σs::AbstractVecOrMat, _ℓs::AbstractVector, x_test::AbstractVector, i::Int; use_gradient::Bool=false, param_str::String="", print_every::Int=10, verbose::Bool=false, show_plots::Bool=false)
# fit a parabola (or line if using gradient) to `_ℓs` and convert to uncertainties
if use_gradient
poly_f = ordinary_lst_sq_f(_ℓs, 1; x=x_test)
σs[i] = sqrt(1 / poly_f.w[2])
max_dif = maximum(abs.((poly_f.(x_test)./_ℓs) .- 1))
if verbose; println("∇_$i: $(poly_f.w[1] + poly_f.w[2] * x[i])") end
else
poly_f = ordinary_lst_sq_f(_ℓs, 2; x=x_test)
σs[i] = sqrt(1 / (2 * poly_f.w[3]))
max_dif = maximum(abs.((poly_f.(x_test)./_ℓs) .- 1))
if verbose; println("∇_$i: $(poly_f.w[2] + 2 * poly_f.w[3] * x[i])") end
end
if show_plots
plt = scatter(x_test, _ℓs; label="ℓ")
plot!(x_test, poly_f.(x_test); label="polynomial fit")
display(plt)
end
if max_dif > 1e-2; @warn param_str * "_σ[$i] misfit at $(round(100*max_dif; digits=2))% level" end
if i%print_every==0; println("done with $i/$(length(σs)) " * param_str * "_σ estimates") end
end
"""
estimate_σ_curvature(mws; kwargs...)
Estimate the uncertainties for the RVs and scores in `mws` based on the local curvature of the loss function.
Faster than `estimate_σ_bootstrap()`, but less reliable from ignoring cross terms in the Hessian.
"""
function estimate_σ_curvature(mws::ModelWorkspace; kwargs...)
model = mws.om
time_var_tel = is_time_variable(model.tel)
time_var_star = is_time_variable(model.star)
# calculate the RV uncertainties
typeof(model) <: OrderModelDPCA ? rvs = copy(model.rv.lm.s) : rvs = copy(model.rv)
ℓ_rv(x) = _loss(mws.o, model, mws.d; rv=x) / 2 # factor of 2 makes curvature estimates correct (χ² -> data fit part of multivariate Gaussian)
rvs_σ = estimate_σ_curvature_helper(rvs, ℓ_rv; param_str="rv", kwargs...)
if typeof(model) <: OrderModelDPCA
rvs = vec(rvs)
rvs .*= -light_speed_nu
rvs_σ .*= light_speed_nu
end
# calculate the model.tel.lm.s uncertainties
if time_var_tel
ℓ_tel(x) = (_loss(mws.o, model, mws.d; tel=vec(model.tel.lm)) + model_s_prior(model.tel.lm.s, model.reg_tel)) / 2 # factor of 2 makes curvature estimates correct (χ² -> data fit part of multivariate Gaussian)
tel_s_σ = estimate_σ_curvature_helper(model.tel.lm.s, ℓ_tel; param_str="tel_s", kwargs...)
else
tel_s_σ = nothing
end
# calculate the model.star.lm.s uncertainties
if time_var_star
ℓ_star(x) = (_loss(mws.o, model, mws.d; star=vec(model.star.lm)) + model_s_prior(model.star.lm.s, model.reg_star)) / 2 # factor of 2 makes curvature estimates correct (χ² -> data fit part of multivariate Gaussian)
star_s_σ = estimate_σ_curvature_helper(model.star.lm.s, ℓ_star; param_str="star_s", kwargs...)
else
star_s_σ = nothing
end
model.metadata[:todo][:err_estimated] = true
return rvs, rvs_σ, tel_s_σ, star_s_σ
end
"""
estimate_σ_bootstrap_reducer(shaper, holder, reducer)
Apply `reducer` on the first axis of `holder` and store the results in an array the shape of `shaper`
"""
function estimate_σ_bootstrap_reducer(shaper::AbstractArray, holder::AbstractArray, reducer::Function)
result = Array{Float64}(undef, size(shaper, 1), size(shaper, 2))
for i in axes(shaper, 1)
result[i, :] .= vec(reducer(view(holder, :, i, :); dims=1))
end
return result
end
"""
estimate_σ_bootstrap_helper!(rv_holder, tel_holder, star_holder, i, mws, data_noise, n; verbose=true)
Refit the RVs and scores after re-injecting photon noise and store the results in `rv_holder`, `tel_holder`, and `star_holder`
"""
function estimate_σ_bootstrap_helper!(rv_holder::AbstractMatrix, tel_holder, star_holder, i::Int, mws::ModelWorkspace, data_noise::AbstractMatrix, n::Int; verbose::Bool=true)
time_var_tel = is_time_variable(mws.om.tel)
time_var_star = is_time_variable(mws.om.star)
_mws = typeof(mws)(copy(mws.om), copy(mws.d))
_mws.d.flux .= mws.d.flux .+ (data_noise .* randn(size(mws.d.var)))
improve_model!(_mws; iter=50, verbose=false)
rv_holder[i, :] = rvs(_mws.om)
if time_var_tel
tel_holder[i, :, :] .= _mws.om.tel.lm.s
end
if time_var_star
star_holder[i, :, :] .= _mws.om.star.lm.s
end
if (verbose && i%10==0); println("done with $i/$n bootstraps") end
end
"""
estimate_σ_bootstrap(mws; n=50, return_holders=false, recalc_mean=false, multithread=nthreads() > 3, verbose=true)
Estimate the uncertainties (and potentially covariances) for the RVs and scores in `mws` based on looking at the distribution of best-fit parameters after re-injecting photon noise.
Slower than `estimate_σ_curvature()`, but more reliable.
"""
function estimate_σ_bootstrap(mws::ModelWorkspace; n::Int=50, return_holders::Bool=false, recalc_mean::Bool=false, multithread::Bool=nthreads() > 3, verbose::Bool=true)
# get data noise levels
mws.d.var[mws.d.var.==Inf] .= 0
data_noise = sqrt.(mws.d.var)
mws.d.var[mws.d.var.==0] .= Inf
# intialized holders
typeof(mws.om) <: OrderModelWobble ?
rv_holder = Array{Float64}(undef, n, length(mws.om.rv)) :
rv_holder = Array{Float64}(undef, n, length(mws.om.rv.lm.s))
time_var_tel = is_time_variable(mws.om.tel)
time_var_star = is_time_variable(mws.om.star)
time_var_tel ?
tel_holder = Array{Float64}(undef, n, size(mws.om.tel.lm.s, 1), size(mws.om.tel.lm.s, 2)) :
tel_holder = nothing
time_var_star ?
star_holder = Array{Float64}(undef, n, size(mws.om.star.lm.s, 1), size(mws.om.star.lm.s, 2)) :
star_holder = nothing
# refit the RVs and scores after re-injecting photon noise
if multithread
@threads for i in 1:n
# # using Polyester # same performance
# @batch per=core for i in 1:n
# using ThreadsX # tiny bit better performance
# ThreadsX.foreach(1:n) do i
estimate_σ_bootstrap_helper!(rv_holder, tel_holder, star_holder, i, mws, data_noise, n; verbose=false)
end
else
for i in 1:n
estimate_σ_bootstrap_helper!(rv_holder, tel_holder, star_holder, i, mws, data_noise, n; verbose=verbose)
end
end
recalc_mean ? _rvs = vec(mean(rv_holder; dims=1)) : _rvs = rvs(mws.om)
rvs_σ = vec(std(rv_holder; dims=1))
if time_var_tel
recalc_mean ?
tel_s = estimate_σ_bootstrap_reducer(mws.om.tel.lm.s, tel_holder, mean) :
tel_s = mws.om.tel.lm.s
tel_s_σ = estimate_σ_bootstrap_reducer(mws.om.tel.lm.s, tel_holder, std)
else
tel_s = nothing
tel_s_σ = nothing
end
if time_var_star
recalc_mean ?
star_s = estimate_σ_bootstrap_reducer(mws.om.star.lm.s, star_holder, mean) :
star_s = mws.om.star.lm.s
star_s_σ = estimate_σ_bootstrap_reducer(mws.om.star.lm.s, star_holder, std)
else
star_s = nothing
star_s_σ = nothing
end
mws.om.metadata[:todo][:err_estimated] = true
if return_holders
return _rvs, rvs_σ, tel_s, tel_s_σ, star_s, star_s_σ, rv_holder, tel_holder, star_holder
else
return _rvs, rvs_σ, tel_s, tel_s_σ, star_s, star_s_σ
end
end
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 1760 | # Expanding ParameterHandling.jl funcs to deal with custom structs and cases
using ParameterHandling
import ParameterHandling.flatten
"""
flatten([eltype=Real], x::LinearModel)
Returns a "flattened" representation of `x::LinearModel` as a vector of vectors and a function
`unflatten` that takes a vector of reals of the same length and returns a LinearModel object
"""
function flatten(::Type{T}, x::LinearModel) where {T<:Real}
x_vec, unflatten = flatten(T, [getfield(x, i) for i in fieldnames(typeof(x))])
function unflatten_to_struct(v::Vector{T})
v_vec_vec = unflatten(v)
return LinearModel(v_vec_vec...)
end
return x_vec, unflatten_to_struct
end
"""
flatten([eltype=Real], x::SubArray)
Returns a "flattened" representation of `x::SubArray` as a vector and a function
`unflatten` that takes a vector of reals of the same length and returns an Array object
"""
function flatten(::Type{T}, x::SubArray) where {T<:Real}
x_vec, from_vec = flatten(T, vec(x))
Array_from_vec(x_vec) = reshape(from_vec(x_vec), size(x))
return x_vec, Array_from_vec
end
flatten(::Type{T}, x::Base.ReshapedArray) where {T<:Real} = custom_vector_flatten(T, x)
flatten(::Type{T}, x::Vector{<:SubArray}) where {T<:Real} = custom_vector_flatten(T, x)
function custom_vector_flatten(::Type{T}, x::AbstractVector) where {T<:Real}
x_vecs_and_backs = map(val -> flatten(T, val), x)
x_vecs, backs = first.(x_vecs_and_backs), last.(x_vecs_and_backs)
function Vector_from_vec(x_vec)
sz = ParameterHandling._cumsum(map(length, x_vecs))
x_Vec = [backs[n](x_vec[(sz[n] - length(x_vecs[n]) + 1):sz[n]]) for n in eachindex(x)]
return x_Vec
end
return reduce(vcat, x_vecs), Vector_from_vec
end
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 13122 | using UnitfulAstro, Unitful
using Statistics
using LinearAlgebra
light_speed = uconvert(u"m/s", 1u"c")
light_speed_nu = ustrip(light_speed)
"""
searchsortednearest(a, x; lower=false)
Find the index of the value closest to `x` in `a` (which is a sorted vector)
"""
function searchsortednearest(a::AbstractVector{T} where T<:Real, x::Real; lower::Bool=false)
idx = searchsortedfirst(a,x)
if (idx==1); return idx; end
if (idx>length(a)); return length(a); end
if (a[idx]==x); return idx; end
if lower || ((abs(a[idx]-x) >= abs(a[idx-1]-x)))
return idx - 1
else
return idx
end
end
function searchsortednearest(a::AbstractVector{T} where T<:Real, x::AbstractVector{T} where T<:Real; kwargs...)
@assert issorted(x)
len_x = length(x)
len_a = length(a)
idxs = Array{Int64}(undef, len_x)
idxs[1] = searchsortednearest(a, x[1]; kwargs...)
for i in 2:len_x
idxs[i] = idxs[i-1] + searchsortednearest(view(a, idxs[i-1]:len_a), x[i]; kwargs...) - 1
end
return idxs
end
"""
clip_vector!(vec; max=Inf, min=-Inf)
Set values in vec above `max` to `max` and below `min` to `min`
"""
function clip_vector!(vec::Vector; max::Number=Inf, min::Number=-Inf)
vec[vec .< min] .= min
vec[vec .> max] .= max
end
"""
make_template(matrix; use_mean=false, kwargs...)
Reduce `matrix` to its median (or mean) and clip the result
"""
function make_template(matrix::Matrix; use_mean::Bool=false, kwargs...)
if use_mean
result = vec(mean(matrix, dims=2))
else
result = vec(median(matrix, dims=2))
end
clip_vector!(result; kwargs...)
return result
end
"""
make_template(matrix, σ²; default=1., use_mean=false, kwargs...)
Reduce `matrix` to its median (or weighted mean) and clip the result
"""
function make_template(matrix::Matrix, σ²::Matrix; default::Real=1., use_mean::Bool=false, kwargs...)
if use_mean
result = vec(weighted_mean(matrix, σ²; default=default, dims=2))
else
result = Array{Float64}(undef, size(matrix, 1))
for i in eachindex(result)
mask = .!(isinf.(view(σ², i, :)))
any(mask) ?
result[i] = median(view(matrix, i, mask)) :
result[i] = default
end
end
clip_vector!(result; kwargs...)
return result
end
"""
observation_night_inds(times_in_days)
Find the indices for each observing night
"""
function observation_night_inds(times_in_days::AbstractVector{<:Real})
difs = (times_in_days[2:end] - times_in_days[1:end-1]) .> 0.5
# obs_in_first_night = findfirst(difs)
if isnothing(findfirst(difs))
return [eachindex(times_in_days)]
else
night_inds = [1:findfirst(difs)]
end
i = night_inds[1][end]
while i < length(times_in_days)
obs_in_night = findfirst(view(difs, i:length(difs)))
if isnothing(obs_in_night)
i = length(times_in_days)
else
i += obs_in_night
append!(night_inds, [night_inds[end][end]+1:i])
end
end
return night_inds
end
observation_night_inds(times::AbstractVector{<:Unitful.Time}) =
observation_night_inds(ustrip.(uconvert.(u"d", times)))
"""
copy_dict!(to, from)
Copy all entries in `from` to `to`
"""
function copy_dict!(to::Dict, from::Dict)
for (key, value) in from
to[key] = from[key]
end
end
"""
parse_args(ind, type, default)
Retrieve ARGS[`ind`] as type `type` if it exists. Otherwise, return `default`
"""
function parse_args(ind::Int, type::DataType, default)
@assert typeof(default) <: type
if length(ARGS) > (ind - 1)
if type <: AbstractString
return ARGS[ind]
else
return parse(type, ARGS[ind])
end
else
return default
end
end
"""
banded_inds(row, span, row_len)
Calculate the bounds of the filled indices for row `row` of a banded matrix of span `span`
"""
function banded_inds(row::Int, span::Int, row_len::Int)
low = max(row - span, 1)
high = min(row + span, row_len)
return low, high
end
"""
_vander(x, n)
Calculate the the Vandermonde matrix.
See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vandermonde_matrix
"""
function _vander(x::AbstractVector, n::Int)
m = ones(length(x), n + 1)
for i in 1:n
m[:, i + 1] .= m[:, i] .* x
end
return m
end
"""
general_lst_sq(dm, data, Σ)
Solve a weighted linear system of equations.
See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Generalized_least_squares#Method_outline
"""
function general_lst_sq(
dm::AbstractMatrix{T},
data::AbstractVector,
Σ::Union{Cholesky,Diagonal}) where {T<:Real}
return (dm' * (Σ \ dm)) \ (dm' * (Σ \ data))
end
general_lst_sq(dm, data, σ²::AbstractVector) =
general_lst_sq(dm, data, Diagonal(σ²))
"""
ordinary_lst_sq(dm, data)
Solve a linear system of equations.
See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ordinary_least_squares#Matrix/vector_formulation
"""
function ordinary_lst_sq(
dm::AbstractMatrix{T},
data::AbstractVector) where {T<:Real}
return (dm' * dm) \ (dm' * data)
end
general_lst_sq(dm, data) = ordinary_lst_sq(dm, data)
"""
multiple_append!(a, b...)
Generalized version of the Julia's append!() function
"""
function multiple_append!(a::Vector{T}, b...) where {T<:Real}
for i in eachindex(b)
append!(a, b[i])
end
return a
end
const _fwhm_2_σ_factor = 1 / (2 * sqrt(2 * log(2)))
"""
fwhm_2_σ(fwhm)
Convert full-width at half-maximum to σ
"""
fwhm_2_σ(fwhm::Real) = _fwhm_2_σ_factor * fwhm
ordinary_lst_sq(
data::AbstractVector,
order::Int;
x::AbstractVector=eachindex(data)) = ordinary_lst_sq(_vander(x, order), data)
general_lst_sq(
data::AbstractVector,
Σ,
order::Int;
x::AbstractVector=eachindex(data)) = general_lst_sq(_vander(x, order), data, Σ)
lst_sq_poly_f(w) = x -> LinearAlgebra.BLAS.dot([x ^ i for i in 0:(length(w)-1)], w)
# fastest of the following
# x -> ([x ^ i for i in 0:order]' * w)
# x -> mapreduce(i -> w[i+1] * x ^ i , +, 0:order)
# x -> sum([x ^ i for i in 0:order] .* w)
"""
ordinary_lst_sq_f(data, order; x=eachindex(data))
Get a polynomial of order `order` fit to `data`
"""
function ordinary_lst_sq_f(data::AbstractVector, order::Int; kwargs...)
w = ordinary_lst_sq(data, order; kwargs...)
return lst_sq_poly_f(w)
end
"""
general_lst_sq_f(data, Σ, order; x=eachindex(data))
Get a polynomial of order `order` fit to `data`
"""
function general_lst_sq_f(data::AbstractVector, Σ, order::Int; kwargs...)
w = general_lst_sq(data, Σ, order; kwargs...)
return lst_sq_poly_f(w)
end
"""
_trapzx2(x1, x2, y1, y2)
Twice the area under the line between (`x1`, `y1`) and (`x2`, `y2`). Used in trapezoidal integration
"""
_trapzx2(x1::Real, x2::Real, y1::Real, y2::Real) = (x2 - x1) * (y1 + y2)
# _trapz_large(x::AbstractVector, y::AbstractVector) =
# mapreduce(i -> (x[i+1] - x[i]) * (y[i] + y[i+1]), +, 1:(length(y) - 1)) / 2
# function trapz_large(x::AbstractVector, y::AbstractVector)
# @assert length(x) == length(y) > 0 "x and y vectors must be of the same (non-zero) length!"
# return _trapz_large(x, y)
# end
# trapz(x::AbstractVector, y::AbstractVector) = trapz_large(x, y)
"""
trapz_small(x, y)
Trapezoidal integration of `y` over `x`.
Shamelessly modified from https://github.com/dextorious/NumericalIntegration.jl/blob/master/src/NumericalIntegration.jl.
See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trapezoidal_rule
"""
function trapz_small(x::AbstractVector, y::AbstractVector)
@assert length(x) == length(y) "x and y vectors must be of the same length!"
integral = 0
@fastmath @simd for i in 1:(length(y) - 1)
# @simd for i in 1:(length(y) - 1)
@inbounds integral += _trapzx2(x[i], x[i+1], y[i], y[i+1])
end
return integral / 2
end
"""
trapz_small(lo_x, hi_x, x, y)
Trapezoidal integration of `y` over `x` from `lo_x` to `hi_x`.
See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trapezoidal_rule
"""
function trapz_small(lo_x::Real, hi_x::Real, x::AbstractVector, y::AbstractVector)
lo_ind, hi_ind = searchsortednearest(x, [lo_x, hi_x])
# make sure that the inds are inside lo_x and hi_x
if x[lo_ind] < lo_x; lo_ind += 1 end
if x[hi_ind] > hi_x; hi_ind -= 1 end
# integrate over main section + edges
integral = trapz_small(view(x, lo_ind:hi_ind), view(y, lo_ind:hi_ind)) +
+ _trapzx2(lo_x, x[lo_ind], y[lo_ind-1] + ((lo_x - x[lo_ind-1]) / (x[lo_ind]-x[lo_ind-1]) * (y[lo_ind] - y[lo_ind-1])), y[lo_ind]) / 2
+ _trapzx2(x[hi_ind], hi_x, y[hi_ind], y[hi_ind] + ((hi_x - x[hi_ind]) / (x[hi_ind+1]-x[hi_ind]) * (y[hi_ind+1] - y[hi_ind]))) / 2
return integral
end
"""
oversamp_interp(lo_x, hi_x, x, y)
Interpolating by getting the average value of `y` from `lo_x` to `hi_x`
"""
oversamp_interp(lo_x::Real, hi_x::Real, x::AbstractVector, y::AbstractVector) =
trapz_small(lo_x, hi_x, x, y) / (hi_x - lo_x)
# function undersamp_interp(x_new::Real, x::AbstractVector, y::AbstractVector)
# ind = searchsortednearest(x, x_new; lower=true)
# dif = (x_new-x[ind]) / (x[ind+1] - x[ind])
# return y[ind] * (1-dif) + y[ind+1] * dif
# end
# pixel_separation(xs::AbstractVector) = multiple_append!([xs[1] - xs[2]], (xs[1:end-2] - xs[3:end]) ./ 2, [xs[end-1] - xs[end]])
"""
bounds_generator!(bounds, xs)
Getting the bounds of each element in `xs` assuming that they fully span the domain
"""
function bounds_generator!(bounds::AbstractVector, xs::AbstractVector)
bounds[1] = (3*xs[1] - xs[2]) / 2
bounds[2:end-1] = (view(xs, 1:(length(xs)-1)) .+ view(xs, 2:length(xs))) ./ 2
bounds[end] = (3*xs[end] - xs[end-1]) / 2
return bounds
end
"""
bounds_generator!(xs)
Getting the bounds of each element in `xs` assuming that they fully span the domain
"""
function bounds_generator(xs::AbstractVector)
bounds = Array{Float64}(undef, length(xs)+1)
bounds_generator!(bounds, xs)
return bounds
end
function bounds_generator(xs::AbstractMatrix)
bounds = Array{Float64}(undef, size(xs, 1)+1, size(xs, 2))
for i in axes(xs, 2)
bounds_generator!(view(bounds, :, i), view(xs, :, i))
end
return bounds
end
"""
Å_to_wavenumber(λ)
Convert `λ` (in Å) to wave number (in 1/cm)
"""
Å_to_wavenumber(λ::Real) = 1e8 / λ
"""
wavenumber_to_Å(wn)
Convert `wn` (in 1/cm) to wavelength (in Å)
"""
wavenumber_to_Å(wn::Real) = Å_to_wavenumber(wn)
"""
vector_zero(θ)
Get a zero version of θ
"""
vector_zero(θ::AbstractVecOrMat) = zero(θ)
vector_zero(θ::Vector{<:AbstractArray}) = [vector_zero(i) for i in θ]
"""
flatten_ranges(ranges)
Returns a range from the largest first element of those in `ranges` to the smallest last element of those in `ranges`
"""
flatten_ranges(ranges::AbstractVector) = maximum([range[1] for range in ranges]):minimum([range[end] for range in ranges])
flatten_ranges(ranges::AbstractMatrix) = [flatten_ranges(view(ranges, :, i)) for i in axes(ranges, 2)]
"""
weighted_mean(x, σ²; default=0., kwargs...)
Calculates the weighted mean of `x` given `σ²`
"""
function weighted_mean(x::AbstractMatrix, σ²::AbstractMatrix; default::Real=0., kwargs...)
result = sum(x ./ σ²; kwargs...) ./ sum(1 ./ σ²; kwargs...)
if ndims(result) > 0
result[isnan.(result)] .= default
elseif isnan(result)
return default
end
return result
end
"""
find_modes(data; amount=3)
Return the indices of local maxima of a data array
"""
function find_modes(data::Vector{T}) where {T<:Real}
# creating index list for inds at modes
mode_inds = [i for i in 2:(length(data)-1) if (data[i]>=data[i-1]) && (data[i]>=data[i+1])]
# if data[1] > data[2]; prepend!(mode_inds, 1) end
# if data[end] > data[end-1]; append!(mode_inds, length(data)) end
# return highest mode indices
return mode_inds[sortperm(-data[mode_inds])]
end
"""
est_∇(f, inputs; dif=1e-7, ignore_0_inputs=false)
Estimate the gradient of `f` at `inputs` using finite differences.
"""
function est_∇(f::Function, inputs::Vector{<:Real}; dif::Real=1e-7, ignore_0_inputs::Bool=false)
# original value
val = f(inputs)
#estimate gradient
j = 1
if ignore_0_inputs
grad = zeros(length(remove_zeros(inputs)))
else
grad = zeros(length(inputs))
end
for i in eachindex(inputs)
if !ignore_0_inputs || inputs[i]!=0
hold = inputs[i]
inputs[i] += dif
grad[j] = (f(inputs) - val) / dif
j += 1
inputs[i] = hold
end
if i%100==0; println("done with $i/$(length(inputs))") end
end
return grad
end
"""
self_cor(a; set_diag=true)
Get the correlation matrix between the rows in `a`
"""
function self_cor(a::AbstractMatrix; set_diag::Bool=true)
n = size(a, 1)
cors = Array{Float64}(undef, n, n)
for i in 1:n
for j in i+1:n
cors[i, j] = cor(view(a, i, :), view(a, j, :))
end
end
if set_diag
cors[diagind(cors)] .= 1
else
cors[diagind(cors)] .= 0
end
return Symmetric(cors)
end
"""
int2ind(a, x)
Find the index where `x` can be found in `a`
"""
function int2ind(a::AbstractVecOrMat, x::Int)
@assert typeof(a).parameters[1] <: Int
i = searchsortedfirst(a, x)
if i <= length(a) && a[i] == x
return i
else
return 0
end
end
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 5259 | """
insert_and_dedup!(v, x)
Insert `x` into sorted list `v` without duplicates
"""
insert_and_dedup!(v::Vector, x) = (splice!(v, searchsorted(v,x), [x]); v)
"""
affected_pixels(bad)
Store the first indicies where `bad`` is true
"""
function affected_pixels(bad::AbstractVecOrMat)
affected = Int64[]
for ij in findall(bad)
insert_and_dedup!(affected, ij[1])
end
return affected
end
"""
affected_pixels!(affected1, affected2)
Store the indicies in both `affected1` and `affected2` in `affected1`
"""
function affected_pixels!(affected1::Vector, affected2::AbstractVector)
for i in affected2
insert_and_dedup!(affected1, i)
end
return affected1
end
"""
mask!(var, bad_inds; using_weights=false)
Setting `var` to reflect that the pixels at `bad_inds` should be masked
"""
function mask!(var::AbstractVecOrMat, bad_inds::AbstractVecOrMat; using_weights::Bool=false)
if using_weights
var[bad_inds] .= 0
else
var[bad_inds] .= Inf
end
return affected_pixels(bad_inds)
end
function mask!(var::AbstractMatrix, bad_inds::AbstractVector; padding::Int=0, using_weights::Bool=false)
bad_inds = sort(bad_inds)
if padding > 0
affected = Int[]
l = size(var, 1)
for i in bad_inds
affected_pixels!(affected, max(1, i-padding):min(i+padding, l))
end
if using_weights
var[affected, :] .= 0
else
var[affected, :] .= Inf
end
return affected
else
if using_weights
var[bad_inds, :] .= 0
else
var[bad_inds, :] .= Inf
end
return bad_inds
end
end
"""
mask_stellar_feature!(var, log_λ_star, log_λ_low, log_λ_high; verbose=true, inverse=false, kwargs...)
Masking where `log_λ_star` is between (or outside if `inverse`=true) `log_λ_low` and `log_λ_high`
"""
function mask_stellar_feature!(var::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_star::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_low::Real, log_λ_high::Real; verbose::Bool=true, inverse::Bool=false, kwargs...)
@assert log_λ_low < log_λ_high
inverse ?
bad = .!(log_λ_low .< log_λ_star .< log_λ_high) :
bad = log_λ_low .< log_λ_star .< log_λ_high
if verbose; println("masked some features in the stellar frame") end
return mask!(var, bad; kwargs...)
end
function mask_stellar_feature!(d::Data, log_λ_low::Real, log_λ_high::Real; verbose::Bool=true, kwargs...)
mask_stellar_feature!(d.var_s, d.log_λ_star, log_λ_low, log_λ_high; verbose=verbose, kwargs...)
return mask_stellar_feature!(d.var, d.log_λ_star, log_λ_low, log_λ_high; verbose=false, kwargs...)
end
"""
mask_stellar_feature!(var, log_λ_obs, log_λ_star, log_λ_low, log_λ_high; verbose=true, include_bary_shifts=true, kwargs...)
Masking where `log_λ_obs` is between `log_λ_low` and `log_λ_high`.
Can also perform in the stellar frame to prevent different lines from coming in at different times with `include_bary_shifts`
"""
function mask_telluric_feature!(var::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_obs::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_star::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_low::Real, log_λ_high::Real; verbose::Bool=true, include_bary_shifts::Bool=true, kwargs...)
@assert log_λ_low < log_λ_high
if include_bary_shifts
log_λ_low_star, log_λ_high_star = extrema(log_λ_star[log_λ_low .< log_λ_obs .< log_λ_high])
if verbose; println("masked some telluric features in the stellar frame") end
return mask_stellar_feature!(var, log_λ_star, log_λ_low_star, log_λ_high_star; verbose=false, kwargs...)
else
if verbose; println("masked some features in the telluric frame") end
return mask!(var, log_λ_low .< log_λ_obs .< log_λ_high; kwargs...)
end
end
function mask_telluric_feature!(d::Data, log_λ_low::Real, log_λ_high::Real; verbose::Bool=true, kwargs...)
mask_telluric_feature!(d.var_s, d.log_λ_obs, d.log_λ_star, log_λ_low, log_λ_high; verbose=verbose, kwargs...)
return mask_telluric_feature!(d.var, d.log_λ_obs, d.log_λ_star, log_λ_low, log_λ_high; verbose=false, kwargs...)
end
"""
mask_stellar_pixel!(var, log_λ_star, log_λ_star_bounds, i; padding=0, verbose=true, kwargs...)
Masking a pixel in the stellar frame to prevent different lines from coming in at different times
"""
function mask_stellar_pixel!(var::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_star::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_star_bounds::AbstractMatrix, i::Int; padding::Int=0, verbose::Bool=true, kwargs...)
log_λ_low = minimum(view(log_λ_star_bounds, max(1, i - padding), :))
log_λ_high = maximum(view(log_λ_star_bounds, min(i + padding + 1, size(log_λ_star_bounds, 1)), :))
if verbose; println("masked some pixels in the stellar frame") end
return mask_stellar_feature!(var, log_λ_star, log_λ_low, log_λ_high; verbose=false, kwargs...)
end
function mask_stellar_pixel!(var::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_star::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_star_bounds::AbstractMatrix, inds::AbstractVector; verbose::Bool=true, kwargs...)
affected = Int64[]
if length(inds) > 0
if verbose; println("masked some pixels in the stellar frame") end
for i in inds
affected2 = mask_stellar_pixel!(var, log_λ_star, log_λ_star_bounds, i; verbose=false, kwargs...)
affected_pixels!(affected, affected2)
end
end
return affected
end
function mask_stellar_pixel!(d::Data, inds_or_i; verbose::Bool=true, kwargs...)
mask_stellar_pixel!(d.var_s, d.log_λ_star, d.log_λ_star_bounds, inds; verbose=verbose, kwargs...)
return mask_stellar_pixel!(d.var, d.log_λ_star, d.log_λ_star_bounds, inds; verbose=false, kwargs...)
end
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 53056 | using AbstractGPs
using LinearAlgebra
using KernelFunctions
using TemporalGPs
import AbstractGPs
using Distributions
import Base.copy
import Base.vec
import Base.getindex
import Base.eachindex
import Base.setindex!
using SparseArrays
using SpecialFunctions
using StaticArrays
using Nabla
import StatsBase: winsor
using Base.Threads
# using ThreadsX
import ExpectationMaximizationPCA as EMPCA
abstract type OrderModel end
abstract type Output end
abstract type Data end
"""
D_to_rv(D)
Approximately converting a Doppler shift `D ≡ log(λ1/λ0)` in log-wavelength space to an RV using `(λ1-λ0)/λ0 = λ1/λ0 - 1 = e^D - 1 ≈ β = v / c` (with an extra negative sign from somewhere)
"""
D_to_rv(D) = light_speed_nu .* (1-exp.(D))
# function D_to_rv(D)
# x = exp.(2 .* D)
# return light_speed_nu .* ((1 .- x) ./ (1 .+ x))
# end
"""
rv_to_D(v)
Approximately converting an RV to a Doppler shift `D ≡ log(λ1/λ0)` in log-wavelength space using `(λ1-λ0)/λ0 = λ1/λ0 - 1 = e^D - 1 ≈ β = v / c` (with an extra negative sign from somewhere)
"""
rv_to_D(v) = log1p.(-v ./ light_speed_nu) # a simple approximation that minimally confuses that we are measuring redshift
# rv_to_D(v) = (log1p.((-v ./ light_speed_nu)) - log1p.((v ./ light_speed_nu))) ./ 2
# rv_to_D(v) = log.((1 .- v ./ light_speed_nu) ./ (1 .+ v ./ light_speed_nu)) ./ 2
"""
_lower_inds!(lower_inds, lower_inds_adj, model_log_λ, rvs, log_λ_obs)
find the `model_log_λ` indices (incl. RV shifts) that bracket each `log_λ_obs`
"""
function _lower_inds!(lower_inds::AbstractMatrix, lower_inds_adj::AbstractMatrix, model_log_λ::AbstractVector{<:Real}, rvs, log_λ_obs::AbstractMatrix)
n_obs = length(rvs)
len = size(log_λ_obs, 1)
@assert size(lower_inds) == size(lower_inds_adj) == (len, n_obs)
log_λ_holder = Array{Float64}(undef, len)
len_model = length(model_log_λ)
for i in 1:n_obs
log_λ_holder[:] = view(log_λ_obs, :, i) .+ rv_to_D(rvs[i])
lower_inds[:, i] .= searchsortednearest(model_log_λ, log_λ_holder; lower=true)
for j in 1:len
if lower_inds[j, i] >= len_model
lower_inds[j, i] = len_model - 1
elseif lower_inds[j, i] < 1
lower_inds[j, i] = 1
end
end
lower_inds_adj[:, i] .= ((i - 1) * len_model) .+ view(lower_inds, :, i)
end
return lower_inds, lower_inds_adj
end
function _lower_inds(model_log_λ::AbstractVector{<:Real}, rvs, log_λ_obs::AbstractMatrix)
n_obs = length(rvs)
len = size(log_λ_obs, 1)
lower_inds = Array{Int64}(undef, len, n_obs)
lower_inds_adj = Array{Int64}(undef, len, n_obs)
return _lower_inds!(lower_inds, lower_inds_adj, model_log_λ, rvs, log_λ_obs)
end
"""
StellarInterpolationHelper
A linear interpolation holding information to interpolate the stellar model shifted by an RV to the data
"""
struct StellarInterpolationHelper{T1<:Real, T2<:Int}
"`log_λ_obs - model_log_λ[lower_inds]` precomputed for coefficient calculations"
log_λ_obs_m_model_log_λ_lo::AbstractMatrix{T1}
"The stellar model log λ uniform step size"
model_log_λ_step::T1
"The lower indices"
lower_inds::AbstractMatrix{T2}
"The lower indices plus 1"
lower_inds_p1::AbstractMatrix{T2}
function StellarInterpolationHelper(
log_λ_obs_m_model_log_λ_lo::AbstractMatrix{T1},
model_log_λ_step::T1,
lower_inds::AbstractMatrix{T2},
lower_inds_p1::AbstractMatrix{T2}) where {T1<:Real, T2<:Int}
# @assert some issorted thing?
return new{T1, T2}(log_λ_obs_m_model_log_λ_lo, model_log_λ_step, lower_inds, lower_inds_p1)
end
end
function StellarInterpolationHelper(
model_log_λ::StepRangeLen,
rvs::AbstractVector{T},
log_λ_obs::AbstractMatrix{T}) where {T<:Real}
sih = StellarInterpolationHelper(Array{Float64}(undef, size(log_λ_obs)), model_log_λ.step.hi, Array{Int}(undef, size(log_λ_obs)), Array{Int}(undef, size(log_λ_obs)))
return StellarInterpolationHelper!(sih, model_log_λ, rvs, log_λ_obs)
end
function (sih::StellarInterpolationHelper)(inds::AbstractVecOrMat, len_model::Int)
lower_inds = copy(sih.lower_inds)
for i in eachindex(inds)
j = inds[i]
lower_inds[:, j] .+= (i - j) * len_model
end
return StellarInterpolationHelper(
view(sih.log_λ_obs_m_model_log_λ_lo, :, inds),
sih.model_log_λ_step,
lower_inds[:, inds],
lower_inds[:, inds] .+ 1)
end
function StellarInterpolationHelper!(
sih::StellarInterpolationHelper,
model_log_λ::StepRangeLen,
total_rvs::AbstractVector{T},
log_λ_obs::AbstractMatrix{T}) where {T<:Real}
@assert sih.model_log_λ_step == model_log_λ.step.hi
lower_inds = Array{Int}(undef, size(sih.lower_inds, 1), size(sih.lower_inds, 2))
_lower_inds!(lower_inds, sih.lower_inds, model_log_λ, total_rvs, log_λ_obs)
sih.log_λ_obs_m_model_log_λ_lo .= log_λ_obs - (view(model_log_λ, lower_inds))
sih.lower_inds_p1 .= sih.lower_inds .+ 1
return sih
end
Base.copy(s::StellarInterpolationHelper) = StellarInterpolationHelper(copy(s.log_λ_obs_m_model_log_λ_lo), s.model_log_λ_step, copy(s.lower_inds), copy(s.lower_inds_p1))
"""
spectra_interp(model_flux, rvs, sih)
Interpolate the stellar model to the data using the lower inds in `sih`
"""
function spectra_interp(model_flux::AbstractMatrix, rvs::AbstractVector, sih::StellarInterpolationHelper)
ratios = (sih.log_λ_obs_m_model_log_λ_lo .+ rv_to_D(rvs)') ./ sih.model_log_λ_step
# prop_bad = sum((ratios .> 1) + (ratios .< 0)) / length(ratios)
# if prop_bad > 0.01; println("$(Int(round((100*prop_bad))))% of ratios are outside [0,1]. Consider running update_interpolation_locations!(::ModelWorkspace)")
return (view(model_flux, sih.lower_inds).* (1 .- ratios)) + (view(model_flux, sih.lower_inds_p1) .* ratios)
end
function spectra_interp_nabla(model_flux, rvs, sih::StellarInterpolationHelper)
ratios = (sih.log_λ_obs_m_model_log_λ_lo .+ rv_to_D(rvs)') ./ sih.model_log_λ_step
return (model_flux[sih.lower_inds] .* (1 .- ratios)) + (model_flux[sih.lower_inds_p1] .* ratios)
end
function spectra_interp(model_flux::AbstractVector, rv::Real, sih::StellarInterpolationHelper; sih_ind::Int=1)
ratios = (view(sih.log_λ_obs_m_model_log_λ_lo, :, sih_ind) .+ rv_to_D(rv)) ./ sih.model_log_λ_step
return (view(model_flux, view(sih.lower_inds, :, sih_ind)) .* (1 .- ratios)) + (view(model_flux, view(sih.lower_inds_p1, :, sih_ind)) .* ratios)
end
spectra_interp(model_flux, rvs, sih::StellarInterpolationHelper) =
spectra_interp_nabla(model_flux, rvs, sih)
@explicit_intercepts spectra_interp Tuple{AbstractMatrix, AbstractVector, StellarInterpolationHelper} [true, false, false]
function Nabla.∇(::typeof(spectra_interp), ::Type{Arg{1}}, _, y, ȳ, model_flux, rvs, sih)
ratios = (sih.log_λ_obs_m_model_log_λ_lo .+ rv_to_D(rvs)') ./ sih.model_log_λ_step
ȳnew = zeros(size(model_flux, 1), size(ȳ, 2))
# samp is λ_obs x λ_model
for k in axes(ȳ, 1) # λ_obs
for j in axes(ȳnew, 2) # time
λ_model_lo = sih.lower_inds[k, j] - size(ȳnew, 1)*(j-1)
# for i in axes(ȳnew, 1) # λ_model
# for i in λ_model_lo:(λ_model_lo+1) # λ_model
# ȳnew[i, j] += sampt[i, k] * ȳ[k, j]
# ȳnew[i, j] += samp[k, i] * ȳ[k, j]
# ȳnew[λ_model_lo, j] += samp[k, λ_model_lo] * ȳ[k, j]
ȳnew[λ_model_lo, j] += (1 - ratios[k, j]) * ȳ[k, j]
ȳnew[λ_model_lo+1, j] += ratios[k, j] * ȳ[k, j]
# end
end
end
return ȳnew
end
allequal(x) = all(y->y==x[1],x)
"""
LSFData
Holds preprocessed data used to optimize SSOF models (including a matrix that approximates convolution with the instrument line spread function)
"""
struct LSFData{T<:Number, AM<:AbstractMatrix{T}, M<:Matrix{<:Number}} <: Data
"Observed normalized flux"
flux::AM
"Observed normalized variance"
var::AM
"Observed normalized variance (with constant masking in barycentric frame)"
var_s::AM
"Log of observed wavelengths"
log_λ_obs::AM
"Pixel boundaries of the observed log wavelengths"
log_λ_obs_bounds::M
"Log of observed wavelengths (after barycentric correction)"
log_λ_star::AM
"Pixel boundaries of the observed log wavelengths (after barycentric correction)"
log_λ_star_bounds::M
"Matrix that approximates convolution with the instrument line spread function"
lsf::Union{Vector{<:SparseMatrixCSC},SparseMatrixCSC}
function LSFData(flux::AM, var::AM, var_s::AM, log_λ_obs::AM, log_λ_obs_bounds::M, log_λ_star::AM, log_λ_star_bounds::M, lsf::Union{Vector{<:SparseMatrixCSC},SparseMatrixCSC}) where {T<:Real, AM<:AbstractMatrix{T}, M<:Matrix{<:Number}}
@assert size(flux) == size(var) == size(var_s) == size(log_λ_obs) == size(log_λ_star)
if typeof(lsf) <: Vector
@assert size(lsf[1], 1) == size(lsf[1], 2) == size(flux, 1)
@assert allequal([size(l, 1) for l in lsf])
@assert allequal([size(l, 2) for l in lsf])
else
@assert size(lsf, 1) == size(lsf, 2) == size(flux, 1)
end
return new{T, AM, M}(flux::AM, var::AM, var_s::AM, log_λ_obs::AM, log_λ_obs_bounds::M, log_λ_star::AM, log_λ_star_bounds::M, lsf)
end
end
function LSFData(flux::AM, var::AM, var_s::AM, log_λ_obs::AM, log_λ_star::AM, lsf::Union{Vector{<:SparseMatrixCSC},SparseMatrixCSC}) where {T<:Real, AM<:AbstractMatrix{T}}
log_λ_obs_bounds = bounds_generator(log_λ_obs)
log_λ_star_bounds = bounds_generator(log_λ_star)
return LSFData(flux, var, var_s, log_λ_obs, log_λ_obs_bounds, log_λ_star, log_λ_star_bounds, lsf)
end
LSFData(flux::AM, var::AM, var_s::AM, log_λ_obs::AM, log_λ_star::AM, lsf::Nothing) where {T<:Real, AM<:AbstractMatrix{T}} =
GenericData(flux, var, var_s, log_λ_obs, log_λ_star)
(d::LSFData)(inds::AbstractVecOrMat) =
LSFData(view(d.flux, :, inds), view(d.var, :, inds), view(d.var_s, :, inds),
view(d.log_λ_obs, :, inds), view(d.log_λ_star, :, inds), d.lsf)
Base.copy(d::LSFData) = LSFData(copy(d.flux), copy(d.var), copy(d.var_s), copy(d.log_λ_obs), copy(d.log_λ_obs_bounds), copy(d.log_λ_star), copy(d.log_λ_star_bounds), copy(d.lsf))
"""
GenericData
Holds preprocessed data used to optimize SSOF models
"""
struct GenericData{T<:Number, AM<:AbstractMatrix{T}, M<:Matrix{<:Number}} <: Data
"Observed normalized flux"
flux::AM
"Observed normalized variance"
var::AM
"Observed normalized variance (with constant masking in barycentric frame)"
var_s::AM
"Log of observed wavelengths"
log_λ_obs::AM
"Pixel boundaries of the observed log wavelengths"
log_λ_obs_bounds::M
"Log of observed wavelengths (after barycentric correction)"
log_λ_star::AM
"Pixel boundaries of the observed log wavelengths (after barycentric correction)"
log_λ_star_bounds::M
function GenericData(flux::AM, var::AM, var_s::AM, log_λ_obs::AM, log_λ_star::AM) where {T<:Number, AM<:AbstractMatrix{T}}
@assert size(flux) == size(var) == size(var_s) == size(log_λ_obs) == size(log_λ_star)
log_λ_obs_bounds = bounds_generator(log_λ_obs)
log_λ_star_bounds = bounds_generator(log_λ_star)
return new{T, AM, typeof(log_λ_obs_bounds)}(flux, var, var_s, log_λ_obs, log_λ_obs_bounds, log_λ_star, log_λ_star_bounds)
end
end
(d::GenericData)(inds::AbstractVecOrMat) =
GenericData(view(d.flux, :, inds), view(d.var, :, inds), view(d.var_s, :, inds),
view(d.log_λ_obs, :, inds), view(d.log_λ_star, :, inds))
Base.copy(d::GenericData) = GenericData(copy(d.flux), copy(d.var), copy(d.var_s), copy(d.log_λ_obs), copy(d.log_λ_star))
GenericData(d::LSFData) = GenericData(d.flux, d.var, d.var_s, d.log_λ_obs, d.log_λ_star)
GenericData(d::GenericData) = d
"""
GenericDatum
Holds a single preprocessed spectrum used to optimize SSOF models
"""
struct GenericDatum{T<:Number, AV<:AbstractVector{T}, V<:Vector{<:Number}} <: Data
"Observed normalized flux"
flux::AV
"Observed normalized variance"
var::AV
"Observed normalized variance (with constant masking in barycentric frame)"
var_s::AV
"Log of observed wavelengths"
log_λ_obs::AV
"Pixel boundaries of the observed log wavelengths"
log_λ_obs_bounds::V
"Log of observed wavelengths (after barycentric correction)"
log_λ_star::AV
"Pixel boundaries of the observed log wavelengths (after barycentric correction)"
log_λ_star_bounds::V
function GenericDatum(flux::AV, var::AV, log_λ_obs::AV, log_λ_star::AV) where {T<:Number, AV<:AbstractVector{T}}
@assert size(flux) == size(var) == size(var_s) == size(log_λ_obs) == size(log_λ_star)
log_λ_obs_bounds = bounds_generator(log_λ_obs)
log_λ_star_bounds = bounds_generator(log_λ_star)
return new{T, AV, typeof(log_λ_obs_bounds)}(flux, var, var_s, log_λ_obs, log_λ_obs_bounds, log_λ_star, log_λ_star_bounds)
end
end
(d::GenericDatum)(inds::AbstractVecOrMat) =
GenericData(view(d.flux, inds), view(d.var, inds), view(d.var_s, inds),
view(d.log_λ_obs, inds), view(d.log_λ_star, inds))
Base.copy(d::GenericDatum) = GenericDatum(copy(d.flux), copy(d.var), copy(d.var_s), copy(d.log_λ_obs), copy(d.log_λ_star))
# combines many GenericDatum into a GenericData object
function GenericData(d::Vector{<:GenericDatum})
len_obs = length(d[1].flux)
n_obs = length(d)
flux_obs = ones(len_obs, n_obs)
var_obs = Array{Float64}(undef, len_obs, n_obs)
var_obs_s = Array{Float64}(undef, len_obs, n_obs)
log_λ_obs = Array{Float64}(undef, len_obs, n_obs)
# log_λ_obs_bounds = Array{Float64}(undef, len_obs+1, n_obs)
log_λ_star = Array{Float64}(undef, len_obs, n_obs)
# log_λ_star_bounds = Array{Float64}(undef, len_obs+1, n_obs)
for i in 1:n_obs # 13s
flux_obs[:, i] .= d[i].flux
var_obs[:, i] .= d[i].var
var_obs_s[:, i] .= d[i].var_s
log_λ_obs[:, i] .= d[i].log_λ_obs
# log_λ_obs_bounds[:, i] .= d[i].log_λ_obs_bounds
log_λ_star[:, i] .= d[i].log_λ_star
# log_λ_star_bounds[:, i] .= d[i].log_λ_star_bounds
end
return GenericData(flux_obs, var_obs, var_obs_s, log_λ_obs, log_λ_star)
end
"""
create_λ_template(log_λ_obs; upscale=1.)
