code
stringlengths 114
1.05M
| path
stringlengths 3
312
| quality_prob
float64 0.5
0.99
| learning_prob
float64 0.2
1
| filename
stringlengths 3
168
| kind
stringclasses 1
value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
# Samplitude [](https://travis-ci.com/pgdr/samplitude)
CLI generation and plotting of random variables:
```bash
$ samplitude "sin(0.31415) | sample(6) | round | cli"
0.0
0.309
0.588
0.809
0.951
1.0
```
The word _samplitude_ is a portmanteau of _sample_ and _amplitude_. This
project also started as an étude, hence should be pronounced _sampl-étude_.
`samplitude` is a chain starting with a _generator_, followed by zero or more
_filters_, followed by a consumer. Most generators are infinite (with the
exception of `range` and `lists` and possibly `stdin`). Some of the filters can
turn infinite generators into finite generators (like `sample` and `gobble`),
and some filters can turn finite generators into infinite generators, such as
`choice`.
_Consumers_ are filters that necessarily flush the input; `list`, `cli`,
`json`, `unique`, and the plotting tools, `hist`, `scatter` and `line` are
examples of consumers. The `list` consumer is a Jinja2 built-in, and other
Jinja2 consumers are `sum`, `min`, and `max`:
```bash
samplitude "sin(0.31415) | sample(5) | round | max | cli"
0.951
```
For simplicity, **s8e** is an alias for samplitude.
## Generators
In addition to the standard `range` function, we support infinite generators
* `exponential(lambd)`: `lambd` is 1.0 divided by the desired mean.
* `uniform(a, b)`: Get a random number in the range `[a, b)` or `[a, b]`
depending on rounding.
* `gauss(mu, sigma)`: `mu` is the mean, and `sigma` is the standard deviation.
* `normal(mu, sigma)`: as above
* `lognormal(mu, sigma)`: as above
* `triangular(low, high)`: Continuous distribution bounded by given lower and
upper limits, and having a given mode value in-between.
* `beta(alpha, beta)`: Conditions on the parameters are `alpha > 0` and `beta >
0`. Returned values range between 0 and 1.
* `gamma(alpha, beta)`: as above
* `weibull(alpha, beta)`: `alpha` is the scale parameter and `beta` is the shape
parameter.
* `pareto(alpha)`: Pareto distribution. `alpha` is the shape parameter.
* `vonmises(mu, kappa)`: `mu` is the mean angle, expressed in radians between 0
and `2*pi`, and `kappa` is the concentration parameter, which must be greater
than or equal to zero. If kappa is equal to zero, this distribution reduces
to a uniform random angle over the range 0 to `2*pi`.
Provided that you have installed the `scipy.stats` package, the
* `pert(low, peak, high)`
distribution is supported.
We have a special infinite generator (filter) that works on finite generators:
* `choice`,
whose behaviour is explained below.
For input from files, either use `words` with a specified environment variable
`DICTIONARY`, or pipe through
* `stdin()`
which reads from `stdin`.
If the file is a csv file, there is a `csv` generator that reads a csv file with
Pandas and outputs the first column (if nothing else is specified). Specify the
column with either an integer index or a column name:
```bash
>>> samplitude "csv('iris.csv', 'virginica') | counter | cli"
0 50
1 50
2 50
```
For other files, we have the `file` generator:
```bash
>>> s8e "file('iris.csv') | sample(1) | cli"
150,4,setosa,versicolor,virginica
```
Finally, we have `combinations` and `permutations` that are inherited from
itertools and behave exactly like those.
```bash
>>> s8e "'ABC' | permutations | cli"
```
However, the output of this is rather non-UNIXy, with the abstractions leaking through:
```bash
>>> s8e "'HT' | permutations | cli"
('H', 'T')
('T', 'H')
```
So to get a better output, we can use an _elementwise join_ `elt_join`:
```bash
>>> s8e "'HT' | permutations | elt_join | cli"
H T
T H
```
which also takes a seperator as argument:
```bash
>>> s8e "'HT' | permutations | elt_join(';') | cli"
H;T
T;H
```
This is already supported by Jinja's `map` function (notice the strings around `join`):
```bash
>>> s8e "'HT' | permutations | map('join', ';') | cli"
H;T
T;H
```
We can thus count the number of permutations of a set of size 10:
```bash
>>> s8e "range(10) | permutations | len"
3628800
```
The `product` generator takes two generators and computes a cross-product of
these. In addition,
## A warning about infinity
All generators are (potentially) infinite generators, and must be sampled with
`sample(n)` before consuming!
## Usage and installation
Install with
```bash
pip install samplitude
```
or to get bleeding release,
```bash
pip install git+https://github.com/pgdr/samplitude
```
### Examples
This is pure Jinja2:
```bash
>>> samplitude "range(5) | list"
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
```
However, to get a more UNIXy output, we use `cli` instead of `list`:
```bash
>>> s8e "range(5) | cli"
0
1
2
3
4
```
To limit the output, we use `sample(n)`:
```bash
>>> s8e "range(1000) | sample(5) | cli"
0
1
2
3
4
```
That isn't very helpful on the `range` generator, which is already finite, but
is much more helpful on an infinite generator. The above example is probably
better written as
```bash
>>> s8e "count() | sample(5) | cli"
0
1
2
3
4
```
However, much more interesting are the infinite random generators, such as the
`uniform` generator:
```bash
>>> s8e "uniform(0, 5) | sample(5) | cli"
3.3900198868059235
1.2002767137709318
0.40999391897569126
1.9394585953696264
4.37327472704115
```
We can round the output in case we don't need as many digits (note that `round`
is a generator as well and can be placed on either side of `sample`):
```bash
>>> s8e "uniform(0, 5) | round(2) | sample(5) | cli"
4.98
4.42
2.05
2.29
3.34
```
### Selection and modifications
The `sample` behavior is equivalent to the `head` program, or from languages
such as Haskell. The `head` alias is supported:
```bash
>>> samplitude "uniform(0, 5) | round(2) | head(5) | cli"
4.58
4.33
1.87
2.09
4.8
```
`drop` is also available:
```bash
>>> s8e "uniform(0, 5) | round(2) | drop(2) | head(3) | cli"
1.87
2.09
4.8
```
To **shift** and **scale** distributions, we can use the `shift(s)` and
`scale(s)` filters.
To get a Poisson distribution process starting at 15, we can run
```bash
>>> s8e "poisson(4) | shift(15) | sample(5) |cli"
18
21
19
22
17
```
or to get the Poisson point process (exponential distribution),
```bash
>>> s8e "exponential(4) | round | shift(15) | sample(5) |cli"
16.405
15.54
15.132
15.153
15.275
```
Both `shift` and `scale` work on generators, so to add `sin(0.1)` and
`sin(0.2)`, we can run
```bash
>>> s8e "sin(0.1) | shift(sin(0.2)) | sample(10) | cli"
```
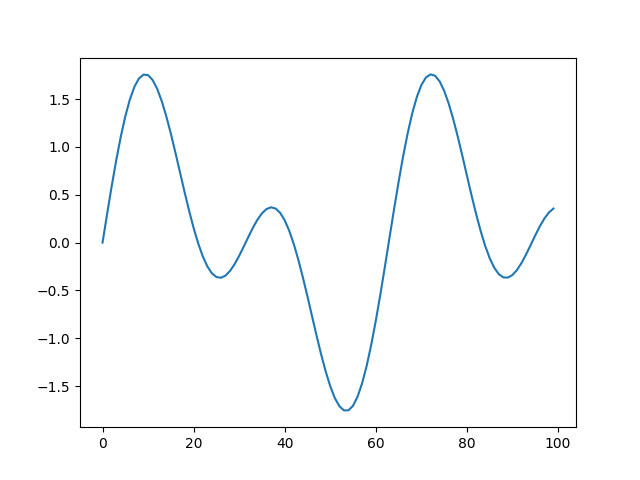
### Choices and other operations
Using `choice` with a finite generator gives an infinite generator that chooses
from the provided generator:
```bash
>>> samplitude "range(0, 11, 2) | choice | sample(6) | cli"
8
0
8
10
4
6
```
Jinja2 supports more generic lists, e.g., lists of strings. Hence, we can write
```bash
>>> s8e "['win', 'draw', 'loss'] | choice | sample(6) | sort | cli"
draw
draw
loss
loss
loss
win
```
... and as in Python, strings are also iterable:
```bash
>>> s8e "'HT' | cli"
H
T
```
... so we can flip six coins with
```bash
>>> s8e "'HT' | choice | sample(6) | cli"
H
T
T
H
H
H
```
We can flip 100 coins and count the output with `counter` (which is
`collections.Counter`)
```bash
>>> s8e "'HT' | choice | sample(100) | counter | cli"
H 47
T 53
```
The `sort` functionality works as expected on a `Counter` object (a
`dict` type), so if we want the output sorted by key, we can run
```bash
>>> s8e "range(1,7) | choice | sample(100) | counter | sort | elt_join | cli" 42 # seed=42
1 17
2 21
3 12
4 21
5 13
6 16
```
There is a minor hack to sort by value, namely by `swap`-ing the Counter twice:
```bash
>>> s8e "range(1,7) | choice | sample(100) |
counter | swap | sort | swap | elt_join | cli" 42 # seed=42
3 12
5 13
6 16
1 17
2 21
4 21
```
The `swap` filter does an element-wise reverse, with element-wise reverse
defined on a dictionary as a list of `(value, key)` for each key-value pair in
the dictionary.
So, to get the three most common anagram strings, we can run
```bash
>>> s8e "words() | map('sort') | counter | swap | sort(reverse=True) |
swap | sample(3) | map('first') | elt_join('') | cli"
aeprs
acerst
opst
```
Using `stdin()` as a generator, we can pipe into `samplitude`. Beware that
`stdin()` flushes the input, hence `stdin` (currently) does not work with
infinite input streams.
```bash
>>> ls | samplitude "stdin() | choice | sample(1) | cli"
some_file
```
Then, if we ever wanted to shuffle `ls` we can run
```bash
>>> ls | samplitude "stdin() | shuffle | cli"
some_file
```
```bash
>>> cat FILE | samplitude "stdin() | cli"
# NOOP; cats FILE
```
### The fun powder plot
For fun, if you have installed `matplotlib`, we support plotting, `hist` being
the most useful.
```bash
>>> samplitude "normal(100, 5) | sample(1000) | hist"
```
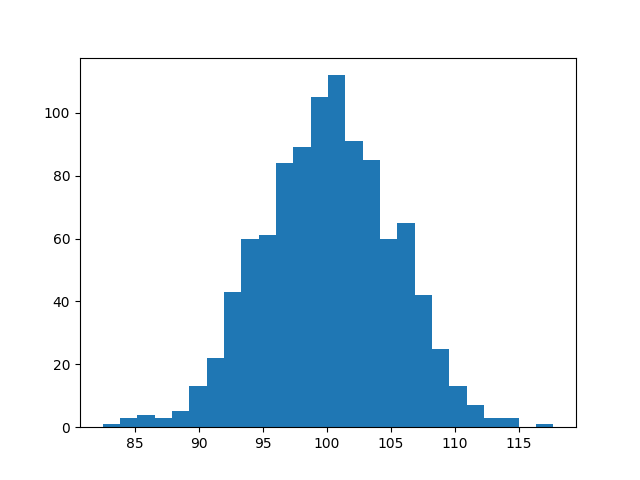
An exponential distribution can be plotted with `exponential(lamba)`. Note that
the `cli` output must be the last filter in the chain, as that is a command-line
utility only:
```bash
>>> s8e "normal(100, 5) | sample(1000) | hist | cli"
```
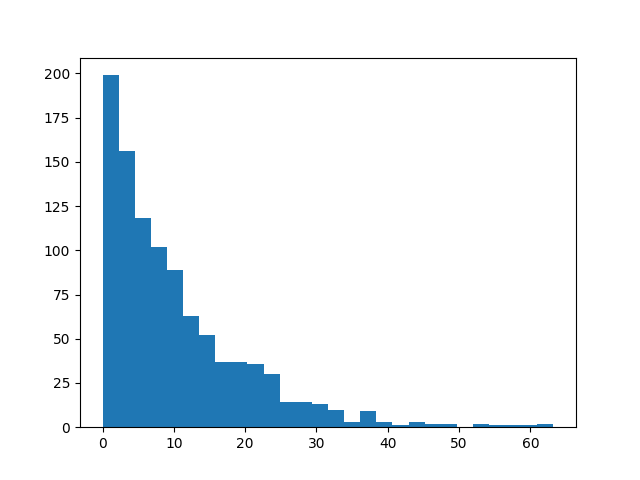
To **repress output after plotting**, you can use the `gobble` filter to empty
the pipe:
```bash
>>> s8e "normal(100, 5) | sample(1000) | hist | gobble"
```
The
[`pert` distribution](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PERT_distribution)
takes inputs `low`, `peak`, and `high`:
```bash
>>> s8e "pert(10, 50, 90) | sample(100000) | hist(100) | gobble"
```
Although `hist` is the most useful, one could imaging running `s8e` on
timeseries, where a `line` plot makes most sense:
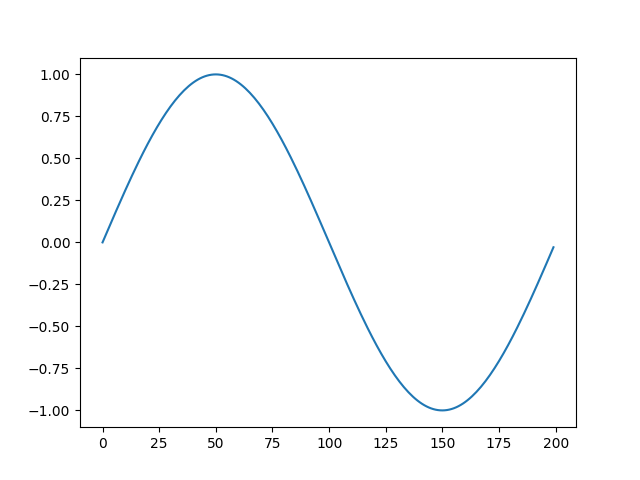
```bash
>>> s8e "sin(22/700) | sample(200) | line"
```
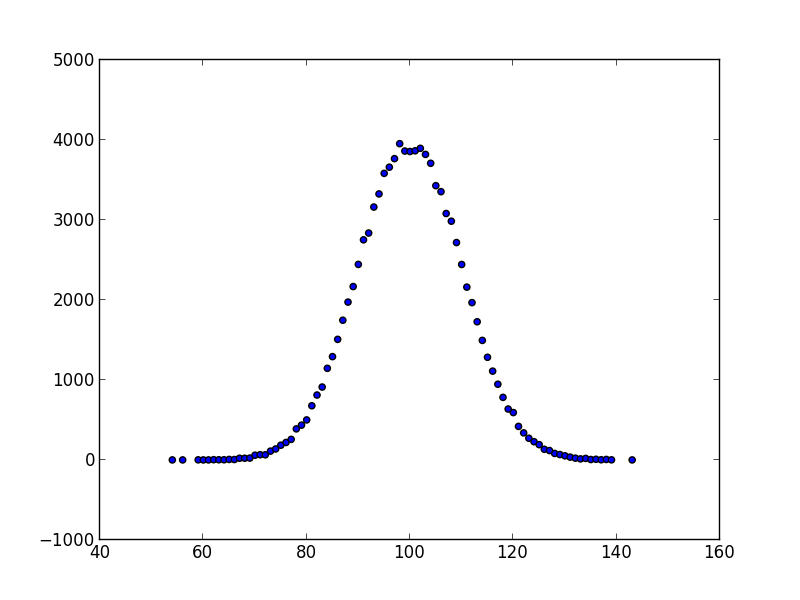
The scatter function can also be used, but requires that the input stream is a
stream of pairs, which can be obtained either by the `product` generator, or via
the `pair` or `counter` filter:
```bash
s8e "normal(100, 10) | sample(10**5) | round(0) | counter | scatter"
```
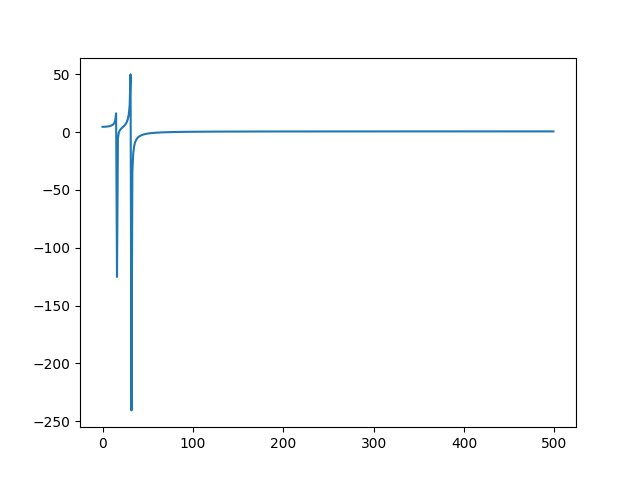
### Fourier
A fourier transform is offered as a filter `fft`:
```bash
>>> samplitude "sin(0.1) | shift(sin(0.2)) | sample(1000) | fft | line | gobble"
```
## Your own filter
If you use Samplitude programmatically, you can register your own filter by
sending a dictionary
```python
{'name1' : filter1,
'name2' : filter2,
#...,
'namen' : filtern,
}
```
to the `samplitude` function.
### Example: secretary problem
Suppose you want to emulate the secretary problem ...
#### Intermezzo: The problem
For those not familiar, you are a boss, Alice, who wants to hire a new secretary
Bob. Suppose you want to hire the tallest Bob of all your candidates, but the
candidates arrive in a stream, and you know only the number of candidates. For
each candidate, you have to accept (hire) or reject the candidate. Once you
have rejected a candidate, you cannot undo the decision.
The solution to this problem is to look at the first `n/e` (`e~2.71828` being
the Euler constant) candidates, and thereafter accept the first candidate taller
than all of the `n/e` first candidates.
#### A Samplitude solution
Let `normal(170, 10)` be the candidate generator, and let `n=100`. We create a
filter `secretary` that takes a stream and an integer (`n`) and picks according
to the solution. In order to be able to assess the quality of the solution
later, the filter must forward the entire list of candidates; hence we annotate
the one we choose with `(c, False)` for a candidate we rejected, and `(c, True)`
denotes the candidate we accepted.
```python
def secretary(gen, n):
import math
explore = int(n / math.e)
target = -float('inf')
i = 0
# explore the first n/e candidates
for c in gen:
target = max(c, target)
yield (c, False)
i += 1
if i == explore:
break
_ok = lambda c, i, found: ((i == n-1 and not found)
or (c > target and not found))
have_hired = False
for c in gen:
status = _ok(c, i, have_hired)
have_hired = have_hired or status
yield c, status
i += 1
if i == n:
return
```
Now, to emulate the secretary problem with Samplitude:
```python
from samplitude import samplitude as s8e
# insert above secretary function
n = 100
filters = {'secretary': secretary}
solution = s8e('normal(170, 10) | secretary(%d) | list' % n, filters=filters)
solution = eval(solution) # Samplitude returns an eval-able string
cands = map(lambda x: x[0], solution)
opt = [s[0] for s in solution if s[1]][0]
# the next line prints in which position the candidate is
print(1+sorted(cands, reverse=True).index(opt), '/', n)
```
In about 67% of the cases we can expect to get one of the top candidates,
whereas the remaining 33% of the cases will be uniformly distributed. Running
100k runs with a population of size 1000 reveals the structure.
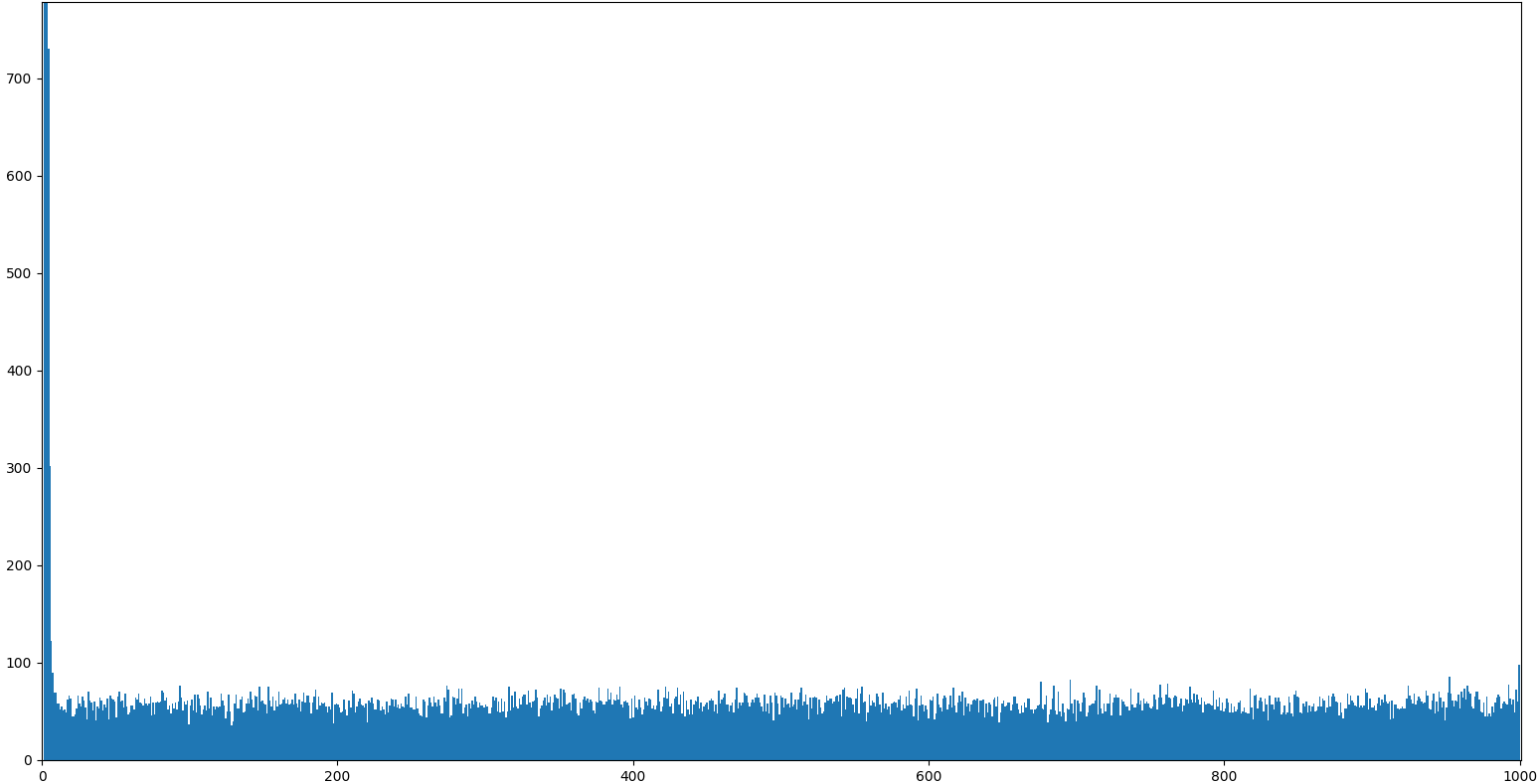
|
/samplitude-0.2.0.tar.gz/samplitude-0.2.0/README.md
| 0.765243 | 0.970882 |
README.md
|
pypi
|
import numpy as np
from .jit_compiled_functions import (sampling_get_potential_targets,
sampling_sample_from_array_condition)
class BaseSamplingSingleSpecies:
"""
Base Class for single species sampling.
"""
def __init__(self, target_species=None, **kwargs):
if target_species is None:
raise ValueError("No agent object provided for the sampling. Should be provided using kwarg "
"'target_species'.")
self.target_species = target_species
class SamplingSingleSpecies:
"""
Introduce the methods for sampling a single species
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
pass
def sample_proportion_from_array(self, array_proportion, condition=None, position_attribute='position',
return_as_pandas_df=False, eliminate_sampled_pop=False):
"""
Take as input an array telling the proportion of agent to sample in each vertex.
:param array_proportion: 1D array of float. array_proportion[i] is the probability for an agent living in the
vertex of index i.
:param condition: optional, 1D array of bool, default None. If not None, tell which agent can be sampled.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'. Tell which attribute of the agents should
be used as position.
:param return_as_pandas_df: optional, boolean, default False. Clear.
:param eliminate_sampled_pop: optional, boolean, default False. If True,
:return: a DataFrameXS if return_as_pandas_df is False, a pandas dataframe otherwise. The returned DF is
the sample of the population taken from df_population
"""
targets = sampling_get_potential_targets(self.target_species.df_population[position_attribute],
array_proportion)
if condition is not None:
targets = targets & condition
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (targets.sum(),))
sampled = sampling_sample_from_array_condition(array_proportion,
self.target_species.df_population[position_attribute],
rand, targets)
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/intervention/sampling.py
| 0.878536 | 0.372077 |
sampling.py
|
pypi
|
import numpy as np
from ..pandas_xs.pandas_xs import DataFrameXS
from .jit_compiled_functions import vaccination_apply_vaccine_from_array_condition
class BaseVaccinationSingleSpeciesDisease:
def __init__(self, disease=None, **kwargs):
if disease is None:
raise ValueError(
"No disease object provided for the vaccination. Should be provided using kwarg 'disease'.")
self.disease = disease
self.target_species = self.disease.host
self.target_species.df_population['vaccinated_' + self.disease.disease_name] = False
self.target_species.dict_default_val['vaccinated_' + self.disease.disease_name] = False
class VaccinationSingleSpeciesDiseaseFixedDuration:
def __init__(self, duration_vaccine=None, **kwargs):
if duration_vaccine is None:
raise ValueError(
"No duration provided for the vaccination duration. Should be provided using kwarg 'duration_vaccine'.")
self.duration_vaccine = int(duration_vaccine)
self.target_species.df_population['cnt_vaccinated_' + self.disease.disease_name] = 0
self.target_species.dict_default_val['cnt_vaccinated_' + self.disease.disease_name] = 0
def update_vaccine_status(self):
"""
Should be call at each time-step of the simulation. Update the attribute that count how many day each individual
has been vaccinated, and remove the vaccinated status of the individual which recieved their dose for more than
'duration_vaccine' time-steps.
"""
self.target_species.df_population['cnt_vaccinated_' + self.disease.disease_name] += 1
arr_lose_vaccine = self.target_species.df_population['cnt_vaccinated_' + self.disease.disease_name] >= \
self.duration_vaccine
not_arr_lose_vaccine = ~arr_lose_vaccine
self.target_species.df_population['cnt_vaccinated_' + self.disease.disease_name] = \
self.target_species.df_population['cnt_vaccinated_' + self.disease.disease_name] * not_arr_lose_vaccine
self.target_species.df_population['vaccinated_' + self.disease.disease_name] = \
self.target_species.df_population['vaccinated_' + self.disease.disease_name] * not_arr_lose_vaccine
self.target_species.df_population['imm_' + self.disease.disease_name] = \
self.target_species.df_population['imm_' + self.disease.disease_name] * not_arr_lose_vaccine
def apply_vaccine_from_array(self, array_vaccine_level, condition=None, position_attribute='position'):
"""
Apply vaccine to the agents based on the 1D array 'array_vaccine_level'. array_vaccine_level[i] is the
probability for an agent on the vertex of index i to get vaccinated.
Note that, by default, infected and contagious agents can get vaccinated. They can be excluded using the
kwarg 'condition'
:param array_vaccine_level: 1D array of float. Floats between 0 and 1.
:param condition: optional, 1D array of bool, default None.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'.
"""
if condition is None:
condition = np.full((self.target_species.df_population.nb_rows,), True, dtype=np.bool_)
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (condition.sum(),))
newly_vaccinated = \
vaccination_apply_vaccine_from_array_condition(
self.target_species.df_population['vaccinated_' + self.disease.disease_name],
self.target_species.df_population['cnt_vaccinated_' + self.disease.disease_name],
self.target_species.df_population['imm_' + self.disease.disease_name],
array_vaccine_level, self.target_species.df_population[position_attribute], rand, condition)
not_newly_vaccinated = ~newly_vaccinated
self.target_species.df_population['inf_' + self.disease.disease_name] *= not_newly_vaccinated
self.target_species.df_population['con_' + self.disease.disease_name] *= not_newly_vaccinated
def apply_vaccine_from_dict(self, graph, dict_vertex_id_to_level, condition=None, position_attribute='position'):
"""
same as apply_vaccine_from_array, but the 1D array is replaced by a dictionary whose keys are vertices ID and
values is the vaccination level on each cell.
:param graph: graph object on which the vaccine is applied
:param dict_vertex_id_to_level: dictionnary-like object with vaccine level
:param condition: optional, 1D array of bool, default None.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'.
"""
array_vac_level = np.full((graph.number_vertices,), 0., dtype=float)
for id_vertex, level in dict_vertex_id_to_level.items():
array_vac_level[graph.dict_cell_id_to_ind[id_vertex]] = level
self.apply_vaccine_from_array(array_vac_level, condition=condition, position_attribute=position_attribute)
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/intervention/vaccination.py
| 0.744099 | 0.390243 |
vaccination.py
|
pypi
|
import numpy as np
from .jit_compiled_functions import culling_apply_culling_from_array_condition
class BaseCullingSingleSpecies:
def __init__(self, species=None, **kwargs):
if species is None:
raise ValueError(
"No agent object provided for the culling. Should be provided using kwarg 'species'.")
self.species = species
class CullingSingleSpecies:
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
pass
def apply_culling_from_array(self, array_culling_level, condition=None, position_attribute='position'):
"""
Kill proportion of agents based on the 1D array 'array_culling_level'. array_culling_level[i] is the
probability for an agent on the vertex of index i to be killed.
By default, all agent can be killed. Use kwarg 'condition' to refine the culling.
:param array_culling_level: 1D array of float
:param condition: optional, 1D array of bool, default None.
:param position_attribute: optionnal, string, default 'position'
"""
if condition is None:
condition = np.full((self.species.df_population.nb_rows,), True, dtype=np.bool_)
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (condition.sum(),))
survive_culling = culling_apply_culling_from_array_condition(array_culling_level,
self.species.df_population[position_attribute],
rand, condition)
self.species.df_population = self.species.df_population[survive_culling]
def apply_culling_from_dict(self, graph, dict_vertex_id_to_level, condition=None, position_attribute='position'):
"""
Same as apply_culling_from_array, but the 1D array is replaced by a dictionary whose keys are vertices ID and
values is the culling level on each cell.
:param graph: graph object on which the culling is applied
:param dict_vertex_id_to_level: dictionnary-like object with culling level
:param condition: optional, 1D array of bool, default None.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'.
"""
array_cul_level = np.full((graph.number_vertices,), 0., dtype=float)
for id_vertex, level in dict_vertex_id_to_level.items():
array_cul_level[graph.dict_cell_id_to_ind[id_vertex]] = level
self.apply_culling_from_array(array_cul_level, condition=condition, position_attribute=position_attribute)
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/intervention/culling.py
| 0.804521 | 0.364353 |
culling.py
|
pypi
|
from .base import BaseTwoSpeciesDisease
from .transition import TransitionCustomProbPermanentImmunity
from .transmission import ContactTransmissionSameGraph
from ...utils.decorators import sampy_class
@sampy_class
class TwoSpeciesContactCustomProbTransitionPermanentImmunity(BaseTwoSpeciesDisease,
TransitionCustomProbPermanentImmunity,
ContactTransmissionSameGraph):
"""
Basic disease, transmission by direct contact (contagion only between agents on the same vertex), transition between
disease states encoded by user given arrays of probabilities, and permanent immunity.
IMPORTANT: We strongly recommend the user to use the "simplified" methods defined here instead of the usual
'contaminate_vertices', 'contact_contagion' and 'transition_between_states'. Indeed, the combination of
building blocks involved in this disease requires many actions to be performed in a precise order,
otherwise the model's behaviour cannot be guaranteed. See each simplified method description to learn
about each respective ordering.
:param disease_name: mandatory kwargs. String.
:param host1: mandatory kwargs. Population object of the first host.
:param host2: mandatory kwargs. Population object of the second host.
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
pass
def simplified_contact_contagion(self, contact_rate_matrix, arr_timesteps_host1, arr_prob_timesteps_host1,
arr_timesteps_host2, arr_prob_timesteps_host2,
position_attribute_host1='position', position_attribute_host2='position',
condition_host1=None, condition_host2=None,
return_arr_new_infected=False, return_type_transmission=False):
"""
Propagate the disease by direct contact using the following methodology. For any vertex X of the graph, we
count the number of contagious agents N_c_host_j, then each non immuned agent of host_k on the vertex X has a
probability of
1 - (1 - contact_rate_matrix[j,k]) ** N_c_host_j
to become infected by a contact with an agent of host_j.
Detailed Explanation: each agent has a series of counter attached, telling how much time-steps they will spend
in each disease status. Those counters have to be initialized when an individual is newly
infected, and that's what this method does to the newly infected individuals.
:param contact_rate_matrix: 2D array of floats of shape (2, 2). Here, contact_rate_matrix[0][0] is the
probability of contact contagion from host1 to host1, contact_rate_matrix[0][1] is
the probability of contact contagion from host1 to host2, etc...
:param arr_timesteps_host1: 1d array of int. work in tandem with arr_prob_timesteps_host1, see below.
:param arr_prob_timesteps_host1: 1D array of float. arr_prob[i] is the probability for an agent to stay infected
but not contagious for arr_nb_timestep[i] time-steps.
:param arr_timesteps_host2: same but for host2.
:param arr_prob_timesteps_host2: same but for host2.
:param position_attribute_host1: optional, string, default 'position'. Name of the agent attribute used as
position for host1.
:param position_attribute_host2: optional, string, default 'position'. Name of the agent attribute used as
position for host2.
:param condition_host1: optional, array of bool, default None. Array of boolean such that the i-th value is
True if and only if the i-th agent of host1 (i.e. the agent at the line i of df_population)
can be infected and transmit disease. All the agent having their corresponding value to False
are protected from infection and cannot transmit the disease.
:param condition_host2: optional, array of bool, default None. Array of boolean such that the i-th value is
True if and only if the i-th agent of host2 (i.e. the agent at the line i of df_population)
can be infected and transmit disease. All the agent having their corresponding value to False
are protected from infection and cannot transmit the disease.
:param return_arr_new_infected: optional, boolean, default False. If True, the method returns two arrays telling
which agent got contaminated in each host species.
:param return_type_transmission: optional, boolean, default False.
:return: Depending on the values of the parameters 'return_arr_new_infected' and 'return_type_transmission',
the return value will either be None (both are False) or a dictionnary whose key-values are:
- 'arr_new_infected_host1', 'arr_new_infected_host2' if return_arr_new_infected is True, and the
values are 1D arrays of bool telling which agents got infected for each host;
- 'arr_type_transmission_host1', 'arr_type_transmission_host2' if return_type_transmission is True,
and the values are 1D arrays of non-negative integers such that the integer at line i is 0 if the
i-th agent has not been contaminated, 1 if it has been contaminated by a member of its own species
2 if it has been contaminated by a member of the other species, 3 if it has been contaminated by
agents from both its species and the other.
"""
dict_contagion = self.contact_contagion(contact_rate_matrix, return_arr_new_infected=True,
return_type_transmission=return_type_transmission,
position_attribute_host1=position_attribute_host1,
position_attribute_host2=position_attribute_host2,
condition_host1=condition_host1, condition_host2=condition_host2)
self.initialize_counters_of_newly_infected('host1', dict_contagion['arr_new_infected_host1'],
arr_timesteps_host1, arr_prob_timesteps_host1)
self.initialize_counters_of_newly_infected('host2', dict_contagion['arr_new_infected_host2'],
arr_timesteps_host2, arr_prob_timesteps_host2)
if not return_type_transmission and not return_arr_new_infected:
return
if return_arr_new_infected:
return dict_contagion
else: # no other case needed
del dict_contagion['arr_new_infected_host1']
del dict_contagion['arr_new_infected_host2']
return dict_contagion
def simplified_transition_between_states(self, prob_death_host1, prob_death_host2,
arr_infectious_period_host1, arr_prob_infectious_period_host1,
arr_infectious_period_host2, arr_prob_infectious_period_host2):
"""
Takes care of the transition between all the disease states. That is, agents that are at the end of their
infected period become contagious and agents at the end of their contagious period either die (with a
probability of 'prob_death') or become immuned.
Detailed Explanation: the method transition_between_states is coded in such a way that when using it for
transitionning from con to imm, all the agents at the end of their contagious period at
the time the method is called transition. Therefore, we have to make the transition
'con' to 'death' first.
:param prob_death_host1: float between 0 and 1, probability for an agent of host1 to die at the end of the
contagious period
:param prob_death_host2: float between 0 and 1, probability for an agent of host2 to die at the end of the
contagious period
:param arr_infectious_period_host1: 1d array of int, works in tandem with arr_prob_infectious_period_host1.
See Below.
:param arr_prob_infectious_period_host1: 1d array of floats, sums to 1. Same shape as
arr_infectious_period_host1. When an agent transition from infected to contagious, then
arr_prob_infectious_period_host1[i] is the probability for this agent to stay
arr_infectious_period_host1[i] timesteps contagious.
:param arr_infectious_period_host2: same as host1
:param arr_prob_infectious_period_host2: same as host1
"""
self.transition_between_states('host1', 'con', 'death', proba_death=prob_death_host1)
self.transition_between_states('host2', 'con', 'death', proba_death=prob_death_host2)
if self.host1.df_population.nb_rows != 0:
self.transition_between_states('host1', 'con', 'imm')
self.transition_between_states('host1', 'inf', 'con', arr_nb_timestep=arr_infectious_period_host1,
arr_prob_nb_timestep=arr_prob_infectious_period_host1)
if self.host2.df_population.nb_rows != 0:
self.transition_between_states('host2', 'con', 'imm')
self.transition_between_states('host2', 'inf', 'con', arr_nb_timestep=arr_infectious_period_host2,
arr_prob_nb_timestep=arr_prob_infectious_period_host2)
def simplified_contaminate_vertices(self, host, list_vertices, level, arr_timesteps, arr_prob_timesteps,
condition=None, position_attribute='position',
return_arr_newly_contaminated=True):
"""
Contaminate a list of vertices.
Detailed explanation: each agent has a series of counter attached, telling how much time-steps they will spend
in each disease status. Those counters have to be initialized when an individual is newly
infected, and that's what this method does to the newly infected individuals.
:param host: string, either 'host1' or 'host2', tells which host to infect.
:param list_vertices: list of vertices ID to be contaminated.
:param level: float, probability for agent on the vertices to be contaminated.
:param arr_timesteps: 1D array of integer. Works in tandem with 'arr_prob_timesteps'. See below.
:param arr_prob_timesteps: 1D array of float. arr_prob_timesteps[i] is the probability for an agent to stay
infected but not contagious for arr_timesteps[i] timesteps.
:param condition: optional, array of bool, default None. If not None, say which agents are susceptible to be
contaminated.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'. Agent attribute to be used to define
their position.
:param return_arr_newly_contaminated: optional, boolean, default True. If True, the method returns an array
telling which agents were contaminated.
:return: if return_arr_newly_contaminated is set to True, returns a 1D array of bool telling which agents where
contaminated. Returns None otherwise.
"""
arr_new_contaminated = self.contaminate_vertices(host, list_vertices, level,
condition=condition, position_attribute=position_attribute,
return_arr_newly_contaminated=True)
self.initialize_counters_of_newly_infected(host, arr_new_contaminated, arr_timesteps, arr_prob_timesteps)
if return_arr_newly_contaminated:
return arr_new_contaminated
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/disease/two_species/builtin_disease.py
| 0.847148 | 0.556038 |
builtin_disease.py
|
pypi
|
import numpy as np
from .jit_compiled_functions import base_contaminate_vertices
class BaseTwoSpeciesDisease:
"""Base class for two species disease. This building block expects the following kwargs:
:param disease_name: mandatory kwargs. String.
:param host1: mandatory kwargs. Population object of the first host.
:param host2: mandatory kwargs. Population object of the second host.
"""
def __init__(self, disease_name='', host1=None, host2=None, **kwargs):
# check values have been given
if not host1:
raise ValueError('No first host given for the disease. Use Kwarg host1.')
if not host2:
raise ValueError('No second host given for the disease. Use Kwarg host2.')
if not disease_name:
raise ValueError('No name given to the disease. Use Kwarg disease_name.')
self.host1 = host1
self.host2 = host2
self.disease_name = disease_name
self.host1.df_population['inf_' + disease_name] = False
self.host1.df_population['con_' + disease_name] = False
self.host1.df_population['imm_' + disease_name] = False
if hasattr(host1, 'dict_default_val'):
self.host1.dict_default_val['inf_' + disease_name] = False
self.host1.dict_default_val['con_' + disease_name] = False
self.host1.dict_default_val['imm_' + disease_name] = False
self.host2.df_population['inf_' + disease_name] = False
self.host2.df_population['con_' + disease_name] = False
self.host2.df_population['imm_' + disease_name] = False
if hasattr(host2, 'dict_default_val'):
self.host2.dict_default_val['inf_' + disease_name] = False
self.host2.dict_default_val['con_' + disease_name] = False
self.host2.dict_default_val['imm_' + disease_name] = False
if not hasattr(self, 'set_disease_status'):
self.set_disease_status = {'inf', 'con', 'imm'}
else:
self.set_disease_status.update(['inf', 'con', 'imm'])
self.on_ticker = []
def tick(self):
"""
execute in order all the methods whose name are in the list 'on_ticker'. Those methods should not accept
any arguments.
"""
for method in self.on_ticker:
getattr(self, method)()
def contaminate_vertices(self, host, list_vertices, level, return_arr_newly_contaminated=True,
condition=None, position_attribute='position'):
"""
Contaminate the vertices given in the list 'list_vertices' with the disease. Each agent on the vertex have a
probability of 'level' to be contaminated.
:param host: string, either 'host1' or 'host2'. If host1 should be targeted, put 'host1', If host2 should be
targeted, put 'host2'. Any other input will lead to an error.
:param list_vertices: list of vertices ID to be contaminated.
:param level: float, probability for agent on the vertices to be contaminated.
:param return_arr_newly_contaminated: optional, boolean, default True. If True, the method returns an array
telling which agents were contaminated.
:param condition: optional, array of bool, default None. If not None, say which agents are susceptible to be
contaminated.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'. Agent attribute to be used to define
their position.
:return: if return_arr_newly_contaminated is set to True, returns a 1D array of bool. Otherwise, returns
None.
"""
# here we check that the given object seems to be the one provided during construction.
if host == 'host1':
host = self.host1
elif host == 'host2':
host = self.host2
else:
raise ValueError('The "host" argument is not recognized. It should be either "host1" or "host2".')
# this is quite inefficient, but this function is not assumed to be called often.
for i, vertex_id in enumerate(list_vertices):
if i == 0:
arr_new_infected = (host.df_population[position_attribute] ==
host.graph.dict_cell_id_to_ind[vertex_id])
continue
arr_new_infected = arr_new_infected | (host.df_population[position_attribute] ==
host.graph.dict_cell_id_to_ind[vertex_id])
arr_new_infected = arr_new_infected & ~(host.df_population['inf_' + self.disease_name] |
host.df_population['con_' + self.disease_name] |
host.df_population['imm_' + self.disease_name])
if condition is not None:
arr_new_infected = arr_new_infected & condition
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (arr_new_infected.sum(),))
base_contaminate_vertices(arr_new_infected, rand, level)
host.df_population['inf_' + self.disease_name] = host.df_population['inf_' + self.disease_name] | \
arr_new_infected
if return_arr_newly_contaminated:
return arr_new_infected
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/disease/two_species/base.py
| 0.77081 | 0.367185 |
base.py
|
pypi
|
import numpy as np
from .jit_compiled_functions import *
from ...utils.errors_shortcut import check_col_exists_good_type
class BaseSingleSpeciesDisease:
def __init__(self, disease_name=None, host=None, **kwargs):
# check values have been given
if host is None:
raise ValueError("No host given for the disease. Use the kwarg 'host'.")
if disease_name is None:
raise ValueError("No name given to the disease. Use the kwarg 'disease_name'.")
self.host = host
self.disease_name = disease_name
self.host.df_population['inf_' + disease_name] = False
self.host.df_population['con_' + disease_name] = False
self.host.df_population['imm_' + disease_name] = False
if hasattr(host, 'dict_default_val'):
self.host.dict_default_val['inf_' + disease_name] = False
self.host.dict_default_val['con_' + disease_name] = False
self.host.dict_default_val['imm_' + disease_name] = False
if not hasattr(self, 'list_disease_status'):
self.set_disease_status = {'inf', 'con', 'imm'}
else:
self.set_disease_status.update(['inf', 'con', 'imm'])
self.on_ticker = []
def tick(self):
"""
execute in order all the methods whose name are in the list 'on_ticker'. Those methods should not accept
any arguments.
"""
for method in self.on_ticker:
getattr(self, method)()
def _sampy_debug_count_nb_status_per_vertex(self, target_status, position_attribute='position'):
if self.host.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
check_col_exists_good_type(self.host.df_population, position_attribute, 'attribute_position',
prefix_dtype='int', reject_none=True)
check_col_exists_good_type(self.host.df_population, target_status + '_' + self.disease_name,
'target_status', prefix_dtype='bool', reject_none=True)
def count_nb_status_per_vertex(self, target_status, position_attribute='position'):
"""
Count the number of agent having the targeted status in each vertex. The status can either be 'inf', 'con' and
'imm', which respectively corresponds to infected, contagious and immunized agents.
:param target_status: string in ['inf', 'con', 'imm'].
:param position_attribute: optional, string.
:return: array counting the number of agent having the target status in each vertex
"""
if self.host.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return np.full((self.host.graph.number_vertices,), 0, dtype=np.int32)
return base_conditional_count_nb_agent_per_vertex(self.host.df_population[target_status + '_' +
self.disease_name],
self.host.df_population[position_attribute],
self.host.graph.weights.shape[0])
def contaminate_vertices(self, list_vertices, level, return_arr_newly_contaminated=True,
condition=None, position_attribute='position'):
"""
Contaminate the vertices given in the list 'list_vertices' with the disease. Each agent on the vertex have a
probability of 'level' to be contaminated.
:param list_vertices: list of vertices ID to be contaminated.
:param level: float, probability for agent on the vertices to be contaminated
:param return_arr_newly_contaminated: optional, boolean, default True. If True, the method returns an array
telling which agents were contaminated.
:param condition: optional, array of bool, default None. If not None, say which agents are susceptible to be
contaminated.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'. Agent attribute to be used to define
their position.
:return: if return_arr_newly_contaminated is set to True, returns a 1D array of bool. Otherwise, returns
None.
"""
for i, vertex_id in enumerate(list_vertices):
if i == 0:
arr_new_infected = (self.host.df_population[position_attribute] ==
self.host.graph.dict_cell_id_to_ind[vertex_id])
continue
arr_new_infected = arr_new_infected | (self.host.df_population[position_attribute] ==
self.host.graph.dict_cell_id_to_ind[vertex_id])
arr_new_infected = arr_new_infected & ~(self.host.df_population['inf_' + self.disease_name] |
self.host.df_population['con_' + self.disease_name] |
self.host.df_population['imm_' + self.disease_name])
if condition is not None:
arr_new_infected = arr_new_infected & condition
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (arr_new_infected.sum(),))
base_contaminate_vertices(arr_new_infected, rand, level)
self.host.df_population['inf_' + self.disease_name] = \
self.host.df_population['inf_' + self.disease_name] | arr_new_infected
if return_arr_newly_contaminated:
return arr_new_infected
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/disease/single_species/base.py
| 0.763043 | 0.289711 |
base.py
|
pypi
|
import numpy as np
import math
import numba as nb
@nb.njit
def topology_convert_1d_array_to_2d_array(arr_1d, arr_fast_squarify, shape_0, shape_1):
rv = np.full((shape_0, shape_1), arr_1d[0])
for i in range(arr_1d.shape[0]):
rv[arr_fast_squarify[i][0]][arr_fast_squarify[i][1]] = arr_1d[i]
return rv
@nb.njit
def topology_convert_2d_array_to_1d_array(arr_2d, arr_fast_flat):
n = arr_2d.shape[0] * arr_2d.shape[1]
rv = np.full((n, ), arr_2d[0][0])
for i in range(arr_2d.shape[0]):
for j in range(arr_2d.shape[1]):
rv[arr_fast_flat[i][j]] = arr_2d[i][j]
return rv
@nb.njit
def compute_sin_attr_with_condition(arr_attr, arr_cond, time, amplitude, period, phase, intercept):
for i in range(arr_cond.shape[0]):
if arr_cond[i]:
arr_attr[i] = amplitude*np.sin(2*math.pi*time/period + phase) + intercept
@nb.njit
def get_oriented_neighborhood_of_vertices(connections):
rv = np.full(connections.shape, -1, dtype=np.int32)
for ind_center in range(connections.shape[0]):
# we first create the set of neighbours
set_neighbours = set()
nb_neighbours = 0
for i in range(connections.shape[1]):
ind_neighb = connections[ind_center][i]
if ind_neighb == -1:
pass
else:
set_neighbours.add(ind_neighb)
nb_neighbours += 1
# we now fill the returned array
for j in range(nb_neighbours):
ind_neighbour = connections[ind_center][j]
if ind_neighbour == -1:
pass
else:
rv[ind_center][0] = ind_neighbour
break
for j in range(1, nb_neighbours):
ind_current_neigh = rv[ind_center][j-1]
for k in range(connections.shape[1]):
ind_neighbour = connections[ind_current_neigh][k]
if ind_neighbour == -1:
pass
elif ind_neighbour in set_neighbours:
if j != 1 and rv[ind_center][j-2] == ind_neighbour:
pass
else:
rv[ind_center][j] = ind_neighbour
break
return rv
@nb.njit
def get_surface_array(oriented_neighbourhood_array, x_coord, y_coord, z_coord, radius):
rv = np.full((oriented_neighbourhood_array.shape[0],), 0., dtype=np.float64)
for index_center in range(oriented_neighbourhood_array.shape[0]):
# get coordinates of the center
x_center = x_coord[index_center]
y_center = y_coord[index_center]
z_center = z_coord[index_center]
# quick loop to determine the number of vertices of the current polygon
nb_vertices = 0
for i in range(oriented_neighbourhood_array.shape[1]):
if oriented_neighbourhood_array[index_center][i] != -1:
nb_vertices += 1
# we first create the normal vectors of each hyperplane defining the spherical polygon. Those vectors are not
# normalized
oriented_normal_vect = np.full((nb_vertices, 3), -1.)
current_index = 0
for i in range(oriented_neighbourhood_array.shape[1]):
index_current_neighbour = oriented_neighbourhood_array[index_center][i]
if index_current_neighbour != -1:
oriented_normal_vect[current_index][0] = x_coord[index_current_neighbour] - x_center
oriented_normal_vect[current_index][1] = y_coord[index_current_neighbour] - y_center
oriented_normal_vect[current_index][2] = z_coord[index_current_neighbour] - z_center
current_index += 1
# we know compute the coordinates of the vertices of the spherical polygon using a cross product.
oriented_vertices_polygon = np.full((nb_vertices, 3), -1.)
for i in range(nb_vertices):
vertex = np.cross(oriented_normal_vect[i][:], oriented_normal_vect[(i+1) % nb_vertices][:])
if x_center * vertex[0] + y_center * vertex[1] + z_center * vertex[2] > 0:
oriented_vertices_polygon[i][:] = vertex / (np.sqrt((vertex ** 2).sum()))
else:
oriented_vertices_polygon[i][:] = - vertex / (np.sqrt((vertex ** 2).sum()))
area = 0.
first_point = oriented_vertices_polygon[0][:]
second_point = oriented_vertices_polygon[1][:]
for i in range(2, nb_vertices):
third_point = oriented_vertices_polygon[i][:]
vec1 = second_point - np.dot(second_point, first_point) * first_point
vec2 = third_point - np.dot(third_point, first_point) * first_point
area += np.arccos(np.dot(vec1, vec2) / (np.linalg.norm(vec1) * np.linalg.norm(vec2)))
vec1 = first_point - np.dot(first_point, second_point) * second_point
vec2 = third_point - np.dot(third_point, second_point) * second_point
area += np.arccos(np.dot(vec1, vec2) / (np.linalg.norm(vec1) * np.linalg.norm(vec2)))
vec1 = first_point - np.dot(first_point, third_point) * third_point
vec2 = second_point - np.dot(second_point, third_point) * third_point
area += np.arccos(np.dot(vec1, vec2) / (np.linalg.norm(vec1) * np.linalg.norm(vec2)))
area -= np.pi
second_point = oriented_vertices_polygon[i][:]
rv[index_center] = (radius**2)*area
return rv
@nb.njit
def icosphere_get_distance_matrix(dist_matrix, connections, lats, lons, radius):
for i in range(dist_matrix.shape[0]):
for j in range(dist_matrix.shape[1]):
if connections[i][j] != -1:
dist_matrix[i][j] = radius * np.arccos(np.sin(lats[i]) * np.sin(lats[connections[i][j]]) +
np.cos(lats[i]) * np.cos(lats[connections[i][j]]) *
np.cos(lons[i] - lons[connections[i][j]]))
return dist_matrix
@nb.njit
def keep_subgraph_from_array_of_bool_equi_weight(arr_keep, connections):
counter = 0
dict_old_to_new = dict()
for i in range(arr_keep.shape[0]):
if arr_keep[i]:
dict_old_to_new[i] = counter
counter += 1
arr_nb_connections = np.full((counter,), 0, dtype=np.int32)
new_arr_connections = np.full((counter, 6), -1, dtype=np.int32)
new_arr_weights = np.full((counter, 6), -1., dtype=np.float32)
counter = 0
for i in range(arr_keep.shape[0]):
if arr_keep[i]:
for j in range(connections.shape[1]):
if connections[i][j] in dict_old_to_new:
new_arr_connections[counter][arr_nb_connections[counter]] = dict_old_to_new[connections[i][j]]
arr_nb_connections[counter] += 1
counter += 1
for i in range(arr_nb_connections.shape[0]):
for j in range(arr_nb_connections[i]):
if j + 1 == arr_nb_connections[i]:
new_arr_weights[i][j] = 1.
else:
new_arr_weights[i][j] = (j + 1) / arr_nb_connections[i]
return new_arr_connections, new_arr_weights
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/graph/jit_compiled_functions.py
| 0.487063 | 0.543045 |
jit_compiled_functions.py
|
pypi
|
from .misc import (create_grid_hexagonal_cells,
create_grid_square_cells,
create_grid_square_with_diagonals,
SubdividedIcosahedron)
from .jit_compiled_functions import (get_oriented_neighborhood_of_vertices,
get_surface_array,
topology_convert_1d_array_to_2d_array,
topology_convert_2d_array_to_1d_array,
icosphere_get_distance_matrix)
import numpy as np
from math import sqrt, pi
import pandas as pd
import os
class BaseTopology:
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.connections = None
self.weights = None
self.type = None
self.dict_cell_id_to_ind = {}
self.time = 0
self.on_ticker = ['increment_time']
def increment_time(self):
self.time += 1
def tick(self):
"""
execute the methods whose names are stored in the attribute on_ticker, in order.
"""
for method in self.on_ticker:
getattr(self, method)()
def save_table_id_of_vertices_to_indices(self, path_to_csv, sep, erase_existing_file=True):
"""
Create and save a two column csv allowing to match vertices id's with vertices indexes.
:param path_to_csv: string, path to the output csv
:param sep: string, separator to use in the csv.
:param erase_existing_file: optional, boolean, default True. If True, the method will check if there is already
a file at path_to_csv and delete it if it exists.
"""
if erase_existing_file:
if os.path.exists(path_to_csv):
os.remove(path_to_csv)
with open(path_to_csv, 'a') as f_out:
f_out.write("id_vertex" + sep + "index_vertex" + "\n")
for id_vertex, index in self.dict_cell_id_to_ind.items():
f_out.write(str(id_vertex) + sep + str(index) + '\n')
return
@property
def number_vertices(self):
return self.connections.shape[0]
class SquareGridWithDiagTopology(BaseTopology):
def __init__(self, shape=None, **kwargs):
if shape is None:
raise ValueError("Kwarg 'shape' is missing while initializing the graph topology. 'shape' should be a "
"tuple like object of the form (a, b), where a and b are integers bigger than 1.")
len_side_a = shape[0]
len_side_b = shape[1]
self.create_square_with_diag_grid(len_side_a, len_side_b)
self.shape = (len_side_a, len_side_b)
self.type = 'SquareGridWithDiag'
def create_square_with_diag_grid(self, len_side_a, len_side_b):
"""
Create a square grid with diagonals, where each vertex X[i][j] is linked to X[i-1][j-1], X[i][j-1], X[i+1][j-1],
X[i+1][j], X[i+1][j+1], x[i][j+1], x[i-1][j+1] and x[i-1][j] if they exist. Note that the weights on the
'diagonal connections' is reduced to take into account the fact that the vertices on the diagonal are 'further
away' (i.e. using sqrt(2) as a distance instead of 1 in the weight computation).
:param len_side_a: integer, x coordinate
:param len_side_b: integer, y coordinate
"""
if (len_side_a < 2) or (len_side_b < 2):
raise ValueError('side length attributes for HexagonalCells should be at least 2.')
self.connections, self.weights = create_grid_square_with_diagonals(len_side_a, len_side_b)
# populate the dictionary from cell coordinates to cell indexes in arrays connection and weights
for i in range(len_side_a):
for j in range(len_side_b):
self.dict_cell_id_to_ind[(i, j)] = j + i*len_side_b
class SquareGridTopology(BaseTopology):
def __init__(self, shape=None, **kwargs):
if shape is None:
raise ValueError("Kwarg 'shape' is missing while initializing the graph topology. 'shape' should be a "
"tuple like object of the form (a, b), where a and b are integers bigger than 1.")
len_side_a = shape[0]
len_side_b = shape[1]
self.create_square_grid(len_side_a, len_side_b)
self.shape = (len_side_a, len_side_b)
self.type = 'SquareGrid'
def create_square_grid(self, len_side_a, len_side_b):
"""
Create a square grid, where each vertex X[i][j] is linked to X[i-1][j], X[i][j-1], X[i+1][j], X[i][j+1] if they
exist.
:param len_side_a: integer, x coordinate
:param len_side_b: integer, y coordinate
"""
if (len_side_a < 2) or (len_side_b < 2):
raise ValueError('side length attributes for HexagonalCells should be at least 2.')
self.connections, self.weights = create_grid_square_cells(len_side_a, len_side_b)
self.shape = (len_side_a, len_side_b)
# populate the dictionary from cell coordinates to cell indexes in arrays connection and weights
for i in range(len_side_a):
for j in range(len_side_b):
self.dict_cell_id_to_ind[(i, j)] = j + i*len_side_b
class SquareGridsConvertBetween1DArrayAnd2DArrays:
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self._array_optimized_squarification = None
self._array_optimized_flat = None
def _sampy_debug_convert_1d_array_to_2d_array(self, input_arr):
if not type(input_arr) is np.ndarray:
raise ValueError("Input variable is not a numpy array.")
if input_arr.shape != (self.number_vertices,):
raise ValueError("Input array of invalid shape.")
def convert_1d_array_to_2d_array(self, input_arr):
"""
Takes a 1D array of shape (nb_vertices,) and convert it into a 2D array of shape self.shape.
:param input_arr: 1D array.
:return: 2D array
"""
if self._array_optimized_squarification is None:
self._array_optimized_squarification = np.full((self.number_vertices, 2), 0)
for key, val in self.dict_cell_id_to_ind.items():
self._array_optimized_squarification[val][0] = key[0]
self._array_optimized_squarification[val][1] = key[1]
return topology_convert_1d_array_to_2d_array(input_arr, self._array_optimized_squarification,
self.shape[0], self.shape[1])
def _sampy_debug_convert_2d_array_to_1d_array(self, input_arr):
if not type(input_arr) is np.ndarray:
raise ValueError("Input variable is not a numpy array.")
if input_arr.shape != self.shape:
raise ValueError("Input array of invalid shape.")
def convert_2d_array_to_1d_array(self, input_array):
"""
:param input_array:
:return:
"""
if self._array_optimized_flat is None:
self._array_optimized_flat = np.full(self.shape, 0)
for key, val in self.dict_cell_id_to_ind.items():
self._array_optimized_flat[key[0], key[1]] = val
return topology_convert_2d_array_to_1d_array(input_array, self._array_optimized_flat)
class IcosphereTopology(BaseTopology):
def __init__(self, nb_sub=None, radius=1., **kwargs):
if nb_sub is None:
raise ValueError("kwarg nb_sub missing")
self.nb_sub = nb_sub
self.radius = float(radius)
icosahedron = SubdividedIcosahedron(nb_sub)
self.connections = np.copy(icosahedron.connections)
self.weights = np.copy(icosahedron.weights)
self.arr_coord = np.copy(icosahedron.arr_coord)
del icosahedron
self.type = 'IcoSphere'
self.three_d_coord_created = False
def create_3d_coord(self):
self.df_attributes['coord_x'] = self.arr_coord[:, 0].astype(np.float64)
self.df_attributes['coord_y'] = self.arr_coord[:, 1].astype(np.float64)
self.df_attributes['coord_z'] = self.arr_coord[:, 2].astype(np.float64)
norm = np.sqrt(self.df_attributes['coord_x']**2 +
self.df_attributes['coord_y']**2 +
self.df_attributes['coord_z']**2)
self.df_attributes['coord_x_normalized'] = self.df_attributes['coord_x'] / norm
self.df_attributes['coord_x'] = self.radius * self.df_attributes['coord_x_normalized']
self.df_attributes['coord_y_normalized'] = self.df_attributes['coord_y'] / norm
self.df_attributes['coord_y'] = self.radius * self.df_attributes['coord_y_normalized']
self.df_attributes['coord_z_normalized'] = self.df_attributes['coord_z'] / norm
self.df_attributes['coord_z'] = self.radius * self.df_attributes['coord_z_normalized']
self.three_d_coord_created = True
def create_pseudo_epsg4326_coordinates(self):
"""
This method approximate the shape of the earth using a sphere, which creates deformations.
"""
if not self.three_d_coord_created:
self.create_3d_coord()
self.df_attributes['lat'] = (180*(pi/2 - np.arccos(self.df_attributes['coord_z_normalized']))/pi).astype(np.float64)
self.df_attributes['lon'] = (180*np.arctan2(self.df_attributes['coord_y_normalized'],
self.df_attributes['coord_x_normalized'])/pi).astype(np.float64)
def compute_distance_matrix_on_sphere(self):
"""
This method compute a distance matrix that gives the distance between each pair of connected vertex of the
graph. The distance is the geodesic distance on a sphere (i.e. the distance
:return: Array of floats with the same shape as the array 'connections'
"""
dist_matrix = np.full(self.connections.shape, -1., dtype=np.float64)
lats_rad = (np.pi * self.df_attributes['lat'] / 180).astype(np.float64)
lons_rad = (np.pi * self.df_attributes['lon'] / 180).astype(np.float64)
dist_matrix = icosphere_get_distance_matrix(dist_matrix, self.connections, lats_rad, lons_rad, self.radius)
return dist_matrix
def create_and_save_radius_cells_as_attribute(self, radius_attribute='radius_each_cell'):
"""
Save radius of each cell. The radius of a cell centered on a vertex v is defined as the maximum distance between
v and its neighbours. The radius is saved within df_attributes.
:param radius_attribute: optional, string, default 'radius_each_cell'. Name of the attribute corresponding to
the radius of each cell.
"""
dist_matrix = self.compute_distance_matrix_on_sphere()
max_distance = np.amax(dist_matrix, axis=1).astype(np.float64)
self.df_attributes[radius_attribute] = max_distance
def compute_surface_array(self):
"""
Return an array giving the surface of each cell of the icosphere
:return: array of floats shape (nb_vertex,)
"""
# note that this orientation is not necessarily clockwise, and can be anti-clockwise for some vertices.
# But this is not important for our purpose of computing the area of each cell of the icosphere.
oriented_neigh_vert = get_oriented_neighborhood_of_vertices(self.connections)
return get_surface_array(oriented_neigh_vert,
self.df_attributes['coord_x_normalized'],
self.df_attributes['coord_y_normalized'],
self.df_attributes['coord_z_normalized'],
self.radius).astype(np.float64)
def create_and_save_surface_array_as_attribute(self):
arr_surface = self.compute_surface_array()
self.df_attributes['surface_cell'] = arr_surface
class OrientedHexagonalGrid(BaseTopology):
"""
Create an hexagonal lattice on a square. Each
"""
def __init__(self, nb_hex_x_axis=None, nb_hex_y_axis=None, **kwargs):
"""
:param nb_hex_x_axis: mandatory kwargs. Integer, number of hexagons on the horizontal axis.
:param nb_hex_y_axis: mandatory kwargs. Integer, number of hexagons on the vertical axis.
"""
pass
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/graph/topology.py
| 0.840357 | 0.441553 |
topology.py
|
pypi
|
import numpy as np
from .jit_compiled_functions import compute_sin_attr_with_condition
from ..pandas_xs.pandas_xs import DataFrameXS
class BaseVertexAttributes:
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
if not hasattr(self, 'df_attributes'):
self.df_attributes = DataFrameXS()
def _sampy_debug_create_vertex_attribute(self, attr_name, value):
if not isinstance(attr_name, str):
raise TypeError("the name of a vertex attribute should be a string.")
arr = np.array(value)
if len(arr.shape) != 0:
if len(arr.shape) > 1:
raise ValueError('Shape of provided array for graph attribute ' + attr_name + ' is ' + str(arr.shape) +
', while Sampy expects an array of shape (' + str(self.weights.shape[0]) +
',).')
if arr.shape[0] != self.weights.shape[0]:
raise ValueError('Provided array for graph attribute ' + attr_name + ' has ' +
str(arr.shape[0]) + 'elements, while the graph has ' + str(self.weights.shape[0]) +
'vertices. Those numbers should be the same.')
def create_vertex_attribute(self, attr_name, value):
"""
Creates a new vertex attribute and populates its values. Accepted input for 'value' are:
- None: in this case, the attribute column is set empty
- A single value, in which case all vertexes will have the same attribute value
- A 1D array, which will become the attribute column.
Note that if you use a 1D array, then you are implicitly working with the indexes of the vertices, that is that
the value at position 'i' in the array corresponds to the attribute value associated with the vertex whose index
is 'i'. If you want to work with vertexes id instead, use the method 'create_vertex_attribute_from_dict'.
:param attr_name: string, name of the attribute
:param value: either None, a single value, or a 1D array.
"""
if self.df_attributes.nb_rows == 0 and len(np.array(value).shape) == 0:
self.df_attributes[attr_name] = [value for _ in range(self.weights.shape[0])]
else:
self.df_attributes[attr_name] = value
def _sampy_debug_create_vertex_attribute_from_dict(self, attr_name, dict_id_to_val, default_val=np.nan):
if (not hasattr(dict_id_to_val, 'items')) or (not hasattr(dict_id_to_val.items, '__call__')):
raise ValueError('the method create_vertex_attribute_from_dict expects a dictionnary-like object, ' +
'which has a method \'items\'.')
if not isinstance(attr_name, str):
raise TypeError("the name of a vertex attribute should be a string.")
for key, _ in dict_id_to_val.items():
if key not in self.dict_cell_id_to_ind:
raise ValueError(str(key) + ' is not the id of any vertex in the graph.')
def create_vertex_attribute_from_dict(self, attr_name, dict_id_to_val, default_val):
"""
Creates a new vertex attribute and populates its values using a dictionary-like object, whose keys are id of
vertices, and values the corresponding attribute values. Note that you can specify a default value for the
vertices not appearing in the dictionary.
IMPORTANT: first, the method creates an array filled with the default value, and then replace the values in the
array using the dictionary. Therefore, the dtype of the attribute will be defined using the default
value. Thus, the user should either chose a default value with appropriate dtype, or change the
type of the attribute after creating the attribute.
:param attr_name: string, name of the attribute.
:param dict_id_to_val: Dictionary like object, whose keys are id of vertices, and values the corresponding
attribute value.
:param default_val: Value used for the vertices for which an attribute value is not provided.
"""
arr_attr = np.full((self.number_vertices,), default_val)
for key, val in dict_id_to_val.items():
arr_attr[self.dict_cell_id_to_ind[key]] = val
self.df_attributes[attr_name] = arr_attr
def change_type_attribute(self, attr_name, str_type):
"""
Change the dtype of the selected attribute. Note that the type should be supported by DataFrameXS
:param attr_name: string, name of the attribute
:param str_type: string, target dtype of the attribute
"""
self.df_attributes.change_type(attr_name, str_type)
class PeriodicAttributes:
"""
Class that adds methods to define periodically varying arguments.
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
if not hasattr(self, 'df_attributes'):
self.df_attributes = DataFrameXS()
def update_periodic_attribute(self, time, attr_name, amplitude, period, phase, intercept, condition=None):
"""
Call this method to update the value of an attribute using the following formula.
amplitude * np.sin(2 * math.pi * time / period + phase) + intercept
Where time is either the value of the attribute 'time' of the graph, or if 'time' parameter is not None
:param time: float or int, used as time parameter in the update formula.
:param attr_name: string, name of the attribute
:param amplitude: float, see formula above
:param phase: float, see formula above
:param period: float, see formula above
:param intercept: float, see formula above
:param condition: optional, default None. Boolean Array saying for which cell to apply the sinusoidal variation.
If None, this method behave like an array of True has been provided.
"""
arr_attr = self.df_attributes[attr_name]
if condition is None:
condition = np.full(arr_attr.shape, True, dtype=np.bool_)
if time is None:
time = self.time
compute_sin_attr_with_condition(arr_attr, condition, time, amplitude,
period, phase, intercept)
class AttributesFrom2DArraysSquareGrids:
"""
Allow the user to add attributes based on 2D arrays. Designed to work with 'SquareGrids' topologies.
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
pass
def create_attribute_from_2d_array(self, attr_name, array_2d):
"""
Create or update an attribute based on a 2D array input.
:param attr_name: string, name of the attribute
:param array_2d: 2d array
"""
if array_2d.shape != self.shape:
raise ValueError('Shapes do not match. Graph of shape ' + str(self.shape) +
' while array of shape ' + str(array_2d.shape) + '.')
arr_attr = np.full((self.number_vertices,), array_2d[0][0])
for i in range(array_2d.shape[0]):
for j in range(array_2d.shape[1]):
arr_attr[self.dict_cell_id_to_ind[(i, j)]] = array_2d[i][j]
self.df_attributes[attr_name] = arr_attr
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/graph/vertex_attributes.py
| 0.741487 | 0.456168 |
vertex_attributes.py
|
pypi
|
from .topology import (SquareGridWithDiagTopology,
SquareGridTopology,
SquareGridsConvertBetween1DArrayAnd2DArrays,
IcosphereTopology)
from .vertex_attributes import PeriodicAttributes, BaseVertexAttributes, AttributesFrom2DArraysSquareGrids
from .from_files import SaveAndLoadSquareGrids
from ..utils.decorators import sampy_class
from .misc import save_as_repository_include_metadata
from .jit_compiled_functions import keep_subgraph_from_array_of_bool_equi_weight
import os
import numpy as np
import glob
import json
@sampy_class
class SquareGridWithDiag(SquareGridWithDiagTopology,
BaseVertexAttributes,
PeriodicAttributes,
AttributesFrom2DArraysSquareGrids,
SaveAndLoadSquareGrids,
SquareGridsConvertBetween1DArrayAnd2DArrays):
"""
Landscape graph. Grid of squares, diagonals included.
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
pass
@sampy_class
class SquareGrid(SquareGridTopology,
BaseVertexAttributes,
PeriodicAttributes,
AttributesFrom2DArraysSquareGrids,
SaveAndLoadSquareGrids,
SquareGridsConvertBetween1DArrayAnd2DArrays):
"""
Landscape graph. Grid of squares, diagonals excluded.
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
pass
@sampy_class
class IcosphereGraph(BaseVertexAttributes,
IcosphereTopology):
"""
Graph of choice for the study of species whose species distribution is big enough so that the shape of the earth
has to be considered.
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
pass
def save(self, path_to_folder, erase_folder=True):
"""
Save the graph structure in a folder using .npy files. The end result is not human-readable.
:param path_to_folder: Path to the folder. If it does not exist, the folder will be created.
:param erase_folder: optional, boolean, default True. If True, any folder already existing at 'path_to_folder'
will be deleted.
"""
metadata_json = {'nb_sub': self.nb_sub,
'type': 'icosphere',
'radius': self.radius}
save_as_repository_include_metadata(path_to_folder, metadata_json, self.df_attributes,
self.connections, self.weights, erase_folder=erase_folder)
@classmethod
def load(cls, path_to_folder, strict_check=True):
"""
Load the graph structure using a folder saved using the save method.
:param path_to_folder: path to a folder where a graph icosphere is saved.
:param strict_check: optional, boolean, default True. If true, check that the loaded graph as type 'icosphere'.
:return: An instanciated IcosphereGraph object
"""
if os.path.exists(path_to_folder):
if not os.path.isdir(path_to_folder):
raise OSError("The object at " + path_to_folder + " is not a directory.")
else:
raise OSError("Nothing at " + path_to_folder + '.')
metadata = json.load(open(path_to_folder + '/metadata_json.json'))
if metadata['type'] != 'icosphere' and strict_check:
raise ValueError("According to the metadata, the graph is not of type icosphere.")
nb_sub = int(metadata['nb_sub'])
radius = float(metadata['radius'])
graph = cls(nb_sub=3, radius=1.)
graph.radius = radius
graph.nb_sub = nb_sub
graph.connections = np.load(path_to_folder + '/connections.npy')
graph.weights = np.load(path_to_folder + '/weights.npy')
for path in glob.glob(path_to_folder + '/*'):
if os.path.basename(path).startswith('attr_'):
name = os.path.basename(path).split('.')[0]
name = name[5:]
graph.df_attributes[name] = np.load(path)
for name in metadata['attributes_none']:
graph.df_attributes[name] = None
return graph
def keep_subgraph(self, array_vertices_to_keep):
"""
Keep the specified vertices and keep the rest. Both attributes, connections and weights are updated accordingly.
:param array_vertices_to_keep: 1d array of bool. array[i] is true if the vertex of index i should be kept.
"""
new_connections, new_weights = keep_subgraph_from_array_of_bool_equi_weight(array_vertices_to_keep,
self.connections)
self.connections = new_connections
self.weights = new_weights
self.df_attributes = self.df_attributes[array_vertices_to_keep]
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/graph/builtin_graph.py
| 0.790207 | 0.266584 |
builtin_graph.py
|
pypi
|
import numpy as np
def create_2d_coords_from_oriented_connection_matrix(connections, index_first_vertex, coord_first_vertex,
list_vectors):
"""
WARNING: The graph is assumed to be connected.
Create the coordinates (2D) of each vertex of the graph. The algorithm starts at the cell given by the
kwarg 'index_first_cell', which receives as coordinates the one given in 'coord_first_cell'. Then we loop
through each neighbours of the starting cell, giving coordinates to each one using the parameter 'list_vector'
(see description of 'list_vector' parameter below for a more detailed explanation). We then repeat the process
with a vertex that has coordinates, and so on until each vertex has coordinates. This algorithm works only if
the graph is connected.
:param connections: 2D array of integers. Connection matrix used in SamPy Graph objects to encode the edges between
vertices. Here it is assumed to be oriented (that is each column correspond to a specific
direction).
:param index_first_vertex: non-negative integer
:param coord_first_vertex: couple of floats
:param list_vectors: list containing connections.shape[1] arrays, each of shape (2,).
:return: a pair (coords_x, coords_y) of 1D arrays of floats giving the coordinates of each vertex.
"""
# we now create the arrays that will contain the x and y coordinates
coord_x = np.full(connections.shape[0], 0., dtype=float)
coord_y = np.full(connections.shape[0], 0., dtype=float)
# we initialize the coordinates and create two data-structure that will allow us to recursively give coordinates
# to each vertex.
coord_x[index_first_vertex] = float(coord_first_vertex[0])
coord_y[index_first_vertex] = float(coord_first_vertex[1])
set_index_vert_with_coords = set([index_first_vertex])
list_index_vert_with_coords = [index_first_vertex]
# now we recursively give coordinates to every vertex
for i in range(connections.shape[0]):
try:
current_vertex = list_index_vert_with_coords[i]
except IndexError:
raise ValueError("Error encountered while creating vertices' coordinates. The most likely explanation"
" is that the graph is not connected.")
for j in range(connections.shape[1]):
if connections[current_vertex, j] not in set_index_vert_with_coords:
coord_x[connections[i, j]] = coord_x[current_vertex] + list_vectors[j][0]
coord_y[connections[i, j]] = coord_y[current_vertex] + list_vectors[j][1]
list_index_vert_with_coords.append(connections[i, j])
set_index_vert_with_coords.add(connections[i, j])
return coord_x, coord_y
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/graph/spatial_functions.py
| 0.744749 | 0.927462 |
spatial_functions.py
|
pypi
|
from ..pandas_xs.pandas_xs import DataFrameXS
from .misc import convert_graph_structure_to_dictionary
import numpy as np
import os
import shutil
import json
import glob
class SaveAndLoadSquareGrids:
"""
Add to the square grids graphs the possibility to save them using their own special format.
We also provide a Json
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
pass
def save(self, path_to_folder, erase_folder=True):
"""
Save the graph structure in a folder using .npy files. The end result is not human readable.
:param path_to_folder: Path to the folder. If it does not exists, the folder will be created.
:param erase_folder: optional, boolean, default True. If True, any folder already existing at 'path_to_folder'
will be deleted.
"""
if os.path.exists(path_to_folder):
if not erase_folder:
raise OSError("Something already exists at " + path_to_folder + '.')
if not os.path.isdir(path_to_folder):
raise OSError("The object at " + path_to_folder + " is not a directory. In doubt, we prefer not to " +
"delete it.")
shutil.rmtree(path_to_folder)
os.mkdir(path_to_folder)
np.save(path_to_folder + '/connections.npy', self.connections)
np.save(path_to_folder + '/weights.npy', self.weights)
attributes_that_are_none = []
for name in self.df_attributes.list_col_name:
if self.df_attributes[name] is not None:
np.save(path_to_folder + '/attr_' + name + '.npy', self.df_attributes[name])
else:
attributes_that_are_none.append(name)
metadata_json = {'shape_0': self.shape[0],
'shape_1': self.shape[1],
'type': self.type,
'attributes_none': attributes_that_are_none}
metadata = open(path_to_folder + '/metadata_json.json', 'w')
metadata.write(json.dumps(metadata_json))
metadata.close()
@classmethod
def load(cls, path_to_folder):
"""
:param path_to_folder:
:return:
"""
if os.path.exists(path_to_folder):
if not os.path.isdir(path_to_folder):
raise OSError("The object at " + path_to_folder + " is not a directory.")
else:
raise OSError("Nothing at " + path_to_folder + '.')
metadata = json.load(open(path_to_folder + '/metadata_json.json'))
shape = (metadata['shape_0'], metadata['shape_1'])
graph_type = metadata['type']
graph = cls(shape=shape)
graph.type = graph_type
graph.shape = shape
graph.connections = np.load(path_to_folder + '/connections.npy')
graph.weights = np.load(path_to_folder + '/weights.npy')
for path in glob.glob(path_to_folder + '/*'):
if os.path.basename(path).startswith('attr_'):
name = os.path.basename(path).split('.')[0]
name = name[5:]
graph.df_attributes[name] = np.load(path)
for name in metadata['attributes_none']:
graph.df_attributes[name] = None
return graph
def save_as_json(self, path_to_json, erase_existing_file=False):
"""
Save a SquareGrid graph as a JSON. This is not the recommended way of saving a
:param path_to_json:
:param erase_existing_file:
"""
if os.path.exists(path_to_json):
if not erase_existing_file:
raise OSError("Something already exists at " + path_to_json + '.')
os.remove(path_to_json)
dict_graph_structure = convert_graph_structure_to_dictionary(self, save_vertices_index=True,
add_to_metadata={'is_SquareGrid': True,
'shape_0': self.shape[0],
'shape_1': self.shape[1]})
graph_json = open(path_to_json, 'w')
graph_json.write(json.dumps(dict_graph_structure))
graph_json.close()
@classmethod
def from_json(cls, path_to_json):
"""
Load a SquareGrid graph from a JSON. Metadata section of the json should contain a flag 'is_SquareGrid" set to
True and vertices index should be provided.
:param path_to_json: string, path to a Json
:return: Square Grid graph object.
"""
graph_as_dict = json.load(open(path_to_json, 'r'))
if 'is_SquareGrid' not in graph_as_dict['metadata'] or not graph_as_dict['metadata']['is_SquareGrid']:
raise TypeError("The file in " + path_to_json + " is not a SquareGrid Json.")
if not graph_as_dict['metadata']['vertices_index_provided']:
raise TypeError("The file in " + path_to_json + " is supposedly a SquareGrid Json, yet vertices index " +
"are not provided.")
shape = (graph_as_dict['metadata']['shape_0'], graph_as_dict['metadata']['shape_1'])
graph = cls(shape=shape)
graph.dict_cell_id_to_ind = {}
for i in range(shape[0]):
for j in range(shape[1]):
graph.dict_cell_id_to_ind[(i, j)] = graph_as_dict['vertices'][str((i, j))]['index']
for name in graph_as_dict['metadata']['empty_attributes']:
graph.df_attributes[name] = None
tmp_dict_attribute = {}
for name in graph_as_dict['metadata']['non_empty_attributes']:
tmp_dict_attribute[name] = [None for _ in range(graph_as_dict['metadata']['nb_vertices'])]
for i in range(shape[0]):
for j in range(shape[1]):
index_vertex = graph.dict_cell_id_to_ind[(i, j)]
for name in tmp_dict_attribute:
tmp_dict_attribute[name][index_vertex] = graph_as_dict['vertices'][str((i, j))][name]
for k in range(graph_as_dict['metadata']['max_degree_vertex']):
if ('n' + str(k)) in graph_as_dict['vertices'][str((i, j))]:
graph.connections[index_vertex][k] = graph_as_dict['vertices'][graph_as_dict['vertices'][str((i, j))][('n' + str(k))]]['index']
graph.weights[index_vertex][k] = graph_as_dict['vertices'][str((i, j))][('w' + str(k))]
else:
graph.connections[index_vertex][k] = -1
graph.weights[index_vertex][k] = -1.
for name in tmp_dict_attribute:
graph.df_attributes[name] = tmp_dict_attribute[name]
return graph
class FromJson:
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
pass
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/graph/from_files.py
| 0.582016 | 0.280302 |
from_files.py
|
pypi
|
import numpy as np
from .jit_compiled_functions import *
from ..pandas_xs.pandas_xs import DataFrameXS
from ..utils.errors_shortcut import (check_col_exists_good_type,
check_input_array)
class TerritorialMovementWithoutResistance:
"""
Add graph based movements abilities to the agents. Agents have both a territory and a position, which can be
different. Generally, the position of an agent will be either its territory vertex, or a vertex neighbouring its
territory.
