code
stringlengths 1
5.19M
| package
stringlengths 1
81
| path
stringlengths 9
304
| filename
stringlengths 4
145
|
|---|---|---|---|
from .private._curry2 import _curry2
from .private._isString import _isString
def inner_nth(offset, arr):
idx = len(arr) + offset if offset < 0 else offset
if _isString(arr):
return arr[idx] if idx < len(arr) and idx >= 0 else ''
else:
return arr[idx] if idx < len(arr) and idx >= 0 else None
nth = _curry2(inner_nth)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/nth.py
|
nth.py
|
from .private._curry1 import _curry1
from .private._reduced import _reduced
reduced = _curry1(_reduced)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/reduced.py
|
reduced.py
|
from .nth import nth
from .private._curry2 import _curry2
from .private._helper import getAttribute
from .private._isInteger import _isInteger
def inner_prop(p, obj):
if obj is None:
return None
return nth(p, obj) if _isInteger(p) else getAttribute(obj, p)
prop = _curry2(inner_prop)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/prop.py
|
prop.py
|
def _includesWith(pred, x, arr):
idx = 0
length = len(arr)
while idx < length:
if pred(x, arr[idx]):
return True
idx += 1
return False
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_includesWith.py
|
_includesWith.py
|
from ._curry1 import _curry1
from ._isPlaceholder import _isPlaceholder
def _curry2(fn):
def f2(*args):
if len(args) == 0:
return f2
elif len(args) == 1:
a = args[0]
if _isPlaceholder(a):
return f2
def f_b(_b): return fn(args[0], _b)
return _curry1(f_b)
else:
a, b = args[0], args[1]
if _isPlaceholder(a) and _isPlaceholder(b):
return f2
elif _isPlaceholder(a):
def f_a(_a): return fn(_a, b)
return _curry1(f_a)
elif _isPlaceholder(b):
def f_b(_b): return fn(a, _b)
return _curry1(f_b)
return fn(a, b)
return f2
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_curry2.py
|
_curry2.py
|
from ._has import _has
from ._isFunction import _isFunction
def _isTransformer(v):
"""
We treat transformer as a dict in Python
"""
return (v is not None) and (_has(v, 'get')) and (_isFunction(v.get('@@transducer/step')))
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_isTransformer.py
|
_isTransformer.py
|
from ._createReduce import _createReduce
from ._helper import getAttribute
from ._xArrayReduce import _xArrayReduce
def _xIterableReduce(xf, acc, iter):
while True:
try:
acc = getAttribute(xf, '@@transducer/step')(acc, next(iter))
if acc and getAttribute(acc, '@@transducer/reduced'):
acc = getAttribute(acc, '@@transducer/value')
break
except StopIteration:
break
return getAttribute(xf, '@@transducer/result')(acc)
def _xMethodReduce(xf, acc, obj, methodName):
result = getAttribute(xf, '@@transducer/result')
method = getAttribute(obj, methodName)
step = getAttribute(xf, '@@transducer/step')
return result(method(step, acc))
_xReduce = _createReduce(_xArrayReduce, _xMethodReduce, _xIterableReduce)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_xReduce.py
|
_xReduce.py
|
from ._helper import getAttribute
from ._reduced import _reduced
from ._xfBase import XfBase
class XFind(XfBase):
def __init__(self, f, xf):
self.xf = xf
self.f = f
self.found = False
def result(self, result):
if not self.found:
result = getAttribute(self.xf, '@@transducer/step')(result, None)
return self.xf.get('@@transducer/result')(result)
def step(self, result, input):
if self.f(input):
self.found = True
result = _reduced(getAttribute(self.xf, '@@transducer/step')(result, input))
return result
def _xfind(f): return lambda xf: XFind(f, xf)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_xfind.py
|
_xfind.py
|
from ._clone import _clone
from ._has import _has
from ._helper import getAttribute
from ._xfBase import XfBase
class XReduceBy(XfBase):
def __init__(self, valueFn, valueAcc, keyFn, xf):
self.valueFn = valueFn
self.valueAcc = valueAcc
self.keyFn = keyFn
self.xf = xf
self.inputs = {}
def result(self, result):
for key in self.inputs:
if _has(self.inputs, key):
result = getAttribute(self.xf, '@@transducer/step')(result, self.inputs[key])
if getAttribute(result, '@@transducer/reduced'):
result = getAttribute(result, '@@transducer/value')
break
self.inputs = None
return getAttribute(self.xf, '@@transducer/result')(result)
def step(self, result, input):
key = self.keyFn(input)
self.inputs[key] = getAttribute(self.inputs, key) or [key, _clone(self.valueAcc, deep=False)]
self.inputs[key][1] = self.valueFn(self.inputs[key][1], input)
return result
def _xReduceBy(valueFn, valueAcc, keyFn): return lambda xf: XReduceBy(valueFn, valueAcc, keyFn, xf)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_xReduceBy.py
|
_xReduceBy.py
|
from typing import Iterable
from ._helper import getAttribute
from ._isArrayLike import _isArrayLike
from ._isFunction import _isFunction
def _createReduce(arrayReduce, methodReduce, iterableReduce):
def _reduce(xf, acc, arr):
if arr is None:
return acc
if _isArrayLike(arr):
return arrayReduce(xf, acc, arr)
if _isFunction(getAttribute(arr, 'fantasy-land/reduce')):
return methodReduce(xf, acc, arr, 'fantasy-land/reduce')
if isinstance(arr, Iterable):
return iterableReduce(xf, acc, arr)
if _isFunction(getattr(arr, 'reduce', None)):
return methodReduce(xf, acc, arr, 'reduce')
raise Exception('reduce: list must be array or iterable')
return _reduce
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_createReduce.py
|
_createReduce.py
|
from ._helper import getAttribute
from ._xfBase import XfBase
class XMap(XfBase):
def __init__(self, f, xf):
self.xf = xf
self.f = f
def step(self, result, input):
return getAttribute(self.xf, '@@transducer/step')(result, self.f(input))
def _xmap(f): return lambda xf: XMap(f, xf)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_xmap.py
|
_xmap.py
|
import pamda as R
from ._identity import _identity
from ._isArrayLike import _isArrayLike
from ._isTransformer import _isTransformer
def _array_step(xs, x):
return xs + [x]
_stepCatArray = {
'@@transducer/init': list,
'@@transducer/step': _array_step,
'@@transducer/result': _identity
}
_stepCatString = {
'@@transducer/init': str,
'@@transducer/step': lambda a, b: str(a) + str(b),
'@@transducer/result': _identity
}
_stepCatDict = {
'@@transducer/init': dict,
# use Python 3.9 feature
'@@transducer/step': lambda result, input: result | (R.objOf(input[0], input[1]) if _isArrayLike(input) else input),
'@@transducer/result': _identity
}
# TODO: add _stepCatObject
def _stepCat(obj):
if _isTransformer(obj):
return obj
if _isArrayLike(obj):
return _stepCatArray
if isinstance(obj, str):
return _stepCatString
if isinstance(obj, dict):
return _stepCatDict
raise Exception(f'Cannot create transformer for {obj}')
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_stepCat.py
|
_stepCat.py
|
from ._curry1 import _curry1
def inner_isArrayLike(x):
return isinstance(x, (list, tuple))
_isArrayLike = _curry1(inner_isArrayLike)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_isArrayLike.py
|
_isArrayLike.py
|
def _isInteger(n):
return isinstance(n, int)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_isInteger.py
|
_isInteger.py
|
from ._helper import getAttribute
from ._reduced import _reduced
from ._xfBase import XfBase
class XAll(XfBase):
def __init__(self, f, xf):
self.xf = xf
self.f = f
self.all = True
def result(self, result):
if self.all:
result = getAttribute(self.xf, '@@transducer/step')(result, True)
return self.xf.get('@@transducer/result')(result)
def step(self, result, input):
if not self.f(input):
self.all = False
result = _reduced(getAttribute(self.xf, '@@transducer/step')(result, False))
return result
def _xall(f): return lambda xf: XAll(f, xf)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_xall.py
|
_xall.py
|
from ._helper import getAttribute
class XfBase:
"""
This is a class which not included in Ramda.
For extracting the common part to deal with transducer related logic.
"""
def init(self):
return getAttribute(self.xf, '@@transducer/init')()
def result(self, result):
return getAttribute(self.xf, '@@transducer/result')(result)
def step(self, result, input):
raise Exception('Child class should implement this')
def get(self, name, default=None):
if name == '@@transducer/init':
return self.init
if name == '@@transducer/result':
return self.result
if name == '@@transducer/step':
return self.step
return default
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_xfBase.py
|
_xfBase.py
|
from ._helper import getAttribute
from ._reduced import _reduced
from ._xfBase import XfBase
class XAny(XfBase):
def __init__(self, f, xf):
self.xf = xf
self.f = f
self.any = False
def result(self, result):
if not self.any:
result = getAttribute(self.xf, '@@transducer/step')(result, False)
return self.xf.get('@@transducer/result')(result)
def step(self, result, input):
if self.f(input):
self.any = True
result = _reduced(getAttribute(self.xf, '@@transducer/step')(result, True))
return result
def _xany(f): return lambda xf: XAny(f, xf)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_xany.py
|
_xany.py
|
from ._helper import getAttribute
from ._isArrayLike import _isArrayLike
from ._isFunction import _isFunction
def _equals(a, b):
if type(a) != type(b):
return False
if isinstance(a, BaseException):
# Exception
return str(a) == str(b)
if _isArrayLike(a) and _isArrayLike(b):
# Array-like
if len(a) != len(b):
return False
for i in range(len(a)):
if not _equals(a[i], b[i]):
return False
return True
if _isFunction(getAttribute(a, 'equals')) and _isFunction(getAttribute(b, 'equals')):
# dispatch to objects' own equals method
return a.equals(b) and b.equals(a)
# default equals
return a == b
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_equals.py
|
_equals.py
|
import pamda as R
from ._isPlaceholder import _isPlaceholder
def _curry1(fn):
def f1(a = R.__, *ignored):
if _isPlaceholder(a):
return f1
else:
return fn(a)
return f1
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_curry1.py
|
_curry1.py
|
def _filter(fn, arr):
idx = 0
length = len(arr)
result = []
while idx < length:
if fn(arr[idx]):
result.append(arr[idx])
idx += 1
return result
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_filter.py
|
_filter.py
|
def _pipe(f, g):
def inner(*arguments):
return g(f(*arguments))
return inner
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_pipe.py
|
_pipe.py
|
import inspect
def _isFunction(fn):
"""
Python class is also callable, so we need to deal with such pattern.
class A:
def b(self):
return False
a = A()
callable(A) # True
callable(a) # False
callable(a.b) # True
inspect.isclass(A) # True
inspect.isclass(a) # False
inspect.isclass(a.b) # False
"""
return callable(fn) and not inspect.isclass(fn)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_isFunction.py
|
_isFunction.py
|
def _arrayReduce(reducer, acc, arr):
index = 0
length = len(arr)
while index < length:
acc = reducer(acc, arr[index])
index += 1
return acc
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_arrayReduce.py
|
_arrayReduce.py
|
import copy
def _clone(value, deep=True):
"""
Unless there is no problem, we will use the built-in copy module.
"""
if deep:
return copy.deepcopy(value)
else:
return copy.copy(value)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_clone.py
|
_clone.py
|
import pamda as R
def _arity(n, fn):
def f0(): return fn()
def f1(a0=R.__, *____): return fn(a0, *____)
def f2(a0=R.__, a1=R.__, *____): return fn(a0, a1, *____)
def f3(a0=R.__, a1=R.__, a2=R.__, *____): return fn(a0, a1, a2, *____)
def f4(a0=R.__, a1=R.__, a2=R.__, a3=R.__, *____): return fn(a0, a1, a2, a3, *____)
def f5(a0=R.__, a1=R.__, a2=R.__, a3=R.__, a4=R.__, *____): return fn(a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, *____)
def f6(a0=R.__, a1=R.__, a2=R.__, a3=R.__, a4=R.__, a5=R.__, *____): return fn(a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, *____)
def f7(a0=R.__, a1=R.__, a2=R.__, a3=R.__, a4=R.__, a5=R.__, a6=R.__, *____): return fn(a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, *____)
def f8(a0=R.__, a1=R.__, a2=R.__, a3=R.__, a4=R.__, a5=R.__, a6=R.__, a7=R.__, *____): return fn(a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, *____)
def f9(a0=R.__, a1=R.__, a2=R.__, a3=R.__, a4=R.__, a5=R.__, a6=R.__, a7=R.__, a8=R.__, *____): return fn(a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, *____)
def f10(a0=R.__, a1=R.__, a2=R.__, a3=R.__, a4=R.__, a5=R.__, a6=R.__, a7=R.__, a8=R.__, a9=R.__, *____): return fn(a0, a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6, a7, a8, a9, *____)
m = {0: f0, 1: f1, 2: f2, 3: f3, 4: f4, 5: f5, 6: f6, 7: f7, 8: f8, 9: f9, 10: f10}
if n in m:
return m[n]
else:
raise Exception('First argument to _arity must be a non-negative integer no greater than ten')
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_arity.py
|
_arity.py
|
def _isArray(val):
"""
Actually array is list in Python,
for now we do not treat tuple as an array type.
"""
return isinstance(val, list)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_isArray.py
|
_isArray.py
|
def _isString(s):
return isinstance(s, str)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_isString.py
|
_isString.py
|
from ._helper import getAttribute
from ._xfBase import XfBase
class XFilter(XfBase):
def __init__(self, f, xf):
self.xf = xf
self.f = f
def step(self, result, input):
return getAttribute(self.xf, '@@transducer/step')(result, input) if self.f(input) else result
def _xfilter(f): return lambda xf: XFilter(f, xf)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_xfilter.py
|
_xfilter.py
|
def _complement(f):
return lambda *arguments: not f(*arguments)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_complement.py
|
_complement.py
|
def _has(obj, key):
if isinstance(obj, dict):
return key in obj or hasattr(obj, key)
return hasattr(obj, key)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_has.py
|
_has.py
|
def _isPlaceholder(a):
if a is None:
return False
return isinstance(a, dict) and a.get('@@functional/placeholder', False)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_isPlaceholder.py
|
_isPlaceholder.py
|
def _map(fn, functor):
idx = 0
length = len(functor)
result = [None] * length
while idx < length:
result[idx] = fn(functor[idx])
idx += 1
return result
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_map.py
|
_map.py
|
from ._helper import getAttribute
from ._isArray import _isArray
from ._isFunction import _isFunction
from ._isTransformer import _isTransformer
def _dispatchable(methodNames, transducerCreator, fn):
def f(*arguments):
if len(arguments) == 0:
return fn()
obj = arguments[-1]
if not _isArray(obj):
idx = 0
while idx < len(methodNames):
"""
There are 2 cases
case1: obj is an instance of some class, that instance has method with given name
case2: obj is a dict or an instance with get method
"""
method = getAttribute(obj, methodNames[idx])
if _isFunction(method):
return method(*arguments[:-1])
idx += 1
if _isTransformer(obj):
transducer = transducerCreator(*arguments[:-1])
return transducer(obj)
return fn(*arguments)
return f
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_dispatchable.py
|
_dispatchable.py
|
from ._helper import getAttribute
def _xArrayReduce(xf, acc, arr):
idx = 0
length = len(arr)
while idx < length:
acc = getAttribute(xf, '@@transducer/step')(acc, arr[idx])
if acc and getAttribute(acc, '@@transducer/reduced'):
acc = getAttribute(acc, '@@transducer/value')
break
idx += 1
return getAttribute(xf, '@@transducer/result')(acc)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_xArrayReduce.py
|
_xArrayReduce.py
|
from ._curry1 import _curry1
from ._curry2 import _curry2
from ._isPlaceholder import _isPlaceholder
def _curry3(fn):
def f3(*args):
if len(args) >= 1:
a = args[0]
if len(args) >= 2:
b = args[1]
if len(args) >= 3:
c = args[2]
def f_ab(_a, _b): return fn(_a, _b, c)
def f_bc(_b, _c): return fn(a, _b, _c)
def f_ac(_a, _c): return fn(_a, b, _c)
def f_a(_a): return fn(_a, b, c)
def f_b(_b): return fn(a, _b, c)
def f_c(_c): return fn(a, b, _c)
if len(args) == 0:
return f3
elif len(args) == 1:
if _isPlaceholder(a):
return f3
else:
return _curry2(f_bc)
elif len(args) == 2:
if _isPlaceholder(a) and _isPlaceholder(b):
return f3
elif _isPlaceholder(a):
return _curry2(f_ac)
elif _isPlaceholder(b):
return _curry2(f_bc)
else:
return _curry1(f_c)
else:
if _isPlaceholder(a) and _isPlaceholder(b) and _isPlaceholder(c):
return f3
elif _isPlaceholder(a) and _isPlaceholder(b):
return _curry2(f_ab)
elif _isPlaceholder(a) and _isPlaceholder(c):
return _curry2(f_ac)
elif _isPlaceholder(b) and _isPlaceholder(c):
return _curry2(f_bc)
elif _isPlaceholder(a):
return _curry1(f_a)
elif _isPlaceholder(b):
return _curry1(f_b)
elif _isPlaceholder(c):
return _curry1(f_c)
else:
return fn(a, b, c)
return f3
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_curry3.py
|
_curry3.py
|
from ._arity import _arity
from ._isPlaceholder import _isPlaceholder
def _curryN(n, received, fn):
def f1(*arguments):
combined = []
argsIdx = 0
left = n
combinedIdx = 0
while combinedIdx < len(received) or argsIdx < len(arguments):
result = None
if combinedIdx < len(received) and ((not _isPlaceholder(received[combinedIdx])) or argsIdx >= len(arguments)):
result = received[combinedIdx]
else:
result = arguments[argsIdx]
argsIdx += 1
combined.append(result)
if not _isPlaceholder(result):
left -= 1
combinedIdx += 1
if left <= 0:
return fn(*combined)
else:
return _arity(left, _curryN(n, combined, fn))
return f1
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_curryN.py
|
_curryN.py
|
def transducer_init():
raise Exception('init not implemented on XWrap')
def _xwrap(fn):
return {
'@@transducer/init': transducer_init,
'@@transducer/result': lambda acc: acc,
'@@transducer/step': lambda acc, x: fn(acc, x)
}
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_xwrap.py
|
_xwrap.py
|
from inspect import getfullargspec
from ._has import _has
def funcArgsLength(fn):
"""
Get the number of args for function fn
Not count *args and **kwargs
"""
fullargspec = getfullargspec(fn)
return len(fullargspec.args)
def toNumber(a):
"""
Convert any input a to a number type
if can not convert, then return nan
"""
if isinstance(a, float) or isinstance(a, int):
return a
try:
return int(a)
except:
try:
return float(a)
except:
return float('nan')
def getAttribute(v, key):
"""
This function is mainly for retrive @@transducer/xxx property, and fantasy-land/xxx property.