Creating a uniform grid of log wavelengths for the SSOF models to be evaluated on
"""
function create_λ_template(log_λ_obs::AbstractMatrix; upscale::Real=1.)
log_min_wav, log_max_wav = extrema(log_λ_obs)
Δ_logλ_og = minimum(view(log_λ_obs, 2:size(log_λ_obs, 1), :) .- view(log_λ_obs, 1:size(log_λ_obs, 1)-1, :)) # minimum pixel separation
# Δ_logλ_og = minimum(view(log_λ_obs, size(log_λ_obs, 1), :) .- view(log_λ_obs, 1, :)) / size(log_λ_obs, 1) # minimum avg pixel separation
# Δ_logλ_og = median(view(log_λ_obs, 2:size(log_λ_obs, 1), :) .- view(log_λ_obs, 1:size(log_λ_obs, 1)-1, :)) # median pixel separation
# Δ_logλ_og = maximum(view(log_λ_obs, 2:size(log_λ_obs, 1), :) .- view(log_λ_obs, 1:size(log_λ_obs, 1)-1, :)) # maximum pixel separation
Δ_logλ = Δ_logλ_og / upscale
log_λ_template = (log_min_wav - 2 * Δ_logλ_og):Δ_logλ:(log_max_wav + 2 * Δ_logλ_og)
λ_template = exp.(log_λ_template)
return log_λ_template, λ_template
end
abstract type LinearModel end
_log_lm_default = true
"""
FullLinearModel
A (log) linear model including a mean (either μ+M*s or μ*exp(M*s))
"""
struct FullLinearModel{T<:Number, AM1<:AbstractMatrix{T}, AM2<:AbstractMatrix{T}, AV<:AbstractVector{T}} <: LinearModel
"Feature vectors/weights that control where the model varies"
M::AM1
"Scores that control how much the model varies at each time"
s::AM2
"Template which controls the average behavior"
μ::AV
"Whether or not the model is log linear"
log::Bool
function FullLinearModel(M::AM1, s::AM2, μ::AV, log::Bool) where {T<:Number, AM1<:AbstractMatrix{T}, AM2<:AbstractMatrix{T}, AV<:AbstractVector{T}}
@assert length(μ) == size(M, 1)
@assert size(M, 2) == size(s, 1)
return new{T, AM1, AM2, AV}(M, s, μ, log)
end
end
FullLinearModel(M::AM1, s::AM2, μ::AV; log::Bool=_log_lm_default) where {T<:Number, AM1<:AbstractMatrix{T}, AM2<:AbstractMatrix{T}, AV<:AbstractVector{T}} =
FullLinearModel(M, s, μ, log)
Base.copy(flm::FullLinearModel) = FullLinearModel(copy(flm.M), copy(flm.s), copy(flm.μ), flm.log)
LinearModel(flm::FullLinearModel, inds::AbstractVecOrMat) =
FullLinearModel(flm.M, view(flm.s, :, inds), flm.μ, flm.log)
"""
BaseLinearModel
A (log) linear model without a mean (either M*s or exp(M*s)).
Used for DPCA models
"""
struct BaseLinearModel{T<:Number, AM1<:AbstractMatrix{T}, AM2<:AbstractMatrix{T}} <: LinearModel
"Feature vectors/weights that control where the model varies"
M::AM1
"Scores that control how much the model varies at each time"
s::AM2
"Whether or not the model is log linear"
log::Bool
function BaseLinearModel(M::AM1, s::AM2, log::Bool) where {T<:Number, AM1<:AbstractMatrix{T}, AM2<:AbstractMatrix{T}}
@assert size(M, 2) == size(s, 1)
return new{T, AM1, AM2}(M, s, log)
end
end
BaseLinearModel(M::AM1, s::AM2; log::Bool=_log_lm_default) where {T<:Number, AM1<:AbstractMatrix{T}, AM2<:AbstractMatrix{T}} =
BaseLinearModel(M, s, log)
Base.copy(blm::BaseLinearModel) = BaseLinearModel(copy(blm.M), copy(blm.s), blm.log)
LinearModel(blm::BaseLinearModel, inds::AbstractVecOrMat) =
BaseLinearModel(blm.M, view(blm.s, :, inds), blm.log)
"""
TemplateModel
A constant model (when there are no feature vectors)
"""
struct TemplateModel{T<:Number, AV<:AbstractVector{T}} <: LinearModel
μ::AV
n::Int
end
Base.copy(tlm::TemplateModel) = TemplateModel(copy(tlm.μ), tlm.n)
LinearModel(tm::TemplateModel, inds::AbstractVecOrMat) = TemplateModel(tm.μ, length(inds))
"Whether a LinearModel is log linear"
log_lm(lm::TemplateModel) = false
log_lm(lm::LinearModel) = lm.log
# setting some syntactic sugar
Base.getindex(lm::LinearModel, s::Symbol) = getfield(lm, s)
Base.eachindex(lm::TemplateModel) = fieldnames(typeof(lm))
Base.eachindex(lm::LinearModel) = fieldnames(typeof(lm))[1:end-1] # dealing with log fieldname
Base.setindex!(lm::LinearModel, a::AbstractVecOrMat, s::Symbol) = (lm[s] .= a)
# getting a vector of the linear model components
vec(lm::LinearModel) = [lm[i] for i in eachindex(lm)]
vec(lm::TemplateModel) = [lm.μ]
vec(lms::Vector{<:LinearModel}) = [vec(lm) for lm in lms]
LinearModel(M::AbstractMatrix, s::AbstractMatrix, μ::AbstractVector; log_lm::Bool=_log_lm_default) = FullLinearModel(M, s, μ, log_lm)
LinearModel(M::AbstractMatrix, s::AbstractMatrix; log_lm::Bool=_log_lm_default) = BaseLinearModel(M, s, log_lm)
LinearModel(μ::AbstractVector, n::Int) = TemplateModel(μ, n)
LinearModel(lm::FullLinearModel, s::AbstractMatrix) = FullLinearModel(lm.M, s, lm.μ, log)
LinearModel(lm::BaseLinearModel, s::AbstractMatrix) = BaseLinearModel(lm.M, s, lm.log)
LinearModel(lm::TemplateModel, s::AbstractMatrix) = lm
# Ref(lm::FullLinearModel) = [Ref(lm.M), Ref(lm.s), Ref(lm.μ)]
# Ref(lm::BaseLinearModel) = [Ref(lm.M), Ref(lm.s)]
# Ref(lm::TemplateModel) = [Ref(lm.μ)]
"""
_eval_lm(M, s, μ; log_lm=false)
Evaluate a LinearModel
"""
_eval_lm(M, s, μ; log_lm::Bool=false) = log_lm ? (return exp.(M * s) .* μ) : (return (M * s) .+ μ)
_eval_lm(M::AbstractMatrix, s::AbstractMatrix, μ::AbstractVector) = muladd(M, s, μ) # faster, but Nabla doesn't handle it
_eval_lm(M, s; log_lm::Bool=false) = log_lm ? (return exp.(M * s)) : (return (M * s))
# _eval_lm(μ, n::Int) = repeat(μ, 1, n)
_eval_lm(μ, n::Int) = μ * ones(n)' # this is faster I dont know why
_eval_lm(flm::FullLinearModel) = _eval_lm(flm.M, flm.s, flm.μ; log_lm=flm.log)
_eval_lm(blm::BaseLinearModel) = _eval_lm(blm.M, blm.s; log_lm=blm.log)
_eval_lm(tlm::TemplateModel) = _eval_lm(tlm.μ, tlm.n)
(lm::LinearModel)() = _eval_lm(lm)
(flm::FullLinearModel)(inds::AbstractVecOrMat) = _eval_lm(view(flm.M, inds, :), flm.s, flm.μ; log_lm=flm.log)
(blm::BaseLinearModel)(inds::AbstractVecOrMat) = _eval_lm(view(blm.M, inds, :), blm.s; log_lm=blm.log)
(tlm::TemplateModel)(inds::AbstractVecOrMat) = repeat(view(tlm.μ, inds), 1, tlm.n)
function copy_TemplateModel!(to::LinearModel, from::LinearModel)
to.μ .= from.μ
end
copy_to_LinearModel!(to::TemplateModel, from::TemplateModel) = copy_TemplateModel!(to, from)
copy_to_LinearModel!(to::LinearModel, from::TemplateModel) = copy_TemplateModel!(to, from)
copy_to_LinearModel!(to::TemplateModel, from::LinearModel) = copy_TemplateModel!(to, from)
function copy_to_LinearModel!(to::LinearModel, from::LinearModel)
@assert typeof(to) == typeof(from)
@assert to.log == from.log
for i in eachindex(from)
getfield(to, i) .= getfield(from, i)
end
end
copy_to_LinearModel!(to::TemplateModel, from::LinearModel, inds) =
copy_to_LinearModel!(to, from)
copy_to_LinearModel!(to::LinearModel, from::TemplateModel, inds) =
copy_to_LinearModel!(to, from)
copy_to_LinearModel!(to::TemplateModel, from::TemplateModel, inds) =
copy_to_LinearModel!(to, from)
nvec(lm::TemplateModel) = 0
nvec(lm::LinearModel) = size(lm.M, 2)
function copy_to_LinearModel!(to::FullLinearModel, from::FullLinearModel, inds)
@assert to.log == from.log
to.μ .= from.μ
to.M[:, inds] .= view(from.M, :, inds)
to.s[inds, :] .= view(from.s, inds, :)
end
function copy_to_LinearModel!(to::LinearModel, from::Vector)
if typeof(to) <: TemplateModel
if typeof(from) <: Vector{<:Real}
to.μ .= from
else
@assert length(from) == 1
to.μ .= from[1]
end
else
fns = eachindex(to)
@assert length(from) == length(fns)
for i in eachindex(fns)
getfield(to, fns[i]) .= from[i]
end
end
end
"""
Submodel
Holds information on the wavelengths, LTISDE representaiton for the GP reguarlization term, and linear model for a SSOF model component
"""
struct Submodel{T<:Number, AV1<:AbstractVector{T}, AV2<:AbstractVector{T}, AA<:AbstractArray{T}}
"Uniform separation log wavelengths of the SSOF model component"
log_λ::AV1
"`exp.(log_λ)`"
λ::AV2
"Linear model"
lm::LinearModel
"State transition matrix"
A_sde::StaticMatrix
"Process noise"
Σ_sde::StaticMatrix
"Coefficients that can be used to calculate the gradient of the GP regularization term"
Δℓ_coeff::AA
end
function Submodel(log_λ_obs::AbstractVecOrMat, n_comp::Int, log_λ_gp::Real; include_mean::Bool=true, log_lm::Bool=_log_lm_default, log_λ::Union{Nothing,AbstractRange}=nothing, kwargs...)
n_obs = size(log_λ_obs, 2)
if isnothing(log_λ)
log_λ, λ = create_λ_template(log_λ_obs; kwargs...)
else
λ = exp.(log_λ)
end
len = length(log_λ)
if include_mean
if n_comp > 0
lm = FullLinearModel(zeros(len, n_comp), zeros(n_comp, n_obs), ones(len), log_lm)
else
lm = TemplateModel(ones(len), n_obs)
end
else
if n_comp > 0
lm = BaseLinearModel(zeros(len, n_comp), zeros(n_comp, n_obs), log_lm)
end
@error "you need a mean if you don't want any components"
end
temporal_gps_λ = 1 / log_λ_gp
A_sde, Σ_sde = gp_sde_prediction_matrices(step(log_λ), temporal_gps_λ)
sparsity = Int(round(0.5 / (step(log_λ) * temporal_gps_λ)))
Δℓ_coeff = gp_Δℓ_coefficients(length(log_λ), A_sde, Σ_sde; sparsity=sparsity)
return Submodel(log_λ, λ, lm, A_sde, Σ_sde, Δℓ_coeff)
end
function Submodel(log_λ::AV1, λ::AV2, lm, A_sde::StaticMatrix, Σ_sde::StaticMatrix, Δℓ_coeff::AA) where {T<:Number, AV1<:AbstractVector{T}, AV2<:AbstractVector{T}, AA<:AbstractArray{T}}
if typeof(lm) <: TemplateModel
@assert length(log_λ) == length(λ) == length(lm.μ) == size(Δℓ_coeff, 1) == size(Δℓ_coeff, 2)
else
@assert length(log_λ) == length(λ) == size(lm.M, 1) == size(Δℓ_coeff, 1) == size(Δℓ_coeff, 2)
end
@assert size(A_sde) == size(Σ_sde)
return Submodel{T, AV1, AV2}(log_λ, λ, lm, A_sde, Σ_sde, Δℓ_coeff)
end
(sm::Submodel)(inds::AbstractVecOrMat) =
Submodel(sm.log_λ, sm.λ, LinearModel(sm.lm, inds), sm.A_sde, sm.Σ_sde, sm.Δℓ_coeff)
Base.copy(sm::Submodel) = Submodel(sm.log_λ, sm.λ, copy(sm.lm), sm.A_sde, sm.Σ_sde, sm.Δℓ_coeff)
"""
_shift_log_λ_model(log_λ_obs_from, log_λ_obs_to, log_λ_model_from)
Getting model log λ in a different reference frame using the shifts in the different `log_λ_obs`
"""
function _shift_log_λ_model(log_λ_obs_from, log_λ_obs_to, log_λ_model_from)
n_obs = size(log_λ_obs_from, 2)
dop = [log_λ_obs_from[1, i] - log_λ_obs_to[1, i] for i in 1:n_obs]
log_λ_model_to = ones(length(log_λ_model_from), n_obs)
for i in 1:n_obs
log_λ_model_to[:, i] .= log_λ_model_from .+ dop[i]
end
return log_λ_model_to
end
# Default regularization values
# They need to be different or else the stellar μ will be surpressed
default_reg_tel = Dict([(:GP_μ, 1e6), (:L2_μ, 1e6), (:L1_μ, 1e5), (:L1_μ₊_factor, 6.),
(:GP_M, 1e7), (:L1_M, 1e7)])
default_reg_star = Dict([(:GP_μ, 1e2), (:L2_μ, 1e-2), (:L1_μ, 1e2), (:L1_μ₊_factor, 6.),
(:GP_M, 1e4), (:L1_M, 1e7)])
default_reg_tel_full = Dict([(:GP_μ, 1e6), (:L2_μ, 1e6), (:L1_μ, 1e5),
(:L1_μ₊_factor, 6.), (:GP_M, 1e7), (:L2_M, 1e4), (:L1_M, 1e7)])
default_reg_star_full = Dict([(:GP_μ, 1e2), (:L2_μ, 1e-2), (:L1_μ, 1e1),
(:L1_μ₊_factor, 6.), (:GP_M, 1e4), (:L2_M, 1e4), (:L1_M, 1e7)])
"""
oversamp_interp_helper(to_bounds, from_x)
Finding the coefficients to integrate the model between observed pixel bounds
"""
function oversamp_interp_helper(to_bounds::AbstractVector, from_x::AbstractVector)
ans = spzeros(length(to_bounds)-1, length(from_x))
bounds_inds = searchsortednearest(from_x, to_bounds)
for i in axes(ans, 1)
x_lo, x_hi = to_bounds[i], to_bounds[i+1] # values of bounds
lo_ind, hi_ind = bounds_inds[i], bounds_inds[i+1] # indices of points in model closest to the bounds
# if necessary, shrink so that so from_x[lo_ind] and from_x[hi_ind] are in the bounds
if from_x[lo_ind] < x_lo; lo_ind += 1 end
if from_x[hi_ind] > x_hi; hi_ind -= 1 end
edge_term_lo = (from_x[lo_ind] - x_lo) ^ 2 / (from_x[lo_ind] - from_x[lo_ind-1])
edge_term_hi = (x_hi - from_x[hi_ind]) ^ 2 / (from_x[hi_ind+1] - from_x[hi_ind])
ans[i, lo_ind-1] = edge_term_lo
ans[i, hi_ind+1] = edge_term_hi
if lo_ind==hi_ind
ans[i, lo_ind] = from_x[lo_ind+1] + from_x[lo_ind] - 2 * x_lo - edge_term_lo - edge_term_hi
else
ans[i, lo_ind] = from_x[lo_ind+1] + from_x[lo_ind] - 2 * x_lo - edge_term_lo
ans[i, lo_ind+1:hi_ind-1] .= view(from_x, lo_ind+2:hi_ind) .- view(from_x, lo_ind:hi_ind-2)
ans[i, hi_ind] = 2 * x_hi - from_x[hi_ind] - from_x[hi_ind-1] - edge_term_hi
end
# println(sum(view(ans, i, lo_ind-1:hi_ind+1))," vs ", 2 * (x_hi - x_lo))
# @assert isapprox(sum(view(ans, i, lo_ind-1:hi_ind+1)), 2 * (x_hi - x_lo); rtol=1e-3)
ans[i, lo_ind-1:hi_ind+1] ./= sum(view(ans, i, lo_ind-1:hi_ind+1))
# ans[i, lo_ind-1:hi_ind+1] ./= 2 * (x_hi - x_lo)
end
dropzeros!(ans)
return ans
end
oversamp_interp_helper(to_bounds::AbstractMatrix, from_x::AbstractVector) =
[oversamp_interp_helper(view(to_bounds, :, i), from_x) for i in axes(to_bounds, 2)]
oversamp_interp_helper(to_x::AbstractVector, from_x::AbstractMatrix) =
[oversamp_interp_helper(to_bounds, view(from_x, :, i)) for i in axes(from_x, 2)]
"""
undersamp_interp_helper(to_x, from_x)
Finding the coefficients to linear interpolate the model at observed pixel locations
"""
function undersamp_interp_helper(to_x::AbstractVector, from_x::AbstractVector)
ans = spzeros(length(to_x), length(from_x))
# ans = sparse(Float64[],Float64[],Float64[],length(to_x),length(from_x))
to_inds = searchsortednearest(from_x, to_x; lower=true)
for i in axes(ans, 1)
x_new = to_x[i]
ind = to_inds[i] # index of point in model below to_x[i]
if ind < length(from_x)
dif = (x_new-from_x[ind]) / (from_x[ind+1] - from_x[ind])
ans[i, ind] = 1 - dif
ans[i, ind + 1] = dif
else
ans[i, ind] = 1
end
end
dropzeros!(ans)
return ans
end
undersamp_interp_helper(to_x::AbstractMatrix, from_x::AbstractVector) =
[undersamp_interp_helper(view(to_x, :, i), from_x) for i in axes(to_x, 2)]
undersamp_interp_helper(to_x::AbstractVector, from_x::AbstractMatrix) =
[undersamp_interp_helper(to_x, view(from_x, :, i)) for i in axes(from_x, 2)]
"""
OrderModelDPCA
SSOF model for a set of 1D spectra using Doppler-constrained PCA to measure the RVs (which are contained in the RV Submodel)
"""
struct OrderModelDPCA{T<:Number} <: OrderModel
"Telluric submodel"
tel::Submodel
"Stellar submodel"
star::Submodel
"RV submodel with Doppler feature vector"
rv::Submodel
"Telluric regularization coefficients"
reg_tel::Dict{Symbol, T}
"Stellar regularization coefficients"
reg_star::Dict{Symbol, T}
"Matrices to interpolate stellar model to observed wavelengths (barycenter 2 observed)"
b2o::AbstractVector{<:SparseMatrixCSC}
"Matrices to interpolate telluric model to observed wavelengths (telluric 2 observed)"
t2o::AbstractVector{<:SparseMatrixCSC}
"Holds the data on the instrument, star, and order of data being as well as whether the model has been optimized or regularized etc."
metadata::Dict{Symbol, Any}
"Number of spectra to be modeled"
n::Int
end
"""
OrderModelWobble
SSOF model for a set of 1D spectra using linear interpolation of the stellar model to measure the RVs
"""
struct OrderModelWobble{T<:Number} <: OrderModel
"Telluric submodel"
tel::Submodel
"Stellar submodel"
star::Submodel
"RVs"
rv::AbstractVector
"Telluric regularization coefficients"
reg_tel::Dict{Symbol, T}
"Stellar regularization coefficients"
reg_star::Dict{Symbol, T}
"Linear interpolation helper objects to interpolate stellar model to observed wavelengths (barycenter 2 observed)"
b2o::StellarInterpolationHelper
"Approximate barycentric correction \"RVs\" (using `(λ1-λ0)/λ0 = λ1/λ0 - 1 = e^D - 1 ≈ β = v / c`)"
bary_rvs::AbstractVector{<:Real}
"Matrices to interpolate telluric model to observed wavelengths (telluric 2 observed)"
t2o::AbstractVector{<:SparseMatrixCSC}
"Holds the data on the instrument, star, and order of data being as well as whether the model has been optimized or regularized etc."
metadata::Dict{Symbol, Any}
"Number of spectra to be modeled"
n::Int
end
"""
OrderModel(d; kwargs...)
Constructor for the `OrderModel`-type objects (SSOF model for a set of 1D spectra)
# Optional arguments
- `instrument::String="None"`: The name of the instrument(s) the data was taken from. For bookkeeping
- `order::Int=0`: What order (if any) the data was taken from. For bookkeeping
- `star_str::String="None"`: The name of the star the data was taken from. For bookkeeping
- `n_comp_tel::Int=5`: Amount of telluric feature vectors
- `n_comp_star::Int=5`: The maximum amount of stellar feature vectors
- `oversamp::Bool=true`: Whether or not to integrate the model or do linear interpolation (for the telluric model)
- `dpca::Bool=false`: Whether to use Doppler-constrained PCA or variable interpolation location to determine the RVs
- `log_λ_gp_star::Real=1/SOAP_gp_params.λ`: The log λ lengthscale of the stellar regularization GP
- `log_λ_gp_tel::Real=1/LSF_gp_params.λ`: The log λ lengthscale of the telluric regularization GP
- `tel_log_λ::Union{Nothing,AbstractRange}=nothing`: The log
- `star_log_λ::Union{Nothing,AbstractRange}=nothing`: The log λ lengthscale of the telluric regularization GP
- `kwargs...`: kwargs passed to `Submodel` constructors
"""
function OrderModel(
d::Data;
instrument::String="None",
order::Int=0,
star_str::String="None",
n_comp_tel::Int=2,
n_comp_star::Int=2,
oversamp::Bool=true,
dpca::Bool=false,
log_λ_gp_star::Real=1/SOAP_gp_params.λ,
log_λ_gp_tel::Real=1/LSF_gp_params.λ,
tel_log_λ::Union{Nothing,AbstractRange}=nothing,
star_log_λ::Union{Nothing,AbstractRange}=nothing,
kwargs...)
# Creating models
tel = Submodel(d.log_λ_obs, n_comp_tel, log_λ_gp_tel; log_λ=tel_log_λ, kwargs...)
star = Submodel(d.log_λ_star, n_comp_star, log_λ_gp_star; log_λ=star_log_λ, kwargs...)
n_obs = size(d.log_λ_obs, 2)
dpca ?
rv = Submodel(d.log_λ_star, 1, log_λ_gp_star; include_mean=false, log_λ=star_log_λ, kwargs...) :
rv = zeros(n_obs)
bary_rvs = D_to_rv.([median(d.log_λ_star[:, i] - d.log_λ_obs[:, i]) for i in 1:n_obs])
todo = Dict([(:initialized, false), (:reg_improved, false), (:err_estimated, false)])
metadata = Dict([(:todo, todo), (:instrument, instrument), (:order, order), (:star, star_str)])
if dpca
if oversamp
b2o = oversamp_interp_helper(d.log_λ_star_bounds, star.log_λ)
t2o = oversamp_interp_helper(d.log_λ_obs_bounds, tel.log_λ)
else
b2o = undersamp_interp_helper(d.log_λ_star, star.log_λ)
t2o = undersamp_interp_helper(d.log_λ_obs, tel.log_λ)
end
return OrderModelDPCA(tel, star, rv, copy(default_reg_tel), copy(default_reg_star), b2o, t2o, metadata, n_obs)
else
b2o = StellarInterpolationHelper(star.log_λ, bary_rvs, d.log_λ_obs)
if oversamp
t2o = oversamp_interp_helper(d.log_λ_obs_bounds, tel.log_λ)
else
t2o = undersamp_interp_helper(d.log_λ_obs, tel.log_λ)
end
return OrderModelWobble(tel, star, rv, copy(default_reg_tel), copy(default_reg_star), b2o, bary_rvs, t2o, metadata, n_obs)
end
end
Base.copy(om::OrderModelDPCA) = OrderModelDPCA(copy(om.tel), copy(om.star), copy(om.rv), copy(om.reg_tel), copy(om.reg_star), om.b2o, om.t2o, copy(om.metadata), om.n)
(om::OrderModelDPCA)(inds::AbstractVecOrMat) =
OrderModelDPCA(om.tel(inds), om.star(inds), om.rv(inds), copy(om.reg_tel),
copy(om.reg_star), view(om.b2o, inds), view(om.t2o, inds), copy(om.metadata), length(inds))
Base.copy(om::OrderModelWobble) = OrderModelWobble(copy(om.tel), copy(om.star), copy(om.rv), copy(om.reg_tel), copy(om.reg_star), copy(om.b2o), om.bary_rvs, om.t2o, copy(om.metadata), om.n)
(om::OrderModelWobble)(inds::AbstractVecOrMat) =
OrderModelWobble(om.tel(inds), om.star(inds), view(om.rv, inds), copy(om.reg_tel),
copy(om.reg_star), om.b2o(inds, length(om.star.lm.μ)), view(om.bary_rvs, inds), view(om.t2o, inds), copy(om.metadata), length(inds))
"""
rm_dict!(d)
Remove all keys in a Dict
"""
function rm_dict!(d::Dict)
for (key, value) in d
delete!(d, key)
end
end
"""
rm_regularization!(om)
Remove all of the keys in the regularization Dicts
"""
function rm_regularization!(om::OrderModel)
rm_dict!(om.reg_tel)
rm_dict!(om.reg_star)
end
"""
rm_dict!(d, key_start)
Remove all keys starting with `key_start` in a Dict
"""
function rm_dict!(d::Dict, key_start::String)
for (key, value) in d
if string(key)[1:length(key_start)] == key_start; delete!(d, key) end
end
end
"""
rm_GP_regularization!(om)
Remove all of the GP keys in the regularization Dicts
"""
function rm_GP_regularization!(om::OrderModel)
rm_dict!(om.reg_tel, "GP_")
rm_dict!(om.reg_star, "GP_")
end
"""
zero_regularization(om; include_L1_factor=false)
Zero-out all of the keys in the regularization Dicts
"""
function zero_regularization(om::OrderModel; include_L1_factor::Bool=false)
for (key, value) in om.reg_tel
if include_L1_factor || (key != :L1_μ₊_factor)
om.reg_tel[key] = 0
end
end
for (key, value) in om.reg_star
if include_L1_factor || (key != :L1_μ₊_factor)
om.reg_star[key] = 0
end
end
end
"""
reset_regularization!(om)
Reset all of the keys in the regularization Dicts to the default values
"""
function reset_regularization!(om::OrderModel)
for (key, value) in om.reg_tel
om.reg_tel[key] = default_reg_tel_full[key]
end
for (key, value) in om.reg_star
om.reg_star[key] = default_reg_star_full[key]
end
end
"""
_eval_lm_vec(om, v; log_lm=_log_lm_default)
Evaluate a vectorized version of a linear model in `v`
"""
function _eval_lm_vec(om::OrderModel, v; log_lm::Bool=_log_lm_default)
@assert 0 < length(v) < 4
if length(v)==1
return _eval_lm(v[1], om.n)
elseif length(v)==2
return _eval_lm(v[1], v[2]; log_lm=log_lm)
elseif length(v)==3
return _eval_lm(v[1], v[2], v[3]; log_lm=log_lm)
end
end
"""
rvs(model)
Get RVs (in m/s) from an OrderModel
The negative sign is only in the DPCA version because of how SSOF was originally coded
"""
rvs(model::OrderModelDPCA) = vec(model.rv.lm.s .* -light_speed_nu)
rvs(model::OrderModelWobble) = model.rv
"""
downsize(lm, n_comp)
Create a smaller version of `lm` that only copies some amount of the feature vectors
"""
function downsize(lm::FullLinearModel, n_comp::Int)
if n_comp > 0
return FullLinearModel(lm.M[:, 1:n_comp], lm.s[1:n_comp, :], copy(lm.μ), lm.log)
else
return TemplateModel(copy(lm.μ), size(lm.s, 2))
end
end
downsize(lm::BaseLinearModel, n_comp::Int) =
BaseLinearModel(lm.M[:, 1:n_comp], lm.s[1:n_comp, :], lm.log)
function downsize(lm::TemplateModel, n_comp::Int)
@assert n_comp==0
return TemplateModel(copy(lm.μ), lm.n)
end
downsize(sm::Submodel, n_comp::Int) =
Submodel(copy(sm.log_λ), copy(sm.λ), downsize(sm.lm, n_comp), copy(sm.A_sde), copy(sm.Σ_sde), copy(sm.Δℓ_coeff))
downsize(m::OrderModelDPCA, n_comp_tel::Int, n_comp_star::Int) =
OrderModelDPCA(
downsize(m.tel, n_comp_tel),
downsize(m.star, n_comp_star),
copy(m.rv), copy(m.reg_tel), copy(m.reg_star), m.b2o, m.t2o, copy(m.metadata), m.n)
downsize(m::OrderModelWobble, n_comp_tel::Int, n_comp_star::Int) =
OrderModelWobble(
downsize(m.tel, n_comp_tel),
downsize(m.star, n_comp_star),
copy(m.rv), copy(m.reg_tel), copy(m.reg_star), copy(m.b2o), m.bary_rvs, m.t2o, copy(m.metadata), m.n)
"""
downsize(lm, n_comp)
Create a smaller view of `lm` that can only see some amount of the feature vectors
"""
function downsize_view(lm::FullLinearModel, n_comp::Int)
if n_comp > 0
return FullLinearModel(view(lm.M, :, 1:n_comp), view(lm.s, 1:n_comp, :), lm.μ, lm.log)
else
return TemplateModel(lm.μ, size(lm.s, 2))
end
end
downsize_view(lm::BaseLinearModel, n_comp::Int) =
BaseLinearModel(view(lm.M, :, 1:n_comp), view(lm.s, 1:n_comp, :), lm.log)
function downsize_view(lm::TemplateModel, n_comp::Int)
@assert n_comp==0
return lm
end
downsize_view(sm::Submodel, n_comp::Int) =
Submodel(sm.log_λ, sm.λ, downsize_view(sm.lm, n_comp), sm.A_sde, sm.Σ_sde, sm.Δℓ_coeff)
downsize_view(m::OrderModelDPCA, n_comp_tel::Int, n_comp_star::Int) =
OrderModelDPCA(
downsize_view(m.tel, n_comp_tel),
downsize_view(m.star, n_comp_star),
m.rv, copy(m.reg_tel), copy(m.reg_star), m.b2o, m.t2o, copy(m.metadata), m.n)
downsize_view(m::OrderModelWobble, n_comp_tel::Int, n_comp_star::Int) =
OrderModelWobble(
downsize_view(m.tel, n_comp_tel),
downsize_view(m.star, n_comp_star),
m.rv, copy(m.reg_tel), copy(m.reg_star), m.b2o, m.bary_rvs, m.t2o, copy(m.metadata), m.n)
"""
spectra_interp(model, interp_helper)
Interpolates `model` using the interoplation described by `interp_helper`
"""
spectra_interp(model, interp_helper::SparseMatrixCSC) =
interp_helper * model
spectra_interp(model::AbstractMatrix, interp_helper::AbstractVector{<:SparseMatrixCSC}) =
hcat([spectra_interp(view(model, :, i), interp_helper[i]) for i in axes(model, 2)]...)
# spectra_interp_nabla(model, interp_helper::AbstractVector{<:SparseMatrixCSC}) =
# hcat([interp_helper[i] * model[:, i] for i in axes(model, 2)]...)
# spectra_interp(model, interp_helper::AbstractVector{<:SparseMatrixCSC}) =
# spectra_interp_nabla(model, interp_helper)
@explicit_intercepts spectra_interp Tuple{AbstractMatrix, AbstractVector{<:SparseMatrixCSC}} [true, false]
Nabla.∇(::typeof(spectra_interp), ::Type{Arg{1}}, _, y, ȳ, model, interp_helper) =
hcat([interp_helper[i]' * view(ȳ, :, i) for i in axes(model, 2)]...)
"""
tel_model(om; lm=om.tel.lm)
Gets telluric model interpolated onto the observed wavelengths
"""
tel_model(om::OrderModel; lm::LinearModel=om.tel.lm) = spectra_interp(lm(), om.t2o)
"""
star_model(om; lm=om.star.lm)
Gets stellar model interpolated onto the observed wavelengths
"""
star_model(om::OrderModelDPCA; lm::LinearModel=om.star.lm) = spectra_interp(lm(), om.b2o)
star_model(om::OrderModelWobble; lm::LinearModel=om.star.lm) = spectra_interp(lm(), om.rv .+ om.bary_rvs, om.b2o)
"""
rv_model(om; lm=om.rv.lm)
Gets RV model interpolated onto the observed wavelengths (used by OrderModelDPCA)
"""
rv_model(om::OrderModelDPCA; lm::LinearModel=om.rv.lm) = spectra_interp(lm(), om.b2o)
# function fix_FullLinearModel_s!(flm, min::Number, max::Number)
# @assert all(min .< flm.μ .< max)
# result = ones(typeof(flm.μ[1]), length(flm.μ))
# for i in axes(flm.s, 2)
# result[:] = _eval_lm(flm.M, flm.s[:, i], flm.μ)
# while any(result .> max) || any(result .< min)
# # println("$i, old s: $(lm.s[:, i]), min: $(minimum(result)), max: $(maximum(result))")
# flm.s[:, i] ./= 2
# result[:] = _eval_lm(flm.M, view(flm.s, :, i), flm.μ)
# # println("$i, new s: $(lm.s[:, i]), min: $(minimum(result)), max: $(maximum(result))")
# end
# end
# end
"""
get_marginal_GP(finite_GP, ys, xs)
Marginalizes a TemporalGPs GP on `ys` and `xs`
"""
function get_marginal_GP(
finite_GP::Distribution{Multivariate,Continuous},
ys::AbstractVector,
xs::AbstractVector)
gp_post = posterior(finite_GP, ys)
gpx_post = gp_post(xs)
return TemporalGPs.marginals(gpx_post)
end
"""
get_mean_GP(finite_GP, ys, xs)
Gets the mean of the posterior of a TemporalGPs GP
"""
function get_mean_GP(
finite_GP::Distribution{Multivariate,Continuous},
ys::AbstractVector,
xs::AbstractVector)
return mean.(get_marginal_GP(finite_GP, ys, xs))
end
"""
build_gp(params)
Builds a Matern 5/2 TemporalGPs GP
"""
function build_gp(params::NamedTuple)
f_naive = AbstractGPs.GP(params.var_kernel * Matern52Kernel() ∘ ScaleTransform(params.λ))
return to_sde(f_naive, SArrayStorage(Float64))
end
# default TemporalGPs lengthscales fit to either SOAP data or a LSF line
SOAP_gp_params = (var_kernel = 0.19222435463373258, λ = 26801.464367577082)
SOAP_gp = build_gp(SOAP_gp_params)
SOAP_gp_var = 1e-6
LSF_gp_params = (var_kernel = 0.2, λ = 185325.)
LSF_gp = build_gp(LSF_gp_params)
LSF_gp_var = 1e-6
# ParameterHandling version
# SOAP_gp_params = (var_kernel = positive(3.3270754364467443), λ = positive(1 / 9.021560480866474e-5))
# flat_SOAP_gp_params, unflatten = value_flatten(SOAP_gp_params)
# # unflatten(flat_SOAP_gp_params) == ParameterHandling.value(SOAP_gp_params) # true
# SOAP_gp = build_gp(ParameterHandling.value(SOAP_gp_params))
"""
_spectra_interp_gp!(fluxes, log_λ, flux_obs, var_obs, log_λ_obs; gp_mean=0., gp_base=SOAP_gp, mask_flux=Array{Bool}(undef, length(flux_obs)), mask_var=Array{Bool}(undef, length(flux_obs)))
Use a GP to interpolate `flux_obs` observed at `log_λ_obs` onto `log_λ`
"""
function _spectra_interp_gp!(fluxes::AbstractVector, log_λ, flux_obs::AbstractVector, var_obs, log_λ_obs; gp_mean::Number=0., gp_base=SOAP_gp, mask_flux::Vector=Array{Bool}(undef, length(flux_obs)), mask_var::Vector=Array{Bool}(undef, length(flux_obs)))
mask_var[:] = isfinite.(var_obs)
if !any(mask_var)
var_obs[.!mask_var] .= 1e6*maximum(var_obs[mask_var])
end
mask_flux[:] = isfinite.(flux_obs)
flux_obs[.!mask_flux] .= gp_mean
gp = get_marginal_GP(gp_base(log_λ_obs, var_obs), flux_obs .- gp_mean, log_λ)
fluxes[:] = mean.(gp) .+ gp_mean
if !any(mask_var)
var_obs[.!mask_var] .= Inf
end
flux_obs[.!mask_flux] .= Inf
return gp
end
function _spectra_interp_gp!(fluxes::AbstractVector, vars, log_λ, flux_obs::AbstractVector, var_obs, log_λ_obs; keep_mask::Bool=true, kwargs...)
gp = _spectra_interp_gp!(fluxes, log_λ, flux_obs, var_obs, log_λ_obs; kwargs...)
vars[:] = var.(gp)
if keep_mask
inds = searchsortednearest(log_λ_obs, log_λ; lower=true)
# for i in eachindex(inds)
for i in eachindex(log_λ)
if log_λ[i] <= log_λ_obs[1]
if isinf(var_obs[1]); vars[i] = Inf end
elseif log_λ[i] >= log_λ_obs[end]
if isinf(var_obs[end]); vars[i] = Inf end
elseif isinf(var_obs[inds[i]]) || isinf(var_obs[inds[i]+1])
vars[i] = Inf
end
end
end
return gp
end
function _spectra_interp_gp!(fluxes::AbstractMatrix, log_λ, flux_obs, var_obs, log_λ_obs; var_kernel=SOAP_gp_params.var_kernel, λ_kernel=SOAP_gp_params.λ, kwargs...)
gp_base = build_gp((var_kernel = var_kernel, λ = λ_kernel))
for i in axes(flux_obs, 2)
_spectra_interp_gp!(view(fluxes, :, i), log_λ, view(flux_obs, :, i), view(var_obs, :, i), view(log_λ_obs, :, i); mask_flux=Array{Bool}(undef, size(flux_obs, 1)), mask_var=Array{Bool}(undef, size(flux_obs, 1)), gp_base=gp_base, kwargs...)
end
end
function _spectra_interp_gp!(fluxes::AbstractMatrix, vars, log_λ, flux_obs, var_obs, log_λ_obs; var_kernel=SOAP_gp_params.var_kernel, λ_kernel=SOAP_gp_params.λ, kwargs...)
gp_base = build_gp((var_kernel = var_kernel, λ = λ_kernel))
for i in axes(flux_obs, 2)
_spectra_interp_gp!(view(fluxes, :, i), view(vars, :, i), log_λ, view(flux_obs, :, i), view(var_obs, :, i), view(log_λ_obs, :, i); mask_flux=Array{Bool}(undef, size(flux_obs, 1)), mask_var=Array{Bool}(undef, size(flux_obs, 1)), gp_base=gp_base, kwargs...)
end
end
"""
remove_lm_score_means!(lm; prop=0.)
Recenter the scores in `lm` around 0
"""
function remove_lm_score_means!(lm::FullLinearModel; prop::Real=0.)
if prop != 0.
mean_s = Array{Float64}(undef, size(lm.s, 1), 1)
for i in axes(lm.s, 1)
mean_s[i, 1] = mean(winsor(view(lm.s, i, :); prop=prop))
end
else
mean_s = mean(lm.s; dims=2)
end
if lm.log
lm.μ .*= exp.(lm.M * mean_s)
else
lm.μ .+= lm.M * mean_s
end
lm.s .-= mean_s
end
remove_lm_score_means!(lm::LinearModel; kwargs...) = nothing
function remove_lm_score_means!(om::OrderModel; kwargs...)
remove_lm_score_means!(om.star.lm; kwargs...)
remove_lm_score_means!(om.tel.lm; kwargs...)
end
function remove_lm_score_means!(lms::Vector{<:LinearModel}; kwargs...)
for lm in lms
remove_lm_score_means!(lm; kwargs...)
end
end
"""
flip_feature_vectors!(lm)
Make each feature vector's median value negative
"""
function flip_feature_vectors!(lm::FullLinearModel)
flipper = -sign.(mean(lm.M; dims=1) - median(lm.M; dims=1)) # make basis vector be absorption features
lm.M .*= flipper
lm.s .*= flipper'
end
flip_feature_vectors!(lm::LinearModel) = nothing
function flip_feature_vectors!(om::OrderModel)
flip_feature_vectors!(om.star.lm)
flip_feature_vectors!(om.tel.lm)
end
function flip_feature_vectors!(lms::Vector{<:LinearModel})
for lm in lms
flip_feature_vectors!(lm)
end
end
"""
fill_TelModel!(om, lm)
Replace the telluric model in `om` with `lm`
"""
fill_TelModel!(om::OrderModel, lm::LinearModel) =
copy_to_LinearModel!(om.tel.lm, lm)
fill_TelModel!(om::OrderModel, lm::LinearModel, inds) =
copy_to_LinearModel!(om.tel.lm, lm, inds)
"""
fill_StarModel!(om, lm; inds=2:size(lm.M, 2))
Replace the stellar model in `om` with `lm`
"""
function fill_StarModel!(om::OrderModel, lm::FullLinearModel; inds=2:size(lm.M, 2))
if length(inds) > 0; @assert inds[1] > 1 end
copy_to_LinearModel!(om.star.lm, lm, inds)
if typeof(om) <: OrderModelDPCA
om.rv.lm.M .= view(lm.M, :, 1)
om.rv.lm.s[:] .= view(lm.s, 1, :)
else
om.rv .= view(lm.s, 1, :) .* -light_speed_nu #TODO check if this is correct
end
end
function fill_StarModel!(om::OrderModel, lm::LinearModel, rvs::Vector, inds)
copy_to_LinearModel!(om.star.lm, lm, inds)
if typeof(om) <: OrderModelDPCA
om.rv.lm.M .= doppler_component(om.star.λ, om.star.lm.μ)
om.rv.lm.s[:] .= rvs ./ -light_speed_nu #TODO check if this is correct
else
om.rv .= rvs
end
end
"""
fill_OrderModel!(om1, om2, inds_tel, inds_star)
Replace the models in `om1` with those in `om2`
"""
function fill_OrderModel!(om1::OrderModel, om2::OrderModel, inds_tel, inds_star)
fill_TelModel!(om1, om2.tel.lm, inds_tel)
if typeof(om2) <: OrderModelWobble
fill_StarModel!(om1, om2.star.lm, om2.rv, inds_star)
else
fill_StarModel!(om1, om2.star.lm, om2.rv.lm.s, inds_star)
end
end
"L1 norm"
L1(a) = sum(abs, a)
"L2 norm"
L2(a) = sum(abs2, a)
"L∞ norm"
L∞(Δ::VecOrMat{<:Real}) = maximum(Δ)
L∞(Δ) = maximum(L∞.(Δ))
"""
shared_attention(M)
Ad-hoc regularization that punishes feature vectors with power in the same place
"""
function shared_attention(M)
shared_attentions = M' * M
return sum(shared_attentions) - sum(diag(shared_attentions))
end
"""
model_prior(lm, om, key)
Calulate the model prior on `lm` with the regularization terms in `om.reg_` * `key`
"""
function model_prior(lm, om::OrderModel, key::Symbol)
reg = getfield(om, Symbol(:reg_, key))
sm = getfield(om, key)
isFullLinearModel = length(lm) > 2
val = 0.
if haskey(reg, :GP_μ) || haskey(reg, :L2_μ) || haskey(reg, :L1_μ) || haskey(reg, :L1_μ₊_factor)
μ_mod = lm[1+2*isFullLinearModel] .- 1
if haskey(reg, :L2_μ); val += L2(μ_mod) * reg[:L2_μ] end
if haskey(reg, :L1_μ)
val += L1(μ_mod) * reg[:L1_μ]
# For some reason dot() works but BLAS.dot() doesn't
if haskey(reg, :L1_μ₊_factor); val += dot(μ_mod, μ_mod .> 0) * reg[:L1_μ₊_factor] * reg[:L1_μ] end
end
# if haskey(reg, :GP_μ); val -= logpdf(SOAP_gp(getfield(om, key).log_λ), μ_mod) * reg[:GP_μ] end
# if haskey(reg, :GP_μ); val -= gp_ℓ_nabla(μ_mod, sm.A_sde, sm.Σ_sde) * reg[:GP_μ] end
if haskey(reg, :GP_μ); val -= gp_ℓ_precalc(sm.Δℓ_coeff, μ_mod, sm.A_sde, sm.Σ_sde) * reg[:GP_μ] end
end
if isFullLinearModel
if haskey(reg, :shared_M); val += shared_attention(lm[1]) * reg[:shared_M] end
if haskey(reg, :L2_M); val += L2(lm[1]) * reg[:L2_M] end
if haskey(reg, :L1_M); val += L1(lm[1]) * reg[:L1_M] end
# if haskey(reg, :GP_μ); val -= gp_ℓ_precalc(sm.Δℓ_coeff, view(lm[1], :, 1), sm.A_sde, sm.Σ_sde) * reg[:GP_μ] end
if haskey(reg, :GP_M)
for i in 1:size(lm[1], 2)
val -= gp_ℓ_precalc(sm.Δℓ_coeff, lm[1][:, i], sm.A_sde, sm.Σ_sde) * reg[:GP_M]
end
end
val += model_s_prior(lm[2], reg)
end
return val
end
model_prior(lm::Union{FullLinearModel, TemplateModel}, om::OrderModel, key::Symbol) = model_prior(vec(lm), om, key)
nonzero_key(reg, key) = haskey(reg, key) && reg[key] != 0
"""
model_s_prior(s, reg)
Add an L2 term to the scores if there are any regularization terms applied to the feature vectors
"""
function model_s_prior(s, reg::Dict)
if (nonzero_key(reg, :L1_M) || nonzero_key(reg, :L2_M) || nonzero_key(reg, :GP_M))
return L2(s)
end
return 0
end
"""
tel_prior(om)
Calulate the telluric model prior on `om.tel.lm` with the regularization terms in `om.reg_tel`
"""
tel_prior(om::OrderModel) = tel_prior(om.tel.lm, om)
tel_prior(lm, om::OrderModel) = model_prior(lm, om, :tel)
"""
star_prior(om)
Calulate the stellar model prior on `om.star.lm` with the regularization terms in `om.star_tel`
"""
star_prior(om::OrderModel) = star_prior(om.star.lm, om)
star_prior(lm, om::OrderModel) = model_prior(lm, om, :star)
"""
total_model(tel, star)
Multiply the telluric and stellar models
"""
total_model(tel, star, rv) = tel .* (star .+ rv)
total_model(tel, star) = tel .* star
"""
OutputDPCA
Holds the current outputs for the models at the observed wavelengths
"""
struct OutputDPCA{T<:Number, AM<:AbstractMatrix{T}, M<:Matrix{T}} <: Output
"Telluric model at the observed wavelengths"
tel::AM
"Stellar model at the observed wavelengths"
star::AM
"RV model at the observed wavelengths"
rv::AM
"Total model at the observed wavelengths"
total::M
function OutputDPCA(tel::AM, star::AM, rv::AM, total::M) where {T<:Number, AM<:AbstractMatrix{T}, M<:Matrix{T}}
@assert size(tel) == size(star) == size(rv) == size(total)
new{T, AM, M}(tel, star, rv, total)
end
end
"""
Output(om, d)
Calculates the current outputs for the models at the observed wavelengths
"""
function Output(om::OrderModelDPCA, d::Data)
@assert size(om.b2o[1], 1) == size(d.flux, 1)
return OutputDPCA(tel_model(om), star_model(om), rv_model(om), d)
end
OutputDPCA(tel, star, rv, d::GenericData) =
OutputDPCA(tel, star, rv, total_model(tel, star, rv))
OutputDPCA(tel, star, rv, d::LSFData) =
OutputDPCA(tel, star, rv, spectra_interp(total_model(tel, star, rv), d.lsf))
Base.copy(o::OutputDPCA) = OutputDPCA(copy(tel), copy(star), copy(rv))
"""
recalc_total!(o, d)
Recalulates the current outputs for the total model at the observed wavelengths
"""
function recalc_total!(o::OutputDPCA, d::GenericData)
o.total .= total_model(o.tel, o.star, o.rv)
end
function recalc_total!(o::OutputDPCA, d::LSFData)
o.total .= spectra_interp(total_model(o.tel, o.star, o.rv), d.lsf)
end
"""
Output!(o, om, d)
Recalculates the current outputs for the models at the observed wavelengths
"""
function Output!(o::OutputDPCA, om::OrderModelDPCA, d::Data)
o.tel .= tel_model(om)
o.star .= star_model(om)
o.rv .= rv_model(om)
recalc_total!(o, d)
end
"""
OutputWobble
Holds the current outputs for the models at the observed wavelengths
"""
struct OutputWobble{T<:Number, AM<:AbstractMatrix{T}, M<:Matrix{T}} <: Output
"Telluric model at the observed wavelengths"
tel::AM
"Stellar model at the observed wavelengths"
star::AM
"Total model at the observed wavelengths"
total::M
function OutputWobble(tel::AM, star::AM, total::M) where {T<:Number, AM<:AbstractMatrix{T}, M<:Matrix{T}}
@assert size(tel) == size(star) == size(total)
new{T, AM, M}(tel, star, total)
end
end
function Output(om::OrderModelWobble, d::Data)
@assert size(om.t2o[1], 1) == size(d.flux, 1)
return OutputWobble(tel_model(om), star_model(om), d)
end
OutputWobble(tel, star, d::GenericData) =
OutputWobble(tel, star, total_model(tel, star))
OutputWobble(tel, star, d::LSFData) =
OutputWobble(tel, star, spectra_interp(total_model(tel, star), d.lsf))
Base.copy(o::OutputWobble) = OutputWobble(copy(tel), copy(star))
function recalc_total!(o::OutputWobble, d::GenericData)
o.total .= total_model(o.tel, o.star)
end
function recalc_total!(o::OutputWobble, d::LSFData)
o.total .= spectra_interp(total_model(o.tel, o.star), d.lsf)
end
function Output!(o::OutputWobble, om::OrderModelWobble, d::Data)
o.tel .= tel_model(om)
o.star .= star_model(om)
recalc_total!(o, d)
end
"""
copy_reg!(from, to)
Copy the regularizations from one OrderModel to another
"""
function copy_reg!(from::OrderModel, to::OrderModel)
copy_dict!(to.reg_tel, from.reg_tel)
copy_dict!(to.reg_star, from.reg_star)
end
"""
no_tellurics(model)
Figure out whether a `model` uses its telluric model
"""
no_tellurics(model::OrderModel) = all(isone.(model.tel.lm.μ)) && !is_time_variable(model.tel) | StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 6049 | total_length(x::Vector{<:AbstractArray}) = sum(total_length.(x))
total_length(x::AbstractArray) = length(x)
"""
total_length(mws)
Calculates the number of parameters of `mws`
"""
total_length(mws::AdamWorkspace) = total_length(mws.total.θ)
total_length(mws::OptimTelStarWorkspace) = length(mws.telstar.p0) + length(mws.rv.p0)
total_length(mws::OptimTotalWorkspace) = length(mws.total.p0)
"""
intra_night_std(rvs, times; thres=3, show_warn=true)
Calculates the intra-night std for `rvs` time series observed at `times` (in days)
"""
function intra_night_std(rvs::AbstractVector, times::AbstractVector; thres::Int=3, show_warn::Bool=true)
intra_night_stds = [std(rvs[i]) for i in observation_night_inds(times) if length(i)>(thres-1)]
if length(intra_night_stds) < 1
if show_warn; @warn "no nights to base the intra night std of the RVs on. Returning the std of all of the observations" end
return Inf
elseif length(intra_night_stds) < 2
if show_warn; @warn "only one night to base the intra night std of the RVs on" end
elseif length(intra_night_stds) < 3
if show_warn; @warn "only a couple of nights to base the intra night std of the RVs on" end
end
return median(intra_night_stds)
end
n_negligible(x::AbstractVecOrMat) = sum(abs.(x) .< (1e-5 * sqrt(sum(abs2, x))))
function n_negligible(x::Submodel)
n = n_negligible(x.lm.μ)
if is_time_variable(x); n += n_negligible(x.lm.M) end
return n
end
function n_negligible(mws::ModelWorkspace)
n = n_negligible(mws.om.star)
if !(typeof(mws) <: FrozenTelWorkspace); n += n_negligible(mws.om.tel) end
return n
end
# function _test_om(mws_inp::ModelWorkspace, om::OrderModel, times::AbstractVector; no_tels::Bool=false, kwargs...)
# if no_tels
# mws = FrozenTelWorkspace(om, mws_inp.d)
# om.tel.lm.μ .= 1
# else
# mws = typeof(mws_inp)(om, mws_inp.d)
# end
# train_OrderModel!(mws; kwargs...) # 16s
# n = total_length(mws) #- n_negligible(mws)
# model_rvs = rvs(mws.om)
# return _loss(mws), n, std(model_rvs), intra_night_std(model_rvs, times; show_warn=false)
# end
# function test_ℓ_for_n_comps(n_comps::Vector, mws_inp::ModelWorkspace, times::AbstractVector, lm_tel::Vector{<:LinearModel}, lm_star::Vector{<:LinearModel}; return_inters::Bool=false, lm_tel_ind::Int=n_comps[2]+1, lm_star_ind::Int=n_comps[1]+1, kwargs...)
