🔄 CycleVO
📌 Overview
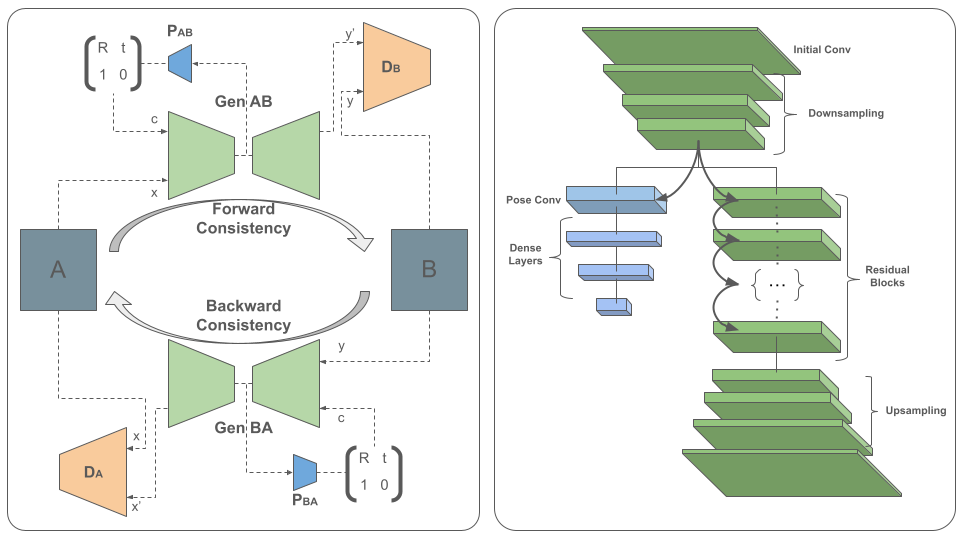
CycleVO is an unsupervised monocular pose estimation model designed to robustly estimate the relative camera pose between consecutive frames from endoscopic video. It addresses challenges such as low-texture surfaces and significant illumination variations common in surgical environments.
✨ Key Features
- 🔄 Unsupervised Learning via Cycle Consistency: Inspired by CycleGAN and InfoGAN
- ⚡ Competitive Performance and Speed: Low inference time compared to state-of-the-art methods
- 🔌 Easy Integration with SLAM Pipelines: Provides ready-to-use motion matrices
🧠 Model Details
CycleVO learns to estimate the relative motion (i.e., camera pose) between consecutive endoscopic frames. The model predicts a motion matrix 𝑀=[𝑅,𝑡unscaled,1,0] using a generator encoder architecture augmented with a pose estimation tail.
| Developed by | Guido Manni, Clemente Lauretti, Francesco Prata, Rocco Papalia, Loredana Zollo, Paolo Soda |
|---|---|
| Model Type | Unsupervised Monocular Visual Odometry / Relative Camera Pose Estimation |
| License | MIT |
| Training | From scratch using a large-scale internal endoscopic dataset |
🚀 Getting Started
For complete documentation, please refer to the GitHub repository.
🔍 Use Cases
✅ Ideal Applications
- Surgical Navigation: Real-time guidance during minimally invasive procedures
- 3D Reconstruction: Enhanced mapping of surgical scenes
- Depth Perception: Accurate pose estimates to complement monocular depth predictors
⛔ Out-of-Scope Applications
- General-purpose visual odometry without proper domain adaptation
📈 Training Details
- Dataset: 300+ hours of endoscopic videos from 100 patients (gastroscopy and prostatectomy)
- Preprocessing: Frame extraction with 128×128 pixel center crop
- Loss Function: Combined adversarial, image cycle consistency, and pose cycle consistency losses
- Optimizer: Adam with standard learning rate schedules
🛡️ Limitations & Recommendations
- Inherent Scale Ambiguity: Common in monocular systems
- Domain Specificity: Trained solely on endoscopic data
- Clinical Deployment: Requires thorough validation and clinical trials
We recommend:
- Validating the model thoroughly in your target environment
- Integrating additional sensors when possible
- Collaborating with clinical experts before surgical deployment
📚 Citation
@misc{manni2024bodyslamgeneralizedmonocularvisual,
title={BodySLAM: A Generalized Monocular Visual SLAM Framework for Surgical Applications},
author={G. Manni and C. Lauretti and F. Prata and R. Papalia and L. Zollo and P. Soda},
year={2024},
eprint={2408.03078},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.03078}
}
📖 Glossary
- Cycle Consistency Loss: Enforces agreement between original and reconstructed inputs after transformations
- Motion Matrix (M): Composed of rotation (R) and unscaled translation vector (tunscaled)
- ATE/RTE/RRE: Absolute Trajectory Error, Relative Trajectory Error, Relative Rotation Error
📫 Contact
For questions or further information, please contact: Guido Manni - [email protected]
Inference Providers
NEW
This model is not currently available via any of the supported Inference Providers.
The model cannot be deployed to the HF Inference API:
The model has no library tag.