We assume dict/object in Python may own such properties.
dict case:
d = {'@@transducer/init': lambda: True}
init_fn = getAttribute(d, '@@transducer/init')
obj case:
class T:
def init(self):
return True
def get(self, type):
if type == '@@transducer/init':
return self.init
t = T()
init_fn = getAttribute(t, '@@transducer/init')
method case:
class Mapper:
def map(fn):
return fn
m = Mapper()
map_fn = getAttribute(m, 'map')
return: function got from key, otherwise None
"""
if isinstance(v, dict) and key in v:
return v[key]
if _has(v, key):
return getattr(v, key, None)
if _has(v, 'get'):
return v.get(key, None)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_helper.py
|
_helper.py
|
from ._arrayReduce import _arrayReduce
from ._createReduce import _createReduce
from ._helper import getAttribute
from ._xwrap import _xwrap
def _iterableReduce(reducer, acc, iter):
while True:
try:
value = next(iter)
acc = reducer(acc, value)
except StopIteration:
break
return acc
def _methodReduce(reducer, acc, obj, methodName):
method = getAttribute(obj, methodName)
return method(reducer, acc)
_reduce = _createReduce(_arrayReduce, _methodReduce, _iterableReduce)
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_reduce.py
|
_reduce.py
|
from ._helper import getAttribute
def _reduced(x):
if getAttribute(x, '@@transducer/reduced'):
return x
else:
return {
'@@transducer/value': x,
'@@transducer/reduced': True
}
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_reduced.py
|
_reduced.py
|
def _concat(set1 = [], set2 = []):
return set1 + set2
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_concat.py
|
_concat.py
|
def _identity(x, *ignore):
return x
|
zydmayday-pamda
|
/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9.tar.gz/zydmayday-pamda-0.0.9/pamda/private/_identity.py
|
_identity.py
|
## 安装
> pip install zyf_timer
>
> 或者
>
> pip install zyf_timer -i https://pypi.python.org/simple
## 使用
### 函数计时
#### 示例1:timeit
```python
from zyf import timeit
@timeit
def sleep(seconds: int):
time.sleep(seconds)
```
运行
```bash
>> sleep(1)
Function sleep -> takes 1.001 seconds
```
#### 示例2:repeat_timeit
```python
from zyf import repeat_timeit
@repeat_timeit(number=5)
def list_insert_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(10000):
l.insert(0, i)
@repeat_timeit(repeat=3, number=5)
def list_append_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(1000000):
l.append(i)
return l
@repeat_timeit(number=5, print_detail=True)
def list_gen_time_test():
l = [i for i in range(1000000)]
return l
@repeat_timeit(repeat=3, number=5, print_detail=True)
def list_extend_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(1000000):
l.extend([i])
@repeat_timeit(repeat=3, number=5, print_detail=True, print_table=True)
def list_range_time_test():
l = list(range(1000000))
```
运行
```bash
>> list_insert_time_test()
Function list_insert_time_test -> 5 function calls: average takes 0.097 seconds
>> list_append_time_test()
Function list_append_time_test -> 3 trials with 5 function calls per trial: average trial 3.269 seconds. average function call 0.654 seconds
>> list_gen_time_test()
Time Spend of 5 function calls:
Function -> list_gen_time_test: total 1.550 seconds, average 0.310 seconds
Average: 0.310 seconds
>> list_extend_time_test()
Time Spend of 3 trials with 5 function calls per trial:
Function -> list_extend_time_test:
best: 3.289 seconds, worst: 3.626 seconds, average: 3.442 seconds
Average trial: 3.442 seconds. Average function call: 0.688 seconds
>> list_range_time_test()
Time Spend of 3 trials with 5 function calls per trial:
+----------------------+---------------+---------------+---------------+-----------------------+
| Function | Best trial | Worst trial | Average trial | Average function call |
+----------------------+---------------+---------------+---------------+-----------------------+
| list_range_time_test | 0.640 seconds | 0.714 seconds | 0.677 seconds | 0.135 seconds |
+----------------------+---------------+---------------+---------------+-----------------------+
```
示例3:构建列表效率对比
```python
from zyf import repeat_timeit
@repeat_timeit(number=3)
def list_insert_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(100000):
l.insert(0, i)
@repeat_timeit(number=5)
def list_extend_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(100000):
l.extend([i])
@repeat_timeit(number=5)
def list_append_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(100000):
l.append(i)
return l
@repeat_timeit(number=5)
def list_gen_time_test():
l = [i for i in range(100000)]
return l
@repeat_timeit(number=5)
def list_range_time_test():
l = list(range(100000))
if __name__ == '__main__':
list_range_time_test()
list_gen_time_test()
list_append_time_test()
list_extend_time_test()
list_insert_time_test()
```
运行结果
```bash
Function list_range_time_test -> 5 function calls: average takes 0.012 seconds
Function list_gen_time_test -> 5 function calls: average takes 0.017 seconds
Function list_append_time_test -> 5 function calls: average takes 0.038 seconds
Function list_extend_time_test -> 5 function calls: average takes 0.067 seconds
Function list_insert_time_test -> 3 function calls: average takes 13.747 seconds
```
|
zyf-timer
|
/zyf_timer-1.8.tar.gz/zyf_timer-1.8/README.md
|
README.md
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Author : ZhangYafei
Description: zyf_timer
"""
import setuptools
with open("README.md", "r", encoding='utf-8') as fh:
long_description = fh.read()
setuptools.setup(
name='zyf_timer', # 模块名称
version="1.8", # 当前版本
author="zhangyafei", # 作者
author_email="[email protected]", # 作者邮箱
description="计时器", # 模块简介
long_description=long_description, # 模块详细介绍
long_description_content_type="text/markdown", # 模块详细介绍格式
# url="https://github.com/zhangyafeii/timer", # 模块github地址
packages=setuptools.find_packages(), # 自动找到项目中导入的模块
# 模块相关的元数据
classifiers=[
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3",
"License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License",
"Operating System :: OS Independent",
],
# 依赖模块
install_requires=['prettytable'],
python_requires='>=3.6',
)
|
zyf-timer
|
/zyf_timer-1.8.tar.gz/zyf_timer-1.8/setup.py
|
setup.py
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
DateTime : 2021/02/21 16:41
Author : ZhangYafei
Description: 函数计时器
使用示例
1. example timeit:
from zyf import timeit
@timeit
def sleep(seconds: int):
time.sleep(seconds)
>> sleep(1)
Function sleep -> takes 1.001 seconds
2. example repeat_timeit
@repeat_timeit(number=5)
def list_insert_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(10000):
l.insert(0, i)
@repeat_timeit(repeat=3, number=5)
def list_append_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(1000000):
l.append(i)
return l
@repeat_timeit(number=5, print_detail=True)
def list_gen_time_test():
l = [i for i in range(1000000)]
return l
@repeat_timeit(repeat=3, number=5, print_detail=True)
def list_extend_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(1000000):
l.extend([i])
@repeat_timeit(repeat=3, number=5, print_detail=True, print_table=True)
def list_range_time_test():
l = list(range(1000000))
>> list_insert_time_test()
Function list_insert_time_test -> 5 function calls: average takes 0.097 seconds
>> list_append_time_test()
Function list_append_time_test -> 3 trials with 5 function calls per trial: average trial 3.269 seconds. average function call 0.654 seconds
>> list_gen_time_test()
Time Spend of 5 function calls:
Function -> list_gen_time_test: total 1.550 seconds, average 0.310 seconds
Average: 0.310 seconds
>> list_extend_time_test()
Time Spend of 3 trials with 5 function calls per trial:
Function -> list_extend_time_test:
best: 3.289 seconds, worst: 3.626 seconds, average: 3.442 seconds
Average trial: 3.442 seconds. Average function call: 0.688 seconds
>> list_range_time_test()
Time Spend of 3 trials with 5 function calls per trial:
+----------------------+---------------+---------------+---------------+-----------------------+
| Function | Best trial | Worst trial | Average trial | Average function call |
+----------------------+---------------+---------------+---------------+-----------------------+
| list_range_time_test | 0.640 seconds | 0.714 seconds | 0.677 seconds | 0.135 seconds |
+----------------------+---------------+---------------+---------------+-----------------------+
"""
import time
from functools import wraps
from prettytable import PrettyTable
def repeat_timeit(repeat: int = 0, number: int = 10, digit: int = 3, print_detail: bool = False,
print_table: bool = False):
def wrap(func):
"""
装饰器: 判断函数执行时间
:param func:
:return:
"""
@wraps(func)
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
func_name, ret = func.__name__, None
if repeat > 0:
r = []
for _ in range(repeat):
end, ret = _timeit(func, number, *args, **kwargs)
r.append(end)
min_time, max_time, avg_time = min(r), max(r), sum(r) / repeat
best_trial_time_string = build_time_print_string(min_time, digit=digit)
worst_trial_time_string = build_time_print_string(max_time, digit=digit)
avg_trial_time_string = build_time_print_string(avg_time, digit=digit)
avg_func_call_time_string = build_time_print_string(avg_time / number, digit)
if print_table:
if print_detail:
print(f'Time Spend of {repeat} trials with {number} function calls per trial:')
table = PrettyTable(
['Function', 'Best trial', 'Worst trial', 'Average trial', 'Average function call'])
table.add_row(
[func_name, best_trial_time_string, worst_trial_time_string, avg_trial_time_string,
avg_func_call_time_string])
else:
table = PrettyTable(['Function', 'Average trial', 'Average function call'])
table.add_row([func_name, avg_trial_time_string, avg_func_call_time_string])
print(table)
else:
if print_detail:
print(
f'Time Spend of {repeat} trials with {number} function calls per trial:\n\tFunction -> {func_name}: \n\t\tbest: {best_trial_time_string}, worst: {worst_trial_time_string}, average: {avg_trial_time_string}')
print(
f'Average trial: {avg_trial_time_string}. Average function call: {avg_func_call_time_string}')
else:
print(
f'Function {func_name} -> {repeat} trials with {number} function calls per trial: average trial {avg_trial_time_string}, average function call {avg_func_call_time_string}')
else:
end, ret = _timeit(func, number, *args, **kwargs)
total_time_string = build_time_print_string(end, digit)
avg_time_string = build_time_print_string(end / number, digit)
if print_table:
if print_detail:
print(f'Time Spend of {number} function calls:')
table = PrettyTable(['Function', 'Total cost', 'Average cost'])
table.add_row([func_name, total_time_string, avg_time_string])
else:
table = PrettyTable(['Function', 'Average cost'])
table.add_row([func_name, avg_time_string])
print(table)
else:
if print_detail:
print(
f'Time Spend of {number} function calls:\n\tFunction -> {func_name}: total {total_time_string}, average {avg_time_string}')
print(f'Average: {avg_time_string}')
else:
print(f'Function {func_name} -> {number} function calls: average takes {avg_time_string}')
return ret
return inner
return wrap
def _timeit(func, number, *args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
num = 1
while num < number:
func(*args, **kwargs)
num += 1
ret = func(*args, **kwargs)
end = time.time() - start
return end, ret
def build_time_print_string(time_seconds: float, digit: int):
if time_seconds > 60:
minutes, seconds = divmod(time_seconds, 60)
return f'{int(minutes)} minutes {seconds:.{digit}f} seconds'
return f'{time_seconds:.{digit}f} seconds'
def timeit(func):
"""
装饰器: 判断函数执行时间
:param func:
:return:
"""
@wraps(func)
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
ret = func(*args, **kwargs)
end = time.time() - start
time_string = build_time_print_string(end, digit=3)
print(f'Function {func.__name__} -> takes {time_string}')
return ret
return inner
|
zyf-timer
|
/zyf_timer-1.8.tar.gz/zyf_timer-1.8/zyf_timer/timer.py
|
timer.py
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Author : ZhangYafei
Description: 计时器
"""
from timer import timeit, repeat_timeit
|
zyf-timer
|
/zyf_timer-1.8.tar.gz/zyf_timer-1.8/zyf_timer/__init__.py
|
__init__.py
|
## 安装
> pip install zyf
>
> 或者
>
> pip install zyf -i https://pypi.python.org/simple
## 使用
### 函数计时
#### 示例1:timeit
```python
from zyf.timer import timeit
@timeit
def sleep(seconds: int):
time.sleep(seconds)
sleep()
```
运行
```
>> sleep(1)
Function sleep -> takes 1.001 seconds
```
#### 示例2:Timeit
```python
from zyf.timer import timeit, Timeit
@Timeit(prefix='跑步')
def run():
time.sleep(3)
run()
```
运行
```
跑步 -> takes 3.000 seconds
```
#### 示例3:repeat_timeit
```python
from zyf.timer import repeat_timeit
@repeat_timeit(number=5)
def list_insert_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(10000):
l.insert(0, i)
@repeat_timeit(repeat=3, number=5)
def list_append_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(1000000):
l.append(i)
return l
@repeat_timeit(number=5, print_detail=True)
def list_gen_time_test():
l = [i for i in range(1000000)]
return l
@repeat_timeit(repeat=3, number=5, print_detail=True)
def list_extend_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(1000000):
l.extend([i])
@repeat_timeit(repeat=3, number=5, print_detail=True, print_table=True)
def list_range_time_test():
l = list(range(1000000))
```
运行
```python
>> list_insert_time_test()
Function list_insert_time_test -> 5 function calls: average takes 0.097 seconds
>> list_append_time_test()
Function list_append_time_test -> 3 trials with 5 function calls per trial: average trial 3.269 seconds. average function call 0.654 seconds
>> list_gen_time_test()
Time Spend of 5 function calls:
Function -> list_gen_time_test: total 1.550 seconds, average 0.310 seconds
Average: 0.310 seconds
>> list_extend_time_test()
Time Spend of 3 trials with 5 function calls per trial:
Function -> list_extend_time_test:
best: 3.289 seconds, worst: 3.626 seconds, average: 3.442 seconds
Average trial: 3.442 seconds. Average function call: 0.688 seconds
>> list_range_time_test()
Time Spend of 3 trials with 5 function calls per trial:
+----------------------+---------------+---------------+---------------+-----------------------+
| Function | Best trial | Worst trial | Average trial | Average function call |
+----------------------+---------------+---------------+---------------+-----------------------+
| list_range_time_test | 0.640 seconds | 0.714 seconds | 0.677 seconds | 0.135 seconds |
+----------------------+---------------+---------------+---------------+-----------------------+
```
#### 示例4:构建列表效率对比
```python
from zyf.timer import repeat_timeit