# _om = downsize(mws_inp.om, max(0, n_comps[1]), n_comps[2])
# # if either of the models are constant, there will only be one initialization
# # that should already be stored in the model
# if (n_comps[1] <= 0) || (n_comps[2] == 0)
# # if n_comps[2] > 0; fill_StarModel!(_om, lm_star[1]; inds=(1:n_comps[2]) .+ 1) end
# l, n, rv_std, in_rv_std = _test_om(mws_inp, _om, times; no_tels=n_comps[1]<0, kwargs...)
# return l, n, rv_std, in_rv_std, 2
# # choose the better of the two initializations
# else
# ls = zeros(2)
# ns = zeros(Int, 2)
# rv_stds = zeros(2)
# in_rv_stds = zeros(2)
# # test telluric components first
# _fill_model!(_om, n_comps, 1, lm_tel, lm_star; lm_tel_ind=lm_tel_ind, lm_star_ind=lm_star_ind)
# ls[1], ns[1], rv_stds[1], in_rv_stds[1] = _test_om(mws_inp, _om, times; kwargs...)
# # test star components next
# _fill_model!(_om, n_comps, 2, lm_tel, lm_star; lm_tel_ind=lm_tel_ind, lm_star_ind=lm_star_ind)
# ls[2], ns[2], rv_stds[2], in_rv_stds[2] = _test_om(mws_inp, _om, times; kwargs...)
# better_model = argmin(ls)
# return ls[better_model], ns[better_model], rv_stds[better_model], in_rv_stds[better_model], better_model
# end
# end
# function _fill_model!(model::OrderModel, n_comps::Vector{<:Int}, better_model::Int, lm_tels::Vector{<:LinearModel}, lm_stars::Vector{<:LinearModel}; lm_tel_ind::Int=n_comps[2]+1, lm_star_ind::Int=n_comps[1]+1)
# # if all(n_comps .> 0)
# @assert better_model in [1,2]
# if better_model == 1
# lm_tel = lm_tels[1]
# lm_star = lm_stars[lm_star_ind]
# else
# lm_tel = lm_tels[lm_tel_ind]
# lm_star = lm_stars[1]
# end
# fill_TelModel!(model, lm_tel, 1:n_comps[1])
# fill_StarModel!(model, lm_star; inds=(1:n_comps[2]) .+ 1)
# # end
# end
"""
ℓ_prereqs(vars)
Calculate some terms needed to calculate the log-likelihood
"""
function ℓ_prereqs(vars::Matrix)
mask = isfinite.(vars)
n = sum(mask)
logdet_Σ = sum(log.(vars[mask]))
return logdet_Σ, n
end
"Gaussian log-likelihood function"
ℓ(χ²::Real, logdet_Σ::Real, n::Int) = -1/2 * (χ² + logdet_Σ + n * _log2π)
"Akaike information criterion"
aic(k::Int, ℓ::Real) = 2 * (k - ℓ)
aic(mws::ModelWorkspace, logdet_Σ::Real, n::Int) =
aic(total_length(mws), ℓ(_loss(mws), logdet_Σ, n))
function aic(mws::ModelWorkspace)
n, logdet_Σ = ℓ_prereqs(mws.d.var)
return aic(mws, logdet_Σ, n)
end
"Akaike information criterion (corrected for small sample sizes)"
aicc(k::Int, ℓ::Real, n::Int) = aic(k, ℓ) + (2k(k+1))/(n-k-1)
aicc(mws::ModelWorkspace, logdet_Σ::Real, n::Int) =
aicc(total_length(mws), ℓ(_loss(mws), logdet_Σ, n), n)
function aicc(mws::ModelWorkspace)
n, logdet_Σ = ℓ_prereqs(mws.d.var)
return aicc(mws, logdet_Σ, n)
end
"Bayesian information criterion"
bic(k::Int, ℓ::Real, n::Int) = k * log(n) - 2 * ℓ
# function choose_n_comps(ls::Matrix, ks::Matrix, test_n_comp_tel::AbstractVector, test_n_comp_star::AbstractVector, var::AbstractMatrix; return_inters::Bool=false, use_aic::Bool=true)
# ## max likelihood
# # ans_ml = argmin(ls)
# n, logdet_Σ = ℓ_prereqs(var)
# ℓs = ℓ.(ls, logdet_Σ, n)
# ℓs[isnan.(ℓs)] .= -Inf
# aics = aic.(ks, ℓs)
# ans_aic = argmin(aics)
# bics = bic.(ks, ℓs, n)
# ans_bic = argmin(bics)
# if ans_aic != ans_bic; @warn "AIC and BIC gave different answers" end
# use_aic ? best_ind = ans_aic : best_ind = ans_bic
# n_comps = [test_n_comp_tel[best_ind[1]], test_n_comp_star[best_ind[2]]]
# if return_inters
# return n_comps, ℓs, aics, bics, best_ind
# else
# return n_comps
# end
# end
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 61653 | # using LineSearches
using ParameterHandling
using Optim
using Nabla
import Base.println
using DataInterpolations
import ExpectationMaximizationPCA as EMPCA
abstract type ModelWorkspace end
abstract type AdamWorkspace<:ModelWorkspace end
abstract type OptimWorkspace<:ModelWorkspace end
# generic χ² loss functions
_χ²_loss_σ(model_m_data, sigma) = (model_m_data ./ sigma) .^ 2
_χ²_loss(model_m_data, variance) = ((model_m_data) .^ 2) ./ variance
_χ²_loss(model, data, variance) = _χ²_loss(model .- data, variance)
_χ²_loss(model, data::Data; use_var_s::Bool=false) = use_var_s ? _χ²_loss(model, data.flux, data.var_s) : _χ²_loss(model, data.flux, data.var)
# χ² loss functions per pixel
__loss_diagnostic(tel, star, rv, d::GenericData; kwargs...) =
_χ²_loss(total_model(tel, star, rv), d; kwargs...)
__loss_diagnostic(tel, star, rv, d::LSFData; kwargs...) =
_χ²_loss(spectra_interp(total_model(tel, star, rv), d.lsf), d; kwargs...)
__loss_diagnostic(tel, star, d::GenericData; kwargs...) =
_χ²_loss(total_model(tel, star), d; kwargs...)
__loss_diagnostic(tel, star, d::LSFData; kwargs...) =
_χ²_loss(spectra_interp(total_model(tel, star), d.lsf), d; kwargs...)
function _loss_diagnostic(o::Output, om::OrderModel, d::Data;
tel=nothing, star=nothing, rv=nothing, kwargs...)
!isnothing(tel) ? tel_o = spectra_interp(_eval_lm_vec(om, tel; log_lm=log_lm(om.tel.lm)), om.t2o) : tel_o = o.tel
if typeof(om) <: OrderModelDPCA
!isnothing(star) ? star_o = spectra_interp(_eval_lm_vec(om, star; log_lm=log_lm(om.star.lm)), om.b2o) : star_o = o.star
!isnothing(rv) ? rv_o = spectra_interp(_eval_lm(om.rv.lm.M, rv), om.b2o) : rv_o = o.rv
return __loss_diagnostic(tel_o, star_o, rv_o, d; kwargs...)
end
if !isnothing(star)
if !isnothing(rv)
star_o = spectra_interp(_eval_lm_vec(om, star; log_lm=log_lm(om.star.lm)), rv .+ om.bary_rvs, om.b2o)
else
star_o = spectra_interp(_eval_lm_vec(om, star; log_lm=log_lm(om.star.lm)), om.rv .+ om.bary_rvs, om.b2o)
end
elseif !isnothing(rv)
star_o = spectra_interp(om.star.lm(), rv .+ om.bary_rvs, om.b2o)
else
star_o = o.star
end
return __loss_diagnostic(tel_o, star_o, d; kwargs...)
end
_loss_diagnostic(mws::ModelWorkspace; kwargs...) = _loss_diagnostic(mws.o, mws.om, mws.d; kwargs...)
# summed χ² loss functions
_loss(tel, star, rv, d::Data; kwargs...) = sum(__loss_diagnostic(tel, star, rv, d; kwargs...))
_loss(tel, star, d::Data; kwargs...) = sum(__loss_diagnostic(tel, star, d; kwargs...))
_loss(o::Output, om::OrderModel, d::Data; kwargs...) = sum(_loss_diagnostic(o, om, d; kwargs...))
_loss(mws::ModelWorkspace; kwargs...) = _loss(mws.o, mws.om, mws.d; kwargs...)
"""
_loss_recalc_rv_basis(o, om, d; kwargs...)
`_loss()` but including an AD-compliant way to recalcuate the Doppler basic vector
"""
function _loss_recalc_rv_basis(o::Output, om::OrderModel, d::Data; kwargs...)
om.rv.lm.M .= doppler_component_AD(om.star.λ, om.star.lm.μ)
return _loss(o, om, d; kwargs...)
end
_loss_recalc_rv_basis(mws::ModelWorkspace; kwargs...) = _loss_recalc_rv_basis(mws.o, mws.om, mws.d; kwargs...)
"""
loss_func(mws; include_priors=false)
Create a loss function for the model and data in `mws`
"""
function loss_func(mws::ModelWorkspace; include_priors::Bool=false)
if include_priors
return (; kwargs...) -> _loss(mws; kwargs...) + tel_prior(mws.om) + star_prior(mws.om)
else
return (; kwargs...) -> _loss(mws; kwargs...)
end
end
"""
loss_funcs_telstar(o, om, d)
Create loss functions for changing
- the telluric and stellar templates, features, and scores
- the telluric and stellar scores
- the RVs
Used to fit scores efficiently with L-BFGS
"""
function loss_funcs_telstar(o::Output, om::OrderModel, d::Data)
l_telstar(telstar; kwargs...) =
_loss(o, om, d; tel=telstar[1], star=telstar[2], kwargs...) +
tel_prior(telstar[1], om) + star_prior(telstar[2], om)
is_star_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.star)
function l_telstar_s(telstar_s)
prior = 0.
if is_time_variable(om.tel)
tel = [om.tel.lm.M, telstar_s[1], om.tel.lm.μ]
prior += model_s_prior(telstar_s[1], om.reg_tel)
if is_star_time_variable
star = [om.star.lm.M, telstar_s[2], om.star.lm.μ]
prior += model_s_prior(telstar_s[2], om.reg_star)
else
star = nothing
end
elseif is_star_time_variable
tel = nothing
star = [om.star.lm.M, telstar_s[1], om.star.lm.μ]
prior += model_s_prior(telstar_s[1], om.reg_star)
else
tel = nothing
star = nothing
end
return _loss(o, om, d; tel=tel, star=star, use_var_s=true) + prior
end
l_rv(rv) = _loss(o, om, d; rv=rv, use_var_s=true)
return l_telstar, l_telstar_s, l_rv
end
loss_funcs_telstar(mws::ModelWorkspace) = loss_funcs_telstar(mws.o, mws.om, mws.d)
"""
loss_funcs_total(o, om, d)
Create loss functions for changing
- the telluric and stellar templates, features, and scores
- the telluric and stellar scores and RVs
Used to fit models with ADAM
"""
function loss_funcs_total(o::Output, om::OrderModelDPCA, d::Data)
l_total(total) =
_loss_recalc_rv_basis(o, om, d; tel=total[1], star=total[2], rv=total[3]) +
tel_prior(total[1], om) + star_prior(total[2], om)
is_tel_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.tel)
is_star_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.star)
function l_total_s(total_s)
prior = 0.
if is_tel_time_variable
tel = [om.tel.lm.M, total_s[1], om.tel.lm.μ]
prior += model_s_prior(total_s[1], om.reg_tel)
if is_star_time_variable
star = [om.star.lm.M, total_s[2], om.star.lm.μ]
prior += model_s_prior(total_s[2], om.reg_star)
else
star = nothing
end
elseif is_star_time_variable
tel = nothing
star = [om.star.lm.M, total_s[1], om.star.lm.μ]
prior += model_s_prior(total_s[1], om.reg_star)
else
tel = nothing
star = nothing
end
return _loss(o, om, d; tel=tel, star=star, rv=total_s[1+is_star_time_variable+is_tel_time_variable], use_var_s=true) + prior
end
return l_total, l_total_s
end
function loss_funcs_total(o::Output, om::OrderModelWobble, d::Data)
l_total(total) =
_loss(o, om, d; tel=total[1], star=total[2], rv=total[3]) +
tel_prior(total[1], om) + star_prior(total[2], om)
is_tel_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.tel)
is_star_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.star)
function l_total_s(total_s)
prior = 0.
if is_tel_time_variable
tel = [om.tel.lm.M, total_s[1], om.tel.lm.μ]
prior += model_s_prior(total_s[1], om.reg_tel)
if is_star_time_variable
star = [om.star.lm.M, total_s[2], om.star.lm.μ]
prior += model_s_prior(total_s[2], om.reg_star)
else
star = nothing
end
elseif is_star_time_variable
tel = nothing
star = [om.star.lm.M, total_s[1], om.star.lm.μ]
prior += model_s_prior(total_s[1], om.reg_star)
else
tel = nothing
star = nothing
end
return _loss(o, om, d; tel=tel, star=star, rv=total_s[1+is_star_time_variable+is_tel_time_variable], use_var_s=true) + prior
end
return l_total, l_total_s
end
loss_funcs_total(mws::ModelWorkspace) = loss_funcs_total(mws.o, mws.om, mws.d)
"""
loss_funcs_frozen_tel(o, om, d)
Create loss functions for changing
- the stellar templates, features, and scores and telluric scores
- the telluric and stellar scores and RVs
Used to fit models with a set telluric model
"""
function loss_funcs_frozen_tel(o::Output, om::OrderModel, d::Data)
is_tel_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.tel)
is_star_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.star)
function l_frozen_tel(total)
is_tel_time_variable ? tel = [om.tel.lm.M, total[1], om.tel.lm.μ] : tel = nothing
star = total[1+is_tel_time_variable]
rv = total[2+is_tel_time_variable]
return _loss(o, om, d; tel=tel, star=star, rv=rv) + star_prior(total[1+is_tel_time_variable], om)
end
function l_frozen_tel_s(total_s)
prior = 0.
if is_tel_time_variable
tel = [om.tel.lm.M, total_s[1], om.tel.lm.μ]
if is_star_time_variable
star = [om.star.lm.M, total_s[2], om.star.lm.μ]
prior += model_s_prior(total_s[2], om.reg_star)
else
star = nothing
end
elseif is_star_time_variable
tel = nothing
star = [om.star.lm.M, total_s[1], om.star.lm.μ]
prior += model_s_prior(total_s[1], om.reg_star)
else
tel = nothing
star = nothing
end
return _loss(o, om, d; tel=tel, star=star, rv=total_s[1+is_star_time_variable+is_tel_time_variable], use_var_s=true) + prior
end
return l_frozen_tel, l_frozen_tel_s
end
loss_funcs_frozen_tel(mws::ModelWorkspace) = loss_funcs_frozen_tel(mws.o, mws.om, mws.d)
## ADAM things
α, β1, β2, ϵ = 2e-3, 0.9, 0.999, 1e-8
"""
Adam
Holds information used for Adaptive Moment Estimation optimization
"""
mutable struct Adam{T<:AbstractArray}
"Learning rate"
α::Float64
"Exponential decay rate for the first moment estimates"
β1::Float64
"Exponential decay rate for the second-moment estimates"
β2::Float64
"Holder for aggregate of gradients"
m::T
"Holder for sum of square of past gradients"
v::T
"Holder for accelerated β1"
β1_acc::Float64
"Holder for accelerated β2"
β2_acc::Float64
"A small positive constant"
ϵ::Float64
end
Adam(θ0::AbstractArray, α::Float64, β1::Float64, β2::Float64, ϵ::Float64) =
Adam(α, β1, β2, vector_zero(θ0), vector_zero(θ0), β1, β2, ϵ)
Adam(θ0::AbstractArray; α::Float64=α, β1::Float64=β1, β2::Float64=β2, ϵ::Float64=ϵ) =
Adam(θ0, α, β1, β2, ϵ)
Adams(θ0s::Vector{<:AbstractArray}, α::Float64, β1::Float64, β2::Float64, ϵ::Float64) =
Adams.(θ0s, α, β1, β2, ϵ)
Adams(θ0s; α::Float64=α, β1::Float64=β1, β2::Float64=β2, ϵ::Float64=ϵ) =
Adams(θ0s, α, β1, β2, ϵ)
Adams(θ0::AbstractVecOrMat{<:Real}, α::Float64, β1::Float64, β2::Float64, ϵ::Float64) =
Adam(θ0, α, β1, β2, ϵ)
Base.copy(opt::Adam) = Adam(opt.α, opt.β1, opt.β2, opt.m, opt.v, opt.β1_acc, opt.β2_acc, opt.ϵ)
"""
AdamState
Holds diagonstic information on the current state of an ADAM opmitization
"""
mutable struct AdamState
"Interation number"
iter::Int
"Loss"
ℓ::Float64
"L1 norm of the gradient"
L1_Δ::Float64
"L2 norm of the gradient"
L2_Δ::Float64
"L∞ norm of the gradient"
L∞_Δ::Float64
"Change in the loss between iterations"
δ_ℓ::Float64
"Change in the L1 norm between iterations"
δ_L1_Δ::Float64
"Change in the L2 norm between iterations"
δ_L2_Δ::Float64
"Change in the L∞ norm between iterations"
δ_L∞_Δ::Float64
end
AdamState() = AdamState(0, 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.)
function println(as::AdamState)
# println("Iter: ", as.iter)
println("ℓ: ", as.ℓ, " ℓ_$(as.iter)/ℓ_$(as.iter-1): ", as.δ_ℓ)
println("L2_Δ: ", as.L2_Δ, " L2_Δ_$(as.iter)/L2_Δ_$(as.iter-1): ", as.δ_L2_Δ)
println()
end
function iterate!(θs::Vector{<:AbstractArray}, ∇θs::Vector{<:AbstractArray}, opts::Vector)
@assert length(θs) == length(∇θs) == length(opts)
@inbounds for i in eachindex(θs)
iterate!(θs[i], ∇θs[i], opts[i])
end
end
"""
iterate!(θ, ∇θ, opt)
Perform an ADAM optimization step based on the contents of `opt` on `θ`
"""
function iterate!(θ::AbstractArray{Float64}, ∇θ::AbstractArray{Float64}, opt::Adam)
α=opt.α; β1=opt.β1; β2=opt.β2; ϵ=opt.ϵ; β1_acc=opt.β1_acc; β2_acc=opt.β2_acc; m=opt.m; v=opt.v
one_minus_β1 = 1.0 - β1
one_minus_β2 = 1.0 - β2
one_minus_β1_acc = 1 - β1_acc
one_minus_β2_acc = 1 - β2_acc
# the matrix and dotted version is slower
@inbounds for n in eachindex(θ)
m[n] = β1 * m[n] + one_minus_β1 * ∇θ[n]
v[n] = β2 * v[n] + one_minus_β2 * ∇θ[n]^2
m̂ = m[n] / one_minus_β1_acc
v̂ = v[n] / one_minus_β2_acc
θ[n] -= α * m̂ / (sqrt(v̂) + ϵ)
end
β1_acc *= β1
β2_acc *= β2
end
function AdamState!_helper(as::AdamState, f::Symbol, val)
setfield!(as, Symbol(:δ_,f), val / getfield(as, f))
setfield!(as, f, val)
end
"""
AdamState!(as, ℓ, Δ)
Update `as` with the next iteration's loss and gradient
"""
function AdamState!(as::AdamState, ℓ, Δ)
as.iter += 1
AdamState!_helper(as, :ℓ, ℓ)
flat_Δ = Iterators.flatten(Iterators.flatten(Δ))
AdamState!_helper(as, :L1_Δ, L1(flat_Δ))
AdamState!_helper(as, :L2_Δ, L2(flat_Δ))
AdamState!_helper(as, :L∞_Δ, L∞(Δ))
end
_verbose_def = false
_iter_def = 100
_f_reltol_def = 1e-4
_g_reltol_def = 1e-3
_g_L∞tol_def = 1e3
_f_reltol_def_s = 0
_g_L∞tol_def_s = 1e-8
"""
AdamSubWorkspace
Holds a set of model parameters and the ADAM optimizer and functions used to optimize them
"""
struct AdamSubWorkspace{T}
"Model parameters to optimize"
θ::T
"Adam optimizer parameters"
opt#::Adam
"Optimization state"
as::AdamState
"Loss function"
l::Function
"Loss and gradient function"
gl::Function
function AdamSubWorkspace(θ::T, opt, as, l, gl) where T
@assert typeof(l(θ)) <: Real
return new{T}(θ, opt, as, l, gl)
end
end
function AdamSubWorkspace(θ, l::Function)
gl = ∇(l; get_output=true)
gl(θ) # compile it
return AdamSubWorkspace(θ, Adams(θ), AdamState(), l, gl)
end
"""
update!(aws; careful_first_step=true, speed_up=false)
Perform an ADAM optimization step for the model parameters in `aws`
"""
function update!(aws::AdamSubWorkspace; careful_first_step::Bool=true, speed_up::Bool=false)
val, Δ = aws.gl(aws.θ)
Δ = only(Δ)
AdamState!(aws.as, val.val, Δ)
# if you want to make sure the learning rate doesn't start too big
if careful_first_step && aws.as.iter==1
first_iterate!(aws.l, val.val, aws.θ, aws.θ, Δ, aws.opt)
# if you want to make sure the learning rate isn't too small (much more dangerous)
elseif speed_up && (aws.as.iter > 10 && aws.as.iter%20==5)
speed_up_iterate!(aws.l, aws.θ, aws.θ, Δ, aws.opt)
else
iterate!(aws.θ, Δ, aws.opt)
end
end
"""
first_iterate!(l, l0, θs, θ, ∇θ, opt; ind=[], verbose=false)
Perform an ADAM optimization step based on the contents of `opt` on `θ` and decreases the learning rate to ensure the loss actually decreases
"""
function first_iterate!(l::Function, l0::Real, θs::Vector{<:AbstractArray}, θ::AbstractArray{Float64}, ∇θ::AbstractArray{Float64}, opt::Adam; ind=[], verbose::Bool=false)
β1=opt.β1; β2=opt.β2; ϵ=opt.ϵ; β1_acc=opt.β1_acc; β2_acc=opt.β2_acc; m=opt.m; v=opt.v
one_minus_β1 = 1.0 - β1
one_minus_β2 = 1.0 - β2
one_minus_β1_acc = 1 - β1_acc
one_minus_β2_acc = 1 - β2_acc
# the matrix and dotted version is slower
θ_step = Array{Float64}(undef, size(m))
@inbounds for n in eachindex(θ)
m[n] = β1 * m[n] + one_minus_β1 * ∇θ[n]
v[n] = β2 * v[n] + one_minus_β2 * ∇θ[n]^2
m̂ = m[n] / one_minus_β1_acc
v̂ = v[n] / one_minus_β2_acc
θ_step[n] = m̂ / (sqrt(v̂) + ϵ)
end
β1_acc *= β1
β2_acc *= β2
θ .-= opt.α .* θ_step
# keep reducing `opt.α` until `l1` is less than `l0`
l1 = l(θs)
factor = 1
while l1 > l0
factor *= 2
opt.α /= 2
θ .+= opt.α * θ_step
l1 = l(θs)
end
if verbose && factor > 1; println("shrunk α$ind by a factor of $factor") end
end
function first_iterate!(l::Function, l0::Real, θs_unchanging::Vector{<:AbstractArray}, θs::Vector{<:AbstractArray}, ∇θs::Vector{<:AbstractArray}, opts::Vector; ind=Int[], kwargs...)
@assert length(θs) == length(∇θs) == length(opts)
@inbounds for i in eachindex(θs)
first_iterate!(l, l0, θs_unchanging, θs[i], ∇θs[i], opts[i]; ind=append!(copy(ind),[i]), kwargs...)
end
end
"""
speed_up_iterate!(l, θs, θ, ∇θ, opt; ind=[], verbose=false)
Perform an ADAM optimization step based on the contents of `opt` on `θ` and increases the learning rate to attempt to speed up the optimization
"""
function speed_up_iterate!(l::Function, θs::Vector{<:AbstractArray}, θ::AbstractArray{Float64}, ∇θ::AbstractArray{Float64}, opt::Adam; ind=[], verbose::Bool=false)
β1=opt.β1; β2=opt.β2; ϵ=opt.ϵ; β1_acc=opt.β1_acc; β2_acc=opt.β2_acc; m=opt.m; v=opt.v
one_minus_β1 = 1.0 - β1
one_minus_β2 = 1.0 - β2
one_minus_β1_acc = 1 - β1_acc
one_minus_β2_acc = 1 - β2_acc
# the matrix and dotted version is slower
θ_step = Array{Float64}(undef, size(m))
@inbounds for n in eachindex(θ)
m[n] = β1 * m[n] + one_minus_β1 * ∇θ[n]
v[n] = β2 * v[n] + one_minus_β2 * ∇θ[n]^2
m̂ = m[n] / one_minus_β1_acc
v̂ = v[n] / one_minus_β2_acc
θ_step[n] = m̂ / (sqrt(v̂) + ϵ)
end
β1_acc *= β1
β2_acc *= β2
θ .-= opt.α .* θ_step
l1 = l(θs)
θ .-= opt.α .* θ_step
# keep increasing `opt.α` while `l2` is still lower than `l1`
l2 = l(θs)
factor = 1
while l1 > l2
factor *= 2
opt.α *= 2
θ .-= opt.α * θ_step
l1 = l2
l2 = l(θs)
end
θ .+= opt.α .* θ_step
if verbose && factor > 1; println("increased α$ind by a factor of $factor") end
end
function speed_up_iterate!(l::Function, θs_unchanging::Vector{<:AbstractArray}, θs::Vector{<:AbstractArray}, ∇θs::Vector{<:AbstractArray}, opts::Vector; ind=Int[], kwargs...)
@assert length(θs) == length(∇θs) == length(opts)
@inbounds for i in eachindex(θs)
speed_up_iterate!(l, θs_unchanging, θs[i], ∇θs[i], opts[i]; ind=append!(copy(ind),[i]), kwargs...)
end
end
"""
check_converged(as, f_reltol, g_reltol, g_L∞tol)
Check to see if the Adam optimization has coverged based on the change in loss or its gradient
"""
function check_converged(as::AdamState, f_reltol::Real, g_reltol::Real, g_L∞tol::Real)
as.ℓ > 0 ? δ_ℓ = as.δ_ℓ : δ_ℓ = 1 / as.δ_ℓ # further reductions in negative cost functions are good!
return ((δ_ℓ > (1 - f_reltol)) && (max(as.δ_L2_Δ,1/as.δ_L2_Δ) < (1+abs(g_reltol)))) || (as.L∞_Δ < g_L∞tol)
end
check_converged(as::AdamState, iter::Int, f_reltol::Real, g_reltol::Real, g_L∞tol::Real) = (as.iter > iter) || check_converged(as, f_reltol, g_reltol, g_L∞tol)
"""
train_SubModel!(aws; iter=_iter_def, f_reltol=_f_reltol_def, g_reltol=_g_reltol_def, g_L∞tol=_g_L∞tol_def, cb=(as::AdamState)->(), careful_first_step=true, speed_up=false, kwargs...)
Train the model parameters in `aws` for up to `iter` Adam iterations until it converges based on `check_converged()`
"""
function train_SubModel!(aws::AdamSubWorkspace; iter=_iter_def, f_reltol = _f_reltol_def, g_reltol = _g_reltol_def, g_L∞tol = _g_L∞tol_def, cb::Function=(as::AdamState)->(), careful_first_step::Bool=true, speed_up::Bool=false, kwargs...)
converged = false # check_converged(aws.as, iter, f_tol, g_tol)
while !converged
update!(aws; careful_first_step=careful_first_step, speed_up=speed_up)
cb(aws.as)
converged = check_converged(aws.as, iter, f_reltol, g_reltol, g_L∞tol)
end
converged = check_converged(aws.as, f_reltol, g_reltol, g_L∞tol)
# converged ? println("Converged") : println("Max Iters Reached")
return converged
end
"""
scale_α_helper!(opt, α_ratio, θ, α, scale_α)
Optionally scale `opt.α` based on the amplitudes in `θ`
"""
function scale_α_helper!(opt::Adam, α_ratio::Real, θ::AbstractVecOrMat, α::Real, scale_α::Bool)
scale_α ? opt.α = α_ratio * rel_step_size(θ) : opt.α = α
end
function scale_α_helper!(opts::Vector, α_ratio::Real, θs, α::Real, scale_α::Bool)
@inbounds for i in eachindex(opts)
scale_α_helper!(opts[i], α_ratio, θs[i], α, scale_α)
end
end
rel_step_size(θ::AbstractVecOrMat) = sqrt(mean(abs2, θ))
_scale_α_def = false
"""
TotalWorkspace
A workspace to optimize all of the parameters in a SSOF model and data it is to be optimized on
Uses our custom implementation of ADAM
"""
struct TotalWorkspace <: AdamWorkspace
"Optimization workspace for all model parameters"
total::AdamSubWorkspace
"SSOF model"
om::OrderModel
"SSOF model output"
o::Output
"pre-formatted SSOF data"
d::Data
"Whether or not the templates and features should be fit"
only_s::Bool
end
function TotalWorkspace(o::Output, om::OrderModel, d::Data; only_s::Bool=false, α::Real=α, scale_α::Bool=_scale_α_def)
l_total, l_total_s = loss_funcs_total(o, om, d)
α_ratio = α * sqrt(length(om.tel.lm.μ)) # = α / rel_step_size(om.tel.lm.M) assuming M starts as L2 normalized basis vectors. Need to use this instead because TemplateModels don't have basis vectors
is_tel_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.tel)
is_star_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.star)
typeof(om) <: OrderModelDPCA ? rvs = om.rv.lm.s : rvs = om.rv
if only_s
if is_tel_time_variable
if is_star_time_variable
total = AdamSubWorkspace([om.tel.lm.s, om.star.lm.s, rvs], l_total_s)
else
total = AdamSubWorkspace([om.tel.lm.s, rvs], l_total_s)
end
elseif is_star_time_variable
total = AdamSubWorkspace([om.star.lm.s, rvs], l_total_s)
else
total = AdamSubWorkspace([rvs], l_total_s)
end
else
total = AdamSubWorkspace([vec(om.tel.lm), vec(om.star.lm), rvs], l_total)
end
if is_tel_time_variable || is_star_time_variable
scale_α_helper!(total.opt[1:(is_tel_time_variable+is_star_time_variable)], α_ratio, total.θ, α, scale_α)
end
scale_α_helper!(total.opt[end], α_ratio, total.θ[end], α, true)
return TotalWorkspace(total, om, o, d, only_s)
end
TotalWorkspace(om::OrderModel, d::Data, inds::AbstractVecOrMat; kwargs...) =
TotalWorkspace(om(inds), d(inds); kwargs...)
TotalWorkspace(om::OrderModel, d::Data; kwargs...) =
TotalWorkspace(Output(om, d), om, d; kwargs...)
Base.copy(mws::TotalWorkspace) = TotalWorkspace(copy(mws.om), mws.d)
"""
FrozenTelWorkspace
A workspace to optimize all of the parameters in a SSOF model (except for the tellruc template and features) and data it is to be optimized on
"""
struct FrozenTelWorkspace <: AdamWorkspace
"Optimization workspace for (nearly) all model parameters"
total::AdamSubWorkspace
"SSOF model"
om::OrderModel
"SSOF model output"
o::Output
"pre-formatted SSOF data"
d::Data
"Whether or not the templates and features should be fit"
only_s::Bool
end
function FrozenTelWorkspace(o::Output, om::OrderModel, d::Data; only_s::Bool=false, α::Real=α, scale_α::Bool=_scale_α_def)
l_frozen_tel, l_frozen_tel_s = loss_funcs_frozen_tel(o, om, d)
α_ratio = α * sqrt(length(om.tel.lm.μ)) # = α / rel_step_size(om.tel.lm.M) assuming M starts as L2 normalized basis vectors. Need to use this instead because TemplateModels don't have basis vectors
is_tel_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.tel)
is_star_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.star)
typeof(om) <: OrderModelDPCA ? rvs = om.rv.lm.s : rvs = om.rv
if only_s
if is_tel_time_variable
if is_star_time_variable
total = AdamSubWorkspace([om.tel.lm.s, om.star.lm.s, rvs], l_frozen_tel_s)
else
total = AdamSubWorkspace([om.tel.lm.s, rvs], l_frozen_tel_s)
end
elseif is_star_time_variable
total = AdamSubWorkspace([om.star.lm.s, rvs], l_frozen_tel_s)
else
total = AdamSubWorkspace([rvs], l_frozen_tel_s)
end
else
is_tel_time_variable ?
total = AdamSubWorkspace([om.tel.lm.s, vec(om.star.lm), rvs], l_frozen_tel) :
total = AdamSubWorkspace([vec(om.star.lm), rvs], l_frozen_tel)
end
if is_tel_time_variable || is_star_time_variable
scale_α_helper!(total.opt[1:(is_tel_time_variable+is_star_time_variable)], α_ratio, total.θ, α, scale_α)
end
scale_α_helper!(total.opt[end], α_ratio, total.θ[end], α, true)
rm_dict!(om.reg_tel)
return FrozenTelWorkspace(total, om, o, d, only_s)
end
FrozenTelWorkspace(om::OrderModel, d::Data, inds::AbstractVecOrMat; kwargs...) =
FrozenTelWorkspace(om(inds), d(inds); kwargs...)
FrozenTelWorkspace(om::OrderModel, d::Data; kwargs...) =
FrozenTelWorkspace(Output(om, d), om, d; kwargs...)
"""
ModelWorkspace(model, data)
Create a workspace for optimizing `model` with `data`
Creates a FrozenTelWorkspace if the model has no telluric feature vectors and an empty telluric template
"""
function ModelWorkspace(model::OrderModel, data::Data)
if no_tellurics(model)
return FrozenTelWorkspace(model, data)
else
return TotalWorkspace(model, data)
end
end
"""
train_OrderModel!(mws; ignore_regularization=false, verbose=_verbose_def, shift_scores=true, μ_positive=true, tel_μ_lt1=false, rm_doppler=true, kwargs...)
Train the model in `mws` with some optional modifications to the optimization (ignore_regularization, shift_score, μ_positive, tel_μ_lt1, rm_doppler)
"""
function train_OrderModel!(mws::AdamWorkspace; ignore_regularization::Bool=false, verbose::Bool=_verbose_def, shift_scores::Bool=true, μ_positive::Bool=true, tel_μ_lt1::Bool=false, rm_doppler::Bool=true, kwargs...)
if rm_doppler; dop_comp_holder = Array{Float64}(undef, length(mws.om.star.lm.μ)) end
update_interpolation_locations!(mws)
# optionally ignore the regularization in `mws.om`
if ignore_regularization
reg_tel_holder = copy(mws.om.reg_tel)
reg_star_holder = copy(mws.om.reg_star)
rm_regularization!(mws.om)
end
# create a callback function that runs after every iteration
function cb(as::AdamState)
# optionally shift the score means to be near 0
if shift_scores
if !(typeof(mws) <: FrozenTelWorkspace)
remove_lm_score_means!(mws.om.tel.lm; prop=0.2)
end
if typeof(mws.om) <: OrderModelWobble
remove_lm_score_means!(mws.om.star.lm; prop=0.2)
end
end
# optionally make the templates always positive
if μ_positive
mws.om.tel.lm.μ[mws.om.tel.lm.μ .< 1e-10] .= 1e-10
mws.om.star.lm.μ[mws.om.star.lm.μ .< 1e-10] .= 1e-10
end
# optionally make the telluric template always less than 1
if tel_μ_lt1
mws.om.tel.lm.μ[mws.om.tel.lm.μ .> 1] .= 1
end
# optionally make the stellar feature vectors orthagonal to a doppler shift
if rm_doppler && is_time_variable(mws.om.star.lm)
if mws.om.star.lm.log
dop_comp_holder[:] = doppler_component_log(mws.om.star.λ, mws.om.star.lm.μ)
else
dop_comp_holder[:] = doppler_component(mws.om.star.λ, mws.om.star.lm.μ)
end
for i in axes(mws.om.star.lm.M, 2)
EMPCA._reorthogonalize_no_renorm!(view(mws.om.star.lm.M, :, i), dop_comp_holder)
end
end
# make sure the interpolation locations are still correct
if as.iter % 10 == 9
update_interpolation_locations!(mws)
end
if verbose; println(as) end
end
# train the model and update `mws.o`
result = train_SubModel!(mws.total; cb=cb, kwargs...)
mws.total.as.iter = 0
Output!(mws)
# reset the regularization
if ignore_regularization
copy_dict!(mws.om.reg_tel, reg_tel_holder)
copy_dict!(mws.om.reg_star, reg_star_holder)
end
return result
end
Output!(mws::ModelWorkspace) = Output!(mws.o, mws.om, mws.d)
## Optim Versions
"""
opt_funcs(loss, pars)
Create an objective object for Optim from `loss` that uses a flattened verison of `pars`
"""
function opt_funcs(loss::Function, pars::AbstractVecOrMat)
flat_initial_params, unflatten = flatten(pars) # unflatten returns Vector of untransformed params
f = loss ∘ unflatten
g_nabla = ∇(loss)
g_val_nabla = ∇(loss; get_output=true)
g_nabla(pars) # compile it
g_val_nabla(pars) # compile it
function g!(G, θ)
G[:], _ = flatten(g_nabla(unflatten(θ)))
end
function fg_obj!(G, θ)
l, g = g_val_nabla(unflatten(θ))
G[:], _ = flatten(g)
return l.val
end
return flat_initial_params, OnceDifferentiable(f, g!, fg_obj!, flat_initial_params), unflatten, g_nabla, g_val_nabla
end
"""
OptimSubWorkspace
Holds a set of model parameters and the Optim optimizer and functions used to optimize them
"""
struct OptimSubWorkspace
"Model parameters to optimize"
θ::AbstractVecOrMat
"Optim objective object"
obj::OnceDifferentiable
"The first order optimizer to use"
opt::Optim.FirstOrderOptimizer
"Flattened version of `θ`"
p0::Vector
"Function to convert `p0` to `θ`"
unflatten::Union{Function,DataType}
end
function OptimSubWorkspace(θ::AbstractVecOrMat, loss::Function; use_cg::Bool=true)
p0, obj, unflatten, _, _ = opt_funcs(loss, θ)
# opt = LBFGS(alphaguess = LineSearches.InitialHagerZhang(α0=NaN))
# use_cg ? opt = ConjugateGradient() : opt = LBFGS()
opt = LBFGS()
# initial_state(method::LBFGS, ...) doesn't use the options for anything
return OptimSubWorkspace(θ, obj, opt, p0, unflatten)
end
"""
OptimTelStarWorkspace
A workspace to go back and forth optimizing the telluric and stellar parameters then the RVs in a SSOF model and data it is to be optimized on
Uses methods in Optim
"""
struct OptimTelStarWorkspace <: OptimWorkspace
"Optimization workspace for stellar and telluric model parameters"
telstar::OptimSubWorkspace
"Optimization workspace for RV model parameters"
rv::OptimSubWorkspace
"SSOF model"
om::OrderModel
"SSOF model output"
o::Output
"pre-formatted SSOF data"
d::Data
"Whether or not the templates and features should be fit"
only_s::Bool
end
function OptimTelStarWorkspace(om::OrderModel, o::Output, d::Data; return_loss_f::Bool=false, only_s::Bool=false)
loss_telstar, loss_telstar_s, loss_rv = loss_funcs_telstar(o, om, d)
typeof(om) <: OrderModelDPCA ?
rv = OptimSubWorkspace(om.rv.lm.s, loss_rv; use_cg=true) :
rv = OptimSubWorkspace(om.rv, loss_rv; use_cg=true)
is_tel_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.tel)
is_star_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.star)
if only_s
if is_tel_time_variable
if is_star_time_variable
telstar = OptimSubWorkspace([om.tel.lm.s, om.star.lm.s], loss_telstar_s; use_cg=!only_s)
else
telstar = OptimSubWorkspace([om.tel.lm.s], loss_telstar_s; use_cg=!only_s)
end
elseif is_star_time_variable
telstar = OptimSubWorkspace([om.star.lm.s], loss_telstar_s; use_cg=!only_s)
else
@error "This model has no time variability, so a workspace that only changes scores makes no sense"
end
else
telstar = OptimSubWorkspace([vec(om.tel.lm), vec(om.star.lm)], loss_telstar; use_cg=!only_s)
end
return OptimTelStarWorkspace(telstar, rv, om, o, d, only_s)
end
OptimTelStarWorkspace(om::OrderModel, d::Data, inds::AbstractVecOrMat; kwargs...) =
OptimTelStarWorkspace(om(inds), d(inds); kwargs...)
OptimTelStarWorkspace(om::OrderModel, d::Data; kwargs...) =
OptimTelStarWorkspace(om, Output(om, d), d; kwargs...)
"""
OptimTotalWorkspace
A workspace to optimize all of the parameters in a SSOF model and data it is to be optimized on
Uses methods in Optim
"""
struct OptimTotalWorkspace <: OptimWorkspace
"Optimization workspace for all model parameters"
total::OptimSubWorkspace
"SSOF model"
om::OrderModel
"SSOF model output"
o::Output
"pre-formatted SSOF data"
d::Data
"Whether or not the templates and features should be fit"
only_s::Bool
end
function OptimTotalWorkspace(om::OrderModel, o::Output, d::Data; return_loss_f::Bool=false, only_s::Bool=false)
l_total, l_total_s = loss_funcs_total(o, om, d)
typeof(om) <: OrderModelDPCA ? rvs = om.rv.lm.s : rvs = om.rv
is_tel_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.tel)
is_star_time_variable = is_time_variable(om.star)
if only_s
if is_tel_time_variable
if is_star_time_variable
total = OptimSubWorkspace([om.tel.lm.s, om.star.lm.s, rvs], l_total_s; use_cg=true)
else
total = OptimSubWorkspace([om.tel.lm.s, rvs], l_total_s; use_cg=true)
end
elseif is_star_time_variable
total = OptimSubWorkspace([om.star.lm.s, rvs], l_total_s; use_cg=true)
else
total = OptimSubWorkspace([rvs], l_total_s; use_cg=true)
end
else
total = OptimSubWorkspace([vec(om.tel.lm), vec(om.star.lm), rvs], l_total)
end
return OptimTotalWorkspace(total, om, o, d, only_s)
end
OptimTotalWorkspace(om::OrderModel, d::Data, inds::AbstractVecOrMat; kwargs...) =
OptimTotalWorkspace(om(inds), d(inds); kwargs...)
OptimTotalWorkspace(om::OrderModel, d::Data; kwargs...) =
OptimTotalWorkspace(om, Output(om, d), d; kwargs...)
"""
_OSW_optimize!(osw, options)
Optimize the model in `osw`
"""
function _OSW_optimize!(osw::OptimSubWorkspace, options::Optim.Options)
result = Optim.optimize(osw.obj, osw.p0, osw.opt, options)
osw.p0[:] = result.minimizer
return result
end
function optim_print(x::OptimizationState)
println()
if x.iteration > 0
println("Iter: ", x.iteration)
println("Time: ", x.metadata["time"], " s")
println("ℓ: ", x.value)
println("L∞(∇): ", x.g_norm)
println()
end
# ends optimization if true
return false
end
function optim_cb_f(; verbose::Bool=true)
if verbose
return (x::OptimizationState) -> optim_print(x::OptimizationState)
else
return (x::OptimizationState) -> false
end
end
"""
train_OrderModel!(ow::OptimTelStarWorkspace; verbose=_verbose_def, iter=_iter_def, f_tol=_f_reltol_def, g_tol=_g_L∞tol_def, train_telstar=true, ignore_regularization=false, μ_positive=false, careful_first_step=true, speed_up=false, kwargs...)
Train the model in `ow`, training the telluric and stellar parameters, then the RVs
"""
function train_OrderModel!(ow::OptimTelStarWorkspace; verbose::Bool=_verbose_def, iter::Int=_iter_def, f_tol::Real=_f_reltol_def, g_tol::Real=_g_L∞tol_def, train_telstar::Bool=true, ignore_regularization::Bool=false, μ_positive::Bool=false, careful_first_step::Bool=true, speed_up::Bool=false, kwargs...)
# `μ_positive`, `careful_first_step`, and `speed_up` are only included to prevent errors and do nothing
optim_cb = optim_cb_f(; verbose=verbose)
# optionally ignore the regularization in `ow.om`
if ignore_regularization
reg_tel_holder = copy(ow.om.reg_tel)
reg_star_holder = copy(ow.om.reg_star)
rm_regularization!(ow.om)
end
# train the telluric and stellar parameters if desired
if train_telstar
options = Optim.Options(;iterations=iter, f_tol=f_tol, g_tol=g_tol, callback=optim_cb, kwargs...)
# optimize tellurics and star
result_telstar = _OSW_optimize!(ow.telstar, options)
lm_vec = ow.telstar.unflatten(ow.telstar.p0)
if ow.only_s
if is_time_variable(ow.om.tel)
ow.om.tel.lm.s[:] = lm_vec[1]
if is_time_variable(ow.om.star)
ow.om.star.lm.s[:] = lm_vec[2]
end
else
ow.om.star.lm.s[:] = lm_vec[1]
end
else
copy_to_LinearModel!(ow.om.tel.lm, lm_vec[1])
copy_to_LinearModel!(ow.om.star.lm, lm_vec[2])
end
ow.o.star .= star_model(ow.om)
ow.o.tel .= tel_model(ow.om)
end
# optimize RVs
result_rv = train_rvs_optim!(ow, optim_cb; f_tol=f_tol, g_tol=g_tol, kwargs...)
if typeof(ow.om) <: OrderModelDPCA
ow.o.rv .= rv_model(ow.om)
else
ow.o.star .= star_model(ow.om)
end
recalc_total!(ow.o, ow.d)
if ignore_regularization
copy_dict!(ow.om.reg_tel, reg_tel_holder)
copy_dict!(ow.om.reg_star, reg_star_holder)
end
return result_telstar, result_rv
end
"""
train_OrderModel!(ow::OptimTelStarWorkspace; verbose=_verbose_def, iter=_iter_def, f_tol=_f_reltol_def, g_tol=_g_L∞tol_def, train_telstar=true, ignore_regularization=false, μ_positive=false, careful_first_step=true, speed_up=false, kwargs...)