Note that both position and territory are stored as integers, i.e. using the vertices indices which generally
differ from their id. If needed, conversion should be performed by the user using the graph attribute
'dict_cell_id_to_ind'. Equivalently, the user may extract a table giving the correspondence between id and indexes
using the graph method 'save_table_id_of_vertices_to_indices'.
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
if not hasattr(self, 'df_population'):
self.df_population = DataFrameXS()
self.df_population['territory'] = None
self.df_population['position'] = None
def _sampy_debug_change_territory(self,
condition=None,
territory_attribute='territory',
position_attribute='position'):
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if condition is not None:
if (not isinstance(condition, np.ndarray)) or \
(condition.shape != (self.df_population.nb_rows,)) or \
(not str(condition.dtype).startswith('bool')):
raise ValueError("if used, condition argument should be a 1D array of bool of same length as the number"
" of individuals.")
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, territory_attribute, prefix_dtype='int')
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, position_attribute, prefix_dtype='int')
def change_territory(self,
condition=None,
territory_attribute='territory',
position_attribute='position'):
"""
Change the territory and the position of the agents. If an agent is on an isolated vertex (a vertex without
any neighbour), then the agent stays on the vertex.
:param condition: optional, array of bool, default None. If not None, array telling which
:param territory_attribute: optional, string, default 'territory'
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'
"""
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if condition is not None:
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (condition.sum(),))
movement_change_territory_and_position_condition(self.df_population[territory_attribute],
self.df_population[position_attribute],
condition, rand,
self.graph.connections, self.graph.weights)
else:
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (self.df_population.shape[0],))
movement_change_territory_and_position(self.df_population[territory_attribute],
self.df_population[position_attribute],
rand, self.graph.connections, self.graph.weights)
def _sampy_debug_mov_around_territory(self,
proba_remain_on_territory,
condition=None,
territory_attribute='territory',
position_attribute='position'):
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if condition is not None:
check_input_array(condition, 'condition', 'bool', shape=(self.df_population.nb_rows,))
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, territory_attribute, 'territory_attribute', prefix_dtype='int',
reject_none=True)
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, position_attribute, 'position_attribute', prefix_dtype='int',
reject_none=True)
def mov_around_territory(self,
proba_remain_on_territory,
condition=None,
territory_attribute='territory',
position_attribute='position'):
"""
Update the average position of the agent around its territory during the current time step.
:param proba_remain_on_territory: float, probability to stay on the territory
:param condition: optional, array of bool, default None. Array of boolean such that the i-th value is
True if and only if the i-th agent (i.e. the agent at the line i of df_population) can
move.
:param territory_attribute: optional, string, default 'territory'
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'
"""
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if condition is not None:
pre_bool_mov = np.random.uniform(0, 1, condition.sum()) > proba_remain_on_territory
bool_mov = movement_mov_around_territory_fill_bool_mov_using_condition(pre_bool_mov, condition)
else:
bool_mov = np.random.uniform(0, 1, self.df_population.shape[0]) > proba_remain_on_territory
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, bool_mov.sum())
movement_mov_around_territory(self.df_population[territory_attribute], self.df_population[position_attribute],
bool_mov, rand, self.graph.connections, self.graph.weights)
def _sampy_debug_dispersion_with_varying_nb_of_steps(self, arr_nb_steps, arr_prob,
condition=None,
territory_attribute='territory',
position_attribute='position'
):
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
check_input_array(arr_nb_steps, 'arr_nb_steps', 'int', nb_dim=1)
check_input_array(arr_prob, 'arr_prob', 'float', nb_dim=1)
if arr_prob.shape != arr_nb_steps.shape:
raise ValueError("Arguments 'arr_nb_steps' and 'arr_prob' have different shapes.")
if condition is not None:
check_input_array(condition, 'condition', 'bool', shape=(self.df_population.nb_rows,))
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, territory_attribute, 'territory_attribute', prefix_dtype='int',
reject_none=True)
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, position_attribute, 'position_attribute', prefix_dtype='int',
reject_none=True)
def dispersion_with_varying_nb_of_steps(self, arr_nb_steps, arr_prob,
condition=None,
territory_attribute='territory',
position_attribute='position'
):
"""
Used to modelize dispersion of agents. Each selected agent will perform a random number of discrete steps on
the graph. The number of steps is determined using the user inputs 'arr_nb_steps' and 'arr_prob'. Both
position and territory are updated.
:param arr_nb_steps: 1D array of int, giving the permissible number of steps.
:param arr_prob: 1D array of float, arr_prob[i] is the probability that a given agent will perform
arr_nb_steps[i] steps.
:param condition: optional, array of bool, default None. Array of boolean such that the i-th value is
True if and only if the i-th agent (i.e. the agent at the line i of df_population) can
move. If left at None, all the agents move.
:param territory_attribute: optional, string, default 'territory'.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'.
"""
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
prob = arr_prob.astype('float64')
prob = prob / prob.sum()
if condition is not None:
# get number of steps
arr_nb_steps = np.random.choice(arr_nb_steps, condition.sum(), p=prob)
else:
arr_nb_steps = np.random.choice(arr_nb_steps, self.df_population.nb_rows, p=prob)
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, arr_nb_steps.sum())
if condition is None:
movement_dispersion_with_varying_nb_of_steps(self.df_population[territory_attribute],
self.df_population[position_attribute],
rand, arr_nb_steps, self.graph.connections, self.graph.weights)
else:
movement_dispersion_with_varying_nb_of_steps_condition(self.df_population[territory_attribute],
self.df_population[position_attribute],
condition,
rand, arr_nb_steps, self.graph.connections,
self.graph.weights)
class TerritorialMovementWithResistance:
"""
Add graph based movements abilities to the agents. Agents have both a territory and a position, which can be
different. Generally, the position of an agent will be either its territory vertex, or a vertex neighbouring its
territory. Here each connection in the graph is assumed to come with probability saying how likely a movement on
that connection is to fail.
Note that both position and territory are stored as integers, i.e. using the vertices indices which generally
differ from their id. If needed, conversion should be performed by the user using the graph attribute
'dict_cell_id_to_ind'. Equivalently, the user may extract a table giving the correspondence between id and indexes
using the graph method 'save_table_id_of_vertices_to_indices'.
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
if not hasattr(self, 'df_population'):
self.df_population = DataFrameXS()
self.df_population['territory'] = None
self.df_population['position'] = None
def _sampy_debug_change_territory_with_resistance(self,
resistance_array,
condition=None,
territory_attribute='territory',
position_attribute='position'):
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if (not isinstance(resistance_array, np.ndarray) or \
resistance_array.shape != self.graph.connections.shape or \
(not str(resistance_array.dtype).startswith('float'))):
raise ValueError("The resistance array should be a 2 dimensional array of floats of shape " +
str(resistance_array.shape))
if condition is not None:
if (not isinstance(condition, np.ndarray)) or \
(condition.shape != (self.df_population.nb_rows,)) or \
(not str(condition.dtype).startswith('bool')):
raise ValueError("if used, condition argument should be a 1D array of bool of same length as the number"
" of individuals.")
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, territory_attribute, prefix_dtype='int')
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, position_attribute, prefix_dtype='int')
def change_territory_with_resistance(self,
resistance_array,
condition=None,
territory_attribute='territory',
position_attribute='position'):
"""
Change the territory and the position of the agents. If an agent is on an isolated vertex (a vertex without
any neighbour), then the agent stays on the vertex.
:param resistance_array: 2d array of float, array of same shape as the connections of the graph, gives the
'resistance to movement' of each connection
:param condition: optional, array of bool, default None. If not None, array telling which
:param territory_attribute: optional, string, default 'territory'
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'
"""
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if condition is not None:
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (condition.sum(),))
movement_change_territory_and_position_condition(self.df_population[territory_attribute],
self.df_population[position_attribute],
condition, rand,
self.graph.connections, self.graph.weights)
else:
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (self.df_population.shape[0],))
movement_change_territory_and_position(self.df_population[territory_attribute],
self.df_population[position_attribute],
rand, self.graph.connections, self.graph.weights)
def _sampy_debug_mov_around_territory(self,
proba_remain_on_territory,
condition=None,
territory_attribute='territory',
position_attribute='position'):
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if condition is not None:
check_input_array(condition, 'condition', 'bool', shape=(self.df_population.nb_rows,))
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, territory_attribute, 'territory_attribute', prefix_dtype='int',
reject_none=True)
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, position_attribute, 'position_attribute', prefix_dtype='int',
reject_none=True)
def mov_around_territory(self,
proba_remain_on_territory,
condition=None,
territory_attribute='territory',
position_attribute='position'):
"""
Update the average position of the agent around its territory during the current time step.
:param proba_remain_on_territory: float, probability to stay on the territory
:param condition: optional, array of bool, default None. Array of boolean such that the i-th value is
True if and only if the i-th agent (i.e. the agent at the line i of df_population) can
move.
:param territory_attribute: optional, string, default 'territory'
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'
"""
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if condition is not None:
pre_bool_mov = np.random.uniform(0, 1, condition.sum()) > proba_remain_on_territory
bool_mov = movement_mov_around_territory_fill_bool_mov_using_condition(pre_bool_mov, condition)
else:
bool_mov = np.random.uniform(0, 1, self.df_population.shape[0]) > proba_remain_on_territory
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, bool_mov.sum())
movement_mov_around_territory(self.df_population[territory_attribute], self.df_population[position_attribute],
bool_mov, rand, self.graph.connections, self.graph.weights)
def _sampy_debug_dispersion_with_varying_nb_of_steps(self, arr_nb_steps, arr_prob,
condition=None,
territory_attribute='territory',
position_attribute='position'
):
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
check_input_array(arr_nb_steps, 'arr_nb_steps', 'int', nb_dim=1)
check_input_array(arr_prob, 'arr_prob', 'float', nb_dim=1)
if arr_prob.shape != arr_nb_steps.shape:
raise ValueError("Arguments 'arr_nb_steps' and 'arr_prob' have different shapes.")
if condition is not None:
check_input_array(condition, 'condition', 'bool', shape=(self.df_population.nb_rows,))
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, territory_attribute, 'territory_attribute', prefix_dtype='int',
reject_none=True)
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, position_attribute, 'position_attribute', prefix_dtype='int',
reject_none=True)
def dispersion_with_varying_nb_of_steps(self, arr_nb_steps, arr_prob,
condition=None,
territory_attribute='territory',
position_attribute='position'
):
"""
Used to modelize dispersion of agents. Each selected agent will perform a random number of discrete steps on
the graph. The number of steps is determined using the user inputs 'arr_nb_steps' and 'arr_prob'. Both
position and territory are updated.
:param arr_nb_steps: 1D array of int, giving the permissible number of steps.
:param arr_prob: 1D array of float, arr_prob[i] is the probability that a given agent will perform
arr_nb_steps[i] steps.
:param condition: optional, array of bool, default None. Array of boolean such that the i-th value is
True if and only if the i-th agent (i.e. the agent at the line i of df_population) can
move. If left at None, all the agents move.
:param territory_attribute: optional, string, default 'territory'.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'.
"""
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
prob = arr_prob.astype('float64')
prob = prob / prob.sum()
if condition is not None:
# get number of steps
arr_nb_steps = np.random.choice(arr_nb_steps, condition.sum(), p=prob)
else:
arr_nb_steps = np.random.choice(arr_nb_steps, self.df_population.nb_rows, p=prob)
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, arr_nb_steps.sum())
if condition is None:
movement_dispersion_with_varying_nb_of_steps(self.df_population[territory_attribute],
self.df_population[position_attribute],
rand, arr_nb_steps, self.graph.connections, self.graph.weights)
else:
movement_dispersion_with_varying_nb_of_steps_condition(self.df_population[territory_attribute],
self.df_population[position_attribute],
condition,
rand, arr_nb_steps, self.graph.connections,
self.graph.weights)
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/agent/movement.py
| 0.772359 | 0.540378 |
movement.py
|
pypi
|
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from .jit_compiled_functions import (count_nb_agent_per_vertex,
conditional_count_nb_agent_per_vertex)
from ..pandas_xs.pandas_xs import DataFrameXS
class BaseAgingAgent:
"""
Base class for aging agents, i.e. agents having an age attribute that is used in the simulation (for instance for
varying probabilities of dispersion or varying mortality rates).
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
try:
self.graph = kwargs['graph']
except KeyError:
raise ValueError("A graph object should be passed to the constructor, using the kwarg 'graph'.")
if not hasattr(self, 'df_population'):
self.df_population = DataFrameXS()
self.df_population['col_id'] = None
self.df_population['age'] = None
if hasattr(self, 'dict_default_val'):
self.dict_default_val['age'] = 0
else:
self.dict_default_val = {'age': 0}
self.counter_id = 0
self.on_ticker = ['increase_age']
self.type = 'agent'
def _sampy_debug_add_attribute(self, name_attr, def_value=np.nan):
if not isinstance(name_attr, str):
raise ValueError("An attribute name should be a string.")
if name_attr in self.df_population.dict_colname_to_index:
raise KeyError("An attribute with the name " + name_attr + " already exists.")
x = np.array([def_value])
if x.shape != (1,):
raise ValueError("A default value should be a single number, integer or np.nan.")
if str(x.dtype) not in self.df_population.ALLOWED_TYPE:
raise ValueError("The chosen default value results in arrays of dtype '" + str(x.dtype) + "', which is not"
" supported by DataFrameXS object. Supported types are:" +
str(self.df_population.LIST_ALLOWED_TYPE) + ".")
def add_attribute(self, name_attr, def_value=np.nan):
"""
add a new column to the dataframe df_population, whose name is the parameter 'name_attr'
:param name_attr: name of the new column
:param def_value: default value for the created column, set the whole column to this value if df_population is
non empty, and save the default value for later calls.
"""
self.df_population[name_attr] = def_value
self.dict_default_val[name_attr] = def_value
def _sampy_debug_set_default_val(self, dict_values, replace=False):
if not hasattr(dict_values, 'items') or not hasattr(getattr(dict_values, 'items'), '__call__'):
raise TypeError("Dict_value parameter should be a dictionary like object, with a method 'items' "
"allowing to loop over keys and values of the object.")
for key, val in dict_values.items():
if not isinstance(key, str):
raise KeyError("Column names should be a string.")
if key not in self.df_population.dict_colname_to_index:
raise KeyError("Trying to set the default value of a non existing column (" + key + ")")
x = np.array([val])
if x.shape != (1,):
raise ValueError("A default value should be a single number, integer or np.nan.")
if str(x.dtype) not in self.df_population.ALLOWED_TYPE:
raise ValueError(
"The chosen default value results in arrays of dtype '" + str(x.dtype) + "', which is not" +
" supported by DataFrameXS object. Supported types are:" +
str(self.df_population.LIST_ALLOWED_TYPE) + ".")
def set_default_val(self, dict_values, replace=False):
"""
Change the defaults values in the attribute dict_default_val. If replace is True, then the attr dict_default_val
is replaced by the content of the argument dict_values. Otherwise, the content of dict_values is added to
dict_values, modifying it if needed.
:param dict_values: dictionary like object, with an items method
:param replace: optional, boolean, default False
"""
if replace:
self.dict_default_val = {}
for name, val in dict_values.items():
self.dict_default_val[name] = val
def _sampy_debug_add_agents(self, dict_values):
if not hasattr(dict_values, 'items') or not hasattr(getattr(dict_values, 'items'), '__call__'):
raise TypeError("Dict_value parameter should be a dictionary like object, with a method 'items' "
"allowing to loop over keys and values of the object.")
nb_rows_added = 0
found_non_cst_col = False
name_first_non_cst_column = None
for key, val in dict_values.items():
if not isinstance(key, str):
raise KeyError("Column names should be a string.")
if key not in self.df_population.dict_colname_to_index:
raise KeyError("The agents have an that is not a column of the population DataFrame (" + key + ").")
x = np.array(val)
if len(x.shape) > 1:
raise ValueError("The value for column " + key + " results in an array of dimension " +
str(x.shape) + " while add_agents expects one dimensional arrays or constants.")
if len(x.shape) == 1:
if found_non_cst_col:
if x.shape[0] != nb_rows_added:
raise ValueError("The value for column " + key + " results in creating " + str(x.shape[0]) +
" lines, while column " + name_first_non_cst_column + " value results in " +
"creating " + str(nb_rows_added) + '.')
else:
nb_rows_added = x.shape[0]
found_non_cst_col = True
name_first_non_cst_column = key
def add_agents(self, dict_values):
"""
add new rows to the dataframe df_population, which corresponds to new individuals. The recommanded use for this
method is to provide a dict_value of the form:
dict_value = {name_col1: list_of_values1, name_col2: list_of_values2, ...}
list of values can be replaced by np.array. Note that some of those lists can be replaced by constants if you
want some columns to be filled with a single value. If the user provides constant for all list_of_values, then a
single line is added. Finally, any non mentioned column will be filled with the associated default value.
Note that the user does not have the hand on the col_id column since it is considered internal, and the user
should add an extra column to identify some individuals.
:param dict_values: values of the attributes of the new individuals.
"""
constant_cols = {}
array_cols = {}
for name, col in dict_values.items():
if col is None:
array_cols[name] = col
else:
arr_col = np.array(col)
if len(arr_col.shape) == 0:
constant_cols[name] = col
else:
array_cols[name] = arr_col
# create a DataFrameXS from the input values
df = DataFrameXS()
# populate the dataframe df. First considering the case where some lists have been provided.
if array_cols:
for name, col in array_cols.items():
df[name] = col
# then add the constant columns
for name, const in constant_cols.items():
df[name] = const
# now the case where only single values have been provided
else:
for name, const in dict_values.items():
if const is None or (len(np.array(const).shape) > 0 and np.array(const).shape[0] == 0) :
df[name] = None
else:
df[name] = [const]
# add the default values if needed.
for name, value in self.dict_default_val.items():
if name not in df.dict_colname_to_index:
df[name] = value
# create the col_id column
df['col_id'] = [self.counter_id + i for i in range(df.nb_rows)]
self.counter_id = df['col_id'][-1] + 1
# concatenate df to df_population
self.df_population.concat(df, inplace=True)
def increase_age(self):
"""
increment by one the age of all the agents
"""
self.df_population['age'] += 1
def tick(self):
"""
execute in order all the methods whose name are in the list 'on_ticker'. Those methods should not accept
any arguments.
"""
for method in self.on_ticker:
getattr(self, method)()
def save_population_to_csv(self, path, sep=';', **kwargs):
"""
Save the dataframe df_population as csv
:param path: full path of the csv file
:param sep: optional. Separator used in csv. Default is ';'
"""
self.df_population.to_csv(path, sep=sep, **kwargs)
def load_population_from_csv(self, path, sep=';', **kwargs):
"""
load a csv film to create the dataframe. Override the existing dataframe df_population, if any.
:param path: full path of the csv file
:param sep: optional. Separator used in csv. Default is ';'
"""
self.df_population = DataFrameXS.read_csv(path, sep=sep, **kwargs)
def _sampy_debug_count_pop_per_vertex(self, position_attribute='position', condition=None):
if condition is not None:
if (not isinstance(condition, np.ndarray)) or \
(condition.shape != (self.df_population.nb_rows,)) or \
(not str(condition.dtype).startswith('bool')):
raise ValueError("if used, condition argument should be a 1D array of bool of same length as the number"
" of individuals.")
def count_pop_per_vertex(self, position_attribute='position', condition=None):
"""
Count the number of agent in each cell, and return the result as a 1D numpy array.
:param position_attribute: Optional, string, default 'position'. Name of the attribute corresponding to cell
index on which agent is.
:param condition: Optional, 1D array of bool, default None. If not None, count only the agent for which the
condition is True.
:return: 1D array X such that X[i] is the number of agent in the cell whose index is i.
"""
if condition is None:
return count_nb_agent_per_vertex(self.df_population[position_attribute],
self.graph.weights.shape[0])
else:
if (not isinstance(condition, np.ndarray)) or \
(len(condition.shape) != 1) or \
(condition.shape[0] != self.df_population.nb_rows) or \
(not str(condition.dtype).startswith('bool')):
raise ValueError("if used, condition argument should be a 1D array of bool of same length as the number"
" of individuals.")
return conditional_count_nb_agent_per_vertex(condition,
self.df_population[position_attribute],
self.graph.weights.shape[0])
@property
def number_agents(self):
return self.df_population.nb_rows
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/agent/base.py
| 0.607547 | 0.419707 |
base.py
|
pypi
|
import numpy as np
from .jit_compiled_functions import (reproduction_find_random_mate_on_position,
reproduction_find_random_mate_on_position_condition,
reproduction_find_random_mate_on_position_polygamous,
reproduction_find_random_mate_on_position_polygamous_condition)
from ..pandas_xs.pandas_xs import DataFrameXS
from .. utils.errors_shortcut import (check_input_is_permutation,
check_input_array,
check_col_exists_good_type,
check_if_gender_array)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# female encoded with 1, male with 0.
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
class FindMateMonogamous:
"""
This class provides methods for a monogamous agent to find mates
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
if not hasattr(self, 'df_population'):
self.df_population = DataFrameXS()
self.df_population['mom_id'] = None
self.df_population['dad_id'] = None
self.df_population['gender'] = None
self.df_population['is_pregnant'] = None
self.df_population['current_mate'] = None
if not hasattr(self, 'dict_default_val'):
self.dict_default_val = {}
self.dict_default_val['mom_id'] = -1
self.dict_default_val['dad_id'] = -1
self.dict_default_val['gender'] = 1
self.dict_default_val['is_pregnant'] = False
self.dict_default_val['current_mate'] = -1
def _sampy_debug_find_random_mate_on_position(self,
prob_get_pregnant,
shuffle=True,
permutation=None,
condition=None,
id_attribute='col_id',
position_attribute='position',
gender_attribute='gender',
mate_attribute='current_mate',
pregnancy_attribute='is_pregnant'):
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if permutation is not None:
check_input_is_permutation(permutation, 'permutation', self.df_population.nb_rows)
if condition is not None:
check_input_array(condition, 'condition', 'bool', shape=(self.df_population.nb_rows,))
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, position_attribute, 'position_attribute',
prefix_dtype='int', reject_none=True)
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, mate_attribute, 'mate_attribute',
prefix_dtype='int', reject_none=True)
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, pregnancy_attribute, 'pregnancy_attribute',
prefix_dtype='bool', reject_none=True)
check_if_gender_array(self.df_population[gender_attribute])
def find_random_mate_on_position(self,
prob_get_pregnant,
shuffle=True,
permutation=None,
condition=None,
id_attribute='col_id',
position_attribute='position',
gender_attribute='gender',
mate_attribute='current_mate',
pregnancy_attribute='is_pregnant'):
"""
Find a mate on the current position of the agent. This mate is randomly picked. By default, the attribute used
as the position if 'position', but the user may want to use 'territory' instead. For that purpose, the key-word
argument 'position_attribute' can be used.
:param prob_get_pregnant: float between 0 and 1. Probability that after mating the female will get pregnant.
:param shuffle: optional, boolean, default True. By default, in this method the random choice of a mate is done
by shuffling the DataFrameXS 'df_population'. If set to False, the df is not shuffled, so that
the first male in a cell is paired with the first female in the cell (as they appear in df),
the second male with the second female, and so on until there is no male anymore (or no female).
:param permutation: optional, default None, 1D array of integer. If not None and shuffle is True, this
permutation is used to shuffle df_population.
:param condition: optional, array of bool, default None. Tells which agents should be included.
:param id_attribute: optional, string, default 'col_id'. Id attribute of the agent. It is not recommended to
change this column, as this column is considered internal, and in the future this fact
could be used in other methods.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'. Position attribute of the agents. Should be
integers corresponding to indexes of the vertices of the graph on which the agents
live.
:param gender_attribute: optional, string, default 'gender'.
:param mate_attribute: optional, string, default 'current_mate'.
:param pregnancy_attribute: optional, string, default 'is_pregnant'.
"""
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if shuffle:
self.df_population.scramble(permutation=permutation)
if condition is None:
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, ((self.df_population[gender_attribute] == 1).sum(),))
reproduction_find_random_mate_on_position(self.df_population[mate_attribute],
self.df_population[pregnancy_attribute],
self.df_population[id_attribute],
self.df_population[position_attribute],
self.df_population[gender_attribute],
self.graph.connections.shape[0],
rand,
prob_get_pregnant)
else:
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (((self.df_population[gender_attribute] == 1) & condition).sum(),))
reproduction_find_random_mate_on_position_condition(self.df_population[mate_attribute],
self.df_population[pregnancy_attribute],
self.df_population[id_attribute],
self.df_population[position_attribute],
self.df_population[gender_attribute],
self.graph.connections.shape[0],
rand,
prob_get_pregnant,
condition)
def get_females(self):
"""
:return: 1D array of bool telling which agents are females.
"""
return self.df_population['gender'] == 1
def get_males(self):
"""
:return: 1D array of bool telling which agents are males.
"""
return self.df_population['gender'] == 0
class FindMatePolygamous:
"""
This class provides methods for a polygamous agent to find mates
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
if not hasattr(self, 'df_population'):
self.df_population = DataFrameXS()
self.df_population['mom_id'] = None
self.df_population['dad_id'] = None
self.df_population['gender'] = None
self.df_population['is_pregnant'] = None
self.df_population['current_mate'] = None
if not hasattr(self, 'dict_default_val'):
self.dict_default_val = {}
self.dict_default_val['mom_id'] = -1
self.dict_default_val['dad_id'] = -1
self.dict_default_val['gender'] = 1
self.dict_default_val['is_pregnant'] = False
self.dict_default_val['current_mate'] = -1
def _sampy_debug_find_random_mate_on_position(self,
prob_get_pregnant,
condition=None,
id_attribute='col_id',
position_attribute='position',
gender_attribute='gender',
mate_attribute='current_mate',
pregnancy_attribute='is_pregnant'):
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if condition is not None:
check_input_array(condition, 'condition', 'bool', shape=(self.df_population.nb_rows,))
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, position_attribute, prefix_dtype='int', reject_none=True)
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, mate_attribute, prefix_dtype='int', reject_none=True)
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, pregnancy_attribute, prefix_dtype='bool', reject_none=True)
check_if_gender_array(self.df_population[gender_attribute])
def find_random_mate_on_position(self,
prob_get_pregnant,
condition=None,
id_attribute='col_id',
position_attribute='position',
gender_attribute='gender',
mate_attribute='current_mate',
pregnancy_attribute='is_pregnant'):
"""
Find a mate on the current position of the agent. This mate is randomly picked. By default, the attribute used
as the position if 'position', but the user may want to use 'territory' instead. For that purpose, the key-word
argument 'position_attribute' can be used.
:param prob_get_pregnant: float between 0 and 1. Probability that after mating the female will get pregnant.
:param condition: optional, array of bool, default None. Tells which agents should be included.
:param id_attribute: optional, string, default 'col_id'. Id attribute of the agent. It is not recommended to
change this column, as this column is considered internal, and in the future this fact
could be used in other methods.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'. Position attribute of the agents. Should be
integers corresponding to indexes of the vertices of the graph on which the agents
live.
:param gender_attribute: optional, string, default 'gender'.
:param mate_attribute: optional, string, default 'current_mate'.
:param pregnancy_attribute: optional, string, default 'is_pregnant'.
"""
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if condition is None:
nb_females = (self.df_population[gender_attribute] == 1).sum()
rand_preg = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (nb_females,))
rand_mate = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (nb_females,))
reproduction_find_random_mate_on_position_polygamous(self.df_population[id_attribute],
self.df_population[position_attribute],
self.df_population[gender_attribute],
self.df_population[mate_attribute],
self.df_population[pregnancy_attribute],
self.graph.connections.shape[0],
rand_preg, rand_mate, prob_get_pregnant)
else:
nb_females = ((self.df_population[gender_attribute] == 1) & condition).sum()
rand_preg = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (nb_females,))
rand_mate = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (nb_females,))
reproduction_find_random_mate_on_position_polygamous_condition(self.df_population[id_attribute],
self.df_population[position_attribute],
self.df_population[gender_attribute],
self.df_population[mate_attribute],
self.df_population[pregnancy_attribute],
self.graph.connections.shape[0],
rand_preg, rand_mate, prob_get_pregnant,
condition)
def get_females(self):
"""
:return: 1D array of bool telling which agents are females.
"""
return self.df_population['gender'] == 1
def get_males(self):
"""
:return: 1D array of bool telling which agents are males.
"""
return self.df_population['gender'] == 0
class OffspringCreationWithCustomProb:
"""
This class sole purpose is to add the method create_offsprings_custom_prob. See its documentation below.
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
pass
def _sampy_debug_create_offsprings_custom_prob(self,
arr_nb_children,
arr_prob_nb_children,
condition=None,
dico_default_values=None,
prob_failure=None,
age_attribute='age',
mother_attribute='mom_id',
father_attribute='dad_id',
gender_attribute='gender',
id_attribute='col_id',
position_attribute='position',
territory_attribute='territory',
mate_attribute='current_mate',
pregnancy_attribute='is_pregnant'):
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
check_input_array(arr_nb_children, 'arr_nb_children', 'int', nb_dim=1)
check_input_array(arr_prob_nb_children, 'arr_prob_nb_children', 'float', nb_dim=1)
if arr_nb_children.shape != arr_prob_nb_children.shape:
raise ValueError("Arguments 'arr_nb_children' and 'arr_prob_nb_children' have different shapes.")
if condition is not None:
check_input_array(condition, 'condition', 'bool', shape=(self.df_population.nb_rows,))
if dico_default_values is not None:
if not hasattr(dico_default_values, 'items') or hasattr(getattr(dico_default_values, 'items'), '__call__'):
raise TypeError("The argument 'dico_default_value' should be a dictionnary-like object. Namely, have a "
"method called 'items' allowing to loop through keys and values.")
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, age_attribute, 'age_attribute', prefix_dtype='int',
reject_none=True)
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, mother_attribute, 'mother_attribute', prefix_dtype='int',
reject_none=True)
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, father_attribute, 'father_attribute', prefix_dtype='int',
reject_none=True)
check_if_gender_array(self.df_population[gender_attribute])
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, position_attribute, 'position_attribute', prefix_dtype='int',
reject_none=True)
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, territory_attribute, 'territory_attribute', prefix_dtype='int',
reject_none=True)
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, mate_attribute, 'mate_attribute', prefix_dtype='int',
reject_none=True)
check_col_exists_good_type(self.df_population, pregnancy_attribute, 'pregnancy_attribute', prefix_dtype='bool',
reject_none=True)
def create_offsprings_custom_prob(self,
arr_nb_children,
arr_prob_nb_children,
condition=None,
dico_default_values=None,
prob_failure=None,
age_attribute='age',
mother_attribute='mom_id',
father_attribute='dad_id',
gender_attribute='gender',
id_attribute='col_id',
position_attribute='position',
territory_attribute='territory',
mate_attribute='current_mate',
pregnancy_attribute='is_pregnant'):
"""
Creates offsprings using two 1D arrays of same size, 'arr_nb_children' and 'arr_prob_nb_children', being
respectively an array of integers and an array of non-negative floats, where for any index i,
arr_prob_nb_children[i] is the probability for pregnant females to give birth to arr_nb_children[i]
offsprings.
Note that arr_prob_nb_children is normalized so that it sums to 1.
:param arr_nb_children: 1D array of int, see above description.
:param arr_prob_nb_children: 1d array of floats, see above description.
:param condition: optional, 1d array of bool, default None. Tells which female and pregnant agents are allowed
to give birth.
:param dico_default_values: optional, dictionnary, default None. Contains default values for the offsprings
attributes. Any attribute not provided will use default values built-in the
population object.
:param prob_failure: optional, float, default None. Probability for an agent trying to give birth to fail such
action. As a result, the agent would no longer be pregnant and would not produce any
offspring.
:param age_attribute: optional, string, default 'age'. Agent attribute used as age
:param mother_attribute: optional, string, default 'mom_id'. Agent attribute used as mother id
:param father_attribute: optional, string, default 'dad_id'. Agent attribute used as father id
:param id_attribute: optional, string, default 'col_id'. Agent attribute used as agent id.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'.
:param territory_attribute: optional, string, default 'territory'. If no territory in the model, the user should
set it to None.
:param mate_attribute: optional, string, default 'current_mate'. Agent attribute used as id of the mate.
:param pregnancy_attribute: optional, string, default 'is_pregnant'.
"""
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if dico_default_values is None:
dico_default_values = dict()
selected_females = self.df_population[pregnancy_attribute]
if condition is not None:
selected_females = selected_females & condition
if prob_failure is not None:
selected_females = selected_females & \
(np.random.uniform(0, 1, (self.df_population.nb_rows,)) >= prob_failure)
df_selected_female = self.df_population[selected_females]
if df_selected_female.nb_rows == 0:
return
# get number of babies per females
prob = arr_prob_nb_children.astype('float64')
prob = prob/prob.sum()
arr_nb_baby = np.random.choice(arr_nb_children, df_selected_female.nb_rows, p=prob)
arr_non_zero_babies = arr_nb_baby > 0
df_selected_female = df_selected_female[arr_non_zero_babies]
if df_selected_female.nb_rows == 0:
return
arr_nb_baby = arr_nb_baby[arr_non_zero_babies]
# start building the children DataFrame
df_children = DataFrameXS()
df_children[mother_attribute] = np.repeat(df_selected_female[id_attribute], arr_nb_baby, axis=0)
df_children[father_attribute] = np.repeat(df_selected_female[mate_attribute], arr_nb_baby, axis=0)
df_children[position_attribute] = np.repeat(df_selected_female[position_attribute], arr_nb_baby, axis=0)
if territory_attribute is not None:
df_children[territory_attribute] = np.repeat(df_selected_female[territory_attribute], arr_nb_baby, axis=0)
# defines the gender of the offsprings
gender = 1 * (np.random.uniform(0, 1, (df_children.shape[0],)) >= 0.5)
df_children[gender_attribute] = gender
# fill non trivial attributes
df_children[pregnancy_attribute] = False
df_children[age_attribute] = 0
df_children[id_attribute] = np.arange(self.counter_id, self.counter_id + df_children.shape[0])
self.counter_id = self.counter_id + df_children.shape[0]
# take care of the provided default values
for attr, def_value in dico_default_values.items():
df_children[attr] = def_value
# take care of the rest
set_treated_col = set([mother_attribute, father_attribute, position_attribute, territory_attribute,
gender_attribute, pregnancy_attribute, age_attribute, id_attribute])
for col_name in self.df_population.list_col_name:
if col_name in set_treated_col or col_name in dico_default_values:
continue
if col_name in self.dict_default_val:
df_children[col_name] = self.dict_default_val[col_name]
else:
df_children[col_name] = None
# set pregnancy of female that gave birth to False
self.df_population[pregnancy_attribute] = self.df_population[pregnancy_attribute] & ~selected_females
# concatenate the two dataframe
self.df_population.concat(df_children)
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/agent/reproduction.py
| 0.5769 | 0.343287 |
reproduction.py
|
pypi
|
import numpy as np
class ParamManager:
def __init__(self, names, values):
for name, value in zip(names, values):
setattr(self, name, value)
class CsvManager:
"""
Realistically, most of Sampy's run will be done during sensitivity analysis to assert that the model is a faithful
representation of the ecological system of interest. The current class is Sampy's solution for dealing with vast CSV
of parameters used to run large scale sensitivity analysis.
The expected CSV structure is as follows.
- Each row should correspond to the parameters used in a single run of the model.
- Each column corresponds either to a constant parameter, or to a single value within an array.
- the current class distinguishes parameters that should be stored in array based on their name in the header.
That is, if a column name is of the form arr_[some name]_[some_number], then the content of this column will
be considered as the [some_number]-th element of an array. The array's name will be [some_name].
Let show the use of CsvManager class on a small example. Assume we have a csv of parameter at the adress path_csv,
and that the two first line of the csv are:
const1;const2;arr_test_array_0;arr_test_array_1;arr_another_array_0
0;wonderful_string_of_chars;2.;3.;True
One can instantiates a CsvManager class the following way:
>>> csv_manager = CsvManager(path_csv, ';', dict_types={'const1': int, 'test_array': float, 'another_array': bool})
Then, by calling the method 'get_parameters', one gets a ParamManager object whose attributes are the parameters
stored in a line of the csv.
>>> param = csv_manager.get_parameters()
>>> print(param.test_array)
array([2., 3.])
If one calls get_parameters another time, it will return another ParamManager object corresponding to the next line
in the csv. Once the end of the csv is reached, get_parameters returns None.
The kwargs 'nb_cores' and 'id_process' are designed for large analysis using multiple cores. If used, the obtained
csv_manager will only return lines 'i' in the csv such that 'i % nb_cores == id_process'.
Finally, when working on very large csv one can use the kwarg buffer_size (default 1000) which says how many
lines of the csv are stored in memory (CsvManager does not try to open the file entirely in memory, and process it
by blocks of buffer_size lines).
"""
def __init__(self, path_to_csv, sep, dict_types=None, buffer_size=1000, nb_cores=1, id_process=0):
self.path_to_csv = path_to_csv
self.sep = sep
if dict_types is None:
self.dict_types = {}
else:
self.dict_types = dict_types
self.buffer_size = buffer_size
self.nb_line_consumed = 0
self.buffer = []
self.counter_buffer = 0
self.nb_usable_lines_in_csv = 0
self.dict_arr = {}
self.dict_const = {}
self.nb_cores = nb_cores
self.id_process = id_process
with open(self.path_to_csv, 'r') as f_in:
for i, line in enumerate(f_in):
if i == 0:
self.header = line.replace('\n', '')
self.extract_info_header()
continue
if i % self.nb_cores == self.id_process:
self.nb_usable_lines_in_csv += 1
def extract_info_header(self):
list_header = self.header.split(self.sep)
dict_col_to_index = {col_name: ind for ind, col_name in enumerate(list_header)}
r_dict_const = {}
temp_dict_arr = {}
for col_name in list_header:
if col_name.split('_')[0] == 'arr':
name_param = '_'.join(col_name.split('_')[1:-1])
try:
temp_dict_arr[name_param].append(col_name)
except KeyError:
temp_dict_arr[name_param] = [col_name]
else:
r_dict_const[col_name] = dict_col_to_index[col_name]
r_dict_arr = {}
for name_arr, arr in temp_dict_arr.items():
sorted_arr = sorted(arr, key=lambda y: int(y.split('_')[-1]))
r_dict_arr[name_arr] = [dict_col_to_index[name_col] for name_col in sorted_arr]
self.dict_arr = r_dict_arr
self.dict_const = r_dict_const
def get_parameters(self):
try:
line = self.buffer[self.counter_buffer]
self.counter_buffer += 1
self.nb_line_consumed += 1
except IndexError:
if self.nb_line_consumed == self.nb_usable_lines_in_csv:
return
self.fill_buffer()
line = self.buffer[0]
self.counter_buffer = 1
self.nb_line_consumed += 1
return self.create_param_manager_from_line(line)
def fill_buffer(self):
self.buffer = []
size_current_buffer = 0
with open(self.path_to_csv) as f:
seen_lines = 0
for i, line in enumerate(f):
if i == 0:
continue
if i % self.nb_cores == self.id_process:
seen_lines += 1
if seen_lines <= self.nb_line_consumed:
continue
self.buffer.append(line.replace('\n', ''))
size_current_buffer += 1
if size_current_buffer == self.buffer_size:
break
return
def create_param_manager_from_line(self, line):
data = line.split(self.sep)
names = []
values = []
for name in self.dict_const:
names.append(name)
if name in self.dict_types:
if self.dict_types[name] == bool:
values.append(data[self.dict_const[name]].lower() == 'true')
else:
values.append(self.dict_types[name](data[self.dict_const[name]]))
else:
values.append(data[self.dict_const[name]])
for name in self.dict_arr:
names.append(name)
if name in self.dict_types:
if self.dict_types[name] == bool:
values.append(np.array([data[u].lower() == 'true' for u in self.dict_arr[name]]))
else:
values.append(np.array([self.dict_types[name](data[u]) for u in self.dict_arr[name]]))
else:
values.append(np.array([data[u] for u in self.dict_arr[name]]))
return ParamManager(names, values)
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/data_processing/csv_manager.py
| 0.657098 | 0.599133 |
csv_manager.py
|
pypi
|
import numpy as np
import numba as nb
@nb.njit
def conditional_proximity_is_step_allowed_return_infos(arr_selected_agents, distances, indices, arr_radius_point,
condition_on_grid):
rv = np.full(arr_selected_agents.shape, False, dtype=np.bool_)
r_d = np.full(arr_selected_agents.shape, -1., dtype=float)
r_ind = np.full(arr_selected_agents.shape, -1, dtype=np.int32)
for i in range(arr_selected_agents.shape[0]):
if arr_selected_agents[i]:
if condition_on_grid[indices[i]] and (distances[i] <= arr_radius_point[indices[i]]):
rv[i] = True
r_d[i] = distances[i]
r_ind[i] = indices[i]
return rv, r_d, r_ind
@nb.njit
def conditional_proximity_is_pos_allowed(indices, distances, arr_radius_points, allowed_points):
rv = np.full(indices.shape, False, dtype=np.bool_)
for i in range(indices.dhape[0]):
if allowed_points[indices[i]] and (distances[i] <= arr_radius_points[indices[i]]):
rv = True
return rv
@nb.njit
def proximity_is_pos_allowed(indices, distances, arr_radius_points):
rv = np.full(indices.shape, False, dtype=np.bool_)
for i in range(indices.dhape[0]):
if distances[i] <= arr_radius_points[indices[i]]:
rv = True
return rv
@nb.njit
def proximity_is_step_allowed_return_infos(arr_selected_agents, distances, indices, arr_radius_point):
rv = np.full(arr_selected_agents.shape, False, dtype=np.bool_)
r_d = np.full(arr_selected_agents.shape, -1., dtype=float)
r_ind = np.full(arr_selected_agents.shape, -1, dtype=np.int32)
for i in range(arr_selected_agents.shape[0]):
if arr_selected_agents[i]:
if distances[i] <= arr_radius_point[indices[i]]:
rv[i] = True
r_d[i] = distances[i]
r_ind[i] = indices[i]
return rv, r_d, r_ind
@nb.njit
def proximity_get_closest_point_expand_dist_and_ind_arrays(selected_agents, distances, indexes):
r_d = np.full(selected_agents.shape, -1., dtype=float)
r_ind = np.full(selected_agents.shape, -1, dtype=np.int32)
counter = 0
for i in range(selected_agents.shape[0]):
if selected_agents[i]:
r_d[i] = distances[counter]
r_ind[i] = indexes[counter]
counter += 1
return r_d, r_ind
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/spatial/jit_compiled_functions.py
| 0.410756 | 0.516717 |
jit_compiled_functions.py
|
pypi
|
import numpy as np
def check_input_array(array, name_argument, prefix_dtype, nb_dim=None, shape=None):
if not isinstance(array, np.ndarray):
raise TypeError("The parameter " + name_argument + " should be an array.")
if not str(array.dtype).startswith(prefix_dtype):
raise TypeError("The parameter " + name_argument + " should be an array of type " + prefix_dtype + ".")
if nb_dim is not None:
if len(array.shape) != nb_dim:
raise ValueError("The parameter " + name_argument + " should be an array of dim " + str(nb_dim) +
", while the input is of dim " + str(len(array.shape)) + ".")
if shape is not None:
if array.shape != shape:
raise ValueError("The parameter " + name_argument + " should be an array of shape " + str(shape) +
", while the input is of shape " + str(array.shape) + ".")
def check_input_is_permutation(array, name_argument, length):
if (not isinstance(array, np.ndarray)) or (not str(array.dtype).startswith('int')):
raise TypeError("The parameter " + name_argument + " should be an array of integers.")
if array.shape != (length,):
raise ValueError("The parameter " + name_argument + " should be an array of shape (nb_agents,).")
if not (np.sort(array) == np.arange(0, length).all()):
raise ValueError("The parameter " + name_argument + " should either be None, or a permutation of all "
"the integers from 0 to " + str(length - 1) + ".")
def check_col_exists_good_type(df, name_col, name_argument, prefix_dtype='', reject_none=False):
if not isinstance(name_col, str):
raise TypeError("A column name should be a string, which is not the case for provided " + name_argument + ".")
if name_col not in df.dict_colname_to_index:
raise KeyError("Provided " + name_argument + " does not match any column name in df_population.")
if reject_none:
if df[name_col] is None:
raise ValueError("The column " + name_col + " is empty while it should contain the age of the agents.")
if not str(df[name_col].dtype).startswith(prefix_dtype):
raise TypeError("The column " + name_col + " is not of the proper type. Expected " + prefix_dtype +
", got " + str(df[name_col].dtype) + ".")
def check_if_gender_array(array):
arr_1 = array == 1
arr_0 = array == 0
if not (arr_1 | arr_0).all():
raise TypeError("The provided column for gender should only contains 0s and 1s, since it is the way gender "
"is encoded in sampy.")
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/utils/errors_shortcut.py
| 0.515376 | 0.450722 |
errors_shortcut.py
|
pypi
|
from ...agent.base import BaseAgingAgent
from ...agent.mortality import NaturalMortalityOrmMethodology, OffspringDependantOnParents
from ...agent.reproduction import (OffspringCreationWithCustomProb,
FindMateMonogamous,
FindMatePolygamous)
from ...agent.movement import TerritorialMovementWithoutResistance
from ...utils.decorators import sampy_class
from .jit_compiled_function import *
from ...agent.jit_compiled_functions import movement_mov_around_territory_fill_bool_mov_using_condition
import numpy as np
class ComponentsFromORM:
"""
This class contains basic methods extracted from ORM source code. Developed for the need of the Leighton Lab.
Add orm-like methods to the agents. That are:
- movement that take into account 'resistance' to the movement (i.e. each agent movement has a probability of
success that depends on the user's landscape;
- when an agent fails to move (for any reason), its displacement ends for the current timestep;
- add a form of discrete correlated random walk, using the hexagonal structure of ORM landscapes (see
dispersion);
- add a series of ways to modelize natural mortality, as found in ORM code;
- some methods make the assumption that each timestep represent a week, with 52 weeks in a year.
IMPORTANT: for some methods, the underlying graph is assumed to come from an ORM xml using the class
GraphFromORMxml
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.df_population['has_moved'] = False
self.dict_default_val['has_moved'] = False
def orm_dispersion(self, timestep, permissible_weeks, condition, arr_nb_steps, arr_prob_nb_steps,
position_attribute='position', territory_attribute='territory', reflexion=False):
"""
This method ignores resistance to movement.
In the ORM, agents' dispersion is dealt with on a yearly basis. That is, each year (52 timesteps each
representing a week) an agent will disperse once and only once. This method takes care of checking if an agent
already dispersed or not. When an agent disperse, it draws a number of steps and performs a discrete
correlated random walk on the hexagonal landscape. At first, the agent choses a random direction among the six
possible neighbours of its current cell (North, north-east, south-est, etc. See GraphORMXml description for
details). If there is no cell in that direction, dispersion stops (but it is still counted as if the agent
dispersed this year). If there is one, the agent jumps to this new cell, then a new direction is picked: with a
60% chance the direction remains unchanged, with 20% it turns left by one notch (if for instance the first
direction was North-east, then there is a 20% chance that the next direction will be North), with 20% it turns
right. We then repeat the process until the agent has made all its steps.
IMPORTANT: This method assumes agents are living on a GraphFromORMxml.
Warning: If reflexion is used, there might be a bias since we recycle an already used random value.
:param timestep: current timestep, number of week since simulation started (starts at 0).
:param permissible_weeks: array-like object of integer saying which week of the year the agents can disperse
(counted from 0 to 51).
:param condition: 1D array of bool of shape (nb_agents,) saying which agents are allowed to disperse.
:param arr_nb_steps: 1D array of non-negative integers, works in tandem with arr_prob_nb_steps.
:param arr_prob_nb_steps: 1D array of float, each between 0 and 1. arr_prob_nb_steps[i] is the probability for
a dispersing agent to do arr_nb_steps[i] steps. Note that this number of step can be
0. Effectively, this would lead to the agent "having dispersed this year" yet without
having moved.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'. Name of the position attribute in the agents.
:param territory_attribute: optional, string, default 'territory'. Name of the territory attribute in the
agents.
:param reflexion: optionnal, boolean, default False.
"""
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
# we reinitialize the 'has_moved' status if first week of the year
if timestep % 52 == 0:
self.df_population['has_moved'] = False
if timestep % 52 not in permissible_weeks:
return
can_move = condition & ~self.df_population['has_moved']
will_move = np.random.uniform(0, 1, can_move.sum()) < \
(permissible_weeks.index(timestep % 52) + 1) / len(permissible_weeks)
prob = arr_prob_nb_steps.astype('float64')
prob = prob / prob.sum()
rand_nb_steps = np.random.choice(arr_nb_steps, will_move.sum(), p=prob)
rand_directions = np.random.uniform(0, 1, rand_nb_steps.sum())
if reflexion:
orm_like_agent_dispersion_with_reflexion(can_move, will_move, rand_nb_steps, rand_directions,
self.df_population[position_attribute],
self.df_population[territory_attribute],
self.df_population['has_moved'],
self.graph.connections, self.graph.weights)
else:
orm_like_agent_orm_dispersion(can_move, will_move, rand_nb_steps, rand_directions,
self.df_population[position_attribute],
self.df_population[territory_attribute],
self.df_population['has_moved'],
self.graph.connections)
def orm_dispersion_with_resistance(self, timestep, permissible_weeks, condition, arr_nb_steps, arr_prob_nb_steps,
position_attribute='position', territory_attribute='territory'):
"""
This method included resistance to movement.
In the ORM, agents' dispersion is dealt with on a yearly basis. That is, each year (52 timesteps each
representing a week) an agent will disperse once and only once. This method takes care of checking if an agent
already dispersed or not. When an agent disperse, it draws a number of steps and performs a discrete
correlated random walk on the hexagonal landscape. At first, the agent choses a random direction among the six
possible neighbours of its current cell (North, north-east, south-est, etc. See GraphORMXml description for
details). If there is no cell in that direction, dispersion stops (but it is still counted as if the agent
dispersed this year). If there is one, the agent jumps to this new cell, then a new direction is picked: with a
60% chance the direction remains unchanged, with 20% it turns left by one notch (if for instance the first
direction was North-east, then there is a 20% chance that the next direction will be North), with 20% it turns
right. We then repeat the process until the agent has made all its steps.
IMPORTANT: This method assumes agents are living on a GraphFromORMxml.
Warning: If reflexion is used, there might be a bias since we recycle an already used random value.
:param timestep: current timestep, number of week since simulation started (starts at 0).
:param permissible_weeks: array-like object of integer saying which week of the year the agents can disperse
(counted from 0 to 51).
:param condition: 1D array of bool of shape (nb_agents,) saying which agents are allowed to disperse.
:param arr_nb_steps: 1D array of non-negative integers, works in tandem with arr_prob_nb_steps.
:param arr_prob_nb_steps: 1D array of float, each between 0 and 1. arr_prob_nb_steps[i] is the probability for
a dispersing agent to do arr_nb_steps[i] steps. Note that this number of step can be
0. Effectively, this would lead to the agent "having dispersed this year" yet without
having moved.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'. Name of the position attribute in the agents.
:param territory_attribute: optional, string, default 'territory'. Name of the territory attribute in the
agents.
"""
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
# we reinitialize the 'has_moved' status if first week of the year
if timestep % 52 == 0:
self.df_population['has_moved'] = False
if timestep % 52 not in permissible_weeks:
return
can_move = condition & ~self.df_population['has_moved']
will_move = np.random.uniform(0, 1, can_move.sum()) < \
(permissible_weeks.index(timestep % 52) + 1) / len(permissible_weeks)
prob = arr_prob_nb_steps.astype('float64')
prob = prob / prob.sum()
rand_nb_steps = np.random.choice(arr_nb_steps, will_move.sum(), p=prob)
rand_directions = np.random.uniform(0, 1, rand_nb_steps.sum())
rand_res = np.random.uniform(0, 1, rand_nb_steps.sum())
orm_like_agent_orm_dispersion_with_resistance(can_move, will_move, rand_nb_steps, rand_directions,
self.df_population[position_attribute],
self.df_population[territory_attribute],
self.df_population['has_moved'], self.graph.connections,
self.graph.prob_successful_move,
rand_res)
def mov_around_with_resistance(self,
proba_remain_on_territory,
condition=None,
territory_attribute='territory',
position_attribute='position'):
"""
This method includes movement resistance. Update the average position of the agent around its territory during
the current time step.
:param proba_remain_on_territory: float, probability to stay on the territory
:param condition: optional, array of bool, default None. Array of boolean such that the i-th value is
True if and only if the i-th agent (i.e. the agent at the line i of df_population) can
move.
:param territory_attribute: optional, string, default 'territory'
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'
"""
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if condition is not None:
pre_bool_mov = np.random.uniform(0, 1, condition.sum()) > proba_remain_on_territory
bool_mov = movement_mov_around_territory_fill_bool_mov_using_condition(pre_bool_mov, condition)
else:
bool_mov = np.random.uniform(0, 1, self.df_population.shape[0]) > proba_remain_on_territory
rand_direction = np.random.uniform(0, 1, bool_mov.sum())
rand_res = np.random.uniform(0, 1, bool_mov.sum())
orm_like_agents_mov_around_with_resistance(self.df_population[territory_attribute],
self.df_population[position_attribute],
self.graph.connections, self.graph.weights,
self.graph.prob_successful_move, bool_mov, rand_direction,
rand_res)
def _mortality_from_v08(self, arr_annual_mortality, condition_count, alpha_beta=None, condition=None,
shuffle=True, age_attribute='age', position_attribute='position'):
"""
(made by Francois Viard)
This is an adaptation of the mortality method found in ARM v08 (file cFox.cs). ARM is not a typo, it is the
'Arctic Rabies Model', which is a variation of ORM. I don't think it's been published or used in publication?
WARNING: There are no sources given in the ORM file for the origin of this method. As such, I cannot guarantee
that I correctly understood what it is supposed to do and why. Therefore, this method is considered
private and should be use with caution.
:param arr_annual_mortality: array of float between 0 and 1. arr_annual_mortality[i] is the target probability
for an agent to die at age i.
:param condition_count: 1D array of bool, tells which agent to count.
:param alpha_beta: Absolute mystery. In the formula used in ARM there is an Alpha and a Beta, but I could not
figure out if those were actually modified or if the default values were always taken. I
finally decided to postpone the inclusion of those option to a later date... However,
every project finally moved away from this method and fell back to the usual ORM mortality.
As it is, DO NOT USE THIS KWARGS.
:param condition: optional, 1D array of bool, default None. If not None, tells which agents can die.
:param shuffle: optional, bool, default True. If True, shuffle the population dataframe before applying method
:param age_attribute: optional, string, default 'age'. Name of the age attribute of the agents.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'. Name of the position attribute of the agents.
"""
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if shuffle:
permutation = self.df_population.scramble(return_permutation=True)
if condition is not None:
condition = condition[permutation]
condition_count = condition_count[permutation]
count_arr = self.count_pop_per_vertex(position_attribute=position_attribute, condition=condition_count)
if alpha_beta is None:
if condition is None:
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, self.df_population.nb_rows)
survive = orm_like_agents_mortality_from_v08_no_condition_no_alpha_beta(count_arr, condition_count,
self.df_population[position_attribute],
self.graph.df_attributes['K'],
arr_annual_mortality,
self.df_population[age_attribute],
rand)
else:
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, self.df_population.nb_rows)
survive = orm_like_agents_mortality_from_v08_with_condition_no_alpha_beta(count_arr, condition_count,
self.df_population[
position_attribute],
self.graph.df_attributes['K'],
arr_annual_mortality,
self.df_population[
age_attribute],
rand, condition)
self.df_population = self.df_population[survive]
def _mortality_from_v08_with_gender(self, arr_female_annual_mortality, arr_male_annual_mortality, condition_count,
alpha_beta=None, condition=None, shuffle=True, age_attribute='age',
position_attribute='position', gender_attribute='gender'):
"""
(made by Francois Viard)
This is an adaptation of the mortality method found in ARM v08 (file cFox.cs). ARM is not a typo, it is the
'Arctic Rabies Model', which is a variation of ORM. I don't think it's been published or used in publication?
WARNING: There are no sources given in the ORM file for the origin of this method. As such, I cannot guarantee
that I correctly understood what it is supposed to do and why. Therefore, this method is considered
private and should be use with caution.
:param arr_female_annual_mortality: array of float between 0 and 1. arr_annual_mortality[i] is the target
probability for a female agent to die at age i.
:param arr_male_annual_mortality: array of float between 0 and 1. arr_annual_mortality[i] is the target
probability for a male agent to die at age i.
:param condition_count: 1D array of bool, tells which agent to count.
:param alpha_beta: Absolute mystery. In the formula used in ARM there is an Alpha and a Beta, but I could not
figure out if those were actually modified or if the default values were always taken. I
finally decided to postpone the inclusion of those option to a later date... However,
every project finally moved away from this method and fell back to the usual ORM mortality.
As it is, DO NOT USE THIS KWARGS.
:param condition: optional, 1D array of bool, default None. If not None, tells which agents can die.
:param shuffle: optional, bool, default True. If True, shuffle the population dataframe before applying method
:param age_attribute: optional, string, default 'age'. Name of the age attribute of the agents.
:param position_attribute: optional, string, default 'position'. Name of the position attribute of the agents.
:param gender_attribute: optional, string, default 'gender'. Name of the gender attribute of the agents.
"""
if self.df_population.nb_rows == 0:
return
if shuffle:
permutation = self.df_population.scramble(return_permutation=True)
if condition is not None:
condition = condition[permutation]
condition_count = condition_count[permutation]
count_arr = self.count_pop_per_vertex(position_attribute=position_attribute, condition=condition_count)
if alpha_beta is None:
if condition is None:
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, self.df_population.nb_rows)
survive = orm_like_agents_mortality_from_v08_with_gender_no_condition_no_alpha_beta(count_arr,
condition_count,
self.df_population[position_attribute],
self.graph.df_attributes['K'],
self.df_population[gender_attribute],
arr_female_annual_mortality,
arr_male_annual_mortality,
self.df_population[age_attribute],
rand)
else:
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (condition.sum(),))
survive = orm_like_agents_mortality_from_v08_with_gender_with_condition_no_alpha_beta(count_arr,
condition_count,
self.df_population[position_attribute],
self.graph.df_attributes['K'],
self.df_population[gender_attribute],
arr_female_annual_mortality,
arr_male_annual_mortality,
self.df_population[age_attribute],
rand,
condition)
self.df_population = self.df_population[survive]
class ExperimentalDensityDependentMortality:
"""
Some experiments that will be moved elsewhere soon.
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self._corrected_beta_female = None
self._corrected_beta_male = None
def compute_and_save_beta_female(self, alpha, arr_female_weekly_mortality):
self._corrected_beta_female = 1. + (1. / alpha) * np.log((1. / arr_female_weekly_mortality) - 1.)
def compute_and_save_beta_male(self, alpha, arr_male_weekly_mortality):
self._corrected_beta_male = 1. + (1. / alpha) * np.log((1. / arr_male_weekly_mortality) - 1.)
def experimental_mortality_logistic_function(self, alpha, arr_female_weekly_mortality, arr_male_weekly_mortality,
age_attribute='age', position_attribute='position', k_attribute='K',
shuffle=True, gender_attribute='gender'):
if self._corrected_beta_female is None:
self.compute_and_save_beta_female(alpha, arr_female_weekly_mortality)
if self._corrected_beta_male is None:
self.compute_and_save_beta_male(alpha, arr_male_weekly_mortality)
if shuffle:
self.df_population.scramble()
count_arr = self.count_pop_per_vertex(position_attribute=position_attribute)
rand = np.random.uniform(0, 1, (self.df_population.nb_rows,))
survive = experimental_density_mortality(count_arr, self.df_population[position_attribute],
self.df_population[age_attribute],
self.graph.df_attributes[k_attribute],
self.df_population[gender_attribute],
self._corrected_beta_male, self._corrected_beta_female,
alpha, rand)
self.df_population = self.df_population[survive]
@sampy_class
class ORMLikeAgent(BaseAgingAgent,
NaturalMortalityOrmMethodology,
OffspringDependantOnParents,
FindMateMonogamous,
OffspringCreationWithCustomProb,
TerritorialMovementWithoutResistance,
ComponentsFromORM):
"""
Basic ORM like agents.
Includes main components from SamPy plus the building block 'ComponentsFromORM'.
:param graph: Mandatory kwargs, a graph object. Some methods expect this to be a "GraphFromORMXml' object.
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
pass
@sampy_class
class ORMMongooses(BaseAgingAgent,
NaturalMortalityOrmMethodology,
OffspringDependantOnParents,
FindMatePolygamous,
OffspringCreationWithCustomProb,
TerritorialMovementWithoutResistance,
ComponentsFromORM):
"""
Mongooses from ORM with some updates for Caroline Sauve projects.
Includes main components from SamPy plus the building block 'ComponentsFromORM'.
:param graph: Mandatory kwargs, a graph object. Some methods expect this to be a GraphFromORMXml object.
:param pregnancy_duration: mandatory kwargs, an integer. Duration in weeks of pregnancy.
"""
def __init__(self, pregnancy_duration=None, **kwargs):
if pregnancy_duration is None:
raise ValueError("A value for pregnancy duration should be given using kwarg 'pregnancy_duration'")
self.pregnancy_duration = pregnancy_duration
self.df_population['nb_weeks_being_pregnant'] = 0
self.dict_default_val['nb_weeks_being_pregnant'] = 0
self.df_population['week_next_potential_mating'] = -1
self.dict_default_val['week_next_potential_mating'] = -1
def increment_number_of_weeks_of_pregnancy(self):
"""
Mongoose object keeps track of pregnancy duration with individual counters. This method increments those
counters. Should be called weekly.
"""
self.df_population['nb_weeks_being_pregnant'] += self.df_population['is_pregnant']
def check_if_mother_free_of_dependent_young(self, age_independence, min_age_reproduction, mother_attribute='mom_id',
id_attribute='col_id', age_attribute='age'):
"""
Checks which females old enough to reproduce do not have offsprings.
:param age_independence: integer, age at which offspring can live on their own.
:param min_age_reproduction: integer, age at which females can reproduce.
:param mother_attribute: optional, string, default 'mom_id'. Name of the attribute giving the id of the mother
of each agent.
:param id_attribute: optional, string, default 'col_id'. Name of the attribute containing the id of the agents.
:param age_attribute: optional, string, default 'age'. Name of the attribute containing the age of the agents.
:return: 1D array of bool, where return[i] is True if and only if the i-th agent is a Female available for
reproduction.
"""
offsprings = self.df_population[age_attribute] < age_independence
mom_id_offsprings = self.df_population[mother_attribute][offsprings]
potential_mothers = (self.df_population[age_attribute] >= min_age_reproduction) & self.get_females()
orm_mongooses_check_if_mother_free_of_juveniles(mom_id_offsprings, self.df_population[id_attribute],
potential_mothers)
return potential_mothers
def give_birth_if_needed(self, arr_nb_children, arr_prob_nb_children, condition=None, prob_failure=None):
"""
Make each female that reached the end of their pregnancy period give birth.
:param arr_nb_children: 1D array of integer, works in tandem with arr_prob_nb_children below.
:param arr_prob_nb_children: 1D array of float between 0 and 1. arr_prob_nb_children[i] is the probability for
a female giving birth to have arr_nb_children[i] offsprings.
:param condition: optional, 1D array of bool, default None. If not None, tells which female agents can give
birth.
:param prob_failure: optional, float between 0 and 1, default one. If not None, gives the probability for the
agent to fail giving birth. Note that this is equivalent with putting 0 as a possible value
in arr_nb_children, and we recommend user to chose one solution or the other.
"""
about_to_give_birth = (self.df_population['nb_weeks_being_pregnant'] >= self.pregnancy_duration)
if condition is None:
condition = about_to_give_birth
else:
condition = condition & about_to_give_birth
self.df_population['nb_weeks_being_pregnant'] *= ~condition
self.create_offsprings_custom_prob(arr_nb_children, arr_prob_nb_children, condition=condition,
prob_failure=prob_failure)
def children_follow_their_mom(self, min_age, max_age, age_attribute='age', mom_id_attribute='mom_id',
id_attribute='col_id', position_attribute='position',
territory_attribute='territory'):
youngs = (self.df_population[age_attribute] >= min_age) & (self.df_population[age_attribute] <= max_age)
id_moms = self.df_population[mom_id_attribute][youngs]
orm_mongooses_update_ter_pos_youngs(id_moms, youngs, self.df_population[territory_attribute],
self.df_population[position_attribute], self.df_population[id_attribute],
self.df_population[mom_id_attribute])
def weekly_mating_checks_and_update(self, current_week, mean_mate_weeks, var_mate_weeks, age_independence,
min_age_reproduction, gender_attribute='gender', mother_attribute='mom_id',
id_attribute='col_id', age_attribute='age', position_attribute='position',
pregnancy_attribute='is_pregnant', mate_attribute='current_mate'):
"""
Method written in order to reproduce the multiple reproduction spikes that can be seen in Mongooses.
:param current_week: integer, value between 0 and 51 representing the current week of the year.
:param mean_mate_weeks:
:param var_mate_weeks:
:param age_independence:
:param min_age_reproduction:
:param gender_attribute:
:param mother_attribute:
:param id_attribute:
:param age_attribute:
:param position_attribute:
:param pregnancy_attribute:
:param mate_attribute:
"""
# we begin with making the females ready to mate attempt to, well, mate
potentially_mating_females = self.df_population['week_next_potential_mating'] == current_week
if potentially_mating_females.sum() > 0:
female_available = self.check_if_mother_free_of_dependent_young(age_independence, min_age_reproduction,
gender_attribute=gender_attribute,
mother_attribute=mother_attribute,
id_attribute=id_attribute,
age_attribute=age_attribute)
female_available = female_available & ~self.df_population[pregnancy_attribute]
mating_females = potentially_mating_females & female_available
mating_males = self.get_males() & (self.df_population[age_attribute] >= min_age_reproduction)
self.find_random_mate_on_position(1., condition=(mating_females | mating_males), id_attribute=id_attribute,
position_attribute=position_attribute, gender_attribute=gender_attribute,
mate_attribute=mate_attribute, pregnancy_attribute=pregnancy_attribute)
# we now (re)-initialize the "week_next_potential_mating" attribute
init_next_week = potentially_mating_females | ((self.df_population['week_next_potential_mating'] == -1) &
(self.df_population[age_attribute] >= min_age_reproduction))
nb_init_to_perform = init_next_week.sum()
if nb_init_to_perform > 0:
rand_gauss = np.random.normal(0, 1, (nb_init_to_perform,))
orm_mongooses_update_mating_week(current_week, mean_mate_weeks, var_mate_weeks,
self.df_population['week_next_potential_mating'],
init_next_week, rand_gauss)
|
/sampy_abm-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/sampy/addons/ORM_related_addons/ORM_like_agents.py
| 0.844313 | 0.558026 |
ORM_like_agents.py
|
pypi
|
import collections
from sampyl.core import auto_grad_logp, np
from sampyl.state import func_var_names, State
class BasePosterior(object):
""" Base posterior model for subclassing. """
def __init__(self):
self._logp_cache = {}
self._grad_cache = {}
def logp(self, state):
""" Return log P(X) given a :ref:`state <state>` X"""
pass
def grad(self, state):
pass
def __call__(self, state):
""" Return log P(X) and grad log P(X) given a :ref:`state <state>` X"""
return self.logp(state), self.grad(state)
def clear_cache(self):
""" Clear caches. """
del self._logp_cache
del self._grad_cache
self._logp_cache = {}
self._grad_cache = {}
class SinglePosterior(BasePosterior):
""" A posterior model for a logp function that returns both the cost function
and the gradient. Caches values to improve performance.
:param logp_func: Function that returns log P(X) and its gradient.
"""
def __init__(self, logp_func):
super(SinglePosterior, self).__init__()
self.logp_func = logp_func
def logp(self, state):
""" Return log P(X) given a :ref:`state <state>` X"""
frozen_state = state.freeze()
if not isinstance(frozen_state, collections.Hashable):
# uncacheable. a list, for instance.
# better to not cache than blow up.
logp_value, _ = self.logp_func(*state.values())
return logp_value
if frozen_state in self._logp_cache:
logp_value = self._logp_cache[frozen_state]
else:
logp_value, grad_value = self.logp_func(*state.values())
self._logp_cache[frozen_state] = logp_value
self._grad_cache[frozen_state] = grad_value
return logp_value
def grad(self, state):
""" Return grad log P(X) given a :ref:`state <state>` X """
# Freeze the state as a tuple so we can use it as a dictionary key
frozen_state = state.freeze()
if not isinstance(frozen_state, collections.Hashable):
# uncacheable. a list, for instance.
# better to not cache than blow up.
_, grad_value = self.logp_func(*state.values())
return grad_value
if frozen_state in self._grad_cache:
grad_value = self._grad_cache[frozen_state]
else:
logp_value, grad_value = self.logp_func(*state.values())
self._logp_cache[frozen_state] = logp_value
self._grad_cache[frozen_state] = grad_value
return grad_value
class Posterior(BasePosterior):
""" A posterior model for separate logp and grad_logp functions.
:param logp:
log P(X) function for sampling distribution.
:param grad_logp: (optional) *function or list of functions.*
Gradient log P(X) function. If left as None, then `grad_logp_flag`
is checked. If the flag is `True`, then the gradient will be
automatically calculated with autograd.
:param grad_logp_flag: (optional) *boolean.*
Flag indicating if the gradient is needed or not.
"""
def __init__(self, logp_func, grad_func=None, grad_logp_flag=False):
super(Posterior, self).__init__()
self.logp_func = check_logp(logp_func)
self.grad_func = check_grad_logp(logp_func, grad_func, grad_logp_flag)
def logp(self, state):
""" Return log P(X) given a :ref:`state <state>` X"""
# Freeze the state as a tuple so we can use it as a dictionary key
frozen_state = state.freeze()
if not isinstance(frozen_state, collections.Hashable):
# uncacheable. a list, for instance.
# better to not cache than blow up.
logp_value = self.logp_func(*state.values())
return logp_value
if frozen_state in self._logp_cache:
logp_value = self._logp_cache[frozen_state]
else:
logp_value = self.logp_func(*state.values())
self._logp_cache[frozen_state] = logp_value
return logp_value
def grad(self, state):
""" Return grad log P(X) given a :ref:`state <state>` X """
# Freeze the state as a tuple so we can use it as a dictionary key
frozen_state = state.freeze()
if not isinstance(frozen_state, collections.Hashable):
# uncacheable. a list, for instance.
# better to not cache than blow up.
grad_value = grad_vec(self.grad_func, state)
return grad_value
if frozen_state in self._grad_cache:
grad_value = self._grad_cache[frozen_state]
else:
grad_value = grad_vec(self.grad_func, state)
self._grad_cache[frozen_state] = grad_value
return grad_value
def init_posterior(logp, grad_logp=None, grad_logp_flag=False):
""" Initialize a posterior model and return it.
:param logp:
log P(X) function for sampling distribution.
:param grad_logp: (optional) *function, list of functions, or boolean.*
Gradient log P(X) function. If left as None, then `grad_logp_flag`
is checked. If the flag is `True`, then the gradient will be
automatically calculated with autograd.
If `grad_logp` is set to True, then a SingleModel is returned.
:param grad_logp_flag: (optional) *boolean.*
Flag indicating if the gradient is needed or not.
"""
if grad_logp is True:
return SinglePosterior(logp)
else:
return Posterior(logp, grad_logp, grad_logp_flag)
def grad_vec(grad_logp, state):
""" grad_logp should be a function, or a dictionary of gradient functions,
respective to each parameter in logp
"""
if hasattr(grad_logp, '__call__'):
# grad_logp is a single function
return np.array([grad_logp(*state.values())])
else:
# got a dictionary instead
grads = {each:grad_logp[each](*state.values()) for each in state}
grads_state = state.copy()
grads_state.update(grads)
return grads_state
def check_logp(logp):
if not hasattr(logp, '__call__'):
raise TypeError("logp must be a function")
elif logp.__code__.co_argcount == 0:
raise ValueError("logp must have arguments")
else:
return logp
def check_grad_logp(logp, grad_logp, grad_logp_flag):
var_names = func_var_names(logp)
if grad_logp_flag and grad_logp is None:
return auto_grad_logp(logp)
elif grad_logp_flag and grad_logp != 'logp':
# User defined grad_logp function
if len(var_names) > 1 and len(grad_logp) != len(var_names):
raise TypeError("grad_logp must be iterable with length equal"
" to the number of parameters in logp.")
else:
return grad_logp
else:
return grad_logp
|
/sampyl-mcmc-0.3.tar.gz/sampyl-mcmc-0.3/sampyl/posterior.py
| 0.830319 | 0.45308 |
posterior.py
|
pypi
|
import numbers
from sampyl.core import np
from scipy.special import gamma
def fails_constraints(*conditions):
""" Utility function for catching out of bound parameters. Returns True if
any of the conditions aren't met. Typically you'll use this at the
beginning of defining the log P(X) functions. Example ::
def logp(x, y):
# Bound x and y to be greater than 0
if outofbounds(x > 0, y > 0):
return -np.inf
"""
for each in conditions:
if not np.all(each):
return True
else:
return False
def normal(x, mu=0, sig=1):
""" Normal distribution log-likelihood.
:param x: *int, float, np.array.*
:param mu: (optional) *int, float, np.array.*
Location parameter of the normal distribution. Defaults to 0.
:param sig: (optional) *int, float.*
Standard deviation of the normal distribution, :math:`\sigma > 0`.
Defaults to 1.
.. math::
\log{P(x; \mu, \sigma)} \propto -\log{\sigma} \
- \\frac{(x - \mu)^2}{2 \sigma^2}
"""
if np.size(mu) != 1 and len(x) != len(mu):
raise ValueError('If mu is a vector, x must be the same size as mu.'
' We got x={}, mu={}'.format(x, mu))
if fails_constraints(sig >= 0):
return -np.inf
return np.sum(-np.log(sig) - (x - mu)**2/(2*sig**2))
def half_normal(x, mu=0, sig=1):
if fails_constraints(x >= 0):
return -np.inf
return normal(x, mu=mu, sig=sig)
def uniform(x, lower=0, upper=1):
""" Uniform distribution log-likelihood. Bounds are inclusive.
:param x: *int, float, np.array.*
:param lower: (optional) *int, float.* Lower bound, default is 0.
:param upper: (optional) *int, float.* Upper bound, default is 1.
.. math ::
\log{P(x; a, b)} = -n\log(b-a)
"""
if fails_constraints(x >= lower, x <= upper):
return -np.inf
return -np.size(x) * np.log(upper-lower)
def discrete_uniform(x, lower=0, upper=1):
""" Discrete Uniform distribution log-likelihood.
:param x: *int, np.array[int].*
:param lower: (optional) *int, float.* Lower bound, default is 0.
:param upper: (optional) *int, float.* Upper bound, default is 1.
.. math ::
\log{P(x; a, b)} = -n\log(b-a)
"""
if fails_constraints(x >= lower, x <= upper):
return -np.inf
if isinstance(x, np.ndarray):
if x.dtype != np.int_:
raise ValueError('x must be integers, function received {}'.format(x))
else:
return -np.size(x) * np.log(upper-lower)
elif isinstance(x, numbers.Integral):
return -np.log(upper-lower)
else:
return -np.inf
def exponential(x, rate=1):
""" Log likelihood of the exponential distribution.
:param x: *int, float, np.array.*
:param rate: (optional) *int, float, np.array.* Rate parameter, :math:`\lambda > 0`. Defaults to 1.
.. math ::
\log{P(x; \lambda)} \propto \log{\lambda} - \lambda x
"""
if fails_constraints(x > 0, rate > 0):
return -np.inf
if np.size(rate) != 1 and len(x) != len(rate):
raise ValueError('If rate is a vector, x must be the same size as rate.'
' We got x={}, rate={}'.format(x, rate))
return np.sum(np.log(rate) - rate*x)
def poisson(x, rate=1):
""" Poisson distribution log-likelihood.
:param x: *int, float, np.array.* Event count.
:param rate: (optional) *int, float, np.array.* Rate parameter, :math:`\lambda > 0`. Defaults to 1.
.. math ::
\log{P(x; \lambda)} \propto x \log{\lambda} - \lambda
"""
if fails_constraints(rate > 0):
return -np.inf
if np.size(rate) != 1 and len(x) != len(rate):
raise ValueError('If rate is a vector, x must be the same size as rate.'
' We got x={}, rate={}'.format(x, rate))
return np.sum(x*np.log(rate)) - np.size(x)*rate
def binomial(k, n, p):
""" Binomial distribution log-likelihood.
:param k: *int, np.array.* Number of successes. :math:`k <= n`
:param n: *int, np.array.* Number of trials. :math:`n > 0`
:param p: *int, float, np.array.* Success probability. :math:`0<= p <= 1`
.. math::
\log{P(k; n, p)} \propto k \log{p} + (n-k)\log{(1-p)}
"""
if k > n:
raise ValueError("k must be less than or equal to n")
if fails_constraints(0 < p, p < 1):
return -np.inf
return np.sum(k*np.log(p) + (n-k)*np.log(1-p))
def bernoulli(k, p):
""" Bernoulli distribution log-likelihood.
:param k: *int, np.array.* Number of successes.
:param p: *int, float, np.array.* Success probability.
Special case of binomial distribution, with n set to 1.
"""
return binomial(k, 1, p)
def beta(x, alpha=1, beta=1):
""" Beta distribution log-likelihood.
:param x: *float, np.array.* :math:`0 < x < 1`
:param alpha: (optional) *int, float.* Shape parameter, :math:`\\alpha > 0`
:param beta: (optional) *int, float.* Shape parameter, :math:`\\beta > 0`
.. math ::
\log{P(x; \\alpha, \\beta)} \propto (\\alpha - 1)\log{x} + \
(\\beta - 1) \log{(1 - x)}
"""
if fails_constraints(0 < x, x < 1, alpha > 0, beta > 0):
return -np.inf
return np.sum((alpha - 1)*np.log(x) + (beta - 1)*np.log(1-x))
def student_t(x, nu=1):
""" Student's t log-likelihood
:param x: *int, float, np.array.*
:param nu: (optional) *int.* Degress of freedom.
.. math ::
\log{P(x; \\nu)} \propto \log{\Gamma \\left(\\frac{\\nu+1}{2} \\right)} - \
\log{\Gamma \left( \\frac{\\nu}{2} \\right) } - \
\\frac{1}{2}\log{\\nu} - \
\\frac{\\nu+1}{2}\log{\left(1 + \\frac{x^2}{\\nu} \\right)}
"""
if fails_constraints(nu >= 1):
return -np.inf
return np.sum(np.log(gamma(0.5*(nu + 1))) - np.log(gamma(nu/2.)) - \
0.5*np.log(nu) - (nu+1)/2*np.log(1+x**2/nu))
def laplace(x, mu, tau):
""" Laplace distribution log-likelihood
:param x: *int, float, np.array.* :math:`-\infty < \mu < \infty`
:param mu: *int, float, np.array.* Location parameter. :math:`-\infty < \mu < \infty`
:param tau: *int, float.* Scale parameter, :math:`\\tau > 0`
.. math ::
\log{P(x; \\mu, \\tau)} \propto \log{\\tau/2} - \\tau \\left|x - \mu \\right|
"""
if fails_constraints(tau > 0):
return -np.inf
return np.sum(np.log(tau) - tau*np.abs(x - mu))
def cauchy(x, alpha=0, beta=1):
""" Cauchy distribution log-likelihood.
:param x: *int, float, np.array.* :math:`-\infty < x < \infty`
:param alpha: *int, float, nparray.* Location parameter, :math:`-\infty < \\alpha < \infty`
:param beta: *int, float.* Scale parameter, :math:`\\beta > 0`
.. math::
\log{P(x; \\alpha, \\beta)} \propto -\log{\\beta} - \
\log{\left[1 + \left(\\frac{x - \\alpha}{\\beta}\\right)^2\\right]}
"""
if fails_constraints(beta > 0):
return -np.inf
return np.sum(-np.log(beta) - np.log(1 + ((x - alpha)/beta)**2))
def half_cauchy(x, alpha=0, beta=1):
""" Half-Cauchy distribution log-likelihood (positive half).
:param x: *int, float, np.array.* :math:`-\infty < x < \infty`
:param alpha: *int, float, nparray.* Location parameter, :math:`-\infty < \\alpha < \infty`
:param beta: *int, float.* Scale parameter, :math:`\\beta > 0`
.. math::
\log{P(x; \\alpha, \\beta)} \propto -\log{\\beta} - \
\log{\left[1 + \left(\\frac{x - \\alpha}{\\beta}\\right)^2\\right]}
"""
if fails_constraints(x > 0):
return -np.inf
return cauchy(x, alpha=alpha, beta=beta)
def weibull(x, l, k):
""" Weibull distribution log-likelihood.
:param x: *int, float, np.array.* :math:`x > 0`
:param l: *float.* Scale parameter. :math:`\\lambda > 0`
:param k: *float.* Shape parameter. :math:`k > 0`
"""
if fails_constraints(l > 0, k > 0, x > 0):
return -np.inf
return np.sum(np.log(k/l) + (k-1)*np.log(x/l) - (x/l)**k)
|
/sampyl-mcmc-0.3.tar.gz/sampyl-mcmc-0.3/sampyl/distributions.py
| 0.902523 | 0.605158 |
distributions.py
|
pypi
|
from __future__ import division
import sampyl
from sampyl.core import np
import collections
class State(collections.OrderedDict):
""" State object for storing parameter values.
Inherits from OrderedDict.
"""
def tovector(self):
""" Return the parameter values as a flat vector. """
return np.hstack(self.values())
def fromvector(self, vec):
""" Update the state using a numpy array.
:param vec: np.array for updating the state.