@repeat_timeit(number=3)
def list_insert_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(100000):
l.insert(0, i)
@repeat_timeit(number=5)
def list_extend_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(100000):
l.extend([i])
@repeat_timeit(number=5)
def list_append_time_test():
l = []
for i in range(100000):
l.append(i)
return l
@repeat_timeit(number=5)
def list_gen_time_test():
l = [i for i in range(100000)]
return l
@repeat_timeit(number=5)
def list_range_time_test():
l = list(range(100000))
if __name__ == '__main__':
list_range_time_test()
list_gen_time_test()
list_append_time_test()
list_extend_time_test()
list_insert_time_test()
```
运行结果
```bash
Function list_range_time_test -> 5 function calls: average takes 0.012 seconds
Function list_gen_time_test -> 5 function calls: average takes 0.017 seconds
Function list_append_time_test -> 5 function calls: average takes 0.038 seconds
Function list_extend_time_test -> 5 function calls: average takes 0.067 seconds
Function list_insert_time_test -> 3 function calls: average takes 13.747 seconds
```
### 请求头
#### user_agent
##### 功能说明
> 支持获取各类请求头,包含移动端和PC端浏览器,可以指定获取某类请求头,也可以随机获取。
##### 使用示例
```python
from zyf.user_agent import UserAgent
ua = UserAgent()
print(ua.random)
print(ua.chrome)
print(ua.firefox)
print(ua.opera)
print(ua.uc)
print(ua.mobile)
```
输出
```bash
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/536.3 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1061.1 Safari/536.3
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.2) AppleWebKit/536.6 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/20.0.1090.0 Safari/536.6
Mozilla/5.0 (X11; U; Linux x86_64; zh-CN; rv:1.9.2.10) Gecko/20100922 Ubuntu/10.10 (maverick) Firefox/3.6.10
Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1; en) Opera 9.50
Openwave/ UCWEB7.0.2.37/28/999
Mozilla/5.0 (iPad; U; CPU OS 4_3_3 like Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/533.17.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.0.2 Mobile/8J2 Safari/6533.18.5
```
### 文件操作
#### scan_directory_contents
##### 功能说明
> 扫描指定文件夹内所有文件,输出文件路径
##### 使用示例
```python
from zyf.file import scan_directory_contents
for file in scan_directory_contents('D:/python/data'):
print(file)
# 可以指定后缀
for file in scan_directory_contents('D:/python/data', suffix='.csv'):
print(file)
```
#### count_word_freq
##### 功能说明
> 对`文献.xlsx`中关键词列的进行`词频统计`,可指定单词分隔符,默认为`; ',也可指定输出词频统计列名,默认为freq和word。
##### 使用示例
```python
from zyf.file import count_word_freq
count_word_freq('文献.xlsx', col_name='关键词', sep='; ', to_col_freq='频数', to_col_word='单词', to_file='文献_关键词_统计.xlsx')
```
### 颜色相关
#### color
##### 功能说明
> 打印功能扩展,添加颜色输出
##### 使用示例
```python
from zyf.color import print_color, Foreground
print_color("这是什么颜色", foreground=Foreground.Red)
print_color("这是什么颜色", foreground=Foreground.White)
print_color("这是什么颜色", foreground=Foreground.Green)
print_color("这是什么颜色", foreground=Foreground.Black)
print_color("这是什么颜色", foreground=Foreground.Blue)
print_color("这是什么颜色", foreground=Foreground.Cyan)
print_color("这是什么颜色", foreground=Foreground.Purplish_red)
print_color("这是什么颜色", foreground=Foreground.Yellow)
```
### 数据下载
#### 政策数据下载
> 根据关键词对政策数据库进行搜索,并将搜索到的政策数据进行下载及字段解析,存储到文件中。
##### 使用说明
```
国务院政策文件库
1. 设置settings中的请求参数 -> gov_policy_params
2. 运行代码
北大法宝
1. 网页登陆之后将cookie复制,修改settings中的cookie信息
2. 根据你的检索词和检索时间修改settings中的QueryBased64Request和Year
3. 运行代码
律商网
1. 网页登陆之后将cookie复制,修改settings中的cookie信息
2. 根据你的检索信息修改settings中的keyword/start/end/page_size
3. 运行代码
```
**注:北大法宝和律商网需要有会员账号才能全部完整政策信息, 所以需要设置cookie信息。**
##### 使用示例
- 国务院政策数据下载
```python
def gov_policy_demo():
from zyf.crawler.policy.goverment_policy import GovPolicyCrawler
spider = GovPolicyCrawler()
spider.run(keyword='疫情', issue_depart=['国务院', '国务院部门', '国务院公报'], page_size=50)
```
- 北大法宝政策数据下载
```python
def pkulaw_policy_demo():
from zyf.crawler.policy.pkulaw_policy import PkulawdCrawler
pkulaw_request_params = {
'cookie': None,
'query_base64_request': {
'疫情': 'eyJGaWVsZE5hbWUiOm51bGwsIlZhbHVlIjpudWxsLCJSdWxlVHlwZSI6NCwiTWFueVZhbHVlU3BsaXQiOiJcdTAwMDAiLCJXb3JkTWF0Y2hUeXBlIjowLCJXb3JkUmF0ZSI6MCwiQ29tYmluYXRpb25UeXBlIjoyLCJDaGlsZE5vZGVzIjpbeyJGaWVsZE5hbWUiOiJLZXl3b3JkU2VhcmNoVHJlZSIsIlZhbHVlIjpudWxsLCJSdWxlVHlwZSI6NCwiTWFueVZhbHVlU3BsaXQiOiJcdTAwMDAiLCJXb3JkTWF0Y2hUeXBlIjowLCJXb3JkUmF0ZSI6MCwiQ29tYmluYXRpb25UeXBlIjoxLCJDaGlsZE5vZGVzIjpbeyJGaWVsZE5hbWUiOiJDaGVja0Z1bGxUZXh0IiwiVmFsdWUiOiLnlqvmg4UiLCJSdWxlVHlwZSI6NCwiTWFueVZhbHVlU3BsaXQiOiJcdTAwMDAiLCJXb3JkTWF0Y2hUeXBlIjoxLCJXb3JkUmF0ZSI6MCwiQ29tYmluYXRpb25UeXBlIjoyLCJDaGlsZE5vZGVzIjpbXSwiQW5hbHl6ZXIiOiJpa19zbWFydCIsIkJvb3N0IjoiMC4xIiwiTWluaW11bV9zaG91bGRfbWF0Y2giOm51bGx9LHsiRmllbGROYW1lIjoiU291cmNlQ2hlY2tGdWxsVGV4dCIsIlZhbHVlIjoi55ar5oOFIiwiUnVsZVR5cGUiOjQsIk1hbnlWYWx1ZVNwbGl0IjoiXHUwMDAwIiwiV29yZE1hdGNoVHlwZSI6MSwiV29yZFJhdGUiOjAsIkNvbWJpbmF0aW9uVHlwZSI6MiwiQ2hpbGROb2RlcyI6W10sIkFuYWx5emVyIjpudWxsLCJCb29zdCI6bnVsbCwiTWluaW11bV9zaG91bGRfbWF0Y2giOm51bGx9XSwiQW5hbHl6ZXIiOm51bGwsIkJvb3N0IjpudWxsLCJNaW5pbXVtX3Nob3VsZF9tYXRjaCI6bnVsbH1dLCJBbmFseXplciI6bnVsbCwiQm9vc3QiOm51bGwsIk1pbmltdW1fc2hvdWxkX21hdGNoIjpudWxsfQ==',
},
'year': [2003, 2004],
'page_size': 100,
}
crawler = PkulawdCrawler(**pkulaw_request_params)
crawler.run()
```
- 律商网政策数据下载
```python
def lexis_policy_demo():
from zyf.crawler.policy.lexis_policy import LexisNexisCrawler
lexis_request_params = {
'cookie': None,
'keywords': '疫情',
'start': '2020-01-01',
'end': '2020-12-31',
'page_size': 100,
}
crawler = LexisNexisCrawler(**lexis_request_params)
crawler.run()
```
- 综合示例
配置文件:settings.py
```python
# 国务院
gov_policy_params = {
'keyword': '医疗联合体',
'min_time': None,
'max_time': None,
'issue_depart': ['国务院', '国务院部门', '国务院公报'],
'searchfield': 'title:content:summary',
'sort': 'pubtime',
'page_size': 50,
'to_file': None
}
# 北大法宝
pkulaw_request_params = {
'cookie': None,
'query_base64_request': {
'疫情': 'eyJGaWVsZE5hbWUiOm51bGwsIlZhbHVlIjpudWxsLCJSdWxlVHlwZSI6NCwiTWFueVZhbHVlU3BsaXQiOiJcdTAwMDAiLCJXb3JkTWF0Y2hUeXBlIjowLCJXb3JkUmF0ZSI6MCwiQ29tYmluYXRpb25UeXBlIjoyLCJDaGlsZE5vZGVzIjpbeyJGaWVsZE5hbWUiOiJLZXl3b3JkU2VhcmNoVHJlZSIsIlZhbHVlIjpudWxsLCJSdWxlVHlwZSI6NCwiTWFueVZhbHVlU3BsaXQiOiJcdTAwMDAiLCJXb3JkTWF0Y2hUeXBlIjowLCJXb3JkUmF0ZSI6MCwiQ29tYmluYXRpb25UeXBlIjoxLCJDaGlsZE5vZGVzIjpbeyJGaWVsZE5hbWUiOiJDaGVja0Z1bGxUZXh0IiwiVmFsdWUiOiLnlqvmg4UiLCJSdWxlVHlwZSI6NCwiTWFueVZhbHVlU3BsaXQiOiJcdTAwMDAiLCJXb3JkTWF0Y2hUeXBlIjoxLCJXb3JkUmF0ZSI6MCwiQ29tYmluYXRpb25UeXBlIjoyLCJDaGlsZE5vZGVzIjpbXSwiQW5hbHl6ZXIiOiJpa19zbWFydCIsIkJvb3N0IjoiMC4xIiwiTWluaW11bV9zaG91bGRfbWF0Y2giOm51bGx9LHsiRmllbGROYW1lIjoiU291cmNlQ2hlY2tGdWxsVGV4dCIsIlZhbHVlIjoi55ar5oOFIiwiUnVsZVR5cGUiOjQsIk1hbnlWYWx1ZVNwbGl0IjoiXHUwMDAwIiwiV29yZE1hdGNoVHlwZSI6MSwiV29yZFJhdGUiOjAsIkNvbWJpbmF0aW9uVHlwZSI6MiwiQ2hpbGROb2RlcyI6W10sIkFuYWx5emVyIjpudWxsLCJCb29zdCI6bnVsbCwiTWluaW11bV9zaG91bGRfbWF0Y2giOm51bGx9XSwiQW5hbHl6ZXIiOm51bGwsIkJvb3N0IjpudWxsLCJNaW5pbXVtX3Nob3VsZF9tYXRjaCI6bnVsbH1dLCJBbmFseXplciI6bnVsbCwiQm9vc3QiOm51bGwsIk1pbmltdW1fc2hvdWxkX21hdGNoIjpudWxsfQ==',
},
'year': [2003, 2004],
'page_size': 100,
}
# 律商网
lexis_request_params = {
'cookie': None,
'keywords': '疫情',
'start': '2020-01-01',
'end': '2020-12-31',
'page_size': 100,
}
```
使用示例
```python
import settings
def policy_spider():
print('请选择政策来源: 1. 国务院政策文件库 2.北大法宝 3.律商网 4. 新冠疫情数据(卫健委)')
choice = input('请选择政策来源(数字)>> ')
if choice == '1':
from zyf.crawler.policy.goverment_policy import GovPolicyCrawler
crawler = GovPolicyCrawler()
crawler.run(**settings.gov_policy_params)
elif choice == '2':
from zyf.crawler.policy.pkulaw_policy import PkulawdCrawler
crawler = PkulawdCrawler(**settings.pkulaw_request_params)
crawler.run()
elif choice == '3':
from zyf.crawler.policy.lexis_policy import LexisNexisCrawler
crawler = LexisNexisCrawler(**settings.lexis_request_params)
crawler.run()
else:
raise Exception('输入的政策来源不正确')
```
#### 图片下载
##### 使用说明
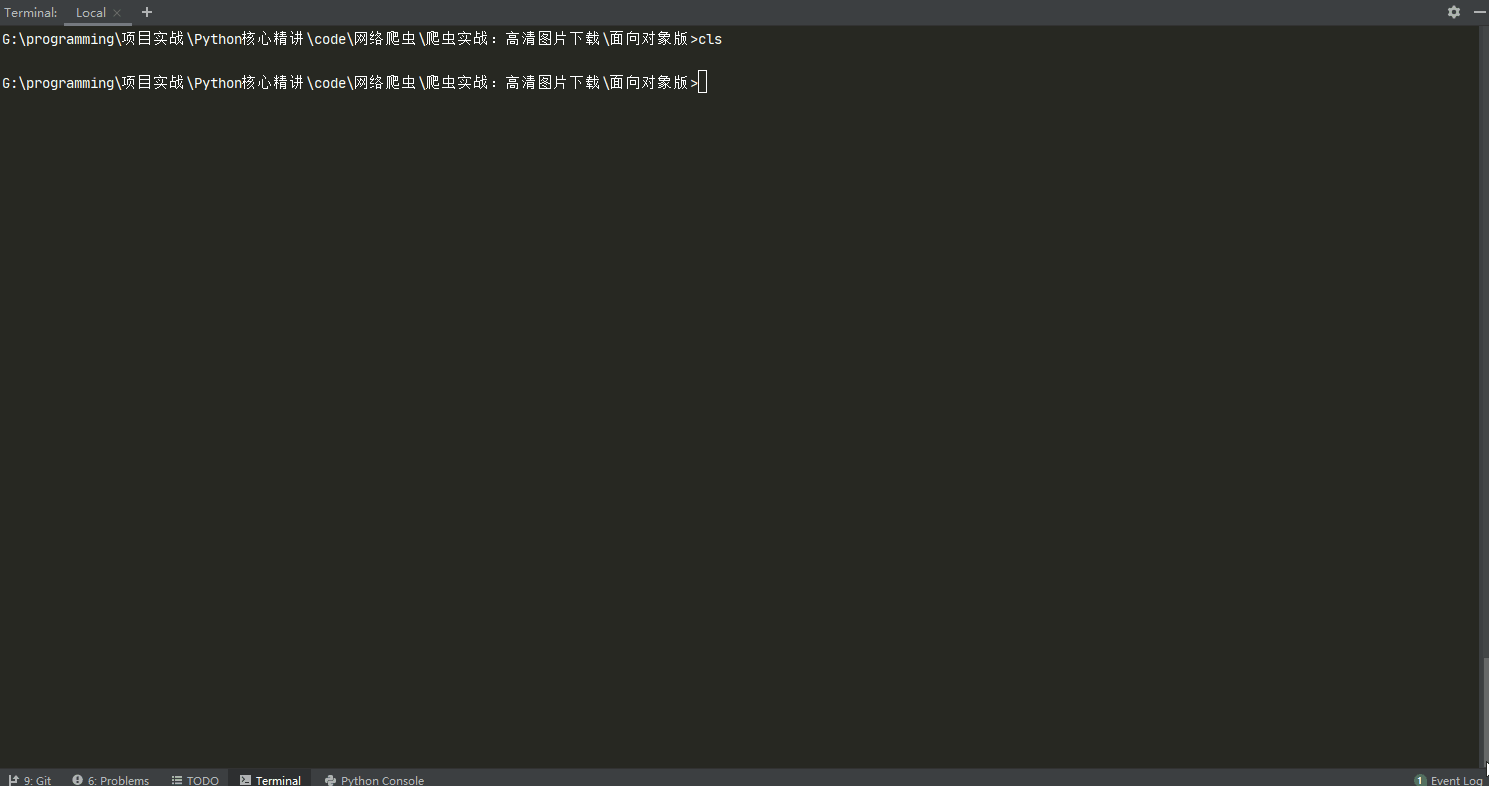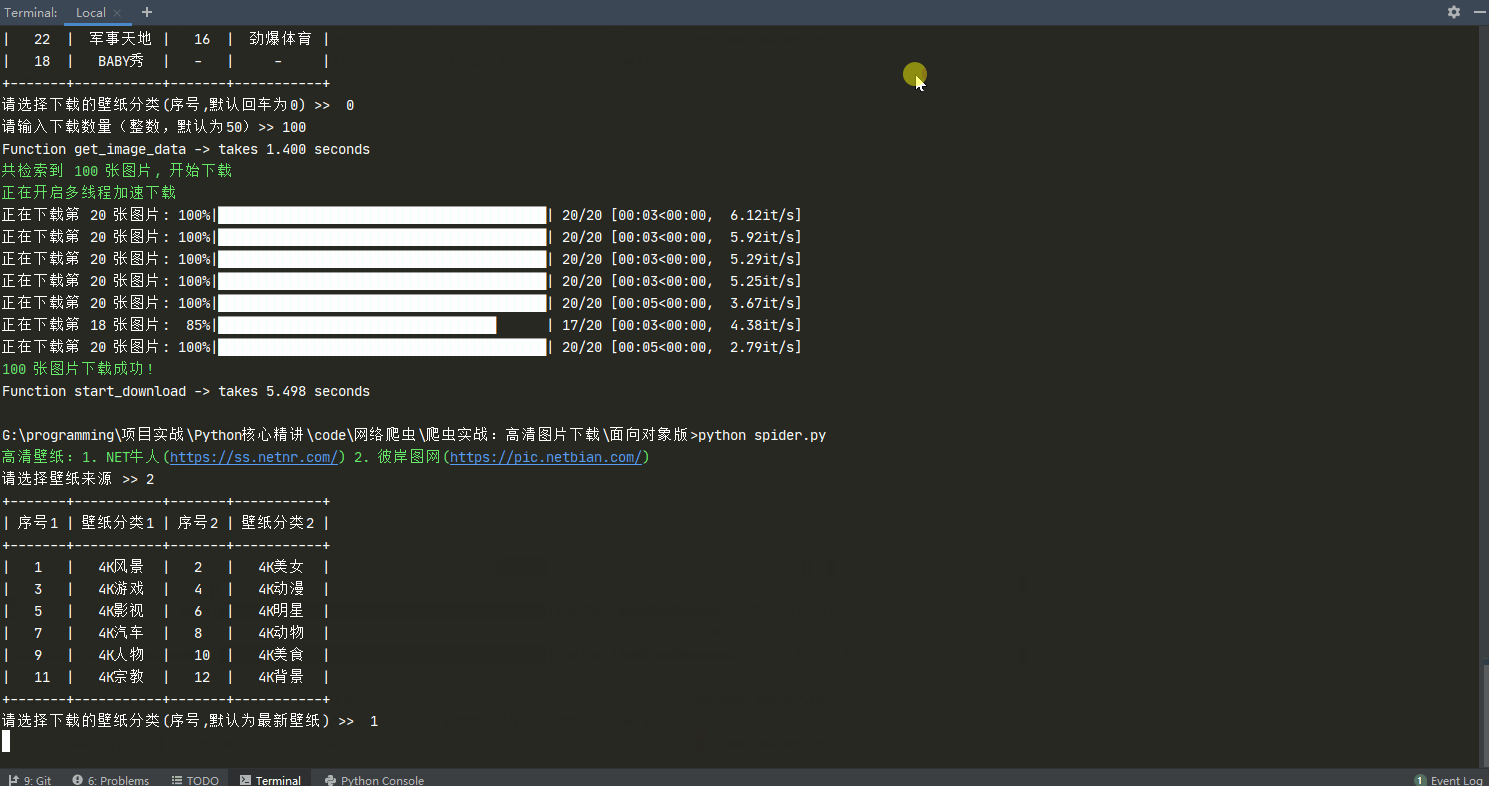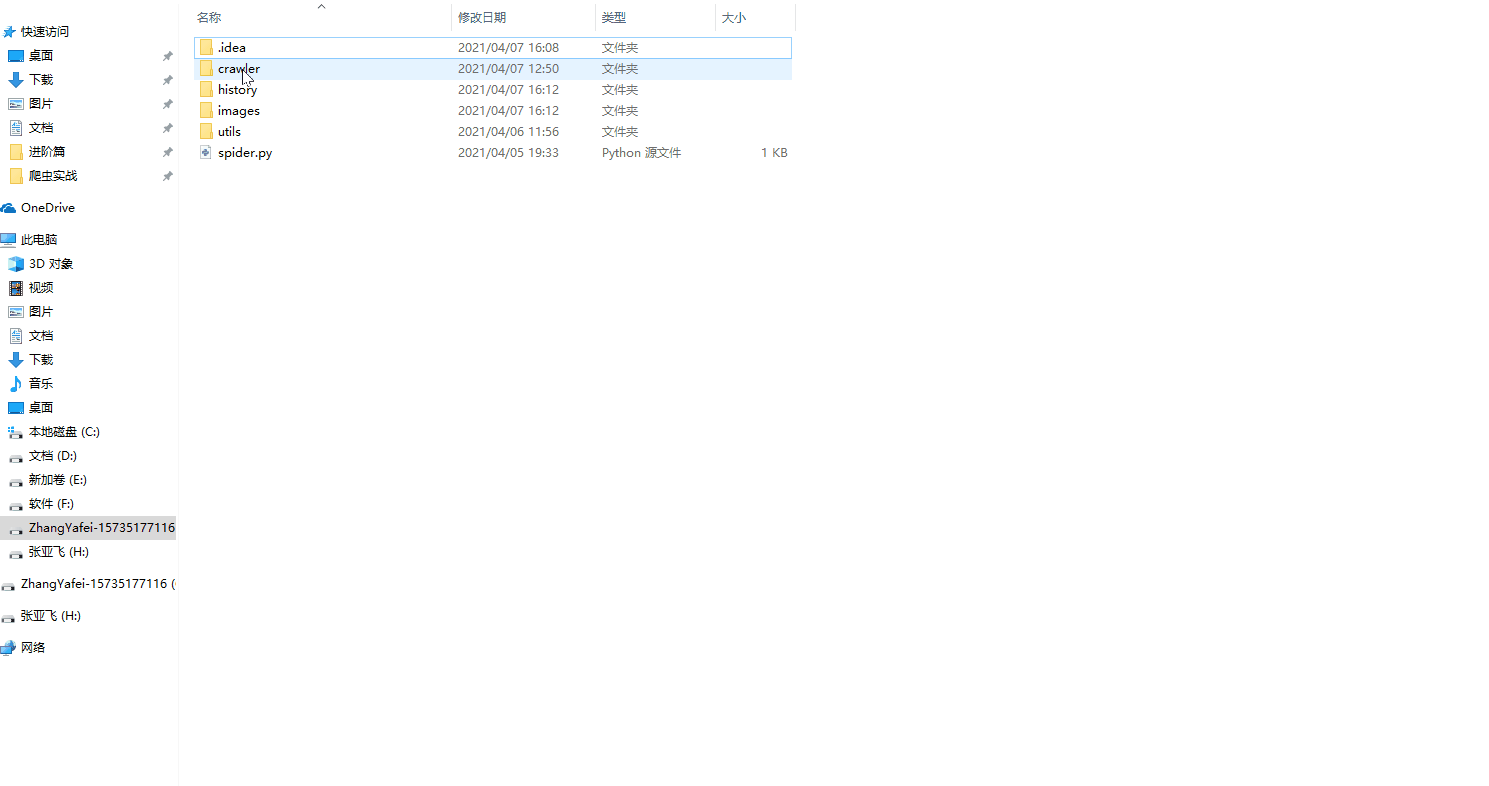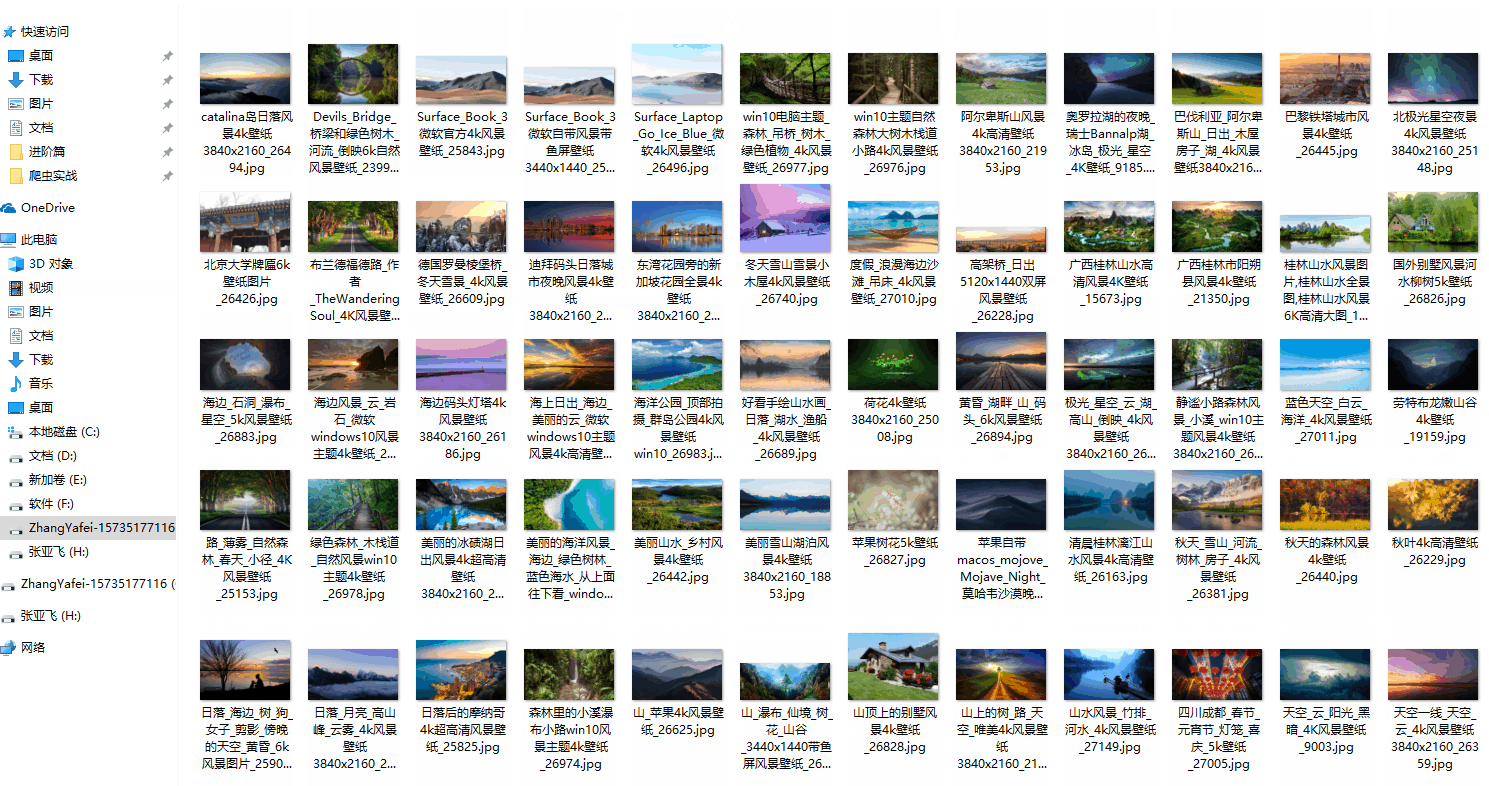
##### 使用示例
```python
from zyf.color import print_color
def start_spider():
print_color('高清壁纸:1. NET牛人(https://ss.netnr.com/) 2. 彼岸图网(https://pic.netbian.com/)')
choice = input('请选择壁纸来源 >> ')
if choice == '1':
from zyf.crawler.image.netnr import NetnrCrawler
crawler = NetnrCrawler(dir_path='images/netnr')
elif choice == '2':
from zyf.crawler.image.netbian import NetbianCrawler
crawler = NetbianCrawler(dir_path='images/netbian')
else:
raise Exception('输入的壁纸来源不正确')
crawler.run()
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_spider()
```
### 数据库连接
#### DBPoolHelper
##### 使用说明
> 提供sqlite3、mysql、postgresql、sqkserver连接池,方便操作,该功能使用依赖于dbutils,需要提前安装,另外,需要安装对应数据库的第三方依赖
>
> postgressql -> psycopg2
>
> mysql -> pymysql
>
> sqlite -> sqlite3
##### 使用示例
```python
from zyf.db import DBPoolHelper
db1 = DBPoolHelper(db_type='postgressql', dbname='student', user='postgres', password='0000', host='localhost', port=5432)
db2 = DBPoolHelper(db_type='mysql', dbname='student', user='root', password='0000', host='localhost', port=3306)
db3 = DBPoolHelper(db_type='sqlite3', dbname='student.db')
```
#### MongoHelper
##### 使用说明
> 为mongodb操作提供便利,需要安装pymongo
##### 使用示例
```python
from zyf.db import MongoHelper
mongo = MongoHelper(mongo_db='flask', mongo_uri='localhost')
data = mongo.read('label')
print(data.head())
condition = {"药品ID": 509881}
data = mongo.dbFind('label', condition)
print(data)
for i in data:
print(i)
for item in mongo.findAll():
print(item)
```
|
zyf
|
/zyf-1.2.tar.gz/zyf-1.2/README.md
|
README.md
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Author : ZhangYafei
Description: zyf
python setup.py sdist bdist_wheel
twine upload --repository-url https://upload.pypi.org/legacy/ dist/*
"""
import setuptools
with open("README.md", "r", encoding='utf-8') as fh:
long_description = fh.read()
setuptools.setup(
name='zyf', # 模块名称
version="1.2", # 当前版本
author="zhangyafei", # 作者
author_email="[email protected]", # 作者邮箱
description="常用函数工具包", # 模块简介
long_description=long_description, # 模块详细介绍
long_description_content_type="text/markdown", # 模块详细介绍格式
# url="https://github.com/zhangyafeii/timer", # 模块github地址
packages=setuptools.find_packages(), # 自动找到项目中导入的模块
# 模块相关的元数据
classifiers=[
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3",
"License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License",
"Operating System :: OS Independent",
],
# 依赖模块
install_requires=['prettytable', 'pandas', 'lxml', 'requests', 'tqdm'],
python_requires='>=3.6',
)
|
zyf
|
/zyf-1.2.tar.gz/zyf-1.2/setup.py
|
setup.py
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from setuptools import setup, find_packages
setup(
name="zyfra-check",
version="0.0.9",
description="A plugin that allows multiple failures per test.",
packages=find_packages(where="src"),
package_dir={"": "src"},
install_requires=["pytest>=3.1.1", "jira>=3.4.1", "testit-adapter-pytest>=1.1.2"],
entry_points={"pytest11": ["check = zyfra_check.plugin"]},
)
|
zyfra-check
|
/zyfra-check-0.0.9.tar.gz/zyfra-check-0.0.9/setup.py
|
setup.py
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pytest
from . import check_methods
@pytest.hookimpl(hookwrapper=True, trylast=True)
def pytest_runtest_makereport(item, call):
outcome = yield
report = outcome.get_result()
evalxfail = getattr(item, "_evalxfail", None)
failures = check_methods.get_failures()
check_methods.clear_failures()
if failures:
if evalxfail and evalxfail.wasvalid() and evalxfail.istrue():
report.outcome = "skipped"
report.wasxfail = evalxfail.getexplanation()
elif outcome._result.longreprtext.startswith("[XPASS(strict)]"):
report.outcome = "skipped"
report.wasxfail = "\n".join(failures)
else:
summary = "Failed Checks: {}".format(len(failures))
longrepr = ["\n".join(failures)]
longrepr.append("-" * 60)
longrepr.append(summary)
report.longrepr = "\n".join(longrepr)
report.outcome = "failed"
def pytest_configure(config):
check_methods.set_stop_on_fail(config.getoption("-x"))
@pytest.fixture(name='check')
def check_fixture():
return check_methods
|
zyfra-check
|
/zyfra-check-0.0.9.tar.gz/zyfra-check-0.0.9/src/zyfra_check/plugin.py
|
plugin.py
|
import functools
import inspect
import os
import pytest
from testit_adapter_pytest import utils as testit
from jira import JIRA, JIRAError
from threading import Lock
__all__ = [
"check",
"equal",
"not_equal",
"is_true",
"is_false",
"is_none",
"is_not_none",
"is_in",
"is_not_in",
"greater",
"greater_equal",
"less",
"less_equal",
"check_func",
"check_dict_values",
"check_status_code"
]
_stop_on_fail = False
_failures = []
class Singleton(type):
""" Класс, реализующий механизм создания одного экземпляра объекта. """
_instances = {}
_lock = Lock()
def __call__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
# делаем блокировку, чтоб не создалось несколько экземпляров объекта
with cls._lock:
if cls not in cls._instances:
# создаем экземпляр объекта, если он еще не создан
cls._instances[cls] = super(Singleton, cls).__call__(*args, **kwargs)
else:
# если экземпляр объекта уже создан, то инициализируем его параметры
cls._instances[cls].__init__(*args, **kwargs)
return cls._instances[cls]
class JiraConnection(metaclass=Singleton):
def __init__(self):
try:
self.client = JIRA(
server=os.environ.get('JIRA_SERVER'),
token_auth=os.environ.get('AUTH_JIRA_TOKEN'))
self.client.myself()
except Exception:
pytest.fail(
"Ошибка авторизации в Jira! Тест падает по дефекту, мы уже работаем над его исправлением!",
pytrace=False)
def clear_failures():
global _failures
_failures = []
def get_failures():
return _failures
def set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail):
global _stop_on_fail
_stop_on_fail = stop_on_fail
class CheckContextManager(object):
def __enter__(self):
return self
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
__tracebackhide__ = True
if exc_type is not None and issubclass(exc_type, AssertionError):
if _stop_on_fail:
return
else:
log_failure(exc_val)
return True
check = CheckContextManager()
def check_func(func):
@functools.wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwds):
__tracebackhide__ = True
try:
func(*args, **kwds)
return True
except AssertionError as e:
if _stop_on_fail:
if kwds.get('bug_link'):
check_issue(kwds.get('bug_link'), e)
log_failure(e)
raise e
if kwds.get('bug_link'):
check_issue(kwds.get('bug_link'), e)
else:
log_failure(e)
return False
return wrapper
@check_func
def equal(
actual_value: any,
expected_value: any,
msg: str = None,
stop_on_fail: bool = False,
bug_link: str = None):
"""
Проверить, что два значения равны. \n
:param actual_value: фактическое значение.
