引言
Rain's SQLCoder 是自然语言生成 SparkSQL 的 SOTA 大型语言模型(LLM),拥有 32B 参数,基于 Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct 微调。 Rain's SQLCoder 针对自然语言到 SparkSQL 转换任务进行了优化,能够有效处理最长达 32k 个 token 的上下文,尤其适用于复杂且大规模的 SQL 查询生成任务。
🤗 Hugging Face | 🖥️ 演示 | 💬 微信 | GitHub
提示词
Rain's SQLCoder 采用了 Alpaca 模板,使用的提示词如下。
Below is an instruction that describes a task.
Write a response that appropriately completes the request.
### Instruction:
[BEGIN OF TASK INSTRUCTION]
You are an expert in composing Spark SQL queries. You are given a user query and a set of table schemas.
Based on the user query, you need to generate one Spark SQL query to achieve the purpose.
{task description for date hint and related question and sqls}
[END OF TASK INSTRUCTION]
[BEGIN OF TABLE SCHEMAS]
{schemas}
[END OF TABLE SCHEMAS]
[BEGIN OF GENERATION HINT]
{date hint}
[END OF GENERATION HINT]
[BEGIN OF RELATED QUERIES]
{related question and sqls}
[END OF RELATED QUERIES]
[BEGIN OF FORMAT INSTRUCTION]
The output MUST strictly adhere to the following format, and NO other text MUST be included.
```sql
your output Spark SQL query
```
[END OF FORMAT INSTRUCTION]
[BEGIN OF QUERY]
User Query: {user question}
[END OF QUERY]
### Response:
评估
我们沿用了 SQL-Eval 中评估预测结果与标准结果的逻辑:
- 如果预测的数据块和标准数据块完全一致,则预测结果正确;
- 标准SQL中不包含排序逻辑,且预测数据块和标准数据块在排序之后完全一致,则预测结果正确;
- 如果标准数据块的列是预测数据块的子集,则预测结果正确;
- 其余情况均认为预测结果错误。
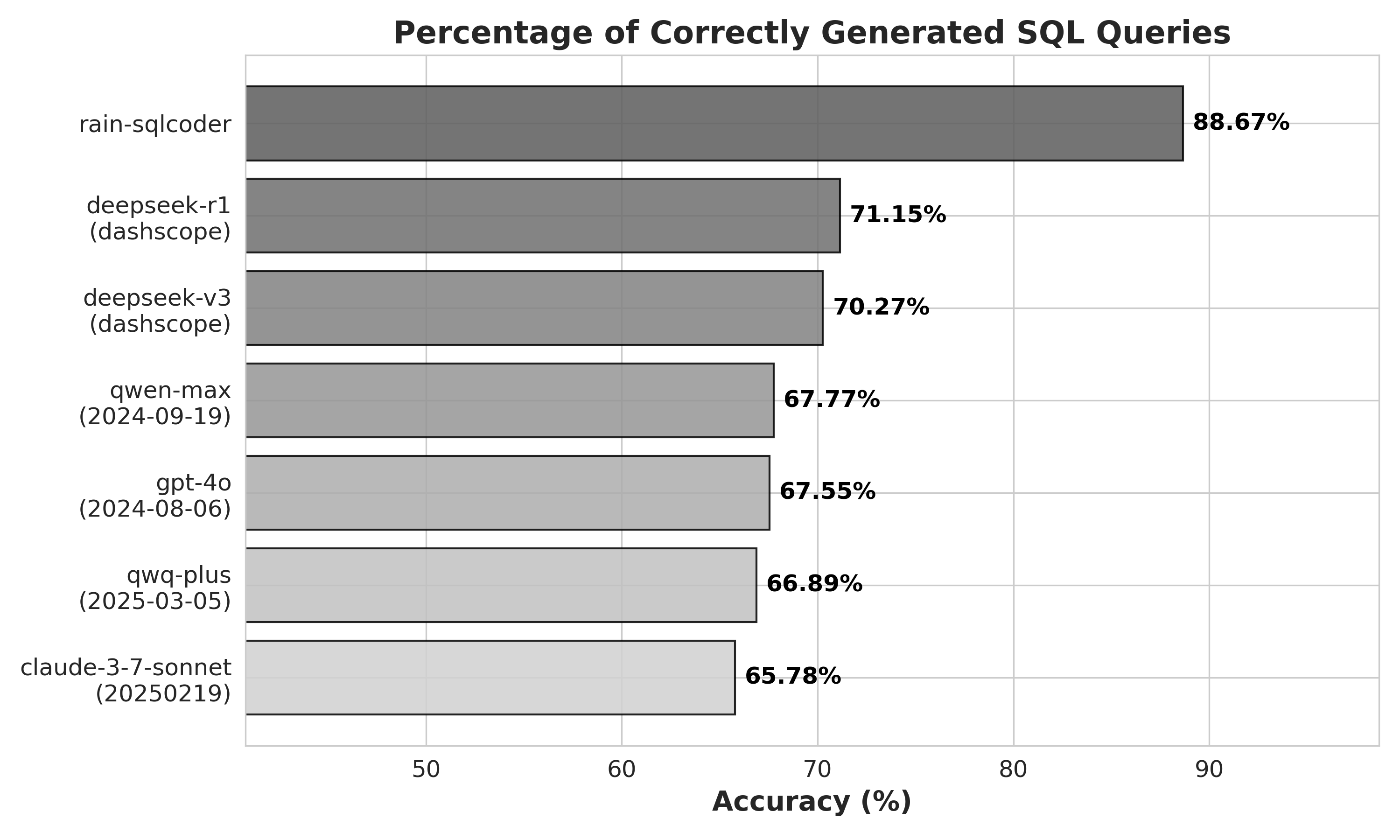
实验结果
我们在两个测试集上对比了Rain's SQLCoder与国内外先进自然语言大模型的生成准确率。其中,基准测试集(Benchmark Dataset)包含基础样本,而增强测试集(Enhanced Dataset)则是在基准测试集的基础上,通过分层抽样方法选取20%的样本,并补充了相关的用户查询及对应的SparkSQL语句,以评估模型在增强上下文信息下的性能表现。实验结果表明,Rain's SQLCoder在查询意图理解、SQL语法准确性和复杂查询处理等方面均展现出显著优势。