"""
var_sizes = self.size()
i = 0
for var in self:
self[var] = np.squeeze(vec[i:(i+var_sizes[var])])
i += var_sizes[var]
return self
def freeze(self):
""" Return a immutable tuple of the state values."""
return tuple(self.tovector())
@staticmethod
def init_fromvector(vec, state):
""
vals = []
var_sizes = state.size()
i = 0
for var in state:
vals.append(np.squeeze(vec[i:(i+var_sizes[var])]))
i += var_sizes[var]
return State(zip(state.keys(), vals))
@staticmethod
def fromfunc(func):
""" Initialize a State from the arguments of a function """
var_names = func_var_names(func)
return State.fromkeys(var_names)
def size(self):
return State([(var, np.size(self[var])) for var in self])
def __add__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, int) or isinstance(other, float):
return handle_number(self, other, '__add__')
elif isinstance(other, collections.Iterable):
return handle_iterable(self, other, '__add__')
else:
raise TypeError("Addition not supported for State and {}".format(other))
def __sub__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, int) or isinstance(other, float):
return handle_number(self, other, '__sub__')
elif isinstance(other, collections.Iterable):
return handle_iterable(self, other, '__sub__')
else:
raise TypeError("Subtraction not supported for State and {}".format(other))
def __mul__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, int) or isinstance(other, float):
return handle_number(self, other, '__mul__')
else:
raise TypeError("Multiplication not supported for State and {}".format(other))
def __truediv__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, int) or isinstance(other, float):
return handle_number(self, other, '__truediv__')
else:
raise TypeError("Division not supported for State and {}".format(other))
def __radd__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, int) or isinstance(other, float):
# Commutative, so nothing changes
return self + other
else:
raise TypeError("Can only broadcast from the left.")
def __rmul__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, int) or isinstance(other, float):
# Commutative, so nothing changes
return self * other
else:
raise TypeError("Can only broadcast from the left.")
def __rsub__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, int) or isinstance(other, float):
return handle_number(self, other, '__rsub__')
elif isinstance(other, collections.Iterable):
return handle_iterable(self, other, '__rsub__')
else:
raise TypeError("Subtraction not supported for State and {}".format(other))
def __rtruediv__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, int) or isinstance(other, float):
return handle_number(self, other, '__truediv__')
else:
raise TypeError("Division not supported for State and {}".format(other))
def handle_number(state, other, operator):
vals = [getattr(state[var], operator)(other) for var in state]
try:
if NotImplemented in vals:
vals = [getattr(other, operator)(state[var]) for var in state]
except ValueError:
pass
return State([(var, val) for var, val in zip(state, vals)])
def handle_iterable(state, other, operator):
if len(other) != len(state):
# This might be the case:
# State({'x': np.array(1, 2, 3)}) + np.array([2,3,4])
# So check if both are numpy arrays, then add
# But first, we can only do this is len(state) is 1.
if len(state) != 1:
raise ValueError("Can't broadcast with sizes state: {},"
" other: {}".format(len(state), len(other)))
var = list(state.keys())[0]
val = state[var]
if type(val) == np.ndarray and type(other) == np.ndarray:
return State([(var, getattr(val, operator)(other))])
else:
raise ValueError("Can only operate on numpy arrays.")
if isinstance(other, dict):
vals = [getattr(state[var], operator)(other[var]) for var in state]
else:
# Otherwise, we have cases like
# State({'x': foo, 'y': bar}) + [foo2, bar2]
vals = [getattr(state[var], operator)(each) for var, each in zip(state, other)]
return State([(var, val) for var, val in zip(state, vals)])
def special_math_func(state, other, operator):
""" A function for special math functions used in the State class.
So, we need to handle state + 1, state + np.array(),
state1 + state2, etc. basically we want to do the same thing
every time but with different operators.
"""
new = State([(var, vals) for var, each in zip(state, vals)])
return new
def func_var_names(func):
""" Returns a list of the argument names in func """
names = func.__code__.co_varnames[:func.__code__.co_argcount]
return names
|
/sampyl-mcmc-0.3.tar.gz/sampyl-mcmc-0.3/sampyl/state.py
| 0.828384 | 0.466299 |
state.py
|
pypi
|
from __future__ import division
from ..core import np
from ..state import State
from .base import Sampler
from ..model import Model
class Hamiltonian(Sampler):
def __init__(self, logp, start, step_size=1, n_steps=5, **kwargs):
""" Hamiltonian MCMC sampler. Uses the gradient of log P(theta) to
make informed proposals.
Arguments
----------
logp: function
log P(X) function for sampling distribution
start: dict
Dictionary of starting state for the sampler. Should have one
element for each argument of logp. So, if logp = f(x, y), then
start = {'x': x_start, 'y': y_start}
Keyword Arguments
-----------------
grad_logp: function or list of functions
Functions that calculate grad log P(theta). Pass functions
here if you don't want to use autograd for the gradients. If
logp has multiple parameters, grad_logp must be a list of
gradient functions w.r.t. each parameter in logp.
scale: dict
Same format as start. Scaling for initial momentum in
Hamiltonian step.
step_size: float
Step size for the deterministic proposals.
n_steps: int
Number of deterministic steps to take for each proposal.
"""
super(Hamiltonian, self).__init__(logp, start, **kwargs)
self.step_size = step_size / (np.hstack(self.state.values()).size)**(1/4)
self.n_steps = n_steps
def step(self):
x = self.state
r0 = initial_momentum(x, self.scale)
y, r = x, r0
for i in range(self.n_steps):
y, r = leapfrog(y, r, self.step_size, self.model.grad)
if accept(x, y, r0, r, self.model.logp):
x = y
self._accepted += 1
self.state = x
self._sampled += 1
return x
@property
def acceptance_rate(self):
return self._accepted/self._sampled
def leapfrog(x, r, step_size, grad):
r1 = r + step_size/2*grad(x)
x1 = x + step_size*r1
r2 = r1 + step_size/2*grad(x1)
return x1, r2
def accept(x, y, r_0, r, logp):
E_new = energy(logp, y, r)
E = energy(logp, x, r_0)
A = np.min(np.array([0, E_new - E]))
return (np.log(np.random.rand()) < A)
def energy(logp, x, r):
r1 = r.tovector()
return logp(x) - 0.5*np.dot(r1, r1)
def initial_momentum(state, scale):
new = State.fromkeys(state.keys())
for var in state:
mu = np.zeros(np.shape(state[var]))
cov = np.diagflat(scale[var])
try:
new.update({var: np.random.multivariate_normal(mu, cov)})
except ValueError:
# If the var is a single float
new.update({var: np.random.normal(0, scale[var])})
return new
|
/sampyl-mcmc-0.3.tar.gz/sampyl-mcmc-0.3/sampyl/samplers/hamiltonian.py
| 0.881806 | 0.62478 |
hamiltonian.py
|
pypi
|
from __future__ import division
from ..core import np
from ..state import State
from .base import Sampler
class Metropolis(Sampler):
# TODO: Allow for sticking in different proposal distributions.
""" Metropolis-Hastings sampler for drawing from a distribution
defined by a logp function.
Has automatic scaling such that acceptance rate stays around 50%
:param logp: function
log P(X) function for sampling distribution.
:param start:
Dictionary of starting state for the sampler. Should have one
element for each argument of logp.
:param scale: *scalar or 1D array-like.*
initial scaling factor for proposal distribution.
:param tune_interval: *int.*
:param scale: **scalar or 1D array-like.**
initial scaling factor for proposal distribution.
:param tune_interval: *int.*
number of samples between tunings of scale factor.
Example::
def logp(x, y):
...
start = {'x': x_start, 'y': y_start}
metro = sampyl.Metropolis(logp, start)
chain = metro.sample(20000, burn=5000, thin=4)
"""
def __init__(self, logp, start, tune_interval=100, **kwargs):
super(Metropolis, self).__init__(logp, start, None, grad_logp_flag=False,
**kwargs)
self.tune_interval = tune_interval
self._steps_until_tune = tune_interval
self._accepted = 0
def step(self):
""" Perform a Metropolis-Hastings step. """
x = self.state
y = proposal(x, scale=self.scale)
if accept(x, y, self.model.logp):
self.state = y
self._accepted += 1
self._sampled += 1
self._steps_until_tune -= 1
if self._steps_until_tune == 0:
self.scale = tune(self.scale, self.acceptance)
self._steps_until_tune = self.tune_interval
return self.state
@property
def acceptance(self):
return self._accepted/self._sampled
def __repr__(self):
return 'Metropolis-Hastings sampler'
def proposal(state, scale):
""" Sample a proposal x from a multivariate normal distribution. """
proposed = State.fromkeys(state.keys())
for i, var in enumerate(state):
proposed.update({var: np.random.normal(state[var], scale[var])})
return proposed
def accept(x, y, logp):
""" Return a boolean indicating if the proposed sample should be accepted,
given the logp ratio logp(y)/logp(x).
"""
delp = logp(y) - logp(x)
if np.isfinite(delp) and np.log(np.random.uniform()) < delp:
return True
else:
return False
def tune(scale, acceptance):
""" Borrowed from PyMC3 """
# Switch statement
if acceptance < 0.001:
# reduce by 90 percent
scale *= 0.1
elif acceptance < 0.05:
# reduce by 50 percent
scale *= 0.5
elif acceptance < 0.2:
# reduce by ten percent
scale *= 0.9
elif acceptance > 0.95:
# increase by factor of ten
scale *= 10.0
elif acceptance > 0.75:
# increase by double
scale *= 2.0
elif acceptance > 0.5:
# increase by ten percent
scale *= 1.1
return scale
|
/sampyl-mcmc-0.3.tar.gz/sampyl-mcmc-0.3/sampyl/samplers/metropolis.py
| 0.613237 | 0.562717 |
metropolis.py
|
pypi
|
from itertools import count
import time
import unicodedata
from ..core import np, auto_grad_logp, AUTOGRAD
from ..parallel import parallel
from ..progressbar import update_progress
from ..state import State, func_var_names
from ..posterior import init_posterior
class Sampler(object):
def __init__(self, logp, start,
grad_logp=None,
scale=None,
condition=None,
grad_logp_flag=True,
random_seed=None):
self.model = init_posterior(logp, grad_logp, grad_logp_flag)
self._logp_func = logp
self._grad_func = grad_logp
self.var_names = func_var_names(logp)
self.state = State.fromkeys(self.var_names)
# Making sure we normalize here because if some parameters use unicode
# symbols, they are normalized through the func_var_names function. Then, we
# need to normalize them here as well or the keys in start won't match the
# keys from var_names
start = {unicodedata.normalize('NFKC', key): val for key, val in start.items()}
self.state.update(start)
self.scale = default_scale(scale, self.state)
self.sampler = None
self._sampled = 0
self._accepted = 0
self.conditional = condition
self._grad_logp_flag = grad_logp_flag
self.seed = random_seed
if random_seed:
np.random.seed(random_seed)
if condition is not None:
self._joint_logp = self._logp_func
def _conditional_step(self):
""" Build a conditional logp and sample from it. """
if self.conditional is None:
return self.step()
frozen_vars = self.conditional
frozen_state = self.state
free_vars = [var for var in self.state if var not in frozen_vars]
def conditional_logp(*args):
conditional_state = State([each for each in zip(free_vars, args)])
# Insert conditional values here, then pass to full logp
for i in frozen_vars:
conditional_state.update({i: frozen_state[i]})
return self._joint_logp(**conditional_state)
self.state = State([(var, frozen_state[var]) for var in free_vars])
self._logp_func = conditional_logp
if self._grad_logp_flag and AUTOGRAD:
self.model.grad_func = auto_grad_logp(conditional_logp, names=self.state.keys())
self.model.logp_func = self._logp_func
state = self.step()
# Add the frozen variables back into the state
new_state = State([(name, None) for name in self.var_names])
for var in state:
new_state.update({var: state[var]})
for var in frozen_vars:
new_state.update({var: frozen_state[var]})
self.state = new_state
return self.state
def step(self):
""" This is what you define to create the sampler. Requires that a
:ref:`state <state>` object is returned."""
pass
def sample(self, num, burn=0, thin=1, n_chains=1, progress_bar=True):
"""
Sample from :math:`P(X)`
:param num: *int.* Number of samples to draw from :math:`P(X)`.
:param burn: (optional) *int.*
Number of samples to discard from the beginning of the chain.
:param thin: (optional) *float.*
Thin the samples by this factor.
:param n_chains: (optional) *int.*
Number of chains to return. Each chain is given its own
process and the OS decides how to distribute the processes.
:param progress_bar: (optional) *boolean.*
Show the progress bar, default = True.
:return: Record array with fields taken from arguments of
logp function.
"""
if self.seed is not None:
np.random.seed(self.seed)
if AUTOGRAD and hasattr(self.model, 'grad_func') \
and self.model.grad_func is None:
self.model.grad_func = auto_grad_logp(self._logp_func)
# Constructing a recarray to store samples
dtypes = [(var, 'f8', np.shape(self.state[var])) for var in self.state]
samples = np.zeros(num, dtype=dtypes).view(np.recarray)
if n_chains != 1:
return parallel(self, n_chains, samples,
burn=burn, thin=thin,
progress_bar=progress_bar)
if self.sampler is None:
self.sampler = (self.step() for _ in count(start=0, step=1))
start_time = time.time() # For progress bar
# Start sampling, add each
for i in range(num):
samples[i] = tuple(next(self.sampler).values())
if progress_bar and time.time() - start_time > 1:
update_progress(i+1, num)
start_time = time.time()
if progress_bar:
update_progress(i+1, num, end=True)
# Clearing the cache after a run to save on memory.
self.model.clear_cache()
return samples[burn::thin]
def __call__(self, num, burn=0, thin=1, n_chains=1, progress_bar=True):
return self.sample(num, burn=burn, thin=thin, n_chains=n_chains,
progress_bar=progress_bar)
def default_scale(scale, state):
""" If scale is None, return a State object with arrays of ones matching
the shape of values in state.
"""
if scale is None:
new_scale = State.fromkeys(state.keys())
for var in state:
new_scale.update({var: np.ones(np.shape(state[var]))})
return new_scale
else:
return scale
|
/sampyl-mcmc-0.3.tar.gz/sampyl-mcmc-0.3/sampyl/samplers/base.py
| 0.569853 | 0.248096 |
base.py
|
pypi
|
from __future__ import division
from ..core import np
from ..state import State
from .base import Sampler
class Slice(Sampler):
""" Slice sampler (Neal, 2003) for creating a Markov chain that
leaves the the distribution defined by logp invariant
For technical details, see Neal's paper:
http://projecteuclid.org/euclid.aos/1056562461
Andrew Miller ([email protected]) 7-13-15
Adapted from code written by Ryan Adams ([email protected])
:param logp: *function.* :math:`\log{P(X)}` function for sampling
distribution.
:param start: *scalar or 1D array-like.* Starting state for sampler.
:param compwise: (optional) *boolean.* Component-wise univariate
slice sample
(or random direction)
:param width: (optional) *int, float.* (Initial) width of the slice
:param step_out: (optional) *boolean.* Perform step-out procedure
:param doubling_step: (optional) *boolean.* If stepping out, double
slice width?
:param max_steps_out: (optional) *int.* Max number of steps out to perform
:param verbose: (optional) *boolean.* Print steps out
"""
def __init__(self, logp,
start,
compwise = False,
width = 1.,
step_out = True,
doubling_step = True,
max_steps_out = 10,
verbose = False,
**kwargs):
super(Slice, self).__init__(logp, start, None, grad_logp_flag=False,
**kwargs)
self._num_evals = 0
# sampler this is either a random direction or component-wise slice sampler
self.compwise = compwise
self.width = width
self.step_out = step_out
self.doubling_step = doubling_step
self.max_steps_out = max_steps_out
self.verbose = verbose
def step(self):
""" Perform a slice sample step """
dims = self.state.tovector().shape[0]
if self.compwise:
ordering = range(dims)
np.random.shuffle(ordering)
new_x = self.state.tovector.copy()
for d in ordering:
direction = np.zeros((dims))
direction[d] = 1.0
new_x = self.direction_slice(direction, new_x)
else:
direction = np.random.randn(dims)
direction = direction / np.sqrt(np.sum(direction**2))
new_x = self.direction_slice(direction, self.state.tovector())
self.state = self.state.fromvector(new_x)
self._sampled += 1
return self.state
def direction_slice(self, direction, init_x):
""" one dimensional directional slice sample along direction specified
Implements the stepping out procedure from Neal
"""
def dir_logprob(z):
self._num_evals += 1
cstate = State.init_fromvector(direction*z + init_x, self.state)
return self.model.logp(cstate)
def acceptable(z, llh_s, L, U):
while (U-L) > 1.1*self.width:
middle = 0.5*(L+U)
splits = (middle > 0 and z >= middle) or (middle <= 0 and z < middle)
if z < middle:
U = middle
else:
L = middle
# Probably these could be cached from the stepping out.
if splits and llh_s >= dir_logprob(U) and llh_s >= dir_logprob(L):
return False
return True
upper = self.width*np.random.rand()
lower = upper - self.width
llh_s = np.log(np.random.rand()) + dir_logprob(0.0)
l_steps_out = 0
u_steps_out = 0
if self.step_out:
if self.doubling_step:
while (dir_logprob(lower) > llh_s or
dir_logprob(upper) > llh_s) and \
(l_steps_out + u_steps_out) < self.max_steps_out:
if np.random.rand() < 0.5:
l_steps_out += 1
lower -= (upper-lower)
else:
u_steps_out += 1
upper += (upper-lower)
else:
while dir_logprob(lower) > llh_s and \
l_steps_out < max_steps_out:
l_steps_out += 1
lower -= self.width
while dir_logprob(upper) > llh_s and \
u_steps_out < max_steps_out:
u_steps_out += 1
upper += self.width
start_upper = upper
start_lower = lower
steps_in = 0
while True:
steps_in += 1
new_z = (upper - lower)*np.random.rand() + lower
new_llh = dir_logprob(new_z)
if np.isnan(new_llh):
print(new_z, direction*new_z + init_x, new_llh,
llh_s, init_x, dir_logprob(init_x))
raise Exception("Slice sampler got a NaN")
if new_llh > llh_s and \
acceptable(new_z, llh_s, start_lower, start_upper):
break
elif new_z < 0:
lower = new_z
elif new_z > 0:
upper = new_z
else:
raise Exception("Slice sampler shrank to zero!")
if self.verbose:
print("Steps Out:", l_steps_out, u_steps_out, " Steps In:", steps_in)
return new_z*direction + init_x
@property
def evals_per_sample(self):
return self._num_evals/float(self._sampled)
def __repr__(self):
return 'Slice sampler'
|
/sampyl-mcmc-0.3.tar.gz/sampyl-mcmc-0.3/sampyl/samplers/slice.py
| 0.822082 | 0.421254 |
slice.py
|
pypi
|
from __future__ import division
import collections
from ..core import np
from .base import Sampler
from .hamiltonian import energy, leapfrog, initial_momentum
class NUTS(Sampler):
""" No-U-Turn sampler (Hoffman & Gelman, 2014) for sampling from a
probability distribution defined by a log P(theta) function.
For technical details, see the paper:
http://www.stat.columbia.edu/~gelman/research/published/nuts.pdf
:param logp: log P(X) function for sampling distribution
:param start:
Dictionary of starting state for the sampler. Should have one
element for each argument of logp.
:param grad_logp: (optional)
Function or list of functions that calculate grad log P(theta).
Pass functions here if you don't want to use autograd for the
gradients. If logp has multiple parameters, grad_logp must be
a list of gradient functions w.r.t. each parameter in logp.
If you wish to use a logp function that returns both the logp
value and the gradient, set grad_logp = True.
:param scale: (optional)
Dictionary with same format as start. Scaling for initial
momentum in Hamiltonian step.
:param step_size: (optional) *float.*
Initial step size for the deterministic proposals.
:param adapt_steps: (optional) *int.*
Integer number of steps used for adapting the step size to
achieve a target acceptance rate.
:param Emax: (optional) *float.* Maximum energy.
:param target_accept: (optional) *float.* Target acceptance rate.
:param gamma: (optional) *float.*
:param k: (optional) *float.* Scales the speed of step size
adaptation.
:param t0: (optional) *float.* Slows initial step size adaptation.
Example ::
def logp(x, y):
...
start = {'x': x_start, 'y': y_start}
nuts = sampyl.NUTS(logp, start)
chain = nuts.sample(1000)
"""
def __init__(self, logp, start,
step_size=0.25,
adapt_steps=100,
Emax=1000.,
target_accept=0.65,
gamma=0.05,
k=0.75,
t0=10.,
**kwargs):
super(NUTS, self).__init__(logp, start, **kwargs)
self.step_size = step_size / len(self.state.tovector())**(1/4.)
self.adapt_steps = adapt_steps
self.Emax = Emax
self.target_accept = target_accept
self.gamma = gamma
self.k = k
self.t0 = t0
self.Hbar = 0.
self.ebar = 1.
self.mu = np.log(self.step_size*10)
def step(self):
""" Perform one NUTS step."""
H = self.model.logp
dH = self.model.grad
x = self.state
r0 = initial_momentum(x, self.scale)
u = np.random.uniform()
e = self.step_size
xn, xp, rn, rp, y = x, x, r0, r0, x
j, n, s = 0, 1, 1
while s == 1:
v = bern(0.5)*2 - 1
if v == -1:
xn, rn, _, _, x1, n1, s1, a, na = buildtree(xn, rn, u, v, j, e, x, r0,
H, dH, self.Emax)
else:
_, _, xp, rp, x1, n1, s1, a, na = buildtree(xp, rp, u, v, j, e, x, r0,
H, dH, self.Emax)
if s1 == 1 and bern(np.min(np.array([1, n1/n]))):
y = x1
dx = (xp - xn).tovector()
s = s1 * (np.dot(dx, rn.tovector()) >= 0) * \
(np.dot(dx, rp.tovector()) >= 0)
n = n + n1
j = j + 1
if self._sampled >= self.adapt_steps:
self.step_size = self.ebar
else:
# Adapt step size
m = self._sampled + 1
w = 1./(m + self.t0)
self.Hbar = (1 - w)*self.Hbar + w*(self.target_accept - a/na)
log_e = self.mu - (m**.5/self.gamma)*self.Hbar
self.step_size = np.exp(log_e)
z = m**(-self.k)
self.ebar = np.exp(z*log_e + (1 - z)*np.log(self.ebar))
self.state = y
self._sampled += 1
return y
def bern(p):
return np.random.uniform() < p
def buildtree(x, r, u, v, j, e, x0, r0, H, dH, Emax):
if j == 0:
x1, r1 = leapfrog(x, r, v*e, dH)
E = energy(H, x1, r1)
E0 = energy(H, x0, r0)
dE = E - E0
n1 = (np.log(u) - dE <= 0)
s1 = (np.log(u) - dE < Emax)
return x1, r1, x1, r1, x1, n1, s1, np.min(np.array([1, np.exp(dE)])), 1
else:
xn, rn, xp, rp, x1, n1, s1, a1, na1 = \
buildtree(x, r, u, v, j-1, e, x0, r0, H, dH, Emax)
if s1 == 1:
if v == -1:
xn, rn, _, _, x2, n2, s2, a2, na2 = \
buildtree(xn, rn, u, v, j-1, e, x0, r0, H, dH, Emax)
else:
_, _, xp, rp, x2, n2, s2, a2, na2 = \
buildtree(xp, rp, u, v, j-1, e, x0, r0, H, dH, Emax)
if bern(n2/max(n1 + n2, 1.)):
x1 = x2
a1 = a1 + a2
na1 = na1 + na2
dx = (xp - xn).tovector()
s1 = s2 * (np.dot(dx, rn.tovector()) >= 0) * \
(np.dot(dx, rp.tovector()) >= 0)
n1 = n1 + n2
return xn, rn, xp, rp, x1, n1, s1, a1, na1
|
/sampyl-mcmc-0.3.tar.gz/sampyl-mcmc-0.3/sampyl/samplers/NUTS.py
| 0.899881 | 0.649912 |
NUTS.py
|
pypi
|
""""""""""""
SamRand
""""""""""""
============
Introduction
============
SamRand is a tool designed to sample datasets and produce statistically representative samples for research purposes.
----------------
Who is this for?
----------------
I developed this primarily for researchers who deal with large datasets, and need to sample them to conduct some qualitative analysis.
While it was meant to pull samples for qualitative purposes, it could be used for quantitative purposes as well.
And even though, at the time, it was meant for researchers, there is no reason to believe that it can be used for non-research use-cases.
As such, this project is licensed under the MIT license.
----------------------------------------------------
How does SamRand sample a dataset?
----------------------------------------------------
SamRand's sampling approach differs depending on the settings you use when sampling a dataset.
These are, however, dependent on the choice of stratification:
- **No Stratification:** SamRand will select rows from the dataset at random without attempting to represent any existing groups within the dataset's population.
- **Stratification with Unknown Dimensions:** SamRand will perform a single-level clustering along the dimension with the least variance (to guarantee diverse strata). Samples are pulled from these two strata based on their proportion to the dataset's distribution. For instance, a dataset with location as the dimension with the least variance (either X or Y with a 60:40 split) will generate a sample of 6 rows in location X and 4 in location Y if the sample size is 10.
- **Stratification with known Dimensions:** If you provide specific dimensions (column indices) when invoking SamRand, it will apply multi-level clustering to generate strata. This means it will split the data by the first dimension, then split the strata resulting from the first split by the second dimension, and so on.
**Important Note:**
Depending on how your dataset is distributed, it is possible that there will be strata with only a single row.
SamRand will extract at least one row from each strata.
This will inflate sample size, resulting in a sample size larger than what you specified.
To reconcile the difference, SamRand will (once it has a representative sample) remove rows at random from that sample until it shrinks down to the desired size.
Consequently, rows from larger strata have a higher probability to be removed towards the end of the sampling process.
There is also whether you choose to sample with or without replacement:
- **with Replacement:** Rows previously sampled may be sampled again. Which means that the dataset may consist of duplicate rows.
- **without Replacement:** Rows previously sampled may not be sampled again. which means that the dataset will not contain duplicates unless the dataset itself contains duplicates.
If there is a sampling strategy you'd like to see implemented or fixed, feel free to open an issue.
I will try to get around to it.
Alternatively, you can submit a merge request.
Stay up-to-date by monitoring SamRand's `issues page <https://gitlab.com/omazhary/SamRand/-/issues>`_.
==========================
How Do I Use SamRand?
==========================
SamRand supports two modes of use:
- as a standalone application, and
- as a module within your python script.
---------------------------------
What Should My Dataset Look Like?
---------------------------------
Right now, SamRand supports two types of datasets, CSV files and JSON files.
For now, CSV files are expected to use commas as delimiters, with double quotes around text (default python CSV settings).
JSON files are expected to be valid.
Examples of both dataset types are included in the `test folder of this repository <https://gitlab.com/omazhary/SamRand/-/tree/master/test>`_.
---------------------------
As a standalone application
---------------------------
Once installed, you can use SamRand as a standalone application in your terminal of choice.
It supports the following arguments:
- **-h**, **--help:** Shows a help message and exits.
- **--dataset <path/to/dataset/file>:** The file containing your dataset.
- **--size <integer>:** The required sample size (n).
- **--header:** When using a CSV dataset file, use this flag to indicate whether the first row is a header.
- **--replacement:** Extract samples with replacement. Not including this flag means without replacement (the default behavior).
- **--stratify:** Balance the extracted sample so that it reflects the population's distribution.
- **--strata '[0, 1, 2, ...]':** When using stratification, use this parameter to indicate which fields should be used as a basis for stratification. Accepts valid JSON arrays of column indices starting with 0.
- **--output:** The output format of the samples. Default is JSON. Can be one of [CSV|JSON].
A typical command using SamRand looks like the following example that samples a CSV dataset with a header for 30 samples, then outputs the sample to _stdout_ in CSV format:
.. code:: shell
$ SamRand --dataset datasets/dataset.csv \
--size 30 \
--header \
--stratify \
--strata '[4, 5]' \
--output CSV
To output the results somewhere other than _stdout_, redirect the output to a file depending on your terminal emulator.
For instance, when redirecting the above command's output to a CSV file in a standard bash session:
.. code:: shell
$ SamRand --dataset datasets/dataset.csv \
--size 30 \
--header \
--stratify \
--strata '[4, 5]' \
--output CSV > output.csv
------------------
As a Python module
------------------
You can build a python script and use SamRand within it to sample datasets on the fly to do with as you please.
For instance, if you wanted to sample a dataset in your python script, you would import SamRand as a dependency, and give it the necessary information:
.. code:: python
import samrand as sr
dataset_path = '/path/to/my/dataset.json'
dataset = sr.reader.read_json(dataset_path)
sample = sr.sampler.sample(dataset, 30, stratify=True, replacement=True)
Further documentation can be found `here <https://samrand.readthedocs.io/>`_.
==============================
How Do I Install SamRand?
==============================
Regardless of whether you want to use it as a standalone application or a module in your project, you can install SamRand via pip as you would any normal python module:
.. code:: shell
$ pip install samrand
|
/samrand-0.1.0.tar.gz/samrand-0.1.0/README.rst
| 0.949412 | 0.885186 |
README.rst
|
pypi
|
from bson import ObjectId
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple, Any, Union
try:
# When used in the SAMS API errors will inherit from Werkzeug errors
# to ensure Eve Validation errors are passed through here
from werkzeug.exceptions import HTTPException, BadRequest as BaseException
except ImportError:
# Otherwise when used in the SAMS Client, normal Exception errors will do
HTTPException = Any
BaseException = Exception
try:
from flask import current_app as app
except ImportError:
app = {'config': {}}
from sams_client.utils import bytes_to_human_readable
class SamsException(BaseException):
"""Base class used for all SAMS Errors
:var str app_code: The unique SAMS code for this error
:var int http_code: The HTTP status code to send to the client
:var str description: The description of the error
:var bool log_exception: If ``True``, the stack trace will be logged
"""
app_code: str = '01001'
http_code: int = 500
description: str = ''
log_exception: bool = False
def __init__(self, payload: Dict[str, Any] = None, exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__()
self.payload = payload or {}
self.exception = exception
self.description = self.description.format(**self.payload)
def get_name(self) -> str:
"""Returns the class name of the exception.
For example::
SamsSetErrors.InvalidStateTransition('usable').get_name()
'InvalidStateTransition'
"""
return self.__class__.__name__
def __str__(self) -> str:
"""Returns a string containing all relevant information
For example::
str(SamsSetErrors.InvalidStateTransition('usable'))
'Error[07001] - InvalidStateTransition: Cannot change state from "usable" to draft'
"""
return 'Error[{}] - {}: {}'.format(
self.app_code,
self.get_name(),
self.description
)
def to_dict(self) -> Dict[str, str or Dict]:
"""Returns a dictionary with all the relevant information
This is used for constructing the response to send to the client.
For example::
SamsSetErrors.InvalidStateTransition('usable').to_dict()
{
'error': '07001',
'name': 'InvalidStateTransition',
'description': 'Cannot change state from "usable" to draft'
}
"""
return {
'error': self.app_code,
'name': self.get_name(),
'description': self.description,
}
def to_error_response(self) -> Tuple[Union[Dict[str, str or Dict], str], int]:
"""Returns a tuple containing a results of ``to_dict()`` and ``http_code``
For example::
SamsSetErrors.InvalidStateTransition('usable').to_error_response()
{
'error': '07001',
'name': 'InvalidStateTransition',
'description': 'Cannot change state from "usable" to draft'
},
400
"""
if (getattr(app, 'config') or {}).get('RETURN_ERRORS_AS_JSON', False):
return self.to_dict(), self.http_code
else:
return str(self), self.http_code
class SamsSystemErrors:
class UnknownError(SamsException):
"""Raised when an unknown/unhandled error has occurred"""
app_code = '01001'
http_code = 500
description = '{message}'
log_exception = True
def __init__(self, message: str, exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__({'message': str(message)}, exception)
class AssertionError(UnknownError):
"""Raised when an assertion has failed in the code"""
app_code = '01002'
http_code = 500
description = '{message}'
log_exception = True
class SystemUpdateNotAllowed(SamsException):
"""Raised when an attempt to force resource update from an API endpoint"""
app_code = '01003'
http_code = 500
description = '"system_update" not allowed in api endpoints'
log_exception = True
class NotImplemented(UnknownError):
"""Raised when a required function has not been implemented"""
app_code = '01004'
http_code = 500
description = '{message}'
log_exception = True
class SamsConfigErrors:
class AuthTypeNotSpecified(SamsException):
"""Raised when the `SAMS_AUTH_TYPE` config attribute is undefined"""
app_code = '02001'
http_code = 500
description = 'Auth type not specified'
log_exception = True
class AuthTypeHasNoGetAuthInstance(SamsException):
"""Raised when loading the Auth module if `get_auth_instance` is undefined"""
app_code = '02002'
http_code = 500
description = 'Configured Auth type must have a "get_auth_instance" method'
log_exception = True
class StorageProviderConfigStringNotProvided(SamsException):
"""Raised when a StorageProvider receives an empty config"""
app_code = '02003'
http_code = 500
description = '"config_string" must be provided'
log_exception = True
class StorageProviderIncorrectConfigArguments(SamsException):
"""Raised when a StorageProvider received incorrect number of config arguments"""
app_code = '02004'
http_code = 500
description = 'Incorrect number of arguments, expected 3 but received {num_args}'
log_exception = True
def __init__(self, num_args: int, exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__({'num_args': num_args}, exception)
class StorageProviderInvalidConfig(SamsException):
"""Raised when a StorageProvider received config for an incompatible StorageProvider"""
app_code = '02005'
http_code = 500
description = 'Incorrect config entry for provider {dest_provider}, received entry for {src_provider}'
log_exception = True
def __init__(self, src_provider: str, dest_provider: str, exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__({'src_provider': src_provider, 'dest_provider': dest_provider}, exception)
class BasicAuthAPIKeysNotProvided(SamsException):
"""Raised when `sams.auth.basic` authentication is used without any API keys defined"""
app_code = '02006'
http_code = 501
description = 'No API keys defined in the config'
log_exception = True
class SamsHTTPError(SamsException):
"""All generic HTTP errors will be raised with this error.
The ``app_code`` will be the supplied ``http_code`` prefixed with ``03``.
For example::
from flask import abort
abort(401, description='Not allowed to do that')
# will raise the following error
{
"error": "03401",
"name": "SamsHTTPError",
"description": "Not allowed to do that"
}
This method solely exists to catch errors that are raised from underlying frameworks, such as ``Eve`` or ``Flask``
It is advised not to use ``abort`` directly, instead implement a new exception that extends the ``SamsException``
class.
"""
app_code = '03'
def __init__(self, error: HTTPException):
self.error = error
self.http_code = error.code
self.app_code = '{}{}'.format(
self.app_code,
self.http_code
)
self.description = error.description
def get_name(self) -> str:
return self.error.name
class SamsResourceErrors:
class ValidationError(SamsException):
"""Raised when receiving an invalid request to create or update a resource
The response will include the list of fields and rules that failed validation, under the ``errors`` attribute.
For example::
"error": "04001",
"name": "ValidationError",
"description": "Validation error",
"errors": {
"name": ["required"]
}
This indicates that the field ``name`` was not supplied with the request (or was ``null``).
"""
app_code = '04001'
http_code = 400
description = 'Validation error'
errors: Dict[str, List[str]] = {}
def __init__(self, errors: Dict[str, str or Dict[str, Any]]):
super().__init__()
self.errors = {}
for field, errors in errors.items():
if isinstance(errors, str):
self.errors[field] = [errors]
elif isinstance(errors, dict):
self.errors[field] = list(errors.keys())
def to_dict(self) -> Dict[str, str or List[str]]:
data = super().to_dict()
data['errors'] = self.errors
return data
class InvalidSearchQuery(SamsException):
"""Raised when an invalid ElasticSearch query was received"""
app_code = '04002'
http_code = 400
description = 'Invalid search query'
log_exception = True
class AuthNotSupplied(SamsException):
"""Raised when authentication failed"""
app_code = '04003'
http_code = 401
description = 'Please provide proper credentials'
class SamsStorageDestinationErrors:
class NotFound(SamsException):
"""Raised when the ``StorageDestination`` could not be found"""
app_code = '05001'
http_code = 404
description = 'Destination "{destination_id}" not registered with the system'
def __init__(self, destination_id: str, exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__({'destination_id': destination_id}, exception)
class SamsStorageProviderErrors:
class NotFound(SamsException):
"""Raised when the ``StorageProvider`` could not be found"""
app_code = '06001'
http_code = 404
description = 'Provider "{provider_id}" not registered with the system'
def __init__(self, provider_id: str, exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__({'provider_id': provider_id}, exception)
class SamsSetErrors:
class InvalidStateTransition(SamsException):
"""Raised when attempting to convert an active Set back to ``draft``"""
app_code = '07001'
http_code = 400
description = 'Cannot change state from "{state}" to draft'
def __init__(self, state: str, exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__({'state': state}, exception)
class DestinationChangeNotAllowed(SamsException):
"""Raised when attempting to change the ``StorageDestination`` of an active Set"""
app_code = '07002'
http_code = 400
description = 'Destination can only be changed in draft state'
class DestinationConfigChangeNotAllowed(SamsException):
"""Raised when attempting to change the ``StorageDestination`` config of an active Set"""
app_code = '07003'
http_code = 400
description = 'Destination config can only be changed in draft state'
class DestinationNotFound(SamsException):
"""Raised when the ``StorageDestination`` could not be found"""
app_code = '07004'
http_code = 400
description = 'Destination "{destination_id}" isnt configured'
def __init__(self, destination_id: str, exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__({'destination_id': destination_id}, exception)
class CannotDeleteActiveSet(SamsException):
"""Raised when attempting to delete an active Set or Inactive Set with Assets"""
app_code = '07005'
http_code = 400
description = 'Can only delete Sets that are in draft state or disabled with no assets'
class SetNotFound(SamsException):
"""Raised when a Set cannot be found"""
app_code = '07006'
http_code = 400
description = 'Set with id {set_id} not found'
def __init__(self, set_id: ObjectId, exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__({'set_id': str(set_id)}, exception)
class SamsAssetErrors:
class BinaryNotSupplied(SamsException):
"""Raised when attempting to create a new Asset without an associated binary data"""
app_code = '08001'
http_code = 400
description = 'Asset must contain a binary to upload'
class AssetNotFound(SamsException):
"""Raised when attempting to download the binary of a non-existent Asset"""
app_code = '08002'
http_code = 404
description = 'Asset with id "{asset_id}" not found'
def __init__(self, asset_id: Union[ObjectId, str], exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__({'asset_id': str(asset_id)}, exception)
class AssetUploadToInactiveSet(SamsException):
"""Raised when attempting to create a new Asset into an inactive set"""
app_code = '08003'
http_code = 400
description = 'Asset upload is not allowed to an inactive Set'
class AssetExceedsMaximumSizeForSet(SamsException):
"""Raised when an Asset size exceeds the configured max size of a Set"""
app_code = '08004'
http_code = 400
description = 'Asset size ({asset_size}) exceeds the maximum size for the Set ({max_size})'
def __init__(self, asset_size: int, max_size: int):
super().__init__({
'asset_size': bytes_to_human_readable(asset_size),
'max_size': bytes_to_human_readable(max_size),
})
class ExternalUserIdNotFound(SamsException):
"""Raised when attempting to create/update Asset without External User Id"""
app_code = '08005'
http_code = 400
description = 'External User ID not found'
class ExternalSessionIdNotFound(SamsException):
"""Raised when attempting to create/update Asset without External Session Id"""
app_code = '08006'
http_code = 400
description = 'External Session ID not found'
class ExternalUserIdDoNotMatch(SamsException):
"""Raised when attempting to create/update Asset with different External User Id"""
app_code = '08007'
http_code = 400
description = 'External User ID does not match'
class ExternalSessionIdDoNotMatch(SamsException):
"""Raised when attempting to create/update Asset with different External Session Id"""
app_code = '08008'
http_code = 400
description = 'External Session ID does not match'
class LockingAssetLocked(SamsException):
"""Raised when attempting to lock an already locked asset"""
app_code = '08009'
http_code = 400
description = 'Can not Lock asset which is already locked'
class UnlockingAssetUnlocked(SamsException):
"""Raised when attempting to unlock an already unlocked asset"""
app_code = '08010'
http_code = 400
description = 'Can not Unlock asset which is already unlocked'
class SamsAmazonS3Errors:
class InvalidAmazonEndpoint(SamsException):
"""Raised when an invalid config is provided"""
app_code = '09001'
http_code = 500
description = 'Invalid Amazon URL'
class InvalidAccessKeyId(SamsException):
"""Raised when an invalid access key id was provided"""
app_code = '09002'
http_code = 500
description = 'Invalid AccessKeyId provided'
class InvalidSecret(SamsException):
"""Raised when an invalid access key id was provided"""
app_code = '09003'
http_code = 500
description = 'Invalid Secret provided'
class MissingAmazonConfig(SamsException):
"""Raised when the config is missing a required field"""
app_code = '09004'
http_code = 500
description = 'Required Amazon config "{key}" missing'
def __init__(self, key: str, exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__({'key': key}, exception)
class InvalidAmazonDestinationConfig(SamsException):
"""Raised when Amazon destination config string was provided"""
app_code = '09005'
http_code = 500
description = 'Invalid Amazon destination config "{config}". Error: {error}'
def __init__(self, config: str, exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__({'config': config, 'error': str(exception)}, exception)
class BucketNotFound(SamsException):
"""Raised when the configured bucket does not exist"""
app_code = '09006'
http_code = 500
description = 'Amazon bucket "{bucket}" not found'
def __init__(self, bucket: str, exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__({'bucket': bucket}, exception)
class BucketAlreadyExists(SamsException):
"""Raised when attempting to create a bucket that already exists"""
app_code = '09007'
http_code = 400
description = 'Amazon bucket "{bucket}" already exists'
def __init__(self, bucket: str, exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__({'bucket': bucket}, exception)
class InvalidBucketName(SamsException):
"""Raised when using an invalid AWS Bucket name"""
app_code = '09008'
http_code = 500
description = 'Invalid Amazon bucket name "{bucket}"'
def __init__(self, bucket: str, exception: Exception = None):
super().__init__({'bucket': bucket}, exception)
class UnknownAmazonException(SamsException):
"""Raised when an unknown Amazon error was raised"""
app_code = '09999'
http_code = 500
description = 'Unknown Amazon error: {error}'
def __init__(self, exception: Exception):
super().__init__({'error': str(exception)}, exception)
class SamsAssetImageErrors:
class RenditionDimensionsNotProvided(SamsException):
"""Raised when an Image Rendition is requested without supplying a width and/or height"""
app_code = '10001'
http_code = 400
description = 'Image Rendition requested without supplying a width and/or height'
|
/sams-client-0.3.2.tar.gz/sams-client-0.3.2/sams_client/errors.py
| 0.894654 | 0.214362 |
errors.py
|
pypi
|
from typing import Dict, Any, List
from requests import Response
from superdesk.default_settings import env
import sams_client.default_settings as default_config
from .constants import DEFAULT_HOST, DEFAULT_PORT, DEFAULT_PROTOCOL
not_analyzed = {'type': 'string', 'index': 'not_analyzed'}
def load_config(config: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, str]:
"""Load host, port from config
:param dict config: Dictionary of configuration provided
:rtype: dict
:return: A dictionary containing base_url, auth_type and auth_key
"""
host = config.get('HOST', DEFAULT_HOST)
port = config.get('PORT', DEFAULT_PORT)
return {
'base_url': f'{DEFAULT_PROTOCOL}://{host}:{port}',
'auth_type': config.get(
'SAMS_AUTH_TYPE', default_config.SAMS_AUTH_TYPE
),
'auth_key': config.get(
'SAMS_AUTH_KEY', env('SAMS_AUTH_KEY', '')
)
}
def schema_relation(
resource: str,
embeddable: bool = True,
required: bool = False,
data_type: str = 'objectid',
nullable: bool = False,
readonly: bool = False
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Creates an Eve/Cerberus relation attribute
This is copied from superdesk.resource.rel so that we don't have to
import Superdesk-Core for the sams_client library
:param str resource: The name of the resource
:param bool embeddable: If the relation can be embedded when fetching
:param bool required: If this relation is required, for validation purposes
:param str data_type: The data type to apply to the schema, defaults to 'objectid'
:param bool nullable: If this relation can have a ``null`` value
:param bool readonly: If this relation is read-only
:return: A dictionary to apply to a Resource schema
:rtype: dict
"""
return {
'type': data_type,
'required': required,
'nullable': nullable,
'readonly': readonly,
'data_relation': {
'resource': resource,
'field': '_id',
'embeddable': embeddable
},
'mapping': {'type': 'keyword'},
}
def bytes_to_human_readable(size: int) -> str:
"""Converts size in bytes to a human readable string
Converts the integer provided into one of the following:
* ``'x bytes'``
* ``'x.yy KB'`` (to 2 decimal places)
* ``'x.yy MB'`` (to 2 decimal places)
:param int size: Size in bytes to convert
:return: A human readable string
:rtype: int
"""
if size < 1024:
return f'{size} bytes'
elif size < 1048576:
return f'{size / 1024:.2f} KB'
else:
return f'{size / 1048576:.2f} MB'
def get_aggregation_buckets(response: Response, bucket_name: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""Utility function to get aggregation buckets
:param requests.Response response: The response object from the API call
:param str bucket_name: The name of the bucket to retrieve
:return: The list of buckets from the aggregation query
:rtype: list
"""
json = response.json()
return ((json.get('_aggregations') or {}).get(bucket_name) or {}).get('buckets') or []
|
/sams-client-0.3.2.tar.gz/sams-client-0.3.2/sams_client/utils.py
| 0.896546 | 0.183685 |
utils.py
|
pypi
|
from typing import NamedTuple, List, Dict, Any, Union
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from datetime import datetime
from bson import ObjectId
from sams_client.utils import schema_relation, not_analyzed
class AssetStates(NamedTuple):
"""Named tuple for Asset states
The state of an *Asset* defines the available actions on it.
An *Asset* can be in any one of the following states:
"""
#: Marks an Asset as not ready for use
DRAFT: str
#: Marks an Asset for internal use only
INTERNAL: str
#: Marks an Asset for public consumption
PUBLIC: str
#: Asset states
ASSET_STATES: AssetStates = AssetStates('draft', 'internal', 'public')
class IAssetTag(TypedDict):
"""Tags that can be associated with an Asset"""
#: String representing the unique id for this Tag
code: str
#: A human readable string for the Tag
name: str
class IAssetRenditionArgs(TypedDict):
"""Arguments used when requesting a rendition to be created
.. versionadded:: 0.3.0
"""
#: Width of the image rendition
width: int
#: Height of the image rendition
height: int
#: Keep image's original aspect ratio
keep_proportions: bool
class IAssetRendition(TypedDict):
"""Asset rendition metadata
.. versionadded:: 0.3.0
"""
# Name of this rendition
name: str
#: Internal media id (used by StorageProvider)
_media_id: str
#: Actual width of the image rendition
width: int
#: Actual height of the image rendition
height: int
#: Parameters used when this rendition was created
params: IAssetRenditionArgs
#: Date/time this rendition was created
versioncreated: datetime
#: Generated filename of this rendition
filename: str
#: Storage size of this rendition
length: int
class IAsset(TypedDict):
"""Asset metadata"""
#: Globally unique id, generated automatically by the system
_id: Union[ObjectId, str]
#: Globally unique id for the asset binary. This ID is generated by the StorageProvider
_media_id: str
#: A field to store the id of the user who uploaded the asset
#:
#: .. versionadded:: 0.2.0
original_creator: str
#: A field to store the id of the user who updated the asset
#:
#: .. versionadded:: 0.2.0
version_creator: str
#: A field to store time, when asset is created
#:
#: .. versionadded:: 0.2.0
firstcreated: datetime
#: A field to store time, when asset is updated
#:
#: .. versionadded:: 0.2.0
versioncreated: datetime
#: An auto-incrementing version field
_version: int
#: The ID of the Set where the Asset is to be stored
set_id: ObjectId
#: An optional ID of a parent Asset
parent_id: ObjectId
#: The state of the Asset (defaults to ``draft``). Can be one of ``draft``, ``internal`` or ``public``
state: str
#: The file name of the Asset Binary
filename: str
#: The size in bytes of the Asset Binary (calculated by the service)
length: int
#: The mimetype of the Asset Binary (calculated by the service)
mimetype: str
#: A name to give to the Asset
name: str
#: A short description describing the Asset
description: str
#: A list of code/name combinations so Assets can be grouped together through tags
tags: List[IAssetTag]
#: An extra dictionary to store further information about the Asset
extra: Dict[str, Any]
#: A special case attribute containing the actual binary data to be uploaded.
#: This attribute will be removed from the metadata document before saving/updating
binary: ObjectId
#: If locked, ID of the external user who locked this asset
#:
#: .. versionadded:: 0.2.0
lock_user: str
#: If locked, ID of the exernal user session who locked this asset
#:
#: .. versionadded:: 0.2.0
lock_session: str
#: If locked, name of the action that for this lock (i.e. ``edit``)
#:
#: .. versionadded:: 0.2.0
lock_action: str
#: If locked, the date and time this asset was locked
#:
#: .. versionadded:: 0.2.0
lock_time: datetime
#: The list of renditions for this Asset (if it is an image)
#:
#: .. versionadded:: 0.3.0
renditions: List[IAssetRendition]
ASSET_SCHEMA = {
'_media_id': {
'type': 'string',
'mapping': not_analyzed
},
'original_creator': {
'type': 'string',
'mapping': not_analyzed
},
'version_creator': {
'type': 'string',
'mapping': not_analyzed
},
'firstcreated': {
'type': 'datetime'
},
'versioncreated': {
'type': 'datetime'
},
'_version': {
'type': 'number'
},
'set_id': schema_relation('sets', required=True),
'parent_id': schema_relation('assets'),
'state': {
'type': 'string',
'allowed': tuple(ASSET_STATES),
'default': ASSET_STATES.DRAFT,
'nullable': False,
'mapping': not_analyzed
},
'filename': {
'type': 'string',
'required': True,
'mapping': {
'type': 'text',
# Use the `filename_analyzer` to tokenize filenames
# i.e. tokenizes
# `bbb_0001.png`
# to
# [`bbb`, `0001`, `png`]
'analyzer': 'filename_analyzer',
'search_analyzer': 'filename_analyzer',
# Keep field data in case we need aggregations
# on each token, otherwise aggregate against `filename.keyword`
'fielddata': True,
# Add subtype `keyword` so that we can sort by `name`
'fields': {
'keyword': {
'type': 'keyword',
'ignore_above': 256
}
}
}
},
'length': {
'type': 'integer',
'mapping': {
'type': 'long'
}
},
'mimetype': {
'type': 'string',
'mapping': not_analyzed
},
'name': {
'type': 'string',
'required': True,
'nullable': False,
'empty': False,
'mapping': {
'type': 'text',
# Use the `filename_analyzer` to tokenize names
# i.e. tokenizes
# `bbb_0001.png`
# to
# [`bbb`, `0001`, `png`]
'analyzer': 'filename_analyzer',
'search_analyzer': 'filename_analyzer',
# Keep field data in case we need aggregations
# on each token, otherwise aggregate against `name.keyword`
'fielddata': True,
# Add subtype `keyword` so that we can sort by `name`
'fields': {
'keyword': {
'type': 'keyword',
'ignore_above': 256
}
}
}
},
'description': {
'type': 'string'
},
'tags': {
'type': 'list',
'nullable': True,
'schema': {
'type': 'dict',
'schema': {
'code': {
'type': 'string',
'required': True,
'mapping': not_analyzed
},
'name': {
'type': 'string',
'required': True,
'mapping': not_analyzed
}
}
},
},
'renditions': {
'type': 'list',
'mapping': {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'name': {'type': 'string'},
'_media_id': {
'type': 'string',
'index': 'not_analyzed',
},
'width': {'type': 'integer'},
'height': {'type': 'integer'},
'params': {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'width': {'type': 'integer'},
'height': {'type': 'integer'},
'keep_proportions': {'type': 'boolean'},
},
},
'versioncreated': {'type': 'date'},
'filename': {'type': 'string'},
'length': {'type': 'long'},
}
}
},
'extra': {
'type': 'dict',
'schema': {},
'allow_unknown': True
},
'binary': {
'type': 'media',
'mapping': not_analyzed
},
'lock_user': {
'type': 'string',
'mapping': not_analyzed,
'required': False,
'nullable': True,
'empty': True
},
'lock_session': {
'type': 'string',
'mapping': not_analyzed,
'required': False,
'nullable': True,
'empty': True
},
'lock_action': {
'type': 'string',
'mapping': not_analyzed,
'required': False,
'nullable': True,
'empty': True
},
'lock_time': {
'type': 'datetime',
'required': False,
'nullable': True,
'empty': True
}
}
|
/sams-client-0.3.2.tar.gz/sams-client-0.3.2/sams_client/schemas/assets.py
| 0.92948 | 0.339992 |
assets.py
|
pypi
|
from typing import NamedTuple
#: Set states
class SetStates(NamedTuple):
DRAFT: str
USABLE: str
DISABLED: str
SET_STATES: SetStates = SetStates('draft', 'usable', 'disabled')
"""
The state of a *Set* defines the available actions on it. \
A *Set* can be in any one of the following states:
* **DRAFT:** allows the administrator to configure the *Set* \
with the correct ``destination_name`` and ``destination_config``.
* ``destination_name`` can be changed
* ``destination_config`` can be changed
* The *Set* can be deleted
* *Assets* **cannot** be uploaded to it
* *Assets* **cannot** be downloaded from it
* **USABLE:** Once the administrator has completed configuring \
the *Set*, they will change the ``state`` to ``usable``. This \
means ``producers`` can now upload *Assets* to the *Set*.
* ``destination_name`` **cannot** be changed
* ``destination_config`` **cannot** be changed
* The *Set* **cannot** be deleted
* The ``state`` can only be changed to ``disabled``
* *Assets* can be uploaded to it
* *Assets* can be downloaded from it
* **DISABLED:** The administrator is able to change a *Set* to \
be in disabled, so ``producers`` are unable to add new *Assets* to it.
* ``destination_name`` **cannot** be changed
* ``destination_config`` **cannot** be changed
* The *Set* **cannot** be deleted
* The ``state`` can only be changed to ``usable``
* *Assets* **cannot** be uploaded to it
* *Assets* can be downloaded from it
.. note::
The attributes ``destination_name`` and ``destination_config`` \
are read-only when the ``state`` is ``usable`` or ``disabled``.\
This is because the system would have to move *Assets* to \
the new destination, which would be better suited to a migrate endpoint.
"""
SET_SCHEMA = {
'name': {
'type': 'string',
'required': True,
'nullable': False,
'empty': False,
'unique': True
},
'state': {
'type': 'string',
'allowed': tuple(SET_STATES),
'default': SET_STATES.DRAFT,
'nullable': False
},
'description': {
'type': 'string'
},
'destination_name': {
'type': 'string',
'required': True
},
'destination_config': {
'type': 'dict',
'schema': {},
'allow_unknown': True,
},
'maximum_asset_size': {
'type': 'integer',
'mapping': {
'type': 'long'
}
},
'original_creator': {
'type': 'string'
},
'version_creator': {
'type': 'string'
},
'firstcreated': {
'type': 'datetime',
},
'versioncreated': {
'type': 'datetime',
}
}
"""
**Set Schema** =
``_id`` *bson.objectid.ObjectId*
Globally unique id, generated automatically by the system.
``state`` *SET_STATE* (:mod:`sams_client.schemas.sets.SET_STATES`)
The state of the Set. One of ``draft``, ``usable``, or ``disabled``.
``name`` *string*
Unique name for the Set
``description`` *string*
A short description on what this set is designated for
``destination_name`` *string*
The name of a registered StorageDestination (:mod:`sams.storage.destinations`)
``destination_config`` *dict*
A dictionary containing the configuration options for the specific destination used
``maximum_asset_size`` *long*
The maximum size of an Asset that can be uploaded to this Set (optional)
``original_creator`` *string*
A field to store the id of the user who created the set
``version_creator`` *string*
A field to store the id of the user who updated the set
``firstcreated`` *string*
A field to store time, when set is created
``versioncreated`` *string*
A field to store time, when set is updated
"""
|
/sams-client-0.3.2.tar.gz/sams-client-0.3.2/sams_client/schemas/sets.py
| 0.889096 | 0.576989 |
sets.py
|
pypi
|
from typing import Dict, Any, Callable, Union, Optional
from bson import ObjectId
import requests
class SamsImagesEndpoint:
"""Helper class for Image Assets"""
_download_image_url = '/consume/assets/images'
_generate_image_rendition_url = '/produce/assets/images'
def __init__(self, client):
# Placing this import at the top of the file causes a cyclic import
# so placing it here to have strong type / autocomplete
from sams_client import SamsClient
self._client: SamsClient = client
def download(
self,
item_id: Union[ObjectId, str],
width: Optional[int] = None,
height: Optional[int] = None,
keep_proportions: Optional[bool] = True,
headers: Dict[str, Any] = None,
callback: Callable[[requests.Response], requests.Response] = None
) -> requests.Response:
r"""Download an Image, optionally providing image dimensions
:param str item_id: The Asset ID
:param int width: Desired image width (optional)
:param int height: Desired image height (optional)
:param bool keep_proportions: If `true`, keeps image width/height ratio
:param dict headers: Dictionary of headers to apply
:param callback: A callback function to manipulate the response
:rtype: requests.Response
:return: The Asset binary, optionally resized
"""
params = {}
if width:
params['width'] = width
if height:
params['height'] = height
if keep_proportions:
params['keep_proportions'] = keep_proportions
return self._client.get(
url=f'{self._download_image_url}/{item_id}',
params=params,
headers=headers,
callback=callback
)
def generate_rendition(
self,
item_id: Union[ObjectId, str],
width: Optional[int] = None,
height: Optional[int] = None,
keep_proportions: Optional[bool] = True,
name: Optional[str] = None,
headers: Dict[str, Any] = None,
callback: Callable[[requests.Response], requests.Response] = None
) -> requests.Response:
r"""Generates an Image rendition
:param str item_id: The Asset ID
:param int width: Desired image width (optional)
:param int height: Desired image height (optional)
:param bool keep_proportions: If `true`, keeps image width/height ratio
:param dict headers: Dictionary of headers to apply
:param callback: A callback function to manipulate the response
:rtype: requests.Response
:return: 200 status code if rendition generated successfully
"""
params = {}
if name:
params['name'] = name
if width:
params['width'] = width
if height:
params['height'] = height
if keep_proportions:
params['keep_proportions'] = keep_proportions
return self._client.post(
url=f'{self._generate_image_rendition_url}/{item_id}',
params=params,
headers=headers,
callback=callback
)
|
/sams-client-0.3.2.tar.gz/sams-client-0.3.2/sams_client/endpoints/images.py
| 0.945311 | 0.170992 |
images.py
|
pypi
|
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from .Generaldistribution import Distribution
class Gaussian(Distribution):
""" Gaussian distribution class for calculating and
visualizing a Gaussian distribution.
Attributes:
mean (float) representing the mean value of the distribution
stdev (float) representing the standard deviation of the distribution
data_list (list of floats) a list of floats extracted from the data file
"""
def __init__(self, mu=0, sigma=1):
Distribution.__init__(self, mu, sigma)
def calculate_mean(self):
"""Function to calculate the mean of the data set.
Args:
None
Returns:
float: mean of the data set
"""
avg = 1.0 * sum(self.data) / len(self.data)
self.mean = avg
return self.mean
def calculate_stdev(self, sample=True):
"""Function to calculate the standard deviation of the data set.
Args:
sample (bool): whether the data represents a sample or population
Returns:
float: standard deviation of the data set
"""
if sample:
n = len(self.data) - 1
else:
n = len(self.data)
mean = self.calculate_mean()
sigma = 0
for d in self.data:
sigma += (d - mean) ** 2
sigma = math.sqrt(sigma / n)
self.stdev = sigma
return self.stdev
def plot_histogram(self):
"""Function to output a histogram of the instance variable data using
matplotlib pyplot library.
Args:
None
Returns:
None
"""
plt.hist(self.data)
plt.title('Histogram of Data')
plt.xlabel('data')
plt.ylabel('count')
def pdf(self, x):
"""Probability density function calculator for the gaussian distribution.
Args:
x (float): point for calculating the probability density function
Returns:
float: probability density function output
"""
return (1.0 / (self.stdev * math.sqrt(2*math.pi))) * math.exp(-0.5*((x - self.mean) / self.stdev) ** 2)
def plot_histogram_pdf(self, n_spaces = 50):
"""Function to plot the normalized histogram of the data and a plot of the
probability density function along the same range
Args:
n_spaces (int): number of data points
Returns:
list: x values for the pdf plot
list: y values for the pdf plot
"""
mu = self.mean
sigma = self.stdev
min_range = min(self.data)
max_range = max(self.data)
# calculates the interval between x values
interval = 1.0 * (max_range - min_range) / n_spaces
x = []
y = []
# calculate the x values to visualize
for i in range(n_spaces):
tmp = min_range + interval*i
x.append(tmp)
y.append(self.pdf(tmp))
# make the plots
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2,sharex=True)
fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=.5)
axes[0].hist(self.data, density=True)
axes[0].set_title('Normed Histogram of Data')
axes[0].set_ylabel('Density')
axes[1].plot(x, y)
axes[1].set_title('Normal Distribution for \n Sample Mean and Sample Standard Deviation')
axes[0].set_ylabel('Density')
plt.show()
return x, y
def __add__(self, other):
"""Function to add together two Gaussian distributions
Args:
other (Gaussian): Gaussian instance
Returns:
Gaussian: Gaussian distribution
"""
result = Gaussian()
result.mean = self.mean + other.mean
result.stdev = math.sqrt(self.stdev ** 2 + other.stdev ** 2)
return result
def __repr__(self):
"""Function to output the characteristics of the Gaussian instance
Args:
None
Returns:
string: characteristics of the Gaussian
"""
return "mean {}, standard deviation {}".format(self.mean, self.stdev)
|
/sams_dsnd_probability-1.2.tar.gz/sams_dsnd_probability-1.2/sams_dsnd_probability/Gaussiandistribution.py
| 0.688364 | 0.853058 |
Gaussiandistribution.py
|
pypi
|
from typing import Dict, List, Any
from eve.utils import ParsedRequest
from flask import json
from bson import ObjectId
from pymongo.cursor import Cursor as MongoCursor
from eve_elastic.elastic import ElasticCursor
from superdesk.services import BaseService
from sams_client.errors import SamsSystemErrors
from sams.factory.service import SamsService
class SamsApiService(SamsService):
"""Sams API Service
Base service for external API endpoints that proxy requests to internal services.
:var BaseService service: The service to proxy requests to
"""
def __init__(self, service: BaseService):
self.service: BaseService = service
super().__init__()
def _remove_system_attributes(self, doc: Dict[str, Any]):
"""Removes system attributes from the document
This will remove ``_created``, ``_updated`` and ``_etag``. The attached
internal service will be in charge of populating these attributes
:param dict doc: The document to strip system attributes from
"""
doc.pop('_created', None)
doc.pop('_updated', None)
doc.pop('_etag', None)
def create(self, docs: List[Dict[str, Any]], **kwargs) -> List[ObjectId]:
"""Proxy method to create a new document
Removes system attributes using :meth:`_remove_system_attributes`.
Then passes the request to the :meth:`sams.factory.service.SamsService.post`
method of the underlying service.
:param list[dict] docs: The list of documents to be created
:param dict kwargs: Extra arguments to pass onto the underlying service
:rtype: list[bson.objectid.ObjectId]
:return: list og generated IDs for the new documents
"""
for doc in docs:
self._remove_system_attributes(doc)
return self.service.post(docs, **kwargs)
def update(self, id: ObjectId, updates: Dict[str, Any], original: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Proxy method to update an existing document
Removes system attributes using :meth:`_remove_system_attributes`.
Then passes the request to the :meth:`sams.factory.service.SamsService.patch`
method of the underlying service
:param bson.objectid.ObjectId id: ID for the document
:param dict updates: Dictionary containing the desired attributes to update
:param dict original: Dictionary containing the original document
:rtype: dict
:return: dictionary containing the updated attributes of the document
"""
self._remove_system_attributes(updates)
return self.service.patch(id, updates)
def system_update(self, id: ObjectId, updates: Dict[str, Any], original: Dict[str, any]):
"""Not to be used with API Service
:raises superdesk.errors.SuperdeskApiError:
"""
raise SamsSystemErrors.SystemUpdateNotAllowed()
def replace(self, id: ObjectId, document: Dict[str, Any], original: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Replaces an existing document with a new one
Passes the request to the :meth:`sams.factory.service.SamsService.replace` method.
:param bson.objectid.ObjectId id: ID of the document to replace
:param dict document: Dictionary containing the original document
:param dict original: Dictionary containing the new document
:rtype: dict
:return: dictionary containing the new document
"""
return self.service.replace(id, document, original)
def delete(self, lookup: Dict[str, Any]):
"""Deletes documents based on a lookup query
Passes the request to the :meth:`sams.factory.service.SamsService.delete` method.
:param dict lookup: Lookup used to determine what documents to delete
:return: The response of the delete action
"""
return self.service.delete_action(lookup)
def delete_ids_from_mongo(self, ids: List[ObjectId]):
"""Deletes documents in mongo based on their IDs
Passes the request to the :meth:`sams.factory.service.SamsService.delete_ids_from_mongo` method.
:param list[bson.objectid.ObjectId] ids: The list of IDs to delete
:return: The response of the delete action
"""
return self.service.delete_ids_from_mongo(ids)
def delete_docs(self, docs: List[Dict[str, Any]]):
"""Deletes documents
Passes the request to the :meth:`sams.factory.service.SamsService.delete_docs` method.
:param list[dict] docs: The list of documents to delete
:return: The response of the delete action
"""
return self.service.delete_docs(docs)
def find_one(self, req: ParsedRequest, **lookup) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Finds a single document based on request and lookup args
Passes the request to the :meth:`sams.factory.service.SamsService.find_one` method.
:param eve.utils.ParsedRequest req: The request object
:param dict lookup: Dictionary containing optional lookup arguments
:rtype: dict
:return: The document if found
"""
return self.service.find_one(req=req, **lookup)
def find(self, where: Dict[str, Any], **kwargs) -> MongoCursor or ElasticCursor:
"""Find documents using the provided query arguments
Passes the request to the :meth:`sams.factory.service.SamsService.find` method.
:param dict where: Dictionary containing query parameters
:param dict kwargs: Dictionary containing optional lookup arguments
:rtype: pymongo.cursor.MongoCursor | eve_elastic.elastic.ElasticCursor
:return: A Mongo or Elastic cursor with the results
"""
return self.service.find(where, **kwargs)
def get(self, req: ParsedRequest, lookup: Dict[str, Any]):
"""Find documents using the provided query arguments
Passes the request to the :meth:`sams.factory.service.SamsService.get` method;
:param eve.utils.ParsedRequest req: The request object
:param dict lookup: Dictionary containing optional lookup arguments
:rtype: pymongo.cursor.MongoCursor | eve_elastic.elastic.ElasticCursor
:return: A Mongo or Elastic cursor with the results
"""
if req is None:
req = ParsedRequest()
return self.service.get(req=req, lookup=lookup)
def get_from_mongo(
self,
req: ParsedRequest,
lookup: Dict[str, Any],
projection: Dict[str, Any] = None
) -> MongoCursor:
"""Find documents using MongoDB.
Passes the request to the :meth:`sams.factory.service.SamsService.get_from_mongo` method.
:param eve.utils.ParsedRequest req: The request object
:param dict lookup: Dictionary containing optional lookup arguments
:param dict projection: Dictionary containing optional projection
:rtype: pymongo.cursor.MongoCursor
:return: A Mongo cursor with the results
"""
if req is None:
req = ParsedRequest()
if not req.projection and projection:
req.projection = json.dumps(projection)
return self.service.get_from_mongo(req=req, lookup=lookup)
def find_and_modify(self, **kwargs):
"""Find and modify documents
Passes the request to the :meth:`sams.factory.service.SamsService.find_and_modify` method.
:param kwargs:
:return: The response of the request
"""
return self.service.find_and_modify(**kwargs)
def search(self, source: Dict[str, Any]) -> ElasticCursor:
"""Find documents using Elasticsearch
Passes the request to the :meth:`sams.factory.service.SamsService.search` method.
:param dict source: The source query to pass to Elasticsearch
:rtype: ElasticCursor
:return: An Elasticsearch cursor with the results
"""
return self.service.search(source)
def remove_from_search(self, item: Dict[str, Any]):
"""Removes a document from Elasticsearch only
Passes the request to the :meth:`sams.factory.service.SamsService.remove_from_search` method.
:param dict item: The document to remove
"""
return self.service.remove_from_search(item)
|
/sams-server-0.3.2.tar.gz/sams-server-0.3.2/sams/api/service.py
| 0.892281 | 0.340814 |
service.py
|
pypi
|
from typing import Dict, List
from sams_client.errors import SamsStorageDestinationErrors
from .providers import Provider, providers
from .providers.base import SamsBaseStorageProvider
class Destination:
"""A Destination instance
:var str config_string: A string from any ``STORAGE_DESTINATION`` config attribute
:var list[str] entries: The entries as provided by the ``config_string``
:var str name: The name of the destination
:var str provider_name: The name of the provider
:var Provider provider: The provider instance
:var str config: The config part from the ``entries``
"""
def __init__(self, config_str: str):
"""Initialise a new Destination instance
:param str config_str: The config string from settings.py
"""
self.config_string: str = config_str
self.entries: List[str] = self.config_string.split(',', 2)
self.name: str = self.entries[1]
self.provider_name: str = self.entries[0]
self.config: str = self.entries[2]
self.provider: Provider = providers.get(self.provider_name)
def provider_instance(self) -> SamsBaseStorageProvider:
"""Retrieve the Storage instance for this destination
:return: An Storage Provider instance
:rtype: SamsBaseStorageProvider
"""
return self.provider.instance(self.config_string)
def to_dict(self):
"""Return a dictionary containing name and provider
:return: A dictionary containing name and provider_name of destination
:rtype: dict
"""
return {
'_id': self.name,
'provider': self.provider_name
}
class Destinations:
"""A mechanism to register storage destinations with the system
This is used when bootstrapping the application to register storage
destinations from strings in the config.
Usage::
from sams.storage.destinations import destinations
destinations.register(...)
destinations.get(...)
destinations.exists(...)
destinations.all(...)
destinations.clear(...)
"""
def __init__(self):
self._destinations: Dict[str, Destination] = dict()
def register(self, config_string: str):
"""Register a storage destination with the system
:param str config_string: A string from any ``STORAGE_DESTINATION`` config attribute
"""
destination = Destination(config_string)
self._destinations[destination.name] = destination
def get(self, name: str) -> Destination:
"""Retrieve a registered storage destination by it's name
:param str name: The name of the storage destination
:return: Returns the Destination instance
:rtype: Destination
:raises sams_client.errors.SamsStorageDestinationErrors.NotFound: if the destination is not found
"""
try:
return self._destinations[name]
except KeyError:
raise SamsStorageDestinationErrors.NotFound(name)
def exists(self, name: str) -> bool:
"""Check if a storage destination with ``name`` exists
:param str name: The name of the storage destination
:returns: ``True`` if the destination exists, ``False`` if not
"""
return name in self._destinations.keys()
def all(self) -> Dict[str, Destination]:
"""Returns all the registered storage destinations"""
return self._destinations
def clear(self):
"""Clears all of the registered storage destinations"""
self._destinations = {}
destinations = Destinations()
|
/sams-server-0.3.2.tar.gz/sams-server-0.3.2/sams/storage/destinations.py
| 0.920812 | 0.280696 |
destinations.py
|
pypi
|
from typing import Union, BinaryIO
from bson import ObjectId
from superdesk.storage.superdesk_file import SuperdeskFile
from sams_client.errors import SamsConfigErrors
class SamsBaseStorageProvider(object):
"""An instance of SamsBaseStorageProvider
"""
type_name: str = None
name: str = None
config_string: str = None
def __init__(self, config_string: str):
"""Creates a new instance of :class:`SamsBaseStorageProvider`.
This is the base class that storage implementations must inherit from.
:param str config_string: A string from any ``STORAGE_DESTINATION`` config attribute
"""
self.process_config_string(config_string)
def process_config_string(self, config_string: str):
"""Extract relevant information from the provided ``config_string``
:param str config_string: A string from any ``STORAGE_DESTINATION`` config attribute
:raises ValueError: If there
"""
if config_string is None:
raise SamsConfigErrors.StorageProviderConfigStringNotProvided()
config_parts = config_string.split(',', 2)
if len(config_parts) != 3:
raise SamsConfigErrors.StorageProviderIncorrectConfigArguments(len(config_parts))
if config_parts[0] != self.type_name:
raise SamsConfigErrors.StorageProviderInvalidConfig(self.type_name, config_parts[0])
self.name = config_parts[1]
self.config_string = config_parts[2]
def exists(self, media_id: Union[ObjectId, str]) -> bool:
"""Checks if a file exists in the storage destination
This method *must* be defined in the derived class
:param media_id: The ID of the asset
:return: ``True`` if a matching file exists, ``False`` otherwise
:raises NotImplementedError: If not defined in derived class
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
def put(self, content: Union[BinaryIO, str], filename: str, mimetype: str = None) -> str:
"""Upload a file to the storage destination
`content` must be an instance of :class:`bytes` or a file-like object
providing a :meth:`read` method.
This method *must* be defined in the derived class
:param bytes content: The data to be uploaded
:param str filename: The filename
:param str mimetype: The mimetype of the content
:return: The ``"id"`` of the created file
:raises NotImplementedError: If not defined in derived class
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
def get(self, media_id: Union[ObjectId, str]) -> SuperdeskFile:
"""Get an asset from the storage
This method *must* be defined in the derived class
:param media_id: The ID of the asset
:return:
:raises NotImplementedError: If not defined in derived class
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
def delete(self, media_id: Union[ObjectId, str]):
"""Delete as asset from the storage
This method *must* be defined in the derived class
:param media_id: The ID of the asset
:raises NotImplementedError: If not defined in derived class
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
def drop(self):
"""Deletes all assets from the storage
This method *must* be defined in the derived class
:raises NotImplementedError: If not defined in derived class
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
|
/sams-server-0.3.2.tar.gz/sams-server-0.3.2/sams/storage/providers/base.py
| 0.939955 | 0.183942 |
base.py
|
pypi
|
from typing import BinaryIO, Union
from pymongo import MongoClient
from gridfs import GridFS
from gridfs.errors import NoFile
from gridfs.grid_file import GridOut, EMPTY
from bson import ObjectId
from superdesk.storage.superdesk_file import SuperdeskFile
from .base import SamsBaseStorageProvider
from sams_client.errors import SamsAssetErrors
class GridfsFileWrapper(SuperdeskFile):
"""SuperdeskFile implementation for GridFS files"""
def __init__(self, gridfs_file: GridOut):
super().__init__()
blocksize = 65636
buf = gridfs_file.read(blocksize)
while buf != EMPTY:
self.write(buf)
buf = gridfs_file.read(blocksize)
self.seek(0)
self.content_type = gridfs_file.content_type
self.length = gridfs_file.length
self._name = gridfs_file.name
self.filename = gridfs_file.filename
self.metadata = gridfs_file.metadata
self.upload_date = gridfs_file.upload_date
self.md5 = gridfs_file.md5
self._id = gridfs_file._id
class MongoGridFSProvider(SamsBaseStorageProvider):
"""Provides storage to/from MongoDB GridFS
:var pymongo.mongo_client.MongoClient _client: A client connected to a MongoDB Database
:var gridfs.GridFS _fs: A client connected to a MongoDB GridFS Collection
:var str type_name: The type name used to identify this provider - ``MongoGridFS``
"""
type_name = 'MongoGridFS'
def __init__(self, config_string: str):
super(MongoGridFSProvider, self).__init__(config_string)
self._client: MongoClient = None
self._fs: GridFS = None
def fs(self) -> GridFS:
"""Returns the underlying GridFS client handle
:return: A GridFS client to the configured database/collection
:rtype: gridfs.GridFS
"""
if self._fs is None:
self._client = MongoClient(self.config_string)
self._fs = GridFS(self._client.get_database())
return self._fs
def exists(self, media_id: Union[ObjectId, str]) -> bool:
"""Checks if a file exists in the storage destination
:param bson.objectid.ObjectId media_id: The ID of the asset
:return: ``True`` if a matching file exists, ``False`` otherwise
:rtype: bool
"""
if isinstance(media_id, str):
media_id = ObjectId(media_id)
return self.fs().exists(media_id)
def put(self, content: Union[BinaryIO, bytes], filename: str, mimetype: str = None) -> str:
"""Upload a file to the storage destination
`content` must be an instance of :class:`bytes` or a file-like object
providing a :meth:`read` method.
:param bytes content: The data to be uploaded
:param str filename: The filename
:param str mimetype: The mimetype of the content (not used here)
:return: The ``"id"`` of the created file
:rtype: str
"""
media_id = self.fs().put(
content,
filename=filename
)
return str(media_id)
def get(self, media_id: Union[ObjectId, str]) -> GridfsFileWrapper:
"""Get an asset from the storage
:param bson.objectid.ObjectId media_id: The ID of the asset
:return: A file-like object providing a :meth:`read` method
:rtype: io.BytesIO
"""
if isinstance(media_id, str):
media_id = ObjectId(media_id)
try:
gridfs_file = self.fs().get(media_id)
if gridfs_file:
return GridfsFileWrapper(gridfs_file)
except NoFile:
raise SamsAssetErrors.AssetNotFound(media_id)
def delete(self, media_id: Union[ObjectId, str]):
"""Delete as asset from the storage
:param bson.objectid.ObjectId media_id: The ID of the asset
"""
if isinstance(media_id, str):
media_id = ObjectId(media_id)
self.fs().delete(media_id)
def drop(self):
"""Deletes all assets from the storage"""
self.fs()
self._client.get_database().drop_collection('fs.files')
self._client.get_database().drop_collection('fs.chunks')
|
/sams-server-0.3.2.tar.gz/sams-server-0.3.2/sams/storage/providers/mongo.py
| 0.923264 | 0.216229 |
mongo.py
|
pypi
|
from importlib import import_module
from typing import Dict, List, Type
from sams_client.errors import SamsStorageProviderErrors
from .base import SamsBaseStorageProvider
class Provider:
"""A Provider instance
:var str config_string: An entry from the ``STORAGE_PROVIDERS`` config attribute
:var list[str] entries: The entries as provided by the config string
:var str module_name: The name of the module, i.e. sams.storage.provider.mongo
:var str class_name: The name of the class, i.e. MongoGridFSProvider
:var module module: A reference to the loaded Python module
:var type[SamsBaseStorageProvider] klass: A reference to the loaded Python class
:var str type_name: The type_name as defined inside ``self.klass``
"""
def __init__(self, config_string: str):
"""Initialise a new Provider instance
:param str config_string: An entry from the ``STORAGE_PROVIDERS`` config attribute
"""
self.config_string: str = config_string
self.entries: List[str] = self.config_string.rsplit('.', 1)
self.module_name: str = self.entries[0]
self.class_name: str = self.entries[1]
self.module = import_module(self.module_name)
self.klass: Type[SamsBaseStorageProvider] = getattr(self.module, self.class_name)
self.type_name: str = getattr(self.klass, 'type_name')
def instance(self, config_string: str) -> SamsBaseStorageProvider:
"""Retrieve the StorageProvider instance for this provider
:param str config_string: A string from any ``STORAGE_DESTINATION`` config attribute
:return: A Storage Provider instance created from ``self.klass``,
passing in the provided ``config_str``
:rtype: SamsBaseStorageProvider
"""
return self.klass(config_string)
class Providers:
"""A mechanism to register storage providers with the system
This is used when bootstrapping the application to register storage
providers from strings in the config.
Usage::
from sams.storage.providers import providers
providers.register(...)
providers.get(...)
providers.exists(...)
providers.all(...)
providers.clear(...)