:param expected_value: ожидаемое значение.
:param msg: сообщение об ошибке. По умолчанию используется сообщение вида:
'Ошибка! Фактическое значение должно быть равно ожидаемому.\n
Фактическое значение = '{actual_value}',\n
Ожидаемое значение = '{expected_value}'.'
:param bug_link: ссылка на баг. По умолчанию = None.
:param stop_on_fail: параметр, отвечающий за необходимость фейлить тест после первой проваленной проверки.
По умолчанию = False.
"""
set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail)
if not msg:
msg = "\nОшибка! Фактическое значение должно быть равно ожидаемому.\n" \
f"Фактическое значение = '{actual_value}',\n" \
f"Ожидаемое значение = '{expected_value}'."
assert actual_value == expected_value, msg
@check_func
def not_equal(
actual_value: any,
expected_value: any,
msg: str = None,
stop_on_fail: bool = False,
bug_link: str = None):
"""
Проверить, что два значения не равны. \n
:param actual_value: фактическое значение.
:param expected_value: ожидаемое значение.
:param msg: сообщение об ошибке. По умолчанию используется сообщение вида:
'Ошибка! Фактическое значение должно быть не равно ожидаемому.\n
Фактическое значение = '{actual_value}',\n
Ожидаемое значение = '{expected_value}'.'
:param bug_link: ссылка на баг. По умолчанию = None.
:param stop_on_fail: параметр, отвечающий за необходимость фейлить тест после первой проваленной проверки.
По умолчанию = False.
"""
set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail)
if not msg:
msg = "\nОшибка! Фактическое значение должно быть не равно ожидаемому.\n" \
f"Фактическое значение = '{actual_value}',\n" \
f"Ожидаемое значение = '{expected_value}'."
assert actual_value != expected_value, msg
@check_func
def is_true(
result: any,
msg: str = None,
stop_on_fail: bool = False,
bug_link: str = None):
"""
Проверить, что результат выполнения операции равен True. \n
:param result: результат выполнения операции.
:param msg: сообщение об ошибке. По умолчанию = None.
:param bug_link: ссылка на баг. По умолчанию = None.
:param stop_on_fail: параметр, отвечающий за необходимость фейлить тест после первой проваленной проверки.
По умолчанию = False.
"""
set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail)
if not msg:
msg = f"\nОшибка! Значение должно быть равно 'True'. Фактическое значение = '{result}'."
assert bool(result), msg
@check_func
def is_false(
result: any,
msg: str = None,
stop_on_fail: bool = False,
bug_link: str = None):
"""
Проверить, что результат выполнения операции равен False. \n
:param result: результат выполнения операции.
:param msg: сообщение об ошибке. По умолчанию = None.
:param bug_link: ссылка на баг. По умолчанию = None.
:param stop_on_fail: параметр, отвечающий за необходимость фейлить тест после первой проваленной проверки.
По умолчанию = False.
"""
set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail)
if not msg:
msg = f"\nОшибка! Значение должно быть равно 'False'. Фактическое значение = '{result}'."
assert not bool(result), msg
@check_func
def is_none(
value: any,
msg: str = None,
stop_on_fail: bool = False,
bug_link: str = None):
"""
Проверить, что значение равно None. \n
:param value: проверяемое значение.
:param msg: сообщение об ошибке. По умолчанию используется сообщение вида:
'Ошибка! Значение должно быть равно 'None'.\n
Фактическое значение = '{value}'.'
:param bug_link: ссылка на баг. По умолчанию = None.
:param stop_on_fail: параметр, отвечающий за необходимость фейлить тест после первой проваленной проверки.
По умолчанию = False.
"""
set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail)
if not msg:
msg = f"\nОшибка! Значение должно быть равно 'None'. Фактическое значение = '{value}'."
assert value is None, msg
@check_func
def is_not_none(
value: any,
msg: str = None,
stop_on_fail: bool = False,
bug_link: str = None):
"""
Проверить, что значение не равно None. \n
:param value: проверяемое значение.
:param msg: сообщение об ошибке. По умолчанию используется сообщение вида:
'Ошибка! Значение должно быть равно 'None'.\n
Фактическое значение = '{value}'.'
:param bug_link: ссылка на баг. По умолчанию = None.
:param stop_on_fail: параметр, отвечающий за необходимость фейлить тест после первой проваленной проверки.
По умолчанию = False.
"""
set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail)
if not msg:
msg = f"\nОшибка! Значение не должно быть равно 'None'. Фактическое значение = '{value}'."
assert value is not None, msg
@check_func
def is_in(
value: any,
sequence: any,
msg: str = None,
stop_on_fail: bool = False,
bug_link: str = None):
"""
Проверить, что значение есть в последовательности. \n
:param value: значение.
:param sequence: последовательность (строка, список, кортеж, множество или словарь).
:param msg: сообщение об ошибке. По умолчанию используется сообщение вида:
'Ошибка! Последовательность '{sequence}' должна содержать значение '{value}'.'
:param bug_link: ссылка на баг. По умолчанию = None.
:param stop_on_fail: параметр, отвечающий за необходимость фейлить тест после первой проваленной проверки.
По умолчанию = False.
"""
set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail)
if not msg:
msg = f"\nОшибка! Последовательность '{sequence}' должна содержать значение '{value}'."
assert value in sequence, msg
@check_func
def is_not_in(
value: any,
sequence: any,
msg: str = None,
stop_on_fail: bool = False,
bug_link: str = None):
"""
Проверить, что значения нет в последовательности. \n
:param value: значение.
:param sequence: последовательность (строка, список, кортеж, множество или словарь).
:param msg: сообщение об ошибке. По умолчанию используется сообщение вида:
'Ошибка! Последовательность '{sequence}' не должна содержать значение '{value}'.'
:param bug_link: ссылка на баг. По умолчанию = None.
:param stop_on_fail: параметр, отвечающий за необходимость фейлить тест после первой проваленной проверки.
По умолчанию = False.
"""
set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail)
if not msg:
msg = f"\nОшибка! Последовательность '{sequence}' не должна содержать значение '{value}'."
assert value not in sequence, msg
@check_func
def greater(
first_value: any,
second_value: any,
msg: str = None,
stop_on_fail: bool = False,
bug_link: str = None):
"""
Проверить, что первое значение больше второго значения. \n
:param first_value: первое значение.
:param second_value: второе значение.
:param msg: сообщение об ошибке. По умолчанию используется сообщение вида:
Ошибка! Значение '{first_value}' должно быть больше значения '{second_value}'.
:param bug_link: ссылка на баг. По умолчанию = None.
:param stop_on_fail: параметр, отвечающий за необходимость фейлить тест после первой проваленной проверки.
По умолчанию = False.
"""
set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail)
if not msg:
msg = f"\nОшибка! Значение '{first_value}' должно быть больше значения '{second_value}'."
assert first_value > second_value, msg
@check_func
def greater_equal(
first_value: any,
second_value: any,
msg: str = None,
stop_on_fail: bool = False,
bug_link: str = None):
"""
Проверить, что первое значение больше или равно второму значению. \n
:param first_value: первое значение.
:param second_value: второе значение.
:param msg: сообщение об ошибке. По умолчанию используется сообщение вида:
Ошибка! Значение '{first_value}' должно быть больше или равно значению '{second_value}'.
:param bug_link: ссылка на баг. По умолчанию = None.
:param stop_on_fail: параметр, отвечающий за необходимость фейлить тест после первой проваленной проверки.
По умолчанию = False.
"""
set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail)
if not msg:
msg = f"\nОшибка! Значение '{first_value}' должно быть больше или равно значению '{second_value}'."
assert first_value >= second_value, msg
@check_func
def less(
first_value: any,
second_value: any,
msg: str = None,
stop_on_fail: bool = False,
bug_link: str = None):
"""
Проверить, что первое значение меньше второго значения. \n
:param first_value: первое значение.
:param second_value: второе значение.
:param msg: сообщение об ошибке. По умолчанию используется сообщение вида:
Ошибка! Значение '{first_value}' должно быть меньше значения '{second_value}'.
:param bug_link: ссылка на баг. По умолчанию = None.
:param stop_on_fail: параметр, отвечающий за необходимость фейлить тест после первой проваленной проверки.
По умолчанию = False.
"""
set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail)
if not msg:
msg = f"\nОшибка! Значение '{first_value}' должно быть меньше значения '{second_value}'."
assert first_value < second_value, msg
@check_func
def less_equal(
first_value: any,
second_value: any,
msg: str = None,
stop_on_fail: bool = False,
bug_link: str = None):
"""
Проверить, что первое значение меньше или равно второму значению. \n
:param first_value: первое значение.
:param second_value: второе значение.
:param msg: сообщение об ошибке. По умолчанию используется сообщение вида:
Ошибка! Значение '{first_value}' должно быть меньше или равно значению '{second_value}'.
:param bug_link: ссылка на баг. По умолчанию = None.
:param stop_on_fail: параметр, отвечающий за необходимость фейлить тест после первой проваленной проверки.
По умолчанию = False.
"""
set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail)
if not msg:
msg = f"\nОшибка! Значение '{first_value}' должно быть меньше или равно значению '{second_value}'."
assert first_value <= second_value, msg
@check_func
def check_dict_values(
actual_data: dict,
expected_data: dict,
verified_fields: list = None,
unverified_fields: list = None,
msg: str = None,
stop_on_fail: bool = False,
bug_link: str = None):
"""
Проверить, что все значения из словаря с ожидаемыми данными равны значениям из словаря с фактическими данными. \n
:param actual_data: словарь с фактическими данными.
:param expected_data: словарь с ожидаемыми данными.
:param verified_fields: список полей, которые нужно проверить.
:param unverified_fields: список полей, которые не нужно проверять.
:param msg: сообщение об ошибке. По умолчанию используется сообщение вида:
'Ошибка! Фактическое значение должно быть равно ожидаемому.\n
Фактическое значение = '{actual_value}',\n
Ожидаемое значение = '{expected_value}'.'
:param bug_link: ссылка на баг. По умолчанию = None.
:param stop_on_fail: параметр, отвечающий за необходимость фейлить тест после первой проваленной проверки.
По умолчанию = False.
"""
set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail)
verified_keys = expected_data.keys()
if verified_fields:
verified_keys = verified_fields
elif unverified_fields:
verified_keys -= unverified_fields
for key in verified_keys:
if not msg:
msg = f"\nОшибка! Фактическое значение поля словаря '{key}' не соответствует ожидаемому.\n" \
f"Фактическое значение = '{actual_data.get(key)}',\n" \
f"Ожидаемое значение = '{expected_data.get(key)}'."
assert actual_data.get(key) == expected_data.get(key), msg
@check_func
def check_status_code(
actual_code: int,
expected_code: int,
msg: str = None,
stop_on_fail: bool = False,
bug_link: str = None):
"""
Проверить, что фактический статус-код соответстует ожидаемому. \n
:param actual_code: фактический статус-код.
:param expected_code: ожидаемый статус-код.
:param msg: сообщение об ошибке. По умолчанию используется сообщение вида:
'Ошибка! Фактический статус-код не соответствует ожидаемому.\n
Фактический статус-код = '{actual_code}',\n
Ожидаемый статус-код = '{expected_code}'.'
:param bug_link: ссылка на баг. По умолчанию = None.
:param stop_on_fail: параметр, отвечающий за необходимость фейлить тест после первой проваленной проверки.
По умолчанию = False.
"""
set_stop_on_fail(stop_on_fail)
if not msg:
msg = f"Ошибка! Фактический статус-код не соответствует ожидаемому.\n" \
f"Фактический статус-код = '{actual_code}',\n" \
f"Ожидаемый статус-код = '{expected_code}'."
assert actual_code == expected_code, msg
def get_full_context(level):
(_, filename, line, funcname, contextlist) = inspect.stack()[level][0:5]
filename = os.path.relpath(filename)
context = contextlist[0].strip()
return (filename, line, funcname, context)
def log_failure(msg):
__tracebackhide__ = True
level = 3
pseudo_trace = []
func = ""
while "test_" not in func:
(file, line, func, context) = get_full_context(level)
if "site-packages" in file:
break
line = "{}:{} in {}() -> {}\n".format(file, line, func, context)
pseudo_trace.append(line)
level += 1
pseudo_trace_str = "\n".join(reversed(pseudo_trace))
entry = "FAILURE: {}\n{}".format(msg if msg else "", pseudo_trace_str)
_failures.append(entry)
def check_issue(issue_number: str, exception: AssertionError):
"""
Проверить актуальность дефектов. \n
:param issue_number: номер задачи.
:param exception: данные об ошибке сравнения.
"""
jira_connection = JiraConnection()
try:
issue_info = jira_connection.client.issue(issue_number, fields="status, fixVersions, priority, resolutiondate")
except JIRAError:
pytest.fail(f"Ошибка! Задача с номером '{issue_number}' не найдена в Jira!", pytrace=False)
unfixed_bug_msg, fixed_bug_msg = '', ''
status_name = issue_info.fields.status.name
if status_name != 'Готово':
unfixed_bug_msg = \
f"\nТест падает по дефекту: {os.environ.get('JIRA_SERVER')}/browse/{issue_info.key},\n" \
f"Приоритет задачи: '{issue_info.fields.priority}'!\n" \
f"Статус задачи: '{status_name}'!\n"
elif status_name == 'Готово':
versions = ', '.join([service.name for service in issue_info.fields.fixVersions])
fixed_bug_msg = \
f"\nВоспроизводится дефект: {os.environ.get('JIRA_SERVER')}/browse/{issue_info.key},\n" \
f"Статус задачи: '{status_name}',\n" \
f"Дата решения задачи: '{issue_info.fields.resolutiondate}',\n" \
f"Баг исправлен в версиях: '{versions}'!\n"
if unfixed_bug_msg:
testit.addLink(type=testit.LinkType.DEFECT, url=f"{os.environ.get('JIRA_SERVER')}/browse/{issue_number}")
reason = exception.args[0] + unfixed_bug_msg
log_failure(reason)
pytest.xfail(reason=reason)
elif fixed_bug_msg:
reason = exception.args[0] + fixed_bug_msg
log_failure(reason)
|
zyfra-check
|
/zyfra-check-0.0.9.tar.gz/zyfra-check-0.0.9/src/zyfra_check/check_methods.py
|
check_methods.py
|
import pytest
pytest.register_assert_rewrite("zyfra_check.check")
from zyfra_check.check_methods import * # noqa: F401, F402, F403
|
zyfra-check
|
/zyfra-check-0.0.9.tar.gz/zyfra-check-0.0.9/src/zyfra_check/__init__.py
|
__init__.py
|
from django.apps import AppConfig
class ZygoatDjangoAppConfig(AppConfig):
name = "zygoat_django"
|
zygoat-django
|
/zygoat_django-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl/zygoat_django/apps.py
|
apps.py
|
from uvicorn.workers import UvicornWorker
class ZygoatUvicornWorker(UvicornWorker):
CONFIG_KWARGS = {"loop": "auto", "http": "auto", "headers": [["server", ""]]}
|
zygoat-django
|
/zygoat_django-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl/zygoat_django/uvicorn_worker.py
|
uvicorn_worker.py
|
from importlib_metadata import version
__version__ = version("zygoat_django")
|
zygoat-django
|
/zygoat_django-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl/zygoat_django/__init__.py
|
__init__.py
|
from django.db import models
class TimestampedModel(models.Model):
created_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
updated_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now=True)
class Meta:
abstract = True
|
zygoat-django
|
/zygoat_django-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl/zygoat_django/models.py
|
models.py
|
"""
Checks every half second to see if your database can be connected to successfully.
Once a connection is made, the command returns 0. If a connection can never be made,
it blocks indefinitely.
"""
from time import sleep
from django.core.management.base import BaseCommand
from django.db import connection
from django.db.utils import OperationalError
class Command(BaseCommand):
def handle(self, *args, **kwargs):
while True:
sleep(0.5)
try:
with connection.temporary_connection():
self.stdout.write(self.style.SUCCESS("Connected to db."))
break
except OperationalError:
self.stdout.write(self.style.WARNING("Still waiting for db..."))
|
zygoat-django
|
/zygoat_django-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl/zygoat_django/management/commands/wait_for_db.py
|
wait_for_db.py
|
"""
A command for marking users as staff.
::
./manage.py set_staff --field email --users [email protected] [email protected]
./manage.py set_staff --int --users 1 2 5
./manage.py set_staff --int --unset --users 1 2 5
"""
from django.core.management.base import BaseCommand
from django.contrib.auth import get_user_model
class Command(BaseCommand):
def add_arguments(self, parser):
parser.add_argument("--users", nargs="+", type=str, help="a list of user keys")
parser.add_argument(
"--field", type=str, default="pk", help="a unique field name on the user model"
)
parser.add_argument(
"--int",
action="store_true",
help="the user keys should be interpreted as integers",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--unset",
action="store_true",
help="set is_staff to False instead of True",
)
def handle(self, *args, **options):
User = get_user_model()
convert = int if options.get("int") else str
user_values = [convert(v.strip()) for v in options.get("users")]
where = {"{}__in".format(options.get("field")): user_values}
users = User.objects.filter(**where)
for u in users:
u.is_staff = not options.get("unset")
users = User.objects.bulk_update(users, ["is_staff"])
|
zygoat-django
|
/zygoat_django-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl/zygoat_django/management/commands/set_staff.py
|
set_staff.py
|
"""
Cache configuration for zygoat projects. We use ``django-redis`` to handle connecting to the cache backend, and then tell django to use a write-through cache backend for sessions. This makes sessions blazingly fast and persistent in the case that the cache gets cleared.
"""
from .environment import prod_required_env
CACHES = {
"default": {
"BACKEND": "django_redis.cache.RedisCache",
"LOCATION": prod_required_env("DJANGO_REDIS_CACHE_URL", "redis://cache:6379/0"),
"OPTIONS": {
"CLIENT_CLASS": "django_redis.client.DefaultClient",
},
}
}
"""
Configures the default cache to point to the zygoat generated docker container.
"""
SESSION_ENGINE = "django.contrib.sessions.backends.cached_db"
"""
.. seealso::
- `How to use sessions <https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.1/topics/http/sessions/>`_
- `Using cached sessions <https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.1/topics/http/sessions/#using-cached-sessions>`_
"""
|
zygoat-django
|
/zygoat_django-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl/zygoat_django/settings/cache.py
|
cache.py
|
"""
``djangorestframework`` (DRF) related configuration values. DRF uses a single dict to describe all of its options and configurations, so be careful not to overwrite this in your settings file.