Train the model in `ow`, training the telluric and stellar parameters, then the RVs
"""
function train_OrderModel!(ow::OptimTotalWorkspace; verbose::Bool=_verbose_def, iter::Int=_iter_def, f_tol::Real=_f_reltol_def, g_tol::Real=_g_L∞tol_def, ignore_regularization::Bool=false, μ_positive::Bool=false, careful_first_step::Bool=true, speed_up::Bool=false, kwargs...)
# `μ_positive`, `careful_first_step`, and `speed_up` are only included to prevent errors and do nothing
optim_cb = optim_cb_f(; verbose=verbose)
# optionally ignore the regularization in `ow.om`
if ignore_regularization
reg_tel_holder = copy(ow.om.reg_tel)
reg_star_holder = copy(ow.om.reg_star)
rm_regularization!(ow.om)
end
options = Optim.Options(;iterations=iter, f_tol=f_tol, g_tol=g_tol, callback=optim_cb, kwargs...)
result_total = _OSW_optimize!(ow.total, options)
lm_vec = ow.total.unflatten(ow.total.p0)
is_tel_time_variable = is_time_variable(ow.om.tel)
is_star_time_variable = is_time_variable(ow.om.star)
if ow.only_s
if is_tel_time_variable
ow.om.tel.lm.s[:] = lm_vec[1]
if is_star_time_variable
ow.om.star.lm.s[:] = lm_vec[2]
end
else
ow.om.star.lm.s[:] = lm_vec[1]
end
if typeof(ow.om) <: OrderModelDPCA
ow.om.rv.lm.s[:] = lm_vec[1+is_tel_time_variable+is_star_time_variable]
else
ow.om.rv[:] = lm_vec[1+is_tel_time_variable+is_star_time_variable]
end
else
copy_to_LinearModel!(ow.om.tel.lm, lm_vec[1])
copy_to_LinearModel!(ow.om.star.lm, lm_vec[2])
if typeof(ow.om) <: OrderModelDPCA
ow.om.rv.lm.s[:] = lm_vec[3]
else
ow.om.rv[:] = lm_vec[3]
end
end
ow.o.tel .= tel_model(ow.om)
ow.o.star .= star_model(ow.om)
if typeof(ow.om) <: OrderModelDPCA; ow.o.rv .= rv_model(ow.om) end
recalc_total!(ow.o, ow.d)
if ignore_regularization
copy_dict!(ow.om.reg_tel, reg_tel_holder)
copy_dict!(ow.om.reg_star, reg_star_holder)
end
return result_total
end
"""
train_rvs_optim!(rv_ws, rv, optim_cb; g_tol=_g_L∞tol_def_s, f_tol=_f_reltol_def_s, iter=_iter_def, ignore_regularization=false, μ_positive=false, kwargs...)
Train the RVs from the `rv_ws` with Optim
"""
function train_rvs_optim!(rv_ws::OptimSubWorkspace, rv::AbstractVector, optim_cb::Function; g_tol::Real=_g_L∞tol_def_s, f_tol::Real=_f_reltol_def_s, iter::Int=_iter_def, ignore_regularization::Bool=false, μ_positive::Bool=false, kwargs...)
# `μ_positive` and `ignore_regularization` are only included to prevent errors and do nothing
options = Optim.Options(; callback=optim_cb, g_tol=g_tol, f_tol=f_tol, iterations=iter, kwargs...)
result_rv = _OSW_optimize!(rv_ws, options)
rv[:] = rv_ws.unflatten(rv_ws.p0)
return result_rv
end
# same as above but for DPCA models
function train_rvs_optim!(rv_ws::OptimSubWorkspace, rv::Submodel, star::Submodel, optim_cb::Function; g_tol::Real=_g_L∞tol_def_s, f_tol::Real=_f_reltol_def_s, iter::Int=_iter_def, kwargs...)
options = Optim.Options(; callback=optim_cb, g_tol=g_tol, f_tol=f_tol, iterations=iter, kwargs...)
rv.lm.M .= doppler_component(star.λ, star.lm.μ)
result_rv = _OSW_optimize!(rv_ws, options)
rv.lm.s[:] = rv_ws.unflatten(rv_ws.p0)
return result_rv
end
train_rvs_optim!(ow::OptimTelStarWorkspace, optim_cb::Function; kwargs...) =
typeof(ow.om) <: OrderModelDPCA ?
train_rvs_optim!(ow.rv, ow.om.rv, ow.om.star, optim_cb; kwargs...) :
train_rvs_optim!(ow.rv, ow.om.rv, optim_cb; kwargs...)
"""
finalize_scores_setup(mws; verbose=_verbose_def, f_tol=_f_reltol_def_s, g_tol=_g_L∞tol_def_s, careful_first_step=true, speed_up=false, kwargs...)
Create a function that optimizes the model scores with Optim
"""
function finalize_scores_setup(mws::ModelWorkspace; verbose::Bool=_verbose_def, f_tol::Real=_f_reltol_def_s, g_tol::Real=_g_L∞tol_def_s, careful_first_step::Bool=true, speed_up::Bool=false, kwargs...)
if is_time_variable(mws.om.tel) || is_time_variable(mws.om.star)
mws_s = OptimTotalWorkspace(mws.om, mws.d; only_s=true) # does not converge reliably
# mws_s = OptimTelStarWorkspace(mws.om, mws.d; only_s=true)
score_trainer() = train_OrderModel!(mws_s; verbose=verbose, f_tol=f_tol, g_tol=g_tol, kwargs...)
return score_trainer
end
optim_cb=optim_cb_f(; verbose=verbose)
loss_rv(rv) = _loss(mws; rv=rv, use_var_s=true)
return _finalize_scores_setup(mws, mws.om, loss_rv, optim_cb; f_tol=f_tol, g_tol=g_tol, kwargs...)
end
function _finalize_scores_setup(mws::ModelWorkspace, om::OrderModelDPCA, loss_rv::Function, optim_cb::Function; kwargs...)
rv_ws = OptimSubWorkspace(mws.om.rv.lm.s, loss_rv; use_cg=true)
rv_trainer() = train_rvs_optim!(rv_ws, mws.om.rv, mws.om.star, optim_cb; kwargs...)
return rv_trainer
end
function _finalize_scores_setup(mws::ModelWorkspace, om::OrderModelWobble, loss_rv::Function, optim_cb::Function; kwargs...)
rv_ws = OptimSubWorkspace(mws.om.rv, loss_rv; use_cg=true)
rv_trainer() = train_rvs_optim!(rv_ws, mws.om.rv, optim_cb; kwargs...)
return rv_trainer
end
"""
finalize_scores!(score_trainer, mws)
Run `score_trainer` and update the output in `mws`
"""
function finalize_scores!(score_trainer::Function, mws::ModelWorkspace)
result = score_trainer()
Output!(mws)
return result
end
"""
finalize_scores!(mws; kwargs...)
Optimize the scores in `mws`
"""
function finalize_scores!(mws::ModelWorkspace; kwargs...)
score_trainer = finalize_scores_setup(mws; kwargs...)
return finalize_scores!(score_trainer, mws)
end
is_time_variable(lm::LinearModel) = !(typeof(lm) <: TemplateModel)
is_time_variable(sm::Submodel) = is_time_variable(sm.lm)
"""
update_interpolation_locations!(om, d; use_mean=false)
Make sure the linear iterpolation locations for going from the stellar model to the data are correct as the RVs change
"""
function update_interpolation_locations!(om::OrderModel, d::Data; use_mean::Bool=false)
# TODO: do this for undersamp_interp_helper as well
if typeof(om) <: OrderModelWobble
if use_mean
StellarInterpolationHelper!(om.b2o,
om.star.log_λ,
om.bary_rvs .+ mean(om.rv),
d.log_λ_obs)
else
StellarInterpolationHelper!(om.b2o,
om.star.log_λ,
om.bary_rvs + om.rv,
d.log_λ_obs)
end
end
end
update_interpolation_locations!(mws::ModelWorkspace; kwargs...) = update_interpolation_locations!(mws.om, mws.d; kwargs...)
"""
improve_model!(mws; verbose=true, kwargs...)
Train the model in `mws` with an extra step to ensure we are at a local maximum for the scores and RVs
"""
function improve_model!(mws::ModelWorkspace; verbose::Bool=true, kwargs...)
train_OrderModel!(mws; verbose=verbose, kwargs...) # 120s
results = finalize_scores!(mws; verbose=verbose, kwargs...)
return results
end
"""
improve_initial_model!(mws; careful_first_step=true, speed_up=false, kwargs...)
Train the model in `mws` with an extra step to ensure we are at a local maximum for the scores and RVs
Defaults to taking a careful first step
"""
improve_initial_model!(mws::ModelWorkspace; careful_first_step::Bool=true, speed_up::Bool=false, kwargs...) = improve_model!(mws; verbose=false, ignore_regularization=true, μ_positive=true, careful_first_step=careful_first_step, speed_up=speed_up, kwargs...)
"""
calculate_initial_model(data; kwargs...)
Find a SSOF model for a given dataset, `data`.
Defaults to returning the AIC-minimum model
# Optional arguments
- `instrument::String="None"`: The name of the instrument(s) the data was taken from. For bookkeeping
- `desired_order::Int=0`: What order (if any) the data was taken from. For bookkeeping
- `star::String="None"`: The name of the star the data was taken from. For bookkeeping
- `times::AbstractVector=1:size(data.flux, 2)`: The list of times (in days). Used to calculate intra-night RMS
- `μ_min::Real=0`: Set the minimum flux value for the output of `make_template()`
- `μ_max::Real=Inf`: Set the maximum flux value for the output of `make_template()`
- `use_mean::Bool=true`: Whether to use the mean or median for `make_template()`
- `stop_early::Bool=false`: Whether to stop the model search the first time adding a component increases the AIC
- `remove_reciprocal_continuum::Bool=false`: Whether you should attempt to remove places where the telluric template and stellar template are opposing each other (i.e. where continuum goes up in one and down in the other)
- `return_full_path::Bool=false`: Whether to return all of the searched models and metrics
- `max_n_tel::Int=5`: The maximum amount of telluric feature vectors to look for
- `max_n_star::Int=5`: The maximum amount of stellar feature vectors to look for
- `use_all_comps::Bool=false`: Whether to use all feature vectors, regardless of AIC
- `careful_first_step::Bool=true`: Whether to shrink the learning rates until the loss improves on the first iteration
- `speed_up::Bool=false`: Whether to inflate the learning rates until the loss is no longer improving throughout the optimization
- `log_λ_gp_star::Real=1/SOAP_gp_params.λ`: The log λ lengthscale of the stellar regularization GP
- `log_λ_gp_tel::Real=1/LSF_gp_params.λ`: The log λ lengthscale of the telluric regularization GP
- `kwargs...`: kwargs passed to `OrderModel` constructor
"""
function calculate_initial_model(data::Data;
instrument::String="None", desired_order::Int=0, star::String="None", times::AbstractVector=1:size(data.flux, 2),
μ_min::Real=0, μ_max::Real=Inf, use_mean::Bool=true, stop_early::Bool=false,
remove_reciprocal_continuum::Bool=false, return_full_path::Bool=false,
max_n_tel::Int=5, max_n_star::Int=5, use_all_comps::Bool=false, careful_first_step::Bool=true, speed_up::Bool=false,
log_λ_gp_star::Real=1/SOAP_gp_params.λ, log_λ_gp_tel::Real=1/LSF_gp_params.λ, kwargs...)
# TODO: Make this work for OrderModelDPCA
# Get non-LSF version of `data`
d = GenericData(data)
@assert max_n_tel >= -1
@assert max_n_star >= 0
# which amounts of feature vectors to test
test_n_comp_tel = -1:max_n_tel
test_n_comp_star = 0:max_n_star
# initialize metric and model storage
aics = Inf .* ones(length(test_n_comp_tel), length(test_n_comp_star))
ℓs = -copy(aics)
bics = copy(aics)
rv_stds = copy(aics)
rv_stds_intra = copy(aics)
oms = Array{OrderModelWobble}(undef, length(test_n_comp_tel), length(test_n_comp_star))
logdet_Σ, n = ℓ_prereqs(d.var)
comp2ind(n_tel::Int, n_star::Int) = (n_tel+2, n_star+1) # converts number of components to storage matrix index
n_obs = size(d.flux, 2)
om = OrderModel(d; instrument=instrument, order=desired_order, star_str=star, n_comp_tel=max_n_tel, n_comp_star=max_n_star, log_λ_gp_star=log_λ_gp_star, log_λ_gp_tel=log_λ_gp_tel, kwargs...)
# get the stellar model wavelengths in observed frame as a function of time
star_log_λ_tel = _shift_log_λ_model(d.log_λ_obs, d.log_λ_star, om.star.log_λ)
# get the telluric model wavelengths in stellar frame as a function of time
tel_log_λ_star = _shift_log_λ_model(d.log_λ_star, d.log_λ_obs, om.tel.log_λ)
flux_star = ones(length(om.star.log_λ), n_obs)
vars_star = SOAP_gp_var .* ones(length(om.star.log_λ), n_obs)
flux_tel = ones(length(om.tel.log_λ), n_obs)
vars_tel = SOAP_gp_var .* ones(length(om.tel.log_λ), n_obs)
"Find places where the telluric and stellar continuums are reciprocals of each other"
function reciprocal_continuum_mask(continuum::AbstractVector, other_interpolated_continuum::AbstractVector; probe_depth::Real=0.02, return_cc::Bool=false)
cc = (1 .- continuum) .* (1 .- other_interpolated_continuum)
ccm = find_modes(-cc)
# find places where the continuums are opposite in sign and changing a similar amount
ccm = [i for i in ccm if ((cc[i] < -(probe_depth^2)) && (0.5 < abs(continuum[i] / other_interpolated_continuum[i]) < 2))]
mask = zeros(Bool, length(cc))
l = length(cc)
for m in ccm
i = m
while i <= l && cc[i] < 0
mask[i] = true
i += 1
end
i = m-1
while i >= 1 && cc[i] < 0
mask[i] = true
i -= 1
end
end
if return_cc
return mask, cc
end
return mask
end
reciprocal_continuum_mask(continuum::AbstractVector, other_interpolated_continuum::AbstractMatrix; kwargs...) =
reciprocal_continuum_mask(continuum, vec(mean(other_interpolated_continuum; dims=2)); kwargs...)
function remove_reciprocal_continuum!(om::OrderModel, flux_star_holder::AbstractMatrix, vars_star_holder::AbstractMatrix, flux_tel_holder::AbstractMatrix, vars_tel_holder::AbstractMatrix; use_stellar_continuum::Bool=true, kwargs...)
lm_tel = om.tel.lm
lm_star = om.star.lm
# Calculate a Rassine-like continuum for the telluric template
_, c_t, _ = calc_continuum(om.tel.λ, lm_tel.μ, ones(length(lm_tel.μ)) ./ 1000;
min_R_factor=1, smoothing_half_width=0,
stretch_factor=10., merging_threshold = 0.)
# Calculate a Rassine-like continuum for the stellar template
_, c_s, _ = calc_continuum(om.star.λ, lm_star.μ, ones(length(lm_star.μ)) ./ 1000;
min_R_factor=1,
stretch_factor=10., merging_threshold = 0.)
# interpolate the stellar continuum to the observed frame
flux_star_holder .= c_s
vars_star_holder .= SOAP_gp_var
_spectra_interp_gp!(flux_tel_holder, vars_tel_holder, om.tel.log_λ, flux_star_holder, vars_star_holder, star_log_λ_tel; gp_mean=1., λ_kernel=1/log_λ_gp_star)
# find where the continuums are reciprocal and remove the difference
m, cc = reciprocal_continuum_mask(c_t, flux_tel_holder; return_cc=true, kwargs...)
use_stellar_continuum ?
lm_tel.μ[m] .*= vec(mean(flux_tel_holder[m, :]; dims=2)) :
lm_tel.μ[m] ./= c_t[m]
did_anything = any(m)
# interpolate the telluric continuum to the stellar frame
flux_tel .= c_t
vars_tel .= SOAP_gp_var
_spectra_interp_gp!(flux_star_holder, vars_star_holder, om.star.log_λ, flux_tel_holder, vars_tel_holder, tel_log_λ_star; gp_mean=1., λ_kernel=1/log_λ_gp_star)
# find where the continuums are reciprocal and remove the difference
m, cc = reciprocal_continuum_mask(c_s, flux_star_holder; return_cc=true, kwargs...)
use_stellar_continuum ?
lm_star.μ[m] ./= c_s[m] :
lm_star.μ[m] .*= vec(mean(flux_star_holder[m, :]; dims=2))
did_anything = did_anything || any(m)
return did_anything
end
# remove the score means and flip the feature vectors
function nicer_model!(mws::ModelWorkspace)
remove_lm_score_means!(mws.om)
flip_feature_vectors!(mws.om)
mws.om.metadata[:todo][:initialized] = true
mws.om.metadata[:todo][:downsized] = true
# copy_dict!(mws.om.reg_tel, default_reg_tel)
# copy_dict!(mws.om.reg_star, default_reg_star)
end
#
function get_metrics!(mws::ModelWorkspace, i::Int, j::Int)
# # could set very small regularizations beforehand if we wanted
# for (k, v) in mws.om.reg_tel
# mws.om.reg_tel[k] = min_reg
# end
# for (k, v) in mws.om.reg_star
# mws.om.reg_star[k] = min_reg
# end
try
# improve the model
improve_initial_model!(mws; careful_first_step=careful_first_step, speed_up=speed_up, iter=50)
# if there is an LSF, do some more fitting
if mws.d != data
mws = typeof(mws)(copy(mws.om), data)
improve_initial_model!(mws; careful_first_step=careful_first_step, speed_up=speed_up, iter=30)
end
nicer_model!(mws)
# calculate metrics
k = total_length(mws)
ℓs[i,j] = ℓ(_loss(mws), logdet_Σ, n)
if isnan(ℓs[i,j]); ℓs[i,j] = -Inf end
aics[i,j] = aic(k, ℓs[i,j])
bics[i,j] = bic(k, ℓs[i,j], n)
model_rvs = rvs(mws.om)
rv_stds[i,j] = std(model_rvs)
rv_stds_intra[i,j] = intra_night_std(model_rvs, times; show_warn=false)
return mws.om
catch err
if isa(err, DomainError)
println("hit a domain error while optimizing")
nicer_model!(mws)
return mws.om
else
rethrow()
end
end
end
# stellar template model assuming no tellurics
n_tel_cur = -1
n_star_cur = 0
search_new_tel = n_tel_cur+1 <= max_n_tel
search_new_star = n_star_cur+1 <= max_n_star
oms[1,1] = downsize(om, 0, 0)
oms[1,1].tel.lm.μ .= 1
_spectra_interp_gp!(flux_star, vars_star, oms[1,1].star.log_λ, d.flux, d.var .+ SOAP_gp_var, d.log_λ_star; gp_mean=1., λ_kernel=1/log_λ_gp_star)
flux_star_no_tel = copy(flux_star)
vars_star_no_tel = copy(vars_star)
oms[1,1].star.lm.μ[:] = make_template(flux_star, vars_star; min=μ_min, max=μ_max, use_mean=use_mean)
# how good is the stellar template at modeling each pixel
dop_comp = doppler_component(oms[1,1].star.λ, oms[1,1].star.lm.μ)
# project_doppler_comp!(mws.om.rv, flux_star_no_tel .- mws.om.star.lm.μ, dop_comp, 1 ./ vars_star)
mask_low_pixels!(flux_star_no_tel, vars_star_no_tel)
mask_high_pixels!(flux_star_no_tel, vars_star_no_tel)
χ²_star = vec(sum(_χ²_loss(star_model(oms[1,1]), d); dims=2)) # TODO: could optimize before checking this
# star_template_χ² = sum(χ²_star)
# get aic for base, only stellar template model
mws = FrozenTelWorkspace(oms[1,1], d)
om_cur = get_metrics!(mws, 1, 1)
# telluric template assuming no stellar (will be overwritten later)
_om = downsize(om, 0, 0)
_om.star.lm.μ .= 1
_spectra_interp_gp!(flux_tel, vars_tel, _om.tel.log_λ, d.flux, d.var .+ SOAP_gp_var, d.log_λ_obs; gp_mean=1., λ_kernel=1/log_λ_gp_star)
_om.tel.lm.μ[:] = make_template(flux_tel, vars_tel; min=μ_min, max=μ_max, use_mean=use_mean)
# how good is the stellar telluric template at modeling each pixel
χ²_tel = vec(sum(_χ²_loss(tel_model(_om), d); dims=2)) # TODO: could optimize before checking this
om_add_star = om_cur
# get `flux_to` in the desired frame after interpolating the data dividing out the other model, `flux_from`
function interp_helper!(flux_to::AbstractMatrix, vars_to::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_to::AbstractVector,
flux_from::AbstractMatrix,
log_λ_data::AbstractMatrix; mask_extrema::Bool=true, keep_data_mask::Bool=true)
try
_spectra_interp_gp!(flux_to, vars_to, log_λ_to, d.flux ./ flux_from, d.var ./ (flux_from .^ 2), log_λ_data; gp_mean=1., keep_mask=keep_data_mask, λ_kernel=1/log_λ_gp_star)
catch err
if isa(err, DomainError)
println("was unable to interpolate using a GP from one frame to another, using linear interpolation instead")
y = d.flux ./ flux_from
v = d.var ./ (flux_from .^ 2)
for i in axes(y,2)
interpolator1 = LinearInterpolation(view(y, :, i), view(log_λ_data, :, i))
flux_to[:, i] = interpolator1.(log_λ_to)
interpolator2 = LinearInterpolation(view(v, :, i), view(log_λ_data, :, i))
vars_to[:, i] = interpolator2.(log_λ_to)
end
else
rethrow()
end
end
if mask_extrema
mask_low_pixels!(flux_to, vars_to)
mask_high_pixels!(flux_to, vars_to)
end
end
interp_to_star!(om::OrderModel; kwargs...) = interp_helper!(flux_star, vars_star, om.star.log_λ,
tel_model(om),
d.log_λ_star; kwargs...)
interp_to_tel!(om::OrderModel; kwargs...) = interp_helper!(flux_tel, vars_tel, om.tel.log_λ,
star_model(om),
d.log_λ_obs; kwargs...)
# # a version of interp helper instead gets `flux_to` in the desired frame after dividing out a GP interpolated version of the other model
# function interp_helper!(flux_to::AbstractMatrix, vars_to::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_to::AbstractVector,
# flux_from::AbstractMatrix, vars_from::AbstractMatrix, log_λ_from::AbstractMatrix,
# log_λ_data::AbstractMatrix; mask_extrema::Bool=true, keep_data_mask::Bool=true)
# vars_from .= SOAP_gp_var
# _spectra_interp_gp_div_gp!(flux_to, vars_to, log_λ_to, d.flux, d.var, log_λ_data, flux_from, vars_from, log_λ_from; keep_mask=keep_data_mask, ignore_model_uncertainty=true)
# if mask_extrema
# mask_low_pixels!(flux_to, vars_to)
# mask_high_pixels!(flux_to, vars_to)
# end
# end
# interp_to_star!(; kwargs...) = interp_helper!(flux_star, vars_star, om.star.log_λ,
# flux_tel, vars_tel, tel_log_λ_star,
# d.log_λ_star; kwargs...)
# interp_to_tel!(; kwargs...) = interp_helper!(flux_tel, vars_tel, om.tel.log_λ,
# flux_star, vars_star, star_log_λ_tel,
# d.log_λ_obs; kwargs...)
# if one wants to search for a telluric template
if search_new_tel
oms[2,1] = downsize(om, 0, 0)
oms[2,1].star.lm.μ .= 1
use_tel = χ²_star .> χ²_tel # which pixels are telluric dominated
# # modify use_tel to be more continuous
# use_tel_window = 11
# use_tel_density = 0.9
# @assert isodd(use_tel_window)
# _use_tel = χ²_star .> χ²_tel # which pixels are telluric dominated
# i = findfirst(_use_tel)
# w = floor(Int, use_tel_window/2)
# thres = floor(Int, use_tel_density * use_tel_window)
# if !isnothing(i)
# i += w+1
# j = sum(view(_use_tel, (i-w-1):min(i+w-1, length(_use_tel)))) # look at first 11 use_tel
# use_tel = zeros(Bool, length(_use_tel))
# if j > thres; use_tel[(i-w-1):min(i+w-1, length(_use_tel))] .= true end
# while (i+w+1) <= length(_use_tel)
# j += _use_tel[i+w] - _use_tel[i-w-1]
# if j > thres; use_tel[(i-w):min(i+w, length(_use_tel))] .= true end
# i += 1
# end
# end
if sum(use_tel) > 0 # if any pixels are telluric dominated
# mask out the telluric dominated pixels for partial stellar template estimation
_var = copy(d.var)
_var[use_tel, :] .= Inf
# get stellar template in portions of spectra where it is dominant
_spectra_interp_gp!(flux_star, vars_star, oms[2,1].star.log_λ, d.flux, _var .+ SOAP_gp_var, d.log_λ_star; gp_mean=1., λ_kernel=1/log_λ_gp_star)
oms[2,1].star.lm.μ[:] = make_template(flux_star, vars_star; min=μ_min, max=μ_max, use_mean=use_mean)
# get telluric template after dividing out the partial stellar template
# flux_star .= oms[2,1].star.lm.μ
interp_to_tel!(oms[2,1]; mask_extrema=false)
oms[2,1].tel.lm.μ[:] = make_template(flux_tel, vars_tel; min=μ_min, max=μ_max, use_mean=use_mean)
# get stellar template after dividing out full telluric template
# flux_tel .= oms[2,1].tel.lm.μ
interp_to_star!(oms[2,1]; mask_extrema=false)
oms[2,1].star.lm.μ[:] = make_template(flux_star, vars_star; min=μ_min, max=μ_max, use_mean=use_mean)
else
# get telluric template after diving out full stellar template we already found
fill_OrderModel!(oms[2,1], oms[1,1], 0:0, 0:0)
# flux_star .= oms[2,1].star.lm.μ
interp_to_tel!(oms[2,1]; mask_extrema=false)
oms[2,1].tel.lm.μ[:] = make_template(flux_tel, vars_tel; min=μ_min, max=μ_max, use_mean=use_mean)
end
if remove_reciprocal_continuum
remove_reciprocal_continuum!(oms[2,1], flux_star, vars_star, flux_tel, vars_tel)
end
# optimize both templates
mws = TotalWorkspace(oms[2,1], d)
# flux_tel .= oms[2,1].tel.lm.μ
# interp_to_star!(; mask_extrema=false)
# mws.om.rv .= vec(project_doppler_comp(flux_star .- mws.om.star.lm.μ, doppler_component(mws.om.star.λ, mws.om.star.lm.μ), 1 ./ vars_star))
om_add_tel = get_metrics!(mws, 2, 1)
else
om_add_tel = om_cur
end
j = comp2ind(n_tel_cur, n_star_cur)
# if we looked for a telluric template, get the aic
search_new_tel ? aic_tel = aics[comp2ind(n_tel_cur+1, n_star_cur)...] : aic_tel = Inf
# was the model with a telluric template better than the current model (just a stellar template)?
added_tel_better = aic_tel < aics[j...]
# if including the telluric template model helped, use it going forward
if added_tel_better; oms[j...] = om_cur end
n_star_next = n_star_cur
n_tel_next = n_tel_cur+added_tel_better
added_tel_better ? aic_next = aic_tel : aic_next = aics[j...]
add_comp = true
println("looking for time variability...")
# while we are looking to add new model components
while add_comp
if added_tel_better
om_cur = om_add_tel
else
om_cur = om_add_star
end
# if we added a component, print some stuff
if (n_tel_cur != n_tel_next) || (n_star_cur != n_star_next)
println("n_comp: ($n_tel_cur,$n_star_cur) -> ($n_tel_next,$n_star_next)")
println("aic : $(aics[comp2ind(n_tel_cur, n_star_cur)...]) -> $(aics[comp2ind(n_tel_next, n_star_next)...])")
println("RV std: $(rv_stds[comp2ind(n_tel_cur, n_star_cur)...]) -> $(rv_stds[comp2ind(n_tel_next, n_star_next)...])")
end
n_tel_cur, n_star_cur = n_tel_next, n_star_next
search_new_tel = n_tel_cur+1 <= max_n_tel
search_new_star = n_star_cur+1 <= max_n_star
j = comp2ind(n_tel_cur, n_star_cur)
# if we want to add a telluric component
if search_new_tel
i = comp2ind(n_tel_cur+1, n_star_cur)
oms[i...] = downsize(om, n_tel_cur+1, n_star_cur)
fill_OrderModel!(oms[i...], oms[j...], 1:n_tel_cur, 1:n_star_cur)
oms[i...].rv .= 0 # the rv is a small effect that we could just be getting wrong
# flux_star .= _eval_lm(oms[i...].star.lm)
interp_to_tel!(oms[i...])# .+ rv_to_D(oms[i...].rv)') # the rv is a small effect that we could just be getting wrong
if n_tel_cur + 1 > 0 # if we are trying to add a feature vector
EMPCA.EMPCA!(oms[i...].tel.lm, flux_tel, 1 ./ vars_tel; inds=(n_tel_cur+1):(n_tel_cur+1))
else # if we are trying to add a template
oms[i...].tel.lm.μ .= make_template(flux_tel, vars_tel; min=μ_min, max=μ_max, use_mean=use_mean)
end
# remove_reciprocal_continuum!(oms[i...], flux_star, vars_star, flux_tel, vars_tel)
mws = TotalWorkspace(oms[i...], d)
om_add_tel = get_metrics!(mws, i...)
end
# if we want to add a stellar component
if search_new_star
i = comp2ind(n_tel_cur, n_star_cur+1)
oms[i...] = downsize(om, max(0, n_tel_cur), n_star_cur+1)
fill_OrderModel!(oms[i...], oms[j...], 1:n_tel_cur, 1:n_star_cur)
dop_comp .= doppler_component(oms[i...].star.λ, oms[i...].star.lm.μ)
if n_tel_cur < 0 # if we don't have a telluric model
oms[i...].tel.lm.μ .= 1
# oms[i...].rv .=
DEMPCA!(oms[i...].star.lm, copy(flux_star_no_tel), 1 ./ vars_star_no_tel, dop_comp; save_doppler_in_M1=false, inds=(n_star_cur+1):(n_star_cur+1), extra_vec=dop_comp)
# remove_reciprocal_continuum!(oms[i...], flux_star, vars_star, flux_tel, vars_tel)
mws = FrozenTelWorkspace(oms[i...], d)
else # if we have a telluric model
# flux_tel .= _eval_lm(oms[i...].tel.lm)
interp_to_star!(oms[i...])
# oms[i...].rv .=
DEMPCA!(oms[i...].star.lm, flux_star, 1 ./ vars_star, dop_comp; save_doppler_in_M1=false, inds=(n_star_cur+1):(n_star_cur+1), extra_vec=dop_comp)
# remove_reciprocal_continuum!(oms[i...], flux_star, vars_star, flux_tel, vars_tel)
mws = TotalWorkspace(oms[i...], d)
end
om_add_star = get_metrics!(mws, i...)
end
# look at the (up to 2) new aics and choose where to go next
oms[j...] = om_cur
search_new_tel ? aic_tel = aics[comp2ind(n_tel_cur+1, n_star_cur)...] : aic_tel = Inf
search_new_star ? aic_star = aics[comp2ind(n_tel_cur, n_star_cur+1)...] : aic_star = Inf
# println("tel: $aic_tel, star: $aic_star")
added_tel_better = aic_tel < aic_star
added_tel_better ? aic_next = aic_tel : aic_next = aic_star
n_tel_next = n_tel_cur+added_tel_better
n_star_next = n_star_cur+1-added_tel_better
add_comp = (isfinite(aic_tel) || isfinite(aic_star)) && (!stop_early || aic_next < aics[j...]) && (search_new_tel || search_new_star)
end
println("stopped at ($n_tel_cur,$n_star_cur)")
# aics[isnan.(aics)] .= Inf
best_aic = argmin(aics)
println("($(test_n_comp_tel[best_aic[1]]),$(test_n_comp_star[best_aic[2]])) was the best at aic = $(aics[best_aic])")
println("best possible aic (k=0, χ²=0) = $(logdet_Σ + n * _log2π)")
if return_full_path
return oms, ℓs, aics, bics, rv_stds, rv_stds_intra, comp2ind, n_tel_cur, n_star_cur
else
if use_all_comps
return oms[comp2ind(n_tel_cur, n_star_cur)...]
else
return oms[best_aic]
end
end
end
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 12300 | # [1]: Jouni Hartikainen and Simo Särkkä 2015? https://users.aalto.fi/~ssarkka/pub/gp-ts-kfrts.pdf
# [2]: Arno Solin and Simo Särkkä 2019 https://users.aalto.fi/~asolin/sde-book/sde-book.pdf
# See also Appendix A of Data-Driven Modeling of Telluric Features and Stellar Variability with StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl (Gilbertson et al. 2023)
# This code is to compute a fast GP-likelihood regularization term using a Matern 5/2 Kernel
using StaticArrays
import TemporalGPs; TGP = TemporalGPs
using SparseArrays
@assert typeof(SOAP_gp.f.kernel.kernel.kernel) <: Matern52Kernel
@assert typeof(LSF_gp.f.kernel.kernel.kernel) <: Matern52Kernel
## Defining necessary params
const σ²_kernel = SOAP_gp_params.var_kernel # = SOAP_gp.f.kernel.kernel.σ²[1]
# p = 2
# ν = 2 * p + 1 / 2
const λ = sqrt(5) # ==sqrt(2 ν) / l, l assumed to be 1, dealt with later by scaling in A_k
const F = SMatrix{3,3}([0. 1 0;0 0 1;-λ^3 -3λ^2 -3λ]) # eq 9+ of [1]
# using SpecialFunctions
# σ^2*2sqrt(π)*gamma(3)/gamma(5/2)*λ^5 # eq 9 of [1]
# D = 3; q = (factorial(D-1))^2/(factorial(2D-2))*((2λ)^(2D-1)) # eq 12.35 in [2]
# q = 16/3*λ^5
# L = [0;0;1]
# Q = L* q *L'
# using MatrixEquations
# F*P∞ + P∞*F' + Q == 0 # eq 6.69 in [2] process is in steady state before we start
# P∞ = lyapc(F, Q)
const P∞ = SMatrix{3,3}([1 0 -5/3; 0 5/3 0; -5/3 0 25]) # steady-state state covariance, derived with the above commented lines
H = [1 0 0] # matrix for extracting only the measured part of the state
const H_k = SMatrix{1,3}(H .* sqrt(σ²_kernel)) # this is how we deal with kernel amplitude
_σ²_meas_def = 1e-12
# Need one of these per timestep
# They are constant if we have constant timestep
# σ²_meas and H_k only inlcuded as kwargs to prevent errors with passing kwargs...
# in SOAP_gp_ℓ(y, Δx::Real; kwargs...)
function gp_sde_prediction_matrices(Δx, Δx_scaler::Real; P∞::AbstractMatrix=P∞, F::AbstractMatrix=F, σ²_meas::Real=_σ²_meas_def, H_k::AbstractMatrix=H_k)
A_k = SMatrix{3,3}(exp(F * Δx * Δx_scaler)) # State transition matrix eq 6.23 in [2]?
Σ_k = SMatrix{3,3}(Symmetric(P∞) - A_k * Symmetric(P∞) * A_k') # eq. 6.71 in [2], the process noise
return A_k, Σ_k
end
SOAP_gp_sde_prediction_matrices(Δx; Δx_scaler::Real=SOAP_gp_params.λ, kwargs...) =
gp_sde_prediction_matrices(Δx, Δx_scaler; kwargs...)
LSF_gp_sde_prediction_matrices(Δx; Δx_scaler::Real=LSF_gp_params.λ, kwargs...) =
gp_sde_prediction_matrices(Δx, Δx_scaler; kwargs...)
function predict!(m_kbar, P_kbar, A_k, m_k, P_k, Σ_k)
m_kbar .= A_k * m_k # state prediction
P_kbar .= A_k * P_k * A_k' + Σ_k # covariance of state prediction
end
function update_sde!(K_k, m_k, P_k, y, H_k, m_kbar, P_kbar, σ²_meas)
v_k = y - only(H_k * m_kbar) # difference btw meas and pred, scalar
S_k = only(H_k * P_kbar * H_k') + σ²_meas # P_kbar[1,1] * σ²_kernel + σ²_meas, scalar
K_k .= P_kbar * H_k' / S_k # 3x1
m_k .= m_kbar + SVector{3}(K_k * v_k)
P_k .= P_kbar - K_k * S_k * K_k'
return v_k, S_k
end
function init_states(n_state)
m_k = @MVector zeros(n_state)
P_k = MMatrix{3,3}(P∞)
m_kbar = @MVector zeros(n_state)
P_kbar = @MMatrix zeros(n_state, n_state)
K_k = @MMatrix zeros(n_state, 1)
return m_k, P_k, m_kbar, P_kbar, K_k
end
# function SOAP_gp_ℓ(y, Δx::Real; kwargs...)
# A_k, Σ_k = SOAP_gp_sde_prediction_matrices(Δx; kwargs...)
# return gp_ℓ(y, A_k, Σ_k; kwargs...)
# end
# function LSF_gp_ℓ(y, Δx::Real; kwargs...)
# A_k, Σ_k = LSF_gp_sde_prediction_matrices(Δx; kwargs...)
# return gp_ℓ(y, A_k, Σ_k; kwargs...)
# end
# Based on Kalman filter update (alg 10.18 in ASDE) for constant Ak and Qk
# changing y only changes m_kbar, v_k, and m_k. Could be faster if
# P_kbar, S_k, K_k, and P_k were saved?
_log2π = log(2π)
"""
gp_ℓ(y, A_k, Σ_k; σ²_meas=_σ²_meas_def, H_k=H_k, P∞=P∞)
Getting the posterior likelihood that `y` is from a LTISDE described by `A_k` and `Σ_k`, equivalent to a GP
"""
function gp_ℓ(y, A_k::AbstractMatrix, Σ_k::AbstractMatrix; σ²_meas::Real=_σ²_meas_def, H_k::AbstractMatrix=H_k, P∞::AbstractMatrix=P∞)
n = length(y)
n_state = 3
ℓ = 0
m_k, P_k, m_kbar, P_kbar, K_k = init_states(n_state)
for k in 1:n
# prediction step
predict!(m_kbar, P_kbar, A_k, m_k, P_k, Σ_k)
# update step
v_k, S_k = update_sde!(K_k, m_k, P_k, y[k], H_k, m_kbar, P_kbar, σ²_meas)
ℓ -= log(S_k) + v_k^2/S_k # 2*ℓ without normalization
end
return (ℓ - n*log(2π))/2
end
# function SOAP_gp_ℓ_nabla(y, Δx::Real; kwargs...)
# A_k, Σ_k = SOAP_gp_sde_prediction_matrices(Δx; kwargs...)
# return gp_ℓ_nabla(y, A_k, Σ_k; kwargs...)
# end
# function LSF_gp_ℓ_nabla(y, Δx::Real; kwargs...)
# A_k, Σ_k = LSF_gp_sde_prediction_matrices(Δx; kwargs...)
# return gp_ℓ_nabla(y, A_k, Σ_k; kwargs...)
# end
"""
gp_ℓ_nabla(y, A_k, Σ_k; σ²_meas=_σ²_meas_def, H_k=H_k, P∞=P∞)
Getting the posterior likelihood that `y` is from a LTISDE described by `A_k` and `Σ_k`, equivalent to a GP.
Same as `gp_ℓ()` but removing things that Nabla doesn't like
"""
function gp_ℓ_nabla(y, A_k::AbstractMatrix, Σ_k::AbstractMatrix; σ²_meas::Real=_σ²_meas_def, H_k::AbstractMatrix=H_k, P∞::AbstractMatrix=P∞)
n = length(y)
ℓ = 0
n_state = 3
m_k = @MMatrix zeros(n_state, 1)
P_k = MMatrix{3,3}(P∞)
# m_kbar = @MVector zeros(n_state)
P_kbar = @MMatrix zeros(n_state, n_state)
K_k = @MMatrix zeros(n_state, 1)
for k in 1:n
# prediction step
m_kbar = A_k * m_k # state prediction
P_kbar .= A_k * P_k * A_k' + Σ_k # covariance of state prediction, all of the allocations are here
# update step
v_k = y[k] - (H_k * m_kbar)[1] # difference btw meas and pred, scalar
S_k = only(H_k * P_kbar * H_k') + σ²_meas # P_kbar[1,1] * σ²_kernel + σ²_meas, scalar
K_k .= P_kbar * H_k' / S_k # 3x1
# m_k .= m_kbar + SVector{3}(K_k * v_k)
m_k = m_kbar + (K_k * v_k)
P_k .= P_kbar - K_k * S_k * K_k'
ℓ -= log(S_k) + v_k^2/S_k # 2*ℓ without normalization
end
return (ℓ - n*log(2π))/2
end
"""
gp_Δℓ_helper_K(n, A_k, Σ_k, H_k, P∞; σ²_meas=_σ²_meas_def)
Precalculate all of the `K` matrices for at each time
"""
function gp_Δℓ_helper_K(n::Int, A_k::AbstractMatrix, Σ_k::AbstractMatrix, H_k::AbstractMatrix, P∞::AbstractMatrix; σ²_meas::Real=_σ²_meas_def)
n_state = 3
_, P_k, _, P_kbar, _ = init_states(n_state)
K = [MMatrix{3,1}(zeros(3,1)) for i in 1:n]
for k in 1:n
# prediction step
P_kbar .= A_k * P_k * A_k' + Σ_k
# update step
S_k = only(H_k * P_kbar * H_k') + σ²_meas # P_kbar[1,1] * σ²_kernel + σ²_meas, scalar
K[k] .= P_kbar * H_k' / S_k # 3x1
P_k .= P_kbar - K[k] * S_k * K[k]'
end
return K
end
"""
gp_Δℓ_helper_γ(y, A_k, Σ_k, H_k, P∞; σ²_meas=_σ²_meas_def)
Precalculate all of the `γ` values for at each time
"""
function gp_Δℓ_helper_γ(y, A_k::AbstractMatrix, Σ_k::AbstractMatrix, H_k::AbstractMatrix, P∞::AbstractMatrix; σ²_meas::Real=_σ²_meas_def)
n_state = 3
n = length(y)
m_k, P_k, m_kbar, P_kbar, K_k = init_states(n_state)
γ = zeros(n)
for k in 1:n
# prediction step
predict!(m_kbar, P_kbar, A_k, m_k, P_k, Σ_k)
# update step
v_k, S_k = update_sde!(K_k, m_k, P_k, y[k], H_k, m_kbar, P_kbar, σ²_meas)
γ[k] = v_k / S_k
end
return γ
end
"""
gp_Δℓ(y, A_k, Σ_k, H_k, P∞; kwargs...)
Calculate the gradient of `gp_ℓ()` w.r.t. `y`
"""
function gp_Δℓ(y, A_k::AbstractMatrix, Σ_k::AbstractMatrix, H_k::AbstractMatrix, P∞::AbstractMatrix; kwargs...)
n = length(y)
K = gp_Δℓ_helper_K(n, A_k, Σ_k, H_k, P∞; kwargs...) # O(n)
γ = gp_Δℓ_helper_γ(y, A_k, Σ_k, H_k, P∞; kwargs...) # O(n)
# now that we have K and γ
α = H_k * A_k
dLdy = copy(γ)
δLδyk_inter = @MMatrix zeros(3, 1)
for i in 1:(n-1)
δLδyk_inter .= K[i]
dLdy[i] -= γ[i+1] * only(α * δLδyk_inter)
for j in (i+1):(n-1)
δLδyk_inter .= (A_k - K[j] * α) * δLδyk_inter
dLdy[i] -= γ[j+1] * only(α * δLδyk_inter)
end
end
return -dLdy
end
"""
gp_Δℓ_coefficients(n, A_k, Σ_k; H_k=H_k, P∞=P∞, sparsity=0, kwargs...)
Precalculate coefficients that can be used to calculate gradient of `gp_ℓ()` w.r.t. `y`
"""
function gp_Δℓ_coefficients(n::Int, A_k::AbstractMatrix, Σ_k::AbstractMatrix; H_k::AbstractMatrix=H_k, P∞::AbstractMatrix=P∞, sparsity::Int=0, kwargs...)
@assert 0 <= sparsity <= n/10
use_sparse = sparsity != 0
K = gp_Δℓ_helper_K(n, A_k, Σ_k, H_k, P∞; kwargs...) # O(n)
α = H_k * A_k
# dLdy_coeffs = spdiagm(-ones(n)) # it's faster to start as dense and convert to sparse after
dLdy_coeffs = diagm(-ones(n))
δLδyk_inter = @MMatrix zeros(3, 1)
for i in 1:(n-1)
δLδyk_inter .= K[i]
dLdy_coeffs[i, i+1] = only(α * δLδyk_inter)
use_sparse ? ceiling = min(i+1+sparsity, n-1) : ceiling = n-1
for j in (i+1):ceiling
δLδyk_inter .= (A_k - K[j] * α) * δLδyk_inter
dLdy_coeffs[i, j+1] = only(α * δLδyk_inter)
end
end
if use_sparse
dLdy_coeffs = sparse(dLdy_coeffs)
dropzeros!(dLdy_coeffs)
end
return dLdy_coeffs
end
# Δℓ_coe = Δℓ_coefficients(y, A_k, Σ_k, H_k, P∞; σ²_meas=σ²_meas)
# Δℓ_coe_s = Δℓ_coefficients(y, A_k, Σ_k, H_k, P∞; σ²_meas=σ²_meas, sparsity=100)
"""
gp_ℓ_precalc(ℓ_coeff, x, A_k, Σ_k; kwargs...)
A version of `gp_ℓ()` using the coefficients calculated by `gp_Δℓ_coefficients()`
"""
gp_ℓ_precalc(Δℓ_coeff::AbstractMatrix, x::AbstractVector, A_k::AbstractMatrix, Σ_k::AbstractMatrix; kwargs...) =
gp_ℓ(x, A_k, Σ_k; kwargs...)
"""
gp_ℓ_precalc(ℓ_coeff, x, A_k, Σ_k; kwargs...)
Calculate the gradient of `gp_ℓ_precalc()` w.r.t. `y`
"""
Δℓ_precalc(Δℓ_coeff::AbstractMatrix, x::AbstractVector, A_k::AbstractMatrix, Σ_k::AbstractMatrix, H_k::AbstractMatrix, P∞::AbstractMatrix; kwargs...) =
Δℓ_coeff * gp_Δℓ_helper_γ(x, A_k, Σ_k, H_k, P∞; kwargs...)
# Tell Nabla that `Δℓ_precalc()` is the gradient of `gp_ℓ_precalc()`
# BE EXTREMELY CAREFUL! AS WE CANT PASS kwargs... THIS WILL ONLY WORK FOR THE DEFAULT VALUES OF H_k, P∞, F, AND σ²_meas
using Nabla
@explicit_intercepts gp_ℓ_precalc Tuple{AbstractMatrix, AbstractVector, AbstractMatrix, AbstractMatrix}
Nabla.∇(::typeof(gp_ℓ_precalc), ::Type{Arg{2}}, _, y, ȳ, Δℓ_coeff, x, A_k, Σ_k) =
ȳ .* Δℓ_precalc(Δℓ_coeff, x, A_k, Σ_k, H_k, P∞)
# sm = mws.om.tel
# μ_mod = sm.lm.μ .- 1
# SSOF.SOAP_gp_ℓ_precalc(sm.Δℓ_coeff, μ_mod, sm.A_sde, sm.Σ_sde)
# import TemporalGPs; TGP = TemporalGPs
# TGP._logpdf(SSOF.SOAP_gp(sm.log_λ), μ_mod)
# n_test=1000
# using Nabla
# f1(y) = SSOF.SOAP_gp_ℓ_precalc(sm.Δℓ_coeff[eachindex(y), eachindex(y)], y, sm.A_sde, sm.Σ_sde)
# f2(y) = SSOF.SOAP_gp_ℓ_nabla(y, sm.A_sde, sm.Σ_sde)
# only(∇(f1)(μ_mod[1:n_test]))
# only(∇(f2)(μ_mod[1:n_test]))
# est_∇(f1, μ_mod[1:n_test])
# SSOF.Δℓ_precalc(sm.Δℓ_coeff[1:n_test, 1:n_test], μ_mod[1:n_test], sm.A_sde, sm.Σ_sde, SSOF.H_k, SSOF.P∞)
# function SOAP_gp_Δℓ_helper_ℓγ(y, A_k::AbstractMatrix, Σ_k::AbstractMatrix, H_k::AbstractMatrix, P∞::AbstractMatrix; σ²_meas::Real=_σ²_meas_def)
# n_state = 3
# n = length(y)
# m_k, P_k, m_kbar, P_kbar, K_k = init_states(n_state)
# γ = zeros(n)
# ℓ = 0
# for k in 1:n
# # prediction step
# predict!(m_kbar, P_kbar, A_k, m_k, P_k, Σ_k)
#
# # update step
# v_k, S_k = update_sde!(K_k, m_k, P_k, y[k], H_k, m_kbar, P_kbar, σ²_meas)
#
# γ[k] = v_k / S_k
# ℓ -= log(S_k) + v_k^2/S_k # 2*ℓ without normalization
# end
# return (ℓ - n*log(2π))/2, γ
# end
# using ChainRulesCore
# function ChainRulesCore.rrule(::typeof(SOAP_gp_ℓ_precalc), Δℓ_coeff::AbstractMatrix, yy::Vector, A_k::AbstractMatrix, Σ_k::AbstractMatrix; kwargs...)