基准测试集

增强测试集
快速开始
我们在此处提供示例,帮助您快速掌握如何加载并使用我们的模型。
注意: Rain's SQLCoder 只被训练用于生成
SELECT语句,当表结构无法支持回答用户问题时,模型会拒绝回答。
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
from utils.prompt import SQLGeneratePrompt
model_name = "SuanChang/rain-SQLCoder"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="auto",
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
question = "What is the name of the department that offers a course that has a description including the word 'Statistics'?"
schemas = [
'''CREATE TABLE `course` (
`crs_code` STRING,
`dept_code` STRING,
`crs_description` STRING,
`crs_credit` DOUBLE
);''',
'''CREATE TABLE `department` (
`dept_code` STRING,
`dept_name` STRING,
`school_code` STRING,
`emp_num` INT,
`dept_address` STRING,
`dept_extension` INT
);''',
'''CREATE TABLE `student` (
`stu_num` INT,
`stu_lname` STRING,
`stu_fname` STRING,
`stu_init` STRING,
`stu_dob` STRING,
`stu_hrs` INT,
`stu_class` STRING,
`stu_gpa` DOUBLE,
`stu_transfer` INT,
`dept_code` STRING,
`stu_phone` INT,
`prof_num` INT
);'''
]
hint = "- Today is 2025-02-01."
data = dict(
question=question,
schema="\n\n".join(schemas),
hint=hint,
related_question_sqls=None,
)
text, _, _ = SQLGeneratePrompt.prompt(data)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=32768
)
generated_ids = [
output_ids[len(input_ids):] for input_ids, output_ids in zip(model_inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
response = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
print(response)
'''
```sql
SELECT d.dept_name FROM department d JOIN course c ON d.dept_code = c.dept_code WHERE c.crs_description LIKE '%Statistics%';
```
'''