MCP Course documentation
Build a Pull Request Agent on the Hugging Face Hub
Build a Pull Request Agent on the Hugging Face Hub
Welcome to Unit 3 of the MCP Course!
In this unit, we’ll build a pull request agent that automatically tags Hugging Face model repositories based on discussions and comments. This real-world application demonstrates how to integrate MCP with webhook listeners and automated workflows.
This unit showcases a real world use case where MCP servers can respond to real-time events from the Hugging Face Hub, automatically creating pull requests to improve repository metadata.
What You’ll Learn
In this unit, you will:
- Create an MCP Server that interacts with the Hugging Face Hub API
- Implement webhook listeners to respond to discussion events
- Set up automated tagging workflows for model repositories
- Deploy a complete webhook-driven application to Hugging Face Spaces
By the end of this unit, you’ll have a working PR agent that can monitor discussions and automatically improve repository metadata through pull requests.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with this unit, make sure you:
- Have completed Units 1 and 2, or have experience with MCP concepts
- Are comfortable with Python, FastAPI, and webhook concepts
- Have a basic understanding of Hugging Face Hub workflows and pull requests
- Have a development environment with:
- Python 3.11+
- A Hugging Face account with API access
Our Pull Request Agent Project
We’ll build a tagging agent that consists of four main components: the MCP server, webhook listener, agent logic, and deployment infrastructure. The agent will be able to tag model repositories based on discussions and comments. This should save model authors time by receiving ready to use PRs, instead of having to manually tag their repositories.

In the diagram above, we have a MCP server that can read and update model tags. We have a webhook listener that can receive webhooks from the Hugging Face Hub. We have an agent that can analyze discussions and comments and create PRs to update model tags. We have a deployment infrastructure that can deploy the MCP server to Hugging Face Spaces.
Project Overview
To build this application we will need the following files:
| File | Purpose | Description |
|---|---|---|
mcp_server.py | Core MCP Server | FastMCP-based server with tools for reading and updating model tags |
app.py | Webhook Listener & Agent | FastAPI app that receives webhooks, processes discussions, and creates PRs |
requirements.txt | Dependencies | Python packages including FastMCP, FastAPI, and huggingface-hub |
pyproject.toml | Project Configuration | Modern Python packaging with uv dependency management |
Dockerfile | Deployment | Container configuration for Hugging Face Spaces |
env.example | Configuration Template | Required environment variables and secrets |
cleanup.py | Utility | Helper script for development and testing cleanup |
Let’s go through each of these files and understand their purpose.
MCP Server ( mcp_server.py )
The heart of our application - a FastMCP server that provides tools for:
- Reading current tags from model repositories
- Adding new tags via pull requests to the Hub
- Error handling and validation
This is where you will implement the MCP server and do most of the work for this project. The Gradio app and FastAPI app will be used to test the MCP server and the webhook listener, and they are ready to use.