# y, γ = SOAP_gp_Δℓ_helper_ℓγ(yy, A_k, Σ_k; kwargs...)
# function SOAP_gp_ℓ_pullback(ȳ)
# f̄ = NoTangent()
# ȳy = Δℓ_precalc(Δℓ_coeff, yy, A_k, Σ_k; kwargs...)
# Ā_k = NoTangent() # this is wrong but shouldn't be needed
# Σ̄_k = NoTangent() # this is wrong but shouldn't be needed
# return f̄, ȳy, Ā_k, Σ̄_k
# end
# return y, foo_mul_pullback
# end
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 23372 |
############
# code shamelessly ripped and modified from https://github.com/RvSpectML/NeidSolarScripts.jl/blob/fc6db7979b649370a2923ac987dbd02424cb1762/src/continuum_rassine_like.jl
# which in turn is based off of the methods in https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13098
# This code is not really used in SSOF but is kept for posterity
##########
# ] add DSP DataInterpolations Distributions NaNMath Polynomials RollingFunctions SortFilters
# using RvSpectMLBase
using Statistics, NaNMath # For mean, median, etc
using DSP # For smoothing flux
using DataInterpolations # For predicting continuum between anchors
using RollingFunctions # For rolling maximum. Used in setting radius of rolling-pin.
using SortFilters # For rolling quantile for fitting polynomial while avoiding lines + computing IQR for sigma clipping. https://github.com/sairus7/SortFilters.jl
# using FITSIO # For reading SED
using Polynomials # For fitting out low-order polynomial
# constants
speed_of_light_mks = 299792458 # m/s TODO: Update number
fwhm_sol = 7.9e3 # m/s TODO: Update number
function calc_mean_snr( flux::AV1, var::AV2 ) where { T1<:Real, T2<:Real, AV1<:AbstractVector{T1}, AV2<:AbstractVector{T2} }
idx_bad = isnan.(flux) .| isnan.(var) .| (var .<=0.0)
return mean(flux[.!idx_bad]./sqrt.(var[.!idx_bad]))
end
function smooth(f::AV2; half_width::Integer = 6 ) where { T2<:Real, AV2<:AbstractVector{T2} }
#println("# size(f) to smooth: ", size(f))
w=DSP.hanning(1+2*half_width)
if 1+2*half_width<3
return f
elseif length(f)<1+2*half_width
return f
else
return y_smooth = conv(f, w/sum(w))[1+half_width:end-half_width]
end
end
function calc_rolling_max(f::AV2; width::Integer = 13 ) where { T2<:Real, AV2<:AbstractVector{T2} }
#shift = max(1,floor(Int64,width//2))
@assert width%2 == 1
shift = max(1,convert(Int64,(width+1)//2))
#println(" size(f) = ",size(f), " width= ", width, " shift = ", shift, " rolling_max = ", size(rolling(NaNMath.maximum,f,width)), " target = ", size((shift+1):(length(f)-shift)))
z = similar(f)
#z[(shift):(length(f)-shift+1)] .= rollmax(f,width)
z[(shift):(end-shift+1)] .= rolling(NaNMath.maximum,f,width)
z[(end-shift+2):end] .= z[end-shift+1]
z[1:shift-1] .= z[shift]
return z
end
function find_local_maxima(f::AV2; half_width::Integer = 6 ) where { T2<:Real, AV2<:AbstractVector{T2} }
rollingmax = calc_rolling_max(f,width=half_width*2+1)
findall(f .== rollingmax)
end
function longest_cluster_same_sign(y::AV) where { T<:Real, AV<:AbstractVector{T} }
longest = 0
current = 1
this_start = 1
start = 1
stop = 1
sign_last = sign(first(y))
for i in 2:length(y)
sign_this = sign(y[i])
if sign_this == sign_last
current += 1
else
if current > longest
longest = current
start = this_start
stop = i-1
end
current = 1
this_start = i
end
sign_last = sign_this
end
if current > longest
longest = current
start = this_start
stop = length(y)
end
return (len=longest, start=start, stop=stop)
end
function calc_rollingpin_radius(λ::AV1, f::AV2; fwhm::Real = fwhm_sol,
S1_width_factor::Real = 40, S2_width_factor::Real = 10,
min_R_factor::Real = 100, ν::Real = 1, verbose::Bool = false ) where { T1<:Real, AV1<:AbstractVector{T1}, T2<:Real, AV2<:AbstractVector{T2} }
λlo = minimum(λ)
S1_width = S1_width_factor*fwhm/speed_of_light_mks*λlo
S1_width = min(2*floor(Int64,S1_width/2),2)+1
S2_width = S2_width_factor*S1_width
S2_width = 2*floor(Int64,S2_width/2)+1
f_max1 = calc_rolling_max(f,width=S1_width)
f_max2 = calc_rolling_max(f,width=S2_width)
(longest_len, longest_start, longest_stop) = longest_cluster_same_sign(f_max2.-f_max1)
longest_Δλoverλ = (λ[longest_stop]-λ[longest_start]) / ((λ[longest_start]+λ[longest_stop])/2)
#penalty = (f_max2.-f_max1)./f_max2
#conversion_fwhm_sig = (10*min_λ/(sqrt(8*log(2))*speed_of_light_kmps))
#min_radius = fwhm * conversion_fwhm_sig # par_R
#radius = min_radius .* λ./min_λ
rollingpin_R_min = min_R_factor*λlo*(fwhm/speed_of_light_mks)/log(8*log(2))
#rollingpin_R_max = max_R_factor*rollingpin_R_min # Arbitrary, not same as Rassine's auto setting, see https://github.com/MichaelCretignier/Rassine_public/blob/master/Rassine.py#L718
rollingpin_R_max = max(λlo*longest_Δλoverλ,rollingpin_R_min*2)
#rollingpin_R_min = 2*floor(Int64,rollingpin_R_min/2)
#rollingpin_R_max = 2*floor(Int64,rollingpin_R_max/2)
if verbose
println("longest_len = ", longest_len)
println("longest_Δλoverλ = ", longest_Δλoverλ)
println("rollingpin_R_min = ", rollingpin_R_min)
println("rollingpin_R_max = ", rollingpin_R_max)
end
rollingpin_radius = (λ./λlo).*(rollingpin_R_min .+ (rollingpin_R_max-rollingpin_R_min).*((f_max2.-f_max1)./f_max2).^ν)
#plot!(lambda,f_max1,color=:red)
#plot!(lambda,f_max2,color=:magenta)
#plot!(lambda,penalty)
return rollingpin_radius
end
function calc_continuum_anchors(λ::AV1, f::AV2; radius::AV3,
stretch_factor::Real = 1.0, fwhm::Real = 7.3 #= km/s=#,
verbose::Bool = false ) where { T1<:Real, T2<:Real, T3<:Real, AV1<:AbstractVector{T1}, AV2<:AbstractVector{T2}, AV3<:AbstractVector{T3} }
@assert length(λ) == length(f)
#speed_of_light_kmps = 3e5
#par_stretching = 2# 0.5# 0.5 #11.385
extrema_λ = extrema(λ)
min_λ = first(extrema_λ)
extrema_f = extrema(f)
#normalization = (extrema_f[2]-extrema_f[1])/(extrema_λ[2]-extrema_λ[1])
quantile_for_extrema = max(0.5,(length(f) >= 4000) ? 0.995 : 1-20/length(f))
(min_f, max_f) = quantile(Iterators.filter(!isnan, f),[1-quantile_for_extrema,quantile_for_extrema])
min_f = 0.0
normalization = (max_f-min_f)/(extrema_λ[2]-extrema_λ[1])
normalization *= stretch_factor
function calc_dist(i::Integer, j::Integer) # TODO OPT: eliminate sqrt
if λ[i]<=λ[j]
return 0.0
else
sqrt((λ[i]-λ[j])^2 +((f[i]-f[j])/normalization)^2)
end
end
numero = range(1,stop=length(λ))
mask = falses(length(λ))
dist = zeros(length(λ))
#conversion_fwhm_sig = (10*min_λ/(sqrt(8*log(2))*speed_of_light_kmps))
#min_radius = fwhm * conversion_fwhm_sig # par_R
#println("# old min_radius = ", min_radius)
if verbose println("# passed radius = ", extrema(radius)) end
#radius = min_radius .* λ./min_λ
keep = Vector{Int64}()
sizehint!(keep,max(32,min(256,2^floor(Int64,log2(length(λ))-2))))
push!(keep,1)
j = 1
while length(λ)-j>2
par_R = radius[j]
if j==1 par_R /= 1.5 end
map!(i->calc_dist(i,j),dist,eachindex(λ))
#mask .= (0.0 .< distance[:,j].<2.0*par_R)
mask .= (0.0 .< dist.<2.0*par_R)
while sum(mask)==0
par_R *= 1.5
#mask .= (0.0 .< distance[:,j].<2.0*par_R)
mask .= (0.0 .< dist.<2.0*par_R)
end
p1 = [ λ[j] f[j]/normalization ]
p2 = hcat(λ[mask], f[mask]./normalization)
delta = p2 .- p1
#c = sqrt.(delta[:,1].^2 .+delta[:,2].^2)
c = sqrt.(vec(sum(delta.^2,dims=2)))
harg = (par_R.^2 .-0.25.*c.^2)
#=
if any(harg.<0)
println("# j = ", j, " dist = ", distance[j:j+10,j])
println("# R^2 = ", par_R^2)
println("# c^2/4 = ", c.^2/4)
println("# harg = ", harg)
end
h = zeros(length(harg))
hmask = harg.>0
h[hmask] .= sqrt.(harg[hmask])
=#
h = sqrt.(harg)
cx = p1[1] .+ 0.5.*delta[:,1] .-h./c.*delta[:,2]
cy = p1[2] .+ 0.5.*delta[:,2] .+h./c.*delta[:,1]
#return (cx,cy)
#cond1 = (cy.-p1[2]).>=0
#theta = zeros(length(cy))
mintheta = Inf
argmintheta = 0
for i in eachindex(cy)
if cy[i]-p1[2] >0
acos_arg = (cx[i]-p1[1])/par_R
if acos_arg > 1.0 acos_arg = 1.0
elseif acos_arg < -1.0 acos_arg = -1.0 end
thetai = -acos(acos_arg)+π
else
asin_arg = (cy[i]-p1[2])/par_R
if asin_arg > 1.0 asin_arg = 1.0
elseif asin_arg < -1.0 asin_arg = -1.0 end
thetai = -asin(asin_arg)+π
end
if thetai < mintheta
mintheta = thetai
argmintheta = i
end
end
#theta[cond1] .= -acos.((cx[cond1].-p1[1])./par_R).+π
#theta[.!cond1] .= -asin.((cy[.!cond1].-p1[2])./par_R).+π
#j2 = argmin(theta)
j2 = argmintheta
j = numero[mask][j2]
push!(keep,j)
end
if verbose println("# using ", length(keep), " anchor points") end
return keep
end
function calc_continuum_from_anchors( λ::AV1, f::AV2, anchors::AV3; λout::AV4 = λ,
verbose::Bool = false ) where {
T1<:Real, T2<:Real, T3<:Integer, T4<:Real, AV1<:AbstractVector{T1}, AV2<:AbstractVector{T2}, AV3<:AbstractVector{T3}, AV4<:AbstractVector{T4} }
calc_continuum_from_anchors_hybrid( λ, f, anchors, λout=λout,verbose=verbose)
end
function calc_continuum_from_anchors_linear( λ::AV1, f::AV2, anchors::AV3; λout::AV4 = λ,
verbose::Bool = false ) where {
T1<:Real, T2<:Real, T3<:Integer, T4<:Real, AV1<:AbstractVector{T1}, AV2<:AbstractVector{T2}, AV3<:AbstractVector{T3}, AV4<:AbstractVector{T4} }
@assert length(anchors) >= 2
#if length(anchors) <= 1 return ones(size(λout)) end
interp_linear = LinearInterpolation(f[anchors],λ[anchors])
function extrap(x::Real)
if x<first(interp_linear.t)
slope = (interp_linear.u[2]-interp_linear.u[1])/(interp_linear.t[2]-interp_linear.t[1])
return first(interp_linear.u)+(x-interp_linear.t[1])*slope
elseif x>last(interp_linear.t)
slope = (interp_linear.u[end]-interp_linear.u[end-1])/(interp_linear.t[end]-interp_linear.t[end-1])
return last(interp_linear.u)+(x-interp_linear.t[end])*slope
else
return interp_linear(x)
end
end
return extrap.(λout)
end
function calc_continuum_from_anchors_cubic( λ::AV1, f::AV2, anchors::AV3; λout::AV4 = λ,
verbose::Bool = false ) where {
T1<:Real, T2<:Real, T3<:Integer, T4<:Real, AV1<:AbstractVector{T1}, AV2<:AbstractVector{T2}, AV3<:AbstractVector{T3}, AV4<:AbstractVector{T4} }
interp_cubic = CubicSpline(f[anchors],λ[anchors])
interp_cubic.(λout)
end
function calc_continuum_from_anchors_hybrid( λ::AV1, f::AV2, anchors::AV3; λout::AV4 = λ,
verbose::Bool = false ) where {
T1<:Real, T2<:Real, T3<:Integer, T4<:Real, AV1<:AbstractVector{T1}, AV2<:AbstractVector{T2}, AV3<:AbstractVector{T3}, AV4<:AbstractVector{T4} }
output = similar(λout)
if length(anchors) < 2
output .= ones(size(λout))
elseif length(anchors) < 9
output .= calc_continuum_from_anchors_linear( λ, f, anchors, λout=λout,verbose=verbose)
else
λmin = λ[anchors[4]]
λmax = λ[anchors[end-3]]
idx_pix_cubic = searchsortedfirst(λout,λmin):searchsortedlast(λout,λmax)
output[idx_pix_cubic] .= calc_continuum_from_anchors_cubic( λ, f, anchors, λout=λout[idx_pix_cubic],verbose=verbose)
idx_pix_linear1 = 1:first(idx_pix_cubic)
idx_pix_linear2 = last(idx_pix_cubic):length(λout)
idx_pix_linear = vcat(idx_pix_linear1,idx_pix_linear2)
if verbose println("# idx_pix_linear = ", idx_pix_linear, " \n # λ_linear = ", λout[idx_pix_linear]) end
output[idx_pix_linear] .= calc_continuum_from_anchors_linear( λ, f, anchors, λout=λout[idx_pix_linear],verbose=verbose)
end
return output
end
function replace_edge_anchor_vals!(f::AV1, n::Integer = 3 ) where { T1<:Real, AV1<:AbstractVector{T1} }
@assert length(f) >= 2*n+1
f[1:(n+1)] .= f[n+1]
f[end-n:end] .= f[length(f)-n-1]
return f
end
function find_clean_anchors_by_slope(anchors::AV1, f::AV2; threshold::Real = 0.995, verbose::Bool = false ) where { T1<:Real, T2<:Real, T3<:Real, AV1<:AbstractVector{T1}, AV2<:AbstractVector{T2}, AV3<:AbstractVector{T3} }
nanchors = length(anchors)
@assert nanchors == length(f)
@assert nanchors >= 8
Δabsslope = zeros(length(anchors))
for i in 2:nanchors-1
slope_hi = (f[i+1]-f[i])/(anchors[i+1]-anchors[i])
slope_lo = (f[i]-f[i-1])/(anchors[i]-anchors[i-1])
Δabsslope[i] = abs(slope_hi-slope_lo)
end
threshold = quantile(Δabsslope[2:end-1],threshold)
mask = Δabsslope.<threshold
return mask
end
function merge_nearby_anchors(anchors::AV1, λ::AV2; threshold::Real = 1, verbose::Bool = false ) where { T1<:Real, T2<:Real, T3<:Real, AV1<:AbstractVector{T1}, AV2<:AbstractVector{T2}, AV3<:AbstractVector{T3} }
Δλ = λ[anchors[2:end]] .- λ[anchors[1:end-1]]
close_anchor_pair_mask = Δλ .<= threshold
nclose = sum(close_anchor_pair_mask)
if verbose println("# Found ", nclose, " close anchor pairs out of ", length(anchors), ".") end
if nclose == 0
return anchors
else
if verbose
println("# Anchors = ", anchors)
println("Close anchor pairs: ", findall(close_anchor_pair_mask), " => ", anchors[findall(close_anchor_pair_mask)])
end
end
old_anchor_mask = falses(length(anchors))
if first(Δλ) > threshold
old_anchor_mask[1] = true
end
for i in 2:length(Δλ)
if (Δλ[i-1] > threshold) && (Δλ[i] > threshold)
old_anchor_mask[i] = true
end
end
if last(Δλ) > threshold
old_anchor_mask[length(anchors)] = true
end
old_anchors = anchors[old_anchor_mask]
if verbose println("# Old anchors = ", old_anchors) end
close_anchor_idx = (1:(length(anchors)-1))[close_anchor_pair_mask]
new_anchors = zeros(Int64,nclose)
resize!(new_anchors,0)
idx_start = 1
for i in 2:nclose
if close_anchor_idx[i]-close_anchor_idx[i-1] == 1
continue
else
idx_stop = i-1
if idx_start == idx_stop
merged_anchor_idx = idx_start
elseif (idx_stop-idx_start)%2 == 0
merged_anchor_idx = idx_start + convert(Int64,(idx_stop-idx_start)//2)
else
merged_anchor_idx = idx_start + convert(Int64,(idx_stop-idx_start+1)//2)
end
merged_anchor = anchors[close_anchor_idx[merged_anchor_idx]]
push!(new_anchors,merged_anchor)
idx_start = i
end
end
if idx_start == nclose == 1
push!(new_anchors,anchors[close_anchor_idx[idx_start]])
elseif idx_start != nclose
idx_stop = nclose
if idx_start == idx_stop
merged_anchor_idx = idx_start
elseif (idx_stop-idx_start)%2 == 0
merged_anchor_idx = idx_start + convert(Int64,(idx_stop-idx_start)//2)
else
merged_anchor_idx = idx_start + convert(Int64,(idx_stop-idx_start+1)//2)
end
merged_anchor = anchors[close_anchor_idx[merged_anchor_idx]]
push!(new_anchors,merged_anchor)
end
if verbose println("# Keeping ", length(new_anchors), " new anchors, ", length(old_anchors), " old anchors.") end
anchors_out = mergesorted(old_anchors,new_anchors)
return anchors_out
end
function calc_continuum(λ::AV1, f_obs::AV2, var_obs::AV3; λout::AV4 = λ, fwhm::Real = fwhm_sol, ν::Real =1.0,
smoothing_half_width::Integer = 6, local_maximum_half_width::Integer = smoothing_half_width+1,
stretch_factor::Real = 5.0, merging_threshold::Real = 0.25, min_R_factor::Real = 100.0, smoothing_half_width_no_anchors::Integer = 1000, verbose::Bool = false ) where { T1<:Real, T2<:Real, T3<:Real, T4<:Real, AV1<:AbstractVector{T1}, AV2<:AbstractVector{T2}, AV3<:AbstractVector{T3}, AV4<:AbstractVector{T4} }
#clip_width_A = 1.0
#clip_width_pix = clip_width_A/(λ[2]-λ[1])
#@assert 1 <= clip_width_pix < Inf
#clip_width_pix = 2*floor(Int64,clip_width_pix/2)
mean_snr_per_pix = calc_mean_snr(f_obs,var_obs)
#smoothing_half_width = (mean_snr_per_pix >= 30) ? smoothing_half_width : 40
if mean_snr_per_pix < 20
smoothing_half_width = min(100, ceil(Int64,6*(20/mean_snr_per_pix)^2))
end
f_smooth = smooth(f_obs, half_width=smoothing_half_width)
idx_local_maxima = find_local_maxima(f_smooth, half_width=local_maximum_half_width)
if verbose println("# Found ", length(idx_local_maxima), " local maxima." ) end
if length(idx_local_maxima) < 7
println("# Warning only ", length(idx_local_maxima), " local maxima, aborting order.")
half_width = min_R_factor*(fwhm/speed_of_light_mks)/log(8*log(2))*minimum(λ)/(λ[2]-λ[1])
f_alt_continuum = smooth(f_obs, half_width=floor(Int64,half_width/2)*2 )
return (anchors=Int64[], continuum=f_alt_continuum, f_filtered=f_smooth)
end
#(f_median_filtered, f_clip_threshold, f_clean) = calc_rolling_median_and_max_to_clip(λ,f_obs, width=clip_width_pix, verbose=verbose)
rollingpin_radius = calc_rollingpin_radius(λ, f_smooth, fwhm=fwhm, min_R_factor=min_R_factor, verbose=verbose, ν=ν)
anch_orig = calc_continuum_anchors(λ[idx_local_maxima],f_smooth[idx_local_maxima],radius=rollingpin_radius[idx_local_maxima], stretch_factor=stretch_factor, verbose=verbose)
if verbose println("# Found ", length(anch_orig), " potential anchors." ) end
anch_orig = idx_local_maxima[anch_orig]
anchor_vals = f_smooth[anch_orig]
if length(anch_orig) >= 8 # 2n+1, for replace_edge_anchor_vals!
replace_edge_anchor_vals!(anchor_vals)
anch_mask = find_clean_anchors_by_slope(anch_orig,anchor_vals, threshold = 0.95, verbose=verbose)
if verbose println("# After rejected high-slope anchors ", sum(anch_mask), " anchors left." ) end
else
anch_mask = trues(length(anch_orig))
end
#anchors_merged = anch_orig[anch_mask]
if merging_threshold > 0 && length(anch_orig) >= 4
anchors_merged = merge_nearby_anchors(anch_orig[anch_mask],λ, threshold=merging_threshold, verbose=verbose)
if verbose println("# After merging ", length(anchors_merged), " anchors left." ) end
else
anchors_merged = anch_orig[anch_mask]
end
if length(anchors_merged) < 4
println("# Warning only ", length(anchors_merged), " anchors found, using simpler smoothing.")
#half_width = min_R_factor*(fwhm/speed_of_light_mks)/log(8*log(2))*minimum(λ)/(λ[2]-λ[1])
#f_alt_continuum = smooth(f_obs, half_width=floor(Int64,half_width/2)*2 )
f_alt_continuum = smooth(f_obs, half_width=smoothing_half_width_no_anchors)
return (anchors=Int64[], continuum=f_alt_continuum, f_filtered=f_smooth)
end
#anchors_merged = anch_orig[anch_mask]
continuum = calc_continuum_from_anchors_hybrid(λ,f_smooth,anchors_merged, λout=λout) # , verbose=verbose)
return (anchors=anchors_merged, continuum=continuum, f_filtered=f_smooth)
end
function calc_continuum(λ::AV1, f_obs::AV2, var_obs::AV3, anchors::AV5; λout::AV4 = λ, smoothing_half_width::Integer = 6, smoothing_half_width_no_anchors::Integer = 1000, verbose::Bool = false ) where { T1<:Real, T2<:Real, T3<:Real, T4<:Real, T5<:Integer, AV1<:AbstractVector{T1}, AV2<:AbstractVector{T2}, AV3<:AbstractVector{T3}, AV4<:AbstractVector{T4}, AV5<:AbstractVector{T5} }
#clip_width_A = 1.0
#clip_width_pix = clip_width_A/(λ[2]-λ[1])
#@assert 1 <= clip_width_pix < Inf
#clip_width_pix = 2*floor(Int64,clip_width_pix/2)
mean_snr_per_pix = calc_mean_snr(f_obs,var_obs)
#smoothing_half_width = (mean_snr_per_pix >= 30) ? smoothing_half_width : 40
if mean_snr_per_pix < 30
smoothing_half_width = min(100, ceil(Int64,6*(30/mean_snr_per_pix)^2))
end
f_smooth = smooth(f_obs, half_width=smoothing_half_width)
if length(anchors) < 4
continuum = smooth(f_obs, half_width=smoothing_half_width_no_anchors)
else
continuum = calc_continuum_from_anchors_hybrid(λ,f_smooth,anchors, λout=λout) # , verbose=verbose)
end
return (anchors=anchors, continuum=continuum, f_filtered=f_smooth)
end
function calc_continuum(λ::AA1, f_obs::AA2, var_obs::AA3; λout::AA4 = λ, fwhm::Real = fwhm_sol, ν::Real =1.0,
stretch_factor::Real = 5.0, merging_threshold::Real = 0.25, smoothing_half_width::Integer = 6, min_R_factor::Real = 100.0, smoothing_half_width_no_anchors::Integer = 1000,
orders_to_use::AbstractVector{<:Integer} = axes(λ,2), verbose::Bool = false ) where {
T1<:Real, T2<:Real, T3<:Real, T4<:Real, AA1<:AbstractArray{T1,2}, AA2<:AbstractArray{T2,2}, AA3<:AbstractArray{T3,2} , AA4<:AbstractArray{T4,2} }
@assert size(λ) == size(f_obs) == size(var_obs)
@assert size(λout,2) == size(λout,2)
num_orders = size(λout,2)
anchors_2d = fill(Int64[],num_orders)
continuum_2d = fill(NaN,size(λout,1),size(λout,2))
f_filtered_2d = fill(NaN,size(λout,1),size(λout,2))
#Threads.@threads for ord_idx in orders_to_use
for ord_idx in orders_to_use
if verbose
println("# Order index = ", ord_idx)
flush(stdout)
end
pix = isfinite.(view(var_obs,:,ord_idx))
λ_use = view(λ,pix,ord_idx)
f_obs_use = convert.(Float64,view(f_obs,pix,ord_idx))
var_obs_use = convert.(Float64,view(var_obs,pix,ord_idx))
if all(isnan.(λ_use)) || all(isnan.(f_obs_use)) || all(isnan.(var_obs_use)) continue end
λout_use = view(λout,pix,ord_idx)
(anchors_1d, continuum_order_1d, f_filtered_1d) = calc_continuum(λ_use,f_obs_use,var_obs_use, λout=λout_use,
stretch_factor=stretch_factor, merging_threshold=merging_threshold, smoothing_half_width=smoothing_half_width, min_R_factor=min_R_factor, smoothing_half_width_no_anchors=smoothing_half_width_no_anchors, verbose=verbose)
anchors_2d[ord_idx] = anchors_1d
continuum_2d[pix,ord_idx] .= continuum_order_1d
f_filtered_2d[pix,ord_idx] .= f_filtered_1d
end
return (anchors=anchors_2d, continuum=continuum_2d, f_filtered=f_filtered_2d)
end
function mergesorted(l1::AbstractVector, l2::AbstractVector)
ll1 = length(l1)
ll2 = length(l2)
if length(l1)==0
return l2
elseif length(l2)==0
return l1
end
result = similar(promote_type(typeof(l1),typeof(l2)), ll1+ll2)
i = j = k = 1
while i <= ll1 && j <= ll2
if l1[i] <= l2[j]
result[k] = l1[i]
i += 1
else
result[k] = l2[j]
j += 1
end
k += 1
end
if i <= ll1
result[k:end] .= l1[i:end]
elseif j <= ll2
result[k:end] .= l2[j:end]
end
return result
end
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 10914 | _reg_fields = [:reg_tel, :reg_star]
"""
_eval_regularization(om, mws, training_inds, testing_inds; kwargs...)
Training `om` on the training data, evaluating `_loss()` on the testing data after optimizing the RVs and scores
"""
function _eval_regularization(om::OrderModel, mws::ModelWorkspace, training_inds::AbstractVecOrMat, testing_inds::AbstractVecOrMat; kwargs...)
train = typeof(mws)(om, mws.d, training_inds)
test = typeof(mws)(om, mws.d, testing_inds; only_s=true)
train_OrderModel!(train; kwargs...) # trains feature vectors and scores at training times
train_OrderModel!(test; shift_scores=false, kwargs...) # trains scores at testing times
return _loss(test)
end
"""
eval_regularization(reg_fields, reg_key, reg_val, mws, training_inds, testing_inds; kwargs...)
Setting regularizaiton values for a copy of `mws.om` then training it on the training data and evaluating `_loss()` on the testing data after optimizing the RVs and scores
"""
function eval_regularization(reg_fields::Vector{Symbol}, reg_key::Symbol, reg_val::Real, mws::ModelWorkspace, training_inds::AbstractVecOrMat, testing_inds::AbstractVecOrMat; kwargs...)
om = copy(mws.om)
for field in reg_fields
getfield(om, field)[reg_key] = reg_val
end
return _eval_regularization(om, mws, training_inds, testing_inds; kwargs...)
end
"""
fit_regularization_helper!(reg_fields, reg_key, before_ℓ, mws, training_inds, testing_inds, test_factor, reg_min, reg_max; start=10e3, cullable=Symbol[], robust_start=true, thres=8, kwargs...)
Setting `reg_key` values in each Dict in mws.om.x (where x is each symbol in ``reg_fields``) for a copy of `mws.om` then training it on the training data and evaluating `_loss()` on the testing data after optimizing the RVs and scores
"""
function fit_regularization_helper!(reg_fields::Vector{Symbol}, reg_key::Symbol, before_ℓ::Real, mws::ModelWorkspace, training_inds::AbstractVecOrMat, testing_inds::AbstractVecOrMat, test_factor::Real, reg_min::Real, reg_max::Real; start::Real=10e3, cullable::Vector{Symbol}=Symbol[], robust_start::Bool=true, thres::Real=8, kwargs...)
# only do anything if
if haskey(getfield(mws.om, reg_fields[1]), reg_key)
om = mws.om
@assert 0 < reg_min < reg_max < Inf
ℓs = Array{Float64}(undef, 2)
# check starting from `reg_min`, `start`, and `reg_max`
if robust_start
starting_ℓs =
[eval_regularization(reg_fields, reg_key, reg_min, mws, training_inds, testing_inds; kwargs...),
eval_regularization(reg_fields, reg_key, start, mws, training_inds, testing_inds; kwargs...),
eval_regularization(reg_fields, reg_key, reg_max, mws, training_inds, testing_inds; kwargs...)]
start_ind = argmin(starting_ℓs)
if reg_key in cullable
if starting_ℓs[start_ind] > before_ℓ
for field in reg_fields
getfield(mws.om, field)[reg_key] = 0.
end
println("a course search suggests $(reg_fields[1])[:$reg_key] isn't useful, so setting it to 0")
return before_ℓ
end
end
if start_ind==1
reg_hold = [reg_min, reg_min*test_factor]
start_ℓ = ℓs[1] = starting_ℓs[1]
start = reg_min
ℓs[2] = eval_regularization(reg_fields, reg_key, reg_hold[2], mws, training_inds, testing_inds; kwargs...)
elseif start_ind==2
reg_hold = [start, start*test_factor]
start_ℓ = ℓs[1] = starting_ℓs[2]
ℓs[2] = eval_regularization(reg_fields, reg_key, reg_hold[2], mws, training_inds, testing_inds; kwargs...)
else
reg_hold = [reg_max/test_factor, reg_max]
start_ℓ = ℓs[2] = starting_ℓs[3]
start = reg_max
ℓs[1] = eval_regularization(reg_fields, reg_key, reg_hold[1], mws, training_inds, testing_inds; kwargs...)
end
else
reg_hold = [start, start*test_factor]
start_ℓ = ℓs[1] = eval_regularization(reg_fields, reg_key, reg_hold[1], mws, training_inds, testing_inds; kwargs...)
ℓs[2] = eval_regularization(reg_fields, reg_key, reg_hold[2], mws, training_inds, testing_inds; kwargs...)
end
# need to try decreasing regularization
if ℓs[2] > ℓs[1]
off_edge = reg_min < reg_hold[1]
while (ℓs[2] > ℓs[1]) && (reg_min < reg_hold[1] < reg_max)
# println("trying a lower regularization")
ℓs[2] = ℓs[1]
reg_hold ./= test_factor
ℓs[1] = eval_regularization(reg_fields, reg_key, reg_hold[1], mws, training_inds, testing_inds; kwargs...)
end
if off_edge
last_checked_ℓ, end_ℓ = choose_reg_and_ℓ(reg_fields, om, reg_key, reg_hold, ℓs, 2)
else
last_checked_ℓ, end_ℓ = choose_reg_and_ℓ(reg_fields, om, reg_key, reg_hold, ℓs, 1)
end
# need to try increasing regularization
else
off_edge = reg_hold[2] < reg_max
while (ℓs[1] > ℓs[2]) && (reg_min < reg_hold[2] < reg_max)
# println("trying a higher regularization")
ℓs[1] = ℓs[2]
reg_hold .*= test_factor
ℓs[2] = eval_regularization(reg_fields, reg_key, reg_hold[2], mws, training_inds, testing_inds; kwargs...)
end
if off_edge
last_checked_ℓ, end_ℓ = choose_reg_and_ℓ(reg_fields, om, reg_key, reg_hold, ℓs, 1)
else
last_checked_ℓ, end_ℓ = choose_reg_and_ℓ(reg_fields, om, reg_key, reg_hold, ℓs, 2)
end
end
println("$(reg_fields[1])[:$reg_key] : $start -> $(getfield(mws.om, reg_fields[1])[reg_key])")
if isapprox(end_ℓ, last_checked_ℓ; rtol=1e-6)
@warn "weak local minimum $end_ℓ vs. $last_checked_ℓ"
end
println("$(reg_fields[1])[:$reg_key] χ²: $start_ℓ -> $end_ℓ (" * ratio_clarifier_string(end_ℓ/start_ℓ) * ")")
println("overall χ² change: $before_ℓ -> $end_ℓ (" * ratio_clarifier_string(end_ℓ/before_ℓ) * ")")
# removing the regularization term if it is significantly bad
if end_ℓ > ((1 + thres/100) * before_ℓ)
for field in reg_fields
getfield(mws.om, field)[reg_key] = 0.
end
println("$(reg_fields[1])[:$reg_key] significantly increased the χ² (by more than $thres%), so setting it to 0")
return before_ℓ
end
return end_ℓ
end
return before_ℓ
end
"""
choose_reg_and_ℓ(reg_fields, om, reg_key, reg_hold, ℓs, j)
Set the `reg_key` regularization for `om` once the local minimum is found
"""
function choose_reg_and_ℓ(reg_fields::Vector{Symbol}, om::OrderModel, reg_key::Symbol, reg_hold::Vector{<:Real}, ℓs::Vector{<:Real}, j::Int)
jis1 = j == 1
@assert jis1 || j == 2
for field in reg_fields
getfield(om, field)[reg_key] = reg_hold[j]
end
jis1 ? (return ℓs[2], ℓs[1]) : (return ℓs[1], ℓs[2])
end
"""
ratio_clarifier_string(ratio)
Convert `ratio` to a nice 3 digit-rounded string
"""
function ratio_clarifier_string(ratio::Real)
x = round(ratio; digits=3)
if x == 1.
if ratio == 1; return "=1.0" end
ratio > 1 ? (return ">1.0") : (return "<1.0")
else
return string(x)
end
end
_key_list = [:GP_μ, :L2_μ, :L1_μ, :L1_μ₊_factor, :GP_M, :L2_M, :L1_M, :shared_M]
_key_list_fit = [:GP_μ, :L2_μ, :L1_μ, :GP_M, :L2_M, :L1_M]
_key_list_bases = [:GP_M, :L2_M, :L1_M, :shared_M]
"""
check_for_valid_regularization(reg)
Make sure all the keys in `reg` are in SSOF._key_list
"""
function check_for_valid_regularization(reg::Dict{Symbol, <:Real})
for i in keys(reg)
@assert i in _key_list "The requested regularization isn't valid"
end
end
min_reg = 1e-3
max_reg = 1e12
"""
fit_regularization!(mws, testing_inds; key_list=_key_list_fit, share_regs=false, kwargs...)
Fit all of the regularization values in `key_list` for the model in `mws`
"""
function fit_regularization!(mws::ModelWorkspace, testing_inds::AbstractVecOrMat; key_list::Vector{Symbol}=_key_list_fit, share_regs::Bool=false, kwargs...)
om = mws.om
n_obs = size(mws.d.flux, 2)
training_inds = [i for i in 1:n_obs if !(i in testing_inds)]
check_for_valid_regularization(om.reg_tel)
check_for_valid_regularization(om.reg_star)
if share_regs; @assert keys(om.reg_tel) == keys(om.reg_star) end
hold_tel = copy(default_reg_star_full)
hold_star = copy(default_reg_tel_full)
copy_dict!(hold_tel, om.reg_tel)
copy_dict!(hold_star, om.reg_star)
zero_regularization(om)
println("starting regularization searches")
before_ℓ = _eval_regularization(copy(mws.om), mws, training_inds, testing_inds)
println("initial training χ²: $before_ℓ")
for key in key_list
if key == :L1_μ₊_factor
test_factor, reg_min, reg_max = 1.2, 1e-1, 1e1
else
test_factor, reg_min, reg_max = 10, min_reg, max_reg
end
if share_regs
before_ℓ = fit_regularization_helper!(_reg_fields, key, before_ℓ, mws, training_inds, testing_inds, test_factor, reg_min, reg_max; start=hold_tel[key], kwargs...)
else
if (!(key in _key_list_bases)) || is_time_variable(om.star)
before_ℓ = fit_regularization_helper!([:reg_star], key, before_ℓ, mws, training_inds, testing_inds, test_factor, reg_min, reg_max; start=hold_star[key], kwargs...)
end
if (!(key in _key_list_bases)) || is_time_variable(om.tel)
before_ℓ = fit_regularization_helper!([:reg_tel], key, before_ℓ, mws, training_inds, testing_inds, test_factor, reg_min, reg_max; start=hold_tel[key], kwargs...)
end
end
end
end
"""
fit_regularization!(mws; verbose=true, testing_ratio=0.33, careful_first_step=true, speed_up=false, kwargs...)
Find the best fit model without regularization then fit all of the regularization values in `key_list` for the model in `mws`
"""
function fit_regularization!(mws::ModelWorkspace; verbose::Bool=true, testing_ratio::Real=0.33, careful_first_step::Bool=true, speed_up::Bool=false, kwargs...)
# if mws.om.metadata[:todo][:reg_improved]
n_obs = size(mws.d.flux, 2)
train_OrderModel!(mws; verbose=verbose, ignore_regularization=true, careful_first_step=careful_first_step, speed_up=speed_up)
n_obs_test = Int(round(testing_ratio * n_obs))
test_start_ind = max(1, Int(round(rand() * (n_obs - n_obs_test))))
testing_inds = test_start_ind:test_start_ind+n_obs_test-1
fit_regularization!(mws, testing_inds; kwargs...)
mws.om.metadata[:todo][:reg_improved] = true
# end
end | StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | code | 3130 | using Test
import TemporalGPs; TGP = TemporalGPs
using Nabla
using SparseArrays
import StellarSpectraObservationFitting as SSOF
using LinearAlgebra
println("Testing...")
function est_∇(f::Function, inputs; dif::Real=1e-7, inds::UnitRange=eachindex(inputs))
val = f(inputs)
grad = Array{Float64}(undef, length(inds))
for i in inds
hold = inputs[i]
inputs[i] += dif
grad[i] = (f(inputs) - val) / dif
inputs[i] = hold
end
return grad
end
@testset "fast GP prior likelihoods (and their gradients)" begin
x = 8.78535917650598:6.616545829861497e-7:8.786020831088965
fx = SSOF.SOAP_gp(x)
y = rand(fx)
# are my likelihood calculations the same as TemporalGPs
# @test isapprox(TGP.logpdf(fx, y), SSOF.SOAP_gp_ℓ(y, step(x)))
# @test isapprox(TGP.logpdf(fx, y), SOAP_gp_ℓ_nabla(y, step(x)))
# setting up constants and precalcuating gradient coefficients
H_k, P∞, σ²_meas = SSOF.H_k, SSOF.P∞, SSOF._σ²_meas_def
A_k, Σ_k = SSOF.SOAP_gp_sde_prediction_matrices(step(x))
sparsity = Int(round(0.5 / (step(x) * SSOF.SOAP_gp_params.λ)))
Δℓ_coe = SSOF.gp_Δℓ_coefficients(length(y), A_k, Σ_k; H_k=H_k, P∞=P∞, σ²_meas=σ²_meas)
Δℓ_coe_s = SSOF.gp_Δℓ_coefficients(length(y), A_k, Σ_k; H_k=H_k, P∞=P∞, σ²_meas=σ²_meas, sparsity=sparsity)
f(y) = SSOF.gp_ℓ(y, A_k, Σ_k; σ²_meas=σ²_meas)
numer = est_∇(f, y; dif=1e-9)
anal = SSOF.gp_Δℓ(y, A_k, Σ_k, H_k, P∞; σ²_meas=σ²_meas)
anal_p = SSOF.Δℓ_precalc(Δℓ_coe, y, A_k, Σ_k, H_k, P∞; σ²_meas=σ²_meas)
anal_p_s = SSOF.Δℓ_precalc(Δℓ_coe_s, y, A_k, Σ_k, H_k, P∞; σ²_meas=σ²_meas)
@test isapprox(numer, anal; rtol=1e-4)
@test isapprox(numer, anal_p; rtol=1e-4)
@test isapprox(numer, anal_p_s; rtol=1e-4)
# f(y) = SSOF.gp_ℓ_nabla(y, A_k, Σ_k; σ²_meas=σ²_meas)
# nabla = only(∇(f)(y_test))
println()
end
@testset "custom spectra_interp() sensitivity" begin
B = rand(3,5)
As = [sparse(rand(2,3)) for i in axes(B, 2)]
C = rand(5,6)
f_custom_sensitivity(x) = sum(SSOF.spectra_interp(x.^2, As) * C)
f_nabla(x) = sum(SSOF.spectra_interp_nabla(x.^2, As) * C)
@test ∇(f_custom_sensitivity)(B) == ∇(f_nabla)(B)
println()
end
@testset "weighted project_doppler_comp!()" begin
flux_star = rand(100, 20)
weights = sqrt.(flux_star)
μ = make_template(flux_star, weights; min=0, max=1.2, use_mean=true)
doppler_comp = doppler_component(LinRange(5000,6000,100), μ)
M = zeros(100, 3)
s = zeros(3, 20)
data_tmp = copy(flux_star)
data_tmp .-= μ
rvs1 = SSOF.project_doppler_comp!(M, s, data_tmp, doppler_comp)
s1 = s[1, :]
M1 = M[:, 1]
data_tmp = copy(flux_star)
data_tmp .-= μ
rvs2 = SSOF.project_doppler_comp!(M, s, data_tmp, doppler_comp, ones(size(data_tmp)))
s2 = s[1, :]
M2 = M[:, 1]
data_tmp = copy(flux_star)
data_tmp .-= μ
rvs3 = SSOF.project_doppler_comp!(M, s, data_tmp, doppler_comp, weights)
s3 = s[1, :]
M3 = M[:, 1]
@test M1 == M2 == M3
@test rvs1 == rvs2
@test s1 == s2
@test rvs2 != rvs3
@test s2 != s3
println()
end
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | docs | 1191 | StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl (SSOF, */suf/* like soufflé)
========
<p align="center">
<img width="400px" src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl/master/docs/src/assets/logo.png"/>
</p>
StellarSpectraObservationFitting (SSOF) is a Julia package for measuring radial velocities and creating data-driven models (with fast, physically-motivated Gaussian Process regularization) for the time-variable spectral features for both the telluric transmission and stellar spectrum measured by Extremely Precise Radial Velocity (EPRV) spectrographs (while accounting for the wavelength-dependent instrumental line-spread function)
# Documentation
For more details and options, see the [documentation](https://christiangil.github.io/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl)
# Installation
This package is in rapid development so do not expect any stability yet, but the current version can be installed with the following
```julia
using Pkg
Pkg.add("StellarSpectraObservationFitting")
# Pkg.develop(;url = "https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl") # if you wanted to be able to locally edit the code easily
```
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | docs | 133 | # Data preprocessing functions
```@autodocs
Modules = [StellarSpectraObservationFitting]
Pages = ["src/continuum_functions.jl"]
``` | StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | docs | 1210 | # Data preparation
SSOF models are meant for clean, high-resolution, continuum-normalized spectra. These spectra should be stored in the [`StellarSpectraObservationFitting.GenericData`](@ref) and [`StellarSpectraObservationFitting.LSFData`](@ref) objects, which are used to ensure that all of the necessary information exists to optimize a SSOF model.
```@docs
StellarSpectraObservationFitting.GenericData
```
```@docs
StellarSpectraObservationFitting.LSFData
```
The functions for creating these objects from observation .fits files are currently outside of SSOF proper to keep unnecessary dependencies down, but you can see the reformat_spectra function in [SSOFUtilities/init.jl](https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl/blob/master/SSOFUtilities/init.jl) (which flags low SNR observations and those with weird wavelength calibration as well as ) and [NEID/init.jl](https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl/blob/master/NEID/init.jl) for a script using it.
Once the data is collected, we recommend running [`StellarSpectraObservationFitting.process!`](@ref) to perform some data preprocessing.
```@docs
StellarSpectraObservationFitting.process!
``` | StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | docs | 131 | # EMPCA functions
```@autodocs
Modules = [StellarSpectraObservationFitting]
Pages = ["src/EMPCA.jl", "src/DPCA_functions.jl"]
``` | StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | docs | 2219 | # Error estimation
The RVs found by SSOF are useless if we don't know how confident we should be in them.
We have implemented 2 methods for estimating the uncertainties on the RVs and model scores based on the photon uncertainties in the original data.
For getting quick estimates of the uncertainties, we can look at the local curvature of the likelihood space.
If one assumes that loss is approximately a Gaussian log-likelihood, then the covariance matrix, $\Sigma_{\beta_M}$ can be approximated as
$$\Sigma_{\beta_M} \approx (-H(\beta_M))^{-1}$$
where
$$H(\beta_M)_{i,j}=\dfrac{\delta^2 \ell(\beta_M)}{\delta \beta_{M,i} \delta \beta_{M,j}}$$
is the Hessian matrix and $\ell(\beta_M)$ is the $\approx$ Gaussian log-likelihood (which in our case is $\dfrac{-\mathcal{L}}{2}$).
The variance of each model parameter can be further approximated assuming that the off-diagonal entries of $H(\beta_M)$ are zero (i.e. assuming any $\beta_{M,i}$ is uncorrelated with $\beta_{M,j}$)
$$\dfrac{1}{\sigma_{\beta_{M,i}}^2} \approx -\dfrac{\delta^2 \ell(\beta_M)}{\delta \beta_{M,i}^2}$$
We effectively approximate $\dfrac{\delta^2 \ell(\beta_M)}{\delta \beta_{M,i}^2}$ with finite differences.
This is made available the user with
```@docs
StellarSpectraObservationFitting.estimate_σ_curvature
```
This method is very fast and recommended when performing repeated, iterative analyses (e.g. during data exploration or survey simulation).
Another method available in SSOF for estimating errors is via bootstrap resampling.
In this method, we repeatedly refit the model to the data after adding white noise to each pixel at the reported variance levels.
An estimate for the covariance of $\beta_M$ can then be found by looking at the distribution of the proposed $\beta_M$ after the repeated refittings.
These estimates for the uncertainties tend to be $\sim 1.1-1.5$x higher than the loss space curvature based estimates (likely due to the ignored off-diagonal terms in $H(\beta_M)$).
This method is slower but gives a better overall estimate for the uncertainties (and covariances if desired) and is recommended when finalizing analysis results.
```@docs
StellarSpectraObservationFitting.estimate_σ_bootstrap
```
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | docs | 120 | # Utility functions
```@autodocs
Modules = [StellarSpectraObservationFitting]
Pages = ["src/general_functions.jl"]
``` | StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | docs | 1344 | # Getting started
## Installation
The most current, tagged version of [StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl](https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl) will soon be able to be easily installed using Julia's Pkg
```julia
Pkg.add("StellarSpectraObservationFitting")
```
For now, use
```julia
using Pkg
Pkg.add(;url = "https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl")
# Pkg.develop(;url = "https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl") # if you wanted to be able to locally edit the code easily
```
## Example
An example notebook can be found [here](https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl/blob/master/examples/example.ipynb)
## Getting Help
To get help on specific functionality you can either look up the
information here, or if you prefer you can make use of Julia's
native doc-system. For example here's how to get
additional information on [`StellarSpectraObservationFitting.calculate_initial_model`](@ref) within Julia's REPL:
```julia
?StellarSpectraObservationFitting.calculate_initial_model
```
If you encounter a bug or would like to participate in the
development of this package come find us on Github.
