filename
stringlengths 7
140
| content
stringlengths 0
76.7M
|
|---|---|
code/shell_script/functions/src/nestedfunction.sh
|
#!/bin/bash
echo "Nested functions"
# First function
function1()
{
echo "Function 1 body"
function2;
}
# Second function
function2()
{
echo "Function 2 body"
}
function1
|
code/shell_script/functions/src/return_code.sh
|
#!/bin/bash
function1()
{
return $(($1*$2))
}
echo "Multiplication in Shell using Functions"
echo "Enter two numbers"
read num1
read num2
function1 $num1 $num2
mul=$?
echo "Multiplied value is $mul"
|
code/shell_script/functions/src/scope.sh
|
#!/bin/bash
# Declaring a global variable
gvar="I am the global variable!!!"
# Define a function
function1()
{
# Declaring a local variable
lvar="I am the local variable"
echo "$gvar"
echo "$lvar"
}
# Call the function
function1
|
code/shell_script/make_and_makefile/Makefile
|
mycalculator: main.c mymath.h add.c subtract.c multiply.c divide.c
gcc -o mycalculator main.c mymath.h add.c subtract.c multiply.c divide.c
|
code/shell_script/make_and_makefile/README.md
|
<div align="center">
<img src="https://github.com/kshitizsaini113/cosmos/blob/master/code/shell_script/make_and_makefile/make.png">
</div>
### Make
An automation tool predominantly used to compile and construct the binary executable files from a complex source code involving multiple imports and libraries.
### Makefile
* The “Make” command uses this “Makefile” to know the steps to build the binaries from the source code.
* By default, the “Make” command searches for a file named “Makefile” if the “Makefile” is not explicitly specified. At most places, the “Makefile” will be given the same name.
For more further information you may reffer [here.](https://iq.opengenus.org/introduction-to-make-and-makefile)
|
code/shell_script/make_and_makefile/add.c
|
#include "mymath.h"
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
|
code/shell_script/make_and_makefile/divide.c
|
#include "mymath.h"
int divide(int a, int b) {
return a / b;
}
|
code/shell_script/make_and_makefile/main.c
|
#include<stdio.h>
#include "mymath.h"
int main() {
int a, b;
printf("Hello World\n\n");
printf("Enter Two Numbers(A B): ");
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
printf("Addition: %d\n", add(a, b));
printf("Subtraction: %d\n", subtract(a, b));
printf("Multiplication: %d\n", multiply(a, b));
printf("Division: %d\n\n", divide(a, b));
return 0;
}
|
code/shell_script/make_and_makefile/multiply.c
|
#include "mymath.h"
int multiply(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
|
code/shell_script/make_and_makefile/mymath.h
|
int add(int a, int b);
int subtract(int a, int b);
int multiply(int a, int b);
int divide(int a, int b);
|
code/shell_script/make_and_makefile/subtract.c
|
#include "mymath.h"
int subtract(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
|
code/sorting/src/Frequency_Sort/Frequency_Sort.py
|
from collections import defaultdict
# Sort by Frequency
def sortByFreq(arr, n):
# arr -> Array to be sorted
# n -> Length of Array
# d is a hashmap(referred as dictionary in python)
d = defaultdict(lambda: 0)
for i in range(n):
d[arr[i]] += 1
# Sorting the array 'arr' where key
# is the function based on which
# the array is sorted
# While sorting we want to give
# first priority to Frequency
# Then to value of item
arr.sort(key=lambda x: (-d[x], x))
# arr = sorted(arr, key = lambda x: (-d[x],x))
return (arr)
# Driver Function
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [2, 5, 2, 6, -1, 9999999, 5, 8, 8, 8]
n = len(arr)
solution = sortByFreq(arr, n)
print(*solution)
|
code/sorting/src/README.md
|
# cosmos
Your personal library of every algorithm and data structure code that you will ever encounter.
A large scale collaboration of [OpenGenus](https://github.com/opengenus)
|
code/sorting/src/Wave_Sort/Wave_Sort.py
|
def sortWave(arr, n):
arr.sort()
# for i in range(0, n, 2):
# if i > 0 and arr[i-1] > arr[i]:
# arr[i], arr[i-1] = arr[i-1], arr[i]
# if i < n-1 and arr[i+1] > arr[i]:
# arr[i], arr[i+1] = arr[i+1], arr[i]
for i in range(0,n-1,2):
arr[i], arr[i+1] = arr[i+1], arr[i]
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [10, 90, 49, 2, 1, 5, 23]
sortWave(arr, len(arr))
print(arr)
|
code/sorting/src/bead_sort/README.md
|
# Bead sort
**Bead sort**, also called **gravity sort**, is a natural sorting algorithm.
In this algorithm, the idea is to represent positive integers by a set of beads, like those in an abacus. Beads are attached to vertical rods and appear to be suspended in air just before sliding down (a number is read by counting the number of beads horizontally). After these beads fall due to gravity, we get a sorted sequence of numbers from top to bottom.
## Explanation