Webhook Integration
Following the Hugging Face Webhooks Guide, our agent:
- Listens for discussion comment events
- Validates webhook signatures for security
- Processes mentions and tag suggestions
- Creates pull requests automatically
Agent Functionality
The agent analyzes discussion content to:
- Extract explicit tag mentions (
tag: pytorch,#transformers) - Recognize implicit tags from natural language
- Validate tags against known ML/AI categories
- Generate appropriate pull request descriptions
Deployment & Production
- Containerized deployment to Hugging Face Spaces
- Environment variable management for secrets
- Background task processing for webhook responses
- Gradio interface for testing and monitoring
Webhook Integration Overview
Our PR agent leverages the same webhook infrastructure used by Hugging Face’s discussion bots. Here’s how webhooks enable real-time responses:
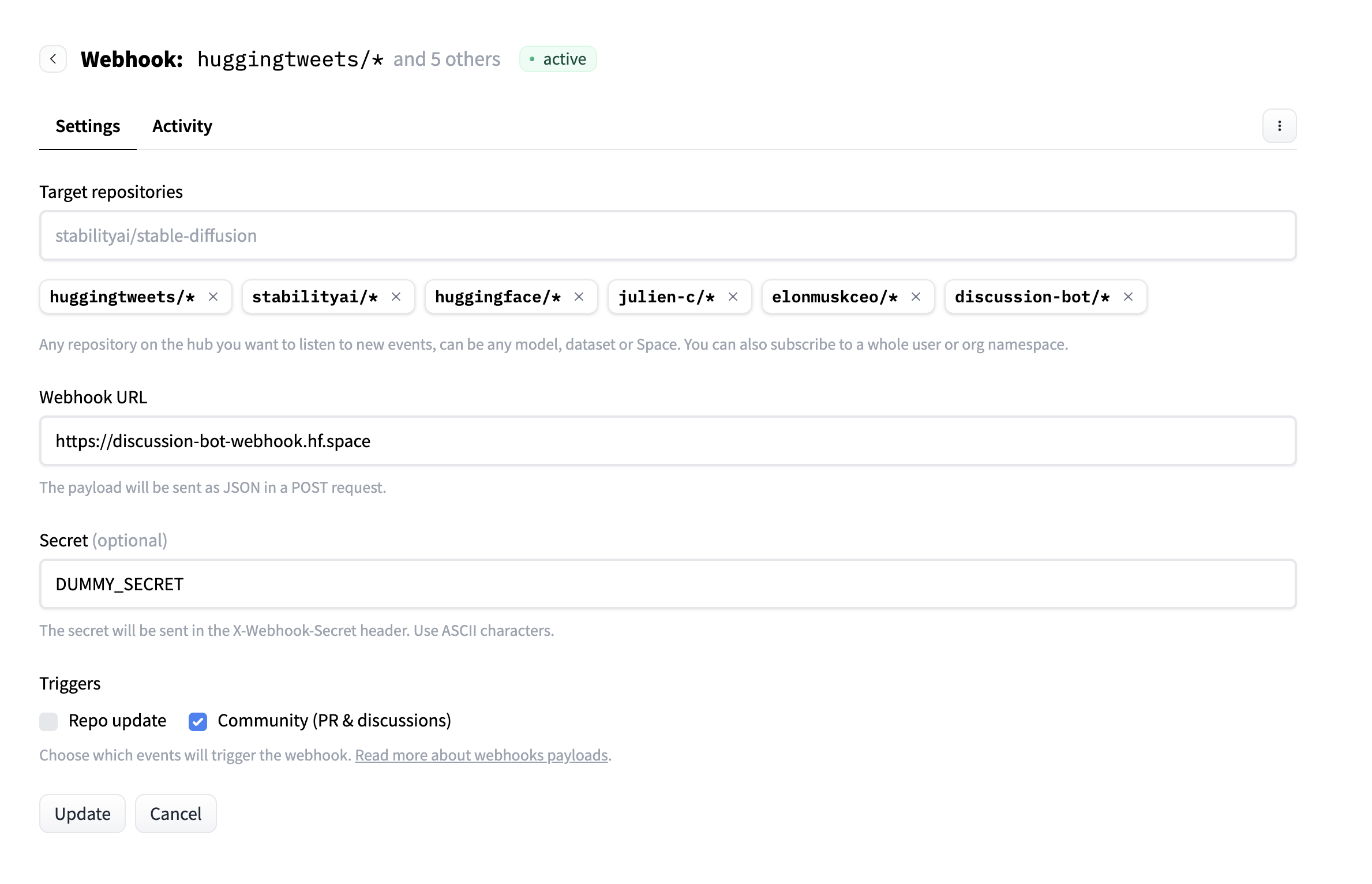
The webhook flow works as follows:
- Event Trigger: A user creates a comment in a model repository discussion
- Webhook Delivery: Hugging Face sends a POST request to our endpoint
- Authentication: We validate the webhook secret for security
- Processing: Our agent analyzes the comment for tag suggestions
- Action: If relevant tags are found, we create a pull request
- Response: The webhook returns immediately while PR creation happens in the background
Let’s Get Started!
Ready to build a production-ready PR agent that can automatically improve Hugging Face repositories? Let’s begin by setting up the project structure and understanding the MCP server implementation.
< > Update on GitHub