- [christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl](https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl) | StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | docs | 987 | ```@meta
CurrentModule = StellarSpectraObservationFitting
```
# StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl (SSOF, */suf/* like soufflé) Documentation
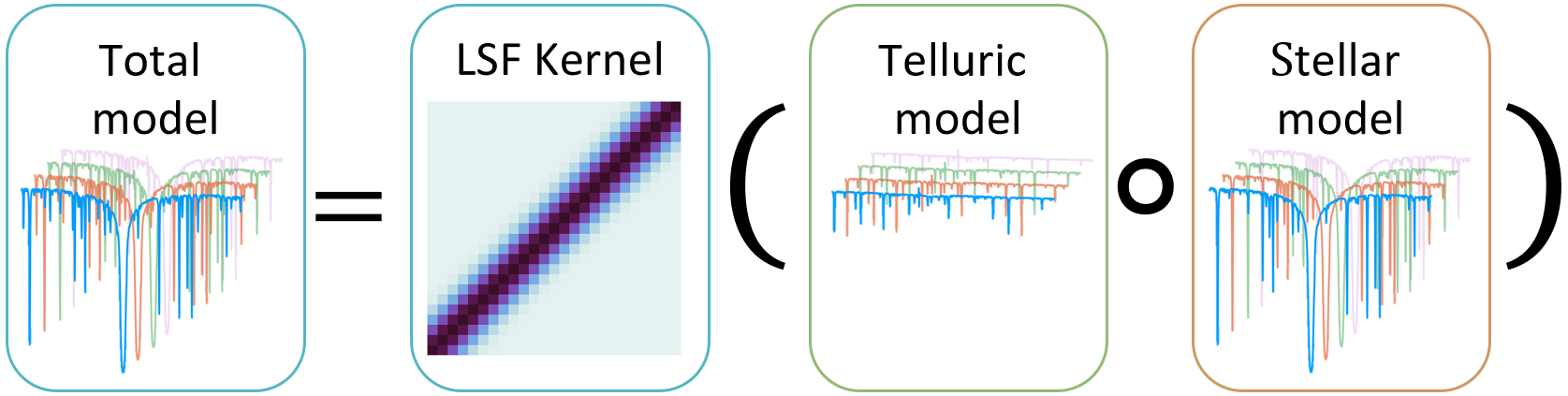
StellarSpectraObservationFitting (SSOF) is a Julia package for creating data-driven models (with fast, physically-motivated Gaussian Process regularization) for the time-variable spectral features for both the telluric transmission and stellar spectrum measured by Extremely Precise Radial Velcotiy (EPRV) spectrographs.
## Where to begin?
If you haven't used SSOF before, a good place to start is the "Getting Started" section. We list how to install the package as well as a simple example
```@contents
Pages = ["gettingstarted.md"]
Depth = 2
```
The User's guide (see the navigation bar) may also be of use
## Indices
All of the package functions can be found here
```@contents
Pages = ["indices.md"]
```
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | docs | 84 | # Index
```@index
```
```@autodocs
Modules = [StellarSpectraObservationFitting]
``` | StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | docs | 550 | # Initialization and model selection
The total SSOF model is most commonly held in a [`StellarSpectraObservationFitting.OrderModelWobble`](@ref) struct.
A good start for a SSOF model for a given dataset can be obtained with
```@docs
StellarSpectraObservationFitting.calculate_initial_model
```
which builds up the SSOF model component by component using noise-weighted [expectation maximization PCA](https://github.com/christiangil/ExpectationMaximizationPCA.jl) and find the AIC-minimum SSOF model for a given maximum amount of feature vectors.
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | docs | 117 | # Model functions
```@autodocs
Modules = [StellarSpectraObservationFitting]
Pages = ["src/model_functions.jl",]
``` | StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | docs | 642 | # Optimization
Before optimization, the SSOF problem (with a SSOF model and the [`StellarSpectraObservationFitting.LSFData`](@ref) it's being fit with) is organized into a work space (like [`StellarSpectraObservationFitting.TotalWorkspace`](@ref)) which includes a suitable chi-squared loss function and its gradient
$$\mathcal{L}(\beta_M) = \sum_{n=1}^N (Y_{D,n} - Y_{M,n})^T \Sigma_n^{-1} (Y_{D,n} - Y_{M,n}) + \textrm{constant}$$
This object can be passed to a function like [`StellarSpectraObservationFitting.improve_model!`](@ref) to optimize the SSOF model on the data.
```@docs
StellarSpectraObservationFitting.improve_model!
```
| StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.3 | 643e23267bea312835d3b1a3e87b857ef7c05314 | docs | 1384 | # Regularization
Many different regularizations can be added to the SSOF loss function to prevent overfitting and encourage model sparsity and smoothness for the model templates and feature vectors. Namely the classic L1 and L2 norms, as well as a fast 𝒪(n) GP term.
$$\mathcal{L}_{R}(\beta_M, \beta_R) = \mathcal{L}(\beta_M) + a_1 \ell_{\textrm{LSF}}(\xi_\oplus, \mu_\oplus - 1) + a_2 \ell_{\texttt{SOAP}}(\xi_\star, \mu_\star - 1) + a_3||\mu_\oplus||_2^2 + a_4||\mu_\star||_2^2 + a_5||\mu_\oplus||_1^1 + a_6||\mu_\star||_1^1 + a_7 \sum_i^{K_\oplus} \ell_{\textrm{LSF}}(\xi_\oplus, W_{\oplus,i}) + a_8 \sum_i^{K_\star} \ell_{\texttt{SOAP}}(\xi_\star, W_{\star,i}) + a_9||W_\oplus||_2^2 + a_{10}||W_\star||_2^2 + a_{11}||W_\oplus||_1^1 + a_{12}||W_\star||_1^1 + ||S_\oplus||_2^2 + ||S_\star||_2^2$$
while the regularization coefficients have default values, you can find the optimal set for the given SSOF model and dataset with cross validation using [`StellarSpectraObservationFitting.fit_regularization!`](@ref)
```@docs
StellarSpectraObservationFitting.fit_regularization!
```
The math behind the Kalman-filtering based methods for the 𝒪(n) GP inference can be found in the appendix of the SSOF paper (submitted) while the actual code is in [src/prior_gp_functions.jl](https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl/blob/master/src/prior_gp_functions.jl) | StellarSpectraObservationFitting | https://github.com/christiangil/StellarSpectraObservationFitting.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.0 | fe05006100a59054e0b7e25dab4f0f42bf068a71 | code | 70 | module TenPuzzle
include("maketen.jl")
export maketen
end # module
| TenPuzzle | https://github.com/kota7/TenPuzzle.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.0 | fe05006100a59054e0b7e25dab4f0f42bf068a71 | code | 4395 | using DocStringExtensions
import Base
using DataStructures
"""
A node represents either a number or operator.
If number, then the node is a leaf.
If operator, then it has left and right nodes.
A mathematical expression can be represented by a binary tree of the nodes.
E.g.,
(1 + 2) * (7 - 2) is represented by
*
├─ +
│ ├─ 1
│ └─ 2
└─ -
├─ 7
└─ 2
"""
struct Node
value::Rational
str::String
isnumber::Bool
left::Union{Node,Nothing}
right::Union{Node,Nothing}
Node(x::Rational) = new(x, replace(string(x), r"//" => "/"),
true, nothing, nothing)
Node(x::Int) = new(Rational(x), string(x), true, nothing, nothing)
Node(op, left::Node, right::Node) = new(op(left.value, right.value),
op == (//) ? "/" : string(op),
false, left, right)
end
Base.:+(a::Node, b::Node) = Node(+, a, b)
Base.:-(a::Node, b::Node) = Node(-, a, b)
Base.:*(a::Node, b::Node) = Node(*, a, b)
Base.:/(a::Node, b::Node) = Node(//, a, b)
"""
Convert a tree into a mathematical expression
"""
function toexpr(node::Node, opprev::String, isright::Bool)::String
if node.isnumber
if occursin("/", node.str)
# rational number should be treated as a chunk
return "($(node.str))"
else
return node.str
end
end
paren = needparen(opprev, node.str, isright)
ret = ""
paren && (ret *= "(")
ret *= toexpr(node.left, node.str, false)
ret *= " $(node.str) "
ret *= toexpr(node.right, node.str, true)
paren && (ret *= ")")
ret
end
toexpr(node::Node) = toexpr(node, "", false)
needparen(opprev::String, op::String, isright::Bool) =
(op=="/" && opprev in ("*","/") && isright) ||
(op in ("+", "-") && opprev in ("*","/")) ||
(op in ("+", "-") && opprev=="-" && isright)
#===================================================================================#
"""
Reduction iterator, given a set of nodes, generates a set of nodes reduced by one-step computation
"""
struct Reductions
ctr::Accumulator{Node,Int}
nodes::Vector{Node}
counts::Vector{Int}
function Reductions(ctr::Accumulator{Node,Int})
nodes = [k for k in keys(ctr)]
counts = [v for v in values(ctr)]
new(ctr, nodes, counts)
end
Reductions(xs::Node...) = Reductions(counter(xs))
end
function Base.iterate(r::Reductions, state::Int)
n = length(r.nodes) # number of unique nodes
(state >= 4*n*n) && return nothing
k = div(state, n*n)
i = div(state-n*n*k, n)
j = state-n*n*k-n*i
i += 1; j += 1; k += 1
n1, n2 = r.nodes[i], r.nodes[j]
op = (+,-,*,/)[k]
# invalid cases
# same node, but count is smaller than 2
(i==j) && (r.counts[i] < 2) && return iterate(r, state+1)
# + and * are order independent
(i>j) && (op in (+,*)) && return iterate(r, state+1)
# zero division
(n2.value==Rational(0)) && (op == (/)) && return iterate(r, state+1)
remain = copy(r.ctr)
n = op(n1, n2)
inc!(remain, n)
dec!(remain, n1)==0 && delete!(remain.map, n1)
dec!(remain, n2)==0 && delete!(remain.map, n2)
remain, state+1
end
Base.iterate(r::Reductions) = iterate(r, 0)
#===================================================================================#
"""
Extract only numbers from a set of nodes
"""
valueonly(xs::Accumulator{Node,Int}) = Set(Pair(n.value,c) for (n,c) = xs)
const NOTFOUND = "NOT FOUND"
"""
Solver of a ten puzzle
"""
function solve!(xs::Accumulator{Node,Int};
tgt=Rational(10), failed=Set{Set{Pair{Rational,Int}}}())::String
valueonly(xs) in failed && return NOTFOUND
if (sum(xs)==1)
node = collect(keys(xs))[1]
return node.value==tgt ? toexpr(node) : NOTFOUND
end
for ys = Reductions(xs)
ans = solve!(ys, tgt=tgt)
ans == NOTFOUND ? push!(failed, valueonly(ys)) : return ans
end
NOTFOUND
end
#===================================================================================#
"""
$(SIGNATURES)
Make ten (or given target value) using given numbers and four arithmetic operations
#Examples
```julia-repl
julia> maketen(1,1,9,9)
"(1 / 9 + 1) * 9"
```
"""
maketen(xs::Union{Int,Rational}...; tgt=10) = solve!(counter(Node.(xs)), tgt=Rational(tgt)) | TenPuzzle | https://github.com/kota7/TenPuzzle.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.0 | fe05006100a59054e0b7e25dab4f0f42bf068a71 | code | 322 | using TenPuzzle
using Test
@testset "Basic fetures" begin
@testset "Typical problems" begin
@test maketen(10) == "10"
@test maketen(5, 5) == "5 + 5"
@test maketen(1, 1, 9, 9) in (
"(1 + 1 / 9) * 9", "(1 / 9 + 1) * 9",
"9 * (1 + 1 / 9)", "9 * (1 / 9 + 1)"
)
end
end
| TenPuzzle | https://github.com/kota7/TenPuzzle.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.0 | fe05006100a59054e0b7e25dab4f0f42bf068a71 | docs | 134 | TenPuzzle.jl
============
Ten Puzzle Solver.
# Usage
```julia
julia> using TenPuzzle
julia> maketen(4,5,6,9)
"4 * 6 - (5 + 9)"
``` | TenPuzzle | https://github.com/kota7/TenPuzzle.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 1188 | using Documenter, ILMPostProcessing
ENV["GKSwstype"] = "nul" # removes GKS warnings during plotting
makedocs(
sitename = "ILMPostProcessing.jl",
doctest = true,
clean = true,
modules = [ILMPostProcessing],
checkdocs = :exports,
pages = [
"Home" => "index.md",
"Manual" => ["manual/pod.md",
"manual/dmdtest.md",
"manual/ftle_continuous.md",
"manual/ftle.md",
"manual/functions.md"
]
#"Internals" => [ "internals/properties.md"]
],
#format = Documenter.HTML(assets = ["assets/custom.css"])
format = Documenter.HTML(
prettyurls = get(ENV, "CI", nothing) == "true",
mathengine = MathJax(Dict(
:TeX => Dict(
:equationNumbers => Dict(:autoNumber => "AMS"),
:Macros => Dict()
)
))
),
#assets = ["assets/custom.css"],
#strict = true
)
#if "DOCUMENTER_KEY" in keys(ENV)
deploydocs(
repo = "github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git",
target = "build",
deps = nothing,
make = nothing
#versions = "v^"
)
#end
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 1096 | struct DMDModes{DT}
modes::Vector{DT}
evals::Vector{ComplexF64}
end
"""
dmd(Xfull,r)
Compute the first `r` DMD modes from the extended snapshot data in `Xfull`.
Both the original and shifted data are drawn from `Xfull`, that is:
`X = Xfull[1:m-1]`
and
`Xp = Xfull[2:m]`
This returns the DMD modes and DMD eigenvalues in a `DMDModes`
structure, with fields `modes` and `evals`.
"""
function dmd(Xplus::Vector{T}, r::Integer) where {T}
nsnap = length(Xplus)
X = view(Xplus,1:nsnap-1)
Xp = view(Xplus,2:nsnap)
# Calculate eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the total [X; Xp] matrix
lambda, psi = _eigen_correlation_matrix(X, Xp)
Q = psi[:,1:r]
o = ones(r)
Xhat = _calculate_U(X,Q,o)
Xphat = _calculate_U(Xp,Q,o)
lambdaX, VX = _eigen_correlation_matrix(Xhat)
ΣX = sqrt.(lambdaX)
UX = _calculate_U(Xhat,VX,ΣX)
UXp = _calculate_U(Xphat,VX,ΣX)
à = _calculate_XTY_via_dot(UX,UXp)
μ, Ṽ = eigen(Ã) #,sortby = x -> abs(angle(x)))
o = ones(length(μ))
V = _calculate_U(UX,Ṽ,o)
return DMDModes{typeof(V[1])}(V,μ)
end | ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 11025 | """
make_interp_fields!(u, v, t_start, t_end, dt, velocity_fn, sol, sys, grid)
Generate an array of interpolatable velocity fields u and v using the solution of a ViscousFlow problem.
Each element of `u` and `v` is essentially a "Vectorfield!" used when solving an ODEProblem. Note: This function could be included in ViscousFlow.jl.
# Arguments
- `u`: x-velocity fields
- `v`: y-velocity fields
- `t_start`: start time of sol
- `t_end`: end time of sol
- `dt`: step size between consecutive velocity fields
- `velocity_fn`: function to compute velocity from solution, should be ViscousFlow.velocity
- `sys`: viscous flow system
- `grid`: physical grid
"""
function make_interp_fields!(u, v, t_start, t_end, dt, velocity_fn, sol, sys, grid)
time = t_start:dt:t_end
for t in time
# Call the passed velocity function
vel = velocity_fn(sol, sys, t)
# Assuming vel contains u and v components
push!(u, interpolatable_field(vel.u, grid))
push!(v, interpolatable_field(vel.v, grid))
end
end
"""
gen_init_conds(X_MIN, X_MAX, Y_MIN, Y_MAX, nx, ny)
Generate a list of initial points (x, y).
These initial conditions represent a collocated grid with `nx` points in (`X_MIN`, `X_MAX`) and `ny` points in (`Y_MIN`, `Y_MAX`). The points are then flattened to a 1D array. The initial conditions could be used to compute FTLE or to visaulize trajectories.
"""
function gen_init_conds(X_MIN, X_MAX, Y_MIN, Y_MAX, nx, ny)
x0 = range(X_MIN, X_MAX, length=nx)
y0 = range(Y_MIN, Y_MAX, length=ny)
dx = x0[2] - x0[1]
dy = y0[2] - y0[1]
# Define the initial conditions as a standard matrix
initial_conditions_matrix = [ [x0[i], y0[j]] for i in 1:nx, j in 1:ny]
initial_conditions_matrix = initial_conditions_matrix'
# Flatten the initial conditions matrix into a 1D array
initial_conditions = vcat(initial_conditions_matrix...)
return initial_conditions, dx, dy
end
"""
euler_forward(initial_conditions, u, v, t0, t_start, dt, T)
Solve the initial value problem (IVP) using forward Euler method.
Integrate forward in time to compute forward FTLE fields.
# Arguments
- `initial_conditions`: generated with function gen_init_conds
- `u`: array of x-velocity fields
- `v`: array of y-velocity fields
- `t0`: initial time
- `t_start`: start time of `u` and `v`
- `dt`: step size between consecutive velocity fields
- `T`: length of integration time
"""
function euler_forward(initial_conditions, u, v, t0, t_start, dt, T)
w = initial_conditions
if T == 0.0
return w
end
start_idx = Int(round((t0 - t_start) / dt + 1))
iters = Int(round(T / dt - 1))
for i = start_idx:start_idx + iters
x = w[:, 1]
y = w[:, 2]
w = w + dt * [u[i].(x, y) v[i].(x, y)]
end
return w
end
"""
euler_backward(initial_conditions, u, v, t0, t_start, dt, T)
Solve the initial value problem (IVP) using forward Euler method.
Integrate backward in time to compute backward FTLE fields. Note: not backward Euler method.
# Arguments
- `initial_conditions`: generated with function gen_init_conds
- `u`: array of x-velocity fields
- `v`: array of y-velocity fields
- `t0`: initial time
- `t_start`: start time of `u` and `v`
- `dt`: step size between consecutive velocity fields
- `T`: length of integration time
"""
function euler_backward(initial_conditions, u, v, t0, t_start, dt, T)
# this is not backward euler, it is forward euler method going back in time
# t0 is the initial time
# t_start is where the starting time of the solution from viscous flow
# dt is the interval between consecutive u and v fields
# T is the integration time
z = initial_conditions
if T == 0.0
return z
end
start_idx = Int(round((t0 - t_start) / dt + 1))
iters = Int(round(T / dt - 1))
for i = start_idx:-1:start_idx - iters
x = z[:, 1]
y = z[:, 2]
z = z - dt * [u[i].(x, y) v[i].(x, y)]
end
return z
end
"""
adams_bashforth_2_forward(initial_conditions, u, v, t0, t_start, dt, T)
Solve the initial value problem (IVP) using 2-step Adams-Bashforth method.
Integrate forward in time to compute forward FTLE fields.
# Arguments
- `initial_conditions`: generated with function gen_init_conds
- `u`: array of x-velocity fields
- `v`: array of y-velocity fields
- `t0`: initial time
- `t_start`: start time of `u` and `v`
- `dt`: step size between consecutive velocity fields
- `T`: length of integration time
"""
function adams_bashforth_2_forward(initial_conditions, u, v, t0, t_start, dt, T)
if T == 0
return initial_conditions
end
start_idx = Int(round((t0 - t_start) / dt + 1))
iters = Int(round(T / dt - 1))
# first generate the 2nd initial condition w2 by using forward euler once
w1 = initial_conditions
x1 = w1[:, 1]
y1 = w1[:, 2]
w2 = w1 - dt * [u[start_idx].(x1, y1) v[start_idx].(x1, y1)]
x2 = w2[:, 1]
y2 = w2[:, 2]
w3 = initial_conditions
for i = 1:iters
w3 = w2 + dt * (3/2*[u[start_idx+i].(x2, y2) v[start_idx+i].(x2, y2)] - 1/2*[u[start_idx+i-1].(x1, y1) v[start_idx+i-1].(x1, y1)])
x1 = x2
y1 = y2
x2 = w3[:,1]
y2 = w3[:,2]
w2 = w3
end
return w3
end
"""
adams_bashforth_2_backward(initial_conditions, u, v, t0, t_start, dt, T)
Solve the initial value problem (IVP) using 2-step Adams-Bashforth method.
Integrate backward in time to compute backward FTLE fields.
# Arguments
- `initial_conditions`: generated with function gen_init_conds
- `u`: array of x-velocity fields
- `v`: array of y-velocity fields
- `t0`: initial time
- `t_start`: start time of `u` and `v`
- `dt`: step size between consecutive velocity fields
- `T`: length of integration time
"""
function adams_bashforth_2_backward(initial_conditions, u, v, t0, t_start, dt, T)
if T == 0
return initial_conditions
end
start_idx = Int(round((t0 - t_start) / dt + 1))
iters = Int(round(T / dt - 1))
# first generate the 2nd initial condition w2 by using forward euler once
w1 = initial_conditions
x1 = w1[:, 1]
y1 = w1[:, 2]
w2 = w1 + dt * [u[start_idx].(x1, y1) v[start_idx].(x1, y1)]
x2 = w2[:, 1]
y2 = w2[:, 2]
w3 = initial_conditions
for i = -1:-1:-iters
w3 = w2 - dt * (3/2*[u[start_idx+i].(x2, y2) v[start_idx+i].(x2, y2)] - 1/2*[u[start_idx+i+1].(x1, y1) v[start_idx+i+1].(x1, y1)])
x1 = x2
y1 = y2
x2 = w3[:,1]
y2 = w3[:,2]
w2 = w3
end
return w3
end
"""
compute_FTLE!(FTLE, nx, ny, T, final_positions, dx, dy)
Compute the `FTLE` field given the final positions of initial points on a collocated grid.
The underlying math is detailed in: https://shaddenlab.berkeley.edu/uploads/LCS-tutorial/computation.html. For each grid point, first compute the gradient of the flow map using two point central differencing. Then, calculate the maximum eigenvalue of the 2 x 2 gradient matrix. Finally, compute the FTLE value using the eigenvalue.
# Arguments
- `FTLE`: an empty 2D array (i.e., `FTLE = zeros(Float64, ny - 2, nx - 2))`, `nx - 2` and `ny - 2` accounts for the boundary points in the central difference formula
- `nx`: number of grid points in x
- `ny`: number of grid points in y
- `T`: length of integration time
- `final_positions`: solutions of the IVP
- `dx`: spacing of initial grids in x
- `dy`: spacing of initial grids in y
"""
function compute_FTLE!(FTLE, nx, ny, T, final_positions, dx, dy)
# Reshape the 2D array into the original 3D matrix format (nx, ny, 2)
final_matrix = reshape(final_positions, ny, nx, 2)
final_x = final_matrix[:,:,1];
final_y = final_matrix[:,:,2];
# Shifted arrays for vector operations
final_x_i_minus = final_x[2:end-1, 1:end-2]
final_x_i_plus = final_x[2:end-1, 3:end]
final_x_j_minus = final_x[1:end-2, 2:end-1]
final_x_j_plus = final_x[3:end, 2:end-1]
final_y_i_minus = final_y[2:end-1, 1:end-2]
final_y_i_plus = final_y[2:end-1, 3:end]
final_y_j_minus = final_y[1:end-2, 2:end-1]
final_y_j_plus = final_y[3:end, 2:end-1]
# Compute the elements of the deformation gradient tensor A
a11 = (final_x_i_plus - final_x_i_minus) / 2 / dx
a12 = (final_x_j_plus - final_x_j_minus) / 2 / dy
a21 = (final_y_i_plus - final_y_i_minus) / 2 / dx
a22 = (final_y_j_plus - final_y_j_minus) / 2 / dy
# Compute the components of delta matrix = A' * A
a = a11.^2 .+ a21.^2
b = a11 .* a12 .+ a21 .* a22
c = a12.^2 .+ a22.^2
# Eigenvalues of the delta matrix using characteristic equation
lambda = (a .+ c .+ sqrt.((a .- c).^2 .+ 4 .* b.^2)) ./ 2
# Compute FTLE (same slicing approach to match the dimensions)
FTLE .= 1 / (2 * abs(T)) .* log.(lambda)
end
"""
compute_FTLE!(FTLE::ScalarGridData, final_x::ScalarGridData, final_y::ScalarGridData, dx::Real, dy::Real, T::Real)
Compute the `FTLE` field given the final positions of initial points on a collocated grid.
The underlying math is detailed in: https://shaddenlab.berkeley.edu/uploads/LCS-tutorial/computation.html. For each grid point, first compute the gradient of the flow map using two point central differencing. Then, calculate the maximum eigenvalue of the 2 x 2 gradient matrix. Finally, compute the FTLE value using the eigenvalue.
# Arguments
- `FTLE`: will hold the FTLE field, in `ScalarGridData` type
- `final_x`: deformed x positions, in `ScalarGridData` type
- `final_y`: deformed y positions, in `ScalarGridData` type
- `dx`: spacing of initial grids in x
- `dy`: spacing of initial grids in y
- `T`: length of integration time
"""
function compute_FTLE!(FTLE, final_x, final_y, dx::Real, dy::Real, T::Real)
nx, ny = size(final_x)
# Shifted arrays for vector operations
final_x_i_minus = view(final_x,2:nx-1, 1:ny-2)
final_x_i_plus = view(final_x,2:nx-1, 3:ny)
final_x_j_minus = view(final_x,1:nx-2, 2:ny-1)
final_x_j_plus = view(final_x,3:nx, 2:ny-1)
final_y_i_minus = view(final_y,2:nx-1, 1:ny-2)
final_y_i_plus = view(final_y,2:nx-1, 3:ny)
final_y_j_minus = view(final_y,1:nx-2, 2:ny-1)
final_y_j_plus = view(final_y,3:nx, 2:ny-1)
# Compute the elements of the deformation gradient tensor A
a11 = (final_x_i_plus - final_x_i_minus) / 2 / dx
a12 = (final_x_j_plus - final_x_j_minus) / 2 / dy
a21 = (final_y_i_plus - final_y_i_minus) / 2 / dx
a22 = (final_y_j_plus - final_y_j_minus) / 2 / dy
# Compute the components of delta matrix = A' * A
a = a11.^2 .+ a21.^2
b = a11 .* a12 .+ a21 .* a22
c = a12.^2 .+ a22.^2
# Eigenvalues of the delta matrix using characteristic equation
lambda = (a .+ c .+ sqrt.((a .- c).^2 .+ 4 .* b.^2)) ./ 2
# Compute FTLE (same slicing approach to match the dimensions)
FTLE_center = view(FTLE,2:nx-1,2:ny-1)
FTLE_center .= 1 / (2 * abs(T)) .* log.(lambda)
end | ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 529 | module ILMPostProcessing
using LinearAlgebra
using Statistics
using OrdinaryDiffEq
using Interpolations
using RecursiveArrayTools
export pod, dmd, PODModes, DMDModes, compute_FTLE!, compute_trajectory,
compute_streamline, compute_streakline, displacement_field, Trajectories,
field_along_trajectory, VectorFieldSequence, ScalarFieldSequence
include("utilities.jl")
include("trajectories.jl")
include("POD.jl")
include("DMD.jl")
include("FTLE.jl")
include("plot_recipes.jl")
end # module ILMPostProcessing
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 3923 | struct PODModes{DT,AT}
Xmean::DT
Xnorm::Vector{DT}
phi::Vector{DT}
a::Matrix{AT}
lambda::Vector{AT}
end
"""
pod(X::Vector{T}[; tolerance=0.99])
Calculate the POD modes and associated time-varying coefficients from an array
of snapshot data `X`. This `X` plays the role of a snapshot matrix, whose columns are
snapshots of the data. However, it is actually to be stored as a type `Vector{T}` where `T<:GridData`.
It can be generated with a function like `velocity(sol,sys,trange)`, where `sol` is a `ODESolution`,
`sys` is an `ILMSystem`, and `trange` is an array of times, e.g., `trange=range(1,10,length=100)`.
The number of POD modes retained in the decomposition is set by `tolerance`: this specifies
the fraction of the total energy to keep, and defaults to 99 percent.
The output of `PODModes` is a structure with the following fields
- `Xmean`: temporal mean of the data. type `T`
- `Xnorm`: original `X` vector with mean removed. Each element is of type `T`
- `phi`: vector of POD modes. Each element is of type `T`
- `a`: matrix of POD coefficients. Number of columns is same as number of entries in `phi`. Column `k` constitutes the time-varying coefficient for mode `k` in `phi`.
- `lambda`: vector of modal energies, arranged in decreasing order, corresponding to the modes in `phi`
- `psi`: matrix of
"""
function pod(X::AbstractVector{T}; tolerance=0.99) where T
Xmean, Xnorm = _split_data_mean_plus_fluctuation(X)
lambda, psi = _eigen_correlation_matrix(Xnorm)
r = _truncate_spectrum_by_tolerance(lambda, tolerance)
# perform truncation of modes
lambda_trunc = lambda[1:r]
psi_trunc = psi[:,1:r]
_podmodes(Xmean,Xnorm,lambda_trunc,psi_trunc)
end
"""
pod(X::Vector{T},r::Int)
Perform POD on snapshot data `X` and truncate to `r` modes
"""
function pod(X::AbstractVector{T},r::Int) where T
Xmean, Xnorm = _split_data_mean_plus_fluctuation(X)
lambda, psi = _eigen_correlation_matrix(Xnorm)
# perform truncation of modes
lambda_trunc = lambda[1:r]
psi_trunc = psi[:,1:r]
_podmodes(Xmean,Xnorm,lambda_trunc,psi_trunc)
end
##### Utilities ######
# Split the data matrix into mean plus the fluctuating part
function _split_data_mean_plus_fluctuation(X)
Xmean = mean(X)
Xnorm = map(col -> col - Xmean, X) # mean removed
return Xmean, Xnorm
end
function _podmodes(Xmean,Xnorm,lambda_trunc,psi_trunc)
# calculate POD modes. Note that Ψ = a/sqrt(Λ)
phi = _calculate_U(Xnorm,psi_trunc,sqrt.(lambda_trunc)) # Φ = X*Ψ/sqrt(Λ)
#a = [dot(Xk, phi_j) for Xk in Xnorm, phi_j in phi] # Xᵀ*Φ = sqrt(Λ)*Ψ
a = psi_trunc*Diagonal(sqrt.(lambda_trunc)) # Xᵀ*Φ = sqrt(Λ)*Ψ
return PODModes{typeof(Xmean),eltype(a)}(Xmean, Xnorm, phi, a, lambda_trunc)
end
# calculate X^*.X matrix and find its eigenvectors/values
function _eigen_correlation_matrix(X)
XTX = _calculate_XTY_via_dot(X,X)
lambda, psi = _eigen_sorted(XTX)
end
# calculate X^*.X + Y^*.Y matrix and find its eigenvectors/values
function _eigen_correlation_matrix(X,Y)
ZTZ = _calculate_XTY_via_dot(X,X) .+ _calculate_XTY_via_dot(Y,Y)
lambda, psi = _eigen_sorted(ZTZ)
end
# Compute the correlation matrix X^*.Y
function _calculate_XTY_via_dot(X,Y)
return [dot(xi,yj) for xi in X, yj in Y]
end
# Compute the eigenvalues/vectors, sorting from largest to smallest
_eigen_sorted(A) = eigen(A,sortby=-)
# filter out eigenvalues based on energy tolerance
function _truncate_spectrum_by_tolerance(lambda,tolerance)
lambda_cumsum = cumsum(lambda)
r = findfirst(lambda_cumsum .>= tolerance*lambda_cumsum[end])
return r
end
# Calculate U = XVΣ^(-1), ensuring that the columns of U have the same
# data type as the columns of X
_calculate_U(X::AbstractVector{T},V::Array,Σ::Vector) where {T} =
[mapreduce((Xi,V_ij) -> Xi .* V_ij/σ_i, +, X, Vcol) for (Vcol,σ_i) in zip(eachcol(V), Σ)]
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 1181 | using RecipesBase
using ColorTypes
#import PlotUtils: cgrad, palette, color_list
@recipe function f(traj::Trajectories; idxs=1:traj.np, trajname = "trajectory", startmarker=false)
xguide --> "x"
yguide --> "y"
aspect_ratio := 1
size --> (700,400)
if !isa(idxs,AbstractVector{<:Int})
error("idxs must be an AbstractVector of integers")
end
for jt in idxs
x, y = traj[jt]
@series begin
linewidth --> 2
label --> "$trajname $jt"
x, y
end
if startmarker
@series begin
markersize --> 4
markershape --> :circle
label --> ""
seriestype = :scatter
[x[1]],[y[1]]
end
end
end
end
@recipe function f(traj::Trajectories,field::T; idxs=1:traj.np, deriv=0, fieldname = "field") where T<:Union{Function,AbstractInterpolation,ScalarFieldSequence}
if !isa(idxs,AbstractVector{<:Int})
error("idxs must be an AbstractVector of integers")
end
for jt in idxs
straj = field_along_trajectory(field,traj,jt,deriv=deriv)
@series begin
label --> "$fieldname on trajectory $jt"
traj.t, straj
end
end
end
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 18485 | # TRAJECTORY CALCULATION #
import Interpolations: AbstractInterpolation
import RecursiveArrayTools: ArrayPartition
const DEFAULT_DT = 0.01
const DEFAULT_DT_STREAK = 0.01
const DEFAULT_ALG = Euler()
const DEFAULT_ADAPTIVE_ALG = Tsit5()
const DEFAULT_T_DURATION = 3.0
"""
Trajectories
Type returned by trajectory calculations, containing a set of one or more trajectories.
For an instance `traj` of this type, the
trajectory time array can be returned with `traj.t`. The number of trajectories is returned
by `traj.np`. Any trajectory contained in the set can be obtained with `traj[p]`, where
`p` must be `0 < p <= traj.np`.
"""
struct Trajectories{TT,XT}
np :: Integer
t :: TT
xhistory :: Vector{XT}
yhistory :: Vector{XT}
end
function Trajectories(sol::ODESolution)
xhist, yhist = _trajectories(sol.u)
Trajectories(length(xhist[1]),sol.t,xhist,yhist)
end
function _trajectories(u::Vector{T}) where {T<:ArrayPartition}
xhist = map(s -> s.x[1],u)
yhist = map(s -> s.x[2],u)
return xhist, yhist
end
function _trajectories(u::Vector{T}) where {T<:Vector}
xhist = map(s -> s[1],u)
yhist = map(s -> s[2],u)
return xhist, yhist
end
Base.size(traj::Trajectories) = traj.np
Base.length(traj::Trajectories) = traj.np
Base.getindex(traj::Trajectories,k::Integer) = _pick_trajectory(traj,k)
function _pick_trajectory(traj::Trajectories,pnum::Integer)
@assert pnum > 0 && pnum <= traj.np "Unavailable trajectory number"
return map(x -> x[pnum],traj.xhistory), map(y -> y[pnum],traj.yhistory)
end
### field sequences ###
abstract type AbstractFieldSequence{FT,TT} end
"""
VectorFieldSequence(t::AbstractVector,v)
This type bundles a time vector `t` with a vector `v` of tuples of interpolatable
fields (i.e., each member of the tuple is of type `AbstractInterpolation`
with two spatial coordinate arguments). It is used in trajectory computations
and for plotting fields along trajectories.
"""
struct VectorFieldSequence{FT,TT} <: AbstractFieldSequence{FT,TT}
t :: TT
v :: Vector{Tuple{FT,FT}}
end
"""
ScalarFieldSequence(t::AbstractVector,s)
This type bundles a time vector `t` with a vector `s` of interpolatable
scalar fields (i.e., each element is of type `AbstractInterpolation`
with two spatial coordinate arguments). It is used for plotting fields along
trajectories.
"""
struct ScalarFieldSequence{FT,TT} <: AbstractFieldSequence{FT,TT}
t :: TT
v :: Vector{FT}
end
Base.step(seq::AbstractFieldSequence{F,T}) where {F,T <: AbstractRange} = step(seq.t)
Base.step(seq::AbstractFieldSequence{F,T}) where {F,T <: Vector} = seq.t[2]-seq.t[1]
# These functions look up the field in the sequence at the time closest to t
function _instantaneous_vector_field_in_series(seq::VectorFieldSequence,t)
jr = searchsorted(seq.t,t)
j1, j2 = first(jr), last(jr)
jt = abs(seq.t[j1] - t) <= abs(seq.t[j2] - t) ? j1 : j2
return seq.v[jt]
end
function _instantaneous_scalar_field_in_series(seq::ScalarFieldSequence,t)
jr = searchsorted(seq.t,t)
j1, j2 = first(jr), last(jr)
jt = abs(seq.t[j1] - t) <= abs(seq.t[j2] - t) ? j1 : j2
return seq.v[jt]
end
## APIs ##
"""
displacement_field(v::VectorFieldSequence,x0,y0,Trange::Tuple[;dt=step(tr),alg=Euler()])
Calculate the displacement of particles initally at coordinates `x0` and `y0` over the range of times `Trange = (ti,tf)`, using the sequence of spatially-interpolated
velocity fields in `v`. (One can also provide the vector of velocity fields and the time array as separate arguments).
The final time in `Trange` can be earlier than the initial time if backward trajectories are desired.
The optional keyword arguments are `dt`, the time step size (which defaults to the step size in `tr`, but could be an integer multiple larger than 1).
"""
function displacement_field(vseq::VectorFieldSequence,x0,y0,Trange::Tuple;dt::Real=step(vseq),alg=DEFAULT_ALG,kwargs...)
ti, tf = Trange
traj = compute_trajectory(vseq,(x0,y0),Trange;dt=dt,alg=alg,saveat=[tf],kwargs...)
xf, yf = traj.xhistory[1], traj.yhistory[1]
return xf, yf
end
displacement_field(vr::Vector{Tuple{T,T}},tr::StepRangeLen,x0,y0,Trange;kwargs...) where T<:AbstractInterpolation =
displacement_field(VectorFieldSequence(tr,vr),x0,y0,Trange;kwargs...)
"""
displacement_field(u::Function,v::Function,x0,y0,Trange::Tuple[;dt=:auto,alg=Euler()])
Calculate the displacement of particles initally at coordinates `x0` and `y0` over the range of times `Trange = (ti,tf)`, using the
velocity functions `u` and `v`. These function can either be autonomous (taking only x and y arguments) or non-autonomous, taking
an additional time argument.
The final time in `Trange` can be earlier than the initial time if backward trajectories are desired.
The optional keyword arguments are `dt`, the time step size (which defaults to `:auto`, for adaptive time marching, but could be specified
to override this). The default time marching algorithm is `Tsit5()`.
"""
function displacement_field(ufcn::Function,vfcn::Function,x0,y0,Trange::Tuple;dt=:auto,alg=DEFAULT_ADAPTIVE_ALG,kwargs...)
ti, tf = Trange
traj = compute_trajectory(ufcn,vfcn,(x0,y0),Trange;dt=dt,alg=alg,saveat=[tf],kwargs...)
xf, yf = traj.xhistory[1], traj.yhistory[1]
return xf, yf
end
"""
compute_trajectory(v::VectorFieldSequence,X₀,Trange::Tuple[;dt=step(tr),alg=Euler()])
Calculate the trajectories of particles with initial location(s) `X₀`. The argument
`v` contains a sequence of spatially-interpolated velocity fields and an associated time array.
(One can also provide the vector of velocity fields and the time array as separate arguments).
`X₀` can be specified as either a single vector `[x0,y0]`, a vector of vectors specifying
x, y pairs, or a tuple of vectors or arrays specifying x and y positions, respectively,
for multiple tracer particles. `Trange` is a tuple of the starting
and ending integration times. The optional keyword arguments are `dt`, the time step size (which defaults to the step size in `tr`, but could be an integer multiple larger than 1). The output is the solution
structure for the `OrdinaryDiffEq` package.
"""
function compute_trajectory(vseq::VectorFieldSequence,X₀,Trange::Tuple;dt::Real=step(vseq),alg=DEFAULT_ALG,kwargs...)
ti, tf = _check_times(vseq.t,Trange,dt)
_dt, _autodt = _standardize_time_step(ti,tf,dt)
u0 = _prepare_initial_conditions(X₀)
vfcn!(dR,R,p,t) = _vfcn_interpolated_series!(dR,R,p,t,vseq)
sol = _solve_trajectory(vfcn!,u0,Trange,_dt,alg,Val(false);kwargs...)
return Trajectories(sol)
end
compute_trajectory(vr::Vector{Tuple{T,T}},tr::StepRangeLen,X₀,Trange::Tuple;kwargs...) where {T<:AbstractInterpolation} = compute_trajectory(VectorFieldSequence(tr,vr),X₀,Trange;kwargs...)
"""
compute_trajectory(u,v,X₀,Trange::Tuple[;dt=0.01])
Calculate the trajectory of a tracer particle with initial location(s) `X₀`, which
can be specified as either a single vector `[x0,y0]`, a vector of vectors specifying
x, y pairs, or a tuple of vectors or arrays specifying x and y positions, respectively,
for multiple tracer particles. The arguments
`u` and `v` are either interpolated velocity field components from a computational solution
or are functions. If they are functions, then each of them should be of the form `u(x,y,t)`
and `v(x,y,t)`; `Trange` is a tuple of the initial and final time of integration (and the final time
can be earlier than the initial time if backward trajectories are desired); and `dt` is the
time step size, which defaults to 0.001. The output is the solution
structure for the `OrdinaryDiffEq` package (or, for multiple particles, a vector
of such solution structures).
"""
function compute_trajectory(ufield::T,
vfield::T,
X₀,Trange::Tuple;dt=DEFAULT_DT,alg=DEFAULT_ADAPTIVE_ALG,kwargs...) where {T<:AbstractInterpolation}
_dt, _autodt = _standardize_time_step(Trange...,dt)
vfcn!(dR,R,p,t) = _vfcn_autonomous!(dR,R,p,t,ufield,vfield)
u0 = _prepare_initial_conditions(X₀)
sol = _solve_trajectory(vfcn!,u0,Trange,_dt,alg,Val(_autodt);kwargs...)
return Trajectories(sol)
end
function compute_trajectory(ufcn::Function,
vfcn::Function,
X₀,Trange::Tuple;dt=DEFAULT_DT,alg=DEFAULT_ADAPTIVE_ALG,kwargs...)
_dt, _autodt = _standardize_time_step(Trange...,dt)
#velfcn(R,p,t) = _is_autonomous_velocity(ufcn) ? _vfcn_autonomous(R,p,t,ufcn,vfcn) : _vfcn_nonautonomous(R,p,t,ufcn,vfcn)
velfcn!(dR,R,p,t) = _is_autonomous_velocity(ufcn) ? _vfcn_autonomous!(dR,R,p,t,ufcn,vfcn) : _vfcn_nonautonomous!(dR,R,p,t,ufcn,vfcn)
u0 = _prepare_initial_conditions(X₀)
sol = _solve_trajectory(velfcn!,u0,Trange,_dt,alg,Val(_autodt);kwargs...)
return Trajectories(sol)
end
compute_trajectory(velfield::Tuple{T1,T2},X₀,Trange::Tuple;kwargs...) where {T1<:Union{AbstractInterpolation,Function},T2<:Union{AbstractInterpolation,Function}} =
compute_trajectory(velfield...,X₀,Trange;kwargs...)
function _standardize_time_step(ti,tf,dt::Real)
tsign = sign(tf-ti)
_dt = tsign != 0 ? tsign*abs(dt) : dt
return _dt, false
end
function _standardize_time_step(ti,tf,dt::Symbol)
return dt, true
end
#######
"""
compute_streamline(u,v,X₀,srange::Tuple,t::Real,[;dt=0.01])
Calculate the streamline(s) passing through location(s) `X₀`, which
can be specified as either a single vector `[x0,y0]`, a vector of vectors specifying
x, y pairs, or a tuple of vectors or arrays specifying x and y positions, respectively,
for a rake of streamlines. The arguments
`u` and `v` are either interpolated velocity field components from a computational solution
or are functions. If they are functions, then each of them should be of the form `u(x,y,t)`
and `v(x,y,t)`; `srange` is a tuple of the initial and final time of integration; `t` is
the current time at which the streamline is depicted; and `Δs` is the
time-like step size, which defaults to 0.001. The output is the solution
structure for the `OrdinaryDiffEq` package (or, for multiple points, a vector
of such solution structures).
"""
function compute_streamline(ufcn::Function,
vfcn::Function,
X₀,srange::Tuple,t::Real;ds=DEFAULT_DT,alg=DEFAULT_ADAPTIVE_ALG,kwargs...)
velfcn(R,p,s) = _is_autonomous_velocity(ufcn) ? _vfcn_autonomous(R,p,s,ufcn,vfcn) : _vfcn_nonautonomous_frozentime(R,p,s,ufcn,vfcn)
_ds, _autods = _standardize_time_step(srange...,ds)
u0 = _prepare_initial_conditions(X₀)
sol = _solve_streamline(velfcn,u0,srange,_ds,t,alg,Val(_autods);kwargs...)
return Trajectories(sol)
end
function compute_streamline(ufield::AbstractInterpolation{T,2},vfield::AbstractInterpolation{T,2},
X₀,srange::Tuple,t::Real;ds=DEFAULT_DT,alg=DEFAULT_ADAPTIVE_ALG,kwargs...) where {T}
vfcn!(dR,R,p,s) = _vfcn_autonomous!(dR,R,p,s,ufield,vfield)
_ds, _autods = _standardize_time_step(srange...,ds)
u0 = _prepare_initial_conditions(X₀)
sol = _solve_streamline(vfcn!,u0,srange,_ds,t,alg,Val(_autods);kwargs...)
return Trajectories(sol)
end
"""
compute_streakline(u,v,X₀::Vector,t[;τmin = t-3.0, dtstreak=0.01,dttraj=0.001]) -> Vector, Vector
Calculate a streakline at time `t` for a velocity field `u` and `v`, based on an injection
point `X₀`. The end of the streakline is set by `τmin`, the earliest time
at which a particle passed through the injection point. It defaults to 3 time
units before the current instant `t`. The time step size `dtstreak` sets the resolution
of the streakline (i.e., how often the particles are sampled along the streakline).
It returns arrays of the x and y coordinates of the streakline.
"""
function compute_streakline(vel::Union{Tuple,Vector},X₀::Vector{S},t::Real;τmin = t-DEFAULT_T_DURATION, dtstreak::Real=DEFAULT_DT_STREAK, dttraj::Real=DEFAULT_DT,alg=DEFAULT_ALG) where {S<:Real} #,kwargs...)
τstreak = τmin:dtstreak:t
xstreak = zeros(length(τstreak))
ystreak = zeros(length(τstreak))
for (i,τ) in enumerate(τstreak)
traj = compute_trajectory(vel,X₀,(τ,t);dt = dttraj,alg=alg) #,kwargs...)
xtraj, ytraj = traj[1]
xstreak[i], ystreak[i] = xtraj[end],ytraj[end]
end
return Trajectories(1,τstreak,xstreak,ystreak)
end
compute_streakline(u::T1,v::T2,X₀::Vector{S},t::Real;kwargs...) where {T1<:Union{AbstractInterpolation,Function}, T2<:Union{AbstractInterpolation,Function}, S<:Real} =
compute_streakline((u,v),X₀,t;kwargs...)
"""
field_along_trajectory(f,traj::Trajectories,p::Integer[,deriv=0])
Evaluate field `f` (given as grid data) along the trajectory number `p` in the
trajectories specified by `traj`.
The output is the history of `f` along this trajectory. If `f` is a vector field,
then the component histories are output as a tuple. If `deriv=1`, then it
computes the time derivative of the field along the trajectory. The default
is `deriv=0` (no derivative).
"""
field_along_trajectory(d,traj,p;deriv=0) = _field_along_trajectory(d,traj,p,Val(deriv))
## Internal helper functions ##
function _solve_trajectory(vfcn,u0,Trange,dt,alg, ::Val{false}; kwargs...)
Path = ODEProblem(vfcn,u0,Trange)
sol = OrdinaryDiffEq.solve(Path,alg; dt = dt, maxiters = 1e8, adaptive = false, dense = false, kwargs...)
end
function _solve_trajectory(vfcn,u0,Trange,dt,alg, ::Val{true}; kwargs...)
Path = ODEProblem(vfcn,u0,Trange)
sol = OrdinaryDiffEq.solve(Path,alg; kwargs...)
end
function _solve_streamline(vfcn,u0,Trange,dt,p,alg,::Val{false}; kwargs...)
Path = ODEProblem(vfcn,u0,Trange,p)
sol = OrdinaryDiffEq.solve(Path,alg; dt = dt, maxiters = 1e8, adaptive = false, dense = false, kwargs...)
end
function _solve_streamline(vfcn,u0,Trange,dt,p,alg,::Val{true}; kwargs...)
