Spaces:
Running
Toy Examples with Code
Preamble
import numpy as np
from pysr import *
1. Simple search
Here's a simple example where we
find the expression 2 cos(x3) + x0^2 - 2.
X = 2 * np.random.randn(100, 5)
y = 2 * np.cos(X[:, 3]) + X[:, 0] ** 2 - 2
model = PySRRegressor(binary_operators=["+", "-", "*", "/"])
model.fit(X, y)
print(model)
2. Custom operator
Here, we define a custom operator and use it to find an expression:
X = 2 * np.random.randn(100, 5)
y = 1 / X[:, 0]
model = PySRRegressor(
binary_operators=["+", "*"],
unary_operators=["inv(x) = 1/x"],
extra_sympy_mappings={"inv": lambda x: 1/x},
)
model.fit(X, y)
print(model)
3. Multiple outputs
Here, we do the same thing, but with multiple expressions at once, each requiring a different feature.
X = 2 * np.random.randn(100, 5)
y = 1 / X[:, [0, 1, 2]]
model = PySRRegressor(
binary_operators=["+", "*"],
unary_operators=["inv(x) = 1/x"],
extra_sympy_mappings={"inv": lambda x: 1/x},
)
model.fit(X, y)
4. Plotting an expression
For now, let's consider the expressions for output 0. We can see the LaTeX version of this with:
model.latex()[0]
or output 1 with model.latex()[1].
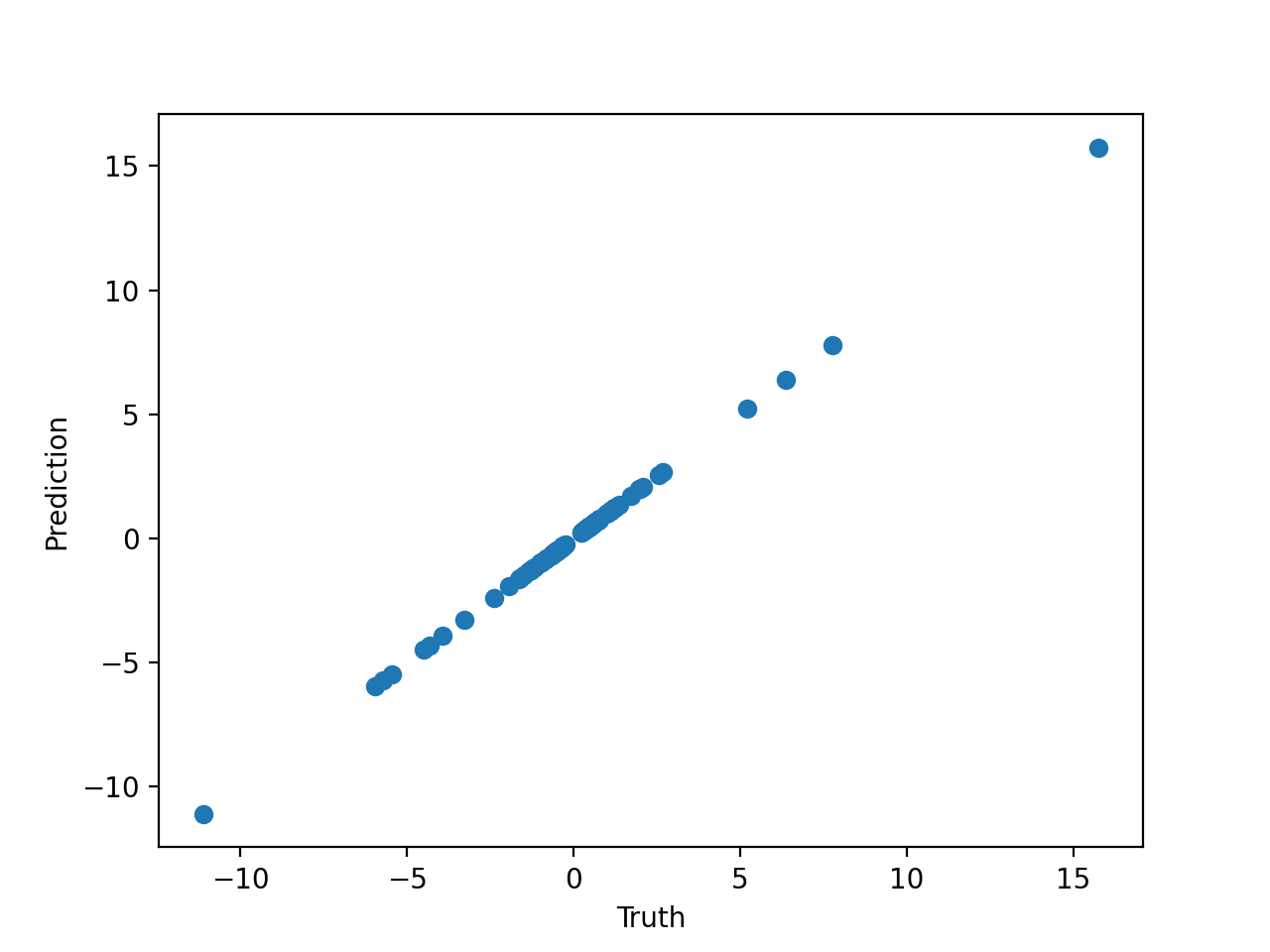
Let's plot the prediction against the truth:
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.scatter(y[:, 0], model.predict(X)[:, 0])
plt.xlabel('Truth')
plt.ylabel('Prediction')
plt.show()
Which gives us:
We may also plot the output of a particular expression
by passing the index of the expression to predict (or
sympy or latex as well)
5. Feature selection
PySR and evolution-based symbolic regression in general performs very poorly when the number of features is large. Even, say, 10 features might be too much for a typical equation search.