"""
def __init__(self):
self._providers: Dict[str, Provider] = dict()
def register(self, config_str: str):
"""Register a provider with the system
:param str config_str: The provider to add
"""
provider = Provider(config_str)
self._providers[provider.type_name] = provider
def get(self, name: str) -> Provider:
"""Retrieve a registered storage provider by it's name
:param str name: The name of the Provider
:return: Returns the Provider instance
:rtype: Provider
:raises sams_client.errors.SamsStorageProviderErrors.NotFound: if the provider is not found
"""
try:
return self._providers[name]
except KeyError:
raise SamsStorageProviderErrors.NotFound(name)
def exists(self, type_name: str) -> bool:
"""Check if a provider for the ``type_name`` exists
:param type_name: The type name
:returns: ``True`` if the provider is registered, ``False`` if not
"""
return type_name in self._providers.keys()
def all(self) -> Dict[str, Provider]:
"""Returns all the registered providers
"""
return self._providers
def clear(self):
"""Clears all of the registered providers
"""
self._providers = {}
providers = Providers()
|
/sams-server-0.3.2.tar.gz/sams-server-0.3.2/sams/storage/providers/__init__.py
| 0.83545 | 0.229352 |
__init__.py
|
pypi
|
from typing import Dict, Any, List
from copy import deepcopy
from bson import ObjectId
from flask import current_app as app
from sams_client.schemas import SET_STATES
from sams.factory.service import SamsService
from sams.storage.destinations import Destination, destinations
from sams.storage.providers.base import SamsBaseStorageProvider
from sams_client.errors import SamsSetErrors
from sams.utils import get_external_user_id
from superdesk.services import Service
from superdesk.utc import utcnow
class SetsService(SamsService):
def post(self, docs: List[Dict[str, Any]], **kwargs) -> List[ObjectId]:
"""Stores the metadata
:param docs: An array of metadata to create
:param kwargs: Dictionary containing the keyword arguments
:return: list of generated IDs for the new documents
:rtype: list[bson.objectid.ObjectId]
"""
for doc in docs:
doc['firstcreated'] = utcnow()
doc['versioncreated'] = utcnow()
external_user_id = get_external_user_id()
if external_user_id:
doc['original_creator'] = external_user_id
doc['version_creator'] = external_user_id
self.validate_post(doc)
return super(Service, self).post(docs, **kwargs)
def patch(self, item_id: ObjectId, updates: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Updates the metadata
:param bson.objectid.ObjectId item_id: ID for the Set
:param dict updates: Dictionary containing the desired metadata to update
:return: Dictionary containing the updated attributes of the Set
:rtype: dict
"""
original = self.get_by_id(item_id)
self.validate_patch(original, updates)
updates['versioncreated'] = utcnow()
external_user_id = get_external_user_id()
if external_user_id:
updates['version_creator'] = external_user_id
return super(Service, self).patch(item_id, updates)
def validate_post(self, doc):
"""Validates the Set on creation
The following additional validation is performed on Sets being created:
* The ``destination_name`` must exist in a ``STORAGE_DESTINATION_`` config attribute
:param doc: The provided document to validate
:raises Superdesk.validation.ValidationError: If there are validation errors
"""
super().validate_post(doc)
self._validate_destination_name(doc)
def validate_patch(self, original, updates):
r"""Validates the Set on update
The following additional validation is performed on Sets being updated:
* Once a set has changed from ``draft`` state, it can never return to ``draft``
* Once a set has changed from ``draft`` state, ``destination_name`` and \
``destination_config`` cannot be changed
* The ``destination_name`` must exist in a ``STORAGE_DESTINATION_`` config attribute
:param original: The original document from the database
:param updates: A dictionary with the desired attributes to update
:raises: Superdesk.validation.ValidationError: if there are validation errors
"""
super().validate_patch(original, updates)
merged = deepcopy(original)
merged.update(updates)
# Check that the state hasn't change from a usable/disabled state to draft
if original.get('state') != SET_STATES.DRAFT:
if merged.get('state') == SET_STATES.DRAFT:
raise SamsSetErrors.InvalidStateTransition(original['state'])
# Check that the destination name hasn't changed for non-draft Sets
if original.get('state') != SET_STATES.DRAFT:
if merged.get('destination_name') != original.get('destination_name'):
raise SamsSetErrors.DestinationChangeNotAllowed()
elif merged.get('destination_config') != original.get('destination_config'):
raise SamsSetErrors.DestinationConfigChangeNotAllowed()
self._validate_destination_name(merged)
def _validate_destination_name(self, doc):
"""Validates that the desired destination is configured in the system
:param doc: The provided document to validate
:raises Superdesk.validation.ValidationError: If there are validation errors
"""
if not destinations.exists(doc.get('destination_name')):
raise SamsSetErrors.DestinationNotFound(doc.get('destination_name'))
def on_delete(self, doc):
"""Validate state on delete
Sets can only be deleted from the system if they are in the state ``SET_STATES.DRAFT``.
:param doc: The Set to delete
:raises: Superdesk.validation.ValidationError: If the Set is not in ``SET_STATES.DRAFT`` state
"""
count = self.get_asset_count(doc.get('_id'))
if doc.get('state') == SET_STATES.USABLE or (doc.get('state') == SET_STATES.DISABLED and count):
raise SamsSetErrors.CannotDeleteActiveSet()
def get_destination(self, set_id: ObjectId) -> Destination:
item = self.get_by_id(set_id)
if not item:
raise SamsSetErrors.SetNotFound(set_id)
return destinations.get(item.get('destination_name'))
def get_provider_instance(self, set_id: ObjectId) -> SamsBaseStorageProvider:
return self.get_destination(set_id).provider_instance()
def get_asset_count(self, set_id: ObjectId):
from sams.assets import get_service as get_assets_service
service = get_assets_service()
response = service.get(req=None, lookup={'set_id': set_id})
return response.count()
def get_max_asset_size(self, set_id: ObjectId) -> int:
"""Returns the maximum allowed size of an Asset for a Set
Based on the configured settings, this method returns:
* ``Set.maximum_asset_size`` if ``MAX_ASSET_SIZE == 0``
* ``MAX_ASSET_SIZE`` if ``Set.maximum_asset_size == 0``
* Otherwise whichever is lowest
:param bson.objectid.ObjectId set_id: The ID of the Set
:return: The configured MAX_ASSET_SIZE of Set.maximum_asset_size, whichever is lower
:rtype: int
"""
set_item = self.get_by_id(set_id)
max_set_size = set_item.get('maximum_asset_size') or 0
max_app_size = app.config.get('MAX_ASSET_SIZE') or 0
if max_app_size == 0:
return max_set_size
elif max_set_size == 0:
return max_app_size
else:
return max_set_size if max_set_size < max_app_size else max_app_size
|
/sams-server-0.3.2.tar.gz/sams-server-0.3.2/sams/sets/service.py
| 0.832203 | 0.195709 |
service.py
|
pypi
|
from typing import Union
from eve.utils import config
from bson import ObjectId
from superdesk.services import Service
from sams_client.errors import SamsResourceErrors
class SamsService(Service):
"""Sams Service
Base service for all endpoints, defines the basic implementation for CRUD functionality.
This version differs from Superdesk.services.Service to provide validation on internal usage
"""
def get_by_id(self, item_id: Union[ObjectId, str], field=config.ID_FIELD):
"""Helper function to retrieve a document by id
:param bson.objectid.ObjectId item_id: ID for the document
:param field: field to use when searching for the document (defaults to '_id')
:return: document found in the system
"""
kwargs = {field: item_id}
return self.find_one(req=None, **kwargs)
def post(self, docs, **kwargs):
"""Create new documents for the specific resource
:param docs: An array of documents to create
:param kwargs: dictionary containing the keyword arguments
:return: list of generated IDs for the new documents
"""
for doc in docs:
self.validate_post(doc)
return super().post(docs, **kwargs)
def patch(self, item_id, updates):
"""Update an existing document for the specific resource
:param bson.ObjectId item_id: ID for the document
:param updates: Dictionary containing the desired attributes to update
:return: dictionary containing the updated attributes of the document
"""
original = self.get_by_id(item_id)
self.validate_patch(original, updates)
return super().patch(item_id, updates)
def validate_post(self, doc):
"""Validates the document upon creation
The validation performed in this step is provided by Eve/Cerberus using the defined
schema for the resource.
:param doc: The provided document to validate
:raises Superdesk.validation.ValidationError: If there are validation errors
"""
validator = self._validator()
if not validator:
return
validator.validate(doc)
if validator.errors:
raise SamsResourceErrors.ValidationError(validator.errors)
def validate_patch(self, original, updates):
"""Validates the document upon update
The validation performed in this step is provided by Eve/Cerberus using the defined
schema for the resource.
:param original: The original document from the database
:param updates: A dictionary with the desired attributes to update
:raises Superdesk.validation.ValidationError: If there are validation errors
"""
validator = self._validator()
if not validator:
return
validator.validate_update(updates, original.get(config.ID_FIELD), original)
if validator.errors:
raise SamsResourceErrors.ValidationError(validator.errors)
|
/sams-server-0.3.2.tar.gz/sams-server-0.3.2/sams/factory/service.py
| 0.924756 | 0.209247 |
service.py
|
pypi
|
import os
import shutil
import numpy as np
import scipy.ndimage
import scipy.stats
import surfa as sf
from samseg.subregions import utils
from samseg.subregions.core import MeshModel
class HippoAmygdalaSubfields(MeshModel):
def __init__(self, side, wmParcFileName, resolution=0.33333, **kwargs):
atlasDir = os.path.join(os.environ.get('FREESURFER_HOME'), 'average', 'HippoSF', 'atlas')
super().__init__(atlasDir=atlasDir, resolution=resolution, **kwargs)
# This is a hippocampus-specific setting to specify
# which hemisphere to segment
self.side = side
# Segmentation mesh-fitting parameters
self.cheatingMeshSmoothingSigmas = [3.0, 2.0]
self.cheatingMaxIterations = [300, 150]
# Image mesh-fitting parameters for cross-sectional processing
self.meshSmoothingSigmas = [1.5, 0.75, 0]
self.imageSmoothingSigmas = [0, 0, 0]
self.maxIterations = [7, 5, 3]
# Image mesh-fitting parameters for longitudinal processing
self.longMeshSmoothingSigmas = [[1.5, 0.75], [0.75, 0]]
self.longImageSmoothingSigmas = [[0, 0], [0, 0]]
self.longMaxIterations = [[6, 3], [2, 1]]
# Cache some useful info
self.wmparc = sf.load_volume(wmParcFileName)
# When creating the smooth atlas alignment target, erode before dilating
self.atlasTargetSmoothing = 'backward'
def preprocess_images(self):
# Define a few hardcoded label constants
self.HippoLabelLeft = 17
self.HippoLabelRight = 53
# Check the hemi
if self.side not in ('left', 'right'):
sf.system.fatal(f'Hemisphere must be either `left` or `right`, but got `{self.side}`')
# Flip hemi for alignment
if self.side == 'right':
atlasImage = sf.load_volume(self.atlasDumpFileName)
affine = atlasImage.geom.vox2world.matrix.copy()
affine[0, :] *= -1
atlasImage.geom.vox2world = affine
self.atlasDumpFileName = os.path.join(self.tempDir, 'flippedAtlasDump.mgz')
atlasImage.save(self.atlasDumpFileName)
# Atlas alignment target is a masked segmentation
sideHippoLabel = self.HippoLabelLeft if self.side == 'left' else self.HippoLabelRight
match_labels = [sideHippoLabel, sideHippoLabel + 1]
mask = np.isin(self.inputSeg.data, match_labels).astype('float32') * 255
self.atlasAlignmentTarget = self.inputSeg.new(mask)
# Now, the idea is to refine the transform based on the thalamus + ventral DE
# First, we prepare a modifided ASEG that we'll segment
data = self.inputSeg.data.copy(order='K')
# There's a bunch of labels in the SEG that we don't have in our atlas
# So we'll have to get rid of those
data[data == 15] = 0 # 4th vent -> background (we're killing brainstem anyway...)
data[data == 16] = 0 # get rid of brainstem
data[data == 7] = 0 # get rid of left cerebellum WM ...
data[data == 8] = 0 # ... and of left cerebellum CT
data[data == 46] = 0 # get rid of right cerebellum WM ...
data[data == 47] = 0 # ... and of right cerebellum CT
data[data == 80] = 0 # non-WM hippo -> background
data[data == 85] = 0 # optic chiasm -> background
data[data == 72] = 4 # 5th ventricle -> left-lat-vent
if self.side == 'left':
data[data == 5] = 4 # left-inf-lat-vent -> left-lat-vent
data[data == 30] = 2 # left-vessel -> left WM
data[data == 14] = 4 # 3rd vent -> left-lat-vent
data[data == 24] = 4 # CSF -> left-lat-vent
data[data == 77] = 2 # WM hippoint -> left WM
data[data > 250] = 2 # CC labels -> left WM
removal_mask = np.isin(data, [44, 62, 63, 41, 42, 43, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 58, 60])
data[removal_mask] = 0
else:
bu = data.copy(order='K')
data.fill(0)
data[bu == 44] = 4 # right-inf-lat-vent -> left-lat-vent
data[bu == 62] = 2 # right-vessel -> left WM
data[bu == 14] = 4 # 3rd vent -> left-lat-vent
data[bu == 24] = 4 # CSF -> left-lat-vent
data[bu == 77] = 2 # WM hippoint -> left WM
data[bu > 250] = 2 # CC labels -> left WM
# left to right
data[bu == 41] = 2 # WM
data[bu == 42] = 3 # CT
data[bu == 43] = 4 # LV
data[bu == 49] = 10 # TH
data[bu == 50] = 11 # CA
data[bu == 51] = 12 # PU
data[bu == 52] = 13 # PA
data[bu == 53] = 17 # HP
data[bu == 54] = 18 # AM
data[bu == 58] = 26 # AA
data[bu == 60] = 28 # DC
data[bu == 63] = 31 # CP
# And convert background to 1
data[data == 0] = 1
segMerged = self.inputSeg.new(data)
# We now merge hippo, amygdala, and cortex. This will be the
# synthetic image used for initial mesh fitting
self.synthImage = segMerged.copy()
self.synthImage[self.synthImage == 17] = 3
self.synthImage[self.synthImage == 18] = 3
# And also used for image cropping around the thalamus
fixedMargin = int(np.round(15 / np.mean(self.inputSeg.geom.voxsize)))
imageCropping = segMerged.new(self.inputSeg == sideHippoLabel).bbox(margin=fixedMargin)
# Let's dilate this mask (ATH not totally sure why there are two masks here)
mask = scipy.ndimage.morphology.binary_dilation(segMerged > 1, structure=np.ones((3, 3, 3)), iterations=2)
mergedMaskDilated = segMerged.new(mask)
# Lastly, use it to make the image mask
mask = (segMerged > 16) & (segMerged < 19)
imageMask = self.synthImage.new(mask)
# Dilate the mask
dilatedMask = scipy.ndimage.morphology.binary_dilation(mask, structure=np.ones((3, 3, 3)), iterations=5)
self.maskDilated5mm = self.synthImage.new(dilatedMask)
# Mask and convert to the target resolution
images = []
for i, image in enumerate(self.inputImages):
# FS python library does not have cubic interpolation yet, so we'll use mri_convert
tempFile = os.path.join(self.tempDir, 'tempImage.mgz')
image[imageCropping].save(tempFile)
utils.run(f'mri_convert {tempFile} {tempFile} -odt float -rt cubic -vs {self.resolution} {self.resolution} {self.resolution}')
image = sf.load_volume(tempFile)
# Resample and apply the first mask in high-resolution target space
maskTempFile = os.path.join(self.tempDir, 'asegModBinDilatedResampled.mgz')
mergedMaskDilated.save(maskTempFile)
utils.run(f'mri_convert {maskTempFile} {maskTempFile} -odt float -rt nearest -rl {tempFile}')
mask = sf.load_volume(maskTempFile)
image[mask == 0] = 0
# Resample and apply the second mask in high-resolution target space
maskTempFile = os.path.join(self.tempDir, 'hippoMaskResampled.mgz')
imageMask.save(maskTempFile)
utils.run(f'mri_convert {maskTempFile} {maskTempFile} -odt float -rt interpolate -rl {tempFile}')
mask = sf.load_volume(maskTempFile) >= 0.5
mask = scipy.ndimage.morphology.binary_dilation(mask, structure=np.ones((3, 3, 3)), iterations=int(np.round(3 / self.resolution)))
image[mask == 0] = 0
self.longMask = mask
images.append(image.data)
# Define the pre-processed target image
self.processedImage = image.new(np.stack(images, axis=-1))
def postprocess_segmentation(self):
"""
Post-process the segmentation and computed volumes.
"""
segFilePrefix = os.path.join(self.outDir, f'{self.side[0]}h.hippoAmygLabels{self.fileSuffix}')
A = self.discreteLabels.copy()
A[A < 200] = 0
A[(A > 246) & (A < 7000)] = 0
A[A == 201] = 0
mask = utils.get_largest_cc(A > 0)
A[mask == 0] = 0
A.save(segFilePrefix + '.mgz')
A.resample_like(self.inputSeg, method='nearest').save(segFilePrefix + '.FSvoxelSpace.mgz')
# Write merged versions to disk as well
# First: tail, body, head
HippoBodyLabel = 231
HippoHeadLabel = 232
HPbodyList = ['subiculum-body', 'CA1-body', 'presubiculum-body', 'molecular_layer_HP-body',
'CA3-body', 'GC-ML-DG-body', 'CA4-body', 'fimbria']
HPheadList = ['subiculum-head', 'presubiculum-head', 'CA1-head', 'parasubiculum',
'molecular_layer_HP-head', 'GC-ML-DG-head', 'CA4-head', 'CA3-head', 'HATA']
HPbodyList = [name.lower() for name in HPbodyList]
HPheadList = [name.lower() for name in HPheadList]
B = A.copy()
for c, name in enumerate(self.names):
name = name.lower().replace(' ', '')
if name in HPbodyList:
B[B == self.FreeSurferLabels[c]] = HippoBodyLabel
if name in HPheadList:
B[B == self.FreeSurferLabels[c]] = HippoHeadLabel
# Kill the fissure
B[B == 215] = 0
B.save(segFilePrefix + '.HBT.mgz')
B.resample_like(self.inputSeg, method='nearest').save(segFilePrefix + '.HBT.FSvoxelSpace.mgz')
# Second: head and body of each subfield
C = A.copy()
C[(A == 233) | (A == 234)] = 204 # presubiculum
C[(A == 235) | (A == 236)] = 205 # subiculum
C[(A == 237) | (A == 238)] = 206 # CA1
C[(A == 239) | (A == 240)] = 208 # CA3
C[(A == 241) | (A == 242)] = 209 # CA4
C[(A == 243) | (A == 244)] = 210 # GC-DG
C[(A == 245) | (A == 246)] = 214 # ML
C.save(segFilePrefix + '.FS60.mgz')
C.resample_like(self.inputSeg, method='nearest').save(segFilePrefix + '.FS60.FSvoxelSpace.mgz')
# Third: same as above, but we get rid of internal labels
D = C.copy()
D[D == 210] = 209 # GC-DG -> CA4
# Molecular layer: replace by nearest label that is not background or fissure
cropping = D.new(D == 214).bbox(margin=2)
V = D[cropping]
labels = [l for l in np.unique(V) if l not in (0, 214, 215)]
mask = V == 214
for i, label in enumerate(labels):
dmap = scipy.ndimage.distance_transform_edt(V != label)
if i == 0:
mini = dmap[mask]
seg = label * np.ones(mini.shape)
else:
dist = dmap[mask]
m = dist < mini
mini[m] = dist[m]
seg[m] = label
V[mask] = seg
D[cropping] = V
D.save(segFilePrefix + '.CA.mgz')
D.resample_like(self.inputSeg, method='nearest').save(segFilePrefix + '.CA.FSvoxelSpace.mgz')
# Extract hippocampal volumes
validLabels = ['subiculum-body', 'subiculum-head', 'Hippocampal_tail', 'molecular_layer_HP-body', 'molecular_layer_HP-head', 'hippocampal-fissure',
'GC-ML-DG-body', 'GC-ML-DG-head', 'CA4-body', 'CA4-head', 'presubiculum-body', 'presubiculum-head', 'CA1-body', 'CA1-head',
'parasubiculum', 'fimbria', 'CA3-body', 'CA3-head', 'HATA']
hippoVolumes = {name: vol for name, vol in self.volumes.items() if name in validLabels}
# Compute total hippocampal volume (ignore fissure)
validLabels = [name for name in validLabels if name != 'hippocampal-fissure']
hippoVolumes['Whole_hippocampus'] = np.sum([vol for name, vol in hippoVolumes.items() if name in validLabels])
# Compute total hippocampal body volume
validLabels = ['subiculum-body', 'CA1-body', 'presubiculum-body', 'molecular_layer_HP-body', 'CA3-body', 'GC-ML-DG-body', 'CA4-body', 'fimbria']
hippoVolumes['Whole_hippocampal_body'] = np.sum([vol for name, vol in hippoVolumes.items() if name in validLabels])
# Compute total hippocampal head volume
validLabels = ['subiculum-head', 'presubiculum-head', 'CA1-head', 'parasubiculum', 'molecular_layer_HP-head', 'GC-ML-DG-head', 'CA4-head', 'CA3-head', 'HATA']
hippoVolumes['Whole_hippocampal_head'] = np.sum([vol for name, vol in hippoVolumes.items() if name in validLabels])
# Write hippo volumes
self.write_volumes(os.path.join(self.outDir, f'{self.side[0]}h.hippoSfVolumes{self.fileSuffix}.txt'), hippoVolumes)
# Extract amygdala volumes
validLabels = ['Left-Amygdala', 'Lateral-nucleus', 'Paralaminar-nucleus', 'Basal-nucleus', 'Hippocampal-amygdala-transition-HATA',
'Accessory-Basal-nucleus', 'Amygdala-background', 'Corticoamygdaloid-transitio', 'Central-nucleus',
'Cortical-nucleus', 'Medial-nucleus', 'Anterior-amygdaloid-area-AAA']
amygdalaVolumes = {name: vol for name, vol in self.volumes.items() if name in validLabels}
# Compute total amygdala volume
amygdalaVolumes['Whole_amygdala'] = np.sum(list(amygdalaVolumes.values()))
# Write amygdala volumes
self.write_volumes(os.path.join(self.outDir, f'{self.side[0]}h.amygNucVolumes{self.fileSuffix}.txt'), amygdalaVolumes)
def get_cheating_label_groups(self):
"""
Return a group (list of lists) of label names that determine the
class reductions for the initial segmentation-fitting stage.
"""
labelGroups = [
['Left-Cerebral-Cortex', 'Left-Hippocampus', 'alveus', 'subiculum-body', 'subiculum-head', 'Hippocampal_tail' ,
'molecular_layer_HP-body', 'molecular_layer_HP-head', 'GC-ML-DG-body', 'GC-ML-DG-head',
'CA4-body', 'CA4-head', 'CA1-body', 'CA1-head', 'CA3-body', 'CA3-head', 'HATA', 'fimbria',
'presubiculum-body', 'presubiculum-head', 'parasubiculum', 'Left-hippocampus-intensity-abnormality',
'Left-Amygdala', 'Lateral-nucleus', 'Paralaminar-nucleus', 'Basal-nucleus',
'Hippocampal-amygdala-transition-HATA', 'Accessory-Basal-nucleus', 'Amygdala-background',
'Corticoamygdaloid-transitio', 'Central-nucleus', 'Cortical-nucleus', 'Medial-nucleus',
'Anterior-amygdaloid-area-AAA'],
['Left-Cerebral-White-Matter'],
['Left-Lateral-Ventricle'],
['Left-choroid-plexus'],
['Background', 'hippocampal-fissure', 'Background-CSF', 'Background-vessels', 'Background-tissue', 'Unknown'],
['Left-VentralDC'],
['Left-Putamen'],
['Left-Pallidum'],
['Left-Thalamus-Proper'],
['Left-Accumbens-area'],
['Left-Caudate'],
['SUSPICIOUS']
]
return labelGroups
def get_cheating_gaussians(self, sameGaussianParameters):
"""
Return a tuple of (means, variances) for the initial segmentation-fitting stage.
"""
means = np.zeros(len(sameGaussianParameters))
variances = 0.01 * np.ones(len(sameGaussianParameters))
for l in range(len(sameGaussianParameters)):
labels = np.array(sameGaussianParameters[l])
if any((labels >= 200) & (labels <= 226) & (labels != 215)):
means[l] = 3 # Hippo SF > Hippo
elif any((labels >= 7000)):
means[l] = 3 # Amygdala Subnuclei -> Amygdala
elif any(labels == 0):
means[l] = 1 # Background is 1 instead of 0
elif any(labels == 999):
means[l] = 55
variances[l] = 55 ** 2 # This is the generic `suspicious` label we use for cysts
else:
means[l] = labels[0]
return (means, variances)
def get_label_groups(self):
"""
Return a group (list of lists) of label names that determine the class reductions for
the primary image-fitting stage.
"""
if not self.highResImage:
labelGroups = [
['Left-Cerebral-Cortex', 'Left-Hippocampus', 'Left-Amygdala', 'subiculum-head', 'subiculum-body',
'Hippocampal_tail', 'GC-ML-DG-head', 'GC-ML-DG-body', 'CA4-head', 'CA4-body', 'presubiculum-head', 'presubiculum-body',
'CA1-head', 'CA1-body', 'parasubiculum', 'CA3-head', 'CA3-body', 'HATA', 'Lateral-nucleus', 'Paralaminar-nucleus',
'Basal-nucleus', 'Hippocampal-amygdala-transition-HATA', 'Accessory-Basal-nucleus', 'Amygdala-background',
'Corticoamygdaloid-transitio', 'Central-nucleus', 'Cortical-nucleus', 'Medial-nucleus',
'Anterior-amygdaloid-area-AAA', 'molecular_layer_HP-body', 'molecular_layer_HP-head']]
else:
labelGroups = [
['Left-Cerebral-Cortex', 'Left-Hippocampus', 'Left-Amygdala', 'subiculum-head', 'subiculum-body',
'Hippocampal_tail', 'GC-ML-DG-head', 'GC-ML-DG-body', 'CA4-head', 'CA4-body', 'presubiculum-head', 'presubiculum-body',
'CA1-head', 'CA1-body', 'parasubiculum', 'CA3-head', 'CA3-body', 'HATA', 'Lateral-nucleus', 'Paralaminar-nucleus',
'Basal-nucleus', 'Hippocampal-amygdala-transition-HATA', 'Accessory-Basal-nucleus', 'Amygdala-background',
'Corticoamygdaloid-transitio', 'Central-nucleus', 'Cortical-nucleus', 'Medial-nucleus',
'Anterior-amygdaloid-area-AAA'],
['molecular_layer_HP-body', 'molecular_layer_HP-head']]
labelGroups.append(['Left-Cerebral-White-Matter', 'fimbria'])
labelGroups.append(['alveus'])
labelGroups.append(['Left-Lateral-Ventricle', 'Background-CSF', 'SUSPICIOUS', 'Left-hippocampus-intensity-abnormality'])
labelGroups.append(['hippocampal-fissure'])
labelGroups.append(['Left-Pallidum'])
labelGroups.append(['Left-Putamen'])
labelGroups.append(['Left-Caudate'])
labelGroups.append(['Left-Thalamus-Proper'])
labelGroups.append(['Left-choroid-plexus'])
labelGroups.append(['Left-VentralDC'])
labelGroups.append(['Left-Accumbens-area'])
labelGroups.append(['Unknown', 'Background-tissue'])
return labelGroups
def get_gaussian_hyps(self, sameGaussianParameters, mesh):
"""
Return a tuple of (meanHyps, nHyps) for Gaussian parameter estimation.
"""
DATA = self.inputImages[0]
WMPARC = self.wmparc
mask = (WMPARC == 0) & (self.maskDilated5mm == 0)
WMPARC[mask] = -1
nHyper = np.zeros(len(sameGaussianParameters))
meanHyper = np.zeros(len(sameGaussianParameters))
for g in range(len(sameGaussianParameters)):
labels = np.array(sameGaussianParameters[g])
if any((labels == 3) | (labels == 17) | (labels == 18) | (labels > 7000) | (labels == 226)):
listMask = 17 if self.side == 'left' else 53
elif any(labels == 2):
listMask = [3006, 3007, 3016] if self.side == 'left' else [4006, 4007, 4016]
elif any(labels == 26):
listMask = 26 if self.side == 'left' else 58
elif any(labels == 4):
listMask = 4 if self.side == 'left' else 43
elif any(labels == 0):
listMask = [0]
elif any(labels == 13):
listMask = 13 if self.side == 'left' else 52
elif any(labels == 12):
listMask = 12 if self.side == 'left' else 51
elif any(labels == 11):
listMask = 11 if self.side == 'left' else 50
elif any(labels == 10):
listMask = 10 if self.side == 'left' else 49
elif any(labels == 31):
listMask = 31 if self.side == 'left' else 63
elif any(labels == 28):
listMask = 28 if self.side == 'left' else 60
else:
listMask = None
if listMask is not None:
if isinstance(listMask, int):
listMask = [listMask]
MASK = np.zeros(DATA.shape, dtype='bool')
for l in range(len(listMask)):
MASK = MASK | (WMPARC == listMask[l])
radius = np.round(1 / np.mean(DATA.geom.voxsize))
MASK = scipy.ndimage.morphology.binary_erosion(MASK, utils.spherical_strel(radius), border_value=1)
total_mask = MASK & (DATA > 0)
data = DATA[total_mask]
meanHyper[g] = np.median(data)
nHyper[g] = 10 + len(data) * np.prod(DATA.geom.voxsize) / (self.resolution ** 3)
# If any NaN, replace by background
# ATH: I don't there would ever be NaNs here?
nans = np.isnan(meanHyper)
meanHyper[nans] = 55
nHyper[nans] = 10
# Here's the part where we simulate partial voluming!
print('Estimating typical intensities of alveus')
WMind = None
GMind = None
ALind = None
MLind = None
FISSind = None
CSFind = None
for g in range(len(sameGaussianParameters)):
labels = np.array(sameGaussianParameters[g])
if any(labels == 2):
WMind = g
if any(labels == 3):
GMind = g
if any(labels == 201):
ALind = g
if any(labels == 245) and self.highResImage:
MLind = g
if any(labels == 215):
FISSind = g
if any(labels == 4):
CSFind = g
imageShape = (mesh.points.max(axis=0) + 1.5).astype(int)
priors = mesh.rasterize(imageShape)
L = np.argmax(priors, axis=-1)
maskPriors = (priors.sum(-1) / 65535) > 0.97
I = np.zeros(imageShape)
for l in range(len(sameGaussianParameters)):
if l == ALind or l == MLind:
I[L == l] = meanHyper[WMind]
elif l == FISSind:
I[L == l] = meanHyper[CSFind]
else:
I[L == l] = meanHyper[l]
I[maskPriors == 0] = 0
sigma = np.mean(DATA.geom.voxsize) / (2.355 * self.resolution)
I_PV = scipy.ndimage.gaussian_filter(I, sigma)
if ALind is not None:
data = I_PV[L == ALind]
# It's multimodal, so regular median won't cut it
kde = scipy.stats.gaussian_kde(data.flatten())
v = np.linspace(data.min(), data.max(), 1000)
meanHyper[ALind] = np.median(v[np.argmax(kde(v))]) # median of argmax??
nHyper[ALind] = (nHyper[GMind] + nHyper[WMind]) / 2
if self.highResImage:
data = I_PV[L == MLind]
meanHyper[MLind] = np.median(I_PV[L == MLind])
nHyper[MLind] = (nHyper[WMind] + nHyper[GMind]) / 2
if FISSind is not None:
meanHyper[FISSind] = np.median(I_PV[L == FISSind])
nHyper[FISSind] = (nHyper[CSFind] + nHyper[GMind]) / 2
return (meanHyper, nHyper)
|
/subregions/hippocampus.py
| 0.531209 | 0.445831 |
hippocampus.py
|
pypi
|
import os
import shutil
import numpy as np
import scipy.ndimage
import surfa as sf
from samseg.subregions import utils
from samseg.subregions.core import MeshModel
class ThalamicNuclei(MeshModel):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
atlasDir = os.path.join(os.environ.get('FREESURFER_HOME'), 'average', 'ThalamicNuclei', 'atlas')
super().__init__(atlasDir=atlasDir, **kwargs)
# Model thalamus with two components
self.useTwoComponents = True
# Segmentation mesh-fitting parameters
self.cheatingMeshSmoothingSigmas = [3.0, 2.0]
self.cheatingMaxIterations = [300, 150]
# Image mesh-fitting parameters
self.meshSmoothingSigmas = [1.5, 1.125, 0.75, 0]
self.imageSmoothingSigmas = [0, 0, 0, 0]
self.maxIterations = [7, 5, 5, 3]
# Longitudinal mesh-fitting parameters
self.longMeshSmoothingSigmas = [[1.5, 1.125, 0.75], [1.125, 0.75, 0]]
self.longImageSmoothingSigmas = [[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]]
self.longMaxIterations = [[7, 5, 3], [3, 2, 1]]
# When creating the smooth atlas alignment target, dilate before eroding
self.atlasTargetSmoothing = 'forward'
def preprocess_images(self):
"""
Preprocess the input seg and images
"""
# Define a few hardcoded label constants
self.THlabelLeft = 10
self.THlabelRight = 49
self.DElabelLeft = 28
self.DElabelRight = 60
# Atlas alignment target is a masked segmentation
match_labels = [self.THlabelLeft, self.THlabelRight, self.DElabelLeft, self.DElabelRight]
mask = np.isin(self.inputSeg.data, match_labels).astype('float32') * 255
self.atlasAlignmentTarget = self.inputSeg.new(mask)
# Now, the idea is to refine the transform based on the thalamus + ventral DE
# First, we prepare a modifided SEG that we'll segment
data = self.inputSeg.data
# There's a bunch of labels in the SEG that we don't have in our atlas
# So we'll have to get rid of those
data[data == 5] = 4 # left-inf-lat-vent -> left-lat-vent
data[data == 44] = 4 # right-inf-lat-vent -> left-lat-vent
data[data == 14] = 4 # 3rd vent -> left-lat-vent
data[data == 15] = 4 # 4th vent -> LV (we're killing brainstem anyway)
data[data == 17] = 3 # left HP -> left cortex
data[data == 53] = 3 # right HP -> left cortex
data[data == 18] = 3 # left amygdala -> left cortex
data[data == 54] = 3 # right amygdala -> left cortex
data[data == 24] = 4 # CSF -> left-lat-vent
data[data == 30] = 2 # left-vessel -> left WM
data[data == 62] = 2 # right-vessel -> left WM
data[data == 72] = 4 # 5th ventricle -> left-lat-vent
data[data == 77] = 2 # WM hippoint -> left WM
data[data == 80] = 0 # non-WM hippo -> background
data[data == 85] = 0 # optic chiasm -> background
data[data > 250] = 2 # CC labels -> left WM
# Next we want to remove hemi-specific lables, so we convert right labels to left
data[data == 41] = 2 # WM
data[data == 42] = 3 # CT
data[data == 43] = 4 # LV
data[data == 46] = 7 # cerebellum WM
data[data == 47] = 8 # cerebellum CT
data[data == 50] = 11 # CA
data[data == 51] = 12 # PU
data[data == 52] = 13 # PA
data[data == 58] = 26 # AA
data[data == 63] = 31 # CP
# Remove a few remainders
removal_mask = np.isin(data, [44, 62, 63, 41, 42, 43, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 58])
data[removal_mask] = 0
# And convert background to 1
data[data == 0] = 1
# Now, create a mask with DE merged into thalamus. This will be the
# synthetic image used for initial mesh fitting
segMerged = self.inputSeg.copy()
segMerged[segMerged == self.DElabelLeft] = self.THlabelLeft
segMerged[segMerged == self.DElabelRight] = self.THlabelRight
self.synthImage = segMerged
# And also used for image cropping around the thalamus
thalamicMask = (segMerged == self.THlabelLeft) | (segMerged == self.THlabelRight)
fixedMargin = int(np.round(15 / np.mean(self.inputSeg.geom.voxsize)))
imageCropping = segMerged.new(thalamicMask).bbox(margin=fixedMargin)
# Lastly, use it to make the image mask
struct = np.ones((3, 3, 3))
mask = scipy.ndimage.morphology.binary_dilation(self.synthImage > 1, structure=struct, iterations=2)
imageMask = self.synthImage.new(mask)
# Mask and convert to the target resolution
images = []
for i, image in enumerate(self.inputImages):
# FS python library does not have cubic interpolation yet, so we'll use mri_convert
tempFile = os.path.join(self.tempDir, 'tempImage.mgz')
image[imageCropping].save(tempFile)
utils.run(f'mri_convert {tempFile} {tempFile} -odt float -rt cubic -vs {self.resolution} {self.resolution} {self.resolution}')
image = sf.load_volume(tempFile)
# Resample and apply the image mask in high-resolution target space
imageMask = imageMask.resample_like(image, method='nearest')
image[imageMask == 0] = 0
images.append(image.data)
self.longMask = imageMask
# Define the pre-processed target image
self.processedImage = image.new(np.stack(images, axis=-1))
def postprocess_segmentation(self):
"""
Post-process the segmentation and computed volumes.
"""
# Recode segmentation
A = self.discreteLabels.copy()
A[(A < 100) & (A != 10) & (A != 49) ] = 0
# Kill reticular labels
leftReticular = self.labelMapping.search('Left-R', exact=True)
rightReticular = self.labelMapping.search('Right-R', exact=True)
A[A == leftReticular] = 0
A[A == rightReticular] = 0
# Get only connected components (sometimes the two thalami are not connected)
left = utils.get_largest_cc((A < 8200) & ((A > 100) | (A == self.THlabelLeft)))
right = utils.get_largest_cc((A > 8200) | (A == self.THlabelRight))
cc_mask = left | right
A[cc_mask == 0] = 0
segFilePrefix = os.path.join(self.outDir, f'ThalamicNuclei{self.fileSuffix}')
A.save(segFilePrefix + '.mgz')
A.resample_like(self.inputSeg, method='nearest').save(segFilePrefix + '.FSvoxelSpace.mgz')
# Prune the volumes to what we care about (also let's leave reticular 'R' out)
validLabels = ['L-Sg', 'LGN', 'MGN', 'PuI', 'PuM', 'H', 'PuL',
'VPI', 'PuA', 'MV(Re)', 'Pf', 'CM', 'LP', 'VLa', 'VPL', 'VLp',
'MDm', 'VM', 'CeM', 'MDl', 'Pc', 'MDv', 'Pv', 'CL', 'VA', 'VPM',
'AV', 'VAmc', 'Pt', 'AD', 'LD']
isValid = lambda name: (name.replace('Left-', '') in validLabels) or (name.replace('Right-', '') in validLabels)
self.volumes = {name: vol for name, vol in self.volumes.items() if isValid(name)}
# Sum up the total volumes per hemisphere
self.volumes['Left-Whole_thalamus'] = np.sum([vol for name, vol in self.volumes.items() if name.startswith('Left')])
self.volumes['Right-Whole_thalamus'] = np.sum([vol for name, vol in self.volumes.items() if name.startswith('Right')])
# Write the volumes
self.write_volumes(segFilePrefix + '.volumes.txt')
def get_cheating_label_groups(self):
"""
Return a group (list of lists) of label names that determine the
class reductions for the initial segmentation-fitting stage.
"""
labelGroups = [
['Unknown'],
['Left-Cerebral-White-Matter'],
['Left-Cerebral-Cortex'],
['Left-Cerebellum-Cortex'],
['Left-Cerebellum-White-Matter'],
['Brain-Stem'],
['Left-Lateral-Ventricle'],
['Left-choroid-plexus'],
['Left-Putamen'],
['Left-Pallidum'],
['Left-Accumbens-area'],
['Left-Caudate'],
]
thalamicLabels = [
'L-Sg', 'LGN', 'MGN', 'PuI', 'PuM', 'H', 'PuL',
'VPI', 'PuA', 'R', 'MV(Re)', 'Pf', 'CM', 'LP', 'VLa',
'VPL', 'VLp', 'MDm', 'VM', 'CeM', 'MDl', 'Pc', 'MDv', 'Pv',
'CL', 'VA', 'VPM', 'AV', 'VAmc', 'Pt', 'AD', 'LD', 'VentralDC'
]
labelGroups.append(['Left-' + label for label in thalamicLabels])
labelGroups.append(['Right-' + label for label in thalamicLabels])
return labelGroups
def get_cheating_gaussians(self, sameGaussianParameters):
"""
Return a tuple of (means, variances) for the initial segmentation-fitting stage.
"""
means = np.zeros(len(sameGaussianParameters))
variances = 0.01 * np.ones(len(sameGaussianParameters))
for i in range(len(sameGaussianParameters)):
label = sameGaussianParameters[i][0]
if label >= 8100 and label < 8200:
means[i] = self.THlabelLeft # left thalamic nuclei + DE -> left TH
elif label >= 8200:
means[i] = self.THlabelRight # right thalamic nuclei + DE -> left TH
elif label == 0:
means[i] = 1 # background is 1 instead of 0
else:
means[i] = label
return (means, variances)
def get_label_groups(self):
"""
Return a group (list of lists) of label names that determine the class reductions for
the primary image-fitting stage.
"""
labelGroups = [
['Unknown'],
['Left-Cerebral-White-Matter', 'Left-R', 'Right-R'],
['Left-Cerebral-Cortex'],
['Left-Cerebellum-Cortex'],
['Left-Cerebellum-White-Matter'],
['Brain-Stem'],
['Left-Lateral-Ventricle'],
['Left-choroid-plexus'],
['Left-Putamen'],
['Left-Pallidum'],
['Left-Accumbens-area'],
['Left-Caudate'],
['Left-VentralDC', 'Right-VentralDC'],
]
# Configure left/right thalamic labels
thalamicLabels = [
'L-Sg', 'LGN', 'MGN', 'PuI', 'PuM', 'H', 'PuL', 'VPI', 'PuA', 'MV(Re)', 'Pf',
'CM', 'LP', 'VLa', 'VPL', 'VLp', 'MDm', 'VM', 'CeM', 'MDl', 'Pc', 'MDv', 'Pv',
'CL', 'VA', 'VPM', 'AV', 'VAmc', 'Pt', 'AD', 'LD',
]
labelGroups.append([f'{side}-{label}' for side in ('Left', 'Right') for label in thalamicLabels])
return labelGroups
def get_gaussian_hyps(self, sameGaussianParameters, mesh):
"""
Return a tuple of (meanHyps, nHyps) for Gaussian parameter estimation.
"""
nHyper = np.zeros(len(sameGaussianParameters))
meanHyper = np.zeros(len(sameGaussianParameters))
# TODO this needs to be adapted for multi-image cases (with masking)
DATA = self.inputImages[0]
for g in range(len(sameGaussianParameters)):
labels = np.array(sameGaussianParameters[g])
if any(labels > 8225): # thalamus
listMask = [10, 49]
elif any(labels == 28): # VDE
listMask = [28, 60]
elif any(labels == 0): # background
listMask = [1]
else:
listMask = labels
if len(listMask) > 0:
MASK = np.zeros(DATA.shape, dtype='bool')
for l in range(len(listMask)):
# Ensure that this uses a modified segmentation
MASK = MASK | (self.inputSeg == listMask[l])
radius = np.round(1 / np.mean(DATA.geom.voxsize))
MASK = scipy.ndimage.morphology.binary_erosion(MASK, utils.spherical_strel(radius), border_value=1)
total_mask = MASK & (DATA > 0)
data = DATA[total_mask]
meanHyper[g] = np.median(data)
if any(labels == 28):
# Special case: VDE is kind of bimodal in FreeSurfer
nHyper[g] = 10
else:
nHyper[g] = 10 + len(data) * np.prod(DATA.geom.voxsize) / (self.resolution ** 3)
# If any NaN, replace by background
# ATH: I don't there would ever be NaNs here?
nans = np.isnan(meanHyper)
meanHyper[nans] = 55
nHyper[nans] = 10
return (meanHyper, nHyper)
def get_second_label_groups(self):
"""
Return a group (list of lists) of label names that determine the class reductions for the
second-component of the primary image-fitting stage.
"""
labelGroups = [
['Unknown'],
['Left-Cerebral-White-Matter', 'Left-R', 'Right-R'],
['Left-Cerebral-Cortex'],
['Left-Cerebellum-Cortex'],
['Left-Cerebellum-White-Matter'],
['Brain-Stem'],
['Left-Lateral-Ventricle'],
['Left-choroid-plexus'],
['Left-Putamen'],
['Left-Pallidum'],
['Left-Accumbens-area'],
['Left-Caudate'],
['Left-VentralDC', 'Right-VentralDC'],
['Left-L-Sg', 'Left-LGN', 'Left-MGN', 'Left-H',
'Left-VPI', 'Left-MV(Re)', 'Left-Pf', 'Left-CM', 'Left-LP', 'Left-VLa', 'Left-VPL', 'Left-VLp',
'Left-VM', 'Left-CeM', 'Left-Pc', 'Left-MDv', 'Left-Pv', 'Left-CL', 'Left-VA', 'Left-VPM',
'Left-AV', 'Left-VAmc', 'Left-Pt', 'Left-AD', 'Left-LD', 'Right-L-Sg', 'Right-LGN', 'Right-MGN', 'Right-H',
'Right-VPI', 'Right-MV(Re)', 'Right-Pf', 'Right-CM', 'Right-LP', 'Right-VLa', 'Right-VPL', 'Right-VLp',
'Right-VM', 'Right-CeM', 'Right-Pc', 'Right-MDv', 'Right-Pv', 'Right-CL', 'Right-VA', 'Right-VPM',
'Right-AV', 'Right-VAmc', 'Right-Pt', 'Right-AD', 'Right-LD'],
['Left-PuA', 'Left-PuI', 'Left-PuL', 'Left-PuM', 'Left-MDl', 'Left-MDm',
'Right-PuA', 'Right-PuI', 'Right-PuL', 'Right-PuM', 'Right-MDl', 'Right-MDm']
]
return labelGroups
def get_second_gaussian_hyps(self, sameGaussianParameters, meanHyper, nHyper):
"""
Return a tuple of (meanHyps, nHyps) for Gaussian parameter estimation in the second-component
of the primary image-fitting stage.
"""
WMind = 1
GMind = 2
ThInt = meanHyper[-1]
# TODO this needs to be enabled with non-T1s are used
if True:
# Lateral, brighter
nHyper[-1] = 25
meanHyper[-1] = ThInt + 5
# Medial, darker
nHyper = np.append(nHyper, 25)
meanHyper = np.append(meanHyper, ThInt - 5)
else:
nHyper[-1] = 25
nHyper = np.append(nHyper, 25)
# Lateral, more WM-ish (e.g., darker, in FGATIR)
meanHyper[-1] = ThInt * (0.95 + 0.1 * (meanHyper[WMind] >= meanHyper[GMind]))
# Medial, more GM-ish (e.g., brighter, in FGATIR)
meanHyper = np.append(meanHyper, ThInt * (0.95 + 0.1 * (meanHyper[WMind] < meanHyper[GMind])))
return (meanHyper, nHyper)
|
/subregions/thalamus.py
| 0.519278 | 0.397354 |
thalamus.py
|
pypi
|
import os
import shutil
import numpy as np
import scipy.ndimage
import surfa as sf
from samseg.subregions import utils
from samseg.subregions.core import MeshModel
class BrainstemSubstructures(MeshModel):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
atlasDir = os.path.join(os.environ.get('FREESURFER_HOME'), 'average', 'BrainstemSS', 'atlas')
super().__init__(atlasDir=atlasDir, **kwargs)
# Segmentation mesh-fitting parameters
self.cheatingMeshSmoothingSigmas = [3.0]
self.cheatingMaxIterations = [300]
# Image mesh-fitting parameters
self.meshSmoothingSigmas = [2, 1, 0]
self.imageSmoothingSigmas = [0, 0, 0]
self.maxIterations = [7, 5, 3]
# Longitudinal mesh-fitting parameters
self.longMeshSmoothingSigmas = [[2, 1], [1, 0]]
self.longImageSmoothingSigmas = [[0, 0], [0, 0]]
self.longMaxIterations = [[6, 3], [2, 1]]
# Let's not smooth the target mask at all
self.atlasTargetSmoothing = None
self.cheatingAlphaMaskStrel = 5
self.alphaMaskStrel = 0
def preprocess_images(self):
"""
Preprocess the input seg and images
"""
# Define a few hardcoded label constants
self.BRAINSTEM = 16
self.DElabelLeft = 28
self.DElabelRight = 60
# Atlas alignment target is a masked segmentation
mask = (self.inputSeg == self.BRAINSTEM).astype('float32') * 255
self.atlasAlignmentTarget = self.inputSeg.new(mask)
# This will be the synthetic image used for initial mesh fitting
self.synthImage = self.inputSeg.copy()
labels = [self.BRAINSTEM, 7, 8, 15, 28, 46, 47, 60]
mask = np.isin(self.synthImage, labels)
self.synthImage.data.fill(1)
self.synthImage[mask] = 255
self.synthImage.save(os.path.join(self.tempDir, 'synthImage.mgz'))
# And also used for image cropping around the brainstem
brainstemMask = (self.inputSeg == self.BRAINSTEM) | (self.inputSeg == self.DElabelLeft) | (self.inputSeg == self.DElabelRight)
fixedMargin = int(np.round(15 / np.mean(self.inputSeg.geom.voxsize)))
imageCropping = self.inputSeg.new(brainstemMask).bbox(margin=fixedMargin)
# Mask and convert to the target resolution
images = []
for i, image in enumerate(self.inputImages):
# FS python library does not have cubic interpolation yet, so we'll use mri_convert
tempFile = os.path.join(self.tempDir, 'tempImage.mgz')
image[imageCropping].save(tempFile)
utils.run(f'mri_convert {tempFile} {tempFile} -odt float -rt cubic -vs {self.resolution} {self.resolution} {self.resolution}')
image = sf.load_volume(tempFile)
images.append(image.data)
# Define the pre-processed target image
self.processedImage = image.new(np.stack(images, axis=-1))
# Resample and apply the seg mask in high-resolution target space
croppedSeg = self.inputSeg[imageCropping].copy()
croppedSeg = croppedSeg.resample_like(self.processedImage, method='nearest')
# Create mask and dilate substantially
radius = int(np.round(5 / self.resolution))
mask = scipy.ndimage.morphology.binary_dilation(croppedSeg > 0, utils.spherical_strel(radius))
self.longMask = mask
# Apply the mask
self.processedImage[mask == 0] = 0
def postprocess_segmentation(self):
"""
Post-process the segmentation and computed volumes.
"""
segFilePrefix = os.path.join(self.outDir, f'brainstemSsLabels{self.fileSuffix}')
# Recode segmentation
A = self.discreteLabels.copy()
A[A < 170] = 0
mask = utils.get_largest_cc(A > 0)
A[mask == 0] = 0
A.save(segFilePrefix + '.mgz')
A.resample_like(self.inputSeg, method='nearest').save(segFilePrefix + '.FSvoxelSpace.mgz')
# Prune the volumes to what we care about
validLabels = ['MAC_Medulla', 'MAC_Pons', 'MAC_Midbrain', 'MAC_Sup_Cerebellum_Ped', 'Medulla', 'Pons', 'Midbrain', 'SCP']
self.volumes = {name: vol for name, vol in self.volumes.items() if name in validLabels}
# Sum up the total volume
self.volumes['Whole_brainstem'] = np.sum(list(self.volumes.values()))
# Write the volumes
self.write_volumes(segFilePrefix + '.volumes.txt')
def get_cheating_label_groups(self):
"""
Return a group (list of lists) of label names that determine the
class reductions for the initial segmentation-fitting stage.
"""
labelGroups = [
# Label group 1
['MAC_Medulla', 'MAC_Pons', 'MAC_Midbrain', 'Left-VentralDC', '4th-Ventricle',
'Left-Cerebellum-White-Matter', 'Left-Cerebellum-Cortex', 'MAC_Sup_Cerebellum_Ped',
'Medulla', 'Pons', 'SCP', 'Midbrain'],
# Label group 2
['Left-Caudate', 'Left-Accumbens-area', 'Left-Pallidum', '3rd-Ventricle', 'Left-Putamen',
'Left-Thalamus-Proper', 'Left-Amygdala', 'Left-Lateral-Ventricle', 'Left-choroid-plexus', 'Left-Hippocampus',
'Left-Cerebral-White-Matter', 'Left-Cerebral-Cortex', 'Background-tissue', 'Background-CSF', 'Background'],
]
return labelGroups
def get_cheating_gaussians(self, sameGaussianParameters):
"""
Return a tuple of (means, variances) for the initial segmentation-fitting stage.
"""
means = np.array([255.0, 1.0])
variances = np.array([1.0, 1.0])
return (means, variances)
def get_label_groups(self):
"""
Return a group (list of lists) of label names that determine the class reductions for
the primary image-fitting stage.
"""
labelGroups = [
['MAC_Medulla', 'MAC_Pons', 'MAC_Midbrain', 'MAC_Sup_Cerebellum_Ped', 'Left-VentralDC', 'Medulla', 'Pons', 'SCP', 'Midbrain'], # Brainstem structures
['3rd-Ventricle', 'Left-Lateral-Ventricle', 'Background-CSF', '4th-Ventricle'], # CSF structures
['Left-Amygdala', 'Left-Cerebral-Cortex', 'Left-Hippocampus'], # Gray matter structures
['Left-Caudate'], # Caudate
['Left-Accumbens-area'], # Accumbens area
['Left-Pallidum'], # Pallidum
['Left-Putamen'], # Putamen
['Left-Thalamus-Proper'], # Thalamus
['Left-choroid-plexus'], # Choroid plexus
['Left-Cerebral-White-Matter'], # Cerebral white matter
['Background-tissue', 'Background'], # Background: misc tissue
['Left-Cerebellum-White-Matter'], # cerebellum white matter
['Left-Cerebellum-Cortex'], # cerebellum cortex
]
return labelGroups
def get_gaussian_hyps(self, sameGaussianParameters, mesh):
"""
Return a tuple of (meanHyps, nHyps) for Gaussian parameter estimation.
"""
# TODO this needs to be adapted for multi-image cases (plus masking)
DATA = self.inputImages[0]
nHyper = np.zeros(len(sameGaussianParameters))
meanHyper = np.zeros(len(sameGaussianParameters))
for g in range(len(sameGaussianParameters)):
labels = np.array(sameGaussianParameters[g])
if any((labels == 3) | (labels == 17) | (labels == 18)): # gray matter
listMask = [3, 42, 17, 53, 18, 54]
elif any(labels == 2): # white matter
listMask = [2, 41]
elif any((labels == 178) | (labels == 34458) | (labels == 28)): # brainstem + diencephalon
listMask = [16, 28, 60]
elif any(labels == 4): # CSF
listMask = [4, 43, 14, 15]
elif any(labels == 11): # caudate
listMask = [11, 50]
elif any(labels == 26): # accumbens
listMask = [26, 58]
elif any(labels == 13): # pallidum
listMask = [13, 52]
elif any(labels == 12): # putamen
listMask = [12, 51]
elif any(labels == 10): # thalamus
listMask = [10, 49]
elif any(labels == 31): # choroid
listMask = [31, 63]
elif any(labels == 0): # background
listMask = [0]
elif any(labels == 7): # cerebellum WM
listMask = [7, 46]
elif any(labels == 8): # cerebellum CT
listMask = [8, 47]
else:
listMask = []
if len(listMask) > 0:
MASK = np.zeros(DATA.shape, dtype='bool')
for l in range(len(listMask)):
MASK = MASK | (self.inputSeg == listMask[l])
MASK = scipy.ndimage.morphology.binary_erosion(MASK, utils.spherical_strel(1), border_value=1)
total_mask = MASK & (DATA > 0)
data = DATA[total_mask]
meanHyper[g] = np.median(data)
nHyper[g] = 10 + 0.1 * len(data) / np.prod(DATA.geom.voxsize)
# If any NaN, replace by background
# ATH: I don't there would ever be NaNs here?
nans = np.isnan(meanHyper)
meanHyper[nans] = 55
nHyper[nans] = 10
return (meanHyper, nHyper)
|
/subregions/brainstem.py
| 0.619817 | 0.338829 |
brainstem.py
|
pypi
|
import os
import scipy.ndimage
import numpy as np
import surfa as sf
from samseg import gems
def run(cmd):
"""
Run a command in a bash shell. Output is silenced, but is printed if an error occurs.
"""
print(f'Running command: {cmd}')
output, ret = sf.system.collect_output(cmd)
if ret != 0:
print(output)
sf.system.fatal('Command failed')
def spherical_strel(radius, pixsize=1.0):
"""
Compute a 3D spherical binary structure for mask manipulation.
"""
pixsize = np.array([pixsize] * 3)
shape = np.ceil(2 * radius / pixsize + 1).astype(int)
shape += np.mod(shape + 1, 2)
center = (shape - 1) / 2
coords = np.array(np.ogrid[:shape[0], :shape[1], :shape[2]], dtype=object)
return np.sum((coords - center) ** 2, axis=0) <= (radius ** 2)
def read_compression_lookup_table(filename):
"""
Read a compressed label lookup table file into an ordered dictionary
to labels and names. This also returns corresponding label indices and names
in a tuple, although we can probably re-extract this info from the labelMapping
object down the road.
"""
labelMapping = sf.LabelLookup()
labels, names, colors = gems.kvlReadCompressionLookupTable(filename)
labels = np.array(labels)
for label, name, color in zip(labels, names, colors):
labelMapping[label] = (name, color)
return (labelMapping, names, labels)
def get_largest_cc(mask):
"""
Find the largest connected component of a binary mask. All over components are
masked away in the returned array.
ATH TODO: This should be implemented as a function of the Volume object.
"""
labels = scipy.ndimage.label(mask)[0]
return labels == np.argmax(np.bincount(labels.flatten())[1:]) + 1
def geometries_differ(a, b):
"""
Compare the similarity of two volume geometries.
"""
if not np.array_equal(a.shape[:3], b.shape[:3]):
return True
if not np.max(np.abs(a.voxsize - b.voxsize)) > 1e-5:
return True
if not np.max(np.abs(a.matrix - b.matrix)) > 1e-5:
return True
return False
|
/subregions/utils.py
| 0.459804 | 0.503723 |
utils.py
|
pypi
|
import os
import numpy as np
import datetime as dt
import surfa as sf
from samseg import gems
from samseg.subregions import utils
from samseg.subregions.thalamus import ThalamicNuclei
from samseg.subregions.brainstem import BrainstemSubstructures
from samseg.subregions.hippocampus import HippoAmygdalaSubfields
model_lookup = {
'thalamus' : ThalamicNuclei,
'brainstem' : BrainstemSubstructures,
'hippo-amygdala' : HippoAmygdalaSubfields,
}
structure_names = list(model_lookup.keys())
def get_model_class(structure):
"""
Get model class from structure name
"""
model_class = model_lookup.get(structure)
if model_class is None:
options = ', '.join(model_lookup.keys())
sf.system.fatal(f'Unknown structure type `{structure}`. Available options are: {options}.')
return model_class
def run_cross_sectional(structure, parameters):
"""
Run full cross-sectional processing
"""
start_time = dt.datetime.now()
# Construct model
model = get_model_class(structure)(**parameters)
# Preprocess
last_time = dt.datetime.now()
print(f'Step 1: preprocessing inputs for {structure} segmentation')
model.initialize()
elapsed = dt.datetime.now() - last_time
print(f'Preprocessing took {elapsed.seconds} seconds\n')
# Atlas alignment
last_time = dt.datetime.now()
print('Step 2: aligning atlas to reference segmentation')
model.align_atlas_to_seg()
elapsed = dt.datetime.now() - last_time
print(f'Initial atlas alignment took {elapsed.seconds} seconds\n')
# Fit to seg
last_time = dt.datetime.now()
print('Step 3: fitting mesh to reference segmentation')
model.prepare_for_seg_fitting()
model.fit_mesh_to_seg()
elapsed = dt.datetime.now() - last_time
print(f'Initial mesh fitting took {elapsed.seconds} seconds\n')
# Fit to image
last_time = dt.datetime.now()
print('Step 4: fitting mesh to image')
model.prepare_for_image_fitting()
model.fit_mesh_to_image()
elapsed = dt.datetime.now() - last_time
print(f'Mesh fitting took {elapsed.seconds} seconds\n')
# Finalize
model.extract_segmentation()
model.postprocess_segmentation()
model.cleanup()
elapsed = dt.datetime.now() - start_time
print(f'\nSegmentation complete! Process took {elapsed.seconds / 60:.2f} minutes')
def run_longitudinal(structure, baseParameters, tpParameters):
"""
Run full longitudinal processing
"""
start_time = dt.datetime.now()
# Construct base and timepoint models
modelClass = get_model_class(structure)
baseModel = modelClass(**baseParameters)
tpModels = [modelClass(**params) for params in tpParameters]
# Preprocess inputs
last_time = dt.datetime.now()
print(f'Step 1: preprocessing all inputs for {structure} segmentation')
baseModel.isLong = True
baseModel.fileSuffix = '.long' + baseModel.fileSuffix
baseModel.initialize()
for tpModel in tpModels:
tpModel.isLong = True
tpModel.fileSuffix = '.long' + tpModel.fileSuffix
tpModel.initialize()
elapsed = dt.datetime.now() - last_time
print(f'Preprocessing took {elapsed.seconds} seconds\n')
# Atlas alignment
last_time = dt.datetime.now()
print('Step 2: aligning atlas to base reference segmentation')
baseModel.align_atlas_to_seg()
elapsed = dt.datetime.now() - last_time
print(f'Initial base atlas alignment took {elapsed.seconds} seconds\n')
# Here we compute an affine aligment of the time points to the base based
# solely on the segmentation. We need to remember the determinant of the
# transform - we'll need to divide the final volume estimates by it.
last_time = dt.datetime.now()
print('Step 3: aligning timepoint segmentations to base')
# First save the cropped base masks
mask = baseModel.atlasAlignmentTarget.crop_to_bbox(margin=6).astype('float32')
baseMaskFile = os.path.join(baseModel.tempDir, 'binaryMaskCropped.mgz')
mask.save(baseMaskFile)
# This is our target resampled image that all timepoints should be resampled to
baseProcessedFile = os.path.join(baseModel.tempDir, 'processedImage.mgz')
baseModel.processedImage.save(baseProcessedFile)
# Now align each TP to the base
baseTransforms = []
for tpModel in tpModels:
# Save the cropped timepoint masks
mask = tpModel.atlasAlignmentTarget.crop_to_bbox(margin=6).astype('float32')
maskFile = os.path.join(tpModel.tempDir, 'binaryMaskCropped.mgz')
mask.save(maskFile)
# Run the actual registration and load the transform
transformFile = os.path.join(tpModel.tempDir, 'toBase.lta')
movedFile = os.path.join(tpModel.tempDir, 'alignedToBase.mgz')
utils.run(f'mri_robust_register --mov {maskFile} --dst {baseMaskFile} --lta {transformFile} --mapmovhdr {movedFile} --affine --sat 50 -verbose 0')
baseTransforms.append(sf.load_affine(transformFile))
# Resample the inputs in processed base space
# Again, since we don't have cubic interpolation yet in the python utils, let's just use mri_convert
resampledFile = os.path.join(tpModel.tempDir, 'resampledImage.mgz')
# ATH this will need to be adapted for multi-image inputs...
utils.run(f'mri_convert {tpModel.inputImageFileNames[0]} {resampledFile} -odt float -rl {baseProcessedFile} -rt cubic -at {transformFile}')
tpModel.processedImage = sf.load_volume(resampledFile)
tpModel.processedImage[baseModel.longMask == 0] = 0
# Since we're now working in base-space, we can reuse the base-aligned atlas for every timepoint
tpModel.alignedAtlas = baseModel.alignedAtlas
elapsed = dt.datetime.now() - last_time
print(f'Timepoint alignment took {elapsed.seconds} seconds\n')
# Okay, now we fit the mesh to the base segmentation
last_time = dt.datetime.now()
print('Step 4: fitting mesh to base segmentation')
baseModel.prepare_for_seg_fitting()
baseModel.fit_mesh_to_seg()
# This doesn't actually do anything but it's useful for mimicking the matlab code
for n, tpModel in enumerate(tpModels):
tpModel.atlasMeshFileName = baseModel.warpedMeshFileName
tpModel.cheatingMeshSmoothingSigmas = []
tpModel.prepare_for_seg_fitting()
tpModel.fit_mesh_to_seg()
elapsed = dt.datetime.now() - last_time
print(f'Initial mesh fitting took {elapsed.seconds} seconds\n')
# Global loop: atlas estimation
last_time = dt.datetime.now()
print('Step 5: global mesh fitting')
# Prepare the base for image fitting so that we can extract some mesh information
baseModel.prepare_for_image_fitting(compute_hyps=False)
atlasPositions = baseModel.meshCollection.get_mesh(-1).points
subjectAtlasPositions = baseModel.mesh.points
# Now that we've the mesh to the base segmentation mask, we
# should use this mesh collection in the timepoint models
for n, tpModel in enumerate(tpModels):
tpModel.originalAlphas = baseModel.originalAlphas
tpModel.prepare_for_image_fitting(compute_hyps=False)
# We should keep the masking consistent across timepoints
tpModel.workingMask = baseModel.workingMask
tpModel.maskIndices = baseModel.maskIndices
tpModel.workingImage[tpModel.workingMask == 0] = 0
# compute hyperparameters with base mesh
tpModel.reducedAlphas = baseModel.reducedAlphas
tpModel.meanHyper, tpModel.nHyper = tpModel.get_gaussian_hyps(baseModel.sameGaussianParameters, baseModel.mesh)
# Gather initial subject timepoint mesh positions
subjectTPpositions = [tpModel.mesh.points for tpModel in tpModels]
# This will be the mesh collection we'll use for temporary data
meshCollection = gems.KvlMeshCollection()
meshCollection.read(baseModel.warpedMeshFileName)
meshCollection.transform(baseModel.transform)
meshCollection.k = baseModel.meshStiffness
mesh = meshCollection.get_mesh(0)
mesh.alphas = baseModel.reducedAlphas
# Start the global iterations
for globalIteration in range(baseModel.maxGlobalLongIterations):
print(f'\nGlobal iteration {globalIteration + 1}: estimating subject-specific atlas\n')
# Set temporary data
meshCollection.set_positions(atlasPositions, [subjectAtlasPositions])
meshSA = meshCollection.get_mesh(0)
meshCollection.set_positions(atlasPositions, subjectTPpositions)
# Get optimizer and plug calculator into it
calculator = gems.KvlCostAndGradientCalculator(meshCollection, baseModel.meshStiffness, baseModel.meshStiffness, baseModel.transform)
maximalDeformationStopCriterion = 1e-10
optimizationParameters = {
'Verbose': 0,
'MaximalDeformationStopCriterion': maximalDeformationStopCriterion,
'LineSearchMaximalDeformationIntervalStopCriterion': 1e-10,
'MaximumNumberOfIterations': 1000,
'BFGS-MaximumMemoryLength': 12
}
optimizer = gems.KvlOptimizer(baseModel.optimizerType, meshSA, calculator, optimizationParameters)
for positionUpdatingIterationNumber in range(400):
# Calculate a good step
minLogLikelihoodTimesPrior, maximalDeformation = optimizer.step_optimizer_samseg()
# Log optimization information
iteration_info = [
f'GlobalIter: {globalIteration + 1}',
f'Iter: {positionUpdatingIterationNumber + 1:03d}',
f'MaxDef: {maximalDeformation:.4f}',
f'MinLLxP: {minLogLikelihoodTimesPrior:.4f}',
]
print(' '.join(iteration_info))
if np.isnan(minLogLikelihoodTimesPrior):
print('error: minLogLikelihoodTimesPrior is NaN')
# Check if we need to stop
if maximalDeformation <= maximalDeformationStopCriterion:
print('maximalDeformation is too small - stopping')
break
# Update positions
subjectAtlasPositions = meshSA.points
baseModel.meshCollection.set_positions(atlasPositions, [subjectAtlasPositions])
baseModel.meshCollection.k = baseModel.meshStiffness
for t, tpModel in enumerate(tpModels):
tpModel.meshCollection.set_positions(subjectAtlasPositions, [subjectTPpositions[t]])
tpModel.meshCollection.k = tpModel.meshStiffness
# Now let's fit each timepoint
for t, tpModel in enumerate(tpModels):
print(f'\nGlobal iteration {globalIteration + 1}: deforming time point {t + 1}\n')
# Update the multi-resolution settings
idx = 0 if globalIteration < 2 else 1
tpModel.meshSmoothingSigmas = tpModel.longMeshSmoothingSigmas[idx]
tpModel.imageSmoothingSigmas = tpModel.longImageSmoothingSigmas[idx]
tpModel.maxIterations = tpModel.longMaxIterations[idx]
# Do the fitting stage
tpModel.fit_mesh_to_image()
# Get updated positions
subjectTPpositions = [tpModel.meshCollection.get_mesh(0).points for tpModel in tpModels]
elapsed = dt.datetime.now() - last_time
print(f'Global mesh fitting took {elapsed.seconds} seconds\n')
# Finalize results
for t, tpModel in enumerate(tpModels):
tpModel.extract_segmentation()
# Let's transform (just the header) the output segmentations back to original timepoint space
trf = baseTransforms[t]
vox2world = tpModel.inputImages[0].geom.vox2world @ trf.convert(
space='vox',
source=tpModel.inputImages[0],
target=tpModel.discreteLabels).inv()
rotation = vox2world.matrix[:3, :3] / tpModel.discreteLabels.geom.voxsize
center = np.matmul(vox2world.matrix, np.append(np.asarray(tpModel.discreteLabels.baseshape) / 2, 1))[:3]
tpModel.discreteLabels.geom.update(center=center, rotation=rotation)
# Also, scale the volumes by the determinant of the transform
det = np.linalg.det(trf.matrix[:3, :3])
print(f'Timepoint {t + 1} volume scaling factor: {det}')
tpModel.volumes = {key: vol / det for key, vol in tpModel.volumes.items()}
# Do the subclass-defined postprocessing and cleanup
tpModel.postprocess_segmentation()
tpModel.cleanup()
# Cleanup the base as well
baseModel.cleanup()
elapsed = dt.datetime.now() - start_time
print(f'\nSegmentation complete! Process took {elapsed.seconds / 60:.2f} minutes')
|
/subregions/process.py
| 0.640523 | 0.357371 |
process.py
|
pypi
|
# Samshee
A schema-agnostic parser and writer for illumina® sample sheets v2 and similar documents.
## Features
- parsing and writing illumina® Sample Sheet v2 files.
- encoding to and parsing from json
- customizable validation, ships with a default validation schema that follows illumina® specs
## Examples
### Reading, modifying and writing
``` python
from samshee.samplesheetv2 import SampleSheetV2, read_samplesheetv2
sheet = read_samplesheetv2(filename)
print(sheet)
sheet.header['RunName'] = 'a_new_name'
with open(filename + '.new', "w") as fh:
sheet.write(fh)
```
### Validation: Add validators when constructing the sample sheet:
``` python
from samshee.samplesheetv2 import SampleSheetV2, read_samplesheetv2
import samshee.validation
sheet = read_samplesheetv2(filename, validation = [
samshee.validation.illuminasamplesheetv2schema,
samshee.validation.illuminasamplesheetv2logic,
lambda doc: samshee.validation.check_index_distance(doc, 3)
])
sheet.applications['BCLConvert']['data'][0]['Index'] = 'ACTGACTG'
sheet.applications['BCLConvert']['data'][1]['Index'] = 'ACTGACTT'
# will fail, because check_index_distance will fail when exporting the sheet:
with open(filename + '.new', "w") as fh:
sheet.write(fh)
```
This will give
```
Exception: anonymous validation function #2 raised validation error: Minimal index distance is 1 between the indices ACTGACTG and ACTGACTT which is less than the expected minimal index distance of 3
```
The first two validators (`illuminasamplesheetv2schema` and `illuminasamplesheetv2logic`) are highly recommended and are meant to enforce illumina® specifications so that the sample sheet is accepted by their tools.
### Command line usage
A sample sheet can also be linted and validated with the command line interface,
``` bash
python -m samshee SampleSheet.csv
```
This will simply read the sample sheet, check if there are any errors and output it again in a normalized form, so it may also be useful to format samplesheets consistently (use `python -m samshee SampleSheet.csv > SampleSheet_formatted.csv`)
## SectionedSheet
A sectioned sheet is a text file that contains one or more ordered sections in ini-file-like syntax. Every section starts with a section header, enclosed in square brackets, e.g. `[Reads]`. Any string on the same line after the section header is ignored.
Text following the line containing a section header until the start of a new section or EOF is part of the section.
Every section can either be a settings section, or a data section. Sections that end with "settings" or that are called "Header" or "Reads" are assumed to be settings by default. Any other section is assumed to be a data section.
A settings section is a set of key-value pairs, separated by a comma. Additional fields are ignored.
A data section is in CSV format with one header line, i.e. the first line of a data section determines the field names of the objects. Every row in the same section following the header defines one object with the fields given in the header.
A SectionedSheet is a relatively free format and no input validation other than what is absolutely necessary to parse a file is performed.
## SampleSheetV2
A SampleSheetV2 is a SectionedSheet that contains a defined set of sections and some required fields within these sections, see validation below. Every section that is not a "Header" or a "Reads" section refers to an "application" that may have settings or data sections, or both. The respective sections are named `[<Application>_Settings]` and `[<Application>_Data]`.
## Reading and writing
Use the functions `read_sectionedsheet` and `read_samplesheetv2`. Construction from strings is possible, too, use `parse_sectionedsheet` and `parse_samplesheetv2`.
Both SampleSheetV2 as well as SectionedSheet implement `__str__` and can be converted to a string using `str(sheet)`. Usually, the schema is revalidated at this point.
## Validation
Using `samshee.validation.validate`, `SectionedSheet`s can be validated using both json schema definitions and functions that may raise exceptions. The listed validators are processed one-by-one, i.e., if the SectionedSheet passes the first validator, it will be handed on to the next, etc. This means that validators later in the queue may make the assumptions that earlier validators have run successfully.
A SampleSheetV2 is constructed from a SectionedSheet that passes a sequence of validation steps. By default these are `illuminasamplesheetv2schema` and `illuminasamplesheetv2logic`. They are highly recommended and meant to enforce illumina® specifications so that the sample sheet is accepted by their tools. These validators are based on the [Sample Sheet v2 Settings document](https://support-docs.illumina.com/IN/NextSeq10002000/Content/SHARE/SampleSheetv2/SampleSheetValidation_fNS_m2000_m1000.htm) that provides admissible values and required fields for the `Header`, `Reads` settings as well as for the `Sequencing` and `BCLConvert` "Applications".
Validation of a sample sheet only happens at construction (unless `validators = None` or `[]`), but intentionally not when a sample sheet is manipulated to allow for intermediate states that would not pass validation (e.g. conflicting values for `Reads.Index1` and `BCLConvert.OverrideCycles`). However, by default, validation is performed when the sample sheet is rendered to a string or written out. This ensures that all output adheres to all listed validators.
Further custom validation beyond the illumina® spec can happen by json schema validation or calling a function with the SectionedSheet as an argument, i.e.
``` python
def my_validator(doc: SectionedSheet) -> None:
if 'myapp' not in doc:
raise Exception('sheet does not include settings for myapp.')
```
This would be equivalent to a json-schema
``` json
{
"type": "object",
"required": ["myapp"]
}
```
Much more complicated use cases are possible, enforcing naming conventions on samples, etc.
The following example would guarantee that the sample shield will adhere to illumina® standards and to our own defined schema (in this case that it has a section "myapp"):
``` python
from samshee import SectionedSheet, SampleSheetV2, read_sectionedsheet
from samshee.validation import illuminasamplesheetv2schema, illuminasamplesheetv2logic
def my_validation_function(sectionedsheet : SectionedSheet) -> None:
# do checks here and raise exceptions.
if 'myapp' not in doc:
raise Exception('sheet does not include settings for myapp.')
my_schema = {} # any json schema
secsheet = read_sectionedsheet(filename)
samplesheet = SampleSheetV2(secsheet, validation = [illuminasamplesheetv2schema, illuminasamplesheetv2logic, my_validation_function, my_schema])
```
Json schemata must follow the [json-schema spec](https://json-schema.org/draft/2020-12/json-schema-validation.html), functions may perform any operations and are expected to raise exceptions if a SectionedSheet is invalid.
|
/samshee-0.1.10.tar.gz/samshee-0.1.10/README.md
| 0.867219 | 0.928668 |
README.md
|
pypi
|
from samson.constructions.merkle_damgard_construction import MerkleDamgardConstruction
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.utilities.manipulation import right_rotate, get_blocks
from samson.core.primitives import Primitive
from samson.core.metadata import ConstructionType, SizeSpec, SizeType, FrequencyType
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
import math
# https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SHA-2
H_256 = [0x6a09e667, 0xbb67ae85, 0x3c6ef372, 0xa54ff53a, 0x510e527f, 0x9b05688c, 0x1f83d9ab, 0x5be0cd19]
H_224 = [0xc1059ed8, 0x367cd507, 0x3070dd17, 0xf70e5939, 0xffc00b31, 0x68581511, 0x64f98fa7, 0xbefa4fa4]
H_512 = [0x6a09e667f3bcc908, 0xbb67ae8584caa73b, 0x3c6ef372fe94f82b, 0xa54ff53a5f1d36f1, 0x510e527fade682d1, 0x9b05688c2b3e6c1f, 0x1f83d9abfb41bd6b, 0x5be0cd19137e2179]
H_384 = [0xcbbb9d5dc1059ed8, 0x629a292a367cd507, 0x9159015a3070dd17, 0x152fecd8f70e5939, 0x67332667ffc00b31, 0x8eb44a8768581511, 0xdb0c2e0d64f98fa7, 0x47b5481dbefa4fa4]
ROT_256 = [7, 18, 3, 17, 19, 10, 6, 11, 25, 2, 13, 22]
ROT_512 = [1, 8, 7, 19, 61, 6, 14, 18, 41, 28, 34, 39]
K_256 = [
0x428a2f98, 0x71374491, 0xb5c0fbcf, 0xe9b5dba5, 0x3956c25b, 0x59f111f1, 0x923f82a4, 0xab1c5ed5,
0xd807aa98, 0x12835b01, 0x243185be, 0x550c7dc3, 0x72be5d74, 0x80deb1fe, 0x9bdc06a7, 0xc19bf174,
0xe49b69c1, 0xefbe4786, 0x0fc19dc6, 0x240ca1cc, 0x2de92c6f, 0x4a7484aa, 0x5cb0a9dc, 0x76f988da,
0x983e5152, 0xa831c66d, 0xb00327c8, 0xbf597fc7, 0xc6e00bf3, 0xd5a79147, 0x06ca6351, 0x14292967,
0x27b70a85, 0x2e1b2138, 0x4d2c6dfc, 0x53380d13, 0x650a7354, 0x766a0abb, 0x81c2c92e, 0x92722c85,
0xa2bfe8a1, 0xa81a664b, 0xc24b8b70, 0xc76c51a3, 0xd192e819, 0xd6990624, 0xf40e3585, 0x106aa070,
0x19a4c116, 0x1e376c08, 0x2748774c, 0x34b0bcb5, 0x391c0cb3, 0x4ed8aa4a, 0x5b9cca4f, 0x682e6ff3,
0x748f82ee, 0x78a5636f, 0x84c87814, 0x8cc70208, 0x90befffa, 0xa4506ceb, 0xbef9a3f7, 0xc67178f2
]
K_512 = [
0x428a2f98d728ae22, 0x7137449123ef65cd, 0xb5c0fbcfec4d3b2f, 0xe9b5dba58189dbbc, 0x3956c25bf348b538,
0x59f111f1b605d019, 0x923f82a4af194f9b, 0xab1c5ed5da6d8118, 0xd807aa98a3030242, 0x12835b0145706fbe,
0x243185be4ee4b28c, 0x550c7dc3d5ffb4e2, 0x72be5d74f27b896f, 0x80deb1fe3b1696b1, 0x9bdc06a725c71235,
0xc19bf174cf692694, 0xe49b69c19ef14ad2, 0xefbe4786384f25e3, 0x0fc19dc68b8cd5b5, 0x240ca1cc77ac9c65,
0x2de92c6f592b0275, 0x4a7484aa6ea6e483, 0x5cb0a9dcbd41fbd4, 0x76f988da831153b5, 0x983e5152ee66dfab,
0xa831c66d2db43210, 0xb00327c898fb213f, 0xbf597fc7beef0ee4, 0xc6e00bf33da88fc2, 0xd5a79147930aa725,
0x06ca6351e003826f, 0x142929670a0e6e70, 0x27b70a8546d22ffc, 0x2e1b21385c26c926, 0x4d2c6dfc5ac42aed,
0x53380d139d95b3df, 0x650a73548baf63de, 0x766a0abb3c77b2a8, 0x81c2c92e47edaee6, 0x92722c851482353b,
0xa2bfe8a14cf10364, 0xa81a664bbc423001, 0xc24b8b70d0f89791, 0xc76c51a30654be30, 0xd192e819d6ef5218,
0xd69906245565a910, 0xf40e35855771202a, 0x106aa07032bbd1b8, 0x19a4c116b8d2d0c8, 0x1e376c085141ab53,
0x2748774cdf8eeb99, 0x34b0bcb5e19b48a8, 0x391c0cb3c5c95a63, 0x4ed8aa4ae3418acb, 0x5b9cca4f7763e373,
0x682e6ff3d6b2b8a3, 0x748f82ee5defb2fc, 0x78a5636f43172f60, 0x84c87814a1f0ab72, 0x8cc702081a6439ec,
0x90befffa23631e28, 0xa4506cebde82bde9, 0xbef9a3f7b2c67915, 0xc67178f2e372532b, 0xca273eceea26619c,
0xd186b8c721c0c207, 0xeada7dd6cde0eb1e, 0xf57d4f7fee6ed178, 0x06f067aa72176fba, 0x0a637dc5a2c898a6,
0x113f9804bef90dae, 0x1b710b35131c471b, 0x28db77f523047d84, 0x32caab7b40c72493, 0x3c9ebe0a15c9bebc,
0x431d67c49c100d4c, 0x4cc5d4becb3e42b6, 0x597f299cfc657e2a, 0x5fcb6fab3ad6faec, 0x6c44198c4a475817
]
class SHA2(MerkleDamgardConstruction):
"""
SHA2 hash function base class.
"""
CONSTRUCTION_TYPES = [ConstructionType.MERKLE_DAMGARD, ConstructionType.DAVIES_MEYER]
USAGE_FREQUENCY = FrequencyType.PROLIFIC
def __init__(self, initial_state: list, digest_size: int, state_size: int, block_size: int, rounds: int, rot: list, k: list):
"""
Parameters:
initial_state (list): Initial state as list of integers.
digest_size (int): Output size in bytes.
state_size (int): Number of elements in state.
block_size (int): Amount of message to digest at a time.
rounds (int): Number of compression rounds to perform.
rot (list): Rotation constants.
k (list): `k` constants.
"""
super().__init__(
initial_state=Bytes(b''.join([int.to_bytes(h_i, state_size, 'big') for h_i in initial_state])),
compression_func=None,
digest_size=digest_size,
block_size=block_size
)
Primitive.__init__(self)
self.state_size = state_size
self.rounds = rounds
self.rot = rot
self.k = k
def yield_state(self, message: bytes):
"""
Yields successive states while processing `message`.
Parameters:
message (bytes): Message to hash.
Returns:
generator: Generator yielding states.
"""
for state in MerkleDamgardConstruction.yield_state(self, message):
yield state[:self.digest_size]
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['initial_state', 'block_size', 'digest_size']
def compression_func(self, block: bytes, state: bytes) -> Bytes:
"""
SHA-2 compression function.
Parameters:
block (bytes): Block being digested.
state (bytes): Current digest state.
Returns:
Bytes: Hash output.