Path = ODEProblem(vfcn,u0,Trange,p)
sol = OrdinaryDiffEq.solve(Path,alg; maxiters = 1e8, dense = false, kwargs...)
end
## Right-hand side functions for trajectories ##
function _vfcn_autonomous!(dR::ArrayPartition,R::ArrayPartition,p,t,u,v)
dR.x[1] .= u.(R.x[1],R.x[2])
dR.x[2] .= v.(R.x[1],R.x[2])
return dR
end
function _vfcn_autonomous!(dR,R,p,t,u,v)
dR[1] = u(R[1],R[2])
dR[2] = v(R[1],R[2])
return dR
end
function _vfcn_autonomous(R::ArrayPartition,p,t,u,v)
dR = similar(R)
dR.x[1] .= u.(R.x[1],R.x[2])
dR.x[2] .= v.(R.x[1],R.x[2])
return dR
end
function _vfcn_autonomous(R,p,t,u,v)
dR = similar(R)
dR[1] = u(R[1],R[2])
dR[2] = v(R[1],R[2])
return dR
end
function _vfcn_nonautonomous!(dR::ArrayPartition,R::ArrayPartition,p,t,u,v)
dR.x[1] .= u(R.x[1],R.x[2],t)
dR.x[2] .= v(R.x[1],R.x[2],t)
return dR
end
function _vfcn_nonautonomous!(dR,R,p,t,u,v)
dR[1] = u(R[1],R[2],t)
dR[2] = v(R[1],R[2],t)
return dR
end
function _vfcn_nonautonomous(R::ArrayPartition,p,t,u,v)
dR = similar(R)
dR.x[1] .= u.(R.x[1],R.x[2],Ref(t))
dR.x[2] .= v.(R.x[1],R.x[2],Ref(t))
return dR
end
function _vfcn_nonautonomous(R,p,t,u,v)
dR = similar(R)
dR[1] = u(R[1],R[2],t)
dR[2] = v(R[1],R[2],t)
return dR
end
function _vfcn_nonautonomous_frozentime(R::ArrayPartition,p,t,u,v)
dR = similar(R)
dR.x[1] .= u.(R.x[1],R.x[2],Ref(p))
dR.x[2] .= v.(R.x[1],R.x[2],Ref(p))
return dR
end
function _vfcn_nonautonomous_frozentime(R,p,t,u,v)
dR = similar(R)
dR[1] = u(R[1],R[2],p)
dR[2] = v(R[1],R[2],p)
return dR
end
function _vfcn_interpolated_series!(dR::ArrayPartition,R::ArrayPartition,p,t,vr)
u, v = _instantaneous_vector_field_in_series(vr,t)
dR.x[1] .= u.(R.x[1],R.x[2])
dR.x[2] .= v.(R.x[1],R.x[2])
return dR
end
function _vfcn_interpolated_series!(dR,R,p,t,vr)
u, v = _instantaneous_vector_field_in_series(vr,t)
dR[1] = u(R[1],R[2])
dR[2] = v(R[1],R[2])
return dR
end
## For computing fields along trajectories ##
function _field_along_trajectory(v::Tuple{T,T},traj::Trajectories,p,::Val{0}) where T<:Union{AbstractInterpolation,Function}
vfield_x, vfield_y = v
xh, yh = traj[p]
vx_traj = vfield_x.(xh,yh)
vy_traj = vfield_y.(xh,yh)
return vx_traj, vy_traj
end
function _field_along_trajectory(sfield::T,traj::Trajectories,p,::Val{0}) where T<:Union{AbstractInterpolation,Function}
xh, yh = traj[p]
s_traj = sfield.(xh,yh)
return s_traj
end
function _field_along_trajectory(vseq::VectorFieldSequence,traj::Trajectories,p,::Val{0})
xh, yh = traj[p]
varray = map((x,y,t) -> (vel = _instantaneous_vector_field_in_series(vseq,t); tuple(vel[1](x,y), vel[2](x,y))),xh,yh,traj.t)
return map(v -> v[1],varray), map(v -> v[2],varray)
end
function _field_along_trajectory(sseq::ScalarFieldSequence,traj::Trajectories,p,::Val{0})
xh, yh = traj[p]
return map((x,y,t) -> (f = _instantaneous_scalar_field_in_series(sseq,t); f(x,y)),xh,yh,traj.t)
end
function _field_along_trajectory(v::Tuple{T,T},traj::Trajectories,p,::Val{1}) where T<:Union{AbstractInterpolation,Function}
utraj, vtraj = _field_along_trajectory(v,traj,p,Val(0))
return ddt(utraj,traj.t), ddt(vtraj,traj.t)
end
_field_along_trajectory(s::T,traj::Trajectories,p,::Val{1}) where T<:Union{AbstractInterpolation,Function,ScalarFieldSequence} =
ddt(_field_along_trajectory(s,traj,p,Val(0)),traj.t,mydiff=:backward_diff)
_evaluate_field_function(x,y,t,field::Function,::Val{4}) = field(x,y,t)
_evaluate_field_function(x,y,t,field::Function,::Val{3}) = field(x,y)
function _check_times(tr,Trange,dt)
ti, tf = Trange
ji, jf = searchsortedfirst(tr,ti), searchsortedfirst(tr,tf)
@assert tr[ji] ≈ ti "First entry in time range is not in supplied time array"
@assert tr[jf] ≈ tf "Last entry in time range is not in supplied time array"
@assert abs(dt/step(tr)) >= 1 "Supplied time step size must be >= than step size in supplied time array"
@assert mod(dt,step(tr)) ≈ 0 "Supplied time step size must be integer multiple of step size in supplied time array"
return ti, tf
end
function _prepare_initial_conditions(X₀::Tuple)
x0, y0 = X₀
return ArrayPartition(deepcopy(x0),deepcopy(y0))
end
function _prepare_initial_conditions(X₀::Vector{Vector{S}}) where {S<:Real}
x0 = map(pt -> pt[1],X₀)
y0 = map(pt -> pt[2],X₀)
return ArrayPartition(x0,y0)
end
function _prepare_initial_conditions(X₀::Vector{S}) where {S<:Real}
return X₀
end
function _is_autonomous_velocity(u::Function)
m = first(methods(u))
# autonomous will have three (fcn name, x, y), non-autonomous will have four (time, as well)
is_aut = m.nargs == 3 ? true : false
return is_aut
end | ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 951 | """
ddt(u::AbstractVector,Δt[,mydiff=:backward_diff])
Calculate the time derivative of vector data `u`, with time step size `Δt`.
The default method is backward differencing, but this can be changed to
`:forward_diff` or `:central_diff`.
"""
function ddt(u::AbstractVector{T},t::AbstractVector{S};mydiff::Symbol=:forward_diff) where {T,S}
du = eval(mydiff)(u)./eval(mydiff)(t)
return du
end
# Some basic differencing routines
function backward_diff(u::AbstractVector{T}) where {T}
du = zero(u)
du[2:end] .= u[2:end] .- u[1:end-1]
du[1] = du[2]
return du
end
function forward_diff(u::AbstractVector{T}) where {T}
du = zero(u)
du[1:end-1] .= u[2:end] .- u[1:end-1]
du[end] = du[end-1]
return du
end
function central_diff(u::AbstractVector{T}) where {T}
du = zero(u)
du[2:end-1] .= 0.5*u[3:end] .- 0.5*u[1:end-2]
du[1] = du[2]
du[end] = du[end-1]
return du
end
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 2874 | using ILMPostProcessing
using ViscousFlow
using LinearAlgebra
@testset "FTLE" begin
# this test setup up an empty problem to compute FTLE fields on zero velocity fields
# setup and solve viscous flow problem
my_params = Dict()
my_params["Re"] = 200
xlim = (-1.0,1.0)
ylim = (-1.0,1.0)
g = setup_grid(xlim,ylim,my_params)
sys = viscousflow_system(g,phys_params=my_params)
u0 = init_sol(sys)
tspan = (0.0,1.0)
integrator = init(u0,tspan,sys)
step!(integrator,1.0)
sol = integrator.sol
# generate velocity fields
#u = []
#v = []
t_start = 0.0
t_end = 1.0
dt = 0.1
tr = t_start:dt:t_end
velxy = velocity_xy(sol,sys,tr)
vseq = VectorFieldSequence(tr,velxy)
u, v = velxy[end]
@test norm(u) < 1e-8
@test norm(v) < 1e-8
# generate initial conditions
X_MIN = -0.5
X_MAX = 0.5
Y_MIN = -0.5
Y_MAX = 0.5
#nx, ny = 10, 10
dx = 0.1
ftlegrid = PhysicalGrid((X_MIN,X_MAX),(Y_MIN,Y_MAX),dx)
ftle_cache = SurfaceScalarCache(ftlegrid)
#initial_conditions, dx, dy = ILMPostProcessing.gen_init_conds(X_MIN, X_MAX, Y_MIN, Y_MAX, nx, ny)
x0, y0 = x_grid(ftle_cache), y_grid(ftle_cache)
# solve the forward and backward IVP using Euler and Adams-Bashforth
# start at t = 0.5 and integrate to t= 1.0 in forward time and to t = 0.0 in backward time
T = 0.5
t0 = 0.5
xf, yf = displacement_field(vseq,x0,y0,(t0,t0+T),alg=Euler())
xb, yb = displacement_field(vseq,x0,y0,(t0,t0-T),alg=Euler())
#a = ILMPostProcessing.euler_forward(initial_conditions, u, v, t0, t_start, dt, T)
#b = ILMPostProcessing.euler_backward(initial_conditions, u, v, t0, t_start, dt, T)
#c = ILMPostProcessing.adams_bashforth_2_forward(initial_conditions, u, v, t0, t_start, dt, T)
#d = ILMPostProcessing.adams_bashforth_2_backward(initial_conditions, u, v, t0, t_start, dt, T)
#@test norm(a - initial_conditions) < 1e-8
#@test norm(b - initial_conditions) < 1e-8
#@test norm(c - initial_conditions) < 1e-8
#@test norm(d - initial_conditions) < 1e-8
@test norm(xf - x0) < 1e-8
@test norm(yf - y0) < 1e-8
@test norm(xb - x0) < 1e-8
@test norm(yf - y0) < 1e-8
# compute FTLE fields, should all be zeros
#ftle_a = ftle_b = ftle_c = ftle_d = zeros(Float64, ny - 2, nx - 2)
#ILMPostProcessing.compute_FTLE!(ftle_a, nx, ny, T, a, dx, dy)
#ILMPostProcessing.compute_FTLE!(ftle_b, nx, ny, T, b, dx, dy)
#ILMPostProcessing.compute_FTLE!(ftle_c, nx, ny, T, c, dx, dy)
#ILMPostProcessing.compute_FTLE!(ftle_d, nx, ny, T, d, dx, dy)
fFTLE = similar(x0)
compute_FTLE!(fFTLE,xf,yf,dx,dx,T)
bFTLE = similar(x0)
compute_FTLE!(bFTLE,xb,yb,dx,dx,T)
@test norm(fFTLE) < 1e-8
@test norm(bFTLE) < 1e-8
#@test norm(ftle_c) < 1e-8
#@test norm(ftle_d) < 1e-8
end | ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 759 | using ILMPostProcessing
using ViscousFlow
using LinearAlgebra
@testset "POD" begin
# setup grid
xlim = (-1.0, 1.0)
ylim = (-1.0, 1.0)
g = PhysicalGrid(xlim, ylim, 0.01)
# setup velocity field cache
cache = SurfaceScalarCache(g)
vel = zeros_gridgrad(cache)
# create velocity snapshot data
vsnap = [zeros_gridgrad(cache) for i=1:10]
# create random velocity fields
for v in vsnap
v .= rand(size(v)...) # ... means splat
end
# extract POD modes
modes = pod(vsnap)
fieldReconst = mapreduce((aj, phi_j) -> aj .* phi_j, +, modes.a[end,:], modes.phi) + modes.Xmean
# compare POD-reconstructed field with original vel field
@test norm(fieldReconst-vsnap[end])/norm(vsnap[end]) < 1e-8
end | ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 1941 | #using Compat.Test
#using Compat
using ILMPostProcessing
using Literate
using Test
##using TestSetExtensions
const GROUP = get(ENV, "GROUP", "All")
ENV["GKSwstype"] = "nul" # removes GKS warnings during plotting
macro mysafetestset(args...)
name, expr = args
quote
ex = quote
name_str = $$(QuoteNode(name))
expr_str = $$(QuoteNode(expr))
mod = gensym(name_str)
ex2 = quote
@eval module $mod
using Test
@testset $name_str $expr_str
end
nothing
end
eval(ex2)
end
eval(ex)
end
end
notebookdir = "../examples"
docdir = "../docs/src/manual"
litdir = "./literate"
if GROUP == "All" || GROUP == "Auxiliary"
include("POD.jl")
include("trajectories.jl")
include("FTLE.jl")
end
if GROUP == "All" || GROUP == "Literate"
for (root, dirs, files) in walkdir(litdir)
for file in files
#endswith(file,".jl") && startswith(file,"caches") && @testset "$file" begin include(joinpath(root,file)) end
#endswith(file,".jl") && @testset "$file" begin include(joinpath(root,file)) end
global file_str = "$file"
global body = :(begin include(joinpath($root,$file)) end)
#endswith(file,".jl") && startswith(file,"s") && @mysafetestset file_str body
endswith(file,".jl") && @mysafetestset file_str body
end
end
end
if GROUP == "Notebooks"
for (root, dirs, files) in walkdir(litdir)
for file in files
#endswith(file,".jl") && startswith(file,"ftle_cont") && Literate.notebook(joinpath(root, file),notebookdir)
endswith(file,".jl") && Literate.notebook(joinpath(root, file),notebookdir)
end
end
end
if GROUP == "Documentation"
for (root, dirs, files) in walkdir(litdir)
for file in files
endswith(file,".jl") && Literate.markdown(joinpath(root, file),docdir)
end
end
end
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 2406 | using ILMPostProcessing
using ViscousFlow
using LinearAlgebra
@testset "Trajectories from computed flow fields" begin
my_params = Dict()
my_params["Re"] = 100
xlim = (-2.0,2.0)
ylim = (-2.0,2.0)
my_params["grid Re"] = 10.0
g = setup_grid(xlim,ylim,my_params)
sys = viscousflow_system(g,phys_params=my_params)
σ = 0.1
x01, y01 = 1.0, 0.0
x02, y02 = -1.0, 0.0
A = 3
twogauss = SpatialGaussian(σ,σ,x01,y01,A) + SpatialGaussian(σ,σ,x02,y02,A)
u0 = init_sol(twogauss,sys)
T = 1.0
tspan = (0.0,T)
integrator = init(u0,tspan,sys)
step!(integrator,1.0)
sol = integrator.sol
velfcn = velocity_xy(integrator)
pts = [ [0.5,1], [-0.5,-0.5], [0.25, -0.3]]
traj = compute_trajectory(velfcn...,pts,(0,1),alg=Tsit5())
@test length(traj.xhistory[end]) == length(traj.yhistory[end]) == length(pts)
tsline = integrator.t
sline = compute_streamline(velfcn...,pts,(0,12),tsline,alg=Tsit5())
t_start = 0.0
t_end = 1.0
dt = timestep(u0,sys)
tr = t_start:dt:t_end
velxy = velocity_xy(sol,sys,tr)
vseq = VectorFieldSequence(tr,velxy)
dx = 0.1
ftlegrid = PhysicalGrid((-2,2),(-2,2),dx,optimize=false)
ftle_cache = SurfaceScalarCache(ftlegrid)
x0, y0 = x_grid(ftle_cache), y_grid(ftle_cache)
traj = compute_trajectory(vseq,(x0,y0),(t_start,t_end),alg=Euler())
@test length(traj.xhistory[end]) == length(traj.yhistory[end]) == length(x0)
end
@testset "Trajectories from velocity functions" begin
ufcn(x,y) = x
vfcn(x,y) = -y
pts = [ [0.5,1], [-0.5,-0.5], [0.25, -0.3]]
traj = compute_trajectory(ufcn,vfcn,pts,(0,1),alg=Tsit5())
@test typeof(traj.xhistory)<:Vector && typeof(traj.yhistory)<:Vector
ufcn2(x,y,t) = 1
vfcn2(x,y,t) = sin(t)
traj = compute_trajectory(ufcn2,vfcn2,pts,(0,1),alg=Tsit5())
@test typeof(traj.xhistory)<:Vector && typeof(traj.yhistory)<:Vector
x1, y1 = traj[1]
@test norm(pts[1][2] .+ 1.0 .- cos.(traj.t) .- y1) < 1e-7
tsline = π
sline = compute_streamline(ufcn2,vfcn2,pts,(0,10),tsline,alg=Tsit5())
x1, y1 = sline[2]
@test norm(y1 .- pts[2][2]) < 1e-7
u(x,y,t) = 1.0
v(x,y,t) = cos(2π*(x-t))
y = [0.0,0.0]
t = 0.0
streak = compute_streakline(u,v,y,t)
xs, ys = streak[1]
@test xs[1] ≈ 3 && ys[1] ≈ 3 && xs[end] ≈ y[1] && ys[end] ≈ y[2]
end
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 3007 | #=
# Dynamic mode decomposition (DMD)
In this example, we will demonstrate the use of the de-biased form of dynamic mode decomposition (DMD) for
decomposing a simple linear dynamical system.
This example is inspired from example 1 of
M.S. Hemati, C.W. Rowley, E.A. Deem, and L.N. Cattafesta
``De-biasing the dynamic mode decomposition for
applied Koopman spectral analysis of noisy datasets,''
Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics (2017).
which introduces the de-biased form of DMD.
The example considers a low-rank linear system with
two undamped modes and one dampled mode. The snapshots taken from the
solution of the linear system are noised up with zero-mean Gaussian noise.
=#
#md # ```@meta
#md # CurrentModule = ILMPostProcessing
#md # ```
using ILMPostProcessing
using LinearAlgebra
using Random
using OrdinaryDiffEq
#!jl using Plots
m = 100 # number of snapshots
n = 250 # number of states
r = 6 # rank of DMD
dt = 0.01 # snapshot time step
meas_cov = 0.05 # measurement noise covariance
init_cov = 0.1; # initial condition covariance
#=
Specify characteristic frequencies and growth/decay rates
associated with continuous-time dynamics.
The DMD rank should be set equal to twice the number of modes
(since each mode consists of conjugate pairs)
=#
f = [1.0, 2.5, 5.5]
g = [0, 0, -0.3];
#=
Create the right hand side matrix for the continuous linear system
=#
k = 2*length(f)
A = zeros(k,k)
for ii in 1:length(f)
i1, i2 = 2*ii-1, 2*ii
Ai = view(A,i1:i2,i1:i2)
Ai .= [g[ii] 2π*f[ii]; -2π*f[ii] g[ii]]
end
#=
The true eigenvalues of the system
=#
true_evals = exp.(eigvals(A)*dt)
#=
Right-hand side of linear system of equations
=#
dynsys(x,p,t) = A*x
#=
### Solve the linear system
Set up a random initial condition with elements drawn from N(1,init_cov)
and solve the problem.
=#
x0 = 1 .+ randn(k)*sqrt(init_cov)
tspan = (0,dt*m)
prob = ODEProblem(dynsys,x0,tspan)
sol = solve(prob,Tsit5(),saveat=dt);
#=
For DMD, use the solution snapshots, but
randomly rotate them and apply noise to each.
(Here, by performing a QR decomposition of a matrix with random entries,
Q is a random unitary matrix)
=#
Q, _ = qr(randn(n,k))
getsnaps(x) = Q*x .+ sqrt(meas_cov)*randn(n)
snaps = map(x -> getsnaps(x),sol.u);
#=
Now perform DMD
=#
dmdmodes = dmd(snaps,r)
#!jl scatter(real(true_evals),imag(true_evals),ratio=1,xlim = (0.7,1.1),ylim=(0,0.4), xlabel="\$Re(\\mu)\$", ylabel="\$Im(\\mu)\$",label="True")
#!jl scatter!(real(dmdmodes.evals),imag(dmdmodes.evals),label="DMD")
#!jl θ = range(0,2π,length=100);
#!jl plot!(cos.(θ),sin.(θ),label="")
#=
### Compare the true and DMD-computed eigenvalues
Note that these may not be ordered the same, so we have to
also determine how to permute the order of them to compare
corresponding eigenvalues. We then compute the l2 error
=#
vals, idex = findmin(abs2.(true_evals .- transpose(dmdmodes.evals)),dims=2)
err = sqrt(sum(vals))
#jl @test err < 0.05
#md # ## DMD functions
#md # ```@docs
#md # dmd
#md # ```
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 5735 | #=
# Finite-Time Lyapunov Exponent (FTLE)
In this example, we will compute the finite-time Laypunov exponent (FTLE) field for a co-rotating vortex pair.
=#
#md # ```@meta
#md # CurrentModule = ILMPostProcessing
#md # ```
using ILMPostProcessing
using ViscousFlow
using Plots
#=
## Setup the Co-rotating Vortices Problem
The grid Re number is chosen at 10.0 to speed up computations.
=#
my_params = Dict()
my_params["Re"] = 300
xlim = (-3.0,3.0)
ylim = (-3.0,3.0)
my_params["grid Re"] = 10.0
g = setup_grid(xlim,ylim,my_params)
sys = viscousflow_system(g,phys_params=my_params)
σ = 0.1
x01, y01 = 1.0, 0.0
x02, y02 = -1.0, 0.0
A = 3
twogauss = SpatialGaussian(σ,σ,x01,y01,A) + SpatialGaussian(σ,σ,x02,y02,A)
u0 = init_sol(twogauss,sys)
plot(vorticity(u0,sys,0.0),sys)
#=
## Solve the Problem
Step the integrator repeatedly until the solution is generated for t = (0.0, 18.0).
=#
T = 19.0
tspan = (0.0,T)
integrator = init(u0,tspan,sys)
@time begin
step!(integrator,T)
end
sol = integrator.sol
plt = plot(layout = (4,5), size = (800, 800), legend=:false)
tsnap = 0.0:1.0:T
for (i, t) in enumerate(tsnap)
plot!(plt[i],vorticity(sol,sys,t),sys,levels=range(0.1,5,length=31))
end
plt
#=
## Generate a Sequence of Velocity Fields
This step obtains the computed velocity field at a sequence of times, and stores them as a sequence of interpolatable
fields in `velseq`. This will greatly speed up the steps in which we compute the flow deformation fields.
=#
t_start = 0.0
t_end = 19.0
dt = timestep(u0,sys)
tr = t_start:dt:t_end
velxy = velocity_xy(sol,sys,tr) # Vector of interpolatable velocities
velseq = VectorFieldSequence(tr,velxy); # Bundle together with the time array
#=
## Generate Initial Conditions
Here, we generate a grid of initial locations from which to integrate
trajectories.
=#
X_MIN = -2.0
X_MAX = 2.0
Y_MIN = -2.0
Y_MAX = 2.0
dx = 0.01
ftlegrid = PhysicalGrid((X_MIN,X_MAX),(Y_MIN,Y_MAX),dx,optimize=false)
ftle_cache = SurfaceScalarCache(ftlegrid)
x0, y0 = x_grid(ftle_cache), y_grid(ftle_cache)
#=
## Solve the IVP and Generate FTLE Fields
### Computing the FTLE Field at One Time Snapshot
To compute the particle displacement field, we choose an integration time `T`.
We also choose a time `t0` at which we desire to see the FTLE field. Note
that we will compute both a forward and backward time FTLE field at `t0`, so
we need to ensure we have velocity data available from `t0 - T` to `t0 + T`.
For integration purposes we use the forward Euler method, but any time marching
method can be used.
=#
T = 6.0
t0 = 6.0
#=
The forward displacement field and FTLE field
=#
xf, yf = displacement_field(velseq,x0,y0,(t0,t0+T),alg=Euler())
fFTLE = similar(x0)
compute_FTLE!(fFTLE,xf,yf,dx,dx,T);
#=
and now the backward displacement field and FTLE field. We don't actually
need to specify the `alg` because `Euler()` is the default.
=#
xb, yb = displacement_field(velseq,x0,y0,(t0,t0-T))
bFTLE = similar(x0)
compute_FTLE!(bFTLE,xb,yb,dx,dx,T);
#=
Plot the fields on top of each other
=#
plot(fFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:inferno,size=(800,800))
plot!(bFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:viridis,xlim=(-2,2),ylim=(-2,2),title="FTLE, t = $t0", xlabel="x", ylabel="y")
#=
### Computing the FTLE Fields at a Range of Times
Let's see some blocks of particles and how they move as the FTLE field evolves.
The example places initial points at `t = 6` near the unstable manifold (orange).
We will compute the FTLE field after 4 time units (`t = 10`) and see the particles.
The initial block of points is roughly colored according to which side of this
manifold it is on.
=#
xp_min = -1.0
xp_max = 0.0
yp_min = 0.5
yp_max = 1.5
dxp = 0.1
p_grid = PhysicalGrid((xp_min,xp_max),(yp_min,yp_max),dxp,optimize=false)
p_cache = SurfaceScalarCache(p_grid);
xp0, yp0 = x_grid(p_cache), y_grid(p_cache);
plot(fFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:inferno,size=(800,800))
plot!(bFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:viridis,xlim=(-2,2),ylim=(-2,2),title="FTLE, t = $t0", xlabel="x", ylabel="y")
scatter!(vec(xp0[1:5,1:end]),vec(yp0[1:5,1:end]))
scatter!(vec(xp0[8:end,1:end]),vec(yp0[8:end,1:end]))
#=
Now we will advance the block of particles to `t = 10` and compute the FTLE fields
at that instant.
=#
t0_ftle = 10.0
xpf, ypf = displacement_field(velseq,xp0,yp0,(t0,t0_ftle))
xf, yf = displacement_field(velseq,x0,y0,(t0_ftle,t0_ftle+T))
compute_FTLE!(fFTLE,xf,yf,dx,dx,T)
xb, yb = displacement_field(velseq,x0,y0,(t0_ftle,t0_ftle-T))
compute_FTLE!(bFTLE,xb,yb,dx,dx,T);
#=
Now plot the FTLE fields and particles
=#
plot(fFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:inferno,size=(800,800))
plot!(bFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:viridis,xlim=(-2,2),ylim=(-2,2),title="FTLE, t = $t0_ftle", xlabel="x", ylabel="y")
scatter!(vec(xpf[1:5,1:end]),vec(ypf[1:5,1:end]))
scatter!(vec(xpf[8:end,1:end]),vec(ypf[8:end,1:end]))
#=
The code here creates a gif
@gif for t0_ftle in 6.5:0.5:12.0
print(t0_ftle)
xpf, ypf = displacement_field(velseq,xp0,yp0,(t0,t0_ftle))
xf, yf = displacement_field(velseq,x0,y0,(t0_ftle,t0_ftle+T))
compute_FTLE!(fFTLE,xf,yf,dx,dx,T)
xb, yb = displacement_field(velseq,x0,y0,(t0_ftle,t0_ftle-T))
compute_FTLE!(bFTLE,xb,yb,dx,dx,T)
plot(fFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:inferno,size=(800,800))
plot!(bFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:viridis,xlim=(-2,2),ylim=(-2,2),title="FTLE, t = $t0_ftle", xlabel="x", ylabel="y")
scatter!(vec(xpf[1:5,1:end]),vec(ypf[1:5,1:end]))
scatter!(vec(xpf[8:end,1:end]),vec(ypf[8:end,1:end]))
end every 1 fps = 2
=#
#md # ## FTLE functions
#md # ```@docs
#md # make_interp_fields!
#md # gen_init_conds
#md # euler_forward
#md # euler_backward
#md # adams_bashforth_2_forward
#md # adams_bashforth_2_backward
#md # compute_FTLE!
#md # ``` | ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 4219 | #=
# Finite-Time Lyapunov Exponent (FTLE) with Continuous Velocity Field
We present two examples where the FTLE is calculated from known continuous velocity fields as opposed to discrete fields specified at grid points.
The first example demonstrates a simple FTLE analysis and lays the conceptual foundation for later analysis on discrete data. The second example showcases an issue of sliding-window FTLE analysis.
=#
#md # ```@meta
#md # CurrentModule = ILMPostProcessing
#md # ```
using ILMPostProcessing
using ImmersedLayers
using Plots
#=
## Example 1: Unsteady Double Gyre
This example replicates the time-dependent double gyre from Shadden 2005. The double gyre velocity field's specification can be found at https://shaddenlab.berkeley.edu/uploads/LCS-tutorial/examples.html#Sec7.1. The results in this simulation is highly similar.
=#
#=
### Generate Initial Conditions for the IVP
=#
X_MIN, X_MAX = 0.0, 2.0
Y_MIN, Y_MAX = 0.0, 1.0
dx = 0.002
ftlegrid = PhysicalGrid((X_MIN,X_MAX),(Y_MIN,Y_MAX),dx,optimize=false);
ftle_cache = SurfaceScalarCache(ftlegrid)
x0, y0 = x_grid(ftle_cache), y_grid(ftle_cache)
#=
### Define the Double Gyre's Vector Field
=#
A = 0.1
epsilon = 0.25
omega = 2 * π / 10
a(s) = epsilon * sin(omega * s)
b(s) = 1 - 2 * epsilon * sin(omega * s)
f(x, t) = a(t) * x^2 + b(t) * x
dfdx(x, t) = 2 * a(t) * x + b(t)
u(x,y,t) = -π * A * sin.(π * f(x, t)) .* cos.(π * y)
v(x,y,t) = π * A * cos.(π * f(x, t)) .* sin.(π * y) .* dfdx(x, t)
#=
### Solve the Forward and Backward IVPs
=#
t0 = 0.0
T = 12
xf, yf = displacement_field(u,v,x0,y0,(t0,t0+T))
xb, yb = displacement_field(u,v,x0,y0,(t0,t0-T))
#=
### Compute the Forward and Backward FTLEs
=#
fFTLE = similar(x0)
bFTLE = similar(x0)
compute_FTLE!(fFTLE,xf,yf,dx,dx,T)
compute_FTLE!(bFTLE,xb,yb,dx,dx,T)
#=
### Plot the FTLEs on Top of Each Other
=#
plot(fFTLE, ftle_cache,fill=false, title="FTLE, t = $t0", xlabel="x", ylabel="y", colorbar=false, levels = 30, c=:inferno)
plot!(bFTLE, ftle_cache, fill=false, colorbar=false, levels = 30, c=:viridis)
#=
The code here creates a gif
fFTLE = similar(x0)
bFTLE = similar(x0)
@gif for t0 in 0.0:1.0:10.0
print(t0)
xf, yf = displacement_field(u,v,x0,y0,(t0,t0+T))
xb, yb = displacement_field(u,v,x0,y0,(t0,t0-T))
compute_FTLE!(fFTLE,xf,yf,dx,dx,T)
compute_FTLE!(bFTLE,xb,yb,dx,dx,T)
plot(fFTLE, ftle_cache,fill=false, title="FTLE, t = $t0", xlabel="x", ylabel="y", colorbar=false, levels = 30, c=:inferno)
plot!(bFTLE, ftle_cache, fill=false, colorbar=false, levels = 30, c=:viridis)
end every 1 fps = 2
=#
#=
## Example 2 - Issues with the Sliding-Window Approach
The sliding-window approach attempts to detect Langragian coherent structures (LCS) by computing the FTLE fields over windows of the form [t0, t0 + T] with varying t0 values. However, this approach does not obey Lagrangian invariance because the LCS's at different t0 values do not evolve into each other (Haller 2015).
This example illustrates the point above.
=#
#=
### First, generate initial conditions.
=#
X_MIN, X_MAX = -6.0, 50.0
Y_MIN, Y_MAX = -2, 2
dx = 0.08
ftlegrid = PhysicalGrid((X_MIN,X_MAX),(Y_MIN,Y_MAX),dx,optimize=false);
ftle_cache = SurfaceScalarCache(ftlegrid)
x0, y0 = x_grid(ftle_cache), y_grid(ftle_cache)
#=
### Define the Vector Field
=#
u2(x,y) = 1 + tanh.(x).^2
v2(x,y) = -2 * tanh.(x) ./ cosh.(x).^2 .* y
#=
### Solve the IVP and Compute FTLEs with the Sliding-Window Approach
As shown in the figure,although the flow is unsteady, the actual LCS is a material line that moves with the flow to the right. Nevertheless, as shown in the gif below, when t0 varies from 0.0 to 10.0, the forward FTLE fields reveals a repelling LCS fixed on the y-axis.

=#
fFTLE = similar(x0)
T = 5
@gif for t0 in 0.0:0.5:10.0
print(t0)
xf, yf = displacement_field(u2,v2,x0,y0,(t0,t0+T))
compute_FTLE!(fFTLE,xf,yf,dx,dx,T)
plot(fFTLE, ftle_cache,fill=false, title="FTLE, t = $t0", xlabel="x", ylabel="y", colorbar=false, levels = 30, c=:inferno)
end every 1 fps = 2 | ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | code | 3296 | #=
# Proper orthogonal decomposition (POD)
In this example, we will demonstrate the use of proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) for
decomposing a flow field into basis modes.
=#
#md # ```@meta
#md # CurrentModule = ILMPostProcessing
#md # ```
using ILMPostProcessing
#!jl using Plots
#=
## Get the flow field data
First, we need some flow field data to analyze. For this purpose, we will use [ViscousFlow.jl](https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ViscousFlow.jl)
to get snapshots of the flow for a flat plate at 30 degrees angle of attack at
Reynolds number 100.
=#
using ViscousFlow
my_params = Dict()
my_params["Re"] = 100
my_params["freestream speed"] = 1.0 # in x-dir
my_params["freestream angle"] = 0.0 # relative to horizontal
xlim = (-1.0, 5.0)
ylim = (-2.0, 2.0)
my_params["grid Re"] = 4.0
g = setup_grid(xlim, ylim, my_params)
Δs = surface_point_spacing(g, my_params)
body = Plate(1.0, Δs)
cent = [0.5,0.0]
α = -30π/180
X = MotionTransform(cent, α)
joint = Joint(X)
m = RigidBodyMotion(joint, body)
x = init_motion_state(body, m)
update_body!(body, x, m)
sys = viscousflow_system(g, body, phys_params = my_params, motions = m);
u0 = init_sol(sys)
tspan = (0.0, 20.0)
integrator = init(u0, tspan, sys)
## Solve to 10 convective time units
step!(integrator, 10)
#=
## Assemble snapshots of the velocity field from the solution data
Here, we make use of the capability of the `velocity` function to
generate an array of velocity fields at a range of times. We will
save every 5th time step in this array.
=#
sol = integrator.sol
tpod = sol.t[2:5:end]
X = velocity(sol, sys, tpod);
#=
## Perform the POD
The POD is simply performed with the `PODModes` function. This provides
a structure containing the modes (`phi`), the expansion coefficients (`a`), and the modal
energies (`lambda`). By default, `PODModes` retains 99% of the energy. This can be changed
with the optional argument `tolerance`.
=#
modes = pod(X);
#=
The `a` array is of size $N_t \times r$, where $N_t$ is the number of time values,
and $r$ is the number of modes. The modes are ordered from highest energy to lowest energy.
=#
modes.a
#=
In this case, 7 modes were retained, at 51 times.
=#
#=
If we wanted to re-assemble the modes and coefficients to recover the flow at some time instant, we could
use the `mapreduce` function, e.g.,
=#
vel_assemble = mapreduce((aj, phi_j) -> aj .* phi_j, +, modes.a[end,:], modes.phi) + modes.Xmean
#=
In this last line, `modes.a[end,:]` obtains the expansion coefficients at the last time
available.
=#
#=
Let's print the first mode, and the corresponding history of the modal coefficient in the decomposition
=#
#!jl plot(layout=[2;1],plot(modes.phi[1].u,sys,title="u"),
#!jl plot(modes.phi[1].v,sys,title="v"),
#!jl plot(tpod,modes.a[:,1],xlim=(0,Inf),xlabel="\$t\$",ylabel="\$a_1(t)\$"))
#=
The energy associated with this mode is
=#
modes.lambda[1]
#=
Now let's print the $r$th mode, and the history of the coefficient in the decomposition
=#
#!jl plot(layout=[2;1],plot(modes.phi[end].u,sys,title="u"),
#!jl plot(modes.phi[end].v,sys,title="v"),
#!jl plot(tpod,modes.a[:,end],xlim=(0,Inf),xlabel="\$t\$",ylabel="\$a_r(t)\$"))
#=
The energy associated with this mode is
=#
modes.lambda[end]
#md # ## POD functions
#md # ```@docs
#md # pod
#md # ``` | ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | docs | 1218 | # ILMPostProcessing.jl
_Tools for post-processing solutions of immersed layer PDEs_
| Documentation | Build Status |
|:---:|:---:|
| [](https://JuliaIBPM.github.io/ILMPostProcessing.jl/stable) [](https://JuliaIBPM.github.io/ILMPostProcessing.jl/dev) | [](https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl/actions) [](https://codecov.io/gh/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl) |
This package contains tools that can be used to post-process and analyze the solutions of partial differential equations computed with the [ImmersedLayers.jl](https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ImmersedLayers.jl) package. Currently implemented methods are
* flow lines (pathlines, streamlines, streaklines)
* proper orthogonal decomposition (POD)
* dynamic mode decomposition (DMD)
* finite-time Lyapunov exponent (FTLE)
The examples in the documentation, which have companion notebooks in the `examples` folder, are the best way to get started.
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | docs | 1106 | # ILMPostProcessing.jl
*Tools for post-processing solutions of immersed layer PDEs*
The objective of this package is to supply a variety of post-processing tools for
solutions of PDEs carried out with the [ImmersedLayers.jl](https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ImmersedLayers.jl) package, and the domain-specific subpackages, such as [ViscousFlow.jl](https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ViscousFlow.jl). The post-processing tools[^1] currently available
are
* Proper orthogonal decomposition (POD)
* Dynamic mode decomposition (DMD)
* Finite-time Lyapunov exponent (FTLE)
## Installation
This package works on Julia `1.7` and above and is registered in the general Julia registry. To install from the REPL, type
e.g.,
```julia
] add ILMPostProcessing
```
Then, in any version, type
```julia
julia> using ILMPostProcessing
```
The plots in this documentation are generated using [Plots.jl](http://docs.juliaplots.org/latest/).
You might want to install that, too, to follow the examples.
## References
[^1]: Taira, K. et al (2017) "Modal Analysis of Fluid Flows: An Overview," *AIAA Journal*, 55(12), 4013--4041.
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | docs | 3316 | ```@meta
EditURL = "../../../test/literate/dmdtest.jl"
```
# Dynamic mode decomposition (DMD)
In this example, we will demonstrate the use of the de-biased form of dynamic mode decomposition (DMD) for
decomposing a simple linear dynamical system.
This example is inspired from example 1 of
M.S. Hemati, C.W. Rowley, E.A. Deem, and L.N. Cattafesta
``De-biasing the dynamic mode decomposition for
applied Koopman spectral analysis of noisy datasets,''
Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics (2017).
which introduces the de-biased form of DMD.
The example considers a low-rank linear system with
two undamped modes and one dampled mode. The snapshots taken from the
solution of the linear system are noised up with zero-mean Gaussian noise.
```@meta
CurrentModule = ILMPostProcessing
```
````@example dmdtest
using ILMPostProcessing
using LinearAlgebra
using Random
using OrdinaryDiffEq
using Plots
m = 100 # number of snapshots
n = 250 # number of states
r = 6 # rank of DMD
dt = 0.01 # snapshot time step
meas_cov = 0.05 # measurement noise covariance
init_cov = 0.1; # initial condition covariance
nothing #hide
````
Specify characteristic frequencies and growth/decay rates
associated with continuous-time dynamics.
The DMD rank should be set equal to twice the number of modes
(since each mode consists of conjugate pairs)
````@example dmdtest
f = [1.0, 2.5, 5.5]
g = [0, 0, -0.3];
nothing #hide
````
Create the right hand side matrix for the continuous linear system
````@example dmdtest
k = 2*length(f)
A = zeros(k,k)
for ii in 1:length(f)
i1, i2 = 2*ii-1, 2*ii
Ai = view(A,i1:i2,i1:i2)
Ai .= [g[ii] 2π*f[ii]; -2π*f[ii] g[ii]]
end
````
The true eigenvalues of the system
````@example dmdtest
true_evals = exp.(eigvals(A)*dt)
````
Right-hand side of linear system of equations
````@example dmdtest
dynsys(x,p,t) = A*x
````
### Solve the linear system
Set up a random initial condition with elements drawn from N(1,init_cov)
and solve the problem.
````@example dmdtest
x0 = 1 .+ randn(k)*sqrt(init_cov)
tspan = (0,dt*m)
prob = ODEProblem(dynsys,x0,tspan)
sol = solve(prob,Tsit5(),saveat=dt);
nothing #hide
````
For DMD, use the solution snapshots, but
randomly rotate them and apply noise to each.
(Here, by performing a QR decomposition of a matrix with random entries,
Q is a random unitary matrix)
````@example dmdtest
Q, _ = qr(randn(n,k))
getsnaps(x) = Q*x .+ sqrt(meas_cov)*randn(n)
snaps = map(x -> getsnaps(x),sol.u);
nothing #hide
````
Now perform DMD
````@example dmdtest
dmdmodes = dmd(snaps,r)
scatter(real(true_evals),imag(true_evals),ratio=1,xlim = (0.7,1.1),ylim=(0,0.4), xlabel="\$Re(\\mu)\$", ylabel="\$Im(\\mu)\$",label="True")
scatter!(real(dmdmodes.evals),imag(dmdmodes.evals),label="DMD")
θ = range(0,2π,length=100);
plot!(cos.(θ),sin.(θ),label="")
````
### Compare the true and DMD-computed eigenvalues
Note that these may not be ordered the same, so we have to
also determine how to permute the order of them to compare
corresponding eigenvalues. We then compute the l2 error
````@example dmdtest
vals, idex = findmin(abs2.(true_evals .- transpose(dmdmodes.evals)),dims=2)
err = sqrt(sum(vals))
````
## DMD functions
```@docs
dmd
```
---
*This page was generated using [Literate.jl](https://github.com/fredrikekre/Literate.jl).*
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | docs | 6057 | ```@meta
EditURL = "../../../test/literate/ftle.jl"
```
# Finite-Time Lyapunov Exponent (FTLE)
In this example, we will compute the finite-time Laypunov exponent (FTLE) field for a co-rotating vortex pair.
```@meta
CurrentModule = ILMPostProcessing
```
````@example ftle
using ILMPostProcessing
using ViscousFlow
using Plots
````
## Setup the Co-rotating Vortices Problem
The grid Re number is chosen at 10.0 to speed up computations.
````@example ftle
my_params = Dict()
my_params["Re"] = 300
xlim = (-3.0,3.0)
ylim = (-3.0,3.0)
my_params["grid Re"] = 10.0
g = setup_grid(xlim,ylim,my_params)
sys = viscousflow_system(g,phys_params=my_params)
σ = 0.1
x01, y01 = 1.0, 0.0
x02, y02 = -1.0, 0.0
A = 3
twogauss = SpatialGaussian(σ,σ,x01,y01,A) + SpatialGaussian(σ,σ,x02,y02,A)
u0 = init_sol(twogauss,sys)
plot(vorticity(u0,sys,0.0),sys)
````
## Solve the Problem
Step the integrator repeatedly until the solution is generated for t = (0.0, 18.0).
````@example ftle
T = 19.0
tspan = (0.0,T)
integrator = init(u0,tspan,sys)
@time begin
step!(integrator,T)
end
sol = integrator.sol
plt = plot(layout = (4,5), size = (800, 800), legend=:false)
tsnap = 0.0:1.0:T
for (i, t) in enumerate(tsnap)
plot!(plt[i],vorticity(sol,sys,t),sys,levels=range(0.1,5,length=31))
end
plt
````
## Generate a Sequence of Velocity Fields
This step obtains the computed velocity field at a sequence of times, and stores them as a sequence of interpolatable
fields in `velseq`. This will greatly speed up the steps in which we compute the flow deformation fields.
````@example ftle
t_start = 0.0
t_end = 19.0
dt = timestep(u0,sys)
tr = t_start:dt:t_end
velxy = velocity_xy(sol,sys,tr) # Vector of interpolatable velocities
velseq = VectorFieldSequence(tr,velxy); # Bundle together with the time array
nothing #hide
````
## Generate Initial Conditions
Here, we generate a grid of initial locations from which to integrate
trajectories.
````@example ftle
X_MIN = -2.0
X_MAX = 2.0
Y_MIN = -2.0
Y_MAX = 2.0
dx = 0.01
ftlegrid = PhysicalGrid((X_MIN,X_MAX),(Y_MIN,Y_MAX),dx,optimize=false)
ftle_cache = SurfaceScalarCache(ftlegrid)
x0, y0 = x_grid(ftle_cache), y_grid(ftle_cache)
````
## Solve the IVP and Generate FTLE Fields
### Computing the FTLE Field at One Time Snapshot
To compute the particle displacement field, we choose an integration time `T`.
We also choose a time `t0` at which we desire to see the FTLE field. Note
that we will compute both a forward and backward time FTLE field at `t0`, so
we need to ensure we have velocity data available from `t0 - T` to `t0 + T`.
For integration purposes we use the forward Euler method, but any time marching
method can be used.
````@example ftle
T = 6.0
t0 = 6.0
````
The forward displacement field and FTLE field
````@example ftle
xf, yf = displacement_field(velseq,x0,y0,(t0,t0+T),alg=Euler())
fFTLE = similar(x0)
compute_FTLE!(fFTLE,xf,yf,dx,dx,T);
nothing #hide
````
and now the backward displacement field and FTLE field. We don't actually
need to specify the `alg` because `Euler()` is the default.
````@example ftle
xb, yb = displacement_field(velseq,x0,y0,(t0,t0-T))
bFTLE = similar(x0)
compute_FTLE!(bFTLE,xb,yb,dx,dx,T);
nothing #hide
````
Plot the fields on top of each other
````@example ftle
plot(fFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:inferno,size=(800,800))
plot!(bFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:viridis,xlim=(-2,2),ylim=(-2,2),title="FTLE, t = $t0", xlabel="x", ylabel="y")
````
### Computing the FTLE Fields at a Range of Times
Let's see some blocks of particles and how they move as the FTLE field evolves.
The example places initial points at `t = 6` near the unstable manifold (orange).
We will compute the FTLE field after 4 time units (`t = 10`) and see the particles.
The initial block of points is roughly colored according to which side of this
manifold it is on.
````@example ftle
xp_min = -1.0
xp_max = 0.0
yp_min = 0.5
yp_max = 1.5
dxp = 0.1
p_grid = PhysicalGrid((xp_min,xp_max),(yp_min,yp_max),dxp,optimize=false)
p_cache = SurfaceScalarCache(p_grid);
xp0, yp0 = x_grid(p_cache), y_grid(p_cache);
plot(fFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:inferno,size=(800,800))
plot!(bFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:viridis,xlim=(-2,2),ylim=(-2,2),title="FTLE, t = $t0", xlabel="x", ylabel="y")
scatter!(vec(xp0[1:5,1:end]),vec(yp0[1:5,1:end]))
scatter!(vec(xp0[8:end,1:end]),vec(yp0[8:end,1:end]))
````
Now we will advance the block of particles to `t = 10` and compute the FTLE fields
at that instant.
````@example ftle
t0_ftle = 10.0
xpf, ypf = displacement_field(velseq,xp0,yp0,(t0,t0_ftle))
xf, yf = displacement_field(velseq,x0,y0,(t0_ftle,t0_ftle+T))
compute_FTLE!(fFTLE,xf,yf,dx,dx,T)
xb, yb = displacement_field(velseq,x0,y0,(t0_ftle,t0_ftle-T))
compute_FTLE!(bFTLE,xb,yb,dx,dx,T);
nothing #hide
````
Now plot the FTLE fields and particles
````@example ftle
plot(fFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:inferno,size=(800,800))
plot!(bFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:viridis,xlim=(-2,2),ylim=(-2,2),title="FTLE, t = $t0_ftle", xlabel="x", ylabel="y")
scatter!(vec(xpf[1:5,1:end]),vec(ypf[1:5,1:end]))
scatter!(vec(xpf[8:end,1:end]),vec(ypf[8:end,1:end]))
````
The code here creates a gif
@gif for t0_ftle in 6.5:0.5:12.0
print(t0_ftle)
xpf, ypf = displacement_field(velseq,xp0,yp0,(t0,t0_ftle))
xf, yf = displacement_field(velseq,x0,y0,(t0_ftle,t0_ftle+T))
compute_FTLE!(fFTLE,xf,yf,dx,dx,T)
xb, yb = displacement_field(velseq,x0,y0,(t0_ftle,t0_ftle-T))
compute_FTLE!(bFTLE,xb,yb,dx,dx,T)
plot(fFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:inferno,size=(800,800))
plot!(bFTLE,ftle_cache,color=:viridis,xlim=(-2,2),ylim=(-2,2),title="FTLE, t = $t0_ftle", xlabel="x", ylabel="y")
scatter!(vec(xpf[1:5,1:end]),vec(ypf[1:5,1:end]))
scatter!(vec(xpf[8:end,1:end]),vec(ypf[8:end,1:end]))
end every 1 fps = 2
## FTLE functions
```@docs
make_interp_fields!
gen_init_conds
euler_forward
euler_backward
adams_bashforth_2_forward
adams_bashforth_2_backward
compute_FTLE!
```
---
*This page was generated using [Literate.jl](https://github.com/fredrikekre/Literate.jl).*
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | docs | 4589 | ```@meta
EditURL = "../../../test/literate/ftle_continuous.jl"
```
# Finite-Time Lyapunov Exponent (FTLE) with Continuous Velocity Field
We present two examples where the FTLE is calculated from known continuous velocity fields as opposed to discrete fields specified at grid points.
The first example demonstrates a simple FTLE analysis and lays the conceptual foundation for later analysis on discrete data. The second example showcases an issue of sliding-window FTLE analysis.
```@meta
CurrentModule = ILMPostProcessing
```
````@example ftle_continuous
using ILMPostProcessing
using ImmersedLayers
using Plots
````
## Example 1: Unsteady Double Gyre
This example replicates the time-dependent double gyre from Shadden 2005. The double gyre velocity field's specification can be found at https://shaddenlab.berkeley.edu/uploads/LCS-tutorial/examples.html#Sec7.1. The results in this simulation is highly similar.