"""
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES": (
"djangorestframework_camel_case.render.CamelCaseJSONRenderer",
),
"DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES": (
"djangorestframework_camel_case.parser.CamelCaseFormParser",
"djangorestframework_camel_case.parser.CamelCaseMultiPartParser",
"djangorestframework_camel_case.parser.CamelCaseJSONParser",
),
}
"""
A DRF configuration dict. By default, it changes ``camelCase`` to ``snake_case`` in request data, and does the opposite for response data. This is to let you keep language-consistent styling in Python and JavaScript code.
"""
|
zygoat-django
|
/zygoat_django-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl/zygoat_django/settings/rest_framework.py
|
rest_framework.py
|
from .environment import * # noqa
from .rest_framework import * # noqa
from .cache import * # noqa
|
zygoat-django
|
/zygoat_django-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl/zygoat_django/settings/__init__.py
|
__init__.py
|
"""
Environment variable configuration for zygoat projects. We utilize `django-environ`_ to make using environment variables painless and easy, and configure the ``DEBUG`` and ``PRODUCTION`` values to distinguish your environments.
This module exposes a few utilities:
.. autodata:: env
"""
import environ
env = environ.Env()
PRODUCTION = env.bool("DJANGO_PRODUCTION", default=False)
"""
:annotation: = False
Whether or not the app is running production mode.
If ``True``, ``DEBUG`` is explicitly set to ``False`` to avoid leaking information.
.. note::
Controlled by the environment variable ``DJANGO_PRODUCTION`` by default
"""
DEBUG = False if PRODUCTION else env.bool("DJANGO_DEBUG", default=True)
"""
:annotation: = True
Used internally by Django to decide how much debugging context is sent to the browser when a failure occurs.
Cannot be ``True`` if ``PRODUCTION`` is ``True``
.. note::
Controlled by the environment variable ``DJANGO_DEBUG`` by default
"""
def prod_required_env(key, default, method="str"):
"""
Throw an exception if PRODUCTION is true and the environment key is not provided
:type key: str
:param key: Name of the environment variable to fetch
:type default: any
:param default: Default value for non-prod environments
:type method: str
:param method: django-environ instance method, used to type resulting data
.. seealso::
- `django-environ <https://github.com/joke2k/django-environ>`_
- `django-environ supported types <https://github.com/joke2k/django-environ#supported-types>`_
"""
if PRODUCTION:
default = environ.Env.NOTSET
return getattr(env, method)(key, default)
ALLOWED_HOSTS = [prod_required_env("DJANGO_ALLOWED_HOST", default="*")]
"""
:annotation: = ['*']
Sets the list of valid ``HOST`` header values. Typically this is handled by a reverse proxy in front of the deploy Django application. In development, this is provided by the Caddy reverse proxy.
.. warning:: Requires ``DJANGO_ALLOWED_HOST`` to be set in production mode
"""
db_config = env.db_url("DATABASE_URL", default="postgres://postgres:postgres@db/postgres")
"""
:annotation: = env.db_url("DATABASE_URL", default="postgres://postgres:postgres@db/postgres")
Parses the ``DATABASE_URL`` environment variable into a Django `databases`_ dictionary.
Uses a standard database URI schema.
"""
DATABASES = {"default": db_config}
"""
Django `databases <https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.1/ref/settings/#databases>`_ configuration value.
The default entry is generated automatically from :py:data:`db_config`.
.. note::
If you need more than one database or a different default setup, you can modify this value in your application's ``settings.py`` file.
"""
DEFAULT_AUTO_FIELD = "django.db.models.BigAutoField"
|
zygoat-django
|
/zygoat_django-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl/zygoat_django/settings/environment.py
|
environment.py
|
import time
from django.conf import settings
SESSION_EXPIRATION_SECONDS = getattr(settings, "SESSION_EXPIRATION_SECONDS", 3600)
SESSION_EXPIRATION_ACTIVITY_RESETS = getattr(
settings, "SESSION_EXPIRATION_ACTIVITY_RESETS", True
)
SESSION_EXPIRATION_KEY = getattr(settings, "SESSION_EXPIRATION_KEY", "_last_active_at")
def has_session(request):
return hasattr(request, "session") and not request.session.is_empty()
def session_expiration_middleware(get_response):
"""
Middleware to expire Django sessions after a predetermined number of seconds has passed.
"""
def middleware(request):
if has_session(request):
last_activity = request.session.get(SESSION_EXPIRATION_KEY)
if (
last_activity is None
or time.time() - last_activity > SESSION_EXPIRATION_SECONDS
):
request.session.flush()
response = get_response(request)
if has_session(request):
last_activity = request.session.get(SESSION_EXPIRATION_KEY)
if last_activity is None or SESSION_EXPIRATION_ACTIVITY_RESETS:
request.session[SESSION_EXPIRATION_KEY] = time.time()
return response
return middleware
|
zygoat-django
|
/zygoat_django-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl/zygoat_django/middleware/session_expiration.py
|
session_expiration.py
|
class ReverseProxyHandlingMiddleware(object):
"""
Normalize all incoming IP addresses from the load balancer
"""
def __init__(self, get_response):
self.get_response = get_response
def __call__(self, request):
if "HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR" in request.META:
ip = request.META["HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR"]
else:
ip = request.META["REMOTE_ADDR"]
request.META["REMOTE_ADDR"] = ip.split(",")[0]
return self.get_response(request)
|
zygoat-django
|
/zygoat_django-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl/zygoat_django/middleware/reverse_proxy.py
|
reverse_proxy.py
|
HEADERS = {
"X-FRAME-Options": "DENY",
"Content-Security-Policy": "frame-ancestors 'none'",
"Strict-Transport-Security": "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains",
"Cache-Control": "no-cache, no-store",
"X-Content-Type-Options": "nosniff",
"X-XSS-Protection": "1; mode=block",
}
class SecurityHeaderMiddleware(object):
"""
Add security headers to all responses
"""
def __init__(self, get_response):
self.get_response = get_response
def __call__(self, request):
response = self.get_response(request)
for k, v in HEADERS.items():
response[k] = v
return response
|
zygoat-django
|
/zygoat_django-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl/zygoat_django/middleware/security_headers.py
|
security_headers.py
|
from .reverse_proxy import ReverseProxyHandlingMiddleware
from .session_expiration import session_expiration_middleware
from .security_headers import SecurityHeaderMiddleware
__all__ = (
"ReverseProxyHandlingMiddleware",
"SecurityHeaderMiddleware",
"session_expiration_middleware",
)
|
zygoat-django
|
/zygoat_django-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl/zygoat_django/middleware/__init__.py
|
__init__.py
|
# zygoat
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/640862/75250233-e287ea80-57a5-11ea-9d9f-553662a17706.jpeg" />
## What is zygoat?
`zygoat` is a command line tool used to bootstrap and configure a React/Django/Postgres stack web application.
Linting, test configuration, boilerplate, and development environment are automatically taken care of using `zygoat` so that you can get up and running faster.
`zygoat` also includes a preset deployment configuration to allow you to deploy your stack to an AWS environment with a single command. You'll get a full serverless AWS stack to keep things inexpensive and nimble.
## How does it work?
`zygoat` works by defining `Components`, defined as parts of projects, and then defining how you implement those components based on whether you're creating a new project, updating an existing project, or deleting a component that's no longer needed.
For instance, for the python backend, we want to include `black`, which is a tool for automatically formatting python code in a standard way to make it pep8 compliant. To install `black` in for the python backend part of the project, we create a `Component` for it, specifically a `FileComponent`, which defines how we treat files that we need in projects. Then we register the `Black` component (defined in [black.py](https://github.com/bequest/zygoat/blob/master/zygoat/components/backend/black.py)) with the `Backend` component (defined in [backend/\_\_init\_\_.py](https://github.com/bequest/zygoat/blob/master/zygoat/components/backend/__init__.py)) as a sub component. This way, whenever you create or update (or delete) a project with the `Backend` component, you'll do the same 'phase' to the `Black` component.
## Installation
```bash
pip install --upgrade zygoat
```
## Usage
```bash
mkdir my-cool-new-app && cd my-cool-new-app
git init
zg new my-cool-new-app
```
For more customization and configuration, [check out the official documentation](https://zygoat.readthedocs.io/en/latest/).
## How do I develop changes for it?
Make a new git repository somewhere, we'll call it test-zg
```bash
mkdir test-zg && cd test-zg
git init
```
Install the zygoat package locally
```bash
pip install --user --upgrade ~/Projects/zygoat # Or wherever you have it
```
If you're using the asdf version manager, reshim
```bash
asdf reshim python
```
Run zg commands, see if they fail
```bash
zg new test
zg update
zg delete
```
---
## Contributing
`zygoat` is developed using the [Poetry](https://python-poetry.org/docs/) packaging framework for Python projects to make development as simple and portable as possible.
---
## Documentation
[Available on ReadTheDocs](https://zygoat.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)
|
zygoat
|
/zygoat-1.19.0.tar.gz/zygoat-1.19.0/README.md
|
README.md
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from setuptools import setup
packages = \
['zygoat',
'zygoat.components',
'zygoat.components.backend',
'zygoat.components.backend.flake8',
'zygoat.components.backend.flake8.resources',
'zygoat.components.backend.resources',
'zygoat.components.backend.settings',
'zygoat.components.frontend',
'zygoat.components.frontend.cypress',
'zygoat.components.frontend.cypress.resources',
'zygoat.components.frontend.dependencies',
'zygoat.components.frontend.dependencies.resources',
'zygoat.components.frontend.eslint',
'zygoat.components.frontend.eslint.resources',
'zygoat.components.frontend.prettier',
'zygoat.components.frontend.prettier.resources',
'zygoat.components.frontend.resources',
'zygoat.components.proxy',
'zygoat.components.proxy.resources',
'zygoat.components.resources',
'zygoat.utils']
package_data = \
{'': ['*']}
install_requires = \
['click>=8.0.1,<9.0.0',
'colorama>=0.4.4,<0.5.0',
'importlib-metadata>=4.11.3,<5.0.0',
'python-box[all]>=5.3.0,<6.0.0',
'redbaron>=0.9.2,<0.10.0',
'requests>=2.26.0,<3.0.0',
'rtd-poetry>=0.1.0,<0.2.0',
'ruamel.yaml>=0.17.10,<0.18.0',
'semver>=2.13.0,<3.0.0',
'toml>=0.10.2,<0.11.0',
'virtualenv>=20.7.0,<21.0.0']
entry_points = \
{'console_scripts': ['zg = zygoat.cli:cli']}
setup_kwargs = {
'name': 'zygoat',
'version': '1.19.0',
'description': '',
'long_description': '# zygoat\n\n<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/640862/75250233-e287ea80-57a5-11ea-9d9f-553662a17706.jpeg" />\n\n## What is zygoat?\n\n`zygoat` is a command line tool used to bootstrap and configure a React/Django/Postgres stack web application.\n\nLinting, test configuration, boilerplate, and development environment are automatically taken care of using `zygoat` so that you can get up and running faster.\n\n`zygoat` also includes a preset deployment configuration to allow you to deploy your stack to an AWS environment with a single command. You\'ll get a full serverless AWS stack to keep things inexpensive and nimble.\n\n## How does it work?\n\n`zygoat` works by defining `Components`, defined as parts of projects, and then defining how you implement those components based on whether you\'re creating a new project, updating an existing project, or deleting a component that\'s no longer needed.\n\nFor instance, for the python backend, we want to include `black`, which is a tool for automatically formatting python code in a standard way to make it pep8 compliant. To install `black` in for the python backend part of the project, we create a `Component` for it, specifically a `FileComponent`, which defines how we treat files that we need in projects. Then we register the `Black` component (defined in [black.py](https://github.com/bequest/zygoat/blob/master/zygoat/components/backend/black.py)) with the `Backend` component (defined in [backend/\\_\\_init\\_\\_.py](https://github.com/bequest/zygoat/blob/master/zygoat/components/backend/__init__.py)) as a sub component. This way, whenever you create or update (or delete) a project with the `Backend` component, you\'ll do the same \'phase\' to the `Black` component.\n\n## Installation\n\n```bash\npip install --upgrade zygoat\n```\n\n## Usage\n\n```bash\nmkdir my-cool-new-app && cd my-cool-new-app\ngit init\nzg new my-cool-new-app\n```\n\nFor more customization and configuration, [check out the official documentation](https://zygoat.readthedocs.io/en/latest/).\n\n## How do I develop changes for it?\n\nMake a new git repository somewhere, we\'ll call it test-zg\n\n```bash\nmkdir test-zg && cd test-zg\ngit init\n```\n\nInstall the zygoat package locally\n\n```bash\npip install --user --upgrade ~/Projects/zygoat # Or wherever you have it\n```\n\nIf you\'re using the asdf version manager, reshim\n\n```bash\nasdf reshim python\n```\n\nRun zg commands, see if they fail\n\n```bash\nzg new test\nzg update\nzg delete\n```\n\n---\n\n## Contributing\n\n`zygoat` is developed using the [Poetry](https://python-poetry.org/docs/) packaging framework for Python projects to make development as simple and portable as possible.\n\n---\n\n## Documentation\n\n[Available on ReadTheDocs](https://zygoat.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)\n',
'author': 'Bequest, Inc.',
'author_email': '[email protected]',
'maintainer': 'None',
'maintainer_email': 'None',
'url': 'None',
'packages': packages,
'package_data': package_data,
'install_requires': install_requires,
'entry_points': entry_points,
'python_requires': '>=3.7,<4.0',
}
setup(**setup_kwargs)
|
zygoat
|
/zygoat-1.19.0.tar.gz/zygoat-1.19.0/setup.py
|
setup.py
|
Zygomorphic
===========
Author: `Scott Torborg <http://www.scotttorborg.com>`_
Example package to figure out bumpr.
License
=======
Zygomorphic is licensed under an MIT license. Please see the LICENSE file for
more information.
|
zygomorphic
|
/zygomorphic-0.2.3.tar.gz/zygomorphic-0.2.3/README.rst
|
README.rst
|
from __future__ import print_function
from setuptools import setup, find_packages
setup(name='zygomorphic',
version='0.2.3',
description='Zygomorphic!',
long_description='',
classifiers=[
'Development Status :: 2 - Pre-Alpha',
'License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License',
'Programming Language :: Python :: 2',
'Programming Language :: Python :: 2.7',
'Topic :: Multimedia :: Graphics',
],
keywords='bumpr test',
url='https://github.com/storborg/zygomorphic',
author='Scott Torborg',
author_email='[email protected]',
install_requires=[
'six>=1.5.2',
],
license='MIT',
packages=find_packages(),
test_suite='nose.collector',
tests_require=['nose'],
include_package_data=True,
zip_safe=False)
|
zygomorphic
|
/zygomorphic-0.2.3.tar.gz/zygomorphic-0.2.3/setup.py
|
setup.py
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
from setuptools import find_packages
from setuptools import setup
setup(
name = 'zygote',
version = '0.5.3',
author = 'Evan Klitzke',
author_email = '[email protected]',
description = 'A tornado HTTP worker management tool',
license = 'Apache License 2.0',
entry_points = {'console_scripts': 'zygote = zygote.main:main'},
packages = find_packages(exclude=['tests']),
install_requires = ['setuptools', 'tornado'],
include_package_data = True,
)
|
zygote
|
/zygote-0.5.3.tar.gz/zygote-0.5.3/setup.py
|
setup.py
|
import logging
import time
import tornado.web
start_time = time.time()
log = logging.getLogger('example')
log.debug('started up')
class StatusHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.content_type = 'text/plain'
self.write('uptime: %1.3f\n' % (time.time() - start_time))
def initialize(*args, **kwargs):
pass
def get_application(*args, **kwargs):
log.debug('creating application for \'example\'')
return tornado.web.Application([('/', StatusHandler)], debug=False)
|
zygote
|
/zygote-0.5.3.tar.gz/zygote-0.5.3/example/example.py
|
example.py
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Generated by the protocol buffer compiler. DO NOT EDIT!
# source: proto/zhiyan_rpc.proto
"""Generated protocol buffer code."""
from google.protobuf import descriptor as _descriptor
from google.protobuf import descriptor_pool as _descriptor_pool
from google.protobuf import message as _message
from google.protobuf import reflection as _reflection
from google.protobuf import symbol_database as _symbol_database
# @@protoc_insertion_point(imports)
_sym_db = _symbol_database.Default()
DESCRIPTOR = _descriptor_pool.Default().AddSerializedFile(b'\n\x16proto/zhiyan_rpc.proto\x12\nzhiyan_rpc\"O\n\rZhiYanRequest\x12\x10\n\x08mod_name\x18\x01 \x01(\t\x12\x0c\n\x04host\x18\x02 \x01(\t\x12\x0c\n\x04time\x18\x03 \x01(\t\x12\x10\n\x08metrices\x18\x04 \x01(\t\"/\n\x0eZhiYanResponse\x12\x0c\n\x04\x63ode\x18\x01 \x01(\t\x12\x0f\n\x07message\x18\x02 \x01(\t\"i\n\x1bZhiYanRegisterModuleRequest\x12\x0c\n\x04name\x18\x01 \x01(\t\x12\x0f\n\x07\x63ontent\x18\x02 \x01(\t\x12\r\n\x05token\x18\x03 \x01(\t\x12\x0c\n\x04host\x18\x04 \x01(\t\x12\x0e\n\x06\x63onfig\x18\x05 \x01(\t\"=\n\x1cZhiYanRegisterModuleResponse\x12\x0c\n\x04\x63ode\x18\x01 \x01(\t\x12\x0f\n\x07message\x18\x02 \x01(\t\"Q\n\x12ZhiYanEventRequest\x12\x10\n\x08mod_name\x18\x01 \x01(\t\x12\x0c\n\x04host\x18\x02 \x01(\t\x12\x0c\n\x04time\x18\x03 \x01(\t\x12\r\n\x05\x65vent\x18\x04 \x01(\t\"4\n\x13ZhiYanEventResponse\x12\x0c\n\x04\x63ode\x18\x01 \x01(\t\x12\x0f\n\x07message\x18\x02 \x01(\t2\x85\x02\n\rZhiYanService\x12@\n\x05zymod\x12\x19.zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanRequest\x1a\x1a.zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanResponse\"\x00\x12\x64\n\rzyregistermod\x12\'.zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanRegisterModuleRequest\x1a(.zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanRegisterModuleResponse\"\x00\x12L\n\x07zyevent\x12\x1e.zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanEventRequest\x1a\x1f.zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanEventResponse\"\x00\x62\x06proto3')
_ZHIYANREQUEST = DESCRIPTOR.message_types_by_name['ZhiYanRequest']
_ZHIYANRESPONSE = DESCRIPTOR.message_types_by_name['ZhiYanResponse']
_ZHIYANREGISTERMODULEREQUEST = DESCRIPTOR.message_types_by_name['ZhiYanRegisterModuleRequest']
_ZHIYANREGISTERMODULERESPONSE = DESCRIPTOR.message_types_by_name['ZhiYanRegisterModuleResponse']
_ZHIYANEVENTREQUEST = DESCRIPTOR.message_types_by_name['ZhiYanEventRequest']
_ZHIYANEVENTRESPONSE = DESCRIPTOR.message_types_by_name['ZhiYanEventResponse']
ZhiYanRequest = _reflection.GeneratedProtocolMessageType('ZhiYanRequest', (_message.Message,), {
'DESCRIPTOR' : _ZHIYANREQUEST,
'__module__' : 'proto.zhiyan_rpc_pb2'
# @@protoc_insertion_point(class_scope:zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanRequest)
})
_sym_db.RegisterMessage(ZhiYanRequest)
ZhiYanResponse = _reflection.GeneratedProtocolMessageType('ZhiYanResponse', (_message.Message,), {
'DESCRIPTOR' : _ZHIYANRESPONSE,
'__module__' : 'proto.zhiyan_rpc_pb2'
# @@protoc_insertion_point(class_scope:zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanResponse)
})
_sym_db.RegisterMessage(ZhiYanResponse)
ZhiYanRegisterModuleRequest = _reflection.GeneratedProtocolMessageType('ZhiYanRegisterModuleRequest', (_message.Message,), {
'DESCRIPTOR' : _ZHIYANREGISTERMODULEREQUEST,
'__module__' : 'proto.zhiyan_rpc_pb2'
# @@protoc_insertion_point(class_scope:zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanRegisterModuleRequest)
})
_sym_db.RegisterMessage(ZhiYanRegisterModuleRequest)
ZhiYanRegisterModuleResponse = _reflection.GeneratedProtocolMessageType('ZhiYanRegisterModuleResponse', (_message.Message,), {
'DESCRIPTOR' : _ZHIYANREGISTERMODULERESPONSE,
'__module__' : 'proto.zhiyan_rpc_pb2'
# @@protoc_insertion_point(class_scope:zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanRegisterModuleResponse)
})
_sym_db.RegisterMessage(ZhiYanRegisterModuleResponse)
ZhiYanEventRequest = _reflection.GeneratedProtocolMessageType('ZhiYanEventRequest', (_message.Message,), {
'DESCRIPTOR' : _ZHIYANEVENTREQUEST,
'__module__' : 'proto.zhiyan_rpc_pb2'
# @@protoc_insertion_point(class_scope:zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanEventRequest)
})
_sym_db.RegisterMessage(ZhiYanEventRequest)
ZhiYanEventResponse = _reflection.GeneratedProtocolMessageType('ZhiYanEventResponse', (_message.Message,), {
'DESCRIPTOR' : _ZHIYANEVENTRESPONSE,
'__module__' : 'proto.zhiyan_rpc_pb2'
# @@protoc_insertion_point(class_scope:zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanEventResponse)
})
_sym_db.RegisterMessage(ZhiYanEventResponse)
_ZHIYANSERVICE = DESCRIPTOR.services_by_name['ZhiYanService']
if _descriptor._USE_C_DESCRIPTORS == False:
DESCRIPTOR._options = None
_ZHIYANREQUEST._serialized_start=38
_ZHIYANREQUEST._serialized_end=117
_ZHIYANRESPONSE._serialized_start=119
_ZHIYANRESPONSE._serialized_end=166
_ZHIYANREGISTERMODULEREQUEST._serialized_start=168
_ZHIYANREGISTERMODULEREQUEST._serialized_end=273
_ZHIYANREGISTERMODULERESPONSE._serialized_start=275
_ZHIYANREGISTERMODULERESPONSE._serialized_end=336
_ZHIYANEVENTREQUEST._serialized_start=338
_ZHIYANEVENTREQUEST._serialized_end=419
_ZHIYANEVENTRESPONSE._serialized_start=421
_ZHIYANEVENTRESPONSE._serialized_end=473
_ZHIYANSERVICE._serialized_start=476
_ZHIYANSERVICE._serialized_end=737
# @@protoc_insertion_point(module_scope)
|
zygrpc
|
/zygrpc-0.0.1.15-py3-none-any.whl/proto/zhiyan_rpc_pb2.py
|
zhiyan_rpc_pb2.py
|
# Generated by the gRPC Python protocol compiler plugin. DO NOT EDIT!
"""Client and server classes corresponding to protobuf-defined services."""
import grpc
from proto import zhiyan_rpc_pb2 as proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2
class ZhiYanServiceStub(object):
"""Missing associated documentation comment in .proto file."""
def __init__(self, channel):
"""Constructor.