"""
bit_mask = 0xFFFFFFFF if self.state_size == 4 else 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
bit_size = self.state_size * 8
state = [int.from_bytes(chunk, 'big') for chunk in state.chunk(self.state_size)]
w = [int.from_bytes(b, 'big') for b in get_blocks(block, self.state_size)] + ([None] * (self.rounds - 16))
for i in range(16, self.rounds):
s0 = right_rotate(w[i-15], self.rot[0], bit_size) ^ right_rotate(w[i-15], self.rot[1], bit_size) ^ (w[i-15] >> self.rot[2])
s1 = right_rotate(w[i-2], self.rot[3], bit_size) ^ right_rotate(w[i-2], self.rot[4], bit_size) ^ (w[i-2] >> self.rot[5])
w[i] = (w[i-16] + s0 + w[i-7] + s1) & bit_mask
a = state[0]
b = state[1]
c = state[2]
d = state[3]
e = state[4]
f = state[5]
g = state[6]
h = state[7]
for i in range(self.rounds):
S1 = right_rotate(e, self.rot[6], bit_size) ^ right_rotate(e, self.rot[7], bit_size) ^ right_rotate(e, self.rot[8], bit_size)
ch = g ^ (e & (f ^ g))
temp1 = (h + S1 + ch + self.k[i] + w[i])
S0 = right_rotate(a, self.rot[9], bit_size) ^ right_rotate(a, self.rot[10], bit_size) ^ right_rotate(a, self.rot[11], bit_size)
maj = (a & b) ^ (a & c) ^ (b & c)
temp2 = (S0 + maj)
h = g
g = f
f = e
e = (d + temp1) & bit_mask
d = c
c = b
b = a
a = (temp1 + temp2) & bit_mask
state[0] += a
state[1] += b
state[2] += c
state[3] += d
state[4] += e
state[5] += f
state[6] += g
state[7] += h
return Bytes(b''.join([int.to_bytes(h_i & bit_mask, self.state_size, 'big') for h_i in state]))
@register_primitive()
class SHA224(SHA2):
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.SINGLE, sizes=224)
def __init__(self, h: list=None):
"""
Parameters:
h (list): Initial state as list of integers.
"""
super().__init__(
initial_state=h or H_224,
digest_size=224 // 8,
state_size=4,
block_size=64,
rounds=64,
rot=ROT_256,
k=K_256
)
@register_primitive()
class SHA256(SHA2):
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.SINGLE, sizes=256)
def __init__(self, h: list=None):
"""
Parameters:
h (list): Initial state as list of integers.
"""
super().__init__(
initial_state=h or H_256,
digest_size=256 // 8,
state_size=4,
block_size=64,
rounds=64,
rot=ROT_256,
k=K_256
)
@register_primitive()
class SHA384(SHA2):
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.SINGLE, sizes=384)
def __init__(self, h: list=None):
"""
Parameters:
h (list): Initial state as list of integers.
"""
super().__init__(
initial_state=h or H_384,
digest_size=384 // 8,
state_size=8,
block_size=128,
rounds=80,
rot=ROT_512,
k=K_512
)
@register_primitive()
class SHA512(SHA2):
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.RANGE, sizes=range(513), typical=[512])
def __init__(self, h: list=None, trunc: int=None):
"""
Parameters:
h (list): Initial state as list of integers.
trunc (int): Truncation length for SHA-512/t.
"""
# FIPS 180-4
if trunc:
h = h or H_512
h_doubleprime = [h ^ 0xa5a5a5a5a5a5a5a5 for h in H_512]
h = [chunk.int() for chunk in SHA512(h=h_doubleprime).hash(f'SHA-512/{trunc}'.encode('utf-8')).chunk(8)]
super().__init__(
initial_state=h or H_512,
digest_size=512 // 8,
state_size=8,
block_size=128,
rounds=80,
rot=ROT_512,
k=K_512
)
self.trunc = trunc or 0
def hash(self, message: bytes) -> Bytes:
"""
Yields the final, hashed state of the `message`.
Parameters:
message (bytes): Message to be hashed.
Returns:
Bytes: Fully-hashed state.
"""
final_state = super().hash(message)
return final_state[:math.ceil((self.trunc or 512) / 8)]
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/hashes/sha2.py
| 0.464902 | 0.261573 |
sha2.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.utilities.manipulation import right_rotate
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.hashes.sha2 import H_512, H_256
from samson.core.primitives import Hash, Primitive
from samson.core.metadata import ConstructionType, SizeSpec, SizeType, FrequencyType
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
from copy import deepcopy
SIGMA = [
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15],
[14, 10, 4, 8, 9, 15, 13, 6, 1, 12, 0, 2, 11, 7, 5, 3],
[11, 8, 12, 0, 5, 2, 15, 13, 10, 14, 3, 6, 7, 1, 9, 4],
[7, 9, 3, 1, 13, 12, 11, 14, 2, 6, 5, 10, 4, 0, 15, 8],
[9, 0, 5, 7, 2, 4, 10, 15, 14, 1, 11, 12, 6, 8, 3, 13],
[2, 12, 6, 10, 0, 11, 8, 3, 4, 13, 7, 5, 15, 14, 1, 9],
[12, 5, 1, 15, 14, 13, 4, 10, 0, 7, 6, 3, 9, 2, 8, 11],
[13, 11, 7, 14, 12, 1, 3, 9, 5, 0, 15, 4, 8, 6, 2, 10],
[6, 15, 14, 9, 11, 3, 0, 8, 12, 2, 13, 7, 1, 4, 10, 5],
[10, 2, 8, 4, 7, 6, 1, 5, 15, 11, 9, 14, 3, 12, 13, 0]
]
class BLAKE2(Hash):
"""
Cryptographic hash function based on ChaCha.
"""
CONSTRUCTION_TYPES = [ConstructionType.HASH_ITERATIVE_FRAMEWORK]
USAGE_FREQUENCY = FrequencyType.UNUSUAL
def __init__(self, key: bytes, desired_hash_len: int):
"""
Parameters:
key (bytes): (Optional) Bytes-like object to key the hash.
desired_hash_len (int): Desired output length.
"""
Primitive.__init__(self)
self.key = key
self.digest_size = desired_hash_len
self.block_size = self.IMPL_BLOCK_SIZE
def padding_func(self, message: bytes) -> bytes:
if len(message) % self.IMPL_BLOCK_SIZE != 0 or len(message) == 0:
message = message + b'\x00' * (self.IMPL_BLOCK_SIZE - (len(message) % self.IMPL_BLOCK_SIZE))
return message
# https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BLAKE_(hash_function)
def mix(self, V_a, V_b, V_c, V_d, x, y):
V_a = (V_a + V_b + x) & self.MASKBITS
V_d = right_rotate(V_d ^ V_a, self.ROTATIONS[0], bits=self.WORD_SIZE)
V_c = (V_c + V_d) & self.MASKBITS
V_b = right_rotate(V_b ^ V_c, self.ROTATIONS[1], bits=self.WORD_SIZE)
V_a = (V_a + V_b + y) & self.MASKBITS
V_d = right_rotate(V_d ^ V_a, self.ROTATIONS[2], bits=self.WORD_SIZE)
V_c = (V_c + V_d) & self.MASKBITS
V_b = right_rotate(V_b ^ V_c, self.ROTATIONS[3], bits=self.WORD_SIZE)
return V_a, V_b, V_c, V_d
def compress(self, h, iv, chunk, t, is_last_block):
V = [None] * 16
V[:8] = h
V[8:] = iv
V[12] ^= t & self.MASKBITS
V[13] ^= t >> self.WORD_SIZE
if is_last_block:
V[14] ^= self.MASKBITS
m = [m_i.to_int() for m_i in chunk.chunk(self.WORD_SIZE // 8)]
for i in range(self.ROUNDS):
S = [None] * 16
S = SIGMA[i % 10]
V[0], V[4], V[8], V[12] = self.mix(V[0], V[4], V[8], V[12], m[S[0]], m[S[1]])
V[1], V[5], V[9], V[13] = self.mix(V[1], V[5], V[9], V[13], m[S[2]], m[S[3]])
V[2], V[6], V[10], V[14] = self.mix(V[2], V[6], V[10], V[14], m[S[4]], m[S[5]])
V[3], V[7], V[11], V[15] = self.mix(V[3], V[7], V[11], V[15], m[S[6]], m[S[7]])
V[0], V[5], V[10], V[15] = self.mix(V[0], V[5], V[10], V[15], m[S[8]], m[S[9]])
V[1], V[6], V[11], V[12] = self.mix(V[1], V[6], V[11], V[12], m[S[10]], m[S[11]])
V[2], V[7], V[8], V[13] = self.mix(V[2], V[7], V[8], V[13], m[S[12]], m[S[13]])
V[3], V[4], V[9], V[14] = self.mix(V[3], V[4], V[9], V[14], m[S[14]], m[S[15]])
h = [x ^ y for x, y in zip(h, V[:8])]
h = [x ^ y for x, y in zip(h, V[8:])]
return h
def hash(self, message: bytes) -> Bytes:
"""
Hashes the `message`.
Parameters:
message (bytes): Message to be hashed.
Returns:
Bytes: The hash digest.
"""
message = Bytes(message, 'little')
state = deepcopy(self.IV)
last_block_size = len(message) % self.IMPL_BLOCK_SIZE
if last_block_size == 0 and len(message) > 0:
last_block_size = self.IMPL_BLOCK_SIZE
state[0] ^= (0x0101 << 16) + (len(self.key) << 8) + (self.digest_size)
if len(self.key) > 0:
message = self.padding_func(self.key) + message
padded_msg = self.padding_func(message)
bytes_compressed = 0
msg_chunks = padded_msg.chunk(self.IMPL_BLOCK_SIZE)
for i, chunk in enumerate(msg_chunks):
is_last_block = i == (len(msg_chunks) - 1)
bytes_compressed += last_block_size if is_last_block else self.IMPL_BLOCK_SIZE
state = self.compress(state, self.IV, chunk, bytes_compressed, is_last_block)
return sum([Bytes(h, byteorder='little').zfill(self.WORD_SIZE // 8) for h in state])[:self.digest_size]
@register_primitive()
class BLAKE2b(BLAKE2):
BLOCK_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.SINGLE, sizes=128)
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.ARBITRARY, typical=[512])
WORD_SIZE = 64
MASKBITS = 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
ROUNDS = 12
IMPL_BLOCK_SIZE = 128
IV = H_512
ROTATIONS = [32, 24, 16, 63]
def __init__(self, desired_hash_len=64, key=b''):
"""
Parameters:
key (bytes): (Optional) Bytes-like object to key the hash.
desired_hash_len (int): Desired output length.
"""
super().__init__(key, desired_hash_len)
@register_primitive()
class BLAKE2s(BLAKE2):
BLOCK_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.SINGLE, sizes=64)
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.ARBITRARY, typical=[256])
WORD_SIZE = 32
MASKBITS = 0xFFFFFFFF
ROUNDS = 10
IMPL_BLOCK_SIZE = 64
IV = H_256
ROTATIONS = [16, 12, 8, 7]
def __init__(self, desired_hash_len=32, key=b''):
"""
Parameters:
key (bytes): (Optional) Bytes-like object to key the hash.
desired_hash_len (int): Desired output length.
"""
super().__init__(key, desired_hash_len)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/hashes/blake2.py
| 0.639736 | 0.415314 |
blake2.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.utilities.manipulation import left_rotate
from samson.constructions.merkle_damgard_construction import MerkleDamgardConstruction
from samson.hashes.md5 import state_to_bytes, bytes_to_state
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.core.primitives import Primitive
from samson.core.metadata import SizeSpec, SizeType
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
import struct
def F(x,y,z):
return (x & y) | (~x & z)
def G(x,y,z):
return (x & y) | (x & z) | (y & z)
def H(x,y,z):
return x ^ y ^ z
iv = [
0x67452301,
0xefcdab89,
0x98badcfe,
0x10325476
]
def compression_func(message, state):
X = list(struct.unpack("<16I", message) + (None,) * (80-16))
h = bytes_to_state(state)
last_state = [x for x in h]
# Round 1
s = (3,7,11,19)
for r in range(16):
i = (16-r)%4
k = r
h[i] = left_rotate((h[i] + F(h[(i+1)%4], h[(i+2)%4], h[(i+3)%4]) + X[k]) % 2**32, s[r%4])
# Round 2
s = (3,5,9,13)
for r in range(16):
i = (16-r)%4
k = 4*(r%4) + r//4
h[i] = left_rotate((h[i] + G(h[(i+1)%4], h[(i+2)%4], h[(i+3)%4]) + X[k] + 0x5a827999) % 2**32, s[r%4])
# Round 3
s = (3,9,11,15)
k = (0,8,4,12,2,10,6,14,1,9,5,13,3,11,7,15)
for r in range(16):
i = (16-r)%4
h[i] = left_rotate((h[i] + H(h[(i+1)%4], h[(i+2)%4], h[(i+3)%4]) + X[k[r]] + 0x6ed9eba1) % 2**32, s[r%4])
new_state = []
for i,v in enumerate(h):
new_state.append((v + last_state[i]) % 2**32)
return Bytes(state_to_bytes(new_state))
@register_primitive()
class MD4(MerkleDamgardConstruction):
"""
Obsolete cryptographic hash function and predecessor to MD5.
"""
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.SINGLE, sizes=128)
def __init__(self, initial_state: bytes=state_to_bytes(iv)):
"""
Parameters:
initial_state (bytes): (Optional) Initial internal state.
"""
super().__init__(
initial_state=initial_state,
compression_func=compression_func,
digest_size=16,
endianness='little'
)
Primitive.__init__(self)
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['initial_state', 'block_size']
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/hashes/md4.py
| 0.44553 | 0.278741 |
md4.py
|
pypi
|
import struct
from samson.utilities.manipulation import left_rotate
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.constructions.merkle_damgard_construction import MerkleDamgardConstruction
from samson.core.primitives import Primitive
from samson.core.metadata import SizeSpec, SizeType, FrequencyType
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
def compression_func(chunk, state):
"""Process a chunk of data and return the new digest variables."""
assert len(chunk) == 64
w = [0] * 80
# Break chunk into sixteen 4-byte big-endian words w[i]
for i in range(16):
w[i] = struct.unpack(b'>I', chunk[i*4:i*4 + 4])[0]
# Extend the sixteen 4-byte words into eighty 4-byte words
for i in range(16, 80):
w[i] = left_rotate(w[i-3] ^ w[i-8] ^ w[i-14] ^ w[i-16], 1)
# Initialize hash value for this chunk
h0, h1, h2, h3, h4 = bytes_to_state(state)
a = h0
b = h1
c = h2
d = h3
e = h4
for i in range(80):
if 0 <= i <= 19:
# Use alternative 1 for f from FIPS PB 180-1 to avoid bitwise not
f = d ^ (b & (c ^ d))
k = 0x5A827999
elif 20 <= i <= 39:
f = b ^ c ^ d
k = 0x6ED9EBA1
elif 40 <= i <= 59:
f = (b & c) | (b & d) | (c & d)
k = 0x8F1BBCDC
elif 60 <= i <= 79:
f = b ^ c ^ d
k = 0xCA62C1D6
a, b, c, d, e = ((left_rotate(a, 5) + f + e + k + w[i]) & 0xffffffff,
a, left_rotate(b, 30), c, d)
# Add this chunk's hash to result so far
h0 = (h0 + a) & 0xffffffff
h1 = (h1 + b) & 0xffffffff
h2 = (h2 + c) & 0xffffffff
h3 = (h3 + d) & 0xffffffff
h4 = (h4 + e) & 0xffffffff
state = [h0, h1, h2, h3, h4]
return Bytes(state_to_bytes(state))
def state_to_bytes(state):
return int.to_bytes(sum(x<<(32*i) for i, x in enumerate(state[::-1])), 20, 'big')
def bytes_to_state(state_bytes):
as_int = int.from_bytes(state_bytes, 'big')
return [(as_int>>(32*i)) & 0xffffffff for i in range(4, -1, -1)]
@register_primitive()
class SHA1(MerkleDamgardConstruction):
"""
Cryptographic hash function considered to be broken but is still widely used.
"""
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.SINGLE, sizes=160)
USAGE_FREQUENCY = FrequencyType.PROLIFIC
def __init__(self, initial_state: bytes=state_to_bytes([0x67452301, 0xefcdab89, 0x98badcfe, 0x10325476, 0xC3D2E1F0])):
"""
Parameters:
initial_state (bytes): (Optional) Initial internal state.
"""
if type(initial_state) is list:
initial_state = state_to_bytes(initial_state)
super().__init__(
initial_state=initial_state,
compression_func=compression_func,
digest_size=20,
)
Primitive.__init__(self)
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['initial_state', 'block_size']
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/hashes/sha1.py
| 0.658966 | 0.460835 |
sha1.py
|
pypi
|
from math import log
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.utilities.manipulation import left_rotate
from samson.constructions.sponge_construction import SpongeConstruction
from samson.core.primitives import Hash, Primitive
from samson.core.metadata import ConstructionType, SizeSpec, SizeType, FrequencyType
# https://github.com/ctz/keccak/blob/master/keccak.py
RC = [
0x0000000000000001, 0x0000000000008082, 0x800000000000808A, 0x8000000080008000,
0x000000000000808B, 0x0000000080000001, 0x8000000080008081, 0x8000000000008009,
0x000000000000008A, 0x0000000000000088, 0x0000000080008009, 0x000000008000000A,
0x000000008000808B, 0x800000000000008B, 0x8000000000008089, 0x8000000000008003,
0x8000000000008002, 0x8000000000000080, 0x000000000000800A, 0x800000008000000A,
0x8000000080008081, 0x8000000000008080, 0x0000000080000001, 0x8000000080008008
]
R = [
[ 0, 1, 62, 28, 27, ],
[ 36, 44, 6, 55, 20, ],
[ 3, 10, 43, 25, 39, ],
[ 41, 45, 15, 21, 8, ],
[ 18, 2, 61, 56, 14, ]
]
# https://keccak.team/keccak_specs_summary.html
class Keccak(SpongeConstruction, Hash):
"""
SHA3 winner based on the SpongeConstruction.
"""
USAGE_FREQUENCY = FrequencyType.NORMAL
CONSTRUCTION_TYPES = [ConstructionType.SPONGE]
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.ARBITRARY, sizes=[224, 256, 384, 512])
def __init__(self, r: int, c: int, digest_bit_size: int, auto_reset_state: bool=True, padding: int=0x01):
"""
Parameters:
r (int): Bit-size of the sponge function.
c (int): Sponge capacity.
digest_bit_size (int): Desired size of output.
auto_reset_state (bool): Whether or not to reset the internal state before hashing.
padding (int): The domain-specific padding number.
"""
super().__init__(self.keccak_f, self.pad, r, c)
Primitive.__init__(self)
self.w = (r + c) // 25
self.n = int(log(self.w, 2) * 2 + 12)
self.digest_size = (digest_bit_size // 8)
self.auto_reset_state = auto_reset_state
self.padding = padding
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['r', 'c', 'n', 'w', 'digest_size', 'block_size']
def pad(self, in_bytes: bytes) -> bytes:
bit_rate_bytes = (self.r + 7) // 8
pad_len = bit_rate_bytes - (len(in_bytes) % bit_rate_bytes)
if pad_len == 0:
pad_len = bit_rate_bytes
if pad_len == 1:
return in_bytes + bytes([self.padding + 0x80])
else:
return in_bytes + bytes([self.padding] + ([0] * (pad_len - 2)) + [0x80])
def keccak_f(self, A):
for i in range(self.n):
A = self.round_func(A, RC[i])
return A
def round_func(self, A, rc):
C = [0] * 5
for x in range(5):
C[x] = A[x][0] ^ A[x][1] ^ A[x][2] ^ A[x][3] ^ A[x][4]
D = [0] * 5
for x in range(5):
D[x] = C[x-1] ^ left_rotate(C[(x+1) % 5], 1, 64)
for x in range(5):
for y in range(5):
A[x][y] = A[x][y] ^ D[x]
B = [[0] * 5 for _ in range(5)]
for x in range(5):
for y in range(5):
B[y][(2*x + 3*y) % 5] = left_rotate(A[x][y], R[y][x], 64)
for x in range(5):
for y in range(5):
A[x][y] = B[x][y] ^ ((~B[(x+1) % 5][y]) & B[(x+2) % 5][y])
A[0][0] ^= rc
return A
def hash(self, message: bytes) -> Bytes:
"""
Hashes the `message`.
Parameters:
message (bytes): Message to be hashed.
Returns:
Bytes: The hash digest.
"""
if self.auto_reset_state:
self.reset()
self.absorb(Bytes.wrap(message))
return sum(self.squeeze(self.digest_size))[:self.digest_size]
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/hashes/keccak.py
| 0.781581 | 0.307131 |
keccak.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.constructions.merkle_damgard_construction import MerkleDamgardConstruction
from samson.utilities.manipulation import left_rotate
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.core.primitives import Primitive
from samson.core.metadata import SizeSpec, SizeType, FrequencyType
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
import math
# https://rosettacode.org/wiki/MD5/Implementation#Python
rotate_amounts = [7, 12, 17, 22, 7, 12, 17, 22, 7, 12, 17, 22, 7, 12, 17, 22,
5, 9, 14, 20, 5, 9, 14, 20, 5, 9, 14, 20, 5, 9, 14, 20,
4, 11, 16, 23, 4, 11, 16, 23, 4, 11, 16, 23, 4, 11, 16, 23,
6, 10, 15, 21, 6, 10, 15, 21, 6, 10, 15, 21, 6, 10, 15, 21]
constants = [int(abs(math.sin(i+1)) * 2**32) & 0xFFFFFFFF for i in range(64)]
functions = 16*[lambda b, c, d: (b & c) | (~b & d)] + \
16*[lambda b, c, d: (d & b) | (~d & c)] + \
16*[lambda b, c, d: b ^ c ^ d] + \
16*[lambda b, c, d: c ^ (b | ~d)]
index_functions = 16*[lambda i: i] + \
16*[lambda i: (5*i + 1)%16] + \
16*[lambda i: (3*i + 5)%16] + \
16*[lambda i: (7*i)%16]
def state_to_bytes(state):
return int.to_bytes(sum(x<<(32*i) for i, x in enumerate(state)), 16, 'little')
def bytes_to_state(state_bytes):
as_int = int.from_bytes(state_bytes, 'little')
return [(as_int>>(32*i)) & 0xffffffff for i in range(4)]
def compression_func(message, state):
new_state = bytes_to_state(state)
for chunk_ofst in range(0, len(message), 64):
a, b, c, d = new_state
chunk = message[chunk_ofst:chunk_ofst+64]
for i in range(64):
f = functions[i](b, c, d)
g = index_functions[i](i)
to_rotate = a + f + constants[i] + int.from_bytes(chunk[4*g:4*g+4], byteorder='little')
new_b = (b + left_rotate(to_rotate, rotate_amounts[i])) & 0xFFFFFFFF
a, b, c, d = d, new_b, b, c
for i, val in enumerate([a, b, c, d]):
new_state[i] += val
new_state[i] &= 0xFFFFFFFF
return Bytes(state_to_bytes(new_state))
@register_primitive()
class MD5(MerkleDamgardConstruction):
"""
Popular but completely broken cryptographic hash function.
"""
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.SINGLE, sizes=128)
USAGE_FREQUENCY = FrequencyType.PROLIFIC
def __init__(self, initial_state: bytes=state_to_bytes([0x67452301, 0xefcdab89, 0x98badcfe, 0x10325476])):
"""
Parameters:
initial_state (bytes): (Optional) Initial internal state.
"""
super().__init__(
initial_state=initial_state,
compression_func=compression_func,
digest_size=16,
endianness='little'
)
Primitive.__init__(self)
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['initial_state', 'block_size']
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/hashes/md5.py
| 0.547464 | 0.272049 |
md5.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.utilities.manipulation import left_rotate
from samson.constructions.merkle_damgard_construction import MerkleDamgardConstruction
from samson.core.primitives import Primitive
from samson.core.metadata import SizeSpec, SizeType
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
# http://cacr.uwaterloo.ca/hac/about/chap9.pdf
RL = [
[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 ],
[ 7, 4, 13, 1, 10, 6, 15, 3, 12, 0, 9, 5, 2, 14, 11, 8 ],
[ 3, 10, 14, 4, 9, 15, 8, 1, 2, 7, 0, 6, 13, 11, 5, 12 ],
[ 1, 9, 11, 10, 0, 8, 12, 4, 13, 3, 7, 15, 14, 5, 6, 2 ],
[ 4, 0, 5, 9, 7, 12, 2, 10, 14, 1, 3, 8, 11, 6, 15, 13 ]
]
RR = [
[ 5, 14, 7, 0, 9, 2, 11, 4, 13, 6, 15, 8, 1, 10, 3, 12 ],
[ 6, 11, 3, 7, 0, 13, 5, 10, 14, 15, 8, 12, 4, 9, 1, 2 ],
[ 15, 5, 1, 3, 7, 14, 6, 9, 11, 8, 12, 2, 10, 0, 4, 13 ],
[ 8, 6, 4, 1, 3, 11, 15, 0, 5, 12, 2, 13, 9, 7, 10, 14 ],
[ 12, 15, 10, 4, 1, 5, 8, 7, 6, 2, 13, 14, 0, 3, 9, 11 ]
]
SL = [
[ 11, 14, 15, 12, 5, 8, 7, 9, 11, 13, 14, 15, 6, 7, 9, 8 ],
[ 7, 6, 8, 13, 11, 9, 7, 15, 7, 12, 15, 9, 11, 7, 13, 12 ],
[ 11, 13, 6, 7, 14, 9, 13, 15, 14, 8, 13, 6, 5, 12, 7, 5 ],
[ 11, 12, 14, 15, 14, 15, 9, 8, 9, 14, 5, 6, 8, 6, 5, 12 ],
[ 9, 15, 5, 11, 6, 8, 13, 12, 5, 12, 13, 14, 11, 8, 5, 6 ]
]
SR = [
[ 8, 9, 9, 11, 13, 15, 15, 5, 7, 7, 8, 11, 14, 14, 12, 6 ],
[ 9, 13, 15, 7, 12, 8, 9, 11, 7, 7, 12, 7, 6, 15, 13, 11 ],
[ 9, 7, 15, 11, 8, 6, 6, 14, 12, 13, 5, 14, 13, 13, 7, 5 ],
[ 15, 5, 8, 11, 14, 14, 6, 14, 6, 9, 12, 9, 12, 5, 15, 8 ],
[ 8, 5, 12, 9, 12, 5, 14, 6, 8, 13, 6, 5, 15, 13, 11, 11 ]
]
F1 = lambda x, y, z: x ^ y ^ z
F2 = lambda x, y, z: (x & y) | (~x & z)
F3 = lambda x, y, z: (x | ~y) ^ z
F4 = lambda x, y, z: (x & z) | (y & ~z)
F5 = lambda x, y, z: x ^ (y | ~z)
FL = [F1, F2, F3, F4, F5]
FR = [F5, F4, F3, F2, F1]
KL = [0x00000000, 0x5A827999, 0x6ED9EBA1, 0x8F1BBCDC, 0xA953FD4E]
KR = [0x50A28BE6, 0x5C4DD124, 0x6D703EF3, 0x7A6D76E9, 0x00000000]
INIT_STATE = Bytes(int.to_bytes(0x0123456789ABCDEFFEDCBA9876543210F0E1D2C3, 20, 'big'), byteorder='little')
def COMPRESS(message, state):
# The authors of RIPEMD160 couldn't decide on whether to use big or little endian, so they used both!
# RIPEMD160 takes in bytes as big endian but operates and outputs bytes of little endian. Man, was this 'fun.'
h = [chunk.to_int() for chunk in state.chunk(4)]
msg_chunks = [chunk[::-1].to_int() for chunk in Bytes.wrap(message, byteorder='big').chunk(4)]
AL = AR = h[0]
BL = BR = h[1]
CL = CR = h[2]
DL = DR = h[3]
EL = ER = h[4]
for curr_round in range(5):
for w in range(16):
T = left_rotate(AL + FL[curr_round](BL, CL, DL) + msg_chunks[RL[curr_round][w]] + KL[curr_round], SL[curr_round][w]) + EL
AL = EL & 0xFFFFFFFF; EL = DL & 0xFFFFFFFF; DL = left_rotate(CL, 10); CL = BL & 0xFFFFFFFF; BL = T & 0xFFFFFFFF
T = left_rotate(AR + FR[curr_round](BR, CR, DR) + msg_chunks[RR[curr_round][w]] + KR[curr_round], SR[curr_round][w]) + ER
AR = ER & 0xFFFFFFFF; ER = DR & 0xFFFFFFFF; DR = left_rotate(CR, 10); CR = BR & 0xFFFFFFFF; BR = T & 0xFFFFFFFF
T = (h[1] + CL + DR) & 0xFFFFFFFF
h[1] = (h[2] + DL + ER) & 0xFFFFFFFF
h[2] = (h[3] + EL + AR) & 0xFFFFFFFF
h[3] = (h[4] + AL + BR) & 0xFFFFFFFF
h[4] = (h[0] + BL + CR) & 0xFFFFFFFF
h[0] = T
return sum([Bytes(state, 'little').zfill(4) for state in h])
@register_primitive()
class RIPEMD160(MerkleDamgardConstruction):
"""
Stands for RACE Integrity Primitives Evaluation Message Digest (RIPEMD). While there exist other
versions of RIPEMD (128, 256, and 320), 160 is the most popular.
"""
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.SINGLE, sizes=160)
def __init__(self, initial_state: bytes=INIT_STATE):
"""
Parameters:
initial_state (bytes): (Optional) Initial internal state.
"""
super().__init__(
initial_state=initial_state,
compression_func=COMPRESS,
digest_size=20,
endianness='little'
)
Primitive.__init__(self)
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['initial_state', 'block_size']
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/hashes/ripemd160.py
| 0.505615 | 0.290132 |
ripemd160.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.hashes.keccak import Keccak
from samson.core.primitives import Primitive
from samson.core.metadata import SizeSpec, SizeType, FrequencyType
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
@register_primitive()
class SHA3_224(Keccak):
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.SINGLE, sizes=224)
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(r=1152, c=448, digest_bit_size=224, padding=0x06)
Primitive.__init__(self)
@register_primitive()
class SHA3_256(Keccak):
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.SINGLE, sizes=256)
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(r=1088, c=512, digest_bit_size=256, padding=0x06)
Primitive.__init__(self)
@register_primitive()
class SHA3_384(Keccak):
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.SINGLE, sizes=384)
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(r=832, c=768, digest_bit_size=384, padding=0x06)
Primitive.__init__(self)
@register_primitive()
class SHA3_512(Keccak):
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.SINGLE, sizes=512)
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(r=576, c=1024, digest_bit_size=512, padding=0x06)
Primitive.__init__(self)
@register_primitive()
class SHAKE128(Keccak):
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.ARBITRARY, typical=[128])
def __init__(self, digest_bit_length: int):
"""
Parameters:
digest_bit_length (int): Desired digest length in bits.
"""
super().__init__(r=1344, c=256, digest_bit_size=digest_bit_length, padding=0x1F)
Primitive.__init__(self)
@register_primitive()
class SHAKE256(Keccak):
OUTPUT_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.ARBITRARY, typical=[256])
def __init__(self, digest_bit_length: int):
"""
Parameters:
digest_bit_length (int): Desired digest length in bits.
"""
super().__init__(r=1088, c=512, digest_bit_size=digest_bit_length, padding=0x1F)
Primitive.__init__(self)
class cSHAKE(Keccak):
"""
References:
https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/specialpublications/nist.sp.800-185.pdf
"""
def __init__(self, r: int, c: int, digest_bit_length: int, w: int, function_name: bytes, customization_str: bytes):
super().__init__(r=r, c=c, digest_bit_size=digest_bit_length, padding=0x1F)
self.function_name = function_name
self.customization_str = customization_str
self.w = w
self.padding = 0x04 if self.function_name or self.customization_str else 0x1F
def _encode(self, x: int, left_encode: bool=True) -> Bytes:
n = max(x.bit_length(), 1)
n += -n % 8
n //= 8
left, right = [], []
len_enc = [n]
if left_encode:
left = len_enc
else:
right = len_enc
return Bytes(left) + Bytes(x) + Bytes(right)
def left_encode(self, x: int) -> Bytes:
return self._encode(x, left_encode=True)
def right_encode(self, x: int) -> Bytes:
return self._encode(x, left_encode=False)
def encode_string(self, message: bytes) -> bytes:
return self.left_encode(len(message)*8) + message
def bytepad(self, message: bytes) -> Bytes:
return (self.left_encode(self.w) + message).pad_congruent_right(self.w)
def pad(self, message: bytes) -> Bytes:
if self.function_name or self.customization_str:
padded = self.bytepad(self.encode_string(self.function_name) + self.encode_string(self.customization_str)) + message
return super().pad(padded)
else:
return super().pad(message)
@register_primitive()
class cSHAKE128(cSHAKE):
def __init__(self, digest_bit_length: int, function_name: bytes=b'', customization_str: bytes=b''):
"""
Parameters:
digest_bit_length (int): Desired digest length in bits.
function_name (bytes): NIST function string.
customization_str (bytes): User defined string.
"""
super().__init__(r=1344, c=256, digest_bit_length=digest_bit_length, w=168, function_name=function_name, customization_str=customization_str)
Primitive.__init__(self)
@register_primitive()
class cSHAKE256(cSHAKE):
def __init__(self, digest_bit_length: int, function_name: bytes=b'', customization_str: bytes=b''):
"""
Parameters:
digest_bit_length (int): Desired digest length in bits.
function_name (bytes): NIST function string.
customization_str (bytes): User defined string.
"""
super().__init__(r=1088, c=512, digest_bit_length=digest_bit_length, w=136, function_name=function_name, customization_str=customization_str)
Primitive.__init__(self)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/hashes/sha3.py
| 0.770508 | 0.163379 |
sha3.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.block_ciphers.des import DES
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.utilities.runtime import RUNTIME
from samson.core.base_object import BaseObject
import itertools
import string
class LM(BaseObject):
def __init__(self, plaintext: bytes=b'KGS!@#$%'):
self.plaintext = plaintext
self.block_size = 7
def hash(self, message: bytes) -> Bytes:
"""
Hash `message` with LM.
Parameters:
message (bytes): Message to be hashed.
Returns:
Bytes: LM hash.
"""
key = Bytes.wrap(message.upper())[:14]
key += b'\x00' * (14 - len(key))
# Add parity bits
key_bits = key.bits()
key = Bytes(int(''.join([str(chunk) + '0' for chunk in key_bits.chunk(7)]), 2)).zfill(16)
return DES(key[:8]).encrypt(self.plaintext) + DES(key[8:]).encrypt(self.plaintext)
def check_halves_null(self, lm_hash: bytes) -> (bool, bool):
"""
Checks if either half of the plaintext is null. LM hashes encrypt each half of the plaintext separately so
attackers can determine if the plaintext is less than eight characters by checking if the second half is 'aad3b435b51404ee'.
Parameters:
lm_hash (bytes): LM hash.
Returns:
(bool, bool): Whether or not each half of the LM hash is null.
"""
return [half == DES(Bytes(b'').zfill(8)).encrypt(self.plaintext) for half in lm_hash.chunk(8)]
@RUNTIME.report
def crack(self, lm_hash: bytes, charset: bytes=None) -> Bytes:
"""
Cracks both halves simultaneously.
Parameters:
lm_hash (bytes): Hash to crack.
charset (bytes): Character set to use.
Returns:
Bytes: Cracked LM hash.
"""
h1, h2 = lm_hash.zfill(16).chunk(8)
h1_pt, h2_pt = None, None
h1_null, h2_null = self.check_halves_null(lm_hash)
if h1_null:
h1_pt = Bytes(b'').zfill(8)
if h2_null:
h2_pt = Bytes(b'').zfill(8)
if not charset:
charset = bytes(string.ascii_uppercase + string.digits + string.punctuation, 'utf-8')
try:
for i in RUNTIME.report_progress(range(1, 8), unit='length'):
for attempt in itertools.product(charset, repeat=i):
b_attempt = bytes(attempt)
hashed = self.hash(b_attempt)[:8]
if hashed == h1:
h1_pt = b_attempt
if hashed == h2:
h2_pt = b_attempt
if h1_pt and h2_pt:
raise KeyboardInterrupt()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
return Bytes(h1_pt or b'\x00').pad_congruent_right(7) + Bytes(h2_pt or b'')
@staticmethod
def lm_to_ntlm(cracked: bytes, ntlm_hex: bytes) -> Bytes:
"""
Since LM hashes uppercase all letters, the password may not match the password for the NTLM hash.
By trying every combination of uppercase and lowercase, the NTLM hash can be bruteforced.
Parameters:
cracked (bytes): Cracked password of LM hash.
ntlm_hex (bytes): Target NTLM hash in hex format.
Returns:
Bytes: The NTLM hash's password.
"""
from samson.hashes.ntlm import NTLM
import string
import itertools
letters = [(idx, chr(l)) for idx, l in enumerate(cracked) if chr(l) in string.ascii_uppercase]
both_cases = [(l, l.lower()) for _idx, l in letters]
cracked_copy = bytearray(cracked)
ntlm = NTLM()
for prod in itertools.product(*both_cases):
for c, (i, _) in zip(prod, letters):
cracked_copy[i] = ord(c)
if ntlm.hash(cracked_copy).hex() == ntlm_hex:
return Bytes(cracked_copy)
@staticmethod
def reconstruct_from_sam(hashcat_lm_list: bytes, sam_ntlm_list: bytes) -> dict:
"""
Given a list of hashcat-formatted, cracked LM halves (<LM>:<PLAINTEXT>) and a list
of SAM accounts (<USERNAME>:<RID>:<LM>:<NTLM>), this function reconstructs the plaintext
passwords with casing.
Parameters:
hashcat_lm_list (bytes): List or newline-delimited bytes of hashcat LM halves.
sam_ntlm_list (bytes): List or newline-delimited bytes of SAM accounts.
Returns:
dict: Dictionary of {`username`: `password`}.
"""
if type(hashcat_lm_list) is bytes:
hashcat_lm_list = hashcat_lm_list.strip().split(b'\n')
if type(sam_ntlm_list) is bytes:
sam_ntlm_list = sam_ntlm_list.strip().split(b'\n')
lookup_table = {}
for kv in hashcat_lm_list:
k,v = kv.split(b':')
lookup_table[k] = v
lookup_table[b'aad3b435b51404ee'] = b''
sam_list = [sam_entry.split(b':') for sam_entry in sam_ntlm_list]
cracked = {}
for sam in sam_list:
try:
username = sam[0]
lm = sam[2]
ntlm = sam[3]
h0, h1 = lm[:16], lm[16:]
lm_pass = lookup_table[h0] + lookup_table[h1]
if lm_pass:
password = LM.lm_to_ntlm(lm_pass, ntlm)
cracked[username] = password
except KeyError:
pass
return cracked
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/hashes/lm.py
| 0.771241 | 0.213336 |
lm.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.kdfs.s2v import dbl
from samson.core.primitives import MAC, Primitive, EncryptionAlg
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
@register_primitive()
class PMAC(MAC):
"""
Parallelizable message authentication code.
http://web.cs.ucdavis.edu/~rogaway/ocb/pmac-bak.htm
"""
def __init__(self, cipher: EncryptionAlg):
"""
Parameters:
cipher (EncryptionAlg): Instantiated encryption algorithm.
"""
Primitive.__init__(self)
self.cipher = cipher
self.L = [self.cipher.encrypt(Bytes(b'').zfill(self.cipher.block_size))]
result = (self.L[0].int() >> 1)
if self.L[0].int() & 1:
result ^= 0x80000000000000000000000000000043
self.L_inv = result
for i in range(1, 32):
self.L.append(dbl(self.L[i-1]))
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['cipher']
def ntz(self, i):
return bin(i)[::-1].index('1')
def generate(self, message: bytes, offset=None) -> Bytes:
"""
Generates a keyed MAC for `message`.
Parameters:
message (bytes): Message to generate a MAC for.
Returns:
Bytes: The MAC.
"""
message = Bytes.wrap(message)
incomplete_block = len(message) % self.cipher.block_size
message_chunks = message.chunk(self.cipher.block_size, allow_partials=True)
offset = offset or Bytes(0x0).zfill(self.cipher.block_size)
sigma = Bytes(0x0).zfill(self.cipher.block_size)
if not message_chunks:
message_chunks = [message]
for i in range(len(message_chunks) - 1):
offset ^= self.L[self.ntz(i+1)]
sigma ^= self.cipher.encrypt(offset ^ message_chunks[i])
M_last = message_chunks[-1]
if incomplete_block or not len(message):
M_last += b'\x80'
M_last = (M_last + (b'\x00' * (self.cipher.block_size - len(M_last))))
sigma ^= M_last
if len(message) % self.cipher.block_size == 0:
sigma ^= self.L_inv
return self.cipher.encrypt(sigma)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/macs/pmac.py
| 0.752468 | 0.245922 |
pmac.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.core.primitives import MAC, Primitive
from samson.core.metadata import FrequencyType, ConstructionType, SecurityProofType
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
_MOD_128 = 2**128
@register_primitive()
class Poly1305(MAC):
"""
Message authentication code using an underlying block cipher. The (r, nonce) combination MUST
be unique to guarantee its security properties. A single reuse can allow for a forgery.
References:
"The Poly1305-AES message-authentication code" (https://cr.yp.to/mac/poly1305-20050329.pdf)
"""
P1305 = (1 << 130) - 5
USAGE_FREQUENCY = FrequencyType.NORMAL
CONSTRUCTION_TYPES = [ConstructionType.WEGMAN_CARTER]
SECURITY_PROOF = SecurityProofType.INFORMATION_THEORETIC
def __init__(self, r: bytes, clamp_r: bool=True):
"""
Parameters:
r (bytes): Bytes-like polynomial.
clamp_r (bool): Whether or not to clamp `r` to ensure correctness. Assumes `r` is big endian.
"""
Primitive.__init__(self)
if clamp_r:
self.r = Poly1305._clamp_r(Bytes.wrap(r).change_byteorder()).to_int()
else:
self.r = Bytes.wrap(r, byteorder='little').int()
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['r']
# https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7539#section-2.5
@staticmethod
def _clamp_r(r: bytearray) -> bytearray:
r[3] &= 15
r[7] &= 15
r[11] &= 15
r[15] &= 15
r[4] &= 252
r[8] &= 252
r[12] &= 252
return r
@staticmethod
def _chunk_message(message: bytes) -> list:
return [(chunk + b'\x01').zfill(17) for chunk in Bytes.wrap(message, byteorder='little').chunk(16, allow_partials=True)]
@staticmethod
def _evaluate(chunks: list, r: int) -> int:
total = 0
for chunk in chunks:
total += chunk.to_int()
total *= r
total %= Poly1305.P1305
return total % _MOD_128
def generate(self, message: bytes, nonce: bytes) -> Bytes:
"""
Generates a keyed MAC for `message`.
Parameters:
message (bytes): Message to generate a MAC for.
nonce (bytes): Bytes-like nonce.
Returns:
Bytes: The MAC.
"""
pt_chunks = Poly1305._chunk_message(message)
total = Poly1305._evaluate(pt_chunks, self.r)
return Bytes((Bytes.wrap(nonce).to_int() + total) % _MOD_128, byteorder='little')
@staticmethod
def nonce_reuse_attack(msg1: bytes, sig1: bytes, msg2: bytes, sig2: bytes) -> list:
"""
Given two message-signature pairs generated by Poly1305 using the same key/nonce,
returns the `key` and the `nonce`.
Parameters:
msg1 (bytes): First message.
sig1 (bytes): First signature.
msg2 (bytes): Second message.
sig2 (bytes): Second signature.
Returns:
list: List of candidates formatted as (`r` "key", `s` "nonce").
Examples:
>>> from samson.macs.poly1305 import Poly1305
>>> from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
>>> s = Bytes(0x0103808afb0db2fd4abff6af4149f51b).change_byteorder()
>>> r = 0x85d6be7857556d337f4452fe42d506a8
>>> msg1 = b'Cryptographic Forum Research Group'
>>> msg2 = b'Hey there friendos! I hope you die'
>>> p13 = Poly1305(r)
>>> sig1 = p13.generate(msg1, s).int()
>>> sig2 = p13.generate(msg2, s).int()
>>> (p13.r, s.int()) in Poly1305.nonce_reuse_attack(msg2, sig2, msg1, sig1)
True
"""
from samson.math.algebra.rings.integer_ring import ZZ
from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
# Given (ma, sa) and (mb, sb) as message-signature pairs using the same nonce
# Assume `ma` and `mb` are both 3 chunks long
# The Poly1305 generation function is essentially just Horner's method evaluated at `r`
# plus a secret constant `s` with coefficients in P1305
# sa = ((((ma1 * r) + ma2) * r) + ma3) * r + s = ma1*r^3 + ma2r*^2 + ma3*r + s
# The whole thing is then modulo 2^128, making the final equation:
# sa = ma1*r^3 + ma2*r^2 + ma3*r + s - n*2^128
# If `s` is reused, we can cancel it (this is basically the Forbidden attack)
# sa - sb = (ma1*r^3 - mb1*r^3) + (ma2*r^2 - mb2*r^2) + (ma3*r - mb3*r) + (s - s) - (n*2^128 - m*2^128)
# sa - sb = (ma1 - mb1)*r^3 + (ma2 - mb2)*r^2 + (ma3 - mb3)*r - (n - m)*2^128
# Since we know `ma` and `mb`, we can calculate these coefficients
# sa - sb = m1*r^3 + m2*r^2 + m3*r - (n - m)*2^128
pt1_chunks, pt2_chunks = [Poly1305._chunk_message(message) for message in [msg1, msg2]]
coeffs = [chunk1.int() - chunk2.int() for chunk1, chunk2 in zip(pt1_chunks, pt2_chunks)]
sig1, sig2 = [Bytes.wrap(sig, byteorder='little').int() for sig in [sig1, sig2]]
sig_diff = sig1 - sig2
R = ZZ/ZZ(Poly1305.P1305)
P = R[Symbol('x')]
p = (P(coeffs[::-1]) << 1) - sig_diff
# Then we move `sa - sb` to the other side
# m1*r^3 + m2*r^2 + m3*r - (n - m)*2^128 - (sa - sb) = 0
# By taking the root of this polynomial, we will find `r`. However,
# we don't know `n` or `m`. What's actually important is the difference between them.
# We'll call this difference `k` (i.e. `k = n - m`). Note that `k` may be negative,
# so we need to try those values as well. `n` and `m` are both in [0, 4], so `k` is in [-4, 4].
# Four is the max value because the polynomial result (`total`) plus the `nonce` is maximally (2^130-6 + 2^128-1) and (2^130-6 + 2^128-1) // 2^128 = 4.
# If `total` + `nonce` < 2^128, then it's always zero. Lastly, `k` is more likely to be closer to zero
# than the extremes, so we try middle values first.
candidates = []
k = 0
while abs(k) < 5:
roots = p.roots()
for r in roots:
ri = int(r)
# `r` is a 128-bit number, so if the root is bigger than that, we can skip it
if ri < _MOD_128:
test_sig1 = Poly1305._evaluate(pt1_chunks, ri)
test_sig2 = Poly1305._evaluate(pt2_chunks, ri)
# Here we check if the current `r` is correct
# (ta - tb) % 2^128 == ((ta + s) - (tb + s)) % 2^128
# If it is, since `s` is a 128-bit number, `s < _MOD_128`
# and it should also be fully recoverable
if (test_sig1 - test_sig2) % _MOD_128 == sig_diff % _MOD_128:
s_prime = abs(sig1 - test_sig1)
if all([Poly1305(ri, clamp_r=False).generate(msg, s_prime).int() == sig for msg, sig in [(msg1, sig1), (msg2, sig2)]]):
candidates.append((ri, s_prime))
# This is just a simple way of testing 0, -1, 1, -2, 2...
k += 1
p += (-1 + 2*(k % 2)) * (_MOD_128*k)
return list(set(candidates))
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/macs/poly1305.py
| 0.902915 | 0.405478 |
poly1305.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.core.primitives import MAC, Primitive
from samson.core.metadata import FrequencyType, UsageType
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
@register_primitive()
class Michael(MAC):
"""
References:
"A Note on the Fragility of the 'Michael' Message Integrity Code"
"""
USAGE_FREQUENCY = FrequencyType.UNUSUAL
USAGE_TYPE = UsageType.WIRELESS
def __init__(self, key: bytes):
Primitive.__init__(self)
self.key = Bytes.wrap(key).zfill(8).change_byteorder('little')
@staticmethod
def ADD32(l: Bytes, r: Bytes) -> Bytes:
return Bytes((l.int() + r.int()) % 2**32, 'little').zfill(4)
@staticmethod
def SUB32(l: Bytes, r: Bytes) -> Bytes:
return Bytes((l.int() - r.int()) % 2**32, 'little').zfill(4)
@staticmethod
def XSWAP(l: Bytes) -> Bytes:
return Bytes([l[1], l[0], l[3], l[2]], 'little')
@staticmethod
def b(l: Bytes, r: Bytes) -> (Bytes, Bytes):
r ^= l.lrot(17)
l = Michael.ADD32(l, r)
r ^= Michael.XSWAP(l)
l = Michael.ADD32(l, r)
r ^= l.lrot(3)
l = Michael.ADD32(l, r)
r ^= l.rrot(2)
l = Michael.ADD32(l, r)
return l, r
@staticmethod
def b_inv(l: Bytes, r: Bytes) -> (Bytes, Bytes):
l = Michael.SUB32(l, r)
r ^= l.rrot(2)
l = Michael.SUB32(l, r)
r ^= l.lrot(3)
l = Michael.SUB32(l, r)
r ^= Michael.XSWAP(l)
l = Michael.SUB32(l, r)
r ^= l.lrot(17)
return l, r
@staticmethod
def pad(message: Bytes) -> Bytes:
return (message + b'\x5a' + b'\x00'*4).pad_congruent_right(4).change_byteorder('little')
def generate(self, message: bytes, pad: bool=True) -> Bytes:
"""
Generates the Michael MIC of `message`.
Parameters:
message (bytes): Message to authenticate.
pad (bool): Whether or not to apply the Michael padding to the plaintext.
Returns:
Bytes: MIC of `message`.
"""
message = Bytes.wrap(message)
if pad:
message = Michael.pad(message)
l, r = self.key.chunk(4)
for chunk in message.chunk(4):
l ^= chunk
l, r = Michael.b(l, r)
return l.zfill(4) + r.zfill(4)
@staticmethod
def crack(message: bytes, mic: bytes, pad: bool=True) -> Bytes:
"""
Inverts the Michael function and cracks the key.
Parameters:
message (bytes): Message.
mic (bytes): Michael MIC of `message`.
pad (bool): Whether or not to apply the Michael padding to the plaintext.
Returns:
Michael: Cracked Michael instance.
Examples:
>>> k = Bytes(0xd55e100510128986)
>>> pt = Bytes.random(50)
>>> m = Michael(k)
>>> mic = m.generate(pt)
>>> Michael.crack(pt, mic).key == k
True
"""
message = Bytes.wrap(message)
mic = Bytes.wrap(mic).zfill(8)
l, r = mic.chunk(4)
if pad:
message = Michael.pad(message)
for chunk in message.chunk(4)[::-1]:
l, r = Michael.b_inv(l, r)
l ^= chunk
return Michael(l.zfill(4) + r.zfill(4))
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/macs/michael.py
| 0.833731 | 0.327211 |
michael.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.macs.cbc_mac import CBCMAC
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.block_ciphers.rijndael import Rijndael
from samson.core.primitives import MAC, Primitive, EncryptionAlg
from samson.core.metadata import FrequencyType
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
@register_primitive()
class CMAC(MAC):
"""
Message authentication code scheme based off of CBCMAC.
"""
USAGE_FREQUENCY = FrequencyType.NORMAL
def __init__(self, cipher: EncryptionAlg=None, iv: bytes=b'\x00' * 16):
"""
Parameters:
cipher (EncryptionAlg): Instantiated encryption algorithm.
iv (bytes): Initialization vector for CBC mode.
"""
Primitive.__init__(self)
self.cipher = cipher or Rijndael(Bytes.random(32))
self.k1, self.k2 = self.generate_subkeys()
self.cbc_mac = CBCMAC(cipher, iv)
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['cipher', 'k1', 'k2']
# https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4493#section-2.3
def generate_subkeys(self) -> (bytes, bytes):
"""
Internal function used to generate CMAC subkeys `k1` and `k2`.
"""
L = self.cipher.encrypt(Bytes(b'').zfill(self.cipher.block_size))
if L.int() & 0x80000000000000000000000000000000:
K1 = (L << 1) ^ 0x00000000000000000000000000000087
else:
K1 = L << 1
if K1.int() & 0x80000000000000000000000000000000:
K2 = (K1 << 1) ^ 0x00000000000000000000000000000087
else:
K2 = K1 << 1
return K1, K2
def generate(self, message: bytes) -> Bytes:
"""
Generates a keyed MAC for `message`.
Parameters:
message (bytes): Message to generate a MAC for.
Returns:
Bytes: The MAC.
"""
message = Bytes.wrap(message)
incomplete_block = len(message) % self.cipher.block_size
message_chunks = message.chunk(self.cipher.block_size, allow_partials=True)
if len(message_chunks) == 0:
message_chunks = [Bytes(b'')]
M_last = message_chunks[-1]
if incomplete_block or not len(message):
M_last += b'\x80'
M_last = (M_last + (b'\x00' * (self.cipher.block_size - len(M_last)))) ^ self.k2
else:
M_last ^= self.k1
return self.cbc_mac.generate(b''.join(message_chunks[:-1]) + M_last, pad=False)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/macs/cmac.py
| 0.697712 | 0.206854 |
cmac.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.core.primitives import MAC, Primitive
from samson.core.metadata import FrequencyType
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
from samson.hashes.sha3 import cSHAKE128, cSHAKE256
class KMAC(MAC):
USAGE_FREQUENCY = FrequencyType.UNUSUAL
def __init__(self, key: bytes, cSHAKE: type, digest_bit_length: int, customization_str: bytes=b''):
"""
Parameters:
key (bytes): Bytes-like object to key the HMAC.
cSHAKE (type): cSHAKE class to use.
digest_bit_size (int): Desired size of output.
customization_str (bytes): User defined string.
"""
self.hash_obj = cSHAKE(
digest_bit_length=digest_bit_length,
function_name=b'KMAC',
customization_str=customization_str
)
self.key = key
self.padded_key = self.hash_obj.bytepad(self.hash_obj.encode_string(self.key))
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['key', 'hash_obj']
def generate(self, message: bytes) -> Bytes:
"""
Generates a keyed MAC for `message`.
Parameters:
message (bytes): Message to generate a MAC for.
Returns:
Bytes: The MAC.
"""
new_x = self.padded_key + Bytes.wrap(message) + self.hash_obj.right_encode(self.hash_obj.digest_size*8)
return self.hash_obj.hash(new_x)
@register_primitive()
class KMAC128(KMAC):
def __init__(self, key: bytes, digest_bit_length: int, customization_str: bytes=b''):
"""
Parameters:
key (bytes): Bytes-like object to key the HMAC.
digest_bit_size (int): Desired size of output.
customization_str (bytes): User defined string.
"""
super().__init__(key=key, cSHAKE=cSHAKE128, digest_bit_length=digest_bit_length, customization_str=customization_str)
Primitive.__init__(self)
@register_primitive()
class KMAC256(KMAC):
def __init__(self, key: bytes, digest_bit_length: int, customization_str: bytes=b''):
"""
Parameters:
key (bytes): Bytes-like object to key the HMAC.
digest_bit_size (int): Desired size of output.
customization_str (bytes): User defined string.
"""
super().__init__(key=key, cSHAKE=cSHAKE256, digest_bit_length=digest_bit_length, customization_str=customization_str)
Primitive.__init__(self)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/macs/kmac.py
| 0.848471 | 0.150434 |
kmac.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.general import is_primitive_root, find_prime, is_safe_prime, is_sophie_germain_prime, next_prime, is_prime
from samson.math.factorization.factors import Factors
from samson.utilities.exceptions import SearchspaceExhaustedException
from samson.auxiliary.roca import gen_roca_prime
import math
class PGen(object):
def __init__(self, size: int):
self.size = size
def generate(self, constraints: list=None) -> int:
for p in self.generate_many(constraints=constraints):
return p
def generate_many(self, constraints: list=None) -> list:
p = 1
constraints = constraints or []
gen = self._gen(constraints)
try:
while True:
while not (is_prime(p) and p.bit_length() == self.size and all([c(p) for c in constraints])):
p = gen.__next__()
yield p
p = 1
except StopIteration:
raise SearchspaceExhaustedException
class RandGen(PGen):
def _gen(self, constraints: list):
while True:
yield find_prime(self.size)
class ROCAGen(PGen):
def __init__(self, size: int):
if size < 256:
raise ValueError('Cannot generate ROCA primes under 256 bits')
self.size = size
def _gen(self, constraints: list):
while True:
p, _, _, _ = gen_roca_prime(self.size)
yield p
class SmoothGen(PGen):
def __init__(self, size: int, base: int=2, glue_prime_exclude: set=None, max_glue_size :int=16, distance: int=1):
self.size = size
self.base = base
self.glue_prime_exclude = set(glue_prime_exclude or [])
self.max_glue_size = max_glue_size
self.distance = distance
def _gen(self, constraints: list):
facs = Factors({self.base: int(math.log(2**(self.size-1), self.base))})
facs += {2: 1}
for i in range(facs[self.base]):
p_1 = (facs - {self.base:i}).recombine()
glue_size = self.size - p_1.bit_length() + 1
# No odd prime this small
if glue_size < 2:
continue
# If we reach 'max_glue_size', we should tack on the smallest prime possible and retry.
# This should work as well as any other method assuming primes are uniformly distributed
if glue_size > self.max_glue_size:
p = next_prime(self.base+1)
while p in self.glue_prime_exclude:
p = next_prime(p+1)
facs += {p: 1}
p_1 = (facs - {self.base:i}).recombine()
glue_size = self.size - p_1.bit_length() + 1
# Try all primes of this bit length
p = next_prime(2**(glue_size-1))
while p.bit_length() == glue_size:
q = p_1*p+self.distance
if is_prime(q):
yield q
p = next_prime(p+1)
while p in self.glue_prime_exclude:
p = next_prime(p+1)
class CongruentGen(PGen):
def __init__(self, size: int, res: int, mod: int):
self.size = size
if not res:
raise ValueError('"res" cannot be zero')
if not res % 2 and not mod % 2:
raise ValueError('Both "res" and "mod" cannot be even')
self.res = res
self.mod = mod
def _gen(self, constraints: list):
mod = self.mod
p = 0
# This ensures we only try odd numbers
if self.mod % 2:
if self.res % 2:
mod *= 2
else:
p += self.mod
mod *= 2
# Construct `p` to be the smallest integer of bitlength `size`
# and congruent to `res` % `mod`
p += mod*(2**(self.size-1) // mod) + mod + self.res
while p.bit_length() == self.size:
if is_prime(p):
yield p
p += mod
class ResidueConstraint(object):
def __init__(self, res: int, mod: int):
self.res = res
self.mod = mod
def __call__(self, p: int) -> bool:
return p % self.mod == self.res
class SafePrimeConstraint(object):
def __call__(self, p: int) -> bool:
return is_safe_prime(p)
class SophieGermainPrimeConstraint(object):
def __call__(self, p: int) -> bool:
return is_sophie_germain_prime(p)
class PrimRootConstraint(object):
def __init__(self, a: int):
self.a = a
def __call__(self, p: int) -> bool:
return is_primitive_root(self.a, p)
class PGGenType(object):
RANDOM = RandGen
SMOOTH = SmoothGen
ROCA = ROCAGen
CONGRUENT = CongruentGen
class PGConstraints(object):
HAS_PRIMITIVE_ROOT = PrimRootConstraint
HAS_RESIDUE = ResidueConstraint
IS_SAFE = SafePrimeConstraint
IS_SOPHIE_GERMAIN = SophieGermainPrimeConstraint
class PrimeEngine(object):
GENS = PGGenType
CONSTRAINTS = PGConstraints
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/prime_gen.py
| 0.502441 | 0.298977 |
prime_gen.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.dense_vector import DenseVector
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring, RingElement
from samson.math.algebra.rings.integer_ring import ZZ
from samson.math.general import gaussian_elimination, lll, gram_schmidt
from samson.utilities.runtime import RUNTIME
from shutil import get_terminal_size
from types import FunctionType
from copy import deepcopy
# Python's string interpolation doesn't like newlines...
NEWLINE = "\n"
class Matrix(RingElement):
def __init__(self, rows: list, coeff_ring: Ring=None, ring: Ring=None):
"""
Parameters:
rows (list): List of lists representing matrix rows.
coeff_ring (Ring): Ring elements will be in.
ring (Ring): Parent ring.
"""
is_coerced = hasattr(rows[0][0], 'ring')
self.coeff_ring = coeff_ring or (rows[0][0].ring if is_coerced else ZZ)
row_lens = [len(row) for row in rows]
if not max(row_lens) == min(row_lens):
raise ValueError("Row lengths must be equal")
c_len = row_lens[0]
r_len = len(rows)
rows = [[self.coeff_ring.coerce(rows[r][c]) for c in range(c_len)] for r in range(r_len)]
self.rows = rows
if not ring:
from samson.math.algebra.rings.matrix_ring import MatrixRing
ring = MatrixRing(size=r_len, ring=self.coeff_ring)
self.ring = ring
def shorthand(self, tinyhand: bool=False) -> str:
if tinyhand:
str_meth = lambda elem: elem.tinyhand()
else:
str_meth = lambda elem: elem.shorthand()
term_max_size = get_terminal_size().columns - 10
row_strs = []
col_adjusts = []
for row in self.T.rows:
max_elem_size = max([len(str_meth(elem)) for elem in row])
col_adjusts.append(min(max_elem_size, term_max_size))
max_row_str = len(str(len(self.rows)))
row_strs.append(" "*(2+max_row_str) + ' '.join([str(idx).rjust(col_adj) for idx, col_adj in enumerate(col_adjusts)]))
for ridx, row in enumerate(self.rows):
row_strs.append(f"{str(ridx).rjust(max_row_str)} [" + ", ".join([str_meth(elem).rjust(col_adjusts[idx]) for idx, elem in enumerate(row)]) + "]")
return "".join([NEWLINE + row_str for row_str in row_strs])
def tinyhand(self) -> str:
return self.shorthand(True)
@property
def __raw__(self):
return RUNTIME.default_short_printer(self)
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['coeff_ring', 'num_rows', 'num_cols', '__raw__']
@property
def num_rows(self) -> int:
return len(self.rows)
@property
def num_cols(self) -> int:
return len(self.rows[0])
@property
def cols(self) -> list:
return self.T.rows
def transpose(self) -> 'Matrix':
"""
Transposes the `Matrix` i.e. flips it along its diagonal.
Returns:
Matrix: Transposed `Matrix`.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import Matrix, ZZ
>>> Matrix([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], ZZ).transpose()
<Matrix: coeff_ring=ZZ, num_rows=3, num_cols=3,
0 1 2
0 [1, 4, 7]
1 [2, 5, 8]
2 [3, 6, 9]>
"""
return Matrix([[self.rows[r][c] for r in range(self.num_rows)] for c in range(self.num_cols)], coeff_ring=self.coeff_ring, ring=self.ring)
@property
def T(self) -> 'Matrix':
return self.transpose()
def is_square(self) -> bool:
"""
Determines whether the `Matrix` is square i.e. the number of columns equals the number of rows.
Returns:
bool: Whether the `Matrix` is square.
"""
return self.num_cols == self.num_rows
@staticmethod
def identity(size: int, coeff_ring: Ring=None, ring: Ring=None) -> 'Matrix':
"""
Creates the identity `Matrix` of `size`.
Parameters:
size (int): Number of rows/columns.
coeff_ring (Ring): Ring elements will be in.
ring (Ring): Parent ring.
Returns:
Matrix: Identity matrix.
"""
return Matrix([[coeff_ring.one if r == c else coeff_ring.zero for r in range(size)] for c in range(size)], coeff_ring=coeff_ring, ring=ring)
@staticmethod
def fill(value: 'RingElement', rows: int, cols: int=None, coeff_ring: Ring=None, ring: Ring=None) -> 'Matrix':
"""
Fills a `Matrix` with `value`.
Parameters:
value (RingElement): Value every element should be.
rows (int): Number of rows.
cols (int): Number of columns.
coeff_ring (Ring): Ring elements will be in.
ring (Ring): Parent ring.
Returns:
Matrix: `Matrix` filled with `value`.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import Matrix, ZZ
>>> Matrix.fill(ZZ.zero, 3, 4)
<Matrix: coeff_ring=ZZ, num_rows=3, num_cols=4,
0 1 2 3
0 [0, 0, 0, 0]
1 [0, 0, 0, 0]
2 [0, 0, 0, 0]>
"""
return Matrix([[value for c in range(cols or rows)] for r in range(rows)], coeff_ring=coeff_ring, ring=ring)
def apply_elementwise(self, func: FunctionType) -> 'Matrix':
"""
Applies a function to each element and returns a `Matrix` of the results.
Parameters:
func (func): Function to apply.
Returns:
Matrix: Result matrix.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import Matrix, ZZ
>>> Matrix([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], ZZ).apply_elementwise(lambda elem: elem**2)
<Matrix: coeff_ring=ZZ, num_rows=3, num_cols=3,
0 1 2
0 [ 1, 4, 9]
1 [16, 25, 36]
2 [49, 64, 81]>
"""
return Matrix([[func(self.rows[r][c]) for c in range(self.num_cols)] for r in range(self.num_rows)])
def change_ring(self, ring: 'Ring') -> 'Matrix':
"""
Returns a new Matrix with the coefficients coerced into `ring`.
Parameters:
ring (Ring): Ring to embed into.
Returns:
Matrix: Resultant Matrix.
"""
return Matrix([[ring(col) for col in row] for row in self.rows], coeff_ring=ring)
def determinant(self) -> 'RingElement':
"""
Finds the determinant of the matrix.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import Matrix, ZZ
>>> A = Matrix([[2,1],[-1,0]], ZZ)
>>> A.determinant()
<IntegerElement: val=1, ring=ZZ>
>>> B = Matrix([[1, 0, 2, -1],[3, 0, 0, 5],[2, 1, 4, -3],[1, 0, 5, 0]], ZZ)
>>> B.determinant()
<IntegerElement: val=30, ring=ZZ>
References:
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/determinant-of-a-matrix/
"""
assert self.is_square()
mat = Matrix([[elem for elem in row] for row in self.rows], coeff_ring=self.coeff_ring)
R = mat.coeff_ring
n = len(mat)
temp = [R.zero] * n
total = R.one
det = R.one
for i in range(n):
idx = i
# Find first nonzero
while not mat[idx, i] and idx < n:
idx += 1
if idx == n:
continue
if idx != i:
for j in range(n):
mat[idx,j], mat[i,j] = mat[i,j], mat[idx,j]
# Sign change when we shift rows
if idx-i % 2:
det = -det
temp = [mat[i,j] for j in range(n)]
for j in range(i+1, n):
a = temp[i]
b = mat[j,i]
for k in range(n):
mat[j,k] = (a*mat[j,k]) - (b*temp[k])
total *= a
# Multiply diagonals
for i in range(n):
det *= mat[i,i]
return det / total
det = determinant
def characteristic_polynomial(self, symbol: 'Symbol'=None) -> 'Polynomial':
"""
Finds the characteristic polynomial `p_a` such that the roots of `p_a` are eigenvalues of `self`.
Parameters:
symbol (Symbol): Symbol to use for polynomial.
Returns:
Polynomial: Characteristic polynomial.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import Matrix, ZZ
>>> A = Matrix([[2,1],[-1,0]], ZZ)
>>> A.characteristic_polynomial()
<Polynomial: x^2 + (-2)*x + 1, coeff_ring=ZZ>
>>> B = Matrix([[1, 0, 2, -1],[3, 0, 0, 5],[2, 1, 4, -3],[1, 0, 5, 0]], ZZ)
>>> B.characteristic_polynomial()
<Polynomial: x^4 + (-5)*x^3 + (16)*x^2 + (-34)*x + 30, coeff_ring=ZZ>
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Characteristic_polynomial#Formal_definition
"""
from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
x = symbol or Symbol('x')
R = self.coeff_ring
I = Matrix.identity(self.num_rows, R)
_ = R[x]
return (I*x - self).det()
def row_join(self, other: 'Matrix') -> 'Matrix':
"""
Extends `self`'s rows with `others`.
Parameters:
other (Matrix): Other `Matrix`.
Returns:
Matrix: The joined matrices.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import Matrix, ZZ
>>> Matrix([[1,2], [3,4]], ZZ).row_join(Matrix([[5,6], [7,8]], ZZ))
<Matrix: coeff_ring=ZZ, num_rows=2, num_cols=4,
0 1 2 3
0 [1, 2, 5, 6]
1 [3, 4, 7, 8]>
"""
type_o = type(other)
if type_o is Matrix:
cols = other.rows
else:
cols = other
return Matrix([row_a + row_b for row_a, row_b in zip(self.rows, cols)], coeff_ring=self.coeff_ring, ring=self.ring)
augment = row_join
def col_join(self, other: 'Matrix') -> 'Matrix':
"""
Extends `self`'s columns with `others`.
Parameters:
other (Matrix): Other `Matrix`.
Returns:
Matrix: The joined matrices.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import Matrix, ZZ
>>> Matrix([[1,2], [3,4]], ZZ).col_join(Matrix([[5,6], [7,8]], ZZ))
<Matrix: coeff_ring=ZZ, num_rows=4, num_cols=2,
0 1
0 [1, 2]
1 [3, 4]
2 [5, 6]
3 [7, 8]>
"""
type_o = type(other)
if type_o is Matrix:
rows = other.rows
else:
rows = other
return Matrix(self.rows + rows, coeff_ring=self.coeff_ring, ring=self.ring)
def LLL(self, delta: float=0.75) -> 'Matrix':
"""
Performs the Lenstra–Lenstra–Lovász lattice basis reduction algorithm.
Parameters:
delta (float): Minimum optimality of the reduced basis.
Returns:
Matrix: Reduced basis.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.matrix import Matrix
>>> from samson.math.all import QQ
>>> m = Matrix([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8]], QQ)
>>> m.LLL()
<Matrix: coeff_ring=Frac(ZZ), num_rows=2, num_cols=4,
0 1 2 3
0 [ 3, 2, 1, 0]
1 [-2, 0, 2, 4]>
"""
return lll(self, delta)
def gram_schmidt(self, full: bool=False) -> 'Matrix':
"""
Performs Gram-Schmidt orthonormalization.
Parameters:
normalize (bool): Whether or not to normalize the vectors.
Returns:
Matrix: Orthonormalized row vectors.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import QQ
>>> from samson.math.matrix import Matrix
>>> out, _ = Matrix([[3,1],[2,2]], QQ).gram_schmidt()
>>> [[float(out[r][c]) for c in range(out.num_cols)] for r in range(out.num_rows)]
[[3.0, 1.0], [-0.4, 1.2]]
"""
return gram_schmidt(self, full)
# TODO: This only works with QQ since we're letting Python's `sqrt` function coerce it into a Python float.
# The root problem is two-fold:
# 1) Finding the square-root of an element in an arbitrary ring
# 2) Handling irrational numbers
# Python's floating-point arithmetic will automatically truncate irrational numbers to 53 bits, however, `Frac(ZZ)` will use arbitrary-precision integers
# to represent the numerator and denominator, resulting in an infinite expansion.
def normalize(self) -> 'Matrix':
"""
Normalizes the `Matrix` by dividing all elements by its magnitude.
Returns:
Matrix: Normalized `Matrix`.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import QQ, Matrix
>>> Matrix([[4,4,4,4]]*4, QQ).normalize()
<Matrix: coeff_ring=Frac(ZZ), num_rows=4, num_cols=4,
0 1 2 3
0 [1/2, 1/2, 1/2, 1/2]
1 [1/2, 1/2, 1/2, 1/2]
2 [1/2, 1/2, 1/2, 1/2]
3 [1/2, 1/2, 1/2, 1/2]>
"""
magnitude = (self.apply_elementwise(lambda elem: elem**2)*Matrix.fill(self.coeff_ring.one, rows=self.num_cols, cols=1))[0,0].sqrt()
return self * ~magnitude
def LUsolve(self, rhs: 'Matrix') -> 'Matrix':
"""
Solves `Ax = b` for `x` where `A` is `self` and `b` is `rhs`.
Parameters:
rhs (Matrix): The right-hand side matrix.
Returns:
Matrix: The `x` matrix.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import QQ
>>> from samson.math.matrix import Matrix
>>> a = Matrix([[3, 2,-4], [2, 3, 3], [5, -3, 1]], coeff_ring=QQ)
>>> b = Matrix([[3], [15], [14]], coeff_ring=QQ)
>>> c = a.LUsolve(b)
>>> a*c == b
True
"""
return gaussian_elimination(self, rhs)
def rref(self) -> 'Matrix':
"""
Returns the reduced row echelon form.
Returns:
Matrix: RREF of `self`.
"""
A = deepcopy(self)
n = A.num_rows
m = A.num_cols
lead = 0
for r in range(n):
if m <= lead:
return A
i = r
while not A[i, lead]:
i += 1
if i == n:
i = r
lead += 1
if lead == m:
return A
if i != r:
A[i], A[r] = A[r], A[i]
scalar = A[r, lead]
A[r] = [e / scalar for e in A[r]]
r_vec = A[r]
for i in range(n):
if i != r:
A[i] = [a-b for a,b in zip(A[i], r_vec*A[i, lead])]
lead += 1
return A
def rcef(self) -> 'Matrix':
"""
Returns the reduced column echelon form.
Returns:
Matrix: RCEF of `self`.
"""
return self.T.rref().T
def right_kernel(self):
"""
Computes the right kernel `x` of `self` such that `self`*`x`.`T`=0.
Returns:
Matrix: Right kernel.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kernel_(linear_algebra)#Computation_by_Gaussian_elimination
"""
AI = self.col_join(Matrix.identity(self.num_cols, self.coeff_ring))
c = AI.T.rref()
return Matrix([row[self.num_rows:] for row in c if not any(row[:self.num_rows])])
def left_kernel(self) -> 'Matrix':
"""
Computes the left kernel `x` of `self` such that `x`*`self`=0.
Returns:
Matrix: Left kernel.
"""
return self.T.right_kernel()
def __getitem__(self, idx: object) -> 'RingElement':
if type(idx) is tuple:
if type(idx[0]) is slice:
val = [row[idx[1]] for row in self.rows[idx[0]]]
if type(val[0]) is not list:
val = [[v] for v in val]
return Matrix(val)
else:
val = self.rows[idx[0]][idx[1]]
if type(val) is list:
if type(idx[0]) is slice:
val = [[v] for v in val]
else:
val = [val]
val = Matrix(val)
return val
else:
if type(idx) is slice:
return Matrix(self.rows[idx])
else:
return DenseVector(self.rows[idx])
def __setitem__(self, idx, value):
# Just trying to get `value` into a list of lists
t_value = type(value)
if t_value is DenseVector:
value = [value.values]
elif t_value is Matrix:
value = value.rows
elif t_value is list:
if type(value[0]) is not list:
value = [value]
else:
value = value
elif value in self.coeff_ring:
value = [self.coeff_ring(value)]
if type(idx) is tuple:
if type(idx[0]) is slice:
if type(idx[1]) is slice:
for row, val in zip(self.rows[idx[0]], value):
row[idx[1]] = val
else:
for row, val in zip(self.rows[idx[0]], value):
row[idx[1]] = val[0]
else:
self.rows[idx[0]][idx[1]] = value[0]
else:
if type(idx) is not slice:
value = value[0]
self.rows[idx] = value
def __len__(self) -> int:
return len(self.rows)
def __or__(self, other: 'Matrix') -> 'Matrix':
return self.row_join(other)
def __neg__(self) -> 'Matrix':
return self.apply_elementwise(lambda elem: -elem)
def __add__(self, other: 'Matrix') -> 'Matrix':
if type(other) == type(self):
return Matrix([[self.rows[r][c] + other.rows[r][c] for c in range(self.num_cols)] for r in range(self.num_rows)], coeff_ring=self.coeff_ring, ring=self.ring)
else:
raise ValueError("other type not addible")
def __mul__(self, other: 'Matrix') -> 'Matrix':
if type(other) is Matrix:
s_rows = self.num_rows
s_cols = self.num_cols
o_cols = other.num_cols
o_rows = other.num_rows
if s_cols != o_rows:
raise ValueError(f"Cannot multiply {s_rows}x{s_cols} matrix by {o_rows}x{o_cols} matrix")
ans = []
for row in range(s_rows):
ans.append([])
for o_col in range(o_cols):
col_total = self.coeff_ring.zero
for col in range(s_cols):
col_total += self.rows[row][col] * other.rows[col][o_col]
ans[-1].append(col_total)
return Matrix(ans, coeff_ring=self.coeff_ring, ring=self.ring)
else:
return self.apply_elementwise(lambda elem: elem * other)
def __invert__(self) -> 'Matrix':
if self.ring:
return gaussian_elimination(self, Matrix.identity(len(self), coeff_ring=self.coeff_ring, ring=self.ring))
else:
raise ArithmeticError('Matrix is not square and has no ring')
def ground_div(self, other: 'RingElement') -> None:
if type(other) is not Matrix and other in self.coeff_ring:
return self * ~self.coeff_ring(other)
def __floordiv__(self, other: 'Matrix') -> 'Matrix':
return self / other
def __eq__(self, other: 'Matrix') -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other) and self.rows == other.rows
def __hash__(self):
return hash((self.__class__, *[tuple(r) for r in self.rows]))
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/matrix.py
| 0.738009 | 0.337395 |
matrix.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.core.base_object import BaseObject
def _calc_continued_fraction(frac: 'FractionFieldElement') -> list:
"""
Calculates the continued fraction form of `frac`.
Parameters:
frac (FractionFieldElement): Fraction.
Returns:
list: Continued fraction.
"""
n, d = frac.numerator, frac.denominator
cf = []
while True:
q,r = divmod(n, d)
cf.append(q)
if not r:
break
n, d = d, r
return cf
class ContinuedFraction(BaseObject):
def __init__(self, element):
self.element = element
self.ring = self.element.ring
self.cf = _calc_continued_fraction(self.element)
@staticmethod
def from_list(cf) -> 'ContinuedFraction':
"""
Derives the fraction form for `cf`.
Parameters:
cf (list): Continued fraction.
Returns:
ContinuedFraction: Corresponding fraction.
"""
w = self.ring(cf[0])
if len(cf) > 1:
w += ~eval_continued_fraction(cf[1:])
return ContinuedFraction(w)
def numerators(self) -> list:
"""
Generates the numerators of the continued fraction.
Returns:
generator: Generator of the numerators.
"""
last, two = self.ring.ring.one, self.ring.ring.zero
for a in self.cf:
h = a*last + two
yield h
last, two = h, last
def denominators(self) -> list:
"""
Generates the denominators of the continued fraction.
Returns:
generator: Generator of the denominators.
"""
last, two = self.ring.ring.zero, self.ring.ring.one
for a in self.cf:
h = a*last + two
yield h
last, two = h, last
def convergents(self) -> list:
"""
Generates the convergents of the continued fraction.
Returns:
generator: Generator of the convergents.
"""
return (self.ring((a,b)) for a,b in zip(self.numerators(), self.denominators()))
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/continued_fraction.py
| 0.887814 | 0.384623 |
continued_fraction.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.utilities.general import binary_search_list
from samson.core.base_object import BaseObject
from sortedcontainers import SortedDict
from copy import copy
class SparseVector(BaseObject):
"""
Sparse vector implementation. Saves on memory when representing high-dimensional vectors with many zeroes.
"""
def __init__(self, items: list, zero: object=None, allow_virtual_len: bool=True):
"""
Parameters:
items (list): Items as dictionary, list of tuples, or just a list.
zero (object): The zero element. This element will not be stored.
"""
if zero is None:
if hasattr(items[0], 'ring'):
zero = items[0].ring.zero
else:
zero = 0
not_empty = len(items)
if type(items) is dict:
self.values = SortedDict({k:v for k,v in items.items() if v != zero})
length = list(items.keys())[-1] if not_empty else 0
elif type(items) is list:
if len(items) == 0 or type(items[0]) is tuple:
self.values = SortedDict([(k, v) for k,v in items if v != zero])
length = items[-1][0] if not_empty else 0
else:
self.values = SortedDict({idx: value for idx, value in enumerate(items) if value != zero})
length = not_empty
else:
raise TypeError("'items' must be dict or list")
for key in self.values.keys():
if not type(key) is int:
raise TypeError('idx must be an integer')
self.zero = zero
self.allow_virtual_len = allow_virtual_len
self.virtual_len = length
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash(tuple([_ for _ in self.values.items()]))
@staticmethod
def wrap(items, *args, **kwargs):
if type(items) is SparseVector:
return items
return SparseVector(items, *args, **kwargs)
def list(self) -> list:
if len(self):
return [self[i] for i in range(len(self))]
else:
return []
def trim(self):
self.virtual_len = self.last() + 1 if self.sparsity else 0
def last(self) -> int:
"""
Returns the index of the last element.
Returns:
int: Index of last element.
"""
return self.values.keys()[-1] if self.values else 0
def __iter__(self):
for item in self.values.items():
yield item
def map(self, func):
vec = SparseVector([func(idx, val) for idx, val in self], zero=self.zero, allow_virtual_len=self.allow_virtual_len)
vec.virtual_len = max(self.virtual_len, vec.last()+1)
return vec
def __getitem__(self, idx: int) -> object:
try:
if type(idx) is slice:
items = self.values.items()
length = len(items)
key = lambda item: item[0]
start_not_none = idx.start is not None
end_not_none = idx.stop is not None
if start_not_none and idx.start < 0 or end_not_none and idx.stop < 0:
raise ValueError("Negative slices not supported for SparseVectors")
start = binary_search_list(items, idx.start, key=key, fuzzy=True) if start_not_none else 0
end = binary_search_list(items, idx.stop, key=key, fuzzy=True) if end_not_none else length
if end < 0:
end = 0
selected_items = items[start:end]
# Need to normalize indices so they start at 0
req_start = idx.start or 0
req_stop = len(self) if idx.stop is None else idx.stop
selected_items = [(i-req_start, val) for i,val in selected_items]
# Handle step
step = idx.step
if step is None:
step = 1
elif step < 0:
step = -step
selected_items = [(req_stop - idx, val) for idx, val in selected_items]
selected_items = [(idx, val) for idx, val in selected_items if not idx % step]
new_vec = SparseVector(selected_items, self.zero, allow_virtual_len=self.allow_virtual_len)
# Calculate 'new_vec' length
calcd_len = (req_stop - req_start) // (idx.step or 1)
new_vec.virtual_len = max(min(calcd_len, self.len()), 0)
return new_vec
else:
if idx < 0:
idx += self.len()
return self.values[idx]
except KeyError:
return self.zero
def __setitem__(self, idx: int, obj: object) -> object:
if not type(idx) is int:
raise ValueError('idx must be an integer')
if obj == self.zero:
if idx in self.values:
del self.values[idx]
else:
self.values[idx] = obj
if idx >= self.len():
self.virtual_len = idx+1
def __contains__(self, item: 'RingElement') -> bool:
return item in self.values
def __eq__(self, other: 'SparseVector') -> bool:
return self.values == other.values
def __len__(self) -> int:
return self.len()
def append(self, item):
self[self.len()] = item
@property
def sparsity(self):
return len(self.values)
def __add__(self, other):
new_self = copy(self)
if type(other) is SparseVector:
last = len(new_self)
new_self.values.update({k+last:v for k,v in other.values.items()})
new_self.virtual_len += other.virtual_len
else:
for item in other:
new_self.append(item)
return new_self
def len(self) -> int:
"""
Calculate the length of the `SparseVector`. Use this instead of __len__ to prevent
integer overflow problems.