If you are dealing with high-dimensional data with a particular type of structure, you might consider using deep learning to break the problem into smaller "chunks" which can then be solved by PySR, as explained in the paper 2006.11287.
For tabular datasets, this is a bit trickier. Luckily, PySR has a built-in feature
selection mechanism. Simply declare the parameter select_k_features=5, for selecting
the most important 5 features.
Here is an example. Let's say we have 30 input features and 300 data points, but only 2 of those features are actually used:
X = np.random.randn(300, 30)
y = X[:, 3]**2 - X[:, 19]**2 + 1.5
Let's create a model with the feature selection argument set up:
model = PySRRegressor(
binary_operators=["+", "-", "*", "/"],
unary_operators=["exp"],
select_k_features=5,
)
Now let's fit this:
model.fit(X, y)
Before the Julia backend is launched, you can see the string:
Using features ['x3', 'x5', 'x7', 'x19', 'x21']
which indicates that the feature selection (powered by a gradient-boosting tree) has successfully selected the relevant two features.
This fit should find the solution quickly, whereas with the huge number of features, it would have struggled.
This simple preprocessing step is enough to simplify our tabular dataset, but again, for more structured datasets, you should try the deep learning approach mentioned above.
6. Denoising
Many datasets, especially in the observational sciences, contain intrinsic noise. PySR is noise robust itself, as it is simply optimizing a loss function, but there are still some additional steps you can take to reduce the effect of noise.
One thing you could do, which we won't detail here, is to create a custom log-likelihood
given some assumed noise model. By passing weights to the fit function, and
defining a custom loss function such as loss="myloss(x, y, w) = w * (x - y)^2",
you can define any sort of log-likelihood you wish. (However, note that it must be bounded at zero)
However, the simplest thing to do is preprocessing, just like for feature selection. To do this,
set the parameter denoise=True. This will fit a Gaussian process (containing a white noise kernel)
to the input dataset, and predict new targets (which are assumed to be denoised) from that Gaussian process.
For example:
X = np.random.randn(100, 5)
noise = np.random.randn(100) * 0.1
y = np.exp(X[:, 0]) + X[:, 1] + X[:, 2] + noise
Let's create and fit a model with the denoising argument set up:
model = PySRRegressor(
binary_operators=["+", "-", "*", "/"],
unary_operators=["exp"],
denoise=True,
)
model.fit(X, y)
print(model)
If all goes well, you should find that it predicts the correct input equation, without the noise term!
7. Julia packages and types
PySR uses SymbolicRegression.jl as its search backend. This is a pure Julia package, and so can interface easily with any other Julia package. For some tasks, it may be necessary to load such a package.
For example, let's say we wish to discovery the following relationship:
where $p_i$ is the $i$th prime number, and $x$ is the input feature.
Let's see if we can discover this using the Primes.jl package.
First, let's manually initialize the Julia backend
(here, with 8 threads and -O3):
import pysr
jl = pysr.julia_helpers.init_julia(julia_kwargs={"threads": 8, "optimize": 3})
jl stores the Julia runtime.
Now, let's run some Julia code to add the Primes.jl package to the PySR environment:
jl.eval("""
import Pkg
Pkg.add("Primes")
""")
This imports the Julia package manager, and uses it to install
Primes.jl. Now let's import Primes.jl:
jl.eval("import Primes")
Now, we define a custom operator:
jl.eval("""
function p(i::T) where T
if (0.5 < i < 1000)
return T(Primes.prime(round(Int, i)))
else
return T(NaN)
end
end
""")
We have created a a function p, which takes an arbitrary number as input.
p first checks whether the input is between 0.5 and 1000.
If out-of-bounds, it returns NaN.
If in-bounds, it rounds it to the nearest integer, compures the corresponding prime number, and then
converts it to the same type as input.
Next, let's generate a list of primes for our test dataset.
Since we are using PyJulia, we can just call p directly to do this:
primes = {i: jl.p(i*1.0) for i in range(1, 999)}
Next, let's use this list of primes to create a dataset of $x, y$ pairs:
import numpy as np
X = np.random.randint(0, 100, 100)[:, None]
y = [primes[3*X[i, 0] + 1] - 5 + np.random.randn()*0.001 for i in range(100)]
Note that we have also added a tiny bit of noise to the dataset.
Finally, let's create a PySR model, and pass the custom operator. We also need to define the sympy equivalent, which we can leave as a placeholder for now:
from pysr import PySRRegressor
import sympy
class sympy_p(sympy.Function):
pass
model = PySRRegressor(
binary_operators=["+", "-", "*", "/"],
unary_operators=["p"],
niterations=100,
extra_sympy_mappings={"p": sympy_p}
)
We are all set to go! Let's see if we can find the true relation:
model.fit(X, y)
if all works out, you should be able to see the true relation (note that the constant offset might not be exactly 1, since it is allowed to round to the nearest integer). You can get the sympy version of the best equation with:
model.sympy()
8. Complex numbers
PySR can also search for complex-valued expressions. Simply pass
data with a complex datatype (e.g., np.complex128),
and PySR will automatically search for complex-valued expressions:
import numpy as np
X = np.random.randn(100, 1) + 1j * np.random.randn(100, 1)
y = (1 + 2j) * np.cos(X[:, 0] * (0.5 - 0.2j))
model = PySRRegressor(
binary_operators=["+", "-", "*"], unary_operators=["cos"], niterations=100,
)
model.fit(X, y)
You can see that all of the learned constants are now complex numbers. We can get the sympy version of the best equation with:
model.sympy()
We can also make predictions normally, by passing complex data:
model.predict(X, -1)
to make predictions with the most accurate expression.
9. Additional features
For the many other features available in PySR, please read the Options section.