### Generate Initial Conditions for the IVP
````@example ftle_continuous
X_MIN, X_MAX = 0.0, 2.0
Y_MIN, Y_MAX = 0.0, 1.0
dx = 0.002
ftlegrid = PhysicalGrid((X_MIN,X_MAX),(Y_MIN,Y_MAX),dx,optimize=false);
ftle_cache = SurfaceScalarCache(ftlegrid)
x0, y0 = x_grid(ftle_cache), y_grid(ftle_cache)
````
### Define the Double Gyre's Vector Field
````@example ftle_continuous
A = 0.1
epsilon = 0.25
omega = 2 * π / 10
a(s) = epsilon * sin(omega * s)
b(s) = 1 - 2 * epsilon * sin(omega * s)
f(x, t) = a(t) * x^2 + b(t) * x
dfdx(x, t) = 2 * a(t) * x + b(t)
u(x,y,t) = -π * A * sin.(π * f(x, t)) .* cos.(π * y)
v(x,y,t) = π * A * cos.(π * f(x, t)) .* sin.(π * y) .* dfdx(x, t)
````
### Solve the Forward and Backward IVPs
````@example ftle_continuous
t0 = 0.0
T = 12
xf, yf = displacement_field(u,v,x0,y0,(t0,t0+T))
xb, yb = displacement_field(u,v,x0,y0,(t0,t0-T))
````
### Compute the Forward and Backward FTLEs
````@example ftle_continuous
fFTLE = similar(x0)
bFTLE = similar(x0)
compute_FTLE!(fFTLE,xf,yf,dx,dx,T)
compute_FTLE!(bFTLE,xb,yb,dx,dx,T)
````
### Plot the FTLEs on Top of Each Other
````@example ftle_continuous
plot(fFTLE, ftle_cache,fill=false, title="FTLE, t = $t0", xlabel="x", ylabel="y", colorbar=false, levels = 30, c=:inferno)
plot!(bFTLE, ftle_cache, fill=false, colorbar=false, levels = 30, c=:viridis)
````
The code here creates a gif
fFTLE = similar(x0)
bFTLE = similar(x0)
@gif for t0 in 0.0:1.0:10.0
print(t0)
xf, yf = displacement_field(u,v,x0,y0,(t0,t0+T))
xb, yb = displacement_field(u,v,x0,y0,(t0,t0-T))
compute_FTLE!(fFTLE,xf,yf,dx,dx,T)
compute_FTLE!(bFTLE,xb,yb,dx,dx,T)
plot(fFTLE, ftle_cache,fill=false, title="FTLE, t = $t0", xlabel="x", ylabel="y", colorbar=false, levels = 30, c=:inferno)
plot!(bFTLE, ftle_cache, fill=false, colorbar=false, levels = 30, c=:viridis)
end every 1 fps = 2
## Example 2 - Issues with the Sliding-Window Approach
The sliding-window approach attempts to detect Langragian coherent structures (LCS) by computing the FTLE fields over windows of the form [t0, t0 + T] with varying t0 values. However, this approach does not obey Lagrangian invariance because the LCS's at different t0 values do not evolve into each other (Haller 2015).
This example illustrates the point above.
### First, generate initial conditions.
````@example ftle_continuous
X_MIN, X_MAX = -6.0, 50.0
Y_MIN, Y_MAX = -2, 2
dx = 0.08
ftlegrid = PhysicalGrid((X_MIN,X_MAX),(Y_MIN,Y_MAX),dx,optimize=false);
ftle_cache = SurfaceScalarCache(ftlegrid)
x0, y0 = x_grid(ftle_cache), y_grid(ftle_cache)
````
### Define the Vector Field
````@example ftle_continuous
u2(x,y) = 1 + tanh.(x).^2
v2(x,y) = -2 * tanh.(x) ./ cosh.(x).^2 .* y
````
### Solve the IVP and Compute FTLEs with the Sliding-Window Approach
As shown in the figure,although the flow is unsteady, the actual LCS is a material line that moves with the flow to the right. Nevertheless, as shown in the gif below, when t0 varies from 0.0 to 10.0, the forward FTLE fields reveals a repelling LCS fixed on the y-axis.

````@example ftle_continuous
fFTLE = similar(x0)
T = 5
@gif for t0 in 0.0:0.5:10.0
print(t0)
xf, yf = displacement_field(u2,v2,x0,y0,(t0,t0+T))
compute_FTLE!(fFTLE,xf,yf,dx,dx,T)
plot(fFTLE, ftle_cache,fill=false, title="FTLE, t = $t0", xlabel="x", ylabel="y", colorbar=false, levels = 30, c=:inferno)
end every 1 fps = 2
````
---
*This page was generated using [Literate.jl](https://github.com/fredrikekre/Literate.jl).*
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | docs | 235 | # Functions and types
## Functions
```@autodocs
Modules = [ILMPostProcessing]
Order = [:function]
```
## Types
```@autodocs
Modules = [ILMPostProcessing]
Order = [:type]
```
## Index
```@index
Pages = ["functions.md"]
```
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | 3607010e6871e1c3f64ccf44d09ac425bb8be461 | docs | 3554 | ```@meta
EditURL = "../../../test/literate/pod.jl"
```
# Proper orthogonal decomposition (POD)
In this example, we will demonstrate the use of proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) for
decomposing a flow field into basis modes.
```@meta
CurrentModule = ILMPostProcessing
```
````@example pod
using ILMPostProcessing
using Plots
````
## Get the flow field data
First, we need some flow field data to analyze. For this purpose, we will use [ViscousFlow.jl](https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ViscousFlow.jl)
to get snapshots of the flow for a flat plate at 30 degrees angle of attack at
Reynolds number 100.
````@example pod
using ViscousFlow
my_params = Dict()
my_params["Re"] = 100
my_params["freestream speed"] = 1.0 # in x-dir
my_params["freestream angle"] = 0.0 # relative to horizontal
xlim = (-1.0, 5.0)
ylim = (-2.0, 2.0)
my_params["grid Re"] = 4.0
g = setup_grid(xlim, ylim, my_params)
Δs = surface_point_spacing(g, my_params)
body = Plate(1.0, Δs)
cent = [0.5,0.0]
α = -30π/180
X = MotionTransform(cent, α)
joint = Joint(X)
m = RigidBodyMotion(joint, body)
x = init_motion_state(body, m)
update_body!(body, x, m)
sys = viscousflow_system(g, body, phys_params = my_params, motions = m);
u0 = init_sol(sys)
tspan = (0.0, 20.0)
integrator = init(u0, tspan, sys)
# Solve to 10 convective time units
step!(integrator, 10)
````
## Assemble snapshots of the velocity field from the solution data
Here, we make use of the capability of the `velocity` function to
generate an array of velocity fields at a range of times. We will
save every 5th time step in this array.
````@example pod
sol = integrator.sol
tpod = sol.t[2:5:end]
X = velocity(sol, sys, tpod);
nothing #hide
````
## Perform the POD
The POD is simply performed with the `PODModes` function. This provides
a structure containing the modes (`phi`), the expansion coefficients (`a`), and the modal
energies (`lambda`). By default, `PODModes` retains 99% of the energy. This can be changed
with the optional argument `tolerance`.
````@example pod
modes = pod(X);
nothing #hide
````
The `a` array is of size $N_t \times r$, where $N_t$ is the number of time values,
and $r$ is the number of modes. The modes are ordered from highest energy to lowest energy.
````@example pod
modes.a
````
In this case, 7 modes were retained, at 51 times.
If we wanted to re-assemble the modes and coefficients to recover the flow at some time instant, we could
use the `mapreduce` function, e.g.,
````@example pod
vel_assemble = mapreduce((aj, phi_j) -> aj .* phi_j, +, modes.a[end,:], modes.phi) + modes.Xmean
````
In this last line, `modes.a[end,:]` obtains the expansion coefficients at the last time
available.
Let's print the first mode, and the corresponding history of the modal coefficient in the decomposition
````@example pod
plot(layout=[2;1],plot(modes.phi[1].u,sys,title="u"),
plot(modes.phi[1].v,sys,title="v"),
plot(tpod,modes.a[:,1],xlim=(0,Inf),xlabel="\$t\$",ylabel="\$a_1(t)\$"))
````
The energy associated with this mode is
````@example pod
modes.lambda[1]
````
Now let's print the $r$th mode, and the history of the coefficient in the decomposition
````@example pod
plot(layout=[2;1],plot(modes.phi[end].u,sys,title="u"),
plot(modes.phi[end].v,sys,title="v"),
plot(tpod,modes.a[:,end],xlim=(0,Inf),xlabel="\$t\$",ylabel="\$a_r(t)\$"))
````
The energy associated with this mode is
````@example pod
modes.lambda[end]
````
## POD functions
```@docs
pod
```
---
*This page was generated using [Literate.jl](https://github.com/fredrikekre/Literate.jl).*
| ILMPostProcessing | https://github.com/JuliaIBPM/ILMPostProcessing.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1.0.0 | b4c9779674bf2a8ed0214685568f034f710a8490 | code | 3064 | module Monomials
export Monomial
export LexicographicOrder
export GradedLexicographicOrder
export GradedReverseLexicographicOrder
export degree
export monomials
"""
Monomial(x, α)
Greate a Monomial from a vector of variables `x` and associated degrees vector `α`.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> Monomial(["x", "y"], [1, 2])
xy^2
```
"""
struct Monomial
x::AbstractVector{String}
α::AbstractVector{Integer}
end
abstract type MonomialOrder end
struct LexicographicOrder <: MonomialOrder
end
struct GradedLexicographicOrder <: MonomialOrder
end
struct GradedReverseLexicographicOrder <: MonomialOrder
end
function (m::Monomial)(x::AbstractVector{<:Real})
return prod(x .^ m.α)
end
function (m::Monomial)(x::AbstractMatrix{<:Real})
return map(xᵢ -> m(xᵢ), eachcol(x))
end
function (mvec::AbstractVector{Monomial})(x::AbstractVector{<:Real})
return [m(x) for m in mvec]
end
function (mvec::AbstractVector{Monomial})(x::AbstractMatrix{<:Real})
return vcat([m(x)' for m in mvec]...)
end
"""
degree(m::Monomial)
Computes the degree of a monomial, which is the sum of the degrees of its variables.
"""
function degree(m::Monomial)
return sum(m.α)
end
"""
monomials(x::AbstractVector{String}, d::Integer, mo::MonomialOrder; include_zero::Bool=false)
Computes all monomials of the variables `x` up to degree `d` ordered in monomial order `mo`.
Pass `include_zero=true` to include the zero degree monomial.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> monomials(["x","y"], 2, LexicographicOrder(); include_zero=true)
5-element Vector{Monomial}:
1
y
y²
x
xy
x²
```
"""
function monomials(x::AbstractVector{String}, d::Integer, mo::MonomialOrder; include_zero::Bool=false)
nvars = length(x)
lb = include_zero ? -1 : 0
exponents = Iterators.filter(α -> lb < sum(α) <= d, Iterators.product(repeat([0:d], nvars)...))
m = map(exponents) do α
Monomial(x, [α...])
end
return order(m, mo)
end
function order(m::AbstractVector{Monomial}, _::LexicographicOrder)
function lt(a::Monomial, b::Monomial)
if a.α != b.α
idx = findfirst(!iszero, a.α .- b.α)
return a.α[idx] < b.α[idx]
end
end
return sort(m; lt=lt)
end
function order(m::AbstractVector{Monomial}, _::GradedLexicographicOrder)
function lt(a::Monomial, b::Monomial)
deg_a, deg_b = degree(a), degree(b)
if deg_a != deg_b
return deg_a < deg_b
end
if a.α != b.α
idx = findfirst(!iszero, a.α .- b.α)
return a.α[idx] < b.α[idx]
end
end
return sort(m; lt=lt)
end
function order(m::AbstractVector{Monomial}, _::GradedReverseLexicographicOrder)
function lt(a::Monomial, b::Monomial)
deg_a, deg_b = degree(a), degree(b)
if deg_a != deg_b
return deg_a < deg_b
end
if a.α != b.α
idx = findlast(!iszero, a.α .- b.α)
return a.α[idx] > b.α[idx]
end
end
return sort(m; lt=lt)
end
include("show.jl")
end
| Monomials | https://github.com/FriesischScott/Monomials.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1.0.0 | b4c9779674bf2a8ed0214685568f034f710a8490 | code | 590 | const superscripts = ["⁰", "¹", "²", "³", "⁴", "⁵", "⁶", "⁷", "⁸", "⁹"]
function Base.show(io::IO, m::Monomial)
if all(m.α .== 0)
print(io, "1")
return nothing
end
str = map(zip(m.x, m.α)) do (x, d)
if d == 0
return ""
elseif d == 1
return x
else
if d < 10
return join([x, superscripts[d+1]])
else
return join([x, superscripts[parse.(Int, split(string(d), "")).+1]...])
end
end
end
print(io, join(str))
return nothing
end
| Monomials | https://github.com/FriesischScott/Monomials.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1.0.0 | b4c9779674bf2a8ed0214685568f034f710a8490 | code | 5007 | using Test
using Monomials
@testset "Orders" begin
@testset "LexicographicOrder" begin
m = monomials(["x1", "x2"], 2, LexicographicOrder())
@test length(m) == 5
@test m[1].α == [0, 1]
@test m[2].α == [0, 2]
@test m[3].α == [1, 0]
@test m[4].α == [1, 1]
@test m[5].α == [2, 0]
m = monomials(["x1", "x2"], 2, LexicographicOrder(); include_zero=true)
@test length(m) == 6
@test m[1].α == [0, 0]
@test m[2].α == [0, 1]
@test m[3].α == [0, 2]
@test m[4].α == [1, 0]
@test m[5].α == [1, 1]
@test m[6].α == [2, 0]
m = monomials(["x1", "x2", "x3"], 2, LexicographicOrder())
@test length(m) == 9
@test m[1].α == [0, 0, 1]
@test m[2].α == [0, 0, 2]
@test m[3].α == [0, 1, 0]
@test m[4].α == [0, 1, 1]
@test m[5].α == [0, 2, 0]
@test m[6].α == [1, 0, 0]
@test m[7].α == [1, 0, 1]
@test m[8].α == [1, 1, 0]
@test m[9].α == [2, 0, 0]
end
@testset "GradedLexicographicOrder" begin
m = monomials(["x1", "x2"], 2, GradedLexicographicOrder())
@test length(m) == 5
@test m[1].α == [0, 1]
@test m[2].α == [1, 0]
@test m[3].α == [0, 2]
@test m[4].α == [1, 1]
@test m[5].α == [2, 0]
m = monomials(["x1", "x2"], 2, GradedLexicographicOrder(); include_zero=true)
@test length(m) == 6
@test m[1].α == [0, 0]
@test m[2].α == [0, 1]
@test m[3].α == [1, 0]
@test m[4].α == [0, 2]
@test m[5].α == [1, 1]
@test m[6].α == [2, 0]
m = monomials(["x1", "x2", "x3"], 2, GradedLexicographicOrder())
@test length(m) == 9
@test m[1].α == [0, 0, 1]
@test m[2].α == [0, 1, 0]
@test m[3].α == [1, 0, 0]
@test m[4].α == [0, 0, 2]
@test m[5].α == [0, 1, 1]
@test m[6].α == [0, 2, 0]
@test m[7].α == [1, 0, 1]
@test m[8].α == [1, 1, 0]
@test m[9].α == [2, 0, 0]
end
@testset "GradedReverseLexicographicOrder" begin
m = monomials(["x1", "x2"], 2, GradedReverseLexicographicOrder())
@test length(m) == 5
@test m[1].α == [0, 1]
@test m[2].α == [1, 0]
@test m[3].α == [0, 2]
@test m[4].α == [1, 1]
@test m[5].α == [2, 0]
m = monomials(["x1", "x2"], 2, GradedReverseLexicographicOrder(); include_zero=true)
@test length(m) == 6
@test m[1].α == [0, 0]
@test m[2].α == [0, 1]
@test m[3].α == [1, 0]
@test m[4].α == [0, 2]
@test m[5].α == [1, 1]
@test m[6].α == [2, 0]
m = monomials(["x1", "x2", "x3"], 2, GradedReverseLexicographicOrder())
@test length(m) == 9
@test m[1].α == [0, 0, 1]
@test m[2].α == [0, 1, 0]
@test m[3].α == [1, 0, 0]
@test m[4].α == [0, 0, 2]
@test m[5].α == [0, 1, 1]
@test m[6].α == [1, 0, 1]
@test m[7].α == [0, 2, 0]
@test m[8].α == [1, 1, 0]
@test m[9].α == [2, 0, 0]
end
end
@testset "Show" begin
vars = ["x", "y"]
@test repr(Monomial(vars, [0, 0])) == "1"
@test repr(Monomial(vars, [1, 0])) == "x"
@test repr(Monomial(vars, [0, 1])) == "y"
@test repr(Monomial(vars, [1, 1])) == "xy"
@test repr(Monomial(vars, [2, 0])) == "x²"
@test repr(Monomial(vars, [0, 2])) == "y²"
@test repr(Monomial(vars, [2, 1])) == "x²y"
@test repr(Monomial(vars, [1, 2])) == "xy²"
@test repr(Monomial(vars, [2, 2])) == "x²y²"
@test repr(Monomial(vars, [2, 11])) == "x²y¹¹"
end
@testset "Evaluation" begin
m = monomials(["x", "y"], 2, LexicographicOrder(); include_zero=true)
x = [1 2 3; 2 3 1]
@testset "Monomial-Vector" begin
@test m[1](x[:, 1]) == 1
@test m[1](x[:, 2]) == 1
@test m[1](x[:, 3]) == 1
@test m[2](x[:, 1]) == 2
@test m[2](x[:, 2]) == 3
@test m[2](x[:, 3]) == 1
@test m[3](x[:, 1]) == 4
@test m[3](x[:, 2]) == 9
@test m[3](x[:, 3]) == 1
@test m[4](x[:, 1]) == 1
@test m[4](x[:, 2]) == 2
@test m[4](x[:, 3]) == 3
@test m[5](x[:, 1]) == 2
@test m[5](x[:, 2]) == 6
@test m[5](x[:, 3]) == 3
@test m[6](x[:, 1]) == 1
@test m[6](x[:, 2]) == 4
@test m[6](x[:, 3]) == 9
end
@testset "Monomial-Matrix" begin
@test m[1](x) == [1, 1, 1]
@test m[2](x) == [2, 3, 1]
@test m[3](x) == [4, 9, 1]
@test m[4](x) == [1, 2, 3]
@test m[5](x) == [2, 6, 3]
@test m[6](x) == [1, 4, 9]
end
@testset "Vector{Monomial}-Vector" begin
@test m(x[:, 1]) == [1, 2, 4, 1, 2, 1]
@test m(x[:, 2]) == [1, 3, 9, 2, 6, 4]
@test m(x[:, 3]) == [1, 1, 1, 3, 3, 9]
end
@testset "Vector{Monomial}-Matrix" begin
@test m(x) == [1 1 1; 2 3 1; 4 9 1; 1 2 3; 2 6 3; 1 4 9]
end
end
| Monomials | https://github.com/FriesischScott/Monomials.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1.0.0 | b4c9779674bf2a8ed0214685568f034f710a8490 | docs | 1959 | # Monomials.jl
 [](https://codecov.io/gh/FriesischScott/Monomials.jl)
A simple apackage to generate, order, and evaluate vectors of monomials. It is designed as an alternative to the [MultivariatePolynomials.jl](https://github.com/JuliaAlgebra/MultivariatePolynomials.jl) ecosystem if all you require is monomials not fully fledged polynomials.
The core functionality is exposed through the `monomials` function. It generates all monomials of the given variables up to a defined maximum degree and sorts them in the requested order. Available monomial orders are:
- `LexicographicOrder`
- `GradedLexicographicOrder`
- `GradedReverseLexicographicOrder`
There are no concrete plans to add more features to the package.
## Examples
The following returns the monomials of two variables with a maximum degree of 2 in lexicographic order.
```julia
monomials(["x","y"], 2, LexicographicOrder())
```
```
5-element Vector{Monomial}:
y
y²
x
xy
x²
```
it is possible to include the zero-degree monomial by passing the `include_zero=true` option.
```julia
m = monomials(["x","y"], 2, LexicographicOrder(); include_zero=true)
```
```
6-element Vector{Monomial}:
1
y
y²
x
xy
x²
```
Monomials can be evaluated by passing a `Vector`.
```julia
m = Monomial(["x", "y"], [1, 2])
m([2, 3])
```
For convenience, a single monomial can be evaluated at multiple points by passing a `Matrix`. In this case, the points are expected to be the columns of the given matrix.
```julia
m = Monomial(["x", "y"], [1, 2])
m(rand(2, 5))
```
Finally, to evaulate all monomials in a vector for one or more points pass the `Vector` or `Matrix` directly to the vector of monomials.
```julia
m = monomials((["x", "y"], 2, LexicographicOrder())
m(rand(2, 5))
```
| Monomials | https://github.com/FriesischScott/Monomials.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.0 | 6d11b8fbee9d09f462f6195d44b10c1413f03489 | code | 234 | module LennardJones
include("./utils.jl")
export lj_potential_uij, lj_potential_fij, lj_potential_uij_cutoff, lj_potential_fij_cutoff
include("./bases.jl")
export lj_potential_wca_uij, lj_potential_wca_fij
include("./wca.jl")
end
| LennardJones | https://github.com/sunoru/LennardJones.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.0 | 6d11b8fbee9d09f462f6195d44b10c1413f03489 | code | 1650 | import LinearAlgebra: norm_sqr
@inline lj_potential_uij(
r::Float64; ϵ = 1.0, σ = 1.0
) = let r² = r ^ 2, σ² = σ ^ 2
@fastmath 4 * ϵ * ((σ² ^ 6) / (r² ^ 6) - (σ² ^ 3) / (r² ^ 3))
end
@inline lj_potential_uij(
r; ϵ = 1.0, σ = 1.0
) = let r² = norm_sqr(r), σ² = σ ^ 2
@fastmath 4 * ϵ * ((σ² ^ 6) / (r² ^ 6) - (σ² ^ 3) / (r² ^ 3))
end
@inline lj_potential_uij(
r₁, r₂;
ϵ = 1.0, σ = 1.0,
dist = default_distance
) = lj_potential_uij(dist(r₁, r₂), ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ)
_lj_potential_wij(
r², ϵ = 1.0, σ² = 1.0
) = @fastmath 24 * ϵ * (2 * (σ² ^ 6) / (r² ^ 6) - (σ² ^ 3) / (r² ^ 3))
@inline function lj_potential_fij(
r; ϵ = 1.0, σ = 1.0
)
r² = norm_sqr(r)
wij = _lj_potential_wij(r², ϵ, σ ^ 2)
fij = r * wij / r²
end
@inline lj_potential_fij(
r₁, r₂;
ϵ = 1.0, σ = 1.0,
dist = default_distance
) = lj_potential_fij(dist(r₁, r₂), ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ)
@inline lj_potential_uij_cutoff(
r;
ϵ = 1.0, σ = 1.0,
r_cutoff = 2.5σ
) = norm_sqr(r) ≥ r_cutoff ^ 2 ? 0.0 :
lj_potential_uij(r, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ) - lj_potential_uij(r_cutoff, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ)
@inline lj_potential_uij_cutoff(
r₁, r₂;
ϵ = 1.0, σ = 1.0,
dist = default_distance,
r_cutoff = 2.5σ
) = lj_potential_uij_cutoff(dist(r₁, r₂), ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ, r_cutoff = r_cutoff)
@inline lj_potential_fij_cutoff(
r;
ϵ = 1.0, σ = 1.0,
r_cutoff = 2.5σ
) = norm_sqr(r) ≥ r_cutoff ^ 2 ? zero(r) :
lj_potential_fij(r, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ)
@inline lj_potential_fij_cutoff(
r₁, r₂;
ϵ = 1.0, σ = 1.0,
dist = default_distance,
r_cutoff = 2.5σ
) = lj_potential_fij_cutoff(dist(r₁, r₂), ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ, r_cutoff = r_cutoff)
| LennardJones | https://github.com/sunoru/LennardJones.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.0 | 6d11b8fbee9d09f462f6195d44b10c1413f03489 | code | 72 | @inline default_distance(r₁, r₂) = r₁ - r₂
const R_MIN = 2 ^ (1.0 / 6)
| LennardJones | https://github.com/sunoru/LennardJones.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.0 | 6d11b8fbee9d09f462f6195d44b10c1413f03489 | code | 641 | # Weeks–Chandler–Anderson potential function, a repulsive potential.
@inline lj_potential_wca_uij(
r; ϵ = 1.0, σ = 1.0
) = norm_sqr(r) ≥ (R_MIN * σ) ^ 2 ? 0.0 :
(lj_potential_uij(r, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ) + ϵ)
@inline lj_potential_wca_uij(
r₁, r₂;
ϵ = 1.0, σ = 1.0,
dist = default_distance
) = lj_potential_wca_uij(dist(r₁, r₂), ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ)
@inline lj_potential_wca_fij(
r; ϵ = 1.0, σ = 1.0
) = norm_sqr(r) ≥ (R_MIN * σ) ^ 2 ? zero(r) :
lj_potential_fij(r, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ)
@inline lj_potential_wca_fij(
r₁, r₂;
ϵ = 1.0, σ = 1.0,
dist = default_distance
) = lj_potential_wca_fij(dist(r₁, r₂), ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ)
| LennardJones | https://github.com/sunoru/LennardJones.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.0 | 6d11b8fbee9d09f462f6195d44b10c1413f03489 | code | 1555 | using Test
using LennardJones
using LinearAlgebra
@testset "Test" begin
@test LennardJones.lj_potential_uij(LennardJones.R_MIN) ≈ -1.0
r₁ = [0.916914, 0.111325, 0.594877]
r₂ = [0.454572, 0.979098, 0.988925]
dr = r₂ - r₁
r = norm(dr)
ϵ = 0.8
σ = 0.9
dist = (a, b) -> a - b
u = LennardJones.lj_potential_uij(r, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ)
@test u ≈ -0.7509440391688087
@test LennardJones.lj_potential_uij(dr, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ) ≈ u
@test LennardJones.lj_potential_uij(r₁, r₂, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ, dist = dist) ≈ u
f = LennardJones.lj_potential_fij(dr, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ)
@test f ≈ [0.7369705345615358, -1.3832252568186918, -0.6281102846008022]
@test LennardJones.lj_potential_fij(r₁, r₂, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ, dist = dist) ≈ -f
cutoff = 2.5
u₂ = LennardJones.lj_potential_uij_cutoff(dr, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ, r_cutoff = cutoff)
@test u₂ ≈ -0.7439934985138913
@test LennardJones.lj_potential_uij_cutoff(r₁, r₂, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ, r_cutoff = cutoff, dist = dist) ≈ u₂
f₂ = LennardJones.lj_potential_fij_cutoff(dr, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ, r_cutoff = cutoff)
@test f₂ ≈ f
@test LennardJones.lj_potential_fij_cutoff(r₁, r₂, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ, r_cutoff = cutoff, dist = dist) ≈ -f₂
r₃ = [0.669256, 0.300412, 0.671123]
dr₂ = r₃ - r₁
u₃ = LennardJones.lj_potential_wca_uij(dr₂, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ)
@test u₃ ≈ 759679.8217248165
@test LennardJones.lj_potential_wca_uij(r₁, r₃, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ, dist = dist) ≈ u₃
f₃ = LennardJones.lj_potential_wca_fij(dr₂, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ)
@test f₃ ≈ [-2.1962740885915317e7, 1.6768563042159226e7, 6.761627492701628e6]
@test LennardJones.lj_potential_wca_fij(r₁, r₃, ϵ = ϵ, σ = σ, dist = dist) ≈ -f₃
end
| LennardJones | https://github.com/sunoru/LennardJones.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.1.0 | 6d11b8fbee9d09f462f6195d44b10c1413f03489 | docs | 925 | # LennardJones.jl
[](https://github.com/sunoru/LennardJones.jl/actions/workflows/ci.yml)
A simple package of functions for Lennard-Jones potential energies.
## Usage
`LennardJones` provides `lj_potential_uij` and `lj_potential_fij`, and their cutoff versions `lj_potential_uij_cutoff` and `lj_potential_fij_cutoff`, for calculating the potential energy and force between two particles.
A repulsive potential called Weeks–Chandler–Anderson potential is also implemented here. See `lj_potential_wca_uij` and `lj_potential_wca_fij`.
You can use keyword arguments to set the LJ parameters. The default values are `ϵ = 1.0`, `σ = 1.0`, `r_cutoff = 2.5σ`,
and a distance function `dist(r₁, r₂)` can be passed to specify the way to calculate the distance between two particles.
## License
The [MIT License](https://sunoru.mit-license.org/).
| LennardJones | https://github.com/sunoru/LennardJones.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | c45074f765d0f729dc12bc23fedb49b041545b3b | code | 293 | module OILMMs
using AbstractGPs
using ChainRulesCore
using FillArrays
using KernelFunctions
using LinearAlgebra
using Random
using AbstractGPs: AbstractGP, FiniteGP
using KernelFunctions: MOInput
include("util.jl")
include("oilmm.jl")
include("missing_data.jl")
export OILMM
end # module
| OILMMs | https://github.com/willtebbutt/OILMMs.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | c45074f765d0f729dc12bc23fedb49b041545b3b | code | 3272 | # Implementation of projection operation under missing data. Probably most of this needs a
# custom gradient implementation.
function project(
S::Diagonal{T},
U::AbstractMatrix{T},
Y::ColVecs{Union{Missing, T}},
σ²::T,
D::Diagonal{T},
) where {T<:Real}
# Compute patterns and assignments of data to patterns.
patterns, rows, idxs, perm = compute_patterns(Y.X)
# Construct the projection matrix for each pattern.
Us = map(row -> U[row, :], rows)
# Project each pattern in the data.
sqrtS = cholesky(S).U
Yproj_blocks = map((U, r, idx) -> sqrtS \ (U \ Y.X[r, idx]), Us, rows, idxs)
# Construct the single projected data matrix, in the correct order.
Yproj = hcat(Yproj_blocks...)[:, perm]
# lens = map(length, idxs)
lens = map_length(idxs)
almost_ΣT_blocks = map(
(U, len) -> repeat(diag(inv(cholesky(Symmetric(U'U + 1e-9I)))), 1, len), Us, lens,
)
# Assemble blocks into a single matrix, with a different scalar observation noise
# for each observation.
almost_ΣT = hcat(almost_ΣT_blocks...)[:, perm]
ΣT = σ² .* diag(inv(S)) .* almost_ΣT .+ diag(D)
return Yproj, ΣT
end
function regulariser(
S::Diagonal{T},
U::AbstractMatrix{T},
σ²::T,
y::ColVecs{Union{Missing, T}},
) where {T<:Real}
# Compute patterns and assignments of data to patterns.
patterns, rows, idxs, _ = compute_patterns(y.X)
# Construct the projection matrix for each pattern.
Us = map(row -> U[row, :], rows)
# Pre-compute one term.
logdet_S = logdet(cholesky(S))
# Compute the regularisation term for each block.
regularisers = map(
(Uo, row, idx) -> begin
n = length(idx)
p, m = size(Uo)
chol_UotUo = cholesky(Symmetric(Uo'Uo + 1e-9I))
Yo = eltype(Uo).(y.X[row, idx])
return -(n * (logdet_S + logdet(chol_UotUo) + (p - m) * log(2π * σ²)) +
(sum(abs2, Yo) - sum(abs2, chol_UotUo.U' \ Uo'Yo)) / σ²) / 2
end,
Us, rows, idxs,
)
return sum(regularisers)
end
# Helper function for `project` that handles various bits of non-differentiable stuff
# that can be safely @nograd-ed.
function compute_patterns(Y::AbstractMatrix{Union{Missing, T}} where {T<:Real})
# Compute unique missing-ness patterns.
missingness = eachcol(ismissing.(Y))
patterns = unique(collect.(missingness))
# For each pattern, compute the rows of `Y` that are not missing.
available_rows = [filter(n -> !p[n], 1:size(Y, 1)) for p in patterns]
# Add the location each column of `Y` to mapping from block-to-columns.
# idxs = Dict(pattern => Int[] for pattern in patterns)
idxs = [Int[] for pattern in patterns]
for (n, data_pattern) in enumerate(missingness)
for (m, pattern) in enumerate(patterns)
if data_pattern == pattern
push!(idxs[m], n)
end
end
end
# Compute the permutation of the data required to restore the original order.
perm = sortperm(vcat(idxs...))
return patterns, available_rows, idxs, perm
end
ChainRulesCore.@non_differentiable compute_patterns(::Any)
map_length(x) = map(length, x)
ChainRulesCore.@non_differentiable map_length(::Any)
| OILMMs | https://github.com/willtebbutt/OILMMs.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | c45074f765d0f729dc12bc23fedb49b041545b3b | code | 5676 | """
OILMM(fs, U, S, D)
An Orthogonal Instantaneous Linear Mixing Model (OILMM) -- a distribution over vector-
valued functions. Let `p` be the number of observed outputs, and `m` the number of latent
processes, then
# Arguments:
- fs: a length-`m` vector of Gaussian process objects from Stheno.jl.
- U: a `p x m` matrix with mutually orthonormal columns.
- S: an `m x m` `Diagonal` matrix. Same dim. as `fs`. Positive entries.
- D: an `m x m` `Diagonal` matrix, variance of noise on each latent process. Same size as
`S`. Positive entries.
We recommend constructing `U` and `S` from the `svd` of some other matrix. e.g.
```julia
H = randn(p, m)
U, s, _ = svd(H)
S = Diagonal(H)
```
"""
struct OILMM{
Tfs<:AbstractVector{<:AbstractGP},
TU<:AbstractMatrix{<:Real},
TS<:Diagonal{<:Real},
TD<:Diagonal{<:Real},
} <: AbstractGP
fs::Tfs
U::TU
S::TS
D::TD
end
noise_var(Σ::Diagonal{<:Real, <:Fill}) = FillArrays.getindex_value(Σ.diag)
function unpack(fx::FiniteGP{<:OILMM, <:MOInput, <:Diagonal{<:Real, <:Fill}})
fs = fx.f.fs
S = fx.f.S
U = fx.f.U
D = fx.f.D
σ² = noise_var(fx.Σy)
x = fx.x.x
# Check that the number of outputs requested agrees with the model.
fx.x.out_dim == size(U, 1) || throw(error("out dim of x != out dim of f."))
return fs, S, U, D, σ², x
end
reshape_y(y::AbstractVector{<:Real}, N::Int) = ColVecs(reshape(y, N, :)')
# Note that `cholesky` exploits the diagonal structure of `S`.
function project(
S::Diagonal{T},
U::AbstractMatrix{T},
Y::ColVecs{T},
σ²::T,
D::Diagonal{T},
) where {T<:Real}
# Compute the projection of the data.
Yproj = cholesky(S).U \ U' * Y.X
# Compute the projected noise, which is a matrix of size `size(Yproj)`.
ΣT = repeat(diag(σ² * inv(S) + D), 1, size(Yproj, 2))
return Yproj, ΣT
end
# Compute the regularisation term in the log marginal likelihood. See e.g. appendix A.4.
function regulariser(
S::Diagonal{T},
U::AbstractMatrix{T},
σ²::T,
Y::ColVecs{T},
) where {T<:Real}
n = length(Y)
p, m = size(U)
return -(n * (logdet(cholesky(S)) + (p - m) * log(2π * σ²)) +
sum(abs2, (I - U * U') * Y.X) / σ²) / 2
end
"""
rand_latent(rng::AbstractRNG, fx::FiniteGP{<:OILMM})
Sample from the latent (noiseless) process.
See also `rand`.
"""
function rand_latent(rng::AbstractRNG, fx::FiniteGP{<:OILMM})
fs, S, U, D, σ², x = unpack(fx)
# Generate from the latent processes.
X = hcat(map((f, d) -> rand(rng, f(x, d)), fs, D.diag)...)
# Transform latents into observed space.
return vec(U * cholesky(S).U * X')
end
"""
rand(rng::AbstractRNG, fx::FiniteGP{<:OILMM})
Sample from the OILMM, including the observation noise.
Follows generative structure of model 2 from [1].
Follows the AbstractGPs.jl API.
See also `rand_latent`.
[1] - Bruinsma et al 2020.
"""
function AbstractGPs.rand(rng::AbstractRNG, fx::FiniteGP{<:OILMM})
# Sample from the latent process.
F = rand_latent(rng, fx)
# Generate iid noise and add to each output.
return F .+ sqrt(noise_var(fx.Σy)) .* randn(rng, size(F))
end
"""
denoised_marginals(fx::FiniteGP{<:OILMM})
Returns the marginal distribution over the OILMM without the IID noise components.
See also `marginals`.
"""
function denoised_marginals(fx::FiniteGP{<:OILMM})
fs, S, U, D, σ², x = unpack(fx)
# Compute the marginals over the independent latents.
fs_marginals = reduce(hcat, map(f -> marginals(f(x)), fs))
M_latent = mean.(fs_marginals)'
V_latent = var.(fs_marginals)'
# Compute the latent -> observed transform.
H = U * cholesky(S).U
# Compute the means.
M = H * M_latent
# Compute the variances.
V = abs2.(H) * V_latent
# Package everything into independent Normal distributions.
return AbstractGPs.Normal.(vec(M'), sqrt.(vec(V')))
end
# See AbstractGPs.jl API docs.
function AbstractGPs.mean_and_var(fx::FiniteGP{<:OILMM})
fs, S, U, D, σ², x = unpack(fx)
# Compute the marginals over the independent latents.
fs_marginals = hcat(map(f -> marginals(f(x)), fs)...)
M_latent = mean.(fs_marginals)'
V_latent = var.(fs_marginals)'
# Compute the latent -> observed transform.
H = U * cholesky(S).U
# Compute the means.
M = H * M_latent
# Compute the variances.
V = abs2.(H) * (V_latent .+ D.diag) .+ σ²
# Package everything into independent Normal distributions.
return vec(M'), vec(V')
end
AbstractGPs.mean(fx::FiniteGP{<:OILMM}) = mean_and_var(fx)[1]
AbstractGPs.var(fx::FiniteGP{<:OILMM}) = mean_and_var(fx)[2]
# See AbstractGPs.jl API docs.
function AbstractGPs.logpdf(fx::FiniteGP{<:OILMM}, y::AbstractVector{<:Real})
fs, S, U, D, σ², x = unpack(fx)
# Projection step.
Y = reshape_y(y, length(x))
Yproj, ΣT = project(S, U, Y, σ², D)
# Latent process log marginal likelihood calculation.
y_rows = collect(eachrow(Yproj))
ΣT_rows = collect(eachrow(ΣT))
lmls_latents = map((f, s, y) -> logpdf(f(x, collect(s)), collect(y)), fs, ΣT_rows, y_rows)
return regulariser(S, U, σ², Y) + sum(lmls_latents)
end
# See AbstractGPs.jl API docs.
function AbstractGPs.posterior(fx::FiniteGP{<:OILMM}, y::AbstractVector{<:Real})
fs, S, U, D, σ², x = unpack(fx)
# Projection step.
Y = reshape_y(y, length(x))
Yproj, ΣT = project(S, U, Y, σ², D)
# Condition each latent process on the projected observations.
y_rows = collect(eachrow(Yproj))
ΣT_rows = collect(eachrow(ΣT))
fs_posterior = map((f, s, y) -> posterior(f(x, collect(s)), collect(y)), fs, ΣT_rows, y_rows)
return OILMM(fs_posterior, U, S, D)
end
| OILMMs | https://github.com/willtebbutt/OILMMs.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | c45074f765d0f729dc12bc23fedb49b041545b3b | code | 967 | function ChainRulesCore.rrule(::typeof(eachrow), X::VecOrMat)
eachrow_pullback(ΔΩ::Tangent) = (NoTangent(), ΔΩ.f.A)
return eachrow(X), eachrow_pullback
end
function ChainRulesCore.rrule(::typeof(inv), D::Diagonal{<:Real})
Ω = inv(D)
function inv_Diagonal_pullback(ΔΩ::NamedTuple{(:diag,)})
return (NoTangent(), (diag = .-ΔΩ.diag .* Ω.diag .^2,))
end
function inv_Diagonal_pullback(ΔΩ::Diagonal)
return (NoTangent(), Diagonal(.-ΔΩ.diag .* Ω.diag .^2))
end
return Ω, inv_Diagonal_pullback
end
function ChainRulesCore.rrule(::typeof(inv), C::Cholesky{<:BLAS.BlasFloat, <:StridedMatrix})
Ω = inv(C)
function inv_Cholesky_pullback(ΔΩ::StridedMatrix{<:BLAS.BlasFloat})
return (NoTangent(), (factors = -C.U' \ (ΔΩ + ΔΩ') * Ω, ))
end
function inv_Cholesky_pullback(ΔΩ::AbstractMatrix{<:BLAS.BlasFloat})
return inv_Cholesky_pullback(collect(ΔΩ))
end
return Ω, inv_Cholesky_pullback
end
| OILMMs | https://github.com/willtebbutt/OILMMs.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | c45074f765d0f729dc12bc23fedb49b041545b3b | code | 3785 | @testset "missing_data" begin
@testset "nothing actually missing" begin
# Construct a toy data set with no missing data.
Y = randn(2, 5)
y = ColVecs(Y)
# Copy the toy data set, but change the type so that it _might_ have missing data.
Y_missing = Matrix{Union{Missing, Float64}}(undef, size(Y))
copy!(Y_missing, Y)
y_missing = ColVecs(Y_missing)
# Construct a random projection.
U, s, _ = svd(randn(2, 1))
S = Diagonal(s)
# Construct noise model.
σ² = 0.93
D = Diagonal(abs.(randn(size(S, 1))) .+ 1e-2)
# Ensure that both projection operations produce the same result.
Yproj, ΣT = OILMMs.project(S, U, y, σ², D)
Yproj_missing, ΣT_missing = OILMMs.project(S, U, y_missing, σ², D)
@test Yproj ≈ Yproj_missing
@test ΣT ≈ ΣT_missing
# Ensure that the regularisation terms agree.
reg = OILMMs.regulariser(S, U, σ², y_missing)
@test reg ≈ OILMMs.regulariser(S, U, σ², y)
@testset "OILMMs.project AD" begin
# Perform forwards-pass and construct pullback.
(Yproj_ad, ΣT_ad), project_pb = Zygote.pullback(
OILMMs.project, S, U, y_missing, σ², D,
)
# Ensure that the forwards-pass is consistent with usual evaluation.
@test Yproj_ad ≈ Yproj_missing
@test ΣT_ad ≈ ΣT_missing
# Estimate / evaluate cotangent of inputs.
ΔYproj = randn(size(Yproj_ad))
ΔΣT_proj = randn(size(ΣT_ad))
Δout = (ΔYproj, ΔΣT_proj)
dX_fd = FiniteDifferences.j′vp(
central_fdm(5, 1),
(S, U, σ², D) -> OILMMs.project(S, U, y_missing, σ², D),
Δout, S, U, σ², D,
)
dX_ad = project_pb(Δout)
# Check for (approximate) equality beteen AD and finite differencing.
@test dX_fd[1] ≈ dX_ad[1]
@test dX_fd[2] ≈ dX_ad[2]
@test dX_fd[3] ≈ dX_ad[4]
@test dX_fd[4] ≈ dX_ad[5]
end
@testset "OILMMs.regulariser AD" begin
# Perform forwards-pass and construct pullback.
reg_ad, regulariser_pd = Zygote.pullback(
OILMMs.regulariser, S, U, σ², y_missing,
)
# Ensure that the forwards-pass is consistent with usual evaluation.
@test reg_ad ≈ reg
# Estimate / evaluate cotangent of inputs.
Δreg = randn()
dX_fd = FiniteDifferences.j′vp(
central_fdm(5, 1),
(S, U, σ²) -> OILMMs.regulariser(S, U, σ², y_missing),
Δreg, S, U, σ²,
)
dX_ad = regulariser_pd(Δreg)
# Check for (approximate) equality beteen AD and finite differencing.
@test dX_fd[1] ≈ dX_ad[1]
@test dX_fd[2] ≈ dX_ad[2]
@test dX_fd[3] ≈ dX_ad[3]
end
end
@testset "identity projection" begin
# Construct a toy data set and make some bits of it missing.
Y = Matrix{Union{Missing, Float64}}(undef, 3, 4)
Y .= randn(3, 4)
Y[1, 2] = missing
Y[2, 1] = missing
y = ColVecs(Y)
# Compute the output of the project. The missings are just zeroed.
Yproj = deepcopy(Y)
Yproj[1, 2] = 0.0
Yproj[2, 1] = 0.0
# Construct the identity transformation.
U, s, _ = svd(Matrix{Float64}(I, 3, 3))
S = Diagonal(s)
# Construct noise model.
σ² = 0.93
D = Diagonal(abs.(randn(size(Y, 1))) .+ 1e-2)
# Ensure that the projection operation recovers the zeroed data.
@test OILMMs.project(S, U, y, σ², D)[1] == Yproj
end
end
| OILMMs | https://github.com/willtebbutt/OILMMs.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | c45074f765d0f729dc12bc23fedb49b041545b3b | code | 4149 | function Base.vcat(x::MOInput, y::MOInput)
x.out_dim == y.out_dim || throw(error("out_dim mismatch"))
return MOInput(vcat(x.x, y.x), x.out_dim)
end
@testset "oilmm" begin
@testset "single output" begin
rng = MersenneTwister(123456)
# Specify inputs and generate observations.
x = collect(range(-3.37, 3.12; length=11))
tr_idx = randperm(rng, length(x))[1:6]
te_idx = setdiff(eachindex(x), tr_idx)
x_tr_raw = x[tr_idx]
x_te_raw = x[te_idx]
# Noise variance.
σ² = 0.12
# Specify the equivalent GPPP.
a = randn(rng)
f_naive = @gppp let
f = a * GP(Matern52Kernel())
end
# Specify equivalent OILMM.
fs = [GP(Matern52Kernel())]
U = reshape([1.0], 1, 1)
S = Diagonal([abs2(a)])
D = Diagonal([0.0])
f = OILMM(fs, U, S, D)
x_tr = MOInput(x_tr_raw, 1)
x_te = MOInput(x_te_raw, 1)
y_tr = rand(rng, f(x_tr, σ²))
y_te = rand(rng, f(x_te, σ²))
consistency_tests(
rng, f, f_naive;
x_tr=x_tr,
x_te=x_te,
x_naive_tr=GPPPInput(:f, x_tr_raw),
x_naive_te=GPPPInput(:f, x_te_raw),
y_tr=y_tr,
y_te=y_te,
σ²=σ²,
)
end
@testset "P independent processes" begin
rng = MersenneTwister(123456)
P = 3
N = 11
# Specify inputs and generate observations.
x = collect(range(-3.37, 3.12; length=N))
tr_idx = randperm(rng, length(x))[1:2]
te_idx = setdiff(eachindex(x), tr_idx)
x_tr_raw = x[tr_idx]
x_te_raw = x[te_idx]
# Noise variance.
σ² = 0.12
# Specify a collection of GPs
as = randn(rng, P)
gpc = Stheno.GPC()
fs = map(p -> as[p] * wrap(GP(Matern52Kernel()), gpc), 1:P)
f_naive = Stheno.GPPP(fs, gpc)
x_naive_tr = BlockData(map(p -> GPPPInput(p, x_tr_raw), 1:P))
x_naive_te = BlockData(map(p -> GPPPInput(p, x_te_raw), 1:P))
# Specify equivalent OILMM.
U = collect(Diagonal(ones(P)))
S = Diagonal(abs2.(as))
D = Diagonal(zeros(P))
f = OILMM([GP(Matern52Kernel()) for p in 1:P], U, S, D)
x_tr = MOInput(x_tr_raw, P)
x_te = MOInput(x_te_raw, P)
y_tr = rand(rng, f(x_tr, σ²))
y_te = rand(rng, f(x_te, σ²))
consistency_tests(
rng, f, f_naive;
x_tr=x_tr,
x_te=x_te,
x_naive_tr=x_naive_tr,
x_naive_te=x_naive_te,
y_tr=y_tr,
y_te=y_te,
σ²=σ²,
)
end
@testset "Full Rank, Dense H" begin
rng = MersenneTwister(123456)
P = 3
N = 15
# Specify inputs and generate observations.
x = collect(range(-3.37, 3.12; length=N))
tr_idx = randperm(rng, length(x))[1:2]
te_idx = setdiff(eachindex(x), tr_idx)
x_tr_raw = x[tr_idx]
x_te_raw = x[te_idx]
# Noise variance.
σ² = 0.12
# Construct a random orthogonal H.
U, S_diag, _ = svd(randn(rng, P, P))
H = U * Diagonal(sqrt.(S_diag))
# Specify a collection of GPs
gpc = Stheno.GPC()
zs = [wrap(GP(Matern52Kernel()), gpc) for p in 1:P]
fs = [sum(H[p, :] .* zs) for p in 1:P]
f_naive = Stheno.GPPP(fs, gpc)
x_naive_tr = BlockData(map(p -> GPPPInput(p, x_tr_raw), 1:P))
x_naive_te = BlockData(map(p -> GPPPInput(p, x_te_raw), 1:P))
# Specify equivalent OILMM.
D = Diagonal(zeros(P))
f = OILMM(zs, U, Diagonal(S_diag), D)
# Specify inputs and generate observations.
x_tr = MOInput(x_tr_raw, P)
x_te = MOInput(x_te_raw, P)
y_tr = rand(rng, f(x_tr, σ²))
y_te = rand(rng, f(x_te, σ²))
consistency_tests(
rng, f, f_naive;
x_tr=x_tr,
x_te=x_te,
x_naive_tr=x_naive_tr,
x_naive_te=x_naive_te,
y_tr=y_tr,
y_te=y_te,
σ²=σ²,
)
end
end
| OILMMs | https://github.com/willtebbutt/OILMMs.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
] | 0.2.4 | c45074f765d0f729dc12bc23fedb49b041545b3b | code | 475 | using AbstractGPs
using Distributions
using FiniteDifferences
using LinearAlgebra
using OILMMs
using Random
using Stheno
using Test
using Zygote
using AbstractGPs: AbstractGP, FiniteGP
using OILMMs: denoised_marginals, rand_latent
using Stheno: GaussianProcessProbabilisticProgramme
# Helper functionality, doesn't actually run any tests.
include("test_util.jl")
@testset "OILMMs.jl" begin
include("util.jl")
include("oilmm.jl")
include("missing_data.jl")
end
| OILMMs | https://github.com/willtebbutt/OILMMs.jl.git |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.