"""
return self.virtual_len if self.allow_virtual_len else (self.last() + 1 if self.values.keys() else 0)
def vec_add(self, other) -> 'SparseVector':
vec = SparseVector([], zero=self.zero)
for idx, coeff in self:
vec[idx] = coeff + other[idx]
for idx, coeff in other:
if not idx in self:
vec[idx] = coeff
vec.virtual_len = self.virtual_len
return vec
def dense_vector(self):
from samson.math.dense_vector import DenseVector
vec = []
last = 0
for k,v in self.values.items():
vec.extend([self.zero]*(k-last-1))
vec.append(v)
last = k
return DenseVector(vec)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/sparse_vector.py
| 0.630116 | 0.344995 |
sparse_vector.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.utilities.general import rand_bytes
from samson.utilities.exceptions import NotInvertibleException, ProbabilisticFailureException, SearchspaceExhaustedException, NoSolutionException
from samson.auxiliary.complexity import add_complexity, KnownComplexities
from samson.utilities.runtime import RUNTIME
from functools import reduce
from typing import Tuple, List
from types import FunctionType
from copy import deepcopy, copy
from enum import Enum
import math
# Resolve circular dependencies while reducing function-level imports
from samson.auxiliary.lazy_loader import LazyLoader
@RUNTIME.global_cache()
def lazy_import(local_name, fqn):
return LazyLoader(local_name, globals(), fqn)
_integer_ring = lazy_import('_integer_ring', 'samson.math.algebra.rings.integer_ring')
_real_field = lazy_import('_real_field', 'samson.math.algebra.fields.real_field')
_complex_field = lazy_import('_complex_field', 'samson.math.algebra.fields.complex_field')
_poly = lazy_import('_poly', 'samson.math.polynomial')
_mat = lazy_import('_mat', 'samson.math.matrix')
_dense = lazy_import('_dense', 'samson.math.dense_vector')
_factor_gen = lazy_import('_factor_gen', 'samson.math.factorization.general')
_ell_curve = lazy_import('_ell_curve', 'samson.math.algebra.curves.weierstrass_curve')
def int_to_poly(integer: int, modulus: int=2) -> 'Polynomial':
"""
Encodes an `integer` as a polynomial.
Parameters:
integer (int): Integer to encode.
modulus (int): Modulus to reduce the integer over.
Returns:
Polynomial: Polynomial representation.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import int_to_poly
>>> int_to_poly(100)
<Polynomial: x^6 + x^5 + x^2, coeff_ring=ZZ/(ZZ(2))>
>>> int_to_poly(128, 3)
<Polynomial: x^4 + x^3 + (2)*x^2 + 2, coeff_ring=ZZ/(ZZ(3))>
"""
Polynomial = _poly.Polynomial
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
base_coeffs = []
# Use != to handle negative numbers
while integer != 0 and integer != -1:
integer, r = divmod(integer, modulus)
base_coeffs.append(r)
return Polynomial(base_coeffs, ZZ/ZZ(modulus))
def poly_to_int(poly: 'Polynomial') -> int:
"""
Encodes an polynomial as a integer.
Parameters:
poly (Polynomial): Polynomial to encode.
modulus (int): Modulus to reconstruct the integer with.
Returns:
int: Integer representation.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import int_to_poly, poly_to_int
>>> poly_to_int(int_to_poly(100))
100
>>> poly_to_int(int_to_poly(100, 3))
100
"""
modulus = poly.coeff_ring.order()
value = 0
for idx, coeff in poly.coeffs:
value += int(coeff) * modulus**idx
return value
def frobenius_monomial_base(poly: 'Polynomial') -> List['Polynomial']:
"""
Generates a list of monomials of x**(i*p) % g for range(`poly`.degrees()). Used with Frobenius map.
Parameters:
poly (Polynomial): Polynomial to generate bases for.
Returns:
List[Polynomial]: List of monomial bases mod g.
References:
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/d1301c58be7ee4cd12fd28f1c5cd0b26322ed277/sympy/polys/galoistools.py
"""
from samson.math.symbols import oo
n = poly.degree()
if n == 0:
return []
P = poly.ring
q = poly.coeff_ring.order() if poly.coeff_ring.order() != oo else poly.coeff_ring.characteristic()
bases = [None]*n
bases[0] = P.one
if q < n:
for i in range(1, n):
bases[i] = (bases[i-1] << q) % poly
elif n > 1:
R = P/poly
x = P.symbol
bases[1] = R(x)**q
for i in range(2, n):
bases[i] = bases[i-1] * bases[1]
# Peel off the quotient ring
for i in range(1, n):
bases[i] = bases[i].val
return bases
def frobenius_map(f: 'Polynomial', g: 'Polynomial', bases: List['Polynomial']=None) -> 'Polynomial':
"""
Computes `f`**p % `g` using the Frobenius map.
Parameters:
f (Polynomial): Base.
g (Polynomial): Modulus.
bases (List[Polynomial]): Frobenius monomial bases. Will generate if not provided.
Returns:
Polynomial: `f`**p % `g`
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Finite_field#Frobenius_automorphism_and_Galois_theory
"""
if not bases:
bases = frobenius_monomial_base(g)
dg = g.degree()
df = f.degree()
P = f.ring
if df >= dg:
f %= g
df = f.degree()
if not f:
return f
sf = P([f.coeffs[0]])
for i in range(1, df+1):
sf += bases[i] * P([f.coeffs[i]])
return sf
def gcd(*args) -> 'RingElement':
"""
Iteratively computes the greatest common divisor.
Parameters:
a (RingElement): First element.
b (RingElement): Second element.
Returns:
RingElement: GCD of `a` and `b`.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import gcd
>>> gcd(256, 640)
128
>>> from samson.math.algebra.all import FF
>>> from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> P = FF(2, 8)[x]
>>> gcd(P(x**2), P(x**5))
<Polynomial: x^2, coeff_ring=F_(2^8)>
"""
total = args[0]
if type(total) is int:
def _gcd(a,b):
while b:
a, b = b, a % b
return a
else:
def _gcd(a,b):
return a.gcd(b)
for arg in args[1:]:
total = _gcd(total, arg)
return total
def xgcd(a: 'RingElement', b: 'RingElement') -> Tuple['RingElement', 'RingElement', 'RingElement']:
"""
Extended Euclidean algorithm form of GCD.
`a`x + `b`y = gcd(`a`, `b`)
Parameters:
a (RingElement): First integer.
b (RingElement): Second integer.
Returns:
Tuple[RingElement, RingElement, RingElement]: Formatted as (GCD, x, y).
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import xgcd
>>> xgcd(10, 5)
(5, 0, 1)
>>> from samson.math.algebra.all import FF
>>> from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> P = FF(2, 8)[x]
>>> xgcd(P(x**2), P(x**5))
(<Polynomial: x^2, coeff_ring=F_(2^8)>, <Polynomial: 1, coeff_ring=F_(2^8)>, <Polynomial: F_(2^8)(ZZ(0)), coeff_ring=F_(2^8)>)
References:
https://anh.cs.luc.edu/331/notes/xgcd.pdf
"""
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
# For convenience
peel_ring = False
if type(a) is int:
peel_ring = True
a = ZZ(a)
b = ZZ(b)
R = a.ring
# Generic xgcd
prevx, x = R.one, R.zero; prevy, y = R.zero, R.one
while b:
q = a // b
x, prevx = prevx - q*x, x
y, prevy = prevy - q*y, y
a, b = b, a % b
g, s, t = a, prevx, prevy
# Normalize if possible
if g.is_invertible() and s:
s_g = s // g
if s_g:
g, s, t = g // g, s_g, t // g
if peel_ring:
g = g.val
s = s.val
t = t.val
return g, s, t
def lcm(*args) -> 'RingElement':
"""
Calculates the least common multiple of `a` and `b`.
Parameters:
a (RingElement): First integer.
b (RingElement): Second integer.
Returns:
RingElement: Least common multiple.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import lcm
>>> lcm(2, 5)
10
>>> from samson.math.algebra.all import FF
>>> from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> P = FF(2, 8)[x]
>>> lcm(P(x**2 + 5), P(x-6))
<Polynomial: x^3 + x, coeff_ring=F_(2^8)>
"""
def _lcm(a, b):
return a // gcd(a, b) * b
total = args[0]
for arg in args[1:]:
total = _lcm(total, arg)
return total
def xlcm(a: 'RingElement', b: 'RingElement') -> Tuple['RingElement', 'RingElement', 'RingElement']:
"""
Extended least common multiple. Finds the LCM and two integers `n` and `m` such that
`l` == `n`*`m` and gcd(`n`, `m`) == 1.
Parameters:
a (RingElement): First element.
b (RingElement): Second element.
Returns:
(RingElement, RingElement, RingElement): Formatted as (LCM, `n`, `m`).
References:
https://github.com/sagemath/sage/blob/fbca269f627bf6a8bc6f0a611ed7e26260ebc994/src/sage/arith/misc.py#L1835
"""
g = gcd(a, b)
l = (a*b) // g
g = gcd(a, b // g)
# Remove all common factors from a
while g != 1:
a //= g
g = gcd(a, g)
return l, a, l // a
@RUNTIME.global_cache()
def mod_inv(a: 'RingElement', n: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
"""
Calculates the modular inverse.
Parameters:
a (RingElement): Element to invert.
n (RingElement): Modulus.
Returns:
RingElement: Modular inverse of `a` over `n`.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import mod_inv
>>> mod_inv(5, 11)
9
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_algorithm#Linear_Diophantine_equations
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extended_Euclidean_algorithm
"""
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
# For convenience
peel_ring = False
if type(a) is int:
peel_ring = True
a = ZZ(a)
n = ZZ(n)
_, x, _ = xgcd(a, n)
R = a.ring
if (a * x) % n != R.one:
raise NotInvertibleException(f"{a} is not invertible over {n}", parameters={'a': a, 'x': x, 'n': n})
if x < R.zero:
x = x + n
if peel_ring:
x = x.val
return x
@add_complexity(KnownComplexities.LOG)
def square_and_mul(g: 'RingElement', u: int, s: 'RingElement'=None) -> 'RingElement':
"""
Computes `s` = `g` ^ `u` over arbitrary rings.
Parameters:
g (RingElement): Base.
u (int): Exponent.
s (RingElement): The 'one' value of the ring.
Returns:
RingElement: `g` ^ `u` within its ring.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import mod_inv
>>> square_and_mul(5, 10, 1)
9765625
>>> from samson.math.algebra.all import ZZ
>>> from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> P = (ZZ/ZZ(127))[x]
>>> square_and_mul(P(x+5), 6)
<Polynomial: x^6 + (30)*x^5 + (121)*x^4 + (87)*x^3 + (104)*x^2 + (81)*x + 4, coeff_ring=ZZ/(ZZ(127))>
"""
invert = False
if u < 0:
invert = True
u = -u
s = s or g.ring.one
while u != 0:
if u & 1:
s = (g * s)
u >>= 1
g = (g * g)
if invert:
s = ~s
return s
@add_complexity(KnownComplexities.LOG)
def fast_mul(a: 'RingElement', b: int, s: 'RingElement'=None) -> 'RingElement':
"""
Computes `s` = `a` * `b` over arbitrary rings.
Parameters:
a (RingElement): Element `a`.
b (int): Multiplier.
s (RingElement): The 'zero' value of the ring.
Returns:
RingElement: `a` * `b` within its ring.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import fast_mul
>>> fast_mul(5, 12, 0)
60
>>> from samson.math.algebra.all import ZZ
>>> from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> P = (ZZ/ZZ(127))[x]
>>> fast_mul(P(x+5), 5)
<Polynomial: (5)*x + 25, coeff_ring=ZZ/(ZZ(127))>
"""
s = s if s is not None else a.ring.zero
if b < 0:
b = -b
a = -a
while b != 0:
if b & 1:
s = (a + s)
b >>= 1
a = (a + a)
if b and a.order_cache and not a.order_cache % b:
s.order_cache = a.order_cache // b
return s
def kth_root(n: int, k: int) -> int:
"""
Calculates the `k`-th integer root of `n`.
Parameters:
n (int): Integer.
k (int): Root (e.g. 2).
Returns:
int: `k`-th integer root of `n
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import kth_root
>>> kth_root(1000, 3)
10
>>> kth_root(129, 7)
3
References:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/23621833/is-cube-root-integer
https://github.com/sympy/sympy/blob/c0bfc81f3ffee97c6d6732ac5e5ccf399e5ab3e2/sympy/core/power.py#L84
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Newton%27s_method
"""
# Estimate the root using floating point exponentiation
# This typically is within 1e-10 of the actual root for large integers
try:
guess = round(n**(1/k))
except OverflowError:
# If we overflow the float's precision, we can use a bit of math
# to calculate it at a lower precision and shift it.
# This still tends to be highly accurate
e = math.log2(n)/k
if e > 53:
shift = int(e - 53)
guess = int(2.0**(e - shift) + 1) << shift
else:
guess = int(2.0**e)
# Newton's method is more likely to screw up small numbers than converge
if guess > 2**50:
# Use Newton's method to rapidly converge on the root
rprev, root, k_1 = -1, guess, k-1
while root > 2:
approx = root**k_1
rprev, root = root, (k_1*root + n//approx) // k
if abs(root - rprev) < 2:
break
else:
root = guess
t = root**k
if t == n:
return root
# If we're very close, then try incrementing/decrementing
diff = n-t
try:
if abs(diff)/n < 0.1:
if diff > 0:
while t < n:
root += 1
t = root**k
else:
while t > n:
root -= 1
t = root**k
return root + (t < n)
except OverflowError:
pass
# If we're still not there, use binary search to comb through the rest of the space
ub = root
lb = 0
while lb < ub:
guess = (lb + ub) // 2
if pow(guess, k) < n:
lb = guess + 1
else:
ub = guess
return lb + (lb**k < n)
def kth_root_qq(n: int, k: int, precision: int=32) -> 'FractionFieldElement':
"""
Calculates the `k`-th rational root of `n` to `precision` bits of precision.
Parameters:
n (int/QQ): Integer.
k (int): Root (e.g. 2).
precision (int): Bits of precision.
Returns:
FractionFieldElement: `k`-th rational root of `n
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import kth_root_qq
>>> kth_root_qq(2, 2, 32)
<FractionFieldElement: numerator=759250125, denominator=536870912, field=Frac(ZZ)>
>>> diff = abs(float(kth_root_qq(2, 2, 32)) - 2**(0.5))
>>> diff < 1/2**32
True
>>> diff < 1/2**64
False
References:
https://stackoverflow.com/a/39802349
"""
from samson.math.all import QQ
n = QQ(n)
lb = QQ.zero
ub = n
precision = QQ((1, 2**precision))
while True:
mid = (lb+ub)/2
mid_k = mid**k
if abs(mid_k-n) < precision:
return mid
elif mid_k < n:
lb = mid
else:
ub = mid
@add_complexity(KnownComplexities.LINEAR)
def crt(residues: List['QuotientElement'], auto_correct: bool=True) -> Tuple['RingElement', 'RingElement']:
"""
Performs the Chinese Remainder Theorem and returns the computed `x` and modulus.
Parameters:
residues (List[QuotientElement]): Residues of `x` as QuotientElements or tuples.
auto_correct (bool): Whether or not to automatically remove redundancy.
Returns:
(RingElement, RingElement): Formatted as (computed `x`, modulus).
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import crt
>>> from samson.math.algebra.all import ZZ
>>> from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> n = 17
>>> residues = [(17 % mod, mod) for mod in [2, 3, 5]]
>>> crt(residues)
(17, 30)
>>> n = 17
>>> residues = [(ZZ/ZZ(mod))(17) for mod in [2, 3, 5]]
>>> crt(residues)
(<IntegerElement: val=17, ring=ZZ>, <IntegerElement: val=30, ring=ZZ>)
>>> P = (ZZ/ZZ(2))[x]
>>> moduli = [P(x + 1), P(x**2 + x + 1), P(x**3 + x + 1)]
>>> n = P[17]
>>> residues = [(P/mod)(n) for mod in moduli]
>>> crt(residues)
(<Polynomial: x^4 + 1, coeff_ring=ZZ/(ZZ(2))>, <Polynomial: x^6 + x^4 + x + 1, coeff_ring=ZZ/(ZZ(2))>)
"""
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
# Auto promote
peel_ring = False
if type(residues[0]) is tuple:
if type(residues[0][0]) is int:
ring = ZZ
peel_ring = True
else:
ring = residues[0][0].ring
residues = [(ring/ring(mod))(res) for res, mod in residues]
# Remove redundancies
if auto_correct:
_tmp_res = [(res.val, res.ring.quotient) for res in residues]
ring = _tmp_res[0][0].ring
x, Nx = _tmp_res[0]
for r, n in _tmp_res[1:]:
n_total = lcm(Nx, n)
new_res = []
n2p = n_total // Nx
n1p = n_total // n
if ring.one in [n1p, n2p]:
if n > Nx:
x, Nx = r, n
else:
new_res.append((ring/n2p)(r))
new_res.append((ring/n1p)(x))
x, Nx = _crt(new_res)
else:
x, Nx = _crt(residues)
if peel_ring:
x, Nx = x.val, Nx.val
return x, Nx
def _crt(residues: List['RingElement']) -> Tuple['RingElement', 'RingElement']:
x = residues[0].val
Nx = residues[0].ring.quotient
for i in range(1, len(residues)):
modulus = residues[i].ring.quotient
x = (mod_inv(Nx, modulus) * (residues[i].val - x)) * Nx + x
Nx = Nx * modulus
x = x % Nx
return x, Nx
def crt_lll(residues: List['QuotientElement'], remove_redundant: bool=True) -> 'QuotientElement':
"""
Imitates the Chinese Remainder Theorem using LLL and returns the computed `x`.
Unlike CRT, this does not require the moduli be coprime. However, this method only
returns a representative since the solution isn't unique.
Parameters:
residues (List[QuotientElement]): Residues of `x` as QuotientElements.
remove_redundant (bool): Whether or not to remove redundant subgroups to minimize the result.
Returns:
QuotientElement: Computed `x` over composite modulus.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import crt_lll
>>> from samson.math.all import ZZ
>>> x = 684250860
>>> rings = [ZZ/ZZ(quotient) for quotient in [229, 246, 93, 22, 408]]
>>> crt_lll([r(x) for r in rings])
<QuotientElement: val=684250860, ring=ZZ/(ZZ(1306272792))>
References:
https://grocid.net/2016/08/11/solving-problems-with-lattice-reduction/
"""
from samson.math.algebra.fields.fraction_field import FractionField as Frac
import operator
Matrix = _mat.Matrix
R = residues[0].ring.ring
Q = Frac(R)
# Remove redundant subgroups to minimize result
if remove_redundant:
reduc_func = lcm
else:
reduc_func = operator.mul
# Calculate composite modulus
L = reduce(reduc_func, [r.ring.quotient for r in residues])
# Build the problem matrix
r_len = len(residues)
A = Matrix([
[Q.one for r in residues] + [Q((R.one, L)), Q.zero],
*[[Q.zero]*idx + [Q(r.ring.quotient)] + [Q.zero]*(1+r_len-idx) for idx, r in enumerate(residues)],
[Q.zero for r in residues] + [Q.one, Q.zero],
[Q(-r.val) for r in residues] + [Q.zero, L]
], Q)
B = A.LLL(0.99)
return (R/R(L))((B[-1, -2] * L).numerator)
class ResidueSymbol(Enum):
EXISTS = 1
DOES_NOT_EXIST = -1
IS_ZERO = 0
def legendre(a: int, p: int) -> ResidueSymbol:
"""
Calculates the Legendre symbol of `a` mod `p`. Nonzero quadratic residues mod `p` return 1 and nonzero, non-quadratic residues return -1. Zero returns 0.
Parameters:
a (int): Possible quadatric residue.
p (int): Modulus.
Returns:
ResidueSymbol: Legendre symbol.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import legendre
>>> legendre(4, 7)
<ResidueSymbol.EXISTS: 1>
>>> legendre(5, 7)
<ResidueSymbol.DOES_NOT_EXIST: -1>
"""
assert is_prime(p)
result = pow(a, (p - 1) // 2, p)
if result == p-1:
result = -1
return ResidueSymbol(result)
def generalized_eulers_criterion(a: int, k: int, p: int, factors: dict=None) -> ResidueSymbol:
"""
Determines if `a` is a `k`-th root over `p`.
Parameters:
a (int): Possible `k`-th residue.
k (int): Root to take.
p (int): Modulus.
factors (dict): Factors of `p`.
Returns:
ResidueSymbol: Legendre symbol (basically).
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import generalized_eulers_criterion
>>> generalized_eulers_criterion(4, 2, 7)
<ResidueSymbol.EXISTS: 1>
>>> generalized_eulers_criterion(5, 2, 7)
<ResidueSymbol.DOES_NOT_EXIST: -1>
>>> generalized_eulers_criterion(4, 3, 11)
<ResidueSymbol.EXISTS: 1>
References:
"A Generalization of Euler’s Criterion to Composite Moduli" (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1507.00098.pdf)
"""
t = totient(p, factors=factors)
result = pow(a, t // gcd(k, t), p)
if result > 1:
result = -1
return ResidueSymbol(result)
def tonelli(n: int, p: int) -> int:
"""
Performs the Tonelli-Shanks algorithm for calculating the square root of `n` mod `p`.
Parameters:
n (int): Integer.
p (int): Modulus.
Returns:
int: Square root of `n` mod `p`.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import tonelli
>>> tonelli(4, 7)
2
>>> tonelli(2, 7)
4
References:
https://crypto.stackexchange.com/questions/22919/explanation-of-each-of-the-parameters-used-in-ecc
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/find-square-root-modulo-p-set-2-shanks-tonelli-algorithm/
https://rosettacode.org/wiki/Tonelli-Shanks_algorithm#Python
"""
leg = legendre(n, p)
if leg == ResidueSymbol.IS_ZERO:
return 0
elif leg == ResidueSymbol.DOES_NOT_EXIST:
raise NoSolutionException()
q = p - 1
s = 0
while q % 2 == 0:
q //= 2
s += 1
if s == 1:
return pow(n, (p + 1) // 4, p)
for z in range(2, p):
if legendre(z, p) == ResidueSymbol.DOES_NOT_EXIST:
break
c = pow(z, q, p)
r = pow(n, (q + 1) // 2, p)
t = pow(n, q, p)
m = s
t2 = 0
while (t - 1) % p != 0:
t2 = (t * t) % p
for i in range(1, m):
if (t2 - 1) % p == 0:
break
t2 = (t2 * t2) % p
b = pow(c, 1 << (m - i - 1), p)
r = (r * b) % p
c = (b * b) % p
t = (t * c) % p
m = i
return r
def tonelli_q(a: int, p: int, q: int) -> int:
"""
Performs the Tonelli-Shanks algorithm for calculating the `q`th-root of `a` mod `p`.
Parameters:
a (int): Integer.
p (int): Modulus.
q (int): Root to take.
Returns:
int: `q`th-root of `a` mod `p`.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import tonelli_q
>>> tonelli_q(4, 7, 2)
2
>>> tonelli_q(2, 7, 2)
4
>>> tonelli_q(8, 67, 3)
58
>>> 58**3 % 67
8
References:
"On Taking Roots in Finite Fields" (https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~glmiller/Publications/AMM77.pdf)
"""
# Step 1 & 2
gec = generalized_eulers_criterion(a, q, p)
if gec == ResidueSymbol.IS_ZERO:
return 0
elif gec == ResidueSymbol.DOES_NOT_EXIST:
raise NoSolutionException()
# Step 3
for g in range(2, p):
if generalized_eulers_criterion(g, q, p) == ResidueSymbol.DOES_NOT_EXIST:
break
# Step 4
p_1 = p - 1
k = 0
# The algorithm only works if q | p-1
assert p_1 % q == 0
n = q
div = gcd(q, p-1)
while div != 1 and div != n:
n = n // div
div = gcd(n, p-1)
if p_1 % n == 0:
k = 1
p_1 //= n
N, N_prime = divmod(p_1, n)
# Step 5
l = 1
while True:
# Step 6
for j in range(k):
if pow(a, q**j*(q*N+N_prime), p) == 1:
break
# Step 7
if j == 0:
# Step 8
return pow(a, mod_inv(n, n*N+N_prime), p) * mod_inv(l, p)
else:
for lamb in range(1, n):
if gcd(lamb, n) == 1:
if (pow(a, pow(2, j-1)*pow(2, N+N_prime), p) * pow(g, lamb*pow(2, k-1)*(2*N+N_prime), p)) % p == 1:
break
a = (a * pow(g, pow(2, (k-j )*lamb), p)) % p
l = (l * pow(g, pow(2, (k-j-1)*lamb), p)) % p
@add_complexity(KnownComplexities.CUBIC)
def gaussian_elimination(system_matrix: 'Matrix', rhs: 'Matrix') -> 'Matrix':
"""
Solves `Ax = b` for `x` where `A` is `system_matrix` and `b` is `rhs`.
Parameters:
system_matrix (Matrix): The `A` matrix.
rhs (Matrix): The right-hand side matrix.
Returns:
Matrix: The `x` matrix.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import QQ
>>> from samson.math.matrix import Matrix
>>> from samson.math.general import gaussian_elimination
>>> a = Matrix([[3, 2,-4], [2, 3, 3], [5, -3, 1]], coeff_ring=QQ)
>>> b = Matrix([[3], [15], [14]], coeff_ring=QQ)
>>> c = gaussian_elimination(a, b)
>>> a*c == b
True
References:
https://rosettacode.org/wiki/Gaussian_elimination#Python
"""
Matrix = _mat.Matrix
A = deepcopy(system_matrix).row_join(rhs)
n = A.num_rows
m = A.num_cols
R = A.coeff_ring
# Forward elimination
for i in range(n):
# Find pivot
k = max(range(i, n), key=lambda r: max(A[r][i], -A[r][i]))
if not A[k, i]:
continue
# Swap rows
A[i], A[k] = A[k], A[i]
# Reduce rows
scalar = ~A[i, i]
for j in range(i+1, n):
A[j] = [A[j, k] - A[i, k] * A[j, i] * scalar for k in range(m)]
# Back substitution
# This works with any size matrix
rhs_cols = m - rhs.num_cols
for i in reversed(range(n)):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
t = A[i, j]
for k in range(rhs_cols, m):
A[i, k] -= t*A[j, k]
if not A[i, i]:
continue
t = ~A[i, i]
for j in range(rhs_cols, m):
A[i, j] *= t
return Matrix(A[:, rhs_cols:m], coeff_ring=R, ring=A.ring)
@add_complexity(KnownComplexities.GRAM)
def gram_schmidt(matrix: 'Matrix', full: bool=False, A_star: 'Matrix'=None, mu: 'Matrix'=None) -> Tuple['Matrix', 'Matrix']:
"""
Performs Gram-Schmidt orthonormalization.
Parameters:
matrix (Matrix): Matrix of row vectors.
full (bool): Whether or not to include zero vectors.
A_star (Matrix): Previous `Q` matrix truncated to required
Returns:
Tuple[Matrix, Matrix]: Formatted as (orthonormalized row vectors, transform matrix).
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import QQ
>>> from samson.math.matrix import Matrix
>>> from samson.math.general import gram_schmidt
>>> out, _ = gram_schmidt(Matrix([[3,1],[2,2]], QQ))
>>> [[float(out[r][c]) for c in range(out.num_cols)] for r in range(out.num_rows)]
[[3.0, 1.0], [-0.4, 1.2]]
References:
https://github.com/sagemath/sage/blob/854f9764d14236110b8d7f7b35a7d52017e044f8/src/sage/modules/misc.py
https://github.com/sagemath/sage/blob/1d465c7e3c82110d39034f3ca7d9d120f435511e/src/sage/matrix/matrix2.pyx
"""
Matrix = _mat.Matrix
DenseVector = _dense.DenseVector
R = matrix.coeff_ring
n = matrix.num_rows
A = matrix
if A_star:
A_star = [DenseVector(row) for row in A_star]
else:
A_star = []
if mu:
mu = deepcopy(mu)
else:
mu = Matrix([[R.zero for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(n)])
# Number of non-zero rows
nnz = len(A_star)
zeroes = []
# Orthogonalization
for j in range(len(A_star), n):
ortho = A[j]
for k in range(nnz):
mu[j,k] = A_star[k].dot(A[j]) / A_star[k].sdot()
ortho -= A_star[k]*mu[j,k]
if ortho.sdot() != R.zero:
A_star.append(ortho)
mu[j, nnz] = R.one
nnz += 1
else:
zeroes.append(j+len(zeroes))
# Manipulating result matrices with zero vectors
if full:
zero = [DenseVector([R.zero for _ in range(n-len(zeroes))])]
for j in zeroes:
A_star = A_star[:j] + zero + A_star[j:]
else:
mu = Matrix([row for row in mu.T if any(row)]).T
Q = Matrix([v.values for v in A_star])
return Q, mu
@add_complexity(KnownComplexities.LLL)
def lll(in_basis: 'Matrix', delta: float=0.75) -> 'Matrix':
"""
Performs the Lenstra–Lenstra–Lovász lattice basis reduction algorithm.
Parameters:
in_basis (Matrix): Matrix representing the original basis.
delta (float): Minimum optimality of the reduced basis.
Returns:
Matrix: Reduced basis.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import lll
>>> from samson.math.matrix import Matrix
>>> from samson.math.all import QQ
>>> m = Matrix([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8]], QQ)
>>> lll(m)
<Matrix: coeff_ring=Frac(ZZ), num_rows=2, num_cols=4,
0 1 2 3
0 [ 3, 2, 1, 0]
1 [-2, 0, 2, 4]>
References:
https://github.com/orisano/olll/blob/master/olll.py
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lenstra%E2%80%93Lenstra%E2%80%93Lov%C3%A1sz_lattice_basis_reduction_algorithm
"""
from samson.math.all import QQ
Matrix = _mat.Matrix
# Prepare ring and basis
if type(in_basis.coeff_ring).__name__ != 'FractionField':
from samson.math.algebra.fields.fraction_field import FractionField
R = FractionField(in_basis.coeff_ring)
in_basis = Matrix([[R(elem) for elem in row] for row in in_basis.rows], coeff_ring=R)
R = in_basis.coeff_ring
basis = deepcopy(in_basis)
n = len(basis)
ortho, _mu = gram_schmidt(in_basis)
# Prepare parameters
delta = QQ(delta)
d_num = int(delta.numerator)
d_den = int(delta.denominator)
half = R((R.ring.one, R.ring.one*2))
def mu_ij(i, j):
return ortho[j].proj_coeff(basis[i])
# Perform LLL
k = 1
while k < n:
for j in reversed(range(k)):
mu_kj = mu_ij(k, j)
if abs(mu_kj) > half:
scalar = round(mu_kj)
basis[k] -= basis[j] * scalar
# Prepare only needed vectors
# 'o_k' needs to be specially handled since 'gram_schmidt' can remove vectors
M_k = ortho[k, :] if len(ortho) >= k+1 else Matrix([[R.zero * in_basis.num_cols]])
M_k1 = ortho[k-1, :]
O = (M_k1 * M_k1.T)[0,0]
# This should be ring-agnostic
if (M_k * M_k.T)[0,0] * d_den >= O*d_num - d_den * mu_ij(k, k-1)**2 * O:
k += 1
else:
basis[k], basis[k-1] = copy(basis[k-1]), copy(basis[k])
# Update ortho
o = ortho[k] + ortho[k-1].project(basis[k-1])
p = ortho[k-1] - o.project(basis[k])
ortho[k-1], ortho[k] = o, p
k = max(k-1, 1)
return basis
def generate_superincreasing_seq(length: int, max_diff: int, starting: int=0) -> List[int]:
"""
Generates a superincreasing sequence.
Parameters:
length (int): Number of elements to generate.
max_diff (int): Maximum difference between the sum of all elements before and the next element.
starting (int): Minimum starting integer.
Returns:
List[int]: List of the superincreasing sequence.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import generate_superincreasing_seq
>>> generate_superincreasing_seq(10, 2)
[...]
"""
seq = []
last_sum = starting
for _ in range(length):
delta = int.from_bytes(rand_bytes(math.ceil(math.log(max_diff, 256))), 'big') % max_diff
seq.append(last_sum + delta)
last_sum = sum(seq)
return seq
def find_coprime(p: int, search_range: List[int]) -> int:
"""
Attempts to find an integer coprime to `p`.
Parameters:
p (int): Integer to find coprime for.
search_range (List[int]): Range to look in.
Returns:
int: Integer coprime to `p`.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import find_coprime
>>> find_coprime(10, range(500, 1000))
501
"""
for i in search_range:
if gcd(p, i) == 1:
return i
def random_int(n: int) -> int:
"""
Finds a unbiased, uniformly-random integer between 0 and `n`-1.
Parameters:
n (int): Upper bound.
Returns:
int: Random integer.
Example:
>>> from samson.math.general import random_int
>>> random_int(1000) < 1000
True
"""
byte_length = math.ceil(n.bit_length() / 8)
max_bit = 2**n.bit_length()
q = max_bit // n
max_num = n * q - 1
while True:
attempt = int.from_bytes(rand_bytes(byte_length), 'big') % max_bit
if attempt <= max_num:
return attempt % n
def random_int_between(a: int, b :int) -> int:
"""
Finds a unbiased, uniformly-random integer between `a` and `b`-1 (i.e. "[`a`, `b`)").
Parameters:
a (int): Lower bound.
b (int): Upper bound.
Returns:
int: Random integer.
Example:
>>> from samson.math.general import random_int_between
>>> n = random_int_between(500, 1000)
>>> n >= 500 and n < 1000
True
"""
return a + random_int(b - a)
def find_prime(bits: int, ensure_halfway: bool=True) -> int:
"""
Finds a prime of `bits` bits.
Parameters:
bits (int): Bit length of prime.
ensure_halfway (bool): Ensures the prime is at least halfway into the bitspace to prevent multiplications being one bit short (e.g. 256-bit int * 256-bit int = 511-bit int).
Returns:
int: Random prime number.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import find_prime
>>> find_prime(512) < 2**512
True
"""
rand_num = random_int(2**bits)
rand_num |= 2**(bits - 1)
if ensure_halfway:
rand_num |= 2**(bits - 2)
return next_prime(rand_num)
def next_prime(start_int: int, step: int=2) -> int:
"""
Finds the next prime.
Parameters:
start_int (int): Integer to start search at.
step (int): Distance to step forward.
Returns:
int: Prime.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import next_prime
>>> next_prime(8)
11
>>> next_prime(11+1)
13
"""
if start_int < 2:
return 2
start_int |= 1
while not is_prime(start_int):
start_int += step
return start_int
def primes(start: int, stop: int=None) -> list:
"""
Generates primes between `start` and `stop`.
Parameters:
start (int): Number to start at (inclusive).
stop (int): Number to stop at (exclusive).
Returns:
list: Primes within the range.
"""
p = start
if p < 3:
yield 2
p = 2
while True:
p = next_prime(p)
if stop and p >= stop:
break
yield p
p += 2
def berlekamp_massey(output_list: List[int]) -> 'Polynomial':
"""
Performs the Berlekamp-Massey algorithm to find the shortest LFSR for a binary output sequence.
Parameters:
output_list (List[int]): Output of LFSR.
Returns:
Polynomial: Polyomial that represents the shortest LFSR.
Examples:
>>> from samson.prngs.flfsr import FLFSR
>>> from samson.math.general import berlekamp_massey
>>> from samson.math.all import Polynomial, ZZ
>>> from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> _ = (ZZ/ZZ(2))[x]
>>> lfsr = FLFSR(3, x**25 + x**20 + x**12 + x**8 + 1)
>>> outputs = [lfsr.generate() for _ in range(50)]
>>> berlekamp_massey(outputs)
<Polynomial: x^25 + x^17 + x^13 + x^5 + 1, coeff_ring=ZZ/(ZZ(2))>
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Berlekamp%E2%80%93Massey_algorithm
"""
Polynomial = _poly.Polynomial
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
n = len(output_list)
b = [1] + [0] * (n - 1)
c = [1] + [0] * (n - 1)
L = 0
m = -1
i = 0
while i < n:
out_vec = output_list[i - L:i][::-1]
c_vec = c[1:L+i]
d = output_list[i] + sum([s_x * c_x for s_x, c_x in zip(out_vec, c_vec)]) % 2
if d == 1:
t = deepcopy(c)
p = [0] * n
for j in range(L):
if b[j] == 1:
p[j + i - m] = 1
c = [(c_x + p_x) % 2 for c_x, p_x in zip(c, p)]
if L <= i / 2:
L = i + 1 - L
m = i
b = t
i += 1
return Polynomial(c[:L + 1][::-1], coeff_ring=ZZ/ZZ(2))
def is_power_of_two(n: int) -> bool:
"""
Determines if `n` is a power of two.
Parameters:
n (int): Integer.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not `n` is a power of two.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import is_power_of_two
>>> is_power_of_two(7)
False
>>> is_power_of_two(8)
True
"""
return n != 0 and (n & (n - 1) == 0)
def totient(n: int, factors: dict=None) -> int:
"""
Calculates Euler's totient of `n`. The totient is the number of elements coprime to `n` that are less than `n`.
Parameters:
n (int): Number to find the totient of.
factors (dict): Factors of `n`.
Returns:
int: Totient of `n`.
"""
if not factors:
factors = _factor_gen.factor(n)
t = 1
for p, e in factors.items():
t *= (p-1) * p**(e-1)
return t
def pollards_kangaroo(g: 'RingElement', y: 'RingElement', a: int, b: int, iterations: int=30, f: FunctionType=None, apply_reduction: bool=True) -> int:
"""
Probabilistically finds the discrete logarithm of base `g` in GF(`p`) of `y` in the interval [`a`, `b`].
Parameters:
g (RingElement): Generator.
y (RingElement): Number to find the discrete logarithm of.
a (int): Interval start.
b (int): Interval end.
iterations (int): Number of times to run the outer loop. If `f` is None, it's used in the pseudorandom map.
f (func): Pseudorandom map function of signature (`y`: RingElement, k: int) -> int.
apply_reduction (bool): Whether or not to reduce the answer by the ring's order.
Returns:
int: The discrete logarithm. Possibly None if it couldn't be found.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import pollards_kangaroo
>>> from samson.math.algebra.all import *
>>> p = find_prime(2048)
>>> g, x = 5, random_int_between(1, p)
>>> R = (ZZ/ZZ(p)).mul_group()
>>> g = R(g)
>>> y = g*x
>>> dlog = pollards_kangaroo(g, y, x-1000, x+1000)
>>> g * dlog == y
True
>>> p = 53
>>> ring = ZZ/ZZ(p)
>>> curve = WeierstrassCurve(a=50, b=7, ring=ring, base_tuple=(34, 25))
>>> start, end = hasse_frobenius_trace_interval(curve.p)
>>> dlog = pollards_kangaroo(g=curve.G, y=curve.POINT_AT_INFINITY, a=start + curve.p, b=end + curve.p)
>>> curve.G * dlog == curve.zero
True
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pollard%27s_kangaroo_algorithm
"""
k = iterations
R = g.ring
# This pseudorandom map function has the following desirable properties:
# 1) Never returns zero. Zero can form an infinite loop
# 2) Works across all rings
if not f:
n = kth_root(b-a, 2)
f = lambda y, k: pow(2, hash(y) % k, n)
while k > 1:
N = (f(g, k) + f(g*b, k)) // 2 * 4
# Tame kangaroo
xT = 0
yT = g*b
for _ in range(N):
f_yT = f(yT, k)
xT += f_yT
yT += g*f_yT
# Wild kangaroo
xW = 0
yW = y
while xW < b - a + xT:
f_yW = f(yW, k)
xW += f_yW
yW += g*f_yW
if yW == yT:
result = b + xT - xW
if apply_reduction:
result %= R.order()
return result
# Didn't find it. Try another `k`
k -= 1
raise ProbabilisticFailureException("Discrete logarithm not found")
def hasse_frobenius_trace_interval(p: int) -> Tuple[int, int]:
"""
Finds the interval relative to `p` in which the Frobenius trace must reside according to Hasse's theorem.
Parameters:
p (int): Prime of the underlying field of the elliptic curve.
Returns:
(int, int): Start and end ranges of the interval relative to `p`.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import hasse_frobenius_trace_interval
>>> hasse_frobenius_trace_interval(53)
(-16, 17)
"""
l = 2 * math.ceil(math.sqrt(p))
return (-l , l + 1)
def sieve_of_eratosthenes(n: int, chunk_size: int=1024, prime_base: set=None) -> list:
"""
Finds all primes up to `n`.
Parameters:
n (int): Limit.
chunk_size (int): Size of internal lists.
prime_base (set): Initial set of primes to sieve against.
Returns:
generator: Generator of prime numbers.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import sieve_of_eratosthenes
>>> list(sieve_of_eratosthenes(100))
[2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97]
"""
n_2 = n // 2
k = kth_root(n, 2)
# Allow preloading, but remove 2 since it's intrinsically removed
if not prime_base:
prime_base = PRIMES_UNDER_1000.difference({2})
# Generate what's in prime_base first
for p in {2}.union(prime_base):
if p < n:
yield p
else:
return
# Chunk the space, but don't redo a chunk the prime_base fully covers
for chunk in range(len(list(prime_base)) // chunk_size, math.ceil(n_2 / chunk_size)):
true_idx = chunk * chunk_size
true_size = min(n_2 - true_idx, chunk_size)
# Remove 1
A = [true_idx != 0] + [True] * (true_size-1)
# Remove all indices based on prime base
for p in prime_base:
for j in range(p - true_idx*2 % (p*2), true_size*2, p*2):
if j < 0:
continue
A[j//2] = False
# Mark off multiples of new primes
# Don't need to if true_idx > k
if true_idx < k:
for i in range(2 if not true_idx else 0, true_size, 2):
true_i = i+true_idx*2+1
if true_size > (true_i // 2) and A[true_i//2]:
for j in range(true_i**2 // 2, true_size, true_i):
A[j] = False
# Add to prime base
new_primes = {(idx + true_idx)*2+1 for idx, is_prime in enumerate(A) if is_prime}
for p in new_primes:
yield p
prime_base = prime_base.union(new_primes)
def primes_product(n: int, blacklist: list=None) -> list:
"""
Returns a list of small primes whose product is greater than or equal to `n`.
Parameters:
n (int): Product to find.
blacklist (list): Primes to skip.
Returns:
list: List of primes.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import primes_product
>>> primes_product(100, [2])
[7, 5, 3]
"""
total = 1
primes = []
blacklist = blacklist if blacklist else []
for prime in sieve_of_eratosthenes(n.bit_length()*2+1):
if total >= n:
# We might be able to remove some of the large primes
primes.reverse()
needed_primes = []
for prime in primes:
if total // prime >= n:
total //= prime
else:
needed_primes.append(prime)
return needed_primes
if prime not in blacklist:
primes.append(prime)
total *= prime
def find_representative(quotient_element: 'QuotientElement', valid_range: range) -> int:
"""
Finds the representative element of `quotient_element` within `valid_range`.
Parameters:
quotient_element (QuotientElement): Element to search for.
valid_range (range): Range to search in.
Returns:
int: Representative element.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import *
>>> find_representative((ZZ/ZZ(11))(3), range(11, 22))
14
"""
remainder = int(quotient_element)
modulus = int(quotient_element.ring.quotient)
if len(valid_range) > modulus:
raise ValueError("Solution not unique")
q, r = divmod(valid_range[0], modulus)
shifted_range = range(r, r + len(valid_range))
if remainder in shifted_range:
return q * modulus + remainder
elif remainder + modulus in shifted_range:
return (q+1) * modulus + remainder
else:
raise ValueError("No solution")
def __fast_double_elliptic_frobenius(T, curve, point):
p_x, p_y = point.x, point.y
Q = p_y.numerator.ring
P = Q.ring.poly_ring
g = Q.quotient.x_poly
monomials = frobenius_monomial_base(g)
Z = Q(curve.defining_polynomial())**((curve.p-1)//2)
Yq = Z*p_y
def frobenius(f):
num = frobenius_map(f.numerator.val.x_poly, g, bases=monomials)
den = frobenius_map(f.denominator.val.x_poly, g, bases=monomials)
return T((num, den))
def compose(f, h):
num = Q(P(f.numerator.val.x_poly.modular_composition(h.numerator.val.x_poly, g)))
den = Q(P(f.denominator.val.x_poly.modular_composition(h.denominator.val.x_poly, g)))
return T((num, den))
Xq = frobenius(p_x)
Xq2 = frobenius(Xq)
Yq2 = Yq * compose(T(Z), Xq)
return point.__class__(x=Xq, y=Yq, curve=point.curve), point.__class__(x=Xq2, y=Yq2, curve=point.curve)
def frobenius_trace_mod_l(curve: 'EllipticCurve', l: int) -> 'QuotientElement':
"""
Finds the Frobenius trace modulo `l` for faster computation.
Parameters:
curve (EllipticCurve): Elliptic curve.
l (int): Prime modulus.
Returns:
QuotientElement: Modular residue of the Frobenius trace.
References:
"Fast algorithms for computing the eigenvalue in the Schoof-Elkies-Atkin algorithm" (https://hal.inria.fr/inria-00001009/document)
"""
EllipticCurve = _ell_curve.EllipticCurve
from samson.math.algebra.fields.fraction_field import FractionField as Frac
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
torsion_quotient_ring = ZZ/ZZ(l)
psi = curve.division_poly(l)
psi.x_poly.cache_div(psi.x_poly.degree()*2)
# Build symbolic torsion group
R = curve.curve_poly_ring
S = R/psi
T = Frac(S, simplify=False)
sym_curve = EllipticCurve(a=T([curve.a]), b=T([curve.b]), ring=T, check_singularity=False)
x = R.poly_ring.symbol
p_x = T(R((x, 0)))
p_y = T(R((0, 1)))
point = sym_curve(p_x, p_y, verify=False)
# Generate symbolic points
if l < 40:
p1, p2 = __fast_double_elliptic_frobenius(T, curve, point)
else:
F = sym_curve.frobenius_endomorphism()
p1 = F(point)
p2 = F(p1)
determinant = (curve.p % l) * point
point_sum = determinant + p2
# Find trace residue
if point_sum == sym_curve.POINT_AT_INFINITY:
return torsion_quotient_ring(0)
# TODO: Can we speed this up? The problem with using BSGS is hashing these points. Since they're over a
# fraction field, we can have equivalent fractions that have different numerators and denominators.
# This is true even if they're simplified. Until I can come up with a better way to hash fractions,
# this will be a linear search.
trace_point = p1
for candidate in range(1, (l + 1) // 2):
if point_sum.x == trace_point.x:
if point_sum.y == trace_point.y:
return torsion_quotient_ring(candidate)
else:
return torsion_quotient_ring(-candidate)
else:
trace_point += p1
raise ArithmeticError("No trace candidate satisfied the Frobenius equation")
def frobenius_trace(curve: 'EllipticCurve') -> int:
"""
Calculates the Frobenius trace of the `curve`.
Parameters:
curve (EllipticCurve): Elliptic curve.
Returns:
int: Frobenius trace.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import frobenius_trace
>>> from samson.math.algebra.all import *
>>> ring = ZZ/ZZ(53)
>>> curve = WeierstrassCurve(a=50, b=7, ring=ring, base_tuple=(34, 25))
>>> frobenius_trace(curve)
-3
"""
from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
search_range = hasse_frobenius_trace_interval(curve.p)
torsion_primes = primes_product(search_range[1] - search_range[0], [curve.ring.characteristic()])
trace_congruences = []
# Handle 2 separately to prevent multivariate poly arithmetic
if 2 in torsion_primes:
x = Symbol('x')
_ = curve.ring[x]
defining_poly = curve.defining_polynomial()
bases = frobenius_monomial_base(defining_poly)
rational_char = bases[1]
rational_char = frobenius_map(rational_char, defining_poly, bases=bases)
if gcd(rational_char - x, defining_poly).degree() == 0:
trace_congruences.append((ZZ/ZZ(2))(1))
else:
trace_congruences.append((ZZ/ZZ(2))(0))
torsion_primes.remove(2)
for l in torsion_primes:
trace_congruences.append(frobenius_trace_mod_l(curve, l))
n, mod = crt(trace_congruences)
return find_representative((ZZ/ZZ(mod))(n), range(*search_range))
def schoofs_algorithm(curve: 'EllipticCurve') -> int:
"""
Performs Schoof's algorithm to count the number of points on an elliptic curve.
Parameters:
curve (EllipticCurve): Elliptic curve to find cardinality of.
Returns:
int: Curve cardinality.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import schoofs_algorithm
>>> from samson.math.algebra.all import *
>>> ring = ZZ/ZZ(53)
>>> curve = WeierstrassCurve(a=50, b=7, ring=ring, base_tuple=(34, 25))
>>> schoofs_algorithm(curve)
57
"""
return curve.p + 1 - frobenius_trace(curve)
@RUNTIME.global_cache(8)
def __build_bsgs_table(g: 'RingElement', end: int, e: 'RingElement'=None, start: int=0) -> Tuple[int, dict]:
search_range = end - start
table = {}
m = kth_root(search_range, 2)
if not e:
e = g.ring.zero
for i in range(m):
table[e] = i
e += g
return m, table
def bsgs(g: 'RingElement', h: 'RingElement', end: int, e: 'RingElement'=None, start: int=0) -> int:
"""
Performs Baby-step Giant-step with an arbitrary finite cyclic group.
Parameters:
g (RingElement): Generator/base.
h (RingElement): The result to find the discrete logarithm of.
end (int): End of the search range.
e (RingElement): Starting point of the aggregator.
start (int): Start of the search range.
Returns:
int: The discrete logarithm of `h` given `g`.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import hasse_frobenius_trace_interval, bsgs, mod_inv
>>> from samson.math.algebra.all import *
>>> ring = ZZ/ZZ(53)
>>> curve = WeierstrassCurve(a=50, b=7, ring=ring, base_tuple=(34, 25))
>>> start, end = hasse_frobenius_trace_interval(curve.p)
>>> bsgs(curve.G, curve.POINT_AT_INFINITY, e=curve.POINT_AT_INFINITY, start=start + curve.p, end=end + curve.p)
57
>>> ring = ZZ/ZZ(53)
>>> mul = ring.mul_group()
>>> base = mul(7)
>>> exponent = 24
>>> h = base * exponent
>>> bsgs(base, h, int(ring.quotient))
24
"""
if hasattr(h, 'bsgs'):
try:
return h.bsgs(g, end=end, start=start, e=e)
except (ValueError, SearchspaceExhaustedException):
# Implementation specific BSGS may not handle all situations
pass
m, table = __build_bsgs_table(g, end, e, start)
factor = g * m
o = g * start
e = h
for i in range(m):
e = h - o
if e in table:
return i*m + table[e] + start
o += factor
raise SearchspaceExhaustedException("This shouldn't happen; check your arguments")
@add_complexity(KnownComplexities.PH)
def pohlig_hellman(g: 'RingElement', h: 'RingElement', n: int=None, factors: dict=None) -> int:
"""
Computes the discrete logarithm for finite abelian groups with a smooth order.
Parameters:
g (RingElement): Generator element.
h (RingElement): Result to find discrete logarithm of.
n (int): Order of the group.
factors (dict): `n`'s factorization.
Returns:
int: The discrete logarithm of `h` given `g`.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import pohlig_hellman
>>> from samson.math.algebra.all import *
>>> p = 7
>>> ring = (ZZ/ZZ(p)).mul_group()
>>> g = ring(3)
>>> exp = 2
>>> h = g * exp
>>> pohlig_hellman(g, h, p-1)
2
>>> p = 2**127-1
>>> ring = (ZZ/ZZ(p)).mul_group()
>>> g = ring(5)
>>> exp = 25347992192497823499464681366516589049
>>> h = g * exp
>>> exp2 = pohlig_hellman(g, h, p-1)
>>> g * exp2 == h
True
>>> ring = ZZ/ZZ(53)
>>> curve = WeierstrassCurve(a=50, b=7, ring=ring, base_tuple=(34, 25))
>>> g = curve.G
>>> exp = 28
>>> h = g * exp
>>> pohlig_hellman(curve.G, h, curve.G.order())
28
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pohlig%E2%80%93Hellman_algorithm
"""
if not n:
n = g.order()
if not factors:
factors = _factor_gen.factor(n)
def pp_bsgs(g, h, p, e):
x = [0]*(e+1)
gamma = g*(p**(e-1))
for k in range(e):
h_k = (g * -x[k] + h) * (p**(e-1-k))
d_k = h_k._plog(gamma, p)
x[k+1] = x[k] + d_k * p**k
return x[-1]
x = []
for p, e in factors.items():
ex_i = (n // p**e)
g_i = g * ex_i
h_i = h * ex_i
x_i = pp_bsgs(g_i, h_i, p, e)
x.append(x_i)
return crt(list(zip(x, [p**e for p, e in factors.items()])))[0]
@add_complexity(KnownComplexities.PH)
def pollards_rho_log(g: 'RingElement', y: 'RingElement', order: int=None) -> int:
"""
Computes the discrete logarithm using Pollard's Rho.
Parameters:
g (RingElement): Generator element.
y (RingElement): Result to find discrete logarithm of.
order (int): Order of the group.
Returns:
int: The discrete logarithm of `y` given `g`.
References:
http://koclab.cs.ucsb.edu/teaching/ecc/project/2015Projects/Blumenfeld-Presentation.pdf
https://math.mit.edu/classes/18.783/2017/LectureNotes10.pdf
"""
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
def xab(x, a, b, g, y):
sub = hash(x) % 3
if sub == 0:
x = x + x
a = a * 2
b = b * 2
elif sub == 1:
x = x + g
a = a + 1
else:
x = x + y
b = b + 1
return x, a, b
residues = []
n = order or g.order()
Z = ZZ/ZZ(n)
# Main loop
while True:
a = Z.random()
x, b = g*int(a), Z.zero
X, A, B = x, a, b
for _ in range(n):
x, a, b = xab(x, a, b, g, y)
X, A, B = xab(X, A, B, g, y)
X, A, B = xab(X, A, B, g, y)
if x == X:
break
r = B-b
if not r:
continue
# Note we might've found just a factor of the order
P = ZZ/ZZ(r.order())
res = P(a-A)/P(r)
residues.append(P(res))
res, _ = crt(residues)
if int(res)*g == y:
return int(res)
else:
Z = ZZ/ZZ(n // r.order())
g *= r.order()
y *= r.order()
def miller_rabin(n: int, k: int=64, bases: list=None) -> bool:
"""
Probabilistic primality test. Each iteration has a 1/4 false positive rate.
Parameters:
n (int): Number to determine if probably prime.
k (int): Number of iterations to run.
Returns:
bool: Whether `n` is probably prime.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import miller_rabin
>>> miller_rabin(127)
True
>>> miller_rabin(6)
False
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Miller%E2%80%93Rabin_primality_test#Miller%E2%80%93Rabin_test
"""
n_1 = n - 1
d = n_1
r = 0
while not d % 2 and d:
r += 1
d //= 2
if not bases:
def generator():
for _ in range(k):
yield random_int_between(2, n_1)
bases = generator()
for a in bases:
x = pow(a, d, n)
if x == 1 or x == n_1:
continue
found = False
for _ in range(r-1):
x = pow(x, 2, n)
if x == n_1:
found = True
break
if not found:
return False
return True
_FB_LARGE_MOD = 3989930175
def is_square(n: int, heuristic_only: bool=False) -> bool:
"""
Determines if `n` is a square using "fenderbender" tests first.
Parameters:
n (int): Number to test.
heuristic_only (bool): Whether or not to only use heuristic tests and not validate.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not `n` is a square.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import is_square
>>> p = 18431211066281663581
>>> is_square(p**2)
True
>>> is_square(6)
False
References:
https://mersenneforum.org/showpost.php?p=110896
"""
if n in [0, 1]:
return True
m = n % 128
if ((m*0x8bc40d7d) & (m*0xa1e2f5d1) & 0x14020a):
return False
n_mod = n % _FB_LARGE_MOD
m = n_mod % 63
if ((m*0x3d491df7) & (m*0xc824a9f9) & 0x10f14008):
return False
m = n_mod % 25
if ((m*0x1929fc1b) & (m*0x4c9ea3b2) & 0x51001005):
return False
if heuristic_only:
return n % 10 not in {2,3,7,8}
return kth_root(n, 2)**2 == n
def jacobi_symbol(n: int, k: int) -> ResidueSymbol:
"""
Generalization of the Legendre symbol.
Parameters:
n (int): Possible quadatric residue.
k (int): Modulus (must be odd).
Returns:
ResidueSymbol: Jacobi symbol.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import jacobi_symbol
>>> jacobi_symbol(4, 7)
<ResidueSymbol.EXISTS: 1>
>>> jacobi_symbol(5, 7)
<ResidueSymbol.DOES_NOT_EXIST: -1>
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jacobi_symbol
"""
assert k > 0 and k % 2 == 1
n %= k
t = 1
while n != 0:
while n % 2 == 0:
n //= 2
r = k % 8
if r in [3, 5]:
t = -t
n, k = k, n
if n % 4 == 3 and k % 4 == 3:
t = -t
n %= k
if k == 1:
return ResidueSymbol(t)
else:
return ResidueSymbol(0)
def generate_lucas_selfridge_parameters(n: int) -> Tuple[int, int, int]:
"""
Generates the Selfridge parameters to use in Lucas strong pseudoprime testing.
Parameters:
n (int): Possible prime.
Returns:
Tuple[int, int, int]: Selfridge parameters.
"""
D = 5
while True:
g = gcd(abs(D), n)
if g > 1 and g != n:
return (0, 0, 0)
if jacobi_symbol(D, n) == ResidueSymbol.DOES_NOT_EXIST:
break
if D > 0:
D = -D - 2
else:
D = -D + 2
return (D, 1, (1-D) // 4)
def generate_lucas_sequence(n: int, P: int, Q: int, k: int) -> Tuple[int, int, int]:
"""
Generates a Lucas sequence. Used internally for the Lucas primality test.
References:
https://docs.sympy.org/latest/_modules/sympy/ntheory/primetest.html#isprime
"""
D = P**2 - 4*Q
assert n > 1
assert k >= 0
assert D != 0
if k == 0:
return (0, 2, Q)
U = 1
V = P
Qk = Q
b = k.bit_length()
while b > 1:
U = U*V % n
V = (V*V - 2*Qk) % n
Qk *= Qk
b -= 1
if (k >> (b - 1)) & 1:
U, V = U*P + V, V*P + U*D
if U & 1:
U += n
if V & 1:
V += n
U >>= 1
V >>= 1
Qk *= Q
Qk %= n
return (U % n, V % n, Qk)
def is_strong_lucas_pseudoprime(n: int) -> bool:
"""
Determines if `n` is at least a strong Lucas pseudoprime.
Parameters:
n (int): Integer to test.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not `n` is at least a strong Lucas pseudoprime.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import is_strong_lucas_pseudoprime
>>> is_strong_lucas_pseudoprime(299360470275914662072095298694855259241)
True
>>> is_strong_lucas_pseudoprime(128)
False
"""
if n == 2:
return True
if n < 2 or n % 2 == 0 or is_square(n):
return False
D, P, Q = generate_lucas_selfridge_parameters(n)
if D == 0:
return False
s = 0
q, r = divmod(n+1, 2)
k = q
while q and not r:
k = q
s += 1
q, r = divmod(q, 2)
U, V, Qk = generate_lucas_sequence(n, P, Q, k)
if U == 0 or V == 0:
return True
for _ in range(s):
V = (V**2 - 2*Qk) % n
if V == 0:
return True
Qk = pow(Qk, 2, n)
return False
PRIMES_UNDER_1000 = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107, 109, 113, 127, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151, 157, 163, 167, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223, 227, 229, 233, 239, 241, 251, 257, 263, 269, 271, 277, 281, 283, 293, 307, 311, 313, 317, 331, 337, 347, 349, 353, 359, 367, 373, 379, 383, 389, 397, 401, 409, 419, 421, 431, 433, 439, 443, 449, 457, 461, 463, 467, 479, 487, 491, 499, 503, 509, 521, 523, 541, 547, 557, 563, 569, 571, 577, 587, 593, 599, 601, 607, 613, 617, 619, 631, 641, 643, 647, 653, 659, 661, 673, 677, 683, 691, 701, 709, 719, 727, 733, 739, 743, 751, 757, 761, 769, 773, 787, 797, 809, 811, 821, 823, 827, 829, 839, 853, 857, 859, 863, 877, 881, 883, 887, 907, 911, 919, 929, 937, 941, 947, 953, 967, 971, 977, 983, 991, 997}
def exhaustive_primality_proof(N: int) -> bool:
"""
Proves whether or not `N` is prime by exhaustively testing for divisors.
Parameters:
N (int): Integer to test.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not `N` is prime.
"""
if N in PRIMES_UNDER_1000:
return True
for p in sieve_of_eratosthenes(kth_root(N, 2)):
if not N % p:
return False
return True
def ecpp(N: int, recursive: bool=True) -> bool:
"""
Uses Atkin-Morain Elliptic curve primality proving to prove whether or not `N` is prime.
Parameters:
N (int): Integer to test.
recursive (bool): Whether or not to recursively test all used primes.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not `N` is prime.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elliptic_curve_primality#Atkin%E2%80%93Morain_elliptic_curve_primality_test_(ECPP)
"""
EllipticCurve = _ell_curve.EllipticCurve
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
factor = _factor_gen.factor
class_one_Ds = [-3, -4, -7, -8, -11, -12, -16, -19, -27, -28, -43, -67, -163]
R = ZZ/ZZ(N)
for d in class_one_Ds:
if gcd(N, -d) == 1 and R(d).is_square():
try:
E = EllipticCurve.generate_curve_with_D(d, R)
# Find a divisor above the bound
m_facs = factor(E.order())
divisors = list(m_facs.divisors())
divisors.sort()
bound = (kth_root(N, 4)+1)**2
for d in divisors[1:]:
if d > bound:
break
if d == E.order() and is_prime(d):
continue
# We do this because it only uses trial division internally
d_facs = m_facs/(m_facs/d)
P = E.find_gen()
if P.order() < d:
continue
for p, e in d_facs.items():
if recursive and not is_prime(p, True):
raise RuntimeError(f'Unexpected ECPP error. {p} is not a prime, so factorization has failed')
if not P*p**e:
return False
return True
except NoSolutionException:
pass
except NotInvertibleException as e:
return False
raise RuntimeError(f'No suitable discriminant found for ECPP over {N}')
def lucas_lehmer_test(n: int) -> bool:
"""
Provably determines whether a Mersenne number `n` is prime.
Parameters:
n (int): Mersenne number to test.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not `n` is prime.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lucas%E2%80%93Lehmer_primality_test
"""
assert is_power_of_two(n+1)
if n == 3:
return True
k = n.bit_length()
if not is_prime(k, prove=True):
return False
s = 4
for _ in range(k-2):
s = ((s*s)-2) % n
return s == 0
def is_prime(n: int, prove: bool=False) -> bool:
"""
Determines if `n` is probably prime using the Baillie-PSW primality test if `prove` is False.
Otherwise, a combination of ECPP, Lucas-Lehmer, and exhaustive testing is used.
Parameters:
n (int): Positive integer.
prove (bool): Whether or not to prove `n` is prime.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not `n` is probably prime.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import is_prime, find_prime
>>> is_prime(7)
True
>>> is_prime(15)
False
>>> is_prime(find_prime(32))
True
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baillie%E2%80%93PSW_primality_test
"""
if n < 0:
return False
if prove:
if is_power_of_two(n+1):
return lucas_lehmer_test(n)
elif n.bit_length() < 35:
return exhaustive_primality_proof(n)
else:
# Attempt to prove composite (fast)
if not is_prime(n, prove=False):
return False
return ecpp(n)
else:
if n in PRIMES_UNDER_1000:
return True
for prime in PRIMES_UNDER_1000:
if (n % prime) == 0:
return False
return miller_rabin(n, bases=[2]) and is_strong_lucas_pseudoprime(n)
def is_primitive_root(a: int, p: int) -> bool:
"""
Returns whether or not `a` is a primitive root in ZZ/ZZ(p)*.
`a` is a primitive root of `p` if `a` is the smallest integer such that `a`'s order is the order of the ring.
Parameters:
a (int): Possible primitive root.
p (int): Modulus.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not `a` is a primitive root.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import is_primitive_root
>>> is_primitive_root(3, 10)
True
>>> is_primitive_root(9, 10)
False
>>> is_primitive_root(45, 2)
True
>>> is_primitive_root(208, 3)
False
>>> is_primitive_root(120, 173)
True
"""
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
Z_star = (ZZ/ZZ(p)).mul_group()
a_star = Z_star(a)
return gcd(a, p) == 1 and a_star*Z_star.order() == Z_star.one and a_star.order() == Z_star.order()
def product(elem_list: List['RingElement'], return_tree: bool=False) -> 'RingElement':
"""
Calculates the product of all elements in `elem_list`.
Parameters:
elem_list (list): List of RingElements.
return_tree (bool): Whether or not to return the intermediate tree results.
Returns:
RingElement: Product of all RingElements.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import product
>>> from samson.math.all import ZZ
>>> product([ZZ(1), ZZ(2), ZZ(3)])
<IntegerElement: val=6, ring=ZZ>
>>> product([ZZ(1), ZZ(2), ZZ(3)], True)
[[<IntegerElement: val=1, ring=ZZ>, <IntegerElement: val=2, ring=ZZ>, <IntegerElement: val=3, ring=ZZ>, <IntegerElement: val=1, ring=ZZ>], [<IntegerElement: val=2, ring=ZZ>, <IntegerElement: val=3, ring=ZZ>], [<IntegerElement: val=6, ring=ZZ>]]
References:
https://facthacks.cr.yp.to/product.html
"""
X = list(elem_list)
if len(X) == 0: return 1
X_type = type(X[0])
tree = [X]
one = 1 if X_type is int else X[0].ring.one
while len(X) > 1:
if len(X) % 2:
X.append(one)
X = [X_type.__mul__(*X[i*2:(i+1)*2]) for i in range(len(X) // 2)]
if return_tree:
tree.append(X)
return tree if return_tree else X[0]
def batch_gcd(elem_list: List['RingElement']) -> List['RingElement']:
"""
Calculates the greatest common divisors of any two elements in `elem_list`.
Parameters:
elem_list (List[RingElement]): List of RingElements.
Returns:
List[RingElement]: Greatest common divisors of any two elements.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import batch_gcd
>>> batch_gcd([1909, 2923, 291, 205, 989, 62, 451, 1943, 1079, 2419])
[1909, 1, 1, 41, 23, 1, 41, 1, 83, 41]
References:
https://facthacks.cr.yp.to/batchgcd.html
"""
prods = product(elem_list, True)
R = prods.pop()
while prods:
elem_list = prods.pop()
R = [R[i // 2] % elem_list[i]**2 for i in range(len(elem_list))]
return [gcd(r // n, n) for r, n in zip(R, elem_list)]
def smoothness(n: int, factors: dict=None, **factor_kwargs) -> float:
"""
Calculates the smoothness of an integer `n` as a ratio of the number of non-trivial factors to the number of bits.
Thus, primes are 0% smooth and 2**n is 100% smooth.
Parameters:
n (int): Integer to analyze.
factors (dict): Factors of `n`.
Returns:
float: Smoothness ratio.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import smoothness, is_prime
>>> p = 211
>>> assert is_prime(p)
>>> smoothness(p)
0.0
>>> smoothness(p-1)
0.5185212203629948
"""
if not factors:
if not factor_kwargs:
factor_kwargs = {"use_rho": False}
factors = _factor_gen.factor(n, **factor_kwargs)
# 'factors' will return {n: 1} if `n` is prime
# Just early-out since there will be zero non-trivials anyway
if n in factors:
return 0.0
return (sum(factors.values())) / math.log(n, 2)
def is_safe_prime(p: int) -> bool:
"""
Determines if `p` is a safe prime.
Parameters:
p (int): Prime to analyze.
Returns:
bool: Whether `p` is a safe prime.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import is_safe_prime
>>> from samson.protocols.diffie_hellman import DiffieHellman
>>> is_safe_prime(DiffieHellman.MODP_2048)
True
"""
q, r = divmod(p-1, 2)
return not r and is_prime(q) and is_prime(p)
def is_sophie_germain_prime(p: int) -> bool:
"""
Determines if `p` is a Sophie Germain prime.
Parameters:
p (int): Prime to analyze.
Returns:
bool: Whether `p` is a Sophie Germain prime.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import is_sophie_germain_prime
>>> from samson.protocols.diffie_hellman import DiffieHellman
>>> is_sophie_germain_prime((DiffieHellman.MODP_2048-1)//2)
True
"""
return is_prime(2*p+1)
def is_carmichael_number(n: int, factors: dict=None) -> bool:
"""
Determines if `n` is a Carmichael number. A Carmichael number is a composite number that
passes the Fermat primality test for all bases coprime to it.
Parameters:
n (int): Integer.
factors (dict): Factors of `n`.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not `n` is a Carmichael number.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carmichael_number#Korselt's_criterion
"""
factors = factors or _factor_gen.factor(n, reraise_interrupt=True)
if max(factors.values()) > 1 or len(factors) == 1:
return False
return not any((n-1) % (p-1) for p in factors)
def find_carmichael_number(min_bits: int=None, k: int=None) -> int:
"""
Finds a Carmichael number with a size of `min_bits` or initialized with `k`.
Parameters:
min_bits (int): Minimum size of number to find.
k (int): Looping multiplier.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carmichael_number#Discovery
"""
if min_bits:
# Take into account `k` three times and 6*12*18 is 11 bits
k = 2**((min_bits-11)//3)
while True:
a = 6*k+1
b = 12*k+1
c = 18*k+1
if all(is_prime(elem) for elem in [a, b, c]):
return a*b*c, (a, b, c)
k += 1
def carmichael_function(n: int, factors: dict=None) -> int:
"""
Finds the smallest positive integer `m` such that `a^m = 1 (mod n)`.
Parameters:
n (int): Modulus.
factors (dict): Factors of `n`.
Returns:
int: The least universal exponent.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carmichael_function
"""
if not factors:
factors = _factor_gen.factor(n)
result = 1
for p, e in factors.items():
a = totient(0, {p: e})
if p == 2 and e > 2:
a //= 2
result = lcm(result, a)
return result
def coppersmiths(N: int, f: 'Polynomial', beta: float=1, epsilon: float=None, X: int=None, m: int=None, t: int=None) -> list:
"""
Finds small roots of a polynomial in `ZZ`/`ZZ`(`N`) using Coppersmith's method.
Parameters:
N (int): Modulus.
f (Polynomial): Polynomial to find roots of.
beta (float): Tweaks the size of the roots we look for in the polynomial. (Roots mod `b`, where `b` > `N`^`beta`)
epsilon (float): Tweaks the size of the matrix.
X (int): Absolute bound for roots.
m (int): Tweaks number of columns.
t (int): Tweaks number of rows.
Returns:
list: List of small roots in Zn[x].
References:
https://github.com/sagemath/sage/blob/develop/src/sage/rings/polynomial/polynomial_modn_dense_ntl.pyx#L401
"Finding Small Solutions to Small Degree Polynomials" (http://cr.yp.to/bib/2001/coppersmith.pdf)
"""
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
Matrix = _mat.Matrix
d = f.degree()
x = f.symbol
if not epsilon:
epsilon = beta/8
m = m or math.ceil(max(beta**2/(d*epsilon), 7*beta/d))
t = t or int(d*m * (1/beta - 1))
if not X:
X = math.ceil(0.5 * N**(beta**2/d - epsilon))
g = [x**j * N**(m-i) * f**i for i in range(m) for j in range(d)]
g.extend([x**i * f**m for i in range(t)])
# Build the problem matrix
B = Matrix.fill(ZZ.zero, len(g), d*m + max(d, t))
for i in range(len(g)):
for j in range(g[i].degree()+1):
B[i,j] = (g[i].coeffs[j]*X**j)
# Solve the problem matrix
B = Matrix(B, ZZ).LLL()
k = sum([x**i*ZZ(B[0, i] // X**i) for i in range(B.num_cols)])
R = k.roots()
Zn = ZZ/ZZ(N)
roots = set(Zn(r) for r in R if abs(r) <= X)
Nb = N**beta
return [root for root in roots if gcd(N, root) >= Nb]
def __get_log_precision(n: int):
RR = _real_field.RR
RealField = _real_field.RealField
# Determine required precision
z = RR(n)
prec = z.log()*z
prec = prec.log(10).ceil()
prec *= RR(10).log(2)
prec = int(prec)+5
return RealField(prec)
def prime_number_theorem(n: int, use_heuristic: bool=False) -> int:
"""
Approximates the number of primes less than `n`.
Parameters:
n (int): Maximum bound.
use_heuristic (bool): Whether to use the fast heuristic.
Returns:
int: Approximate number of primes less than `n`.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prime_number_theorem
"""
# The simple version is generally more accurate for `n` < 3000 (empirically)
if n < 3000 or use_heuristic:
return n // math.floor(math.log(n))
else:
RR = __get_log_precision(n)
return int(round(RR(n).li(offset=True)))
pnt = prime_number_theorem
def approxmiate_nth_prime(n: int) -> int:
"""
Approximates the `n`-th prime using the prime number theorem.
Parameters:
n (int): Which prime to approxmiate.
Returns:
int: Approximation of the prime.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prime_number_theorem#Approximations_for_the_nth_prime_number
"""
RR_high = __get_log_precision(n)
n = RR_high(n)
logn = n.log()
llogn = logn.log()
b = logn + llogn - 1 + (llogn-2)/logn - (llogn**2-6*llogn+11)/(2*logn**2)
return int(round(n*b))
@add_complexity(KnownComplexities.IC)
def index_calculus(g: 'MultiplicativeGroupElement', y: 'MultiplicativeGroupElement', order: int=None) -> int:
"""
Computes the discrete logarithm of `y` to base `g`
Parameters:
g (MultiplicativeGroupElement): Generator.
y (MultiplicativeGroupElement): Target of form `g`^`x`.
order (int): Order of `g`.
Returns:
int: The discrete logarithm of `y`.
Examples:
>>> from samson.all import ZZ, index_calculus
>>> p, q, g, d, y = 3272514023, 1636257011, 2, 1390585808, 1244484161
>>> R = (ZZ/ZZ(p)).mul_group()
>>> index_calculus(R(g), R(y))
1390585808
References:
https://github.com/Gr1zz/dlog/blob/master/index_calculus.sage
http://moais.imag.fr/membres/jean-louis.roch/perso_html/transfert/2009-06-19-IntensiveProjects-M1-SCCI-Reports/AlnuaimiKhuloud.pdf
"""
from math import exp, sqrt, log, ceil
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
Matrix = _mat.Matrix
trial_division = _factor_gen.trial_division
def is_smooth_trial(n, B):
facs = trial_division(n, prime_base=B)
return facs.recombine() == n, facs
Fq = ZZ/ZZ(order or g.order())
q = Fq.order()
p = g.ring.characteristic()
g = g.cache_mul(q.bit_length())
y = y.cache_mul(q.bit_length())
if not is_prime(q):
raise ValueError('Index calculus requires a prime group')
B = ceil(exp(0.5*sqrt(2*log(p)*log(log(p)))))
base = list(sieve_of_eratosthenes(B+1))
# Precompute indices
indices = {p:i for i,p in enumerate(base)}
S = len(base)
relations = Matrix.fill(Fq.zero, S+1, S)
# Find smooth relations
row = []
k = 0
while (k < S+1):
while True:
a = Fq.random()
b = Fq.random()
if not (a,b) in row:
break
z = g*int(a)+y*int(b)
is_smooth, facs = is_smooth_trial(int(z), base)
if is_smooth:
row.append((a,b))
for p_i, e_i in facs.items():
i = indices[p_i]
relations[k, i] = Fq(e_i)
k += 1
# Solve
ker = relations.left_kernel()[0]
A, B = 0, 0
for ker_i, row_i in zip(ker, row):
A += ker_i*row_i[0]
B += ker_i*row_i[1]
return int(-A * ~Fq(B))
def estimate_L_complexity(a, c, n):
return math.e**(c*math.log(n)**a * (math.log(math.log(n)))**(1-a))
def log(y: 'RingElement', base: 'RingElement') -> int:
"""
Computes the logarithm of `y` to `base`.
Parameters:
base (RingElement): Base.
Returns:
int: `x` such that `base`^`x` == `y`.
"""
if type(y) in [int, float]:
return math.log(y, base)
else:
return y.log(base)
def find_smooth_close_to(n: int, max_j: int=5, primes: list=None) -> int:
# 'mod' flips between 1 and -1 so we add and subtract
curr_facs = 1
mod = 1
for prime in (primes or PRIMES_UNDER_1000):
if curr_facs*prime > n:
break
# Figure out where we need to jump to to be divisible
r = (mod*n) % prime
j = -(mod_inv(curr_facs, prime)*r) % prime
if j <= max_j:
n += mod*curr_facs*j
mod *= -1
curr_facs *= prime
return n
def cornacchias_algorithm(d: int, p: int, all_sols: bool=False, **root_kwargs) -> Tuple[int, int]:
"""
Solves the Diophantine equation `x`^2 + `d`*`y`^2 = `p`.
Parameters:
d (int): `d` parameter.
p (int): `p` parameter.
all_sols (bool): Whether or not to return all (primitive) solutions.
Returns:
Tuple[int, int]: Formatted as (`x`, `y`).
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import cornacchias_algorithm
>>> d, p = 3, 52
>>> x, y = cornacchias_algorithm(d, p)
>>> x, y
(5, 3)
>>> x**2 + d*y**2 == p
True
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cornacchia%27s_algorithm
"""
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
d = int(d)
R = ZZ/ZZ(p)
D = R(-d)
sols = []
if D.is_square():
for root in D.kth_root(2, True, **root_kwargs):
t = int(root)
bound = kth_root(p, 2)
n = p
while True:
n, t = t, n % t
if t < bound:
break
result = ZZ(p-t**2)/d
if result in ZZ and result.is_square():
sol = (t, int(result.kth_root(2)))
if all_sols:
sols.append(sol)
else:
return sol
if sols:
return set(sols)
else:
raise NoSolutionException()
def binary_quadratic_forms(D: int) -> List[Tuple[int]]:
"""
Returns the list of primitive binary quadratic forms satisfying `a`*`x`^2 + `b`*`x`*`y` + `c`*`y`^2 (i.e. `b`^2 - 4`a``c` = -`D`).
Parameters:
D (int): Discriminant.
Returns:
List[Tuple[int]]: List of primitives BQFs satsifying the equation for D.
References:
https://crypto.stanford.edu/pbc/notes/ep/hilbert.html
"""
D = abs(D)
B = int((D/3)**(1/2))
bqfs = []
b = D % 2
while b <= B:
t = (b**2 + D) // 4
a = max(b, 1)
while a**2 <= t:
c = t // a
if not t % a and gcd(c, a, b) == 1:
if not (a == b or a**2 == t or b == 0):
bqfs.append((a, -b, c))
bqfs.append((a, b, c))
a += 1
b += 2
return bqfs
@RUNTIME.global_cache()
def hilbert_class_polynomial(D: int) -> 'Polynomial':
"""
Generates the Hilbert class polynomial for discriminant `D`.
Parameters:
D (int): Discriminant.
Returns:
Polynomial: Hilbert class polynomial.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.general import hilbert_class_polynomial
>>> hilbert_class_polynomial(3)
<Polynomial: y, coeff_ring=ZZ>
>>> hilbert_class_polynomial(7)
<Polynomial: y + 3375, coeff_ring=ZZ>
>>> hilbert_class_polynomial(31)
<Polynomial: y^3 + (39491307)*y^2 + (-58682638134)*y + 1566028350940383, coeff_ring=ZZ>
References:
https://github.com/sagemath/sage/blob/master/src/sage/schemes/elliptic_curves/cm.py
"""
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
RR = _complex_field.CC(0).real().ring
if D < 0:
D = -D
if not -D % 4 in [0, 1]:
raise ValueError(f'{-D} is not a discriminant')
# Calculate required precision
bqfs = binary_quadratic_forms(D)
h = len(bqfs)
c1 = 3.05682737291380
c2 = sum([1/RR(qf[0]) for qf in bqfs], RR(0))
prec = c2*RR(3.142)*RR(D).sqrt() + h*c1
prec *= 1.45
prec += 10
prec = prec.ceil()
C2 = _complex_field.ComplexField(int(prec))
from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
def j_func(tau):
return C2(C2.ctx.kleinj(tau.val)*1728)
x = Symbol('x')
R = C2[x]
P = R(1)
dsqrt = C2(-D).sqrt()
for qf in bqfs:
a,b,_ = qf
P *= x - j_func((-b + dsqrt)/(2*a))
Q = ZZ[Symbol('y')]
return Q([round(c.real()) for c in P])
def newton_method_sizes(prec: int) -> List[int]:
"""
Generates a precision ladder for Netwon's method.
Parameters:
prec (int): Desired final precision.
Returns:
List[int]: Optimized precision ladder.
"""
output = []
while prec > 1:
output.append(prec)
prec = (prec + 1) >> 1
output.append(1)
output.reverse()
return output
def batch_inv(elements: List['RingElement']) -> List['RingElement']:
"""
Efficiently inverts a list of elements using a single inversion (cost 3m + I).
Parameters:
elements (List[RingElement]): Elements to invert.
Returns:
List[RingElement]: List of inverted elements.