Args:
channel: A grpc.Channel.
"""
self.zymod = channel.unary_unary(
'/zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanService/zymod',
request_serializer=proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanRequest.SerializeToString,
response_deserializer=proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanResponse.FromString,
)
self.zyregistermod = channel.unary_unary(
'/zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanService/zyregistermod',
request_serializer=proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanRegisterModuleRequest.SerializeToString,
response_deserializer=proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanRegisterModuleResponse.FromString,
)
self.zyevent = channel.unary_unary(
'/zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanService/zyevent',
request_serializer=proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanEventRequest.SerializeToString,
response_deserializer=proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanEventResponse.FromString,
)
class ZhiYanServiceServicer(object):
"""Missing associated documentation comment in .proto file."""
def zymod(self, request, context):
"""Missing associated documentation comment in .proto file."""
context.set_code(grpc.StatusCode.UNIMPLEMENTED)
context.set_details('Method not implemented!')
raise NotImplementedError('Method not implemented!')
def zyregistermod(self, request, context):
"""Missing associated documentation comment in .proto file."""
context.set_code(grpc.StatusCode.UNIMPLEMENTED)
context.set_details('Method not implemented!')
raise NotImplementedError('Method not implemented!')
def zyevent(self, request, context):
"""Missing associated documentation comment in .proto file."""
context.set_code(grpc.StatusCode.UNIMPLEMENTED)
context.set_details('Method not implemented!')
raise NotImplementedError('Method not implemented!')
def add_ZhiYanServiceServicer_to_server(servicer, server):
rpc_method_handlers = {
'zymod': grpc.unary_unary_rpc_method_handler(
servicer.zymod,
request_deserializer=proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanRequest.FromString,
response_serializer=proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanResponse.SerializeToString,
),
'zyregistermod': grpc.unary_unary_rpc_method_handler(
servicer.zyregistermod,
request_deserializer=proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanRegisterModuleRequest.FromString,
response_serializer=proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanRegisterModuleResponse.SerializeToString,
),
'zyevent': grpc.unary_unary_rpc_method_handler(
servicer.zyevent,
request_deserializer=proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanEventRequest.FromString,
response_serializer=proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanEventResponse.SerializeToString,
),
}
generic_handler = grpc.method_handlers_generic_handler(
'zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanService', rpc_method_handlers)
server.add_generic_rpc_handlers((generic_handler,))
# This class is part of an EXPERIMENTAL API.
class ZhiYanService(object):
"""Missing associated documentation comment in .proto file."""
@staticmethod
def zymod(request,
target,
options=(),
channel_credentials=None,
call_credentials=None,
insecure=False,
compression=None,
wait_for_ready=None,
timeout=None,
metadata=None):
return grpc.experimental.unary_unary(request, target, '/zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanService/zymod',
proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanRequest.SerializeToString,
proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanResponse.FromString,
options, channel_credentials,
insecure, call_credentials, compression, wait_for_ready, timeout, metadata)
@staticmethod
def zyregistermod(request,
target,
options=(),
channel_credentials=None,
call_credentials=None,
insecure=False,
compression=None,
wait_for_ready=None,
timeout=None,
metadata=None):
return grpc.experimental.unary_unary(request, target, '/zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanService/zyregistermod',
proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanRegisterModuleRequest.SerializeToString,
proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanRegisterModuleResponse.FromString,
options, channel_credentials,
insecure, call_credentials, compression, wait_for_ready, timeout, metadata)
@staticmethod
def zyevent(request,
target,
options=(),
channel_credentials=None,
call_credentials=None,
insecure=False,
compression=None,
wait_for_ready=None,
timeout=None,
metadata=None):
return grpc.experimental.unary_unary(request, target, '/zhiyan_rpc.ZhiYanService/zyevent',
proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanEventRequest.SerializeToString,
proto_dot_zhiyan__rpc__pb2.ZhiYanEventResponse.FromString,
options, channel_credentials,
insecure, call_credentials, compression, wait_for_ready, timeout, metadata)
|
zygrpc
|
/zygrpc-0.0.1.15-py3-none-any.whl/proto/zhiyan_rpc_pb2_grpc.py
|
zhiyan_rpc_pb2_grpc.py
|
def available():
print("The powerful tools are setup!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
available()
|
zyh
|
/zyh-0.0.2-py3-none-any.whl/zyh-0.0.2.data/scripts/setup_test.py
|
setup_test.py
|
""" This is noly a test1 from head first python.
This module is my first try for python."""
import sys
def print_lol(the_list, indent = False, level = 0, fn = sys.stdout) :
for each_item in the_list :
if isinstance(each_item, list) :
print_lol(each_item,indent, level+1, fn)
else:
if indent :
for tap_stop in range(level) :
print ("\t",end='', file = fn)
print (each_item, file = fn)
|
zyk_hfp_test1
|
/zyk_hfp_test1-1.4.0.zip/zyk_hfp_test1-1.4.0/zyk_hfp_test1.py
|
zyk_hfp_test1.py
|
from distutils.core import setup
setup(
name = 'zyk_hfp_test1',
version = '1.4.0',
py_modules = ['zyk_hfp_test1'],
author = 'zyk',
author_email = '[email protected]',
url = 'null',
description = 'just a test',
)
|
zyk_hfp_test1
|
/zyk_hfp_test1-1.4.0.zip/zyk_hfp_test1-1.4.0/setup.py
|
setup.py
|
==========
Zyklop ◎
==========
This program is a wrapper around rsync. It will help you:
* if you need to sync files from remote server frequently
* No need to keep the location of the file in your mind. It finds
them for you.
Requirements
==============
* Python >= 2.6 (Python >= 2.7 for tests)
* rsync installed
* locate installed with up-to-date database on the remote system
First Steps
===========
If you are new to ssh, setup an ssh configuration first. If you are
dealing with a lot of servers, giving them an alias makes them easier to
remember and you don't have to type as much.
#. Create an ssh configuration in your SSH home, e.g.::
vim ~/.ssh/config
You can use the following example as a starter::
Host spameggs
Hostname 12.112.11.122
Compression yes
CompressionLevel 9
User guido
but be sure to check the `documentation
<https://duckduckgo.com/?q=ssh+config+documentation&t=canonical>`_
or the man page (5) for `ssh_config`
#. Make the config only readable for the owner::
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/config
#. Test if you can login to your configured host using only your
alias::
ssh spameggs
Examples
========
#. Syncing ZODB from remote server configured in ``~/.ssh/config``
as spameggs. We choose not the first database, but the second::
$ zyklop spameggs:Data.fs .
Use /opt/otherbuildout/var/filestorage/Data.fs? Y(es)/N(o)/A(bort) n
Use /opt/buildout/var/filestorage/Data.fs? Y(es)/N(o)/A(bort) y
#. Syncing a directory providing a path segment::
$ zyklop spameggs:buildout/var/filestorage$ .
#. Syncing a directory which ends with `blobstorage``, excluding any
other `blobstorage` directories with postfixes in the name (e.g.
`blobstorage.old`)::
$ zyklop spameggs:blobstorage$ .
#. Use an **absolute path** if you know exactly where to copy from::
$ zyklop spameggs:/tmp/Data.fs .
#. Syncing a directory which needs higher privileges. We use the
``-s`` argument::
$ zyklop -s spameggs:blobstorage$ .
#. **Dry run** prints out all found remote paths and just exits::
$ zyklop -d spameggs:blobstorage$ .
/opt/otherbuildout/var/blobstorage
/opt/otherbuildout/var/blobstorage.old
/opt/buildout/var/blobstorag
#. Sync the first result zyklop finds automatically **without
prompting**::
$ zyklop -y spameggs:blobstorage$ .
Known Problems
--------------
Zyklop just hangs
This can be caused by paramiko and a not sufficient SSH setup. Make
sure you can login without problems by simply issuing a::
ssh myhost
If that does not solve your problem, try to provide an absolute path
from the source. Sometimes users don't have many privileges on the
remote server and the paramiko just waits for the output of a remote
command::
zyklop myhost:/path/to/file .
Motivation
==========
I'm dealing with Zope servers most of my time. Some of them have a
*huge* Data.fs - an object oriented database. I do have in 99% of the
cases an older version of the clients database on my PC. Copying the
whole database will take me ages. Using rsync and simply downloading a
binary patch makes updating my local database a quick thing.
To summarize, with zyklop I'd like to address two things:
1. Downloading large ZODBs takes a long time and
bandwidth. I simply don't want to wait that long and download that
much.
2. Most of the time I can not remember the exact path where the item
to copy is on the remote server.
TODO
====
* tty support: sometimes needed if SSH is configured to only allow
tty's to connect.
* Don't hang if only password auth is configured for SSH
Development
===========
If you're interested in hacking, clone zyklop on github:
https://github.com/romanofski/zyklop
|
zyklop
|
/zyklop-0.5.2.zip/zyklop-0.5.2/README.rst
|
README.rst
|
# coding: utf-8
from setuptools import setup, find_packages
from zyklop import __author__
from zyklop import __author_email__
from zyklop import __description__
from zyklop import __name__
from zyklop import __version__
setup(
name=__name__,
version=__version__,
description=__description__,
long_description=(
open("README.rst").read() + '\n\n' +
open("docs/CHANGES.txt").read()
),
classifiers=[
"Environment :: Console",
"Intended Audience :: Developers",
"License :: OSI Approved :: GNU General Public License (GPL)",
"Programming Language :: Python",
"Topic :: Internet",
"Topic :: Software Development :: Libraries :: Python Modules",
"Topic :: System :: Archiving :: Backup",
"Topic :: System :: Archiving :: Mirroring",
"Topic :: System :: Systems Administration",
],
keywords='server',
author=__author__,
author_email=__author_email__,
url='http://zyklop.rtfd.org',
license='GPL',
packages=find_packages(exclude=['ez_setup']),
include_package_data=True,
zip_safe=False,
install_requires=[
'setuptools',
'paramiko',
'argparse',
],
extras_require=dict(
test=['mock', ]
),
entry_points={
'console_scripts': [
'zyklop = zyklop.command:sync',
]
}
)
|
zyklop
|
/zyklop-0.5.2.zip/zyklop-0.5.2/setup.py
|
setup.py
|
##############################################################################
#
# Copyright (c) 2006 Zope Corporation and Contributors.
# All Rights Reserved.
#
# This software is subject to the provisions of the Zope Public License,
# Version 2.1 (ZPL). A copy of the ZPL should accompany this distribution.
# THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND ANY AND ALL EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
# WARRANTIES ARE DISCLAIMED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
# WARRANTIES OF TITLE, MERCHANTABILITY, AGAINST INFRINGEMENT, AND FITNESS
# FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
#
##############################################################################
"""Bootstrap a buildout-based project
Simply run this script in a directory containing a buildout.cfg.
The script accepts buildout command-line options, so you can
use the -c option to specify an alternate configuration file.
"""
import os, shutil, sys, tempfile, urllib2
from optparse import OptionParser
tmpeggs = tempfile.mkdtemp()
is_jython = sys.platform.startswith('java')
# parsing arguments
parser = OptionParser()
parser.add_option("-v", "--version", dest="version",
help="use a specific zc.buildout version")
parser.add_option("-d", "--distribute",
action="store_true", dest="distribute", default=False,
help="Use Disribute rather than Setuptools.")
parser.add_option("-c", None, action="store", dest="config_file",
help=("Specify the path to the buildout configuration "
"file to be used."))
options, args = parser.parse_args()
# if -c was provided, we push it back into args for buildout' main function
if options.config_file is not None:
args += ['-c', options.config_file]
if options.version is not None:
VERSION = '==%s' % options.version
else:
VERSION = ''
# We decided to always use distribute, make sure this is the default for us
# USE_DISTRIBUTE = options.distribute
USE_DISTRIBUTE = True
args = args + ['bootstrap']
to_reload = False
try:
import pkg_resources
if not hasattr(pkg_resources, '_distribute'):
to_reload = True
raise ImportError
except ImportError:
ez = {}
if USE_DISTRIBUTE:
exec urllib2.urlopen('http://python-distribute.org/distribute_setup.py'
).read() in ez
ez['use_setuptools'](to_dir=tmpeggs, download_delay=0, no_fake=True)
else:
exec urllib2.urlopen('http://peak.telecommunity.com/dist/ez_setup.py'
).read() in ez
ez['use_setuptools'](to_dir=tmpeggs, download_delay=0)
if to_reload:
reload(pkg_resources)
else:
import pkg_resources
if sys.platform == 'win32':
def quote(c):
if ' ' in c:
return '"%s"' % c # work around spawn lamosity on windows
else:
return c
else:
def quote (c):
return c
cmd = 'from setuptools.command.easy_install import main; main()'
ws = pkg_resources.working_set
if USE_DISTRIBUTE:
requirement = 'distribute'
else:
requirement = 'setuptools'
if is_jython:
import subprocess
assert subprocess.Popen([sys.executable] + ['-c', quote(cmd), '-mqNxd',
quote(tmpeggs), 'zc.buildout' + VERSION],
env=dict(os.environ,
PYTHONPATH=
ws.find(pkg_resources.Requirement.parse(requirement)).location
),
).wait() == 0
else:
assert os.spawnle(
os.P_WAIT, sys.executable, quote (sys.executable),
'-c', quote (cmd), '-mqNxd', quote (tmpeggs), 'zc.buildout' + VERSION,
dict(os.environ,
PYTHONPATH=
ws.find(pkg_resources.Requirement.parse(requirement)).location
),
) == 0
ws.add_entry(tmpeggs)
ws.require('zc.buildout' + VERSION)
import zc.buildout.buildout
zc.buildout.buildout.main(args)
shutil.rmtree(tmpeggs)
|
zyklop
|
/zyklop-0.5.2.zip/zyklop-0.5.2/bootstrap.py
|
bootstrap.py
|
.. zyklop documentation master file, created by
sphinx-quickstart on Thu Feb 9 18:32:45 2012.
You can adapt this file completely to your liking, but it should at least
contain the root `toctree` directive.
.. moduleauthor:: Róman Joost <[email protected]>
.. default-domain:: py
.. toctree::
:maxdepth: 2
.. include:: ../README.rst
.. include:: CHANGES.txt
API
===
.. automodule:: zyklop
:members:
SSH
---
.. automodule:: zyklop.ssh
:members:
Implemented Search
------------------
.. automodule:: zyklop.search
:members:
Indices and tables
==================
* :ref:`genindex`
* :ref:`modindex`
* :ref:`search`
|
zyklop
|
/zyklop-0.5.2.zip/zyklop-0.5.2/docs/index.rst
|
index.rst
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#
# zyklop documentation build configuration file, created by
# sphinx-quickstart on Thu Feb 9 18:32:45 2012.
#
# This file is execfile()d with the current directory set to its containing dir.
#
# Note that not all possible configuration values are present in this
# autogenerated file.
#
# All configuration values have a default; values that are commented out
# serve to show the default.
import sys, os
# If extensions (or modules to document with autodoc) are in another directory,
# add these directories to sys.path here. If the directory is relative to the
# documentation root, use os.path.abspath to make it absolute, like shown here.
sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath('..'))
# -- General configuration -----------------------------------------------------
# If your documentation needs a minimal Sphinx version, state it here.
#needs_sphinx = '1.0'
# Add any Sphinx extension module names here, as strings. They can be extensions
# coming with Sphinx (named 'sphinx.ext.*') or your custom ones.
extensions = ['sphinx.ext.autodoc', 'sphinx.ext.doctest', 'sphinx.ext.intersphinx', 'sphinx.ext.todo', 'sphinx.ext.coverage', 'sphinx.ext.ifconfig', 'sphinx.ext.viewcode']
# Add any paths that contain templates here, relative to this directory.
templates_path = ['_templates']
# The suffix of source filenames.
source_suffix = '.rst'
# The encoding of source files.
#source_encoding = 'utf-8-sig'
# The master toctree document.
master_doc = 'index'
# General information about the project.
project = u'zyklop'
copyright = u'2012, Roman Joost'
# The version info for the project you're documenting, acts as replacement for
# |version| and |release|, also used in various other places throughout the
# built documents.
#
# The short X.Y version.
version = '0.5'
# The full version, including alpha/beta/rc tags.
release = '0.5'
# The language for content autogenerated by Sphinx. Refer to documentation
# for a list of supported languages.
#language = None
# There are two options for replacing |today|: either, you set today to some
# non-false value, then it is used:
#today = ''
# Else, today_fmt is used as the format for a strftime call.
#today_fmt = '%B %d, %Y'
# List of patterns, relative to source directory, that match files and
# directories to ignore when looking for source files.
exclude_patterns = []
# The reST default role (used for this markup: `text`) to use for all documents.
#default_role = None
# If true, '()' will be appended to :func: etc. cross-reference text.
#add_function_parentheses = True
# If true, the current module name will be prepended to all description
# unit titles (such as .. function::).
#add_module_names = True
# If true, sectionauthor and moduleauthor directives will be shown in the
# output. They are ignored by default.
#show_authors = False
# The name of the Pygments (syntax highlighting) style to use.
pygments_style = 'sphinx'
# A list of ignored prefixes for module index sorting.
#modindex_common_prefix = []
# -- Options for HTML output ---------------------------------------------------
# The theme to use for HTML and HTML Help pages. See the documentation for
# a list of builtin themes.
html_theme = 'default'
# Theme options are theme-specific and customize the look and feel of a theme
# further. For a list of options available for each theme, see the
# documentation.
#html_theme_options = {}
# Add any paths that contain custom themes here, relative to this directory.
#html_theme_path = []
# The name for this set of Sphinx documents. If None, it defaults to
# "<project> v<release> documentation".
#html_title = None
# A shorter title for the navigation bar. Default is the same as html_title.
#html_short_title = None
# The name of an image file (relative to this directory) to place at the top
# of the sidebar.
#html_logo = None
# The name of an image file (within the static path) to use as favicon of the
# docs. This file should be a Windows icon file (.ico) being 16x16 or 32x32
# pixels large.
#html_favicon = None
# Add any paths that contain custom static files (such as style sheets) here,
# relative to this directory. They are copied after the builtin static files,
# so a file named "default.css" will overwrite the builtin "default.css".
html_static_path = ['_static']
# If not '', a 'Last updated on:' timestamp is inserted at every page bottom,
# using the given strftime format.
#html_last_updated_fmt = '%b %d, %Y'
# If true, SmartyPants will be used to convert quotes and dashes to
# typographically correct entities.
#html_use_smartypants = True
# Custom sidebar templates, maps document names to template names.
#html_sidebars = {}
# Additional templates that should be rendered to pages, maps page names to
# template names.
#html_additional_pages = {}
# If false, no module index is generated.
#html_domain_indices = True
# If false, no index is generated.
#html_use_index = True
# If true, the index is split into individual pages for each letter.
#html_split_index = False
# If true, links to the reST sources are added to the pages.
#html_show_sourcelink = True
# If true, "Created using Sphinx" is shown in the HTML footer. Default is True.
#html_show_sphinx = True
# If true, "(C) Copyright ..." is shown in the HTML footer. Default is True.
#html_show_copyright = True
# If true, an OpenSearch description file will be output, and all pages will
# contain a <link> tag referring to it. The value of this option must be the
# base URL from which the finished HTML is served.
#html_use_opensearch = ''
# This is the file name suffix for HTML files (e.g. ".xhtml").
#html_file_suffix = None
# Output file base name for HTML help builder.
htmlhelp_basename = 'zyklopdoc'
# -- Options for LaTeX output --------------------------------------------------
# The paper size ('letter' or 'a4').
#latex_paper_size = 'letter'
# The font size ('10pt', '11pt' or '12pt').
#latex_font_size = '10pt'
# Grouping the document tree into LaTeX files. List of tuples
# (source start file, target name, title, author, documentclass [howto/manual]).
latex_documents = [
('README', 'zyklop.tex', u'zyklop Documentation',
u'Roman Joost', 'manual'),
]
# The name of an image file (relative to this directory) to place at the top of
# the title page.
#latex_logo = None
# For "manual" documents, if this is true, then toplevel headings are parts,
# not chapters.
#latex_use_parts = False
# If true, show page references after internal links.
#latex_show_pagerefs = False
# If true, show URL addresses after external links.
#latex_show_urls = False
# Additional stuff for the LaTeX preamble.
#latex_preamble = ''
# Documents to append as an appendix to all manuals.
#latex_appendices = []
# If false, no module index is generated.
#latex_domain_indices = True
# -- Options for manual page output --------------------------------------------
# One entry per manual page. List of tuples
# (source start file, name, description, authors, manual section).
man_pages = [
('README', 'zyklop', u'zyklop Documentation',
[u'Roman Joost'], 1)
]
# Example configuration for intersphinx: refer to the Python standard library.
intersphinx_mapping = {'http://docs.python.org/': None}
|
zyklop
|
/zyklop-0.5.2.zip/zyklop-0.5.2/docs/conf.py
|
conf.py
|
#Zyklus
A simple event loop for executing functions within the loop's thread.
