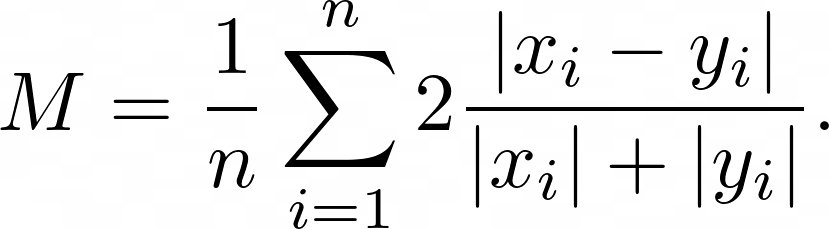Spaces:
Sleeping
A newer version of the Gradio SDK is available:
5.12.0
title: sMAPE
emoji: 🤗
colorFrom: blue
colorTo: red
sdk: gradio
sdk_version: 3.19.1
app_file: app.py
pinned: false
tags:
- evaluate
- metric
description: >-
Symmetric Mean Absolute Percentage Error (sMAPE) is the symmetric mean
percentage error difference between the predicted and actual values defined by
Chen and Yang (2004).
Metric Card for sMAPE
Metric Description
Symmetric Mean Absolute Error (sMAPE) is the symmetric mean of the percentage error of difference between the predicted $x_i$ and actual $y_i$ numeric values:
How to Use
At minimum, this metric requires predictions and references as inputs.
>>> smape_metric = evaluate.load("smape")
>>> predictions = [2.5, 0.0, 2, 8]
>>> references = [3, -0.5, 2, 7]
>>> results = smape_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references)
Inputs
Mandatory inputs:
predictions: numeric array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples,n_outputs), representing the estimated target values.references: numeric array-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples,n_outputs), representing the ground truth (correct) target values.
Optional arguments:
sample_weight: numeric array-like of shape (n_samples,) representing sample weights. The default isNone.multioutput:raw_values,uniform_averageor numeric array-like of shape (n_outputs,), which defines the aggregation of multiple output values. The default value isuniform_average.raw_valuesreturns a full set of errors in case of multioutput input.uniform_averagemeans that the errors of all outputs are averaged with uniform weight.- the array-like value defines weights used to average errors.
Output Values
This metric outputs a dictionary, containing the mean absolute error score, which is of type:
float: if multioutput isuniform_averageor an ndarray of weights, then the weighted average of all output errors is returned.- numeric array-like of shape (
n_outputs,): if multioutput israw_values, then the score is returned for each output separately.
Each sMAPE float value ranges from 0.0 to 2.0, with the best value being 0.0.
Output Example(s):
{'smape': 0.5}
If multioutput="raw_values":
{'smape': array([0.5, 1.5 ])}
Values from Popular Papers
Examples
Example with the uniform_average config:
>>> smape_metric = evaluate.load("smape")
>>> predictions = [2.5, 0.0, 2, 8]
>>> references = [3, -0.5, 2, 7]
>>> results = smape_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references)
>>> print(results)
{'smape': 0.5787...}
Example with multi-dimensional lists, and the raw_values config:
>>> smape_metric = evaluate.load("smape", "multilist")
>>> predictions = [[0.5, 1], [-1, 1], [7, -6]]
>>> references = [[0.1, 2], [-1, 2], [8, -5]]
>>> results = smape_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references)
>>> print(results)
{'smape': 0.8874...}
>>> results = smape_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references, multioutput='raw_values')
>>> print(results)
{'smape': array([1.3749..., 0.4])}
Limitations and Bias
This metric is called a measure of "percentage error" even though there is no multiplier of 100. The range is between (0, 2) with it being two when the target and prediction are both zero.
Citation(s)
@article{article,
author = {Chen, Zhuo and Yang, Yuhong},
year = {2004},
month = {04},
pages = {},
title = {Assessing forecast accuracy measures}
}