References:
https://math.mit.edu/classes/18.783/2015/LectureNotes8.pdf
"""
if not elements:
return []
R = elements[0].ring
B = [R.one]
for a in elements:
B.append(B[-1]*a)
gamma = ~B[-1]
invs = []
for i in reversed(range(1, len(elements)+1)):
invs.append(B[i-1]*gamma)
gamma *= elements[i-1]
return invs[::-1]
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/general.py
| 0.917344 | 0.358269 |
general.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.utilities.runtime import RUNTIME
from samson.core.base_object import BaseObject
from samson.math.general import gcd
from samson.math.algebra.rings.integer_ring import ZZ
from samson.math.fft.all import ntt_convolution, gss_convolution
from types import FunctionType
class DenseVector(BaseObject):
def __init__(self, values: list, coeff_ring: 'Ring'=None):
if coeff_ring:
self.coeff_ring = coeff_ring
else:
self.coeff_ring = values[0].ring if hasattr(values[0], 'ring') else ZZ
self.values = [self.coeff_ring(v) for v in values]
def shorthand(self, tinyhand: bool=False) -> str:
if tinyhand:
str_meth = lambda elem: elem.tinyhand()
else:
str_meth = lambda elem: elem.shorthand()
return "[" + ", ".join([str_meth(val) for val in self.values]) + "]"
def tinyhand(self) -> str:
return self.shorthand(True)
@property
def __raw__(self):
return RUNTIME.default_short_printer(self)
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['__raw__']
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash(self.values)
def __add__(self, other: 'DenseVector') -> 'DenseVector':
return DenseVector([a+b for a,b in zip(self.values, other.values)])
def __sub__(self, other: 'DenseVector') -> 'DenseVector':
return DenseVector([a-b for a,b in zip(self.values, other.values)])
def __neg__(self) -> 'DenseVector':
return DenseVector([-a for a in self.values])
def __mul__(self, other: object) -> 'DenseVector':
return DenseVector([a*other for a in self.values])
def __iter__(self):
return self.values.__iter__()
def __getitem__(self, idx: object) -> 'RingElement':
result = self.values[idx]
if type(idx) is slice:
return DenseVector(result)
else:
return result
def __setitem__(self, idx, value):
self.values[idx] = value
def __len__(self):
return len(self.values)
def dot(self, other: 'DenseVector') -> object:
return sum([a*b for a,b in zip(self.values, other.values)], self.coeff_ring.zero)
def sdot(self) -> object:
return self.dot(self)
def proj_coeff(self, other: 'DenseVector') -> object:
return self.dot(other) / self.sdot()
def project(self, other: 'DenseVector') -> 'DenseVector':
return self * self.proj_coeff(other)
def apply_elementwise(self, func: FunctionType) -> 'DenseVector':
"""
Applies a function to each element and returns a `DenseVector` of the results.
Parameters:
func (func): Function to apply.
Returns:
DenseVector: Result DenseVector.
"""
return DenseVector([func(e) for e in self.values])
def change_ring(self, ring: 'Ring') -> 'DenseVector':
"""
Returns a new DenseVector with the coefficients coerced into `ring`.
Parameters:
ring (Ring): Ring to embed into.
Returns:
DenseVector: Resultant DenseVector.
"""
return DenseVector(self.values, coeff_ring=ring)
def convolve(self, other: 'DenseVector') -> 'DenseVector':
"""
Performs linear convolution between two vectors.
Parameters:
other (DenseVector): Other vector to convolve with.
Returns:
DenseVector: Convolved vector.
"""
l_self = len(self)
for i in range(l_self):
if self[i]:
break
p1_min = i
l_other = len(other)
for i in range(l_other):
if other[i]:
break
p2_min = i
max_deg = max(l_self-p1_min, l_other-p2_min)
logn = max_deg.bit_length()
n = 2**logn
vec_a = self[p1_min:]
vec_b = other[p2_min:]
# Decide whether to do naive convolution or FFT convo
if max_deg and max_deg**2 > 10*(3*n*logn+n):
if self.coeff_ring == ZZ:
return DenseVector(ntt_convolution(vec_a.values, vec_b.values))
elif self.coeff_ring == ZZ.fraction_field():
content_a = gcd(*vec_a.values)
content_b = gcd(*vec_b.values)
vec_a_zz = vec_a * ~content_a
vec_b_zz = vec_b * ~content_b
vec_c_zz = DenseVector(ntt_convolution(vec_a_zz.values, vec_b_zz.values))
return vec_c_zz*(content_a*content_b)
# TODO: Check for Quotient ring
else:
return gss_convolution(vec_a.values, vec_b.values).dense_vector()
else:
vec = [0]*(len(vec_a) + len(vec_b))
for i, a in enumerate(vec_a):
for j, b in enumerate(vec_b):
vec[i+j] += a*b
return DenseVector(vec)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/dense_vector.py
| 0.659953 | 0.444746 |
dense_vector.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.sparse_vector import SparseVector
from math import ceil, log
def _split(v, m, k):
K = 1 << (k-1)
zero = v[0].ring.zero
zeroes = [zero] * K
return [v[i:i+K] + zeroes for i in range(0, K << m, K)]
def _combine(L, m, k):
M = 1 << m
half_K = 1 << (k-1)
return L[0][:half_K] + \
[L[i+1][j] + L[i][j+half_K] \
for i in range(M-1) for j in range(half_K)]
def _nega_combine(L, m, k):
M = 1 << m
half_K = 1 << (k-1)
return [L[0][j] - L[M-1][j+half_K] for j in range(half_K)] + \
[L[i+1][j] + L[i][j+half_K] \
for i in range(M-1) for j in range(half_K)]
def _convolution_naive(L1, L2):
assert L1 and L2
new_coeffs = [L1[0].ring.zero] * (len(L1)+len(L2))
for i, coeff_h in enumerate(L1):
for j, coeff_g in enumerate(L2):
new_coeffs[i+j] += coeff_h*coeff_g
return new_coeffs
def _forward_butterfly(L1, L2, r):
assert len(L1) == len(L2)
assert 0 <= r <= len(L1)
K = len(L1)
nL1 = []
nL2 = []
for i in range(K):
a = L1[i]
b = L2[(i-r)%K]
nL1.append(a-b)
nL2.append(a+b)
v1 = nL1[:r] + nL2[r:]
v2 = nL2[:r] + nL1[r:]
return v1, v2
def _inverse_butterfly(L1, L2, r):
assert len(L1) == len(L2)
assert 0 <= r <= len(L1)
K = len(L1)
v1 = [L1[i] + L2[i] for i in range(K)]
v2 = [L1[i] - L2[i] for i in range(r, K)] + [L2[i] - L1[i] for i in range(r)]
return v1, v2
def _fft(L, K, start, depth, root):
half = 1 << (depth - 1)
start2 = start + half
# reduce mod (x^(D/2) - y^root) and mod (x^(D/2) + y^root)
for i in range(half):
L[start + i], L[start2 + i] = \
_forward_butterfly(L[start + i], L[start2 + i], root)
# recurse into each half
if depth >= 2:
_fft(L, K, start, depth - 1, root >> 1)
_fft(L, K, start2, depth - 1, (root + K) >> 1)
def _ifft(L, K, start, depth, root):
half = 1 << (depth - 1)
start2 = start + half
# recurse into each half
if depth >= 2:
_ifft(L, K, start, depth - 1, root >> 1)
_ifft(L, K, start2, depth - 1, (root + K) >> 1)
# CRT together (x^(D/2) - y^root) and mod (x^(D/2) + y^root)
for i in range(half):
L[start + i], L[start2 + i] = \
_inverse_butterfly(L[start + i], L[start2 + i], root)
def _negaconvolution_naive(L1, L2):
assert len(L1)
assert len(L1) == len(L2)
N = len(L1)
new_coeffs = []
for j in range(N):
a = sum([L1[i] * L2[j-i] for i in range(j+1)])
b = sum([L1[i] * L2[N+j-i] for i in range(j+1, N)])
new_coeffs.append(a-b)
return new_coeffs
def _negaconvolution_fft(L1, L2, n):
R = L1[0].ring
# split into 2^m pieces of 2^(k-1) coefficients each, with k as small
# as possible, subject to m <= k (so that the ring of Fourier coefficients
# has enough roots of unity)
m = (n + 1) >> 1
k = n + 1 - m
M = 1 << m
K = 1 << k
# split inputs into polynomials
L1 = _split(L1, m, k)
L2 = _split(L2, m, k)
# fft each input
_fft(L1, K, 0, m, K >> 1)
_fft(L2, K, 0, m, K >> 1)
# pointwise multiply
L3 = [_negaconvolution(L1[i], L2[i], k) for i in range(M)]
# inverse fft
_ifft(L3, K, 0, m, K >> 1)
# combine back into a single list
L3 = _nega_combine(L3, m, k)
# normalise
return [R(val / M) for val in L3]
def _negaconvolution(L1, L2, n):
if n <= 3: # arbitrary cutoff
return _negaconvolution_naive(L1, L2)
else:
return _negaconvolution_fft(L1, L2, n)
# TODO: Currently, this is all heavily ripped out of Sage. Will require a complete rework.
def _convolution(L1, L2):
"""
Generalized Schonhage-Strassen polynomial multiplication for arbitrary rings. Very much pulled from Sage.
References:
"Fast Multiplication of Polynomials over Arbitrary Rings" (http://kaltofen.math.ncsu.edu/bibliography/87/CaKa87_techrep.pdf)
https://github.com/sagemath/sage/blob/860e4dc9881966a36ef8808a0d1fae0c6b54f741/src/sage/rings/polynomial/convolution.py#L368
"""
R = L1[0].ring
# choose n so that output convolution length is 2^n
len1 = len(L1)
len2 = len(L2)
outlen = len1 + len2 - 1
n = int(ceil(log(outlen, 2)))
# split into 2^m pieces of 2^(k-1) coefficients each, with k as small
# as possible, subject to m <= k + 1 (so that the ring of Fourier
# coefficients has enough roots of unity)
m = (n >> 1) + 1
k = n + 1 - m
N = 1 << n
M = 1 << m
K = 1 << k
# zero pad inputs up to length N
zero = R.zero
L1 += [zero] * (N - len1)
L2 += [zero] * (N - len2)
# split inputs into polynomials
L1 = _split(L1, m, k)
L2 = _split(L2, m, k)
# fft each input
_fft(L1, K, 0, m, K)
_fft(L2, K, 0, m, K)
# pointwise multiply
L3 = [_negaconvolution(L1[i], L2[i], k) for i in range(M)]
# inverse fft
_ifft(L3, K, 0, m, K)
# combine back into a single list
L3 = SparseVector.wrap(_combine(L3, m, k))
# normalise, and truncate to correct length
return L3.map(lambda idx, val: (idx, R(val / M)))
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/fft/gss.py
| 0.54359 | 0.537891 |
gss.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring, RingElement
from samson.math.algebra.rings.integer_ring import ZZ
from samson.math.factorization.general import factor
from samson.math.map import Map
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.utilities.exceptions import CoercionException
from typing import Tuple
# https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7748
def cswap(swap: int, x_2: int, x_3: int) -> Tuple[int, int]:
"""
Conditional constant-time swap.
Parameters:
swap (int): 0 or 1. 1 means swap.
x_2 (int): First int.
x_3 (int): Second int.
Returns:
(int, int): Formatted as (x_2, x_3)
"""
dummy = swap * (x_2 - x_3)
x_2 = x_2 - dummy
x_3 = x_3 + dummy
return (x_2, x_3)
# https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7748#section-4.1
class MontgomeryCurve(Ring):
"""
Montgomery Curve
Basically just decouples parameters from `MontgomeryPoint`.
"""
# https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7748#section-3
def __init__(self, A: RingElement, U: RingElement=None, V: RingElement=None, a24: int=None, oid: str=None, ring: Ring=None, order: int=None, B: RingElement=None):
"""
Parameters:
A (int): An element in the finite field GF(p), not equal to -2 or 2.
U (int): The u-coordinate of the elliptic curve point P on a Montgomery curve.
V (int): The v-coordinate of the elliptic curve point P on a Montgomery curve.
a24 (int): Constant for curve multiplication.
"""
self.A = A
self.a24 = a24 or (A-2) // 4
self.U = U
self.V = V
self.oid = oid
self.ring = ring or A.ring
self.B = B or self.ring.one
self.zero = self(0)
self._order = order
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['A', 'B', 'ring']
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'MontgomeryCurve{{A={self.A}, B={self.B}, ring={self.ring}}}'
def random(self, size: int=None) -> 'MontgomeryPoint':
"""
Generate a random element.
Parameters:
size (int): The ring-specific 'size' of the element.
Returns:
MontgomeryPoint: Random element of the algebra.
"""
while True:
try:
return self(self.ring.random(size))
except CoercionException:
pass
@property
def p(self) -> int:
return self.ring.characteristic()
@property
def G(self) -> 'MontgomeryPoint':
if not self.U:
self.U = self.find_gen().x
return self(self.U, self.V)
def order(self) -> int:
if not self._order:
self._order = self.to_weierstrass_form()[0].order() // 2
return self._order
def element_at(self, x: int) -> 'MontgomeryPoint':
"""
Returns the `x`-th element w.r.t to the generator.
Parameters:
x (int): Element ordinality.
Returns:
MontgomeryPoint: The `x`-th point.
"""
return self.G*x
def __call__(self, x: 'RingElement', y: 'RingElement'=None, verify: bool=True) -> 'MontgomeryPoint':
return self.coerce(x, y, verify)
def coerce(self, x: 'RingElement', y: 'RingElement'=None, verify: bool=True) -> 'MontgomeryPoint':
if type(x) is MontgomeryPoint:
if x.curve == self:
return x
else:
return self(x.x, x.y)
if verify:
v = (x**3 + self.A*x**2 + x)/self.B
if y:
if y**2 != v:
raise CoercionException(f"({x}, {y}) is not on curve {self}")
elif not v.is_square():
raise CoercionException(f"{x} is not on curve {self}")
else:
y = v.sqrt()
if not y:
v = (x**3 + self.A*x**2 + x)/self.B
y = v.sqrt()
return MontgomeryPoint(self.ring(x), self.ring(y), self)
def __eq__(self, other) -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other) and self.p == other.p and self.A == other.A and self.B == other.B
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return Bytes(self.oid.encode()).int() if self.oid else hash((self.A, self.B))
def to_weierstrass_form(self) -> Tuple['WeierstrassCurve', Map]:
"""
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Montgomery_curve#Equivalence_with_Weierstrass_curves
"""
from samson.math.algebra.curves.weierstrass_curve import WeierstrassCurve
A = self.A
B = self.B
inv_B = ~B
inv_B3 = ~(B*3)
if self.U is not None and self.V is not None:
x = (self.U*inv_B) + (A*inv_B3)
y = self.V*inv_B
G = (x, y)
else:
G = None
def map_func(point):
return curve((point.x*inv_B) + (A*inv_B3), point.y*inv_B)
a = (3-A**2) * (inv_B3*inv_B)
b = (2*A**3 - 9*A) * (inv_B3**3)
curve = WeierstrassCurve(a=a, b=b, base_tuple=G, cardinality=self.order()*2 if self._order else None)
def inv_map_func(point):
return self(self.B*(point.x-self.A*inv_B3), self.B*point.y)
point_map = Map(self, curve, map_func, inv_map=inv_map_func)
return curve, point_map
def find_gen(self) -> 'MontgomeryPoint':
E, _ = self.to_weierstrass_form()
G = E.find_gen()
s = self.B
alpha = self.A/(3*s)
return self(s*(G.x-alpha))
def __two_isogeny(self, P):
x2 = P.x
A, B = 2*(1-2*x2), self.B*x2
curve = MontgomeryCurve(A=A, B=B)
def map_func(Q):
x, y = Q.x, Q.y
xp2x = x**2*x2
xp2 = x-x2
xp2_inv = ~xp2
xP = (xp2x - x)*xp2_inv
yP = y*(xp2x-2*x*x2**2+x2)*(xp2_inv**2)
return curve(xP, yP)
return Map(domain=self, codomain=curve, map_func=map_func)
def isogeny(self, P: 'MontgomeryPoint') -> 'EllipticCurveIsogeny':
if P.ring != self:
raise ValueError(f'{P} is not on {self}')
n = P.order()
n_facs = factor(n)
phi = None
for p, e in n_facs.items():
Q = P*(n // p**e)
for i in range(1, e+1):
old_phi = phi
phi = self.__two_isogeny(Q*(p**(e-i)))
#phi = EllipticCurveIsogeny(E, Q*(p**(e-i)), pre_isomorphism=phi)
Q = phi(Q)
phi.pre_isomorphism = old_phi
P = phi(P)
return phi
class MontgomeryPoint(RingElement):
"""
Point on a Montgomery Curve
Provides scalar multiplication.
"""
def __init__(self, x: RingElement, y: RingElement, curve: MontgomeryCurve):
"""
Parameters:
x (RingElement): x-coordinate.
y (RingElement): y-coordinate.
curve (MontgomeryCurve): The underlying curve.
"""
self.x = curve.ring(x)
self.y = curve.ring(y)
self.curve = curve
self.order_cache = None
def __hash__(self):
return hash((self.curve, self.x, self.y))
@property
def ring(self):
return self.curve
def tinyhand(self):
return str(self.x) if type(self.x) is int else self.x.val.tinyhand()
def __eq__(self, other: 'MontgomeryPoint') -> bool:
return self.x == other.x and self.y == other.y and self.curve == other.curve
def __double__(self) -> 'MontgomeryPoint':
A, B = self.curve.A, self.curve.B
x1, y1 = self.x, self.y
x12 = x1*x1
xA = (3*x12+2*A*x1+1)
xA2 = xA*xA
yB = (2*B*y1)
iyB = ~yB
iyB2 = iyB*iyB
x3 = B*xA2*iyB2-A-x1-x1
y3 = (2*x1+x1+A)*xA*iyB-B*xA*xA2*iyB2*iyB-y1
return MontgomeryPoint(x3, y3, self.curve)
def __add__(self, P2: 'MontgomeryPoint') -> 'MontgomeryPoint':
"""
References:
http://hyperelliptic.org/EFD/g1p/auto-montgom.html
"""
# This throws a ZeroDivisionError otherwise
if not self:
return P2
elif not P2:
return self
elif P2 == self:
return self.__double__()
elif -P2 == self:
return self.curve.zero
A, B = self.curve.A, self.curve.B
x1, y1 = self.x, self.y
x2, y2 = P2.x, P2.y
x3 = B*(y2-y1)**2/(x2-x1)**2-A-x1-x2
y3 = (2*x1+x2+A)*(y2-y1)/(x2-x1)-B*(y2-y1)**3/(x2-x1)**3-y1
return MontgomeryPoint(x3, y3, self.curve)
def __neg__(self) -> 'MontgomeryPoint':
return MontgomeryPoint(self.x, -self.y, self.curve)
def to_weierstrass_coordinate(self) -> Tuple[RingElement, RingElement]:
A = self.curve.A
B = self.curve.B
inv_B = ~B
return (self.x*inv_B) + (A/(B*3)), self.y*inv_B
class Curve25519Crv(MontgomeryCurve):
def __init__(self):
ring = ZZ/ZZ(2**255 - 19)
super().__init__(A=ring(486662), a24=121665, U=ring(9), V=ring(14781619447589544791020593568409986887264606134616475288964881837755586237401), oid='1.3.101.110', order=(2**252 + 0x14def9dea2f79cd65812631a5cf5d3ed)*8)
def clamp_to_curve(self, x: int) -> int:
"""
Coerces `x` to a valid x-coordinate on Curve25519.
Parameters:
x (int): `x` value to coerce.
Returns:
int: Valid MontgomeryPoint.
"""
x = int(x)
x &= ~7
x &= ~(128 << 8 * 31)
x |= 64 << 8 * 31
return x
class Curve448Crv(MontgomeryCurve):
def __init__(self):
ring = ZZ/ZZ(2**448 - 2**224 - 1)
super().__init__(A=ring(156326), a24=39081, U=ring(5), V=ring(355293926785568175264127502063783334808976399387714271831880898435169088786967410002932673765864550910142774147268105838985595290606362), oid='1.3.101.111', order=(2**446 - 0x8335dc163bb124b65129c96fde933d8d723a70aadc873d6d54a7bb0d)*4)
def clamp_to_curve(self, x: int) -> int:
"""
Coerces `x` to a valid x-coordinate on Curve448.
Parameters:
x (int): `x` value to coerce.
Returns:
int: Valid MontgomeryPoint.
"""
x = int(x)
x &= ~3
x |= 128 << 8 * 55
return x
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/curves/montgomery_curve.py
| 0.956759 | 0.425128 |
montgomery_curve.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring, RingElement
from samson.math.general import random_int
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
def bit(h,i):
return (h[i//8] >> (i%8)) & 1
# https://ed25519.cr.yp.to/python/ed25519.py
# https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8032
class TwistedEdwardsCurve(Ring):
"""
Twisted Edwards Curve
Provides general curve operations and parameter decoupling.
"""
# https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8032#section-5
# https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8032#section-3
def __init__(self, oid: str, a: int, c: int, n: int, b: int, magic: bytes, l: int, d: int, B: (int, int), ring: Ring=None):
"""
Parameters:
oid (str): Curve OID.
a (int): Twist parameter. a=1 is untwisted, the special case.
c (int): Base 2 logarithm of cofactor
n (int): Defines the number of bits in EdDSA scalars.
b (int): Number of bits the curve can encode.
magic (bytes): The magic byte-string (if any) of the curve.
l (int): Order of the curve.
d (int): A non-zero element in the finite field GF(q), not equal to 1, in the case of an Edwards curve, or not equal to -1, in the case of a twisted Edwards curve
B ((int, int)): Base point.
"""
self.oid = oid
self.a = a
self.c = c
self.n = n
self.b = b
self.magic = magic
self.l = l
self.d = d
self.ring = ring or d.ring
self.B = TwistedEdwardsPoint(*B, self)
self.I = ring(2) ** ((self.q-1) // 4)
self.zero = TwistedEdwardsPoint(0, 1, self)
self.one = self.B
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['b', 'q', 'l']
def random(self, size: int=None) -> 'TwistedEdwardsPoint':
"""
Generate a random element.
Parameters:
size (int): The ring-specific 'size' of the element.
Returns:
TwistedEdwardsCurve: Random element of the algebra.
"""
return self.B * random_int(size or self.q)
@property
def q(self):
return self.ring.characteristic()
def order(self):
return self.q
def element_at(self, x: int) -> 'TwistedEdwardsPoint':
"""
Returns the `x`-th element w.r.t to the generator.
Parameters:
x (int): Element ordinality.
Returns:
TwistedEdwardsPoint: The `x`-th point.
"""
return self.B*x
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'TwistedEdwardsCurve{{a={self.a}, l={self.l}, q={self.q}, B={(str(self.B.x), str(self.B.y))}}}'
def __eq__(self, other) -> bool:
return issubclass(type(other), TwistedEdwardsCurve) and self.b == other.b and self.q == other.q and self.l == other.l and self.d == other.d
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return Bytes(self.oid.encode()).int() if self.oid else hash((self.a, self.d))
def clamp_to_curve(self, x: int, swap_bit_order: bool=True) -> int:
"""
Coerces `x` to a valid x-coordinate on the curve.
Parameters:
x (int): `x` value to coerce.
swap_bit_order (bool): Whether or not to swap the bit order before processing.
Returns:
int: Valid x-coordinate.
"""
from samson.utilities.manipulation import get_blocks
as_bits = bin(x)[2:].zfill(self.b)
if swap_bit_order:
as_bits = ''.join([block[::-1] for block in get_blocks(as_bits, 8)])
return 2**(self.n) | sum(2**i * int((as_bits)[i]) for i in range(self.c, self.n))
def is_on_curve(self, P: (int, int)) -> bool:
"""
Determines if the point `P` is on the curve.
Parameters:
P (int, int): The point formatted as (x, y).
Returns:
bool: Whether or not the point is on the curve.
"""
x, y = P
return self.a * x*x + y*y - self.ring.one - self.d * x*x*y*y == self.ring.zero
def recover_point_from_y(self, y: int) -> 'TwistedEdwardsPoint':
"""
Recovers the full TwistedEdwardsPoint from the y-coordinate.
Parameters:
y (int): y-coordinate of a valid TwistedEdwardsPoint.
Returns:
TwistedEdwardsPoint: Full TwistedEdwardsPoint.
"""
y = self.ring.coerce(y)
xx = (y*y-1) * ~(self.d*y*y-self.a)
if self.q % 8 == 5:
x = xx ** ((self.q+3)//8)
if (x*x - xx) != self.ring.zero:
x = (x*self.I)
if x % 2 != self.ring.zero:
x = -x
elif self.q % 4 == 3:
x = xx**((self.q+1)//4)
else:
raise ValueError("Unsupported prime `q`.")
return TwistedEdwardsPoint(x, y, self)
class TwistedEdwardsPoint(RingElement):
"""
Point on a Twisted Edwards Curve
Provides scalar multiplication and point addition.
"""
def __init__(self, x: int, y: int, curve: TwistedEdwardsCurve, validate: bool=True):
"""
Parameters:
x (int): x-coordinate.
y (int): y-coordinate.
curve (TwistedEdwardsCurve): Underlying curve.
validate (bool): Whether or not to validate the point against the curve.
"""
self.curve = curve
self.x = self.curve.ring.coerce(x)
self.y = self.curve.ring.coerce(y)
if validate and not curve.is_on_curve((self.x, self.y)):
raise ValueError(f"({x}, {y}) is not on {curve}")
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['x', 'y', 'curve']
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'{self.curve.shorthand()}({{x={self.x}, y={self.y}}})'
def tinyhand(self) -> str:
return self.shorthand()
@property
def ring(self):
return self.curve
def __eq__(self, other: 'TwistedEdwardsPoint') -> bool:
return self.x == other.x and self.y == other.y and self.curve == other.curve
def __neg__(self) -> 'TwistedEdwardsPoint':
return TwistedEdwardsPoint(self.x, -self.y, self.curve)
def __add__(self, other: 'TwistedEdwardsPoint') -> 'TwistedEdwardsPoint':
if type(other) != TwistedEdwardsPoint:
raise TypeError(f"TwistedEdwardsPoint addition only defined between points. Type {type(other)} given.")
assert self.curve == other.curve
ring = self.curve.ring
x1, y1 = self.x, self.y
x2, y2 = other.x, other.y
x3 = (x1*y2+x2*y1) * ~(ring.one+self.curve.d * x1*x2*y1*y2)
y3 = (y1*y2 - self.curve.a*x1*x2) * ~(ring.one-self.curve.d * x1*x2*y1*y2)
return TwistedEdwardsPoint(x3, y3, self.curve)
def __sub__(self, other: 'TwistedEdwardsPoint') -> 'TwistedEdwardsPoint':
if type(other) != TwistedEdwardsPoint:
raise TypeError("TwistedEdwardsPoint subtraction only defined between points.")
assert self.curve == other.curve
return self + -other
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/curves/twisted_edwards_curve.py
| 0.849191 | 0.410697 |
twisted_edwards_curve.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.curves.weierstrass_curve import EllipticCurve, WeierstrassPoint
from samson.math.map import Map
from samson.utilities.exceptions import NoSolutionException
from samson.utilities.runtime import RUNTIME
from samson.core.base_object import BaseObject
class EllipticCurveIsomorphism(Map):
def __init__(self, domain: EllipticCurve, codomain: EllipticCurve, u, r, s, t, pre_isomorphism: 'Map'=None):
self.domain = domain
self.codomain = codomain
self.u = u
self.r = r
self.s = s
self.t = t
self.pre_isomorphism = pre_isomorphism
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['domain', 'codomain', 'u', 'r', 's', 't']
def __str__(self):
return f'ϕ: {self.true_domain} (u={self.u}, r={self.r}, s={self.s}, t={self.t}) -> {self.codomain}'
def map_func(self, P):
if not P:
return self.codomain.zero
x, y = P.x, P.y
x -= self.r
y -= (self.s*x+self.t)
return self.codomain(x/self.u**2, y/self.u**3)
def __hash__(self):
return hash((self.domain, self.codomain, self.u, self.r, self.s, self.t, self.pre_isomorphism))
@staticmethod
def identity(domain, codomain):
R = domain.ring
return EllipticCurveIsomorphism(domain, codomain, R.one, R.zero, R.zero, R.zero)
def is_identity(self):
return self.u == self.u.ring.one and not any([self.r, self.s, self.t])
def __invert__(self):
u, r, s, t = self.u, self.r, self.s, self.t
return EllipticCurveIsomorphism(self.codomain, self.domain, u=1/u, r=-r/u**2, s=-s/u, t=(r*s-t)/u**3)
def __mul__(self, other):
us, rs, ss, ts = self.u, self.r, self.s, self.t
uo, ro, so, to = other.u, other.r, other.s, other.t
return EllipticCurveIsomorphism(self.domain, self.codomain, u=us*uo, r=(us**2) * ro + rs, s=us*so + ss, t=(us**3) * to + ss * (us**2) * ro + ts)
def __truediv__(self, other):
return self * ~other
def __neg__(self):
return EllipticCurveIsomorphism(self.domain, self.codomain, u=-self.u, r=self.r, s=self.s, t=self.t)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/curves/elliptic_curve_isomorphism.py
| 0.517083 | 0.204521 |
elliptic_curve_isomorphism.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring, RingElement
from samson.math.general import mod_inv, xgcd, gcd, tonelli, generalized_eulers_criterion, ResidueSymbol, random_int
from samson.utilities.exceptions import CoercionException
from samson.auxiliary.lazy_loader import LazyLoader
_integer_ring = LazyLoader('_integer_ring', globals(), 'samson.math.algebra.rings.integer_ring')
_poly = LazyLoader('_poly', globals(), 'samson.math.polynomial')
class QuotientElement(RingElement):
"""
Element of a `QuotientRing`.
"""
def __init__(self, val: RingElement, ring: Ring):
"""
Parameters:
val (RingElement): Value of the element.
ring (Ring): Parent ring.
"""
super().__init__(ring)
self.val = val % self.ring.quotient
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['val', 'ring']
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return self.val.shorthand()
def ordinality(self) -> int:
"""
The ordinality of this element within the set.
Returns:
int: Ordinality.
"""
return self.val.ordinality()
def __call__(self, x: int) -> RingElement:
return self.val(x)
# We explicitly include these operators to prevent a ring coercion (speed reasons)
def __elemadd__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return QuotientElement(self.val + other.val, self.ring)
def __elemmul__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return QuotientElement(self.val * other.val, self.ring)
def __elemmod__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return QuotientElement(self.val % other.val, self.ring)
def __invert__(self) -> 'QuotientElement':
return QuotientElement(mod_inv(self.val, self.ring.quotient), self.ring)
def __neg__(self) -> 'QuotientElement':
return QuotientElement(-self.val, self.ring)
def __eq__(self, other: 'QuotientElement') -> bool:
try:
other = self.ring(other)
return self.val == other.val and self.ring == other.ring
except CoercionException:
return False
def __hash__(self) -> bool:
return hash((self.val, self.ring))
def is_invertible(self) -> bool:
"""
Determines if the element is invertible.
Returns:
bool: Whether the element is invertible.
"""
return gcd(self.val, self.ring.quotient) == self.ring.ring.one
def sqrt(self) -> 'QuotientElement':
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
if self.ring.ring == ZZ and self.ring.is_field():
return self.ring(tonelli(int(self), int(self.ring.quotient)))
else:
return self.kth_root(2)
def is_square(self) -> bool:
ZZ = _integer_ring.ZZ
if self.ring.ring == ZZ:
return generalized_eulers_criterion(int(self), 2, int(self.ring.quotient)) != ResidueSymbol.DOES_NOT_EXIST
else:
return super().is_square()
def partial_inverse(self):
d, n, _ = xgcd(self.val, self.ring.quotient)
return n, d
class QuotientRing(Ring):
"""
Ring built from an underlying ring and quotient.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import *
>>> quot_ring = ZZ/ZZ(53)
>>> quot_ring(5) * ~quot_ring(4)
<QuotientElement: val=41, ring=ZZ/(ZZ(53))>
"""
def __init__(self, quotient: RingElement, ring: Ring):
"""
Parameters:
quotient (RingElement): Element from the underlying ring.
ring (Ring): Underlying ring.
"""
assert(quotient.ring == ring)
super().__init__()
self.ring = ring
self.quotient = quotient
self.zero = QuotientElement(self.ring.zero, self)
self.one = QuotientElement(self.ring.one, self)
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['ring', 'quotient']
def characteristic(self) -> int:
IntegerElement = _integer_ring.IntegerElement
Polynomial = _poly.Polynomial
quotient = self.quotient.get_ground()
if type(quotient) is IntegerElement:
return int(quotient)
elif type(quotient) is Polynomial:
return quotient.ring.ring.characteristic()
else:
raise NotImplementedError
@property
def p(self) -> int:
IntegerElement = _integer_ring.IntegerElement
if type(self.quotient) is IntegerElement:
return int(self.quotient)
def order(self) -> int:
IntegerElement = _integer_ring.IntegerElement
Polynomial = _poly.Polynomial
quotient = self.quotient.get_ground()
type_o = type(quotient)
if type_o is IntegerElement:
return int(quotient)
elif type_o is Polynomial:
return quotient.ring.ring.order()**quotient.degree()
else:
raise NotImplementedError
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'{self.ring.shorthand()}/({self.quotient.shorthand()})'
def coerce(self, other: int) -> QuotientElement:
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (object): Object to coerce.
Returns:
QuotientElement: Coerced element.
"""
if hasattr(other, 'ring') and other.ring == self:
return other
else:
return QuotientElement(self.ring(other), self)
def element_at(self, x: int) -> QuotientElement:
"""
Returns the `x`-th element of the set.
Parameters:
x (int): Element ordinality.
Returns:
QuotientElement: The `x`-th element.
"""
return self(self.ring.element_at(x))
def __eq__(self, other: 'QuotientRing') -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other) and self.ring == other.ring and self.quotient == other.quotient
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash((self.ring, self.__class__, self.quotient))
def is_field(self) -> bool:
return self.quotient.is_irreducible()
def random(self, size: object=None) -> object:
"""
Generate a random element.
Parameters:
size (int/RingElement): The maximum ordinality/element (non-inclusive).
Returns:
RingElement: Random element of the algebra.
"""
if not size:
size = self.order()-1
if type(size) is int:
return self[random_int(size)]
else:
r = self[random_int(size.ordinality())]
while r >= size:
r = self[random_int(size.ordinality())]
return r
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/rings/quotient_ring.py
| 0.876925 | 0.386995 |
quotient_ring.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring
from samson.utilities.exceptions import CoercionException, NoSolutionException
from samson.math.matrix import Matrix
class MatrixRing(Ring):
"""
Ring of square matrices over a ring.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import *
>>> M = MatrixRing(ZZ, 3)
>>> M.one * 5
<Matrix: coeff_ring=ZZ, num_rows=3, num_cols=3,
0 1 2
0 [5, 0, 0]
1 [0, 5, 0]
2 [0, 0, 5]>
"""
def __init__(self, ring: Ring, size: int):
"""
Parameters:
ring (Ring): Underlying ring.
size (int): Size of matrices.
"""
self.ring = ring
self.size = size
self.order_cache = None
self.zero = Matrix.fill(self.ring.zero, self.size, coeff_ring=self.ring, ring=self)
self.one = Matrix.identity(self.size, coeff_ring=self.ring, ring=self)
def characteristic(self) -> int:
raise NotImplementedError()
def order(self) -> int:
raise NotImplementedError()
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['size', 'ring']
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'M_{self.size}({self.ring})'
def coerce(self, other: object) -> Matrix:
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (object): Object to coerce.
Returns:
Matrix: Coerced element.
"""
type_o = type(other)
if type_o is list:
elem = Matrix(other, coeff_ring=self.ring, ring=self)
elif type_o is Matrix:
elem = other
else:
raise CoercionException(self, other)
if not elem.is_square():
raise CoercionException(elem, "Elements must be square in a MatrixRing")
return elem
def __eq__(self, other: object) -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other) and self.ring == other.ring and self.size == other.size
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash((self.ring, self.__class__, self.size))
def random(self, size: object=None) -> 'RingElement':
"""
Generate a random element.
Parameters:
size (int/RingElement): The maximum ordinality/element (non-inclusive).
Returns:
RingElement: Random element of the algebra.
"""
return Matrix([[self.ring.random(size) for _ in range(self.size)] for _ in range(self.size)])
def dft(self, w: 'RingElement'=None, unitary: bool=False) -> 'Matrix':
if not w:
roots = self.ring.one.kth_root(self.size, return_all=True)
non_trivial = [r for r in roots if r != self.ring.one]
if not non_trivial:
raise NoSolutionException(f'{self.ring} does not have a non-trivial {self.size}-th root of unity')
w = non_trivial[0]
dft = Matrix([[w**(i*j) for j in range(self.size)] for i in range(self.size)])
if unitary:
dft /= self.ring(self.size).sqrt()
return dft
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/rings/matrix_ring.py
| 0.900836 | 0.419172 |
matrix_ring.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring, RingElement
from samson.utilities.exceptions import CoercionException
from samson.math.general import random_int
from samson.math.map import Map
from types import FunctionType
_NEG_MAP = lambda e: -e
class Endomorphism(RingElement):
def __init__(self, val: int, ring: Ring, post_map: FunctionType=None):
"""
Parameters:
val (int): Value of the element.
ring (Ring): Parent ring.
"""
self.val = val
self.post_map = post_map
super().__init__(ring)
def tinyhand(self) -> str:
return str(self.val)
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['val', 'ring']
def degree(self) -> int:
return self.val.degree()
def order(self) -> int:
"""
The minimum number of times the element can be added to itself before reaching the additive identity.
Returns:
int: Order.
"""
raise NotImplementedError
def __call__(self, element):
val = self.val(element)
if self.post_map:
val = self.post_map(val)
return val
def __elemadd__(self, other):
# Mathematically, these checks aren't needed. However, this gives us the possibility
# of not using a wrapper Map which would prevent negation and inversion.
if not self:
return -other
elif not other:
return self
elif self == -other or other == -self:
return self.ring.zero
else:
val = Map(self.ring.ring, self.ring.ring, lambda e: self(e) + other(e))
return Endomorphism(val, self.ring)
def __invert__(self):
return Endomorphism(~self.val, self.ring)
def __neg__(self) -> 'IntegerElement':
try:
return Endomorphism(-self.val, self.ring)
except TypeError:
return Endomorphism(self.val, self.ring, _NEG_MAP)
class EndomorphismRing(Ring):
def __init__(self, ring):
self.ring = ring
self.isomorphisms = ring.isomorphisms(ring)
self.zero = self(lambda e: ring.zero)
self.one = self( [phi for phi in self.isomorphisms if phi.is_identity()][0])
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['ring']
def characteristic(self) -> int:
return NotImplementedError
def order(self) -> int:
return NotImplementedError
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash((self.__class__, self.ring))
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'End({self.ring})'
def coerce(self, other: int) -> Endomorphism:
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (int): Object to coerce.
Returns:
Endomorphism: Coerced element.
"""
type_o = type(other)
if type_o is Endomorphism and other.ring == self:
return other
elif issubclass(type_o, Map):
return Endomorphism(other, self)
elif issubclass(type_o, FunctionType):
return Endomorphism(Map(self.ring, self.ring, other), self)
raise CoercionException(self, other)
def __eq__(self, other: 'IntegerRing') -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other) and self.ring == other.ring
def element_at(self, x: int) -> Endomorphism:
"""
Returns the `x`-th element of the set.
Parameters:
x (int): Element ordinality.
Returns:
Endomorphism: The `x`-th element.
"""
return Endomorphism(self.isomorphisms[x], self)
def random(self, size=None):
return self[random_int(len(self.isomorphisms))]
End = EndomorphismRing
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/rings/endomorphism_ring.py
| 0.852014 | 0.299765 |
endomorphism_ring.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring, RingElement
from samson.utilities.exceptions import CoercionException
from samson.auxiliary.lazy_loader import LazyLoader
from samson.math.general import mod_inv
from samson.math.symbols import oo
from samson.auxiliary.theme import PADIC_COEFF, PADIC_DEGREE, color_format
_integer_ring = LazyLoader('_integer_ring', globals(), 'samson.math.algebra.rings.integer_ring')
class PAdicIntegerElement(RingElement):
"""
Element of an `PAdicIntegerRing`.
"""
def __init__(self, val: int, ring: Ring):
"""
Parameters:
val (int): Value of the element.
ring (Ring): Parent ring.
"""
self.val = ([int(e) for e in val] + [0] * (ring.prec-len(val)))[:ring.prec]
super().__init__(ring)
def shorthand(self, idx_mod: int=0) -> str:
parts = []
p = str(self.ring.p)
for i, e in enumerate(self.val):
if e:
i += idx_mod
e = color_format(PADIC_COEFF, e)
if not i:
parts.append(str(e))
elif i == 1:
parts.append(f"{e}*{p}")
else:
parts.append(f"{e}*{p}^{color_format(PADIC_DEGREE, i)}")
vals = ' + '.join(parts)
if not vals:
vals = '0'
return vals + f' + O({self.ring.p}^{self.ring.prec})'
def tinyhand(self) -> str:
return self.shorthand()
def order(self) -> int:
"""
The minimum number of times the element can be added to itself before reaching the additive identity.
Returns:
int: Order.
"""
return oo
def ordinality(self) -> int:
"""
The ordinality of this element within the set.
Returns:
int: Ordinality.
"""
return int(self)
def __int__(self) -> int:
"""
The ordinality of this element within the set.
Returns:
int: Ordinality.
"""
return sum([e*self.ring.p**i for i, e in enumerate(self.val)])
def valuation(self) -> int:
for i, e in enumerate(self.val):
if e:
break
return i
def __getitem__(self, idx: int) -> object:
return self.val[idx]
def __elemadd__(self, other: 'PAdicIntegerElement') -> 'PAdicIntegerElement':
result = []
carry = 0
for a,b in zip(self.val, other.val):
c = a+b+carry
carry = c // self.ring.p
c %= self.ring.p
result.append(c)
return PAdicIntegerElement(result, self.ring)
def __elemmul__(self, other: 'PAdicIntegerElement') -> 'PAdicIntegerElement':
result = [0]*self.ring.prec*2
for i, a in enumerate(self.val):
carry = 0
for j, b in enumerate(other.val):
result[i+j] += a*b+carry
carry = result[i+j] // self.ring.p
result[i+j] %= self.ring.p
if carry:
result.append(carry)
return PAdicIntegerElement(result, self.ring)
def __abs__(self):
return self.valuation()
def __invert__(self) -> 'FractionFieldElement':
if not self:
raise ZeroDivisionError
return self.ring.one / self
def __lshift__(self, num: int):
if num < 0:
return self >> -num
else:
return PAdicIntegerElement(([0]*num + [e for e in self.val])[:self.ring.prec], self.ring)
def __rshift__(self, num: int):
if num < 0:
return self << -num
else:
return PAdicIntegerElement([e for e in self.val][num:] + [0]*num, self.ring)
def __elemtruediv__(self, other: 'PAdicIntegerElement'):
"""
References:
https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/250097/how-do-you-take-the-multiplicative-inverse-of-a-p-adic-number
"""
divisor = other
result = []
dividend = PAdicIntegerElement([e for e in self.val], self.ring)
if not dividend:
return dividend
a = divisor.val[0]
if not a:
raise ZeroDivisionError
i = 0
a_inv = mod_inv(a, self.ring.p)
while i < self.ring.prec:
b = dividend.val[i]
if a:
c = (b*a_inv) % self.ring.p
dividend -= (divisor << i) * c
else:
c = 0
result.append(c)
i += 1
return PAdicIntegerElement(result, self.ring)
def __elemdivmod__(self, other: 'PAdicIntegerElement') -> ('PAdicIntegerElement', 'PAdicIntegerElement'):
return self / other, self.ring.zero
def __elemmod__(self, other: 'PAdicIntegerElement') -> 'PAdicIntegerElement':
return self.ring.zero
def __elemfloordiv__(self, other: 'PAdicIntegerElement') -> 'PAdicIntegerElement':
return self / other
def __neg__(self) -> 'PAdicIntegerElement':
p = self.ring.p
carry, coeff_zero = divmod(p-self.val[0], p)
places = [coeff_zero]
for e in self.val[1:]:
carry, v = divmod(p-1-e+carry, p)
places.append(v)
return PAdicIntegerElement(places, self.ring)
def __eq__(self, other: 'PAdicIntegerElement') -> bool:
other = self.ring(other)
return self.val == other.val
def __hash__(self):
return hash((self.ring, tuple(self.val)))
class PAdicIntegerRing(Ring):
def __init__(self, p: int, prec: int=20):
super().__init__()
self.p = int(p)
self.prec = int(prec)
self.zero = self(0)
self.one = self(1)
def characteristic(self) -> int:
return 0
def order(self) -> int:
return oo
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash((self.__class__, self.p, self.prec))
def element_at(self, x: int) -> PAdicIntegerElement:
"""
Returns the `x`-th element of the set.
Parameters:
x (int): Element ordinality.
Returns:
PAdicIntegerElement: The `x`-th element.
"""
return self(x)
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['p', 'prec']
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'Zp_{self.p}'
def _decompose_integer(self, element: int) -> list:
base_coeffs = []
# Use != to handle negative numbers
while element != 0 and element != -1:
element, r = divmod(element, self.p)
base_coeffs.append(r)
return base_coeffs
def fraction_field(self) -> 'Ring':
"""
Returns:
FractionField: A fraction field of self.
"""
from samson.math.algebra.rings.padic_numbers import PAdicNumberField
return PAdicNumberField(self)
def coerce(self, other: int) -> PAdicIntegerElement:
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (int): Object to coerce.
Returns:
PAdicIntegerElement: Coerced element.
"""
if type(other) is PAdicIntegerElement:
return other
if other in _integer_ring.ZZ:
other = int(_integer_ring.ZZ(other))
if type(other) is int:
return PAdicIntegerElement(self._decompose_integer(other), self)
raise CoercionException(self, other)
def __eq__(self, other: 'PAdicIntegerRing') -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other) and self.p == other.p and self.prec == other.prec
def random(self, size: object=None) -> object:
"""
Generate a random element.
Parameters:
size (int/RingElement): The maximum ordinality/element (non-inclusive).
Returns:
RingElement: Random element of the algebra.
"""
from samson.math.general import random_int
if type(size) is int:
return self[random_int(size)]
else:
return self(random_int(self.p**self.prec))
Zp = PAdicIntegerRing
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/rings/padic_integers.py
| 0.76454 | 0.238462 |
padic_integers.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring, RingElement
from samson.utilities.exceptions import CoercionException
from samson.math.algebra.rings.polynomial_ring import PolynomialRing
from samson.math.polynomial import Polynomial
class CurvePolynomialElement(RingElement):
"""
Element of a `CurvePolynomialRing`.
"""
def __init__(self, x_poly: Polynomial, y_poly: Polynomial, ring: Ring):
"""
Parameters:
x_poly (Polynomial): Polynomial representing the x-coordinate.
y_poly (Polynomial): Polynomial representing the y-coordinate.
ring (Ring): Parent ring.
"""
self.x_poly = x_poly
self.y_poly = y_poly or ring.poly_ring.zero
super().__init__(ring)
def __repr__(self):
return f"<CurvePolynomialElement: x_poly={self.x_poly}, y_poly={self.y_poly}, ring={self.ring}>"
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'{self.ring.shorthand()}({self.x_poly.shorthand()}, {self.y_poly.shorthand()})'
def tinyhand(self) -> str:
return self.shorthand()
def __hash__(self):
return hash((self.x_poly, self.y_poly, self.ring))
def __add__(self, other: 'CurvePolynomialElement') -> 'CurvePolynomialElement':
other = self.ring.coerce(other)
return CurvePolynomialElement(self.x_poly + other.x_poly, self.y_poly + other.y_poly, self.ring)
def __sub__(self, other: 'CurvePolynomialElement') -> 'CurvePolynomialElement':
return CurvePolynomialElement(self.x_poly - other.x_poly, self.y_poly - other.y_poly, self.ring)
def __elemmul__(self, other: 'CurvePolynomialElement') -> 'CurvePolynomialElement':
nx = self.x_poly * other.x_poly
xy = self.x_poly * other.y_poly
yx = self.y_poly * other.x_poly
y = xy + yx
x = self.ring.poly_ring.symbol
if self.y_poly and other.y_poly:
nx += self.y_poly * other.y_poly * self.ring.poly_ring(x**3 + self.ring.a*x + self.ring.b)
return CurvePolynomialElement(nx, y, self.ring)
def __divmod__(self, other: 'CurvePolynomialElement') -> 'CurvePolynomialElement':
if not other:
raise ZeroDivisionError
if not self:
return self.ring.zero, self.ring.zero
if other.y_poly and (self.x_poly or other.x_poly):
raise NotImplementedError("Multivariate polynomial division not supported")
if other.x_poly:
qx, rx = divmod(self.x_poly, other.x_poly)
qy, ry = divmod(self.y_poly, other.x_poly)
else:
qx, rx = divmod(self.y_poly, other.y_poly)
qy, ry = self.ring.zero.x_poly, self.ring.zero.x_poly
return (CurvePolynomialElement(qx, qy, self.ring), CurvePolynomialElement(rx, ry, self.ring))
def __truediv__(self, other: 'CurvePolynomialElement') -> 'CurvePolynomialElement':
other = self.ring.coerce(other)
return self.__divmod__(other)[0]
__floordiv__ = __truediv__
def __mod__(self, other: 'CurvePolynomialElement') -> 'CurvePolynomialElement':
other = self.ring.coerce(other)
return self.__divmod__(other)[1]
def __neg__(self) -> 'CurvePolynomialElement':
return CurvePolynomialElement(-self.x_poly, -self.y_poly, self.ring)
def __eq__(self, other: 'CurvePolynomialElement') -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other) and self.x_poly == other.x_poly and self.y_poly == other.y_poly and self.ring == other.ring
def __bool__(self) -> bool:
return bool(self.x_poly) or bool(self.y_poly)
def __lt__(self, other: 'CurvePolynomialElement') -> bool:
return self.x_poly < other.x_poly
def __gt__(self, other: 'CurvePolynomialElement') -> bool:
return self.x_poly > other.x_poly
@property
def val(self):
return self.x_poly
class CurvePolynomialRing(Ring):
"""
Polynomial ring that represents an Elliptic curve.
"""
def __init__(self, poly_ring: PolynomialRing, a: int, b: int):
"""
Parameters:
poly_ring (PolynomialRing): Underlying polynomial ring.
a (int): `a` coefficient of the curve.
b (int): `b` constant of the curve.
"""
super().__init__()
self.poly_ring = poly_ring
self.a = a
self.b = b
self.zero = CurvePolynomialElement(Polynomial([self.poly_ring.ring(0)], self.poly_ring.ring), None, self)
self.one = CurvePolynomialElement(Polynomial([self.poly_ring.ring(1)], self.poly_ring.ring), None, self)
def characteristic(self) -> int:
return self.poly_ring.ring.characteristic()
def random(self, size: int=None) -> CurvePolynomialElement:
"""
Generate a random element.
Parameters:
size (int): The ring-specific 'size' of the element.
Returns:
CurvePolynomialElement: Random element of the algebra.
"""
return CurvePolynomialElement(self.poly_ring.random(size.x_poly), None, self)
def __repr__(self):
return f"<CurvePolynomialRing: poly_ring={self.poly_ring}>"
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'{self.poly_ring.shorthand()}[y]'
def __eq__(self, other: CurvePolynomialElement) -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other) and self.poly_ring == other.poly_ring and self.a == other.a and self.b == other.b
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash((self.poly_ring, self.__class__, self.a, self.b))
def coerce(self, other: object) -> CurvePolynomialElement:
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (object): Object to coerce.
Returns:
CurvePolynomialElement: Coerced element.
"""
if type(other) is CurvePolynomialElement:
return other
if type(other) is tuple:
x_poly = other[0]
y_poly = other[1] or self.poly_ring.zero
else:
x_poly = other
y_poly = self.poly_ring.zero
coerced = []
for poly in [x_poly, y_poly]:
if type(poly) is list:
coerced.append(Polynomial(poly, self.poly_ring.ring))
elif issubclass(type(poly), Polynomial):
coerced.append(poly)
elif type(poly) is int:
coerced.append(Polynomial([poly], self.poly_ring.ring))
else:
raise CoercionException(self, other)
return CurvePolynomialElement(*coerced, ring=self)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/rings/curve_polynomial_ring.py
| 0.901258 | 0.578805 |
curve_polynomial_ring.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring, RingElement
from samson.math.general import totient, index_calculus
from samson.math.symbols import oo
from samson.utilities.runtime import RUNTIME
class MultiplicativeGroupElement(RingElement):
"""
Element of a `MultiplicativeGroup`.
"""
def __init__(self, val: int, ring: Ring):
"""
Parameters:
val (int): Value of the element.
ring (Ring): Parent ring.
"""
self.val = val
super().__init__(ring)
def __elemadd__(self, other: 'MultiplicativeGroupElement') -> 'MultiplicativeGroupElement':
return MultiplicativeGroupElement(self.val * other.val, self.ring)
def __mul__(self, other: 'MultiplicativeGroupElement') -> 'MultiplicativeGroupElement':
other = int(other)
if self.ring.order() and self.ring.order() != oo:
other %= self.ring.order()
return MultiplicativeGroupElement(self.val ** other, self.ring)
def __neg__(self) -> 'MultiplicativeGroupElement':
return MultiplicativeGroupElement(~self.val, self.ring)
def __truediv__(self, other: 'MultiplicativeGroupElement') -> int:
if type(other) is int:
return self.val.kth_root(other)
else:
return self.val.log(other.val)
__floordiv__ = __truediv__
def ordinality(self) -> int:
return self.val.ordinality() - 1
def is_invertible(self) -> bool:
"""
Determines if the element is invertible.
Returns:
bool: Whether the element is invertible.
"""
return self.val.is_invertible()
def is_primitive_root(self) -> bool:
"""
Determines if the element is a primitive root.
Returns:
bool: Whether the element is a primitive root.
"""
return self.order() == self.ring.order()
def _plog(self, base: 'RingElement', order: int) -> int:
"""
Internal function for 'prime logarithm'. Called by Pohlig-Hellman
to allow rings to define their own subalgorithms.
"""
if order.bit_length() >= RUNTIME.index_calculus_supremacy:
from samson.math.algebra.rings.integer_ring import ZZ
if hasattr(self.ring.ring, 'quotient') and self.ring.ring.ring == ZZ:
return index_calculus(base, self, order=order)
return super()._plog(base, order)
class MultiplicativeGroup(Ring):
"""
The group of a ring under multiplication. This basically just 'promotes' multiplication to the addition operator.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import *
>>> a, b = 36, 9
>>> ring = ZZ/ZZ(53)
>>> mul_ring = ring.mul_group()
>>> g = mul_ring(2)
>>> (g*a)*(g*b) # Perform Diffie-Hellman
<MultiplicativeGroupElement: val=15, ring=ZZ/(ZZ(53))*>
"""
def __init__(self, ring: Ring):
"""
Parameters:
ring (Ring): Underlying ring.
"""
self.ring = ring
self.order_cache = None
self.zero = MultiplicativeGroupElement(self.ring.one, self)
self.one = self.zero
def characteristic(self) -> int:
return self.ring.characteristic()
def order(self) -> int:
if not self.order_cache:
from samson.math.algebra.rings.quotient_ring import QuotientRing
from samson.math.algebra.rings.integer_ring import IntegerElement
from samson.math.algebra.fields.finite_field import FiniteField
from samson.math.polynomial import Polynomial
if type(self.ring) is QuotientRing:
quotient = self.ring.quotient
if type(quotient) is IntegerElement:
self.order_cache = totient(int(quotient))
elif type(quotient) is Polynomial:
if quotient.is_prime():
self.order_cache = int(quotient) - 1
else:
self.order_cache = totient(int(quotient))
else:
raise NotImplementedError()
elif type(self.ring) is FiniteField:
self.order_cache = self.ring.order()-1
elif self.ring.order() == oo:
self.order_cache = oo
else:
raise NotImplementedError()
return self.order_cache
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['ring']
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'{self.ring}*'
def coerce(self, other: object) -> MultiplicativeGroupElement:
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (object): Object to coerce.
Returns:
MultiplicativeGroupElement: Coerced element.
"""
if type(other) is not MultiplicativeGroupElement or other.ring.ring != self.ring:
if not other:
raise ValueError("Zero is not part of the multiplicative group")
return MultiplicativeGroupElement(self.ring(other), self)
else:
return other
def element_at(self, x: int) -> MultiplicativeGroupElement:
"""
Returns the `x`-th element of the set.
Parameters:
x (int): Element ordinality.
Returns:
MultiplicativeGroupElement: The `x`-th element.
"""
return self(self.ring[x+1])
def __eq__(self, other: 'MultiplicativeGroup') -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other) and self.ring == other.ring
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash((self.ring, self.__class__))
def random(self, size: object=None) -> object:
r = None
while not r:
r = self.ring.random(size)
return self(r)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/rings/multiplicative_group.py
| 0.870529 | 0.231973 |
multiplicative_group.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring, RingElement
from samson.utilities.exceptions import CoercionException, NoSolutionException
from samson.math.general import is_prime, kth_root
from samson.math.factorization.general import factor
from samson.math.factorization.factors import Factors
from samson.math.symbols import oo
from functools import lru_cache
class IntegerElement(RingElement):
"""
Element of an `IntegerRing`.
"""
def __init__(self, val: int, ring: Ring):
"""
Parameters:
val (int): Value of the element.
ring (Ring): Parent ring.
"""
self.val = val
super().__init__(ring)
# Explicitly define for speed
def __elemadd__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return IntegerElement(self.val + other.val, self.ring)
def __elemmul__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return IntegerElement(self.val * other.val, self.ring)
def __elemmod__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return IntegerElement(self.val % other.val, self.ring)
def tinyhand(self) -> str:
return str(self.val)
def factor(self, **kwargs) -> dict:
return Factors({ZZ(k):v for k,v in factor(self.val, **kwargs).items()})
def is_prime(self) -> bool:
return is_prime(self.val)
def is_irreducible(self) -> bool:
return self.is_prime()
def kth_root(self, k: int, strict: bool=True) -> 'IntegerElement':
root = kth_root(int(self), k)
if strict and self != root**k:
raise NoSolutionException
return ZZ(root)
def is_square(self) -> bool:
return self.kth_root(2, strict=False)**2 == self
def valuation(self, p: int) -> int:
from samson.math.symbols import oo
if not self:
return oo
v = -1
r = 0
int_self = int(self)
while not r:
v += 1
int_self, r = divmod(int_self, p)
return v
def order(self) -> int:
"""
The minimum number of times the element can be added to itself before reaching the additive identity.
Returns:
int: Order.
"""
return oo
def ordinality(self) -> int:
"""
The ordinality of this element within the set.
Returns:
int: Ordinality.
"""
return self.val
def ground_mul(self, other: 'IntegerElement') -> 'IntegerElement':
try:
return IntegerElement(self.val * int(other), self.ring)
except Exception:
pass
def __neg__(self) -> 'IntegerElement':
return IntegerElement(-self.val, self.ring)
def __eq__(self, other: 'IntegerElement') -> bool:
if type(other) is IntegerElement:
other = other.val
return self.val == other
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return super().__hash__()
class IntegerRing(Ring):
"""
The ring of integers, Z.
"""
def __init__(self):
self.zero = IntegerElement(0, self)
self.one = IntegerElement(1, self)
def characteristic(self) -> int:
return 0
def order(self) -> int:
return oo
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash(self.__class__)
def element_at(self, x: int) -> IntegerElement:
"""
Returns the `x`-th element of the set.
Parameters:
x (int): Element ordinality.
Returns:
IntegerElement: The `x`-th element.
"""
return self(x)
def __reprdir__(self):
return []
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return 'ZZ'
def coerce(self, other: int) -> IntegerElement:
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (int): Object to coerce.
Returns:
IntegerElement: Coerced element.
"""
type_o = type(other)
if type_o is IntegerElement:
return other
elif type_o is int:
return IntegerElement(other, self)
elif other.ring == _get_QQ() and other.denominator == ZZ.one:
return other.numerator
try:
if other.ring(int(other)) == other:
return self.coerce(int(other))
except:
pass
raise CoercionException(self, other)
def __eq__(self, other: 'IntegerRing') -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other)
ZZ = IntegerRing()
@lru_cache(1)
def _get_QQ():
return ZZ.fraction_field()
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/rings/integer_ring.py
| 0.843992 | 0.298364 |
integer_ring.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring
from samson.math.algebra.rings.padic_integers import PAdicIntegerRing
from samson.math.algebra.fields.negative_degree_field import NegativeDegreeElement, NegativeDegreeField
from samson.auxiliary.lazy_loader import LazyLoader
_integer_ring = LazyLoader('_integer_ring', globals(), 'samson.math.algebra.rings.integer_ring')
class PAdicNumberElement(NegativeDegreeElement):
"""
Element of an `PAdicNumberField`.
"""
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return self.val.shorthand(-self.shift)
def tinyhand(self) -> str:
return self.shorthand()
def __int__(self) -> int:
"""
The ordinality of this element within the set.
Returns:
int: Ordinality.
"""
return sum([e*self.ring.p**(i-self.shift) for i, e in enumerate(self.val)])
class PAdicNumberField(NegativeDegreeField):
ELEMENT = PAdicNumberElement
def __init__(self, ring: Ring):
super().__init__(ring)
self.zero = self(0)
self.one = self(1)
def _precheck_val(self, other):
other = int(other)
decomp = self.ring._decompose_integer(other)
i = 0
for i, e in enumerate(decomp):
if e:
break
return other // self.ring.p**i, i
def element_at(self, x: int) -> PAdicNumberElement:
"""
Returns the `x`-th element of the set.
Parameters:
x (int): Element ordinality.
Returns:
PAdicNumberElement: The `x`-th element.
"""
return self(x)
def is_field(self):
return _integer_ring.ZZ(self.p).is_prime()
@property
def p(self):
return self.ring.p
@property
def prec(self):
return self.ring.prec
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['p', 'prec']
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'Qp_{self.ring.p}'
def Qp(p, prec):
return PAdicIntegerRing(p=p, prec=prec).fraction_field()
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/rings/padic_numbers.py
| 0.842831 | 0.353958 |
padic_numbers.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.general import fast_mul, square_and_mul, is_prime, pohlig_hellman, bsgs, pollards_rho_log, mod_inv, xlcm, gcd
from samson.math.factorization.general import factor
from samson.math.factorization.factors import Factors
from types import FunctionType
from samson.utilities.runtime import RUNTIME
from samson.auxiliary.lazy_loader import LazyLoader
from samson.utilities.exceptions import CoercionException, NotInvertibleException, NoSolutionException, SearchspaceExhaustedException
from samson.utilities.general import binary_search_unbounded, binary_search
from samson.core.base_object import BaseObject
_poly = LazyLoader('_poly', globals(), 'samson.math.polynomial')
_quot = LazyLoader('_quot', globals(), 'samson.math.algebra.rings.quotient_ring')
_frac = LazyLoader('_frac', globals(), 'samson.math.algebra.fields.fraction_field')
_symb = LazyLoader('_symb', globals(), 'samson.math.symbols')
def set_precendence_override(should_override):
def _wrapper(func):
func.has_precedence_override = should_override
return func
return _wrapper
class Ring(BaseObject):
def order_factors(self):
oo = _symb.oo
if not hasattr(self, '_order_factor_cache'):
self._order_factor_cache = None
if not self._order_factor_cache and self.order() != oo:
self._order_factor_cache = factor(self.order())
return self._order_factor_cache
def shorthand(self) -> str:
pass
def tinyhand(self) -> str:
return ""
def __str__(self):
return self.shorthand()
def structure_depth(self):
if hasattr(self, 'ring'):
return self.ring.structure_depth()+1
else:
return 1
def is_superstructure_of(self, R: 'Ring') -> bool:
"""
Determines whether `self` is a superstructure of `R`.
Parameters:
R (Ring): Possible substructure.
Returns:
bool: Whether `self` is a superstructure of `R`.
"""
if hasattr(self, 'coeff_ring'):
if self.coeff_ring == R:
return True
else:
return self.coeff_ring.is_superstructure_of(R)
elif hasattr(self, 'ring'):
if self.ring == R:
return True
else:
return self.ring.is_superstructure_of(R)
return False
def random(self, size: object) -> 'RingElement':
"""
Generate a random element.
Parameters:
size (int/RingElement): The maximum ordinality/element (non-inclusive).
Returns:
RingElement: Random element of the algebra.
"""
from samson.math.general import random_int
if type(size) is int:
return self[random_int(size)]
else:
return self[random_int(size.ordinality())]
def fraction_field(self) -> 'Ring':
"""
Returns:
FractionField: A fraction field of self.
"""
from samson.math.algebra.fields.fraction_field import FractionField
return FractionField(self)
def base_coerce(self, other: object) -> 'RingElement':
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (object): Object to coerce.
Returns:
RingElement: Coerced element.
"""
t_o = type(other)
if t_o is _quot.QuotientElement and other.ring.ring == self:
return other.val
elif t_o is _frac.FractionFieldElement and other.ring.ring == self:
scaled = other.numerator / other.denominator
if scaled.ring == other.ring:
raise CoercionException(self, other)
else:
return scaled
else:
return other
def mul_group(self) -> 'MultiplicativeGroup':
"""
Returns the `MultiplicativeGroup` of `self`.
"""
from samson.math.algebra.rings.multiplicative_group import MultiplicativeGroup
return MultiplicativeGroup(self)
def __call__(self, args, **kwargs) -> 'RingElement':
return self.coerce(self.base_coerce(args), **kwargs)
def __contains__(self, element: 'RingElement') -> bool:
try:
self.coerce(element)
return True
except CoercionException:
return False
def element_at(self, x: int) -> 'RingElement':
"""
Returns the `x`-th element of the set.
Parameters:
x (int): Element ordinality.
Returns:
RingElement: The `x`-th element.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
def order(self) -> int:
raise NotImplementedError()
def isomorphisms(self) -> list:
raise NotImplementedError()
def find_gen(self) -> 'RingElement':
"""
Finds a generator of the `Ring`.
Returns:
RingElement: A generator element.
"""
oo = _symb.oo
if self.order() == oo:
return self.one
return self.find_element_of_order(self.order())
def find_element_of_order(self, n: int=None, n_facs: 'Factors'=None, allow_order_call: bool=True) -> 'RingElement':
"""
Finds an element of order `n`.
Parameters:
n (int): Size of the subgroup.
n_facs (Factors): Factors of the size of the subgroup.
Returns:
RingElement: Element of order `n`.
"""
if allow_order_call:
if self.order() % n:
raise ValueError(f"Ring order is not divisible by {n}. No element exists with this order.")
max_order = None
while True:
elem = self.random()
o = elem.order()
if elem:
if o % n:
# Merge elements to find elements of successively higher order
if max_order:
merged = max_order.merge(elem)
if not merged.order() % n:
return merged * (merged.order() // n)
max_order = merged
else:
max_order = elem
else:
return elem * (o // n)
else:
if not n_facs:
n_facs = factor(n)
while True:
elem = self.random()
if not n*elem and elem.find_maximum_subgroup(n=n, n_facs=n_facs) == n:
elem.order_cache = n
return elem
def __truediv__(self, element: 'RingElement') -> 'QuotientRing':
if element.ring != self:
raise ValueError("'element' must be an element of the ring")
return _quot.QuotientRing(element, self)
def __getitem__(self, x: int) -> 'RingElement':
type_x = type(x)
if type_x.__name__ == 'Symbol' or type_x is tuple and type(x[0]).__name__ == 'Symbol':
from samson.math.algebra.rings.polynomial_ring import PolynomialRing
if type_x is tuple:
ring = self
for symbol in x:
ring = PolynomialRing(ring, symbol)
return ring
else:
return PolynomialRing(self, x)
elif type_x is list and type(x[0]).__name__ == 'Symbol':
from samson.math.algebra.rings.power_series_ring import PowerSeriesRing
return PowerSeriesRing(self, x[0])
else:
return self.element_at(x)
def is_field(self) -> bool:
oo = _symb.oo
return self.order() != oo and is_prime(self.order())
def frobenius_endomorphism(self) -> 'Map':
from samson.math.map import Map
p = self.characteristic()
if not is_prime(p):
raise ValueError(f'Characteristic of {self} not prime')
return Map(domain=self, codomain=self, map_func=lambda r: self(r)**p)
class RingElement(BaseObject):
def __init__(self, ring: Ring):
self.ring = ring
self.order_cache = None
def __reprdir__(self):
return list(self.__dict__.keys() - {'order_cache'})
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'{self.ring.shorthand()}({str(self.val)})'
def tinyhand(self) -> str:
return f'{self.val.tinyhand()}'
def __str__(self):
return RUNTIME.default_short_printer(self)
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash((self.ring, self.val))
def __elemadd__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return self.ring(self.val + other.val)
def __elemsub__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return self + -other
def __elemmul__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return self.ring(self.val * other.val)
def __elemmod__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return self.ring(self.val % other.val)
def __elemfloordiv__(self, other: 'QuotientElement') -> 'QuotientElement':
return self.ring(self.val // other.val)
def __elemdivmod__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> ('RingElement', 'RingElement'):
return self // other, self % other
def __elemtruediv__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return self * ~other
def __check_precendence_override(self, other, other_func):
try:
return getattr(other, other_func).has_precedence_override
except AttributeError:
return False
def __add__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
if hasattr(other, 'ring'):
if self.ring == other.ring:
return self.__elemadd__(other)
elif other.ring.is_superstructure_of(self.ring):
return other.ring(self) + other
return self.__elemadd__(self.ring.coerce(other))
def __radd__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return self.ring.coerce(other) + self
def __sub__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
if hasattr(other, 'ring') and other.ring.is_superstructure_of(self.ring):
return other.ring(self) - other
else:
return self.__elemsub__(self.ring.coerce(other))
def __rsub__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return self.ring.coerce(other) - self
def __mul__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
gmul = self.ground_mul(other)
if gmul is not None:
return gmul
if hasattr(other, 'ring'):
if self.ring == other.ring:
return self.__elemmul__(other)
elif other.ring.is_superstructure_of(self.ring):
return other.ring(self) * other
return self.__elemmul__(self.ring.coerce(other))
__pow__ = square_and_mul
def __rmul__(self, other: int) -> 'RingElement':
if type(other) is int:
return self * other
return self.ring.coerce(other) * self
def __mod__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
if hasattr(other, 'ring') and other.ring.is_superstructure_of(self.ring):
return other.ring(self) % other
elif self.__check_precendence_override(other, '__relemmod__'):
return other.__relemmod__(self)
else:
return self.__elemmod__(self.ring.coerce(other))
def __rmod__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return self.ring.coerce(other) % self
def __floordiv__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
if hasattr(other, 'ring') and other.ring.is_superstructure_of(self.ring):
return other.ring(self) // other
else:
return self.__elemfloordiv__(self.ring.coerce(other))
def __divmod__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> ('RingElement', 'RingElement'):
if hasattr(other, 'ring') and other.ring.is_superstructure_of(self.ring):
return divmod(other.ring(self), other)
elif self.__check_precendence_override(other, '__relemdivmod__'):
return other.__relemdivmod__(self)
else:
return self.__elemdivmod__(self.ring.coerce(other))
def __rdivmod__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return divmod(self.ring.coerce(other), self)
def __invert__(self) -> 'RingElement':
if self in [self.ring.one, -self.ring.one]:
return self
raise NotInvertibleException(f'{self} is not invertible', parameters={'a': self})
def __truediv__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
if not other:
raise ZeroDivisionError
# Is this just integer division?
gmul = self.ground_div(other)
if gmul is not None:
return gmul
# Try special cases
if self.ring and other in self.ring:
other = self.ring.coerce(other)
if other == self.ring.one:
return self
elif other == self:
return self.ring.one
# Either we have element division or we have to promote
try:
return self.__elemtruediv__(other)
except NotInvertibleException:
if RUNTIME.auto_promote:
elem = _frac.FractionField(self.ring)((self, other))
if elem.denominator == self.ring.one:
elem = elem.numerator
return elem
else:
raise
def __rtruediv__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return self.ring.coerce(other) / self
def __rfloordiv__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return self.ring.coerce(other) // self
def __bool__(self) -> bool:
return self != self.ring.zero
def __eq__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> bool:
other = self.ring.coerce(other)
return self.val == other.val and self.ring == other.ring
def __lt__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> bool:
other = self.ring.coerce(other)
if self.ring != other.ring:
raise ValueError("Cannot compare elements with different underlying rings.")
return self.val < other.val
def __le__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> bool:
return self < other or self == other
def __gt__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> bool:
other = self.ring.coerce(other)
if self.ring != other.ring:
raise ValueError("Cannot compare elements with different underlying rings.")
return self.val > other.val
def __ge__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> bool:
return self > other or self == other
def __int__(self) -> int:
return int(self.val)
def __abs__(self) -> 'RingElement':
return self if self >= self.ring.zero else -self
def ground_mul(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
"""
Tries "special" multiplications first.
Parameter:
other (RingElement): Other operand.
Returns:
RingElement/None: Returns the special __mul__ if possible.
"""
type_o = type(other)
if type_o is int:
return fast_mul(self, other)
def ground_div(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
"""
Tries "special" divisions first.
Parameter:
other (RingElement): Other operand.
Returns:
RingElement/None: Returns the special __div__ if possible.
"""
type_o = type(other)
if type_o is int and self.order() > 1:
oo = _symb.oo
if self.order() != oo:
other = mod_inv(other, self.order())
return fast_mul(self, other)
def is_invertible(self) -> bool:
"""
Determines if the element is invertible.
Returns:
bool: Whether the element is invertible.
"""
return False
def cache_op(self, start: 'RingElement', operation: FunctionType, size: int) -> 'BitVectorCache':
"""
Caches a repeated `operation` in a `BitVectorCache`.
Parameters:
start (RingElement): Starting value.
operation (func): Operation to cache.
size (int): Size of cache.
Returns:
BitVectorCache: Cached vector.
"""
from samson.math.bit_vector_cache import BitVectorCache
return BitVectorCache(self, start, operation, size)
def cache_mul(self, size: int) -> 'BitVectorCache':
"""
Caches scalar multiplication (i.e. repeated addition) in a `BitVectorCache`.
Parameters:
size (int): Size of cache.
Returns:
BitVectorCache: Cached vector.
"""
return self.cache_op(self.ring.zero, self.__class__.__add__, size)
def cache_pow(self, size: int) -> 'BitVectorCache':
"""
Caches exponentiation (i.e. repeated multiplication) in a `BitVectorCache`.
Parameters:
size (int): Size of cache.
Returns:
BitVectorCache: Cached vector.
"""
return self.cache_op(self.ring.one, self.__class__.__mul__, size)
def get_ground(self) -> 'RingElement':
"""
Gets the "ground" value (i.e. IntegerElement or Polynomial). Useful for traversing complex
algebras.
Returns:
RingElement: Ground element.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.algebra.all import FF
>>> F = FF(2, 8)
>>> R = F/F[11]
>>> R[5].get_ground()
<Polynomial: x^2 + 1, coeff_ring=ZZ/(ZZ(2))>
"""
from samson.math.algebra.rings.integer_ring import IntegerElement
from samson.math.algebra.rings.padic_integers import PAdicIntegerElement
if type(self) in [IntegerElement, _poly.Polynomial, _frac.FractionFieldElement, PAdicIntegerElement]:
return self
else:
return self.val.get_ground()
def order(self) -> int:
"""
The minimum number of times the element can be added to itself before reaching the additive identity.
Returns:
int: Order.
"""
if not self.order_cache:
oo = _symb.oo
if self.ring.order() == oo:
return oo
ro_facs = self.ring.order_factors()
self.order_cache = self.find_maximum_subgroup(n_facs=ro_facs)
return self.order_cache
def find_maximum_subgroup(self, n: int=None, n_facs: 'Factors'=None) -> int:
"""
Finds the maximum order of `self` in the subgroup of the size `n`.
Parameters:
n (int): Size of the subgroup.
n_facs (Factors): Factors of the size of the subgroup.
Returns:
int: Maximum order.
"""
if not n and not n_facs:
raise ValueError("Either 'n' or 'n_facs' must be provided")
if n_facs:
n = n_facs.recombine()
else:
n_facs = factor(n)
so_facs = Factors()
elem = self.cache_mul(n.bit_length())
for p in n_facs:
e = n_facs[p]
if e < 4:
for i in range(1,e+2):
o = n // p**i
if elem*o != self.ring.zero:
break
else:
i = binary_search(lambda i: not elem*(n // p**i), e+1)
so_facs[p] = e-(i-1)
return so_facs.recombine()
def is_irreducible(self) -> bool:
"""
Determines if the element is irreducible by trial by division.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not the element is irreducible.
"""
from samson.math.general import kth_root
sord = self.ordinality()
stop = kth_root(sord, 2)+1
stop = min(stop, sord)
for i in range(2, stop):
if not self % self.ring[i]:
return False
return True
def factor(self, attempts: int=1000) -> 'Factors':
"""
Factors the element.
Parameters:
attempts (int): Number of ECM attempts before failure.
Returns:
Factors: Dictionary-like Factors object.
"""
from samson.math.factorization.general import ecm
from samson.math.factorization.factors import Factors
from samson.analysis.general import count_items
factors = []
n = self
try:
while not n.is_irreducible():
q = ecm(n, attempts)
n /= q
q_facs = [[k for _ in range(v)] for k,v in q.factor().items()]
factors.extend([item for sublist in q_facs for item in sublist])
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
if n != self.ring.one:
factors.append(n)
return Factors(count_items(factors))
def kth_root(self, k: int, return_all: bool=False, **root_kwargs) -> 'RingElement':
"""
Computes the `k`-th root of `self`.
Parameters:
k (int): Root to take.
return_all (bool): Whether or not to return all roots or just one.
root_kwargs (kwargs): Kwargs to use with polynomial roots function.
Returns:
RingElement: Root(s).
"""
Symbol = _symb.Symbol
x = Symbol('x')
_ = self.ring[x]
if not return_all:
root_kwargs['user_stop_func'] = lambda S: any(f.degree() == 1 for f in S)
roots = (x**k - self).roots(**root_kwargs)
if not roots:
raise NoSolutionException()
if not return_all:
roots = roots[0]
return roots
def sqrt(self) -> 'RingElement':
return self.kth_root(2)
def is_square(self) -> bool:
try:
self.sqrt()
return True
except NoSolutionException:
return False
def gcd(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
a, b = self, other
while b:
a, b = b, a % b
return a
def _plog(self, base: 'RingElement', order: int) -> int:
"""
Internal function for 'prime logarithm'. Called by Pohlig-Hellman
to allow rings to define their own subalgorithms.
"""
# BSGS is deterministic and generally faster, but it takes sqrt space.
# This should cap memory usage at one million objects before moving to rho
if order.bit_length() <= 40:
return bsgs(base, self, end=order)
else:
return pollards_rho_log(base, self, order=order)
def log(self, base: 'RingElement') -> int:
"""
Computes the logarithm of `self` to `base`.
Parameters:
base (RingElement): Base.
Returns:
int: `x` such that `base`^`x` == `self`.
"""
oo = _symb.oo
mul = self.ring.mul_group()
h = mul(self)
g = mul(base)
if self.ring.order() == oo:
k = binary_search_unbounded(lambda guess: g*guess < h)
if g*k == h:
return k
else:
raise NotInvertibleException("Logarithm not found", parameters={'g': g, 'k': k, 'h': h})
else:
return pohlig_hellman(g, h)
def merge(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
"""
Constructs an element such that its order is the LCM of the orders of `self` and `other`.
Parameters:
other (RingElement): Second element.
Returns:
RingElement: Element with order lcm(`self`.order(), `other`.order()).
"""
n1 = self.order()
n2 = other.order()
if not n1 % n2:
return self
elif not n2 % n1:
return other
l, k1, k2 = xlcm(n1, n2)
g = (self*(n1 // k1)) + (other*(n2 // k2))
g.order_cache = l
assert not g*l
return g
def linear_relation(self, other: 'RingElement') -> (int, int):
"""
Finds a relation `n` and `m` such that `self`*`n` == `other`*`m`.
Parameters:
other (RingElement): Other element.
Returns:
(int, int): Formatted as (`n`, `m`).
"""
n1 = self.order()
n2 = other.order()
g = gcd(n1, n2)
if g == 1:
return 0, n2
n1 //= g
n2 //= g
P = self*n1
Q = other*n2
for h in factor(g).divisors():
try:
Q2 = Q*h
return n1 * (Q2/P), n2*h
except SearchspaceExhaustedException:
pass
raise NoSolutionException("No solution for linear relation (how did this happen?)")
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/rings/ring.py
| 0.881104 | 0.237686 |
ring.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import RingElement
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring
from samson.utilities.exceptions import CoercionException
from samson.math.polynomial import Polynomial
from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
from samson.math.general import random_int
class PolynomialRing(Ring):
"""
Ring of polynomials over a ring.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import *
>>> from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> poly_ring = (ZZ/ZZ(53))[x]
>>> poly_ring(x**3 + 4*x - 3)
<Polynomial: x^3 + (4)*x + 50, coeff_ring=ZZ/(ZZ(53))>
"""
def __init__(self, ring: Ring, symbol: Symbol=None, use_karatsuba: bool=False):
"""
Parameters:
ring (Ring): Underlying ring.
"""
super().__init__()
self.use_karatsuba = use_karatsuba
self.ring = ring
self.symbol = symbol or Symbol('x')
self.symbol.build(self)
symbol.top_ring = self
self.zero = Polynomial([self.ring.zero], coeff_ring=self.ring, ring=self, symbol=self.symbol)
self.one = Polynomial([self.ring.one], coeff_ring=self.ring, ring=self, symbol=self.symbol)
def characteristic(self):
return self.ring.characteristic()
def order(self) -> int:
from samson.math.symbols import oo
return oo
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['ring']
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'{self.ring.shorthand()}[{self.symbol}]'
def __eq__(self, other: 'PolynomialRing') -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other) and self.ring == other.ring
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash((self.ring, self.__class__))
def coerce(self, other: object) -> Polynomial:
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (object): Object to coerce.
Returns:
Polynomial: Coerced element.