## Usage
### Current thread
```python
from zyklus import Zyklus
def output(what):
print(what)
zyklus = Zyklus()
zyklus.post(lambda: output(1))
zyklus.post(lambda: output(2))
zyklus.post(lambda: output(3))
zyklus.post_delayed(lambda: output(5), 1)
zyklus.post(lambda: output(4))
zyklus.post_delayed(zyklus.terminate, 1.1)
zyklus.loop()
output("done")
```
output:
```
1
2
3
4
5
done
```
### In background
```python
from zyklus import Zyklus
import threading
def output(what):
print(what)
zyklus = Zyklus()
zyklusThread = threading.Thread(target=zyklus.loop)
zyklusThread.start()
zyklus.post(lambda: output(1))
zyklus.post(lambda: output(2))
zyklus.post(lambda: output(3))
zyklus.post_delayed(lambda: output(5), 1)
zyklus.post(lambda: output(4))
zyklus.post_delayed(zyklus.terminate, 1.5)
zyklusThread.join()
output("done")
```
output:
```
1
2
3
4
5
done
```
## Installation
```
pip install zyklus
```
|
zyklus
|
/zyklus-0.2.tar.gz/zyklus-0.2/README.md
|
README.md
|
#!/usr/bin/env python
from __future__ import print_function
from setuptools import setup, find_packages
import zyklus
setup(
name='zyklus',
version=zyklus.__version__,
url='http://github.com/tgalal/zyklus/',
license='MIT',
author='Tarek Galal',
tests_require=[],
install_requires = [],
author_email='[email protected]',
description='A simple event loop library',
#long_description=long_description,
packages= find_packages(),
include_package_data=True,
platforms='any',
# test_suite='',
classifiers = [
'Programming Language :: Python',
'Development Status :: 4 - Beta',
'Natural Language :: English',
#'Environment :: Web Environment',
'Intended Audience :: Developers',
'License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License',
'Operating System :: OS Independent',
'Topic :: Software Development :: Libraries :: Python Modules'
],
)
|
zyklus
|
/zyklus-0.2.tar.gz/zyklus-0.2/setup.py
|
setup.py
|
# _data_utils_ and _model_utils_
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/README.md
|
README.md
|
from setuptools import setup, find_packages
setup(
name='zyl_utils',
version='0.1.4',
description=(
'optimizer'
),
long_description=open('README.md').read(),
long_description_content_type='text/markdown',
author='zyl',
author_email='[email protected]',
maintainer='zyl',
maintainer_email='[email protected]',
packages=find_packages(),
platforms=["all"],
url='https://github.com/ZYuliang/zyl-utils',
install_requires=[
"tqdm",
"transformers",
"torch",
"wandb",
"loguru",
"langid",
"matplotlib",
"numpy",
"pandas",
"typing",
"simpletransformers",
],
classifiers=[
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3',
"License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License",
"Operating System :: OS Independent",
],
)
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/setup.py
|
setup.py
|
import pandas as pd
def use_cmd_argument():
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='set some parameters')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字',default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
parser.add_argument('--', type=str, help='传入的数字', default='a')
args = parser.parse_args()
# 获得integers参数
print(args.integers)
return args
parser.add_argument('integers', metavar='N', type=int, nargs='+',
help='an integer for the accumulator')
parser.add_argument('--sum', dest='accumulate', action='store_const',
const=sum, default=max,
help='sum the integers (default: find the max)')
args = parser.parse_args()
print(args.accumulate(args.integers))
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/zyl_utils/test_utils.py
|
test_utils.py
|
# encoding: utf-8
"""
@author: zyl
@file: __init__.py
@desc: import
"""
from .data_utils.analysis import Analyzer
# data
from .data_utils.processing import Processor
from .data_utils.text_processing import MyTokenizer
from .data_utils.text_processing import TextProcessor
from .data_utils.html_processing import HtmlProcessor
from .data_utils.image_processing import ImageProcessor
from .data_utils.pdf_processing import PDFProcessor
# processing
split_data_evenly = Processor.split_data_evenly # 均分数据
split_train_eval = Processor.split_train_eval # 切分训练集和评估集
two_classification_sampling = Processor.two_classification_sampling # 二分类采样
remove_some_model_files = Processor.remove_some_model_files # 删除模型冗余文件
save_dataframe_to_excel = Processor.save_dataframe_to_excel # df保存至excel,sheet
# text processing
# 切句切词: my_tokenizer = MyTokenizer() \ my_tokenizer.cut_paragraph_to_sentences, my_tokenizer.cut_sentence_to_words
clean_text = TextProcessor.clean_text # 清洗数据
ner_find = TextProcessor.ner_find # 从文本中搜寻实体---继续优化
remove_illegal_chars = TextProcessor.remove_illegal_chars # 移除非法字符
remove_invisible_chars = TextProcessor.remove_invisible_chars # 移除不可见字符
remove_html_tags = TextProcessor.remove_html_tags # 移除html标签---待优化
# analysis
get_text_language = Analyzer.get_text_language # 文本的语言
get_text_string_length = Analyzer.get_text_string_length # 文本字符串长度
get_text_token_length = Analyzer.get_text_token_length # 文本model_token长度
show_dataframe_base_info = Analyzer.show_dataframe_base_info # df基本信息
show_dataframe_completely = Analyzer.show_dataframe_completely # df完全显示
show_plt_completely = Analyzer.show_plt_completely # plt显示问题
analyze_numerical_array = Analyzer.analyze_numerical_array # 分析数值数组
analyze_category_array = Analyzer.analyze_category_array # 分析分类数组
show_bio_data_info = Analyzer.show_bio_data_info # 分析实体识别bio数据
# image processing
ImgProcessor = ImageProcessor()
show_image = ImgProcessor.show_image
format_image = ImgProcessor.format_image
read_image = ImgProcessor.read_image
save_image = ImgProcessor.save_image
get_text_from_one_image = ImgProcessor.get_text_from_one_image
get_tables_from_image = ImgProcessor.get_tables_from_image
# html processing
turn_html_content_to_pdf = HtmlProcessor.turn_html_content_to_pdf
# pdf processing
extract_tables_from_non_scanned_pdf = PDFProcessor.extract_tables_from_non_scanned_pdf
get_text_from_pdf_area = PDFProcessor.get_text_from_pdf_area
get_texts_and_tables_from_pdf = PDFProcessor.get_texts_and_tables_from_pdf
#########################################################################
# model
from .model_utils.model_utils import ModelUtils
# model_uitls
get_best_cuda_device = ModelUtils.get_best_cuda_device # 获取最好的若干cuda
fix_torch_multiprocessing = ModelUtils.fix_torch_multiprocessing # fix_torch_multiprocessing
predict_with_multi_gpus = ModelUtils.predict_with_multi_gpus
# models
from .model_utils.models.ner_bio import NerBIO, NerBIOModel
from .model_utils.models.ner_t5 import NerT5
# metric
from .model_utils.metrics.ner_metric import entity_recognition_metrics # 实体识别t5评估标准
# algorithm
from .model_utils.algorithms.sunday_match import sunday_match # 子序列匹配
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/zyl_utils/__init__.py
|
__init__.py
|
"""
用cv2处理
"""
import ast
import base64
import io
import PIL
import cv2
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pytesseract
import requests
from PIL import Image
from cv2 import cv2
from collections import Counter
class ImageProcessor:
def __init__(self):
self.pharmcube_ocr_url = 'http://localhost/2txt'
# self.pharmcube_ocr_url ='http://101.201.249.176:1990/2txt'
# self.pharmcube_ocr_url = 'http://localhost/2txt_CV'
self.baidu_ocr_url = "https://aip.baidubce.com/rest/2.0/ocr/v1/accurate"
self.request_url, self.headers = None,None
def get_baidu_ocr_config(self):
# 获取access_token , client_id 为官网获取的AK, client_secret 为官网获取的SK
appid = "25533636"
client_id = "PLvUz16ePip4txCcYXk2Ablh"
client_secret = "8HXb8DIo2t7eNaw1aD6XGZi4U1Kytj41"
token_url = "https://aip.baidubce.com/oauth/2.0/token"
host = f"{token_url}?grant_type=client_credentials&client_id={client_id}&client_secret={client_secret}"
response = requests.get(host)
access_token = response.json().get("access_token")
request_url = "https://aip.baidubce.com/rest/2.0/ocr/v1/accurate"
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"}
request_url = f"{request_url}?access_token={access_token}"
return request_url, headers
@staticmethod
def read_image(image: str, method='cv2'):
# opencv 读取图片数据格式为numpy.ndarray,(高、宽、通道)
# PIL用PIL.Image.Image (宽、高、通道), Image对象有crop功能,也就是图像切割功能
if method == 'PIL':
# PIL.PngImagePlugin.PngImageFile,PIL读取顺序RGB 并通过.convert来定义读取图片类型:1:位图 L:灰度图 RGB:彩色图
image = Image.open(image)
elif method == 'cv2':
image = cv2.imread(image, flags=1) # ndarray,opencv读取顺序BGR, flag=1默认彩色图片, 0:读取灰度图
else:
image = mpimg.imread(image) # ndarray, 二维grb ,3个通道
return image
@staticmethod
def show_image(img, other_mode=False):
# rgb 格式显示图像,cv2.imshow() BGR模式显示,img.show() PIL对象自带,RGB模式, plt.imshow() RGB
if isinstance(img, str): # 图像路径
img = ImageProcessor.read_image(img, method='cv2') # ndarray
try:
if other_mode:
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # BGR转RGB
finally:
plt.imshow(img)
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
def format_image(self, image, format='Image'):
if format == 'Image':
if isinstance(image, str):
image = Image.open(image)
elif isinstance(image, np.ndarray):
image = Image.fromarray(image) # -np数组转化为img对象
else:
if isinstance(image, str):
image = cv2.imread(image, 1)
elif isinstance(image, PIL.PpmImagePlugin.PpmImageFile) | isinstance(image, PIL.Image.Image):
image = np.array(image) # img对象转化为np数组
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
return image
def save_image(self):
# PIL.Image.save()保存RGB图像
# cv2.imwrite()--opencv---保存图片,等效BGR2RGB
pass
def get_text_from_one_image(self, image, method='pharmcube_ocr'):
"""
使用ocr提取图像中的文本
Args:
image: 图像-路径/Image/ndarray
method: pharmcube_ocr/baidu_ocr/pytesseract
Returns:
"""
image = self.format_image(image, 'Image') # imgae-RGB-IMGAGE对象
if image.mode != 'GBA':
image = image.convert('RGB')
if method == 'pharmcube_ocr':
buf = io.BytesIO()
image.save(buf, format='JPEG')
byte_im = buf.getvalue()
response = requests.post(self.pharmcube_ocr_url, files={'file': byte_im})
text = ast.literal_eval(response.text)
text = '\n'.join(text)
elif method == 'baidu_ocr': # 付费
image = np.array(image)
image = cv2.imencode('.jpg', image)[1]
image = image.tobytes()
image = base64.b64encode(image).decode('utf8')
body = {
"image": image,
"language_type": "auto_detect",
"recognize_granularity": "small",
"detect_direction": "true",
"vertexes_location": "true",
"paragraph": "true",
"probability": "true",
}
if not self.request_url:
self.request_url, self.headers, = self.get_baidu_ocr_config()
response = requests.post(self.request_url, headers=self.headers, data=body)
content = response.content.decode("UTF-8")
content = eval(content)
text = ''
if 'words_result' in content.keys():
content= content['words_result']
for c in content:
text += (c['words'].replace(' ', '') + '\n')
else: # pytesseract
text = pytesseract.image_to_string(image, lang="chi_sim") # png
text = text.replace(' ', '')
return text
def get_tables_from_image(self, image, ocr_method=None):
"""
从图像中获取若干表格的位置以及表格内容
Args:
image:
ocr_method: 使用ocr识别单元格文本
Returns:
"""
image = self.format_image(image, 'cv2')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # convert raw to gray picture and binary
binary = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(~gray, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 35, -5)
# get horizontal and vertical line
rows, cols = binary.shape
scale = 40
# 识别横线:
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (cols // scale, 1))
eroded = cv2.erode(binary, kernel, iterations=1)
dilated_col = cv2.dilate(eroded, kernel, iterations=1)
# 识别竖线
scale = 40 # can use different threshold
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (1, rows // scale))
eroded = cv2.erode(binary, kernel, iterations=1)
dilated_row = cv2.dilate(eroded, kernel, iterations=1)
mat_mask = dilated_col + dilated_row # 表格的线(横线+竖线)
bitwise_and = cv2.bitwise_and(dilated_col, dilated_row) # 交点
ys, xs = np.where(bitwise_and > 0)
# '''get the start coordinate of each line'''
# lines_pos = np.where(dilated_col > 0)
# linepos = Counter(lines_pos[0])
# start = 0
# starts = []
# for i in linepos:
# num = linepos[i]
# tmp = lines_pos[1][start:start + num][0]
# start += num
# starts.append(tmp)
# start_pos = min(starts)
#
# '''mark left margin if it do not been recognized'''
# linecols = Counter(ys)
# st = 0
# for i in linecols:
# ys = np.insert(ys, st, i)
# xs = np.insert(xs, st, start_pos)
# st += linecols[i]
# st += 1
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(mat_mask, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
tables_location = []
tables = []
for c in contours:
if c.size > 4:
if cv2.contourArea(c) > image.shape[1]:
left = np.min(c, axis=0)[0][0]
top = np.min(c, axis=0)[0][1]
right = np.max(c, axis=0)[0][0]
bottom = np.max(c, axis=0)[0][1]
tmp_xs = []
tmp_ys = []
for x, y in zip(xs, ys):
if ((left - 10) < x < (right + 10)) and ((top - 10) < y < (bottom + 10)):
tmp_xs.append(x)
tmp_ys.append(y) # 顺序,点是从左到右一次排
if (not tmp_ys) | (not tmp_xs):
continue
tmp_xs = self._format_coordinates(tmp_xs)
tmp_ys = self._format_coordinates(tmp_ys)
table = self._get_table_from_coordinates(tmp_xs, tmp_ys)
tables_location.append((left, top, right, bottom))
if ocr_method:
tmp_table = []
for row in table:
t = []
for cell in row:
cell_image = gray[max(0,cell[1]-5):cell[3], cell[0]:cell[2]]
t.append(self.get_text_from_one_image(cell_image, ocr_method))
tmp_table.append(t)
tables.append(tmp_table)
else:
tables.append(table)
# 在图像中表格从上往下排
sorted_tables = []
tmp_tables_location = {t[1]: e for e, t in enumerate(tables_location)}
for t in sorted(tmp_tables_location.keys()):
sorted_tables.append(tables[tmp_tables_location.get(t)])
tables_location.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
return sorted_tables, tables_location
def _format_coordinates(self, coordinates):
# 对于一个表格,格式化表格坐标,【0,1,40,10,11,40】--》【0,0,10,10,40,40】
sorted_coordinates = np.sort(coordinates)
format_dict = {sorted_coordinates[0]: sorted_coordinates[0]}
start_point = sorted_coordinates[0]
for i in range(len(sorted_coordinates) - 1):
if sorted_coordinates[i + 1] - sorted_coordinates[i] > 10:
start_point = sorted_coordinates[i + 1]
format_dict.update({sorted_coordinates[i + 1]: start_point})
return [format_dict.get(c) for c in coordinates] # 有重复
def _get_table_from_coordinates(self, xs, ys):
"""
# 对于一个表格,根据横向和纵向坐标,扣取其中的单元格坐标信息
Args:
xs: 横向坐标
ys: 竖向坐标
Returns:格式化的表格,列表,每个元素是一行(列表),每行中有若干(left, top, right, bottom)
【[(left, top, right, bottom)]】
"""
table_dict = dict()
table = []
column = None
for x, y in zip(xs, ys):
if y != column:
table_dict[y] = {x}
column = y
else:
table_dict[y].add(x)
# 不存在一个字段名称在上,两个字段值对应在下的情况
if len(table_dict) > 1:
columns = sorted(list(table_dict.keys()))
for c in range(len(columns) - 1):
top = columns[c]
bottom = columns[c + 1]
all_xs = table_dict.get(top) & table_dict.get(bottom)
all_xs = sorted(list(all_xs))
t = []
if len(all_xs) >= 2:
for x in range(len(all_xs) - 1):
left = all_xs[x]
right = all_xs[x + 1]
t.append((left, top, right, bottom))
table.append(t)
return table
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = "/home/zyl/disk/PharmAI/pharm_ai/intel/data/test.PNG"
i_p = ImageProcessor()
t, t_l = i_p.get_tables_from_image(img,'pharmcube_ocr')
print(t)
print(t_l)
# t, t_l = i_p.get_tables_from_image(img, 'baidu_ocr')
# print(t)
# print(t_l)
#
# t, t_l = i_p.get_tables_from_image(img, 'tr_ocr')
# print(t)
# print(t_l)
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/zyl_utils/data_utils/image_processing.py
|
image_processing.py
|
# encoding: utf-8
"""
@author: zyl
@file: collection.py
@time: 2021/11/29 9:40
@desc:
"""
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/zyl_utils/data_utils/collection.py
|
collection.py
|
# encoding: utf-8
"""
@author: zyl
@file: preprocessing.py
@time: 2021/11/25 17:45
@desc:
"""
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/zyl_utils/data_utils/preprocessing.py
|
preprocessing.py
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/zyl_utils/data_utils/preparation.py
|
preparation.py
|
|
import pandas as pd
class Processor:
def __init__(self):
pass
@staticmethod
def split_data_evenly(data, num) -> list:
"""
split_data_evenly,顺序均分数据,遵循最后一份最少的原则
Args:
data: may be list,dataframe,tuple... should have __len__
num: the number of sub_data
Returns:
list of sub_data
"""
data_length = len(data)
step = int(data_length / num)
other_data = data_length % num
if data_length <= num:
print('Warning: data_length <= data_num')
return data
if other_data == 0:
return [data[i:i + step] for i in range(0, data_length, step)]
else:
first_part_data = [data[i:i + step + 1] for i in range(0, int((step + 1) * other_data), step + 1)]
second_part_list = [data[i:i + step] for i in range(int((step + 1) * other_data), data_length, step)]
first_part_data.extend(second_part_list)
return first_part_data
@staticmethod
def split_train_eval(data: pd.DataFrame, max_eval_size=5000):
"""
切分训练集和评估集
Args:
data: pd.DataFrame
max_eval_size: 评估集最大size
Returns:
train,eval
"""
from sklearn.utils import resample
raw_data = resample(data, replace=False)
cut_point = min(max_eval_size, int(0.2 * len(raw_data)))
eval_df = raw_data[0:cut_point]
train_df = raw_data[cut_point:]
return train_df, eval_df
@staticmethod
def two_classification_sampling(train_df: pd.DataFrame, column='labels', neg_label='|', mode='up_sampling'):
"""
训练集二分类采样:上采样和下采样
Args:
train_df: pd.DataFrame
column: the column to sampling
neg_label: neg_label
mode:up_sampling/down_sampling
Returns:
data: pd.DataFrame
"""
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.utils import resample
negative_df = train_df[train_df[column] == neg_label]
neg_len = negative_df.shape[0]
positive_df = train_df[train_df[column] != neg_label]
pos_len = positive_df.shape[0]
if neg_len > pos_len:
if mode == 'down_sampling':
down_sampling_df = resample(negative_df, replace=False, n_samples=pos_len, random_state=242)
train_df = pd.concat([positive_df, down_sampling_df], ignore_index=True)
else:
up_sampling_df = resample(positive_df, replace=True, n_samples=(neg_len - pos_len), random_state=242)
train_df = pd.concat([train_df, up_sampling_df], ignore_index=True)
elif neg_len < pos_len:
if mode == 'down_sampling':
down_sampling_df = resample(positive_df, replace=False, n_samples=neg_len, random_state=242)
train_df = pd.concat([down_sampling_df, negative_df], ignore_index=True)
else:
up_sampling_df = resample(negative_df, replace=True, n_samples=(pos_len - neg_len), random_state=242)
train_df = pd.concat([train_df, up_sampling_df], ignore_index=True)
train_df = resample(train_df, replace=False)
return train_df
@staticmethod