"""
from samson.math.sparse_vector import SparseVector
type_o = type(other)
if type_o in [list, dict, SparseVector]:
return Polynomial(other, coeff_ring=self.ring, ring=self, symbol=self.symbol)
elif type_o is Polynomial:
if other.ring == self:
return other
# This check is in case we're using multivariate polynomials
elif other.ring == self.ring:
return self.coerce([other])
elif self.ring.is_superstructure_of(other.coeff_ring):
try:
coeff_coerced = other.change_ring(self.ring)
coeff_coerced.symbol = self.symbol
return coeff_coerced
except CoercionException:
pass
elif type_o is Symbol and other.var.ring == self:
return other.var
# Handle grounds
elif type_o is int or hasattr(other, 'ring') and other in self.ring:
return self.coerce([self.ring(other)])
raise CoercionException(self, other)
def element_at(self, x: int) -> Polynomial:
"""
Returns the `x`-th element of the set.
Parameters:
x (int): Element ordinality.
Returns:
Polynomial: The `x`-th element.
"""
base_coeffs = []
modulus = self.ring.order()
if modulus != 0:
# Use != to handle negative numbers
while x != 0 and x != -1:
x, r = divmod(x, modulus)
base_coeffs.append(self.ring[r])
return self(base_coeffs)
else:
return self([x])
def find_gen(self) -> 'Polynomial':
"""
Finds a generator of the `Ring`.
Returns:
RingElement: A generator element.
"""
return self.symbol
def find_irreducible_poly(self, n: int, sparsity: int=None, elem_size: RingElement=None) -> Polynomial:
"""
Finds a sparse, irreducible polynomial. Uses as many unit values as possible.
Parameters:
n (int): Degree.
sparsity (int): Number of non-zeroes to have.
elem_size (RingElement): Maximum size of randomly generated element.
Returns:
Polynomial: Irreducible polynomial
"""
logn = n.bit_length()
sparsity = sparsity or logn-2
x = self.symbol
p = x**n
degrees = list(range(1,n))
R = self.ring
one = R.one
max_attempts = n*logn
while True:
for _ in range(max_attempts):
degrees.sort(key=lambda i: random_int(n**2))
q = p
for d in degrees[:sparsity-1]:
q += one*x**d
q += R.random(elem_size)*x**degrees[sparsity-1]
q += one
if q.is_irreducible():
return q
sparsity += 1
def random(self, size: object) -> object:
"""
Generate a random element.
Parameters:
size (int/RingElement): The maximum ordinality/element (non-inclusive).
Returns:
RingElement: Random element of the algebra.
"""
if self.characteristic():
return super().random(size)
else:
deg = size.degree()
max_val = max(size.coeffs.values.values()) + self.ring.one
return self([self.ring.random(max_val) for _ in range(deg)])
def interpolate(self, points: list) -> Polynomial:
"""
Given a list of `points`, returns the polynomial that generates them (i.e. interpolation).
Parameters:
points (list): List of points formatted as [(x,y), ...].
Returns:
Polynomial: Interpolated polynomial.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.all import ZZ, Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> P = ZZ[x]
>>> q = 10*x**8 + 7*x**7 + 25*x**6 + 6*x**5 + 8*x**4 + 9*x**3 + 4*x**2 + 4*x + 3
>>> P.interpolate([(i, q(i)) for i in range(q.degree()+1)]) == q
True
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polynomial_interpolation#Constructing_the_interpolation_polynomial
"""
from samson.utilities.exceptions import NoSolutionException
from samson.math.algebra.fields.fraction_field import FractionField
from samson.math.matrix import Matrix
R = self.ring
not_field = not R.is_field()
# Gaussian elimination requires a field
if not_field:
R = FractionField(R)
points = [(R(x), R(y)) for x,y in points]
# Build the Vandermonde matrix
degree = len(points)
a = Matrix([[p[0] for p in points]], R).T
vand = a.apply_elementwise(lambda elem: elem**(degree-1))
for e in reversed(range(degree-1)):
vand = vand.row_join(a.apply_elementwise(lambda elem: elem**e))
# Calculate poly
y = Matrix([[p[1] for p in points]], R).T
result = list(vand.LUsolve(y).T[0])
if not_field:
if not all([c.denominator == self.ring.one for c in result]):
raise NoSolutionException(f"No solution in ring {self.ring}")
result = [c.numerator for c in result]
return self(result[::-1])
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/rings/polynomial_ring.py
| 0.931688 | 0.332825 |
polynomial_ring.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring, RingElement
from samson.utilities.exceptions import CoercionException, NotInvertibleException
from samson.math.general import newton_method_sizes
from samson.math.symbols import oo, Symbol
from samson.math.algebra.rings.polynomial_ring import PolynomialRing, Polynomial
from samson.utilities.runtime import RUNTIME
class PowerSeriesElement(RingElement):
"""
Element of an `PowerSeriesRing`.
"""
def __init__(self, val: Polynomial, ring: Ring):
"""
Parameters:
val (Polynomial): Value of the element.
ring (Ring): Parent ring.
"""
self.val = val[:ring.prec]
super().__init__(ring)
def __getattribute__(self, name):
try:
attr = object.__getattribute__(self, name)
except AttributeError:
attr = object.__getattribute__(self.val, name)
return attr
def __call__(self, val):
return self.val(val)
def derivative(self) -> 'PowerSeriesElement':
return self.ring(self.val.derivative())
def integral(self) -> 'PowerSeriesElement':
return self.ring(self.val.integral())
def degree(self) -> 'PowerSeriesElement':
return self.val.degree()
def tinyhand(self) -> str:
return str(self.val)
def valuation(self) -> int:
coeffs = list(self.val.coeffs.values.items())
if coeffs:
return coeffs[0][0]
else:
return 0
def order(self) -> int:
"""
The minimum number of times the element can be added to itself before reaching the additive identity.
Returns:
int: Order.
"""
return oo
def __iter__(self):
return self.val.__iter__()
def __getitem__(self, idx: int) -> object:
result = self.val[idx]
if type(result) is Polynomial:
return self.ring(result)
else:
return result
def __setitem__(self, idx: int, value: 'RingElement'):
self.val.coeffs[idx] = value
def __lshift__(self, num: int):
return PowerSeriesElement(self.val << num, self.ring)
def __rshift__(self, num: int):
return PowerSeriesElement(self.val >> num, self.ring)
def __invert__(self) -> 'PowerSeriesElement':
p = self.val
const = p[0]
if const:
P = p.ring
current = P(~const)
def mul_trunc(p, q, prec):
return ((p[:prec])*(q[:prec]))[:prec]
for next_prec in newton_method_sizes(self.ring.prec)[1:]:
z = mul_trunc(current, p, next_prec)
z = mul_trunc(current, z, next_prec)
current += current - z
return PowerSeriesElement(current, self.ring)
# Promote to Laurent series
elif RUNTIME.auto_promote:
return ~self.ring.fraction_field()(self)
else:
raise NotInvertibleException('Power series element not invertible when constant is zero', parameters={'p': p})
def __neg__(self) -> 'PowerSeriesElement':
return PowerSeriesElement(-self.val, self.ring)
def __eq__(self, other: 'PowerSeriesElement') -> bool:
if type(other) is PowerSeriesElement:
other = other.val
return self.val == other
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return super().__hash__()
class PowerSeriesRing(Ring):
def __init__(self, ring: Ring, symbol: Symbol=None, prec: int=20):
"""
Parameters:
ring (Ring): Underlying ring.
"""
super().__init__()
self._polyring = PolynomialRing(ring, symbol)
symbol.top_ring = self
self.symbol = symbol
self.ring = ring
self.prec = prec
self.zero = self(0)
self.one = self(1)
def characteristic(self) -> int:
return 0
def order(self) -> int:
return oo
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash((self._polyring, self.__class__, self.prec))
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['ring', 'prec']
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'{self.ring.shorthand()}[[{self.symbol}]]'
def fraction_field(self) -> 'Ring':
"""
Returns:
FractionField: A fraction field of self.
"""
from samson.math.algebra.fields.laurent_series import LaurentSeriesRing
return LaurentSeriesRing(self)
def coerce(self, other: int) -> PowerSeriesElement:
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (int): Object to coerce.
Returns:
PowerSeriesElement: Coerced element.
"""
if type(other) is PowerSeriesElement and other.ring == self:
return PowerSeriesElement(other.val, self)
else:
return PowerSeriesElement(self._polyring(other), self)
raise CoercionException(self, other)
def __eq__(self, other: 'PowerSeriesRing') -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other) and other._polyring == self._polyring and self.prec == self.prec
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/rings/power_series_ring.py
| 0.829008 | 0.336713 |
power_series_ring.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.fields.real_field import RealField, RealElement
from samson.utilities.exceptions import CoercionException
class ComplexElement(RealElement):
"""
Element of a `ComplexField`.
"""
def sqrt(self) -> 'ComplexElement':
return self.field(self.field.ctx.sqrt(self.val))
def kth_root(self, k: int, return_all: bool=False) -> 'ComplexElement':
C = self.field
base = self**(C(1)/C(k))
if return_all:
roots = [base]
roots.extend([base*C.e**(2*C.pi*1j*i / k) for i in range(1, k)])
return roots
else:
return base
def real(self):
return RealField(ctx=self.field.ctx)(self.val.real)
def imag(self):
return RealField(ctx=self.field.ctx)(self.val.imag)
class ComplexField(RealField):
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return 'CC'
def coerce(self, other: object) -> ComplexElement:
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (object): Object to coerce.
Returns:
ComplexElement: Coerced element.
"""
if hasattr(other, 'ring') and other.ring == self:
return other
else:
imag = 0
type_o = type(other)
if type_o in [tuple, list]:
other, imag = other
elif type_o == RealElement:
other = other.val
try:
return ComplexElement(self.ctx.mpc(other, imag), self)
except (ValueError, TypeError) as e:
raise CoercionException((other, imag)) from e
def random(self, size: object=None) -> ComplexElement:
"""
Generate a random element.
Parameters:
size (int/ComplexElement): The maximum ordinality/element (non-inclusive).
Returns:
ComplexElement: Random element of the algebra.
"""
return self(super().random(size) + super().random(size)*1j)
CC = ComplexField()
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/fields/complex_field.py
| 0.766905 | 0.284446 |
complex_field.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring, RingElement
from samson.utilities.exceptions import CoercionException
from samson.math.symbols import oo
import operator
class NegativeDegreeElement(RingElement):
"""
Element of an `NegativeDegreeField`.
"""
def __init__(self, val: RingElement, shift: int, ring: Ring):
"""
Parameters:
val (RingElement): Value of the element.
ring (Ring): Parent ring.
"""
self.val = val
self.shift = shift
super().__init__(ring)
def valuation(self) -> 'int':
return self.val.valuation()-self.shift
def truncate(self, precision: int) -> 'NegativeDegreeElement':
return self.ring.ELEMENT(self.val[:precision+self.shift], self.shift, self.ring)
def order(self) -> int:
"""
The minimum number of times the element can be added to itself before reaching the additive identity.
Returns:
int: Order.
"""
return oo
def __iter__(self):
return self.val.__iter__()
def __getitem__(self, idx: int) -> object:
idx_modded = idx+self.shift
if idx_modded >= 0:
return self.val[idx_modded]
else:
return self.val.val.coeff_ring.zero
def __setitem__(self, idx: int, value: 'RingElement'):
idx_modded = idx+self.shift
if idx_modded < 0:
self.val.val = self.val.val << -idx_modded
self.shift += -idx_modded
idx_modded = 0
self.val.val[idx_modded] = value
def __lshift__(self, num: int):
return self.ring.ELEMENT(self.val, self.shift-num, self.ring)
def __rshift__(self, num: int):
return self.ring.ELEMENT(self.val, self.shift+num, self.ring)
def __do_op(self, other, op):
other = self.ring.coerce(other)
s_val, o_val = self.val, other.val
s_shift, o_shift = self.shift, other.shift
# If they have a shift of the same sign, we can remove it before
# calculations for greater precision
rel_shift = 0
if (s_shift > 0) == (o_shift > 0):
rel_shift = min(abs(s_shift), abs(o_shift))
if s_shift < 0:
rel_shift = -rel_shift
s_shift -= rel_shift
o_shift -= rel_shift
# Prevent poly underflow
u_shift = max(max(s_shift - s_val.valuation(), o_shift - o_val.valuation()), 0)
s_val <<= u_shift
o_val <<= u_shift
# Align
s_val <<= -s_shift
o_val <<= -o_shift
# For mul, we need to undo the underflow shift twice
# since degrees add
if op == operator.mul:
u_shift *= 2
rel_shift *= 2
val = self.ring(op(s_val, o_val)) >> u_shift + rel_shift
return val
def __elemadd__(self, other: 'NegativeDegreeElement') -> 'NegativeDegreeElement':
return self.__do_op(other, operator.add)
def __elemsub__(self, other: 'NegativeDegreeElement') -> 'NegativeDegreeElement':
return self.__do_op(other, operator.sub)
def __invert__(self) -> 'NegativeDegreeElement':
return self.ring.ELEMENT(~self.val, -self.shift, self.ring)
def __elemmul__(self, other: 'NegativeDegreeElement') -> 'NegativeDegreeElement':
return self.__do_op(other, operator.mul)
def __neg__(self) -> 'NegativeDegreeElement':
return self.ring.ELEMENT(-self.val, self.shift, self.ring)
def __eq__(self, other: 'NegativeDegreeElement') -> bool:
if type(other) is self.ring.ELEMENT:
other = other.val >> other.shift
return self.val >> self.shift == other
def __hash__(self):
return hash((self.val, self.shift, self.ring))
class NegativeDegreeField(Ring):
ELEMENT = None
def __init__(self, ring: Ring):
"""
Parameters:
ring (Ring): Underlying ring.
"""
self.ring = ring
def characteristic(self) -> int:
return 0
def order(self) -> int:
return oo
def is_field(self) -> bool:
return self.ring.is_field()
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash((self.ring, self.__class__))
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['ring']
def coerce(self, other: int) -> NegativeDegreeElement:
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (int): Object to coerce.
Returns:
NegativeDegreeElement: Coerced element.
"""
if type(other) is self.ELEMENT and other.ring == self:
return self.ELEMENT(other.val, other.shift, self)
else:
other, val = self._precheck_val(other)
other = self.ring(other)
if val is None:
val = other.valuation()
return self.ELEMENT(other, -val, self)
raise CoercionException(self, other)
def __eq__(self, other: 'NegativeDegreeField') -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other) and other.ring == self.ring
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/fields/negative_degree_field.py
| 0.82308 | 0.24049 |
negative_degree_field.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.general import is_prime
from samson.math.algebra.fields.field import Field, FieldElement
from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
from samson.math.polynomial import Polynomial
class FiniteFieldElement(FieldElement):
"""
Element of a `FiniteField`.
"""
def __init__(self, val: Polynomial, field: Field):
"""
Parameters:
val (Polynomial): Value of the element.
field (FiniteField): Parent field.
"""
self.val = field.internal_field.coerce(val)
super().__init__(field)
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return self.field.shorthand() + f'({self.val.shorthand()})'
def __call__(self, arg):
return self.val(arg)
def __iter__(self):
return self.val.val.__iter__()
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return self.val.val[idx]
def ordinality(self) -> int:
"""
The ordinality of this element within the set.
Returns:
int: Ordinality.
"""
return int(self)
def __invert__(self) -> 'FiniteFieldElement':
return FiniteFieldElement(~self.val, self.field)
def __neg__(self) -> 'FiniteFieldElement':
return FiniteFieldElement(-self.val, self.field)
def __elemfloordiv__(self, other: 'FiniteFieldElement') -> 'FiniteFieldElement':
return self.__truediv__(other)
class FiniteField(Field):
"""
Finite field of GF(p**n) constructed using a `PolynomialRing`.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math import *
>>> from samson.math.symbols import Symbol
>>> x = Symbol('x')
>>> F = FiniteField(2, 8)
>>> assert F[5] / F[5] == F(1)
>>> F[x]/(x**7 + x**2 + 1)
<QuotientRing: ring=F_(2^8)[x], quotient=x^7 + x^2 + 1>
"""
def __init__(self, p: int, n: int=1, reducing_poly: Polynomial=None, symbol_repr: str='x'):
"""
Parameters:
p (int): Prime.
n (int): Exponent.
reducing_poly (Polynomial): Polynomial to reduce the `PolynomialRing`.
"""
from samson.math.algebra.rings.integer_ring import ZZ
assert is_prime(p)
self.p = p
self.n = n
self.internal_ring = ZZ/ZZ(p)
if reducing_poly:
assert reducing_poly.coeff_ring == self.internal_ring
x = reducing_poly.symbol
P = self.internal_ring[x]
else:
x = Symbol(symbol_repr)
P = self.internal_ring[x]
if n == 1:
reducing_poly = Polynomial([0, 1], self.internal_ring)
elif p == 2:
from samson.auxiliary.gf2_irreducible_poly_db import build_gf2_irreducible_poly
reducing_poly = build_gf2_irreducible_poly(P, n)
else:
reducing_poly = P.find_irreducible_poly(n)
self.reducing_poly = reducing_poly
self.internal_field = P/P(reducing_poly)
if n > 1:
self.internal_field.quotient.cache_div((n-1)*2)
self.symbol = x
self.symbol.top_ring = self
self.zero = self.coerce(0)
self.one = self.coerce(1)
super().__init__()
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['p', 'n', 'reducing_poly',]
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash((self.internal_field, self.reducing_poly, self.__class__))
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'F_({self.p}^{self.n})' if self.n > 1 else f'F_{self.p}'
def characteristic(self) -> int:
return self.p
def order(self) -> int:
return self.p**self.n
def is_superstructure_of(self, R: 'Ring') -> bool:
"""
Determines whether `self` is a superstructure of `R`.
Parameters:
R (Ring): Possible substructure.
Returns:
bool: Whether `self` is a superstructure of `R`.
"""
return self.internal_field.is_superstructure_of(R)
def coerce(self, other: object) -> FiniteFieldElement:
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (object): Object to coerce.
Returns:
FiniteFieldElement: Coerced element.
"""
if not type(other) is FiniteFieldElement:
other = FiniteFieldElement(self.internal_field(other), self)
return other
def element_at(self, x: int) -> FiniteFieldElement:
"""
Returns the `x`-th element of the set.
Parameters:
x (int): Element ordinality.
Returns:
FiniteFieldElement: The `x`-th element.
"""
return FiniteFieldElement(self.internal_field.element_at(x), self)
def random(self, size: FiniteFieldElement=None) -> FiniteFieldElement:
if size is not None:
size = size.val
return self(self.internal_field.random(size))
def __eq__(self, other: 'FiniteField') -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other) and self.p == other.p and self.n == other.n
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/fields/finite_field.py
| 0.885173 | 0.535524 |
finite_field.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.fields.field import Field, FieldElement
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring
from samson.math.algebra.rings.integer_ring import ZZ
from fractions import Fraction
class FractionFieldElement(FieldElement):
"""
Element of a `FractionField`.
"""
def __init__(self, numerator: FieldElement, denominator: FieldElement, field: Field):
"""
Parameters:
numerator (FieldElement): Numerator of the fraction.
denominator (FieldElement): Denominator of the fraction.
field (FractionField): Parent field.
"""
if field.simplify:
try:
# Simplification in non-integral domains
# Total ring of fractions
if hasattr(denominator, 'partial_inverse'):
n, d = denominator.partial_inverse()
numerator *= n
denominator = d
d = numerator.gcd(denominator)
numerator //= d
denominator //= d
except Exception:
pass
if denominator == field.ring.zero:
raise ZeroDivisionError
self.numerator = numerator
self.denominator = denominator
super().__init__(field)
if self.ring.precision:
self.trim_to_precision()
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'{self.field.shorthand()}({self.numerator}/{self.denominator})'
def tinyhand(self) -> str:
return f'{self.numerator.tinyhand()}{"/" + str(self.denominator.tinyhand()) if self.denominator != self.ring.ring.one else ""}'
def __hash__(self):
return hash((self.numerator, self.denominator, self.field))
def __eq__(self, other: 'FractionFieldElement'):
other = self.ring.coerce(other)
return type(self) == type(other) and self.numerator * other.denominator == self.denominator * other.numerator
def __call__(self, x: int) -> 'RingElement':
return self.numerator(x) / self.denominator(x)
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['numerator', 'denominator', 'field']
def valuation(self, p: int) -> int:
from samson.math.symbols import oo
if not self:
return oo
return self.numerator.valuation(p) - self.denominator.valuation(p)
def sqrt(self) -> 'FractionFieldElement':
return FractionFieldElement(self.numerator.sqrt(), self.denominator.sqrt(), self.ring)
def trim_to_precision(self) -> 'FractionFieldElement':
"""
WARNING: Side effect based.
Attempts to trim `self` so that the error is less than `precision`.
"""
precision = self.ring.precision
precision_type = self.ring.precision_type
if precision_type == 'relative':
if self.numerator != self.denominator and self.ring.ring.one not in [self.numerator, self.denominator]:
if self.numerator > self.denominator:
q,r = divmod(self.numerator, self.denominator)
den = self.ring.ring.one
num = q
compare_num = r
compare_den = abs(q)
elif self.numerator < self.denominator:
q,r = divmod(self.denominator, self.numerator)
num = self.ring.ring.one
den = q
compare_num = r
compare_den = self.denominator
if compare_num * precision.denominator < precision.numerator * compare_den:
self.numerator = num
self.denominator = den
else:
if self.denominator > precision:
q,r = divmod(self.numerator, self.denominator)
c = self.ring(r / self.denominator * precision)
self.numerator = q * precision + c.numerator // c.denominator
self.denominator = precision
def gcd(self, other):
from samson.math.general import lcm
return self.ring((self.numerator.gcd(other.numerator), lcm(self.denominator, other.denominator)))
def __elemadd__(self, other: 'FractionFieldElement') -> 'FractionFieldElement':
return FractionFieldElement(self.numerator * other.denominator + self.denominator * other.numerator, self.denominator * other.denominator, self.ring)
def __elemmul__(self, other: 'FractionFieldElement') -> 'FractionFieldElement':
return FractionFieldElement(self.numerator * other.numerator, self.denominator * other.denominator, self.ring)
def __floordiv__(self, other: 'FractionFieldElement') -> 'FractionFieldElement':
return self.__truediv__(other)
def __neg__(self) -> 'FractionFieldElement':
return FractionFieldElement(-self.numerator, self.denominator, self.ring)
def __invert__(self) -> 'FractionFieldElement':
if not self:
raise ZeroDivisionError
return FractionFieldElement(self.denominator, self.numerator, self.ring)
def __float__(self):
return int(self.numerator) / int(self.denominator)
def __int__(self):
return int(self.numerator) // int(self.denominator)
def __round__(self):
q,r = divmod(self.numerator, self.denominator)
R = self.ring.ring
return q + (R.one if r*2 >= self.denominator else R.zero)
def __lt__(self, other: 'FractionFieldElement') -> bool:
other = self.ring.coerce(other)
if self.ring != other.ring:
raise ValueError("Cannot compare elements with different underlying rings.")
return self.numerator * other.denominator < other.numerator * self.denominator
def __gt__(self, other: 'FractionFieldElement') -> bool:
other = self.ring.coerce(other)
if self.ring != other.ring:
raise ValueError("Cannot compare elements with different underlying rings.")
return self.numerator * other.denominator > other.numerator * self.denominator
class FractionField(Field):
"""
Fraction field over a ring.
Examples:
>>> from samson.math.algebra.rings.integer_ring import IntegerRing
>>> QQ = FractionField(IntegerRing())
>>> assert QQ(5) * QQ((1, 5)) == QQ.one
"""
def __init__(self, ring: Ring, simplify: bool=True):
"""
Parameters:
ring (Ring): Underlying ring.
simplify (bool): Whether or not to simplify the fraction.
"""
super().__init__()
self.ring = ring
self.simplify = simplify
self.precision = None
self.precision_type = None
self.zero = FractionFieldElement(self.ring.zero, self.ring.one, self)
self.one = FractionFieldElement(self.ring.one, self.ring.one, self)
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['ring']
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash((self.ring, self.__class__))
def __eq__(self, other: 'FractionField'):
return type(self) == type(other) and self.ring == other.ring
def characteristic(self):
return self.ring.characteristic()
def order(self) -> int:
return self.ring.order()**2
def set_precision(self, precision: FractionFieldElement, precision_type: str='absolute'):
"""
Sets the element used for determine whether a trim is acceptable.
"""
self.precision = precision
self.precision_type = precision_type
def random(self, size: int=None) -> FractionFieldElement:
"""
Generate a random element.
Parameters:
size (int): The ring-specific 'size' of the element.
Returns:
FractionFieldElement: Random element of the algebra.
"""
if type(size) is int:
numerator = size
denominator = size
elif size and size in self:
size = self(size)
numerator = size.numerator
denominator = size.denominator
else:
numerator = self.ring.random(size)
denominator = self.ring.random(size)
return FractionFieldElement(self.ring.random(numerator), max(self.ring.one, self.ring.random(denominator)), self)
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'Frac({self.ring})'
def coerce(self, other: object) -> FractionFieldElement:
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (object): Object to coerce.
Returns:
FractionFieldElement: Coerced element.
"""
type_other = type(other)
if type_other is FractionFieldElement:
return other
elif type_other is float and self.ring == ZZ:
frac = Fraction(other)
result = (self.ring.coerce(frac.numerator), self.ring.coerce(frac.denominator))
elif type_other is tuple:
if len(other) < 2:
denom = self.ring.one
else:
denom = self.ring.coerce(other[1])
result = (self.ring.coerce(other[0]), denom)
else:
result = (self.ring.coerce(other), self.ring.one)
return FractionFieldElement(*result, self)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/fields/fraction_field.py
| 0.856182 | 0.241752 |
fraction_field.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.fields.field import Field, FieldElement
from samson.utilities.exceptions import CoercionException, NoSolutionException
from samson.utilities.runtime import RUNTIME
import mpmath
import math
class RealElement(FieldElement):
"""
Element of a `RealField`.
"""
def __init__(self, val: FieldElement, field: Field):
"""
Parameters:
val (MPF): Value of the element.
field (Field): Parent field.
"""
self.val = val
super().__init__(field)
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return str(self.val)
def tinyhand(self) -> str:
return self.shorthand()
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash((self.val, self.field))
def __pow__(self, other: 'RealElement') -> 'RealElement':
return self.field(self.val**self.field(other).val)
def __abs__(self):
return self.field(abs(self.val))
def __round__(self):
a = abs(self)
n = int(a) + ((a - int(a)) > 0.5)
if self < 0:
n = -n
return n
def __invert__(self) -> 'RealElement':
return self**-1
def __neg__(self) -> 'RealElement':
return self.field(-self.val)
def __eq__(self, other: 'RealElement') -> bool:
if type(other) is int:
return self.val == other
return type(self) == type(other) and self.val == other.val and self.field == other.field
def __elemtruediv__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'RingElement':
return self.field(self.val / other.val)
def is_invertible(self) -> bool:
"""
Determines if the element is invertible.
Returns:
bool: Whether the element is invertible.
"""
return True
def sqrt(self) -> 'RealElement':
return self.field(self.field.ctx.sqrt(self.val))
def kth_root(self, k: int, return_all: bool=False) -> 'RealElement':
if self < 0 and not k % 2:
raise NoSolutionException(f'No even roots for negative number')
base = self**(self.field(1)/self.field(k))
if return_all:
if k % 2:
return [base]
else:
return [base, -base]
else:
return base
def get_ground(self) -> 'RealElement':
return self
def log(self, other: 'RealElement'=None) -> 'RealElement':
if other is None:
other = self.field.e
else:
other = self.field(other)
return self.field(self.field.ctx.log(self.val, other.val))
def exp(self) -> 'RealElement':
return self.field(self.field.ctx.exp(self.val))
def ceil(self) -> 'RealElement':
return self.field(self.field.ctx.ceil(self.val))
def floor(self) -> 'RealElement':
return self.field(self.field.ctx.floor(self.val))
def li(self, offset: bool=False):
return self.field(self.field.ctx.li(self.val, offset=offset))
def sin(self):
return self.field(self.field.ctx.sin(self.val))
def cos(self):
return self.field(self.field.ctx.sin(self.val))
def is_effectively_zero(self) -> bool:
return abs(self) < self.field(1)/2**self.field.prec
class RealField(Field):
def __init__(self, prec: int=53, ctx: object=None):
"""
Parameters:
prec (int): Desired precision in bits.
"""
self.prec = prec
if ctx:
self.ctx = ctx
else:
self.ctx = mpmath.ctx_mp.MPContext()
self.ctx.dps = math.ceil(prec/math.log(10, 2))
self.zero = self(0)
self.one = self(1)
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['prec']
def __getstate__(self):
return {'prec': self.prec}
def __setstate__(self, state):
R = self.__class__(state['prec'])
self.prec = R.prec
self.ctx = R.ctx
self.one = R.one
self.zero = R.zero
@property
def e(self):
return self(self.ctx.e)
@property
def pi(self):
return self(self.ctx.pi)
@property
@RUNTIME.global_cache()
def mills_constant(self):
_mills_constant = RealField(23000)('1.30637788386308069046861449260260571291678458515671364436805375996643405376682659882150140370119739570729696093810308688223886144781635348688713392214619435345787110033188140509357535583193264801721383236152235906221860161085667905721519797609516199295279707992563172152784123713076584911245631751842633105652153513186684155079079372385923352208421842040532051768902602579344300869529063620569896872621227499787666438515766191438772844982077590564825560915004123788524793626088046688154064374425340131073611440941376503643793012676721171310302652283866154666880487476095144107907540698417260347310774677574064007810935083421437442654204085311165490420993090855747058348793757769523336364858305492927387281493416741250273266926840468154062676311322374882380011804120628601384191443885715160918938894478991212554338474935909274442208280226020332302710637502228813106477844481700372333640604211874260838332822176968781235304962300880267221110401606508880971834777831402249082184410637749400023282419270071233303228854128584088916313729295257781669730936517951304701393525757057288415991731506781288275420005462290126288405806701552761743270631625705587885293887371663631869096785158480771725887503591755610651534304682508915720529218979451918656896107079679454091800398939472486242136261078017853543289004499330170496366824138991559390863407971519521054913832178750248935369436911007271030372613750972234285323116168628543944188065497790739237618709141899171623410941638308575746659514814198482696364651230580936617898571875292558924261792245960356189889945433295534390881876592175906931349704982012002981508269262773957866658038145591108464886110468516407348185577243382357535106352307875344503736037838146195058744437695954021414795859146776591545494401109935654810772503967175528395344823084606557828681289689384614534165259471045306184655570366212320938191176810381233247253675736561304035755604547613371766377266971117183495978029379922544269328238014462785471209936042634321006067930688472340905417664961257818765871227138054411028447678272208307254218662463667140139208332516803107194312353439003733543362667688155625905758738529747773437738355179799412075295861926866856592393937944044411992374104665470412500729650562289210559394937378671958351698375401681664617904333164804654514551239786534043776844797858223960962567035174406052308516273142917789552042936119712189359417511822684797317199476896968574646542612093168137035545490473027842694285052774299830119108405852525490656936684918052060227862098426188943223273332962887985907514802843644810209721222062851531779152653379240571303754370370597347393652365911795290648972635555555224555386169027564729760620345978644195955284059662204269287015568072312327295604919727555511738117439498041178256210035809874869434916176191141295706845838552772863501841984663375127036529444439179207888054631776156250565779654136866796619380331130009197428721105633447629347130496591577215749135475277505222815477233978270120671561346966752804453952883111137252330053792614609357410427386312480186390768802945076995238398448614294191476796552668964049478665682961301301675438607090068292961653932904642971344179205976063902545223569955003052071195850888436123956828060826314788600212196350968420489139757361620582728000288149999846265315837340424306574514618190921607090999464130039578123880026534637749856602130498930866063860167711749535913793996985724202986141711750841749694602075413197419292673832233696943664475949535945764182503918416484065268129703655243164913157058869201706784764989192050345243177710382510270046152790744153335903760320635695814488343970457480747191673054881037020380739733012545080675386237181104881879417763684067705038190250759583527842546026758842178602262942258759036032893300473708351234243128370227522368019421280442334584092147812591553937623750349951252025035397409518550011784546409823614149011014385509097799760452725081702835606574395318910638350859635260229513451047445893832691237099494674629049061649152292459467031981572295275443336694369737587692027052974932948599484445311120001696102905319193242316698089865355152116152430880177196690349426332587516531945322075760326737735089096342377091494723463304853281714913663742781658034409201436443637441425875156889725905759765243559037733958553668812781413607074557559745834337002061889944349605480724879707723775757783637685477797660031287452066904181225452259669049728881890255242074528078789766062705701297442423605191625086793633902581662142837419236183835596389839562197072238370164172413015372794142720478835725712249198103805635092717683265524633642503935487435366214009638438506704846748273329440551876473106106359333538969800878455288880882758955653651575416672738952846733500282052735787205957746478395697144783863673824663593558975269844694518267167887273635864934818399661995116922325237131908258989790684856792379756950628129464604481007713651156385156554987043852085173926022404236851875777187118321674352074710183785603902974024102002135940276130313048350829959688693148574443720877611259682918744937065216856433203886927099820446716376366319501957660099023666608818680048958673949179266323712967806856317043428414258146940444748789412507270680282648847479528961522016841739598697004591313783325749705331757896415245432580622105659806570889155827539380090382025127737821128790944743435769808022587563440899915149346308117570878428464027551937639808867153736985463306927473302989228160716868505806448158298982405886146598699032059023965893915565575840169191025711877427271513432029157486196601246695745900462760630594646774548114419602536600284415427826762959333445514857637940237005116623163674563171581825468449292558236197212588593812550247928587066681046691326526742894535620510883580276188405574854937376159074089242727557916553354542070006329370831815974640003811308093052888435355773535898559497944446328484883408971205935215498298829189876847064787638520769047247066645816369514711901005020144329876805116217157416057484395140423548295613811506044306623318085817279115834644789870485547517440088915221097258138917056727586684466400405569873054936863405913311968464665816382681217100998412847671425263323194049631673095457966054927109350885466276364069186561794310343022042375220382772217953256525551904146485053285357535237996706188326965690379894418952087818808745146620799001529955625302605418936611702679188260831989450025708813052528968949777641124868829276075588145077731317588025395755322566729331468845113607860822372293902580486707922641593180424819040420206821539261419442811920518128113821528108707138765152324308993856330857983714084031464267010755656427539174983268434634064456155803691866791479798061632243905779666598936016240402809963846427106357628850537662456090881943230011663758479632310329538234572312801137496440939882446584456055239393711146324194901740423381065700955532841429577270781677779128815119265114237841584078799598123992951398684353191107306')
if self.prec <= _mills_constant.ring.prec:
return self(_mills_constant)
else:
from samson.math.general import next_prime
nn = 1
p = 2
prev = 0
A = 1
# Check for precision overflow
while 'e' not in str(A-prev):
prev = A
A = self(p)**(self(1)/(3**nn))
nn += 1
p = next_prime(round(A**3**nn))
return A
def characteristic(self) -> int:
return 0
def order(self) -> int:
from samson.math.symbols import oo
return oo
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return 'RR'
def coerce(self, other: object) -> RealElement:
"""
Attempts to coerce other into an element of the algebra.
Parameters:
other (object): Object to coerce.
Returns:
RealElement: Coerced element.
"""
if hasattr(other, 'ring'):
if other.ring == self:
return other
elif type(other.ring) == RealField:
return self(other.val)
else:
try:
return RealElement(self.ctx.mpf(other), self)
except (ValueError, TypeError) as e:
raise CoercionException(other) from e
def element_at(self, x: int) -> RealElement:
"""
Returns the `x`-th element of the set.
Parameters:
x (int): Element ordinality.
Returns:
RealElement: The `x`-th element.
"""
return self(x)
def __eq__(self, other: 'RealField') -> bool:
return type(self) == type(other) and self.prec == other.prec
def __hash__(self) -> int:
return hash((self.prec, self.__class__))
def random(self, size: object=None) -> object:
"""
Generate a random element.
Parameters:
size (int/FieldElement): The maximum ordinality/element (non-inclusive).
Returns:
FieldElement: Random element of the algebra.
"""
return self(self.ctx.rand())
RR = RealField()
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/fields/real_field.py
| 0.756762 | 0.223441 |
real_field.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.rings.ring import Ring
from samson.math.algebra.rings.power_series_ring import PowerSeriesElement
from samson.math.algebra.rings.polynomial_ring import Polynomial
from samson.math.algebra.fields.negative_degree_field import NegativeDegreeElement, NegativeDegreeField
class LaurentSeriesElement(NegativeDegreeElement):
"""
Element of an `LaurentSeriesRing`.
"""
def __getattribute__(self, name):
try:
attr = object.__getattribute__(self, name)
except AttributeError:
attr = object.__getattribute__(self.val, name)
return attr
@property
def __raw__(self):
return self.tinyhand()
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['__raw__', 'val', 'shift', 'ring']
def __call__(self, val):
return self.val(val) / val**self.shift
def tinyhand(self) -> str:
return self.val.val.shorthand(tinyhand=True, idx_mod=-self.shift)
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return self.tinyhand()
def degree(self) -> 'int':
return self.val.degree()-self.shift
def derivative(self) -> 'LaurentSeriesElement':
val = self.ring.ring._polyring({idx:c*(idx-self.shift) for idx, c in self.val.val.coeffs.values.items()})
return LaurentSeriesElement(self.ring.ring(val), self.shift+1, self.ring)
def integral(self) -> 'LaurentSeriesElement':
val = self.ring.ring._polyring({idx:c/(idx-self.shift+1) for idx, c in self.val.val.coeffs.values.items()})
return LaurentSeriesElement(self.ring.ring(val), self.shift-1, self.ring)
def __getitem__(self, idx: int) -> object:
result = super().__getitem__(idx)
if type(result) is PowerSeriesElement:
return LaurentSeriesElement(result, self.shift, self.ring)
else:
return result
class LaurentSeriesRing(NegativeDegreeField):
ELEMENT = LaurentSeriesElement
def __init__(self, ring: Ring):
"""
Parameters:
ring (Ring): Underlying ring.
"""
super().__init__(ring)
self.zero = self(0)
self.one = self(1)
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['ring']
def shorthand(self) -> str:
return f'{self.ring.ring.shorthand()}(({self.ring.symbol}))'
def _precheck_val(self, other):
if type(other) is PowerSeriesElement:
val = other.valuation()
return other << -val, val
elif type(other) is Polynomial:
val = list(other.coeffs.values.keys())[0]
return other << -val, val
else:
return other, None
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/algebra/fields/laurent_series.py
| 0.730866 | 0.283639 |
laurent_series.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.utilities.general import add_or_increment
from samson.analysis.general import count_items
from samson.math.general import kth_root
from samson.core.base_object import BaseObject
from functools import reduce
from itertools import combinations, chain
from sortedcontainers import SortedDict
class Factors(BaseObject):
def __init__(self, factors=None):
self.factors = SortedDict(factors or {})
def __str__(self):
facs = list(self.factors.items())
if facs and type(facs[0][0]) is int:
fac_format = "{fac}"
else:
fac_format = "({fac})"
return ' * '.join([f"{fac_format.format(fac=fac)}{'**' + str(exponent) if exponent > 1 else ''}" for fac, exponent in facs])
def __getitem__(self, idx: int):
return self.factors[idx]
def __setitem__(self, idx: int, value):
self.factors[idx] = value
def __iter__(self):
return self.factors.__iter__()
def __getstate__(self):
return self.factors
def __setstate__(self, state):
self.factors = state
def __len__(self) -> int:
return len(self.factors)
def __hash__(self):
return hash(self.recombine())
def _compare(self, other, func):
t = type(other)
if t in [dict, SortedDict]:
other = Factors(other)
elif t is not Factors:
return func(self.recombine(), other)
return func(self.recombine(), other.recombine())
def __eq__(self, other):
return self._compare(other, lambda a, b: a == b)
def __lt__(self, other):
return self._compare(other, lambda a, b: a < b)
def __gt__(self, other):
return self._compare(other, lambda a, b: a > b)
def __ge__(self, other):
return self._compare(other, lambda a, b: a >= b)
def __le__(self, other):
return self._compare(other, lambda a, b: a <= b)
def __add__(self, other: dict) -> 'Factors':
new_facs = Factors()
for key in self:
new_facs.add(key, self[key])
for key in other:
new_facs.add(key, other[key])
return new_facs
def __truediv__(self, other: 'RingElement') -> 'Factors':
t = type(other)
if t is int:
from samson.math.factorization.general import trial_division
keys = list(self.keys())
if -1 in keys:
keys.remove(-1)
other = trial_division(other, prime_base=keys)
elif t not in [Factors, dict, SortedDict]:
other = other.factor()
return self.difference(other)
__mul__ = __add__
__floordiv__ = __truediv__
__sub__ = __truediv__
def __getattr__(self, name: str):
try:
attr = object.__getattribute__(self, name)
except AttributeError:
attr = getattr(self.factors, name)
return attr
def add(self, factor: 'RingElement', number: int=1):
add_or_increment(self.factors, factor, number)
def remove(self, factor: 'RingElement', number: int=1):
if number >= self.factors[factor]:
del self.factors[factor]
else:
self.factors[factor] -= number
def difference(self, other: dict) -> 'Factors':
facs = Factors({})
for key in self:
facs[key] = self[key]
if key in other:
facs.remove(key, other[key])
if not facs:
if key and hasattr(key, 'ring'):
facs[key.ring.one] = 1
else:
facs[1] = 1
return facs
def expand(self) -> list:
facs = [[fac]*exponent for fac, exponent in self.factors.items()]
return [item for sublist in facs for item in sublist]
def combinations(self, n: int) -> list:
return (Factors(count_items(c)) for c in combinations(self.expand(), n))
def number_of_factors(self) -> int:
return sum(self.factors.values())
def all_combinations(self) -> list:
return chain(*[self.combinations(i) for i in range(1, self.number_of_factors()+1)])
def all_divisors(self) -> set:
return {c.recombine() for c in self.all_combinations()}.union({1})
def square_free(self) -> 'Factors':
"""
Returns the square-free portion of the factors. Checks to make sure factors
aren't squares themselves.
"""
squares = Factors({p: e for p,e in self.items() if p > 0 and kth_root(p, 2)**2 == p})
sqrt = Factors({p: e // 2 for p,e in self.items()})
return self // sqrt.recombine()**2 // squares
divisors = all_divisors
def mobius(self) -> int:
n = self.recombine()
if (hasattr(n, 'ring') and n == n.ring.one) or n == 1:
return 1
elif max(self.factors.values()) > 1:
return 0
elif self.number_of_factors() % 2:
return -1
else:
return 1
def recombine(self) -> 'RingElement':
if not self.factors:
return 1
elem0 = list(self.factors.keys())[0]
mul = type(elem0).__mul__
one = elem0.ring.one if hasattr(elem0, 'ring') else 1
return reduce(mul, [p**e for p,e in self.factors.items()], one)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/math/factorization/factors.py
| 0.543348 | 0.169991 |
factors.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.curves.named import P256
from samson.math.algebra.curves.weierstrass_curve import WeierstrassPoint
from samson.math.general import random_int
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.core.primitives import KeyExchangeAlg, Primitive
from samson.core.metadata import SizeType, SizeSpec, FrequencyType
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
@register_primitive()
class ECDHE(KeyExchangeAlg):
"""
Elliptical curve Diffie-Hellman (Ephemeral).
"""
KEY_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.RANGE, sizes=[192, 224, 256, 384, 521])
USAGE_FREQUENCY = FrequencyType.PROLIFIC
def __init__(self, d: int=None, pub: WeierstrassPoint=None, G: WeierstrassPoint=P256.G):
"""
Parameters:
d (int): Secret key.
G (WeierstrassPoint): Generator point on an elliptical curve.
"""
Primitive.__init__(self)
self.d = d or random_int(G.ring.cardinality())
self.G = G
self.pub = pub
if not pub:
self.recompute_pub()
def recompute_pub(self) -> WeierstrassPoint:
"""
Gets the challenge.
Returns:
Point: The challenge.
"""
self.pub = self.d * self.G
def derive_point(self, challenge: WeierstrassPoint) -> WeierstrassPoint:
"""
Derives the shared key from the other instance's challenge.
Parameters:
challenge (WeierstrassPoint): The other instance's challenge.
Returns:
WeierstrassPoint: Shared key.
"""
return self.d * challenge
def derive_key(self, challenge: WeierstrassPoint) -> Bytes:
"""
Derives the shared key from the other instance's challenge.
Parameters:
challenge (WeierstrassPoint): The other instance's challenge.
Returns:
Bytes: Shared key.
"""
shared_key = self.d * challenge
if not shared_key:
raise ValueError('Cannot derive bytes from point at infinity')
return Bytes(int(shared_key.x) % self.G.curve.p).zfill((self.G.curve.p.bit_length() + 7) // 8)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/protocols/ecdhe.py
| 0.887674 | 0.22448 |
ecdhe.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.public_key.rsa import RSA
from samson.padding.pkcs1v15_padding import PKCS1v15Padding
from samson.encoding.general import bytes_to_der_sequence
from samson.encoding.asn1 import HASH_OID_LOOKUP, INVERSE_HASH_OID_LOOKUP
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from pyasn1.type.univ import Sequence, OctetString, Null
from pyasn1.codec.der import encoder
class PKCS1v15RSASigner(object):
"""
PKCS1v15 RSA Signing and Padding Scheme
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3447#section-8.2.1
"""
def __init__(self, rsa: RSA, hash_obj: object):
"""
Parameters:
rsa (RSA): RSA object.
hash_object (object): Object satisfying the hash interface.
"""
self.rsa = rsa
self.padder = PKCS1v15Padding(rsa.bits, block_type=1)
self.hash_obj = hash_obj
def sign(self, plaintext: bytes) -> Bytes:
"""
Signs the `plaintext`.
Parameters:
plaintext (bytes): Plaintext to sign.
Returns:
Bytes: Signature.
"""
alg_id = Sequence()
alg_id.setComponentByPosition(0, HASH_OID_LOOKUP[type(self.hash_obj)])
alg_id.setComponentByPosition(1, Null())
top_seq = Sequence()
top_seq.setComponentByPosition(0, alg_id)
top_seq.setComponentByPosition(1, OctetString(self.hash_obj.hash(plaintext)))
der_encoded = encoder.encode(top_seq)
return self.rsa.decrypt(self.padder.pad(der_encoded)).zfill((self.rsa.n.bit_length() + 7) // 8)
def verify(self, plaintext: bytes, signature: bytes, strict_type_match: bool=True) -> bool:
"""
Verifies the `plaintext` against the `signature`.
Parameters:
plaintext (bytes): Plaintext to verify.
signature (bytes): Signature to verify plaintext against.
strict_type_match (bool): Whether or not to force use of `hash_obj` vs using the OID provided in the signature.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not the signature passed verification.
"""
from samson.utilities.runtime import RUNTIME
try:
padded = Bytes(self.rsa.encrypt(signature))
der_encoded = self.padder.unpad(padded)
items = bytes_to_der_sequence(der_encoded)
hash_obj = self.hash_obj
if not strict_type_match:
hash_obj = INVERSE_HASH_OID_LOOKUP[items[0][0]]()
hashed_value = Bytes(items[1])
return RUNTIME.compare_bytes(hashed_value, hash_obj.hash(plaintext))
except Exception:
return False
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/protocols/pkcs1v15_rsa_signer.py
| 0.831246 | 0.153422 |
pkcs1v15_rsa_signer.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.hashes.md5 import MD5
from samson.core.base_object import BaseObject
class RADIUS(BaseObject):
"""
Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2865)
"""
def __init__(self, key: bytes):
"""
Parameters:
key (bytes): Encryption key.
"""
self.key = key
def encrypt(self, authenticator: bytes, password: bytes) -> Bytes:
"""
Encrypts the `password`.
Parameters:
authenticator (bytes): Client authenticator.
password (bytes): Password.
Returns:
Bytes: RADIUS-encrypted password.
"""
if len(password) > 128:
raise ValueError('Password exceeds maximum of 128 bytes')
password = Bytes.wrap(password).pad_congruent_right(16)
md5 = MD5()
result, last = Bytes(), authenticator
for chunk in password.chunk(16):
result += md5.hash(self.key + last) ^ chunk
last = result[-16:]
return result
def decrypt(self, authenticator: bytes, encrypted_password: bytes) -> Bytes:
"""
Decrypts the `encrypted_password`.
Parameters:
authenticator (bytes): Client authenticator.
encrypted_password (bytes): RADIUS-encrypted password.
Returns:
Bytes: Plaintext password.
"""
return Bytes(self.encrypt(authenticator, encrypted_password).rstrip(b'\x00'))
@staticmethod
def recover_key_hash(encrypted_password: bytes, password: bytes) -> Bytes:
"""
Performs a known-plaintext attack on RADIUS encryption giving the key hash.
Parameters:
encrypted_password (bytes): Password encrypted by RADIUS authentication.
password (bytes): Plaintext password.
Returns:
Bytes: RADIUS key hash as MD5(key + AUTHENTICATOR).
Examples:
>>> from samson.protocols.radius import RADIUS
>>> from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
>>> from samson.hashes.md5 import MD5
>>> rad = RADIUS(Bytes.random(32))
>>> c_salt = Bytes.random(16)
>>> my_pass = b'mypass'
>>> enc_pass = rad.encrypt(c_salt, my_pass)
>>> RADIUS.recover_key_hash(enc_pass, my_pass) == MD5().hash(rad.key + c_salt)
True
"""
return encrypted_password ^ Bytes(password).pad_congruent_right(16)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/protocols/radius.py
| 0.840029 | 0.194062 |
radius.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.protocols.diffie_hellman import DiffieHellman
from samson.math.general import mod_inv
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.core.base_object import BaseObject
class SocialistMillionare(BaseObject):
"""
Zero-Knowledge Proof of a secret using Diffie-Hellman exchanges.
"""
def __init__(self, h: int=2, p: int=DiffieHellman.MODP_1536, key: bytes=None, exp1: int=None, exp2: int=None, validate: bool=True):
"""
Parameters:
h (int): Generator.
p (int): Prime modulus.
key (bytes): Secret.
exp1 (int): First random exponent.
exp2 (int): Second random exponent.
validate (bool): Whether or not to validate challenges to prevent exploits.
"""
self.h = h
self.p = p
self.key = Bytes.wrap(key).int() or Bytes.random(16).int()
self.validate = validate
# We do this explicitly with None so users can easily set these values to zero :)
if exp1 is None:
exp1 = Bytes.random(16).int()
if exp2 is None:
exp2 = Bytes.random(16).int()
self.exp1 = exp1
self.exp2 = exp2
self.P_b = None
self.P = None
self.Q = None
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['key', 'h', 'p', 'exp1', 'exp2', 'validate']
def get_initial_challenge(self) -> (int, int):
"""
Creates the initial Diffie-Hellman challenges.
Returns:
(int, int): The Diffie-Hellman challenges of the random exponents.
"""
return pow(self.h, self.exp1, self.p), pow(self.h, self.exp2, self.p)
def receive_initial_challenge(self, challenge: (int, int), r: int=None) -> (int, int):
"""
Receives the Diffie-Hellman challenges and produces the next challenge parameters.
Parameters:
challenge ((int, int)): Challenge from peer.
r (int): Ephemeral random exponent.
Returns:
(int, int): P and Q values to send to its peer.
"""
h_a1, h_a2 = challenge
if self.validate:
assert h_a1 != 1
assert h_a2 != 1
r = r or Bytes.random(16).int()
g, R = pow(h_a1, self.exp1, self.p), pow(h_a2, self.exp2, self.p)
self.P = pow(R, r, self.p)
self.Q = (pow(self.h, r, self.p) * pow(g, self.key, self.p)) % self.p
return self.P, self.Q
def get_final_challenge(self, challenge: (int, int)) -> int:
"""
Uses its peer's P and Q values to generate the final challenge.
Parameters:
challenge ((int, int)): P and Q values of peer's challenge.
Returns:
int: The final challenge.
"""
self.P_b, Q_b = challenge
if self.validate:
assert self.P != self.P_b
assert self.Q != Q_b
return pow(Q_b * mod_inv(self.Q, self.p), self.exp2, self.p)
def assert_correct(self, c_b: int) -> bool:
"""
Processes the final challenge and asserts its correctness.
Parameters:
c_b (int): Peer's final challenge.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not the challenge was correct.
"""
c = pow(c_b, self.exp2, self.p)
return c == ((self.P * mod_inv(self.P_b, self.p)) % self.p)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/protocols/socialist_millionare.py
| 0.807802 | 0.353986 |
socialist_millionare.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.hashes.sha3 import SHAKE256
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
from samson.core.primitives import KeyExchangeAlg, Primitive
from samson.core.metadata import SizeType, SizeSpec, FrequencyType
from samson.protocols.sidh import SIDH, extract_prime_powers
from samson.math.algebra.curves.montgomery_curve import MontgomeryCurve
def G(m, e):
return SHAKE256(e).hash(m)
H = G
def encode_fp2(fp2):
p = fp2[0].ring.characteristic()
blen = (p.bit_length() + 7) // 8
return b''.join([Bytes(int(a), 'little').zfill(blen) for a in fp2][::-1])
def decode_fp2(fp2, fp2_bytes):
p = fp2.characteristic()
blen = (p.bit_length() + 7) // 8
chunks = [chunk.int() for chunk in Bytes.wrap(fp2_bytes, 'little').chunk(blen)]
i = fp2.symbol
return [fp2(a + b*i) for b,a in zip(chunks[::2], chunks[1::2])]
def F(j, n):
j_bytes = encode_fp2(j)
return SHAKE256(n).hash(j_bytes)
@register_primitive()
class SIKE(KeyExchangeAlg):
"""
Supersingular Isogeny Key Encapsulation.
"""
KEY_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.ARBITRARY, typical=[434, 503, 610, 751])
USAGE_FREQUENCY = FrequencyType.UNUSUAL
def __init__(self, curve: 'EllipticCurve', Pa: 'WeierstrassPoint', Qa: 'WeierstrassPoint', Ra: 'WeierstrassPoint', Pb: 'WeierstrassPoint', Qb: 'WeierstrassPoint', Rb: 'WeierstrassPoint', use_a: bool, n: int, m: int=None):
"""
Parameters:
curve (EllipticCurve): Starting curve.
Pa (WeierstrassPoint): `A`'s `P` point.
Qa (WeierstrassPoint): `A`'s `Q` point.
Pb (WeierstrassPoint): `B`'s `P` point.
Qb (WeierstrassPoint): `B`'s `Q` point.
use_a (bool): Whether to use `A` points or `B` points.
n (int): Bit strength.
m (int): `Q` coefficient.
"""
Primitive.__init__(self)
self.sidh_params = curve, Pa, Qa, Pb, Qb, use_a
self.n = n
self.sidh = SIDH(*self.sidh_params, n=1)
self.R = Ra if use_a else Rb
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['n', 'sidh']
def encrypt(self, key: int, message: bytes, public_key: tuple) -> (tuple, 'Bytes'):
sidh = SIDH(*self.sidh_params, n=1, m=key)
j_inv = sidh.derive_key(public_key)
return (sidh.iU, sidh.iV, sidh.phi(self.R)), message ^ F(j_inv, len(message)*8)
def decrypt(self, public_key, ciphertext: bytes):
return self.encrypt(self.sidh.m, ciphertext, public_key)[1]
def encapsulate(self, public_key_bytes: bytes):
m = Bytes.random(self.n // 8)
r = G(m + public_key_bytes, self.sidh.prime_power[1])
c0, c1 = self.encrypt(key=r.int(), message=m, public_key=self.reconstruct_curve(public_key_bytes))
K = H(m + (c0, c1), self.n)
return c0, c1, K
def decapsulate(self, c0, c1):
m = self.decrypt(c0, c1)
#r = G(m + self.pub, self.sidh.prime_power[1])
return H(m + (c0, c1), self.n)
def reconstruct_curve(self, public_key_bytes: bytes):
p, q, r = decode_fp2(self.sidh.curve.ring, public_key_bytes)
A = (1-p*q-p*r-q*r)**2/(4*p*q*r) - p - q - r
return MontgomeryCurve(A).to_weierstrass_form()
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/protocols/sike.py
| 0.747984 | 0.330228 |
sike.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.protocols.srp_client import SRPClient
from samson.hashes.sha2 import SHA256
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
class SRPServer(object):
"""
Secure Remote Password protocol server
"""
def __init__(self, g: int=2, N: int=SRPClient.MODP_1024, hash_obj: object=SHA256(), b: int=None):
"""
Parameters:
g (int): Generator.
N (int): Prime modulus.
hash_obj (object): Instantiated object with compatible hash interface
b (int): Random private value.
"""
self.g = g
self.N = N
self.hash_obj = hash_obj
self.accounts = {}
self.requests = {}
self.salt = Bytes.random(4)
self.b = b or Bytes.random(4).int() % N
self.k = hash_obj.hash(Bytes(N) + self.PAD(g)).int()
def PAD(self, in_bytes: bytes) -> Bytes:
"""
If a conversion is explicitly specified with the operator PAD(), the integer will first be implicitly converted, then the resultant byte-string will be left-padded with zeros (if necessary) until its length equals the implicitly-converted length of N.
"""
return Bytes.wrap(in_bytes).zfill((self.N.bit_length() + 7) // 8)
def create_account(self, identity: bytes, password: bytes):
"""
Creates a new account entry with the server.
Parameters:
identity (bytes): Username.
password (bytes): Password.
"""
x = self.hash_obj.hash(self.salt + self.hash_obj.hash(identity + b':' + password)).int()
v = pow(self.g, x, self.N)
self.accounts[identity] = v
def respond_with_challenge(self, identity: bytes, A: int) -> (bytes, int):
"""
Receives the client's challenge and returns the server's challenge.
Parameters:
identity (bytes): Username.
A (int): Client's challenge.
Returns:
(bytes, int): Formatted as (server salt, server's challenge `B`)
"""
v = self.accounts[identity]
B = (self.k * v + pow(self.g, self.b, self.N)) % self.N
self.requests[identity] = {'A': A, 'B': B}
return self.salt, B
def check_challenge(self, identity: bytes, client_hash: bytes) -> bool:
"""
Checks if the client's challenge is correct.
Parameters:
identity (bytes): Username.
client_hash (bytes): Client's hash challenge.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not the challenge is correct.
"""
request = self.requests[identity]
v = self.accounts[identity]
A = request['A']
uH = self.hash_obj.hash(self.PAD(A) + self.PAD(request['B'])).int()
p1 = (A * pow(v, uH, self.N))
sS = pow(p1, self.b, self.N)
sK = self.hash_obj.hash(Bytes(sS))
return self.hash_obj.hash(sK + self.salt) == client_hash
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/protocols/srp_server.py
| 0.844216 | 0.307293 |
srp_server.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.math.algebra.curves.montgomery_curve import MontgomeryCurve
from samson.math.algebra.curves.named import Curve25519
from samson.math.general import random_int_between
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.core.primitives import KeyExchangeAlg, Primitive
from samson.core.metadata import SizeType, SizeSpec, FrequencyType
from samson.ace.decorators import register_primitive
@register_primitive()
class DH25519(KeyExchangeAlg):
"""
Elliptical curve Diffie-Hellman using Montgomery curves.
"""
KEY_SIZE = SizeSpec(size_type=SizeType.ARBITRARY, typical=[255, 448])
USAGE_FREQUENCY = FrequencyType.OFTEN
def __init__(self, d: int=None, pub: int=None, base: int=None, curve: MontgomeryCurve=Curve25519):
"""
Parameters:
d (int): Secret key that will be clamped to the curve.
base (MontgomeryPoint): Base point.
curve (MontgomeryCurve): The curve used.
"""
Primitive.__init__(self)
self.d = Bytes.wrap(d or random_int_between(1, curve.ring.order())).int()
self.curve = curve
self.key = curve.clamp_to_curve(self.d)
self.base = base or curve.G
self.pub = pub
if not pub:
self.recompute_public()
def recompute_public(self) -> int:
"""
Gets the challenge.
Returns:
int: The integer challenge representing an `x` value on the curve.
"""
self.pub = self.key * self.base
def get_pub_bytes(self) -> Bytes:
return Bytes(int(self.pub.x), 'little')
def derive_key(self, challenge: int) -> Bytes:
"""
Derives the shared key from the other instance's challenge.
Parameters:
challenge (int): The other instance's challenge.
Returns:
int: Shared key.
"""
return Bytes(int((self.key * self.curve(challenge)).x)).zfill((self.curve.p.bit_length() + 7) // 8)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/protocols/dh25519.py
| 0.912834 | 0.153771 |
dh25519.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.encoding.general import url_b64_decode, url_b64_encode
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.utilities.exceptions import DecryptionException
from samson.protocols.jwt.jwa import JWA_ALG_MAP, JWAContentEncryptionAlg, JWAKeyEncryptionAlg
from samson.core.base_object import BaseObject
import json
class JWE(BaseObject):
"""
JSON Web Encryption
"""
def __init__(self, header: bytes, encrypted_key: bytes, iv: bytes, ciphertext: bytes, tag: bytes, aad: bytes):
"""
Parameters:
header (bytes): JWE JSON header.
encrypted_key (bytes): Encrypted Content-Encrypting Key.
iv (bytes): Initialization vector.
ciphertext (bytes): Encrypted body.
tag (bytes): Authentication tag.
"""
self.header = header
self.encrypted_key = encrypted_key
self.iv = iv
self.ciphertext = ciphertext
self.tag = tag
self.aad = aad
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['header', 'jose_header', 'encrypted_key', 'iv', 'ciphertext', 'tag', 'aad']
def serialize(self) -> Bytes:
"""
Serialize the JWE into its compact representation.
Returns:
Bytes: BASE64-URL encoded JWE.
"""
return Bytes(b'.'.join([url_b64_encode(part) for part in [self.header, self.encrypted_key, self.iv, self.ciphertext, self.tag]]))
@staticmethod
def parse(token: bytes) -> 'JWE':
"""
Parses a compact bytestring `token` into a JWE object.
Parameters:
token (bytes): The JWE token to parse.
Returns:
JWE: JWE representation.
"""
header, encrypted_key, iv, body, tag = [url_b64_decode(part) for part in token.split(b'.')]
return JWE(header, encrypted_key, iv, body, Bytes.wrap(tag), None)
@staticmethod
def generate_cek(alg: JWAKeyEncryptionAlg, enc: JWAContentEncryptionAlg, key: object, header: dict, cek: bytes=None, iv: bytes=None) -> (object, bytes):
generated_params = JWA_ALG_MAP[enc].generate_encryption_params()
if alg == JWAKeyEncryptionAlg.dir:
cek = key
elif alg == JWAKeyEncryptionAlg.ECDH_ES:
cek = JWA_ALG_MAP[alg].derive(key, len(generated_params[0]), header)
cek, iv = [user_param or generated_param for user_param, generated_param in zip((cek, iv), generated_params)]
return cek, iv
@staticmethod
def create(alg: JWAKeyEncryptionAlg, enc: JWAContentEncryptionAlg, body: bytes, key: object, cek: bytes=None, iv: bytes=None, aad: bytes=None, **additional_headers) -> 'JWE':
"""
Convenience method to create (and encrypt) a JWE.
Parameters:
alg (JWAKeyEncryptionAlg): JWA algorithm for key encryption.
enc (JWAContentEncryptionAlg): JWA algorithm for content encryption.
body (bytes): Body to be encrypted.
key (object): Key-encrypting key. Object type depending on the JWAKeyEncryptionAlg.
cek (bytes): Content-encrypting key for JWAContentEncryptionAlg. Random key will be generated if not specified.
iv (bytes): IV for JWAContentEncryptionAlg. Random key will be generated if not specified.
**additional_headers (kwargs): Additional key-value pairs to place in JWE header.
Returns:
JWE: JWE representation.
"""
header = {'alg': alg.value, 'enc': enc.value}
header.update(JWA_ALG_MAP[alg].generate_encryption_params())
header.update(additional_headers)
cek, iv = JWE.generate_cek(alg, enc, key, header, cek, iv)
encrypted_key = JWA_ALG_MAP[alg].encrypt(key, cek, header)
json_header = json.dumps(header, separators=(',', ':')).encode('utf-8')
full_aad = url_b64_encode(json_header) + b'.' + url_b64_encode(aad) if aad else url_b64_encode(json_header)
ciphertext, tag = JWA_ALG_MAP[enc].encrypt_and_auth(cek, iv, body, full_aad)
return JWE(json_header, encrypted_key, iv, ciphertext, tag, aad)
@property
def alg(self):
alg = JWAKeyEncryptionAlg[self.jose_header['alg'].replace('+', '_plus_').replace('-', '_')]
return alg
@property
def enc(self):
header = json.loads(self.header.decode())
enc = JWAContentEncryptionAlg[header['enc'].replace('-', '_')]
return enc
@property
def jose_header(self):
header = json.loads(self.header.decode())
if hasattr(self, 'unprotected_header'):
header.update(self.unprotected_header)
return header
def decrypt(self, key: object) -> Bytes:
"""
Decrypts the JWE.
Parameters:
key (object): Object type depending on the JWAKeyEncryptionAlg.
Returns:
Bytes: The plaintext payload.
"""
aad = url_b64_encode(self.header) + b'.' + url_b64_encode(self.aad) if self.aad else url_b64_encode(self.header)
cek = JWA_ALG_MAP[self.alg].decrypt(key, self.encrypted_key, self.jose_header)
return JWA_ALG_MAP[self.enc].decrypt(cek, self.iv, self.ciphertext, aad, self.tag)
class JWESet(BaseObject):
def __init__(self, enc: JWAContentEncryptionAlg, ciphertext: bytes, tag: bytes, cek: bytes, iv: bytes, protected_header: bytes, payload: bytes=None, recipients: list=None, unprotected_header: dict=None, aad: bytes=None):
"""
Parameters:
enc (JWAContentEncryptionAlg): Algorithm used to encrypt the payload.
ciphertext (bytes): Ciphertext representation of the payload.
tag (bytes): Authentication tag for JWAContentEncryptionAlg.
cek (bytes): Content encryption key for JWAContentEncryptionAlg.
iv (bytes): Initialization for JWAContentEncryptionAlg.
payload (bytes): Payload to be encrypted by all keys.
recipients (list): List of recipients to initialize with.
unprotected_header (dict): Unprotected header to include with the JWE.
aad (bytes): Additional authenticated data.
"""
self.payload = payload
self.recipients = recipients or []
self.enc = enc
self.cek = cek
self.iv = iv
self.unprotected_header = unprotected_header
self.protected_header = protected_header
self.ciphertext = ciphertext
self.tag = tag
self.aad = aad
self.i_know_what_im_doing = False
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['payload', 'enc', 'cek', 'iv', 'aad', 'protected_header', 'unprotected_header', 'ciphertext', 'recipients']
@staticmethod
def create(enc: JWAContentEncryptionAlg, payload: bytes, cek: bytes=None, iv: bytes=None, aad: bytes=None, additional_protected_headers: dict=None, unprotected_header: dict=None) -> 'JWESet':
"""
Creates a new JWESet.
Parameters:
enc (JWAContentEncryptionAlg): Algorithm used to encrypt the payload.
payload (bytes): Payload to be encrypted by all keys.
cek (bytes): Content encryption key for JWAContentEncryptionAlg.
aad (bytes): Additional authenticated data.
iv (bytes): Initialization for JWAContentEncryptionAlg.
recipients (list): List of recipients to initialize with.
additional_protected_headers (dict): Additional values to put in the protected header.
unprotected_header (dict): Unprotected header to include with the JWE.
Returns:
JWESet: JWESet representation.
"""
cek, iv = JWE.generate_cek(alg=None, enc=enc, key=None, header=None, cek=cek, iv=iv)
protected_header = {'enc': enc.value}
protected_header.update(additional_protected_headers or {})
json_header = json.dumps(protected_header, separators=(',', ':')).encode('utf-8')
full_aad = url_b64_encode(json_header) + b'.' + url_b64_encode(aad) if aad else url_b64_encode(json_header)
ciphertext, tag = JWA_ALG_MAP[enc].encrypt_and_auth(cek, iv, payload, full_aad)
return JWESet(enc=enc, cek=cek, iv=iv, ciphertext=ciphertext, tag=tag, payload=payload, protected_header=json_header, unprotected_header=unprotected_header, aad=aad)
def serialize(self, flatten: bool=False) -> bytes:
"""
Serializes the JWESet into a JSON object via https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7515#section-3.2.
Parameters:
flatten (bool): Whether or not to flatten the structure if there's only one recipient.
Returns:
bytes: JSON encoding as bytes.
"""
json_set = {
'protected': url_b64_encode(self.protected_header).decode(),
'recipients': [{'header': jwe.unprotected_header, 'encrypted_key': url_b64_encode(jwe.encrypted_key).decode()} for jwe in self.recipients],
'iv': url_b64_encode(self.iv).decode(),
'ciphertext': url_b64_encode(self.ciphertext).decode(),
'tag': url_b64_encode(self.tag).decode()
}
if self.unprotected_header:
json_set['unprotected'] = url_b64_encode(json.dumps(self.unprotected_header, separators=(',', ':')).encode('utf-8')).decode()
if self.aad:
json_set['aad'] = url_b64_encode(self.aad).decode()
if flatten and len(json_set['recipients']) == 1:
json_set.update(json_set['recipients'][0])
del json_set['recipients']
return json.dumps(json_set, separators=(',', ':')).encode('utf-8')
def add_recipient(self, alg: JWAKeyEncryptionAlg, key: object, **additional_headers):
"""
Adds a JWE to the set.
Parameters:
alg (JWAKeyEncryptionAlg): JWA key-encrypting to use for encryption.
key (object): Encryption key. Object type depending on the JWAKeyEncryptionAlg.
**additional_headers (kwargs): Additional key-value pairs to place in JWE header.
"""
unprotected_header = {'alg': alg.value}
unprotected_header.update(additional_headers)
if (alg in [JWAKeyEncryptionAlg.dir, JWAKeyEncryptionAlg.ECDH_ES] or any([recip.alg in [JWAKeyEncryptionAlg.dir, JWAKeyEncryptionAlg.ECDH_ES] for recip in self.recipients])) and len(self.recipients) > 0 and not self.i_know_what_im_doing:
raise ValueError(f"Cannot add a recipient using {alg} when there are other recipients. This is because {alg} is either Direct Key Agreement or Direct Encryption. Use the 'i_know_what_im_doing' flag to do it anyway.")
jwe = JWE.create(alg, self.enc, self.payload, key, cek=self.cek, iv=self.iv, aad=self.aad, **additional_headers)
unprotected_header.update(json.loads(jwe.header.decode()))
del unprotected_header['enc']
jwe.unprotected_header = unprotected_header
self.recipients.append(jwe)
@staticmethod
def process_recipient(protected_header: bytes, recipient_dict: dict, iv: bytes, ciphertext: bytes, tag: bytes, aad: bytes) -> JWE:
"""
Internal method to decode recipients into individual JWEs.
"""
jwe = JWE(protected_header, url_b64_decode(recipient_dict['encrypted_key'].encode('utf-8')), iv, ciphertext, tag, aad)
jwe.unprotected_header = recipient_dict['header']
return jwe
@staticmethod
def parse(token: bytes) -> 'JWESet':
"""
Parses a JSON bytestring `token` into a JWESet object.
Parameters:
token (bytes): The JWESet token to parse.
Returns:
JWESet: JWESet representation.
"""
token_dict = json.loads(token.decode())
unprotected_header = None
aad = None
if 'unprotected' in token_dict:
unprotected_header = token_dict['unprotected']
if 'aad' in token_dict:
aad = url_b64_decode(token_dict['aad'].encode('utf-8'))
protected_header = url_b64_decode(token_dict['protected'].encode('utf-8'))
protected_header_dict = json.loads(protected_header.decode())
ciphertext = url_b64_decode(token_dict['ciphertext'].encode('utf-8'))
iv = url_b64_decode(token_dict['iv'].encode('utf-8'))
tag = url_b64_decode(token_dict['tag'].encode('utf-8'))
# Is this a flattened token?
if 'encrypted_key' in token_dict:
recipients = [JWESet.process_recipient(protected_header, token_dict, iv, ciphertext, tag, aad)]
else:
recipients = [JWESet.process_recipient(protected_header, jwe_dict, iv, ciphertext, tag, aad) for jwe_dict in token_dict['recipients']]
return JWESet(enc=JWAContentEncryptionAlg[protected_header_dict['enc'].replace('-', '_')], ciphertext=ciphertext, tag=tag, cek=None, iv=iv, payload=None, recipients=recipients, protected_header=protected_header, unprotected_header=unprotected_header, aad=aad)
def decrypt(self, key: object, kid: str=None) -> Bytes:
"""
Decrypts the ciphertext. If `kid` is not specified, all encrypted keys are tried.
Parameters:
key (object): Decryption key with object type depending on the JWAKeyEncryptionAlg.
kid (str): (Optional) 'kid' in unprotected header that identifies the encrypted_key.
Returns:
Bytes: Plaintext.
"""
if kid:
plaintext = [jwe for jwe in self.recipients if 'kid' in jwe.unprotected_header and jwe.unprotected_header['kid'] == kid][0].decrypt(key)
else:
plaintext = None
for recipient in self.recipients:
try:
plaintext = recipient.decrypt(key)
break
except Exception:
pass
if not plaintext:
raise DecryptionException('No recipient able to decrypt.')
return plaintext
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/protocols/jwt/jwe.py
| 0.808899 | 0.219902 |
jwe.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.encoding.general import url_b64_decode, url_b64_encode
from samson.utilities.bytes import Bytes
from samson.protocols.jwt.jwa import JWA_ALG_MAP, JWASignatureAlg
from samson.core.base_object import BaseObject
import json
class JWS(BaseObject):
"""
JSON Web Signature
"""
def __init__(self, header: bytes, body: bytes, signature: bytes):
"""
Parameters:
header (bytes): JWS JSON header.
body (bytes): Body to be signed or verified.
signature (bytes): Signature value.
"""
self.header = header
self.body = body
self.signature = signature
def serialize(self) -> Bytes:
"""
Serialize the JWS into its compact representation.
Returns:
Bytes: BASE64-URL encoded JWS.
"""
return Bytes(b'.'.join([url_b64_encode(part) for part in [self.header, self.body, self.signature]]))
@staticmethod
def parse(token: bytes) -> 'JWS':
"""
Parses a compact bytestring `token` into a JWS object.
Parameters:
token (bytes): The JWS token to parse.
Returns:
JWS: JWS representation.
"""
header, body, signature = [url_b64_decode(part) for part in token.split(b'.')]
return JWS(header, body, Bytes.wrap(signature))
@staticmethod
def create(alg: JWASignatureAlg, body: bytes, key: object, **additional_headers) -> 'JWS':
"""
Convenience method to create (and sign) a JWS.
Parameters:
alg (JWASignatureAlg): JWA signature algorithm to use for signing and verification.
body (bytes): Body to be signed or verified.
key (object): Signing key. Object type depending on the JWASignatureAlg.
**additional_headers (kwargs): Additional key-value pairs to place in JWS header.
Returns:
JWS: JWS representation.
"""
header = {'alg': alg.value}
header.update(additional_headers)
json_header = json.dumps(header, separators=(',', ':')).encode('utf-8')
jws = JWS(json_header, body, b'')
jws.recompute_signature(key)
return jws
def recompute_signature(self, key: object):
"""
Recomputes the signature given a `key`.
Parameters:
key (object): Signing key. Object type depending on the JWASignatureAlg.
"""
self.signature = JWA_ALG_MAP[self.alg].sign(key, url_b64_encode(self.header) + b'.' + url_b64_encode(self.body))
@property
def alg(self):
return JWASignatureAlg[json.loads(self.header.decode())['alg']]
def verify(self, key: object) -> bool:
"""
Verifies the signature on the JWS.
Parameters:
key (object): Verification key with object type depending on the JWASignatureAlg.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not it passed verification.
"""
data = url_b64_encode(self.header) + b'.' + url_b64_encode(self.body)
return JWA_ALG_MAP[self.alg].verify(key, data, self.signature)
class JWSSet(BaseObject):
def __init__(self, payload: bytes, signatures: list=None):
"""
Parameters:
payload (bytes): Payload to be signed by all signatures.
signatures (list): (Optional) List of signatures to initialize with.
"""
self.payload = payload
self.signatures = signatures or []
def serialize(self, flatten: bool=False) -> bytes:
"""
Serializes the JWSSet into a JSON object via https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7515#section-3.2.
Parameters:
flatten (bool): Whether or not to flatten the structure if there's only one signature.
Returns:
bytes: JSON encoding as bytes.
"""
json_set = {
'payload': url_b64_encode(self.payload).decode(),
'signatures': [{'protected': url_b64_encode(jws.header).decode(), 'header': unprotected_header, 'signature': url_b64_encode(jws.signature).decode()} for jws, unprotected_header in self.signatures]
}
if flatten and len(json_set['signatures']) == 1:
json_set.update(json_set['signatures'][0])
del json_set['signatures']
return json.dumps(json_set, separators=(',', ':')).encode('utf-8')
def add_signature(self, alg: JWASignatureAlg, key: object, unprotected_header: dict=None, **additional_headers):
"""
Adds a signature to the set.
Parameters:
alg (JWASignatureAlg): JWA signature algorithm to use for signing and verification.
key (object): Signing key. Object type depending on the JWASignatureAlg.
unprotected_header (dict): Unprotected header to include with the JWS.
**additional_headers (kwargs): Additional key-value pairs to place in JWS header.
"""
unprotected_header = unprotected_header or {}
self.signatures.append((JWS.create(alg, self.payload, key, **additional_headers), unprotected_header))
@staticmethod
def process_signature(jws_dict: dict, payload: bytes) -> (JWS, dict):
"""
Internal method to decode signatures.
"""
jws = JWS(url_b64_decode(jws_dict['protected'].encode('utf-8')), payload, url_b64_decode(jws_dict['signature'].encode('utf-8')))
unprotected_header = jws_dict['header'] if 'header' in jws_dict else {}
return (jws, unprotected_header)
@staticmethod
def parse(token: bytes) -> 'JWSSet':
"""
Parses a JSON bytestring `token` into a JWSSet object.
Parameters:
token (bytes): The JWSSet token to parse.
Returns:
JWSSet: JWSSet representation.
"""
token_dict = json.loads(token.decode())
payload = url_b64_decode(token_dict['payload'].encode('utf-8'))
# Is this a flattened token?
if 'signature' in token_dict:
jwsset = JWSSet(payload, [JWSSet.process_signature(token_dict, payload)])
else:
jwsset = JWSSet(payload)
for jws_dict in token_dict['signatures']:
jwsset.signatures.append(JWSSet.process_signature(jws_dict, payload))
return jwsset
def verify(self, key: object, kid: str=None) -> bool:
"""
Verifies a signature. If `kid` is not specified, all signatures are tried.
Parameters:
key (object): Verification key with object type depending on the JWASignatureAlg.
kid (str): (Optional) 'kid' in unprotected header that identifies the signature.
Returns:
bool: Whether or not it passed verification.
"""
verified = False
if kid:
verified = [sig for sig in self.signatures if 'kid' in sig[1] and sig[1]['kid'] == kid][0][0].verify(key)
else:
for sig, _ in self.signatures:
try:
verified = sig.verify(key)
if verified:
break
except Exception:
pass
return verified
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/protocols/jwt/jws.py
| 0.797793 | 0.247135 |
jws.py
|
pypi
|
from samson.analysis.general import count_items
from samson.math.general import is_prime, is_sophie_germain_prime, smoothness
from samson.math.factorization.general import factor
from samson.core.base_object import BaseObject
from samson.protocols.diffie_hellman import DiffieHellman
WELL_KNOWN_GROUPS = {
DiffieHellman.MODP_768: 'MODP_768',
DiffieHellman.MODP_1024: 'MODP_1024',
DiffieHellman.MODP_1536: 'MODP_1536',
DiffieHellman.MODP_2048: 'MODP_2048',
DiffieHellman.MODP_3072: 'MODP_3072',
DiffieHellman.MODP_4096: 'MODP_4096',
DiffieHellman.MODP_6144: 'MODP_6144',
DiffieHellman.MODP_8192: 'MODP_8192'
}
class IntegerAnalysis(BaseObject):
def __init__(self, n: int, is_prime: bool, byte_aligned: bool, smoothness_ratio: float, is_safe_prime: bool, prime_name: bool, percent_one: float, is_uniform: bool, small_factors: dict):
self.n = n
self.is_prime = is_prime
self.smoothness_ratio = smoothness_ratio
self.byte_aligned = byte_aligned
self.is_safe_prime = is_safe_prime
self.prime_name = prime_name
self.percent_one = percent_one
self.is_uniform = is_uniform
self.small_factors = small_factors
def __repr__(self):
return f"<IntegerAnalysis: is_prime={self.is_prime}, smoothness_ratio={self.smoothness_ratio}, byte_aligned={self.byte_aligned}, is_safe_prime={self.is_safe_prime}, prime_name='{self.prime_name}', percent_one={self.percent_one}, is_uniform={self.is_uniform}, small_factors={self.small_factors}>"
def __reprdir__(self):
return ['is_prime', 'smoothness_ratio', 'byte_aligned', 'is_safe_prime', 'prime_name', 'percent_one', 'is_uniform', 'small_factors']
@staticmethod
def analyze(n: int) -> 'IntegerAnalysis':
n_is_prime = is_prime(n)
byte_aligned = not n % 8
is_safe_prime = is_sophie_germain_prime(n)
prime_name = WELL_KNOWN_GROUPS.get(n)
# Determine bit distribution
bits = bin(n)[2:]
bit_distribution = count_items(bits)
percent_one = bit_distribution['1'] / len(bits)
uniform_dist = abs(0.50 - percent_one) < 0.05
factor_mod = n - (1 if n_is_prime else 0)
small_factors = factor(factor_mod, use_rho=False, use_siqs=False, use_smooth_p=False)
smoothness_ratio = smoothness(factor_mod, factors=small_factors)
return IntegerAnalysis(n=n, is_prime=n_is_prime, smoothness_ratio=smoothness_ratio, byte_aligned=byte_aligned, is_safe_prime=is_safe_prime, prime_name=prime_name, percent_one=percent_one, is_uniform=uniform_dist, small_factors=small_factors)
|
/samson-crypto-0.3.0.tar.gz/samson-crypto-0.3.0/samson/analysis/integer_analysis.py
| 0.667148 | 0.237211 |
integer_analysis.py
|
pypi
|
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.