def remove_some_model_files(model_args):
"""
simple-transformer 根据模型参数自动删除模型相关文件
Args:
model_args: simple-transformer的args
Returns:
"""
import os
if os.path.isdir(model_args.output_dir):
cmd = 'rm -rf ' + model_args.output_dir.split('outputs')[0] + 'outputs/'
os.system(cmd)
if os.path.isdir(model_args.output_dir.split('outputs')[0] + '__pycache__/'):
cmd = 'rm -rf ' + model_args.output_dir.split('outputs')[0] + '__pycache__/'
os.system(cmd)
if os.path.isdir(model_args.output_dir.split('outputs')[0] + 'cache/'):
cmd = 'rm -rf ' + model_args.output_dir.split('outputs')[0] + 'cache/'
os.system(cmd)
@staticmethod
def save_dataframe_to_excel(dataframe, excel_path, sheet_name='default'):
"""
df添加sheet
Args:
dataframe: df
excel_path: path
sheet_name: sheet
Returns:
"""
try:
from openpyxl import load_workbook
book = load_workbook(excel_path)
writer = pd.ExcelWriter(excel_path, engine='openpyxl')
writer.book = book
except:
writer = pd.ExcelWriter(excel_path, engine='openpyxl')
dataframe.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=sheet_name, index=False)
writer.save()
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(Processor.split_data_evenly([0, 2, 3, 4, 5], 3))
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/zyl_utils/data_utils/processing.py
|
processing.py
|
# encoding: utf-8
'''
@author: zyl
@file: Analyzer.py
@time: 2021/11/11 9:34
@desc:
'''
import langid
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class BaseAnalyzer:
def __init__(self):
pass
def run(self):
pass
@staticmethod
def get_text_string_length(text:str):
return len(text)
@staticmethod
def get_text_word_length(text: str):
if langid.classify(text)[0]=='zh':
return len(text) # zh -word-piece
else:
return len(text.split()) # en - split by space
@staticmethod
def get_text_token_length(text: str, tokenizer=None):
if not tokenizer:
from transformers import BertTokenizer
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-multilingual-cased')
return len(tokenizer.tokenize(text))
@staticmethod
def show_df_base_info(df):
desc = df.describe(percentiles=[0.10,0.25,0.5,0.75,0.85,0.95,0.99])
print(desc)
info = df.info()
print(info)
@staticmethod
def draw_box(df,column):
plt.subplots()
plt.boxplot(df[column])
plt.show()
@staticmethod
def draw_hist(df,column):
# df['input_text_length'].plot.hist(bins=2000) # 列的直方图
plt.subplots()
plt.hist(df[column])
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
pass
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/zyl_utils/data_utils/Analysis.py
|
Analysis.py
|
# encoding: utf-8
"""
@author: zyl
@file: html_processing.py
@time: 2022/1/20 10:32
@desc:
"""
import pandas as pd
import pdfkit
class HtmlProcessor:
def __init__(self):
pass
def run(self):
self.test()
pass
def test(self):
df = pd.read_excel("/home/zyl/disk/PharmAI/pharm_ai/intel/data/v1/test_gov_purchase.xlsx")
contents = df['content'].tolist()[0]
HtmlProcessor.turn_html_content_to_pdf(contents, './data/v1/s.pdf')
@staticmethod
def turn_html_content_to_pdf(content, to_pdf='./data/v1/s.pdf'):
""" 把html文本写入pdf中--
df = pd.read_excel("/home/zyl/disk/PharmAI/pharm_ai/intel/data/v1/test_gov_purchase.xlsx")
contents = df['content'].tolist()[0]
ProcessingHtml.turn_html_content_to_pdf(contents,'./data/v1/s.pdf')
"""
config = pdfkit.configuration(wkhtmltopdf="/usr/bin/wkhtmltopdf")
content = content.replace('FangSong', 'SimHei') # 把仿宋体变为黑体,中文字体要变换/或者直接在系统的fonts中添加对应字体
content = content.replace('宋体', 'SimHei')
content = content.replace('Simsun', 'SimHei')
html = '<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"></head>' \
'<body><div align="left"><p>%s</p></div></body></html>' % content
pdfkit.from_string(html, to_pdf, configuration=config)
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/zyl_utils/data_utils/html_processing.py
|
html_processing.py
|
import html
import re
import langid
class MyTokenizer:
def __init__(self,do_lower_case=False):
# 把连号‘-’分开,空格也作为一个词
self.sentences_tokenizer_en = self.get_sentences_tokenizer_en()
self.words_tokenizer_en = self.get_word_tokenizer_en(do_lower_case=do_lower_case)
@staticmethod
def cut_paragraph_to_sentences_zh(para: str, drop_empty_line=True, strip=True, deduplicate=False):
"""
中文切句
Args:
para: 输入段落文本
drop_empty_line: 是否丢弃空行
strip: 是否对每一句话做一次strip
deduplicate: 是否对连续标点去重,帮助对连续标点结尾的句子分句
Returns:
sentences: list[str]
"""
if deduplicate:
para = re.sub(r"([。!?\!\?])\1+", r"\1", para)
para = re.sub('([。!?\?!])([^”’])', r"\1\n\2", para) # 单字符断句符
para = re.sub('(\.{6})([^”’])', r"\1\n\2", para) # 英文省略号
para = re.sub('(\…{2})([^”’])', r"\1\n\2", para) # 中文省略号
para = re.sub('([。!?\?!][”’])([^,。!?\?])', r'\1\n\2', para)
# 如果双引号前有终止符,那么双引号才是句子的终点,把分句符\n放到双引号后,注意前面的几句都小心保留了双引号
para = para.rstrip() # 段尾如果有多余的\n就去掉它
# 很多规则中会考虑分号;,但是这里我把它忽略不计,破折号、英文双引号等同样忽略,需要的再做些简单调整即可。
sentences = para.split("\n")
if strip:
sentences = [sent.strip() for sent in sentences]
if drop_empty_line:
sentences = [sent for sent in sentences if len(sent.strip()) > 0]
return sentences
@staticmethod
def get_sentences_tokenizer_en():
"""
the tokenizer for cutting paragraph to sentences
Returns:
tokenizer
"""
from nltk.tokenize.punkt import PunktSentenceTokenizer, PunktParameters
punkt_param = PunktParameters()
abbreviation = ['et al.', 'i.e.', 'e.g.', 'etc.', 'i.e', 'e.g', 'etc', ' et al']
punkt_param.abbrev_types = set(abbreviation)
tokenizer = PunktSentenceTokenizer(punkt_param)
return tokenizer
@staticmethod
def cut_sentence_to_words_zh(sentence: str):
"""
cut_sentence_to_words_zh
Args:
sentence: a sentence ,str
Returns:
sentences: list[str]
"""
english = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789αγβδεζηθικλμνξοπρστυφχψω'
output = []
buffer = ''
for s in sentence:
if s in english or s in english.upper(): # 英文或数字
buffer += s
else: # 中文
if buffer:
output.append(buffer)
buffer = ''
output.append(s)
if buffer:
output.append(buffer)
return output
@staticmethod
def get_word_tokenizer_en(do_lower_case=False):
"""
the tokenizer for cutting sentence to words
Returns:
tokenizer
"""
from transformers import BasicTokenizer
return BasicTokenizer(do_lower_case=do_lower_case)
# from nltk import WordPunctTokenizer
# return WordPunctTokenizer() # ').' 分不开,垃圾
def cut_sentence_to_words(self, sentence: str,return_starts = False):
if langid.classify(sentence)[0] == 'zh':
words = self.cut_sentence_to_words_zh(sentence)
else:
words = self.words_tokenizer_en.tokenize(sentence)
if return_starts:
starts = [] # 每个word在句子中的位置
i = 0
for j in words:
while i < len(sentence):
if sentence[i:i + len(j)] == j:
starts.append(i)
i += len(j)
break
else:
i += 1
return words,starts
return words
def cut_paragraph_to_sentences(self, paragraph: str):
if langid.classify(paragraph)[0] == 'zh':
return self.cut_paragraph_to_sentences_zh(paragraph)
else:
return self.sentences_tokenizer_en.tokenize(paragraph)
class TextProcessor:
def __init__(self):
pass
@staticmethod
def clean_text(text: str):
"""
清洗数据
Args:
text: 文本
Returns:
text
"""
import re
text = re.sub('<[^<]+?>', '', text).replace('\n', '').strip() # 去html中的<>标签
text = ' '.join(text.split()).strip()
return text
@staticmethod
def ner_find(text: str, entities: dict, ignore_nested=True):
"""
find the loaction of entities in a text
Args:
text: a text, like '我爱吃苹果、大苹果,小苹果,苹果【II】,梨子,中等梨子,雪梨,梨树。'
entities: {'entity_type1':{entity_str1,entity_str2...},
'entity_type2':{entity_str1,entity_str2...},
...}
like : {'apple': ['苹果', '苹果【II】'], 'pear': ['梨', '梨子'],}
ignore_nested: if nested
#>>>IndexedRuleNER().ner(text, entities, False)
Returns:
indexed_entities:{'entity_type1':[[start_index,end_index,entity_str],
[start_index,end_index,entity_str]...]
'entity_type2':[[start_index,end_index,entity_str],
[start_index,end_index,entity_str]...]
...}
#>>>{'apple': [[3, 5, '苹果'], [7, 9, '苹果'], [11, 13, '苹果'], [14, 16, '苹果'], [14, 20, '苹果【II】']],
'pear': [[21, 22, '梨'], [26, 27, '梨'], [30, 31, '梨'], [32, 33, '梨'], [21, 23, '梨子'], [26, 28, '梨子']]}
"""
indexed_entities = dict()
for every_type, every_value in entities.items():
every_type_value = []
for every_entity in list(every_value):
special_character = set(re.findall('\W', str(every_entity)))
for i in special_character:
every_entity = every_entity.replace(i, '\\' + i)
re_result = re.finditer(every_entity, text)
for i in re_result:
res = [i.span()[0], i.span()[1], i.group()]
if res != []:
every_type_value.append([i.span()[0], i.span()[1], i.group()])
indexed_entities[every_type] = every_type_value
if ignore_nested:
for key, value in indexed_entities.items():
all_indexs = [set(range(i[0], i[1])) for i in value]
for i in range(len(all_indexs)):
for j in range(i, len(all_indexs)):
if i != j and all_indexs[j].issubset(all_indexs[i]):
value.remove(value[j])
indexed_entities[key] = value
elif i != j and all_indexs[i].issubset(all_indexs[j]):
value.remove(value[i])
indexed_entities[key] = value
return indexed_entities
@staticmethod
def remove_illegal_chars(text: str):
"""
移除非法字符
Args:
text:
Returns:
"""
ILLEGAL_CHARACTERS_RE = re.compile(r'[\000-\010]|[\013-\014]|[\016-\037]')
return ILLEGAL_CHARACTERS_RE.sub(r'', text) # 非法字符
@staticmethod
def remove_invisible_chars(text, including_char=('\t', '\n', '\r')):
"""移除所有不可见字符,除'\t', '\n', '\r'外"""
str = ''
for t in text:
if (t not in including_char) and (not t.isprintable()):
str += ' '
else:
str += t
return str
@staticmethod
def remove_html_tags(text):
# soup = BeautifulSoup(raw_str, features="html.parser")
# return ''.join([s.text.replace('\n', '') for s in soup.contents if hasattr(s, 'text') and s.text])
# text = re.sub('<[^<]+?>', '', text).replace('\n', '').strip() # 去html中的<>标签
# text = ' '.join(text.split()).strip()
return html.unescape(text) # html转义字符
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/zyl_utils/data_utils/text_processing.py
|
text_processing.py
|
# encoding: utf-8
"""
@author: zyl
@file: pdf_processing.py
@time: 2022/1/20 10:32
@desc:
"""
from pdf2image import convert_from_path
from zyl_utils.data_utils.image_processing import ImageProcessor
IMAGEPROCESSOR = ImageProcessor()
import fitz
import pdfplumber
from tabula import read_pdf
class PDFProcessor:
def __init__(self):
pass
@staticmethod
def extract_tables_from_non_scanned_pdf(pdf: str, start_page: int = 0, end_page: int = None,
method='tabula'):
"""extract tables from a pdf
Args:
pdf: PDF File
start_page: the first page to begin extract,from 0 to start
end_page: the last page to extract
method:
Returns:
table_list : list/dict
"""
pdf_object = pdfplumber.open(pdf)
pdf_pages = pdf_object.pages[start_page:] if end_page is None else pdf_object.pages[
start_page:end_page + 1]
tables = []
for i in range(len(pdf_pages)):
if method == 'tabula':
tables_df = read_pdf(pdf, pages=start_page + i + 1, multiple_tables=True)
for t in tables_df:
table = []
table.append(list(t.columns))
for j in range(len(t)):
table.append(list(t.iloc[j]))
tables.append(table)
else: # 'pdfplumber'
table = pdf_pages[i].extract_tables()
for t in table:
if t:
tables.append(t)
return tables
@staticmethod
def get_text_from_pdf_area(pdf_page, left, top, right, bottom, mode='text'):
# clip = fitz.Rect(0, start_height, pdf_page.rect.width, tables[i]['top'])
clip = fitz.Rect(left, top, right, bottom)
if mode == 'text':
ss = '\n'
else:
ss = ' '
text = ''
lines_texts = pdf_page.get_textpage(clip=clip).extractBLOCKS()
last_line_bottom = 0
for l in range(len(lines_texts)):
if (last_line_bottom - lines_texts[l][1]) < 0.1 * (lines_texts[l][3] - lines_texts[l][1]):
text += '\n'
last_line_bottom = max(last_line_bottom, lines_texts[l][3])
spans = lines_texts[l][4].split('\n')
for s in range(len(spans) - 1):
if spans[s] in spans[s + 1]:
continue
else:
text += (str(spans[s]) + ss)
return text
@staticmethod
def get_texts_and_tables_from_pdf(pdf, ocr_method='pharmcube_ocr'):
images = convert_from_path(pdf, dpi=72)
pdf_doc = fitz.Document(pdf)
pdf_texts = ''
all_tables = []
for pg in range(0, len(images)):
img = images[pg]
pdf_page = pdf_doc.load_page(pg)
if not pdf_page.get_text():
is_scanned = True
img = img.crop((10, 10, pdf_page.rect.width - 10, pdf_page.rect.height - 10))
else:
is_scanned = False
tables, tables_location = IMAGEPROCESSOR.get_tables_from_image(img, ocr_method)
all_tables.extend(tables)
text_page = ''
if tables_location:
start_height = 0
for i in range(len(tables_location)):
if tables_location[i][1] < start_height:
continue
if is_scanned:
text_area = IMAGEPROCESSOR.get_text_from_one_image(img, method=ocr_method)
text_page += text_area
else:
text_area = PDFProcessor.get_text_from_pdf_area(pdf_page, left=0, top=start_height,
right=pdf_page.rect.width,
bottom=tables_location[i][1])
text_page += (text_area + '\n<表格>\n')
start_height = tables_location[i][-1]
if i == (len(tables_location) - 1):
text_area = PDFProcessor.get_text_from_pdf_area(pdf_page, left=0, top=start_height,
right=pdf_page.rect.width,
bottom=pdf_page.rect.height)
text_page += text_area
else:
if is_scanned:
text_page = IMAGEPROCESSOR.get_text_from_one_image(img, method=ocr_method)
else:
text_page = PDFProcessor.get_text_from_pdf_area(pdf_page, left=0, top=0,
right=pdf_page.rect.width,
bottom=pdf_page.rect.height)
pdf_texts += (text_page + '\n')
return pdf_texts, all_tables
if __name__ == '__main__':
pdf = "/home/zyl/disk/PharmAI/pharm_ai/intel/data/v1/test_dt_pdfs/6310ee78a81a81d4d4a6de3169ccb40d.pdf"
print(PDFProcessor.extract_tables_from_non_scanned_pdf(pdf))
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/zyl_utils/data_utils/pdf_processing.py
|
pdf_processing.py
|
# encoding: utf-8
"""
@author: zyl
@file: utils.py
@time: 2021/11/26 9:09
@desc:
"""
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/zyl_utils/data_utils/utils.py
|
utils.py
|
import langid
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
class Analyzer:
def __init__(self):
pass
@staticmethod
def get_text_language(text: str):
"""
注意:短语尽量不要输入判断,越短越不准,# ’癌症‘判断为‘ja'
Args:
text:
Returns:
"""
return langid.classify(text)[0]
@staticmethod
def get_text_string_length(text: str):
return len(text)
@staticmethod
def get_text_token_length(text: str, model_tokenizer=None):
if not model_tokenizer:
from transformers import BertTokenizer
model_tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-multilingual-cased')
return len(model_tokenizer.tokenize(text))
@staticmethod
def show_dataframe_base_info(df: pd.DataFrame, column=None):
if column:
df = df[column]
print(df.describe())
print(df.info())
@staticmethod
def show_dataframe_completely():
"""
完全显示pandas的dataframe的所有值
Returns:
"""
import pandas as pd
pd.set_option('max_colwidth', 500) # 设置value的显示长度为200,默认为50
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None) # 显示所有列,把行显示设置成最大
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None) # 显示所有行,把列显示设置成最大
@staticmethod
def show_plt_completely():
"""
plt显示问题
Returns:
"""
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号
@staticmethod
def analyze_numerical_array(data):
"""
分析数值数组
Args:
data:
Returns:
"""
Analyzer.show_plt_completely()
if not isinstance(data, np.ndarray):
data = np.array(data)
q1 = np.percentile(data, 25) # 第一四分位数,从小到大25%,下四分位数
q2 = np.percentile(data, 50) # 第二四分位数,从小到大50%,中位数
q3 = np.percentile(data, 75) # 第三四分位数,从小到大75%,上四分位数
iqr = q3 - q1 # 四分位数差(IQR,interquartile range),上四分位数-下四分位数
lower_limit = q1 - 1.5 * iqr
upper_limit = q3 + 1.5 * iqr
print(f"""
计数: {len(data)}
均值: {data.mean()}
标准差: {data.std()}
方差: {data.var()}
最大值: {np.max(data)}
最小值: {np.min(data)}
下四分位数: {q1}
中位数: {q2}
上四分位数: {q3}
下异常值界限:{lower_limit} ,异常值数:{len(np.where(data < lower_limit)[0])}
上异常值界限:{upper_limit} ,异常值数:{len(np.where(data > upper_limit)[0])}
"""
)
plt.subplot(211)
plt.hist(data)
plt.subplot(212)
plt.boxplot(data, vert=False)
plt.show()
@staticmethod
def analyze_category_array(data: pd.Series):
"""
分析类型数据
Args:
data:
Returns:
"""
Analyzer.show_plt_completely()
if not isinstance(data, pd.Series):
data = pd.Series(data)
data_value_counts = data.value_counts()
data_pie = data_value_counts / len(data)
print(f"""
data:
{data_value_counts}
data_percent:
{data_pie.sort_values}
"""
)
plt.subplot()
data_value_counts.plot.bar()
plt.show()
plt.subplot()
data_pie.plot.pie(autopct='%.1f%%', title='pie', )
plt.show()
@staticmethod
def show_bio_data_info(bio_dt: pd.DataFrame, label='DISEASE'):
"""
show bio format data info
Args:
bio_dt: ["sentence_id", "words", "labels"]
label: entity cls
Returns:
info
"""
labels = bio_dt.groupby(by=['sentence_id'], sort=False)
from zyl_utils.model_utils.models.ner_bio import NerBIO
labels = labels.apply(lambda x: x['labels'].tolist())
y_true = [set(NerBIO.get_id_entity(l, label=label)) for l in labels]
pos = [y for y in y_true if y != set()]
neg = [y for y in y_true if y == set()]
print(f'数据集大小(句): {len(labels)}句')
print(f'其中有实体的样本数: {len(pos)}句')
print(f'其中没有实体的样本数: {len(neg)}句')
print(f'数据集大小(词): {len(bio_dt)}词')
print(f"其中‘O’标签大小(词): {len(bio_dt[bio_dt['labels'] == 'O'])}词")
print(f"其中‘B’标签大小(词): {len(bio_dt[bio_dt['labels'].str.startswith('B')])}词")
print(f"其中‘I’标签大小(词): {len(bio_dt[bio_dt['labels'].str.startswith('I')])}词")
if __name__ == '__main__':
df = pd.read_hdf('/home/zyl/disk/PharmAI/pharm_ai/panel/data/v4/processing_v4_4.h5',
'disease_eval_bio')
Analyzer.show_bio_data_info(df, label='DISEASE')
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/zyl_utils/data_utils/analysis.py
|
analysis.py
|
# encoding: utf-8
'''
@author: zyl
@file: Analyzer.py
@time: 2021/11/11 9:34
@desc:
'''
import langid
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class BaseAnalyzer:
def __init__(self):
pass
def run(self):
pass
@staticmethod
def get_text_string_length(text:str):
return len(text)
@staticmethod
def get_text_word_length(text: str):
if langid.classify(text)[0]=='zh':
return len(text) # zh -word-piece
else:
return len(text.split()) # en - split by space
@staticmethod
def get_text_token_length(text: str, tokenizer=None):
if not tokenizer:
from transformers import BertTokenizer
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-multilingual-cased')
return len(tokenizer.tokenize(text))
@staticmethod
def show_df_base_info(df):
desc = df.describe(percentiles=[0.10,0.25,0.5,0.75,0.85,0.95,0.99])
print(desc)
info = df.info()
print(info)
@staticmethod
def draw_box(df,column):
plt.subplots()
plt.boxplot(df[column])
plt.show()
@staticmethod
def draw_hist(df,column):
# df['input_text_length'].plot.hist(bins=2000) # 列的直方图
plt.subplots()
plt.hist(df[column])
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
pass
|
zyl-utils
|
/zyl_utils-0.1.4.tar.gz/zyl_utils-0.1.4/zyl_utils/data_utils/Analyzer.py
|
Analyzer.py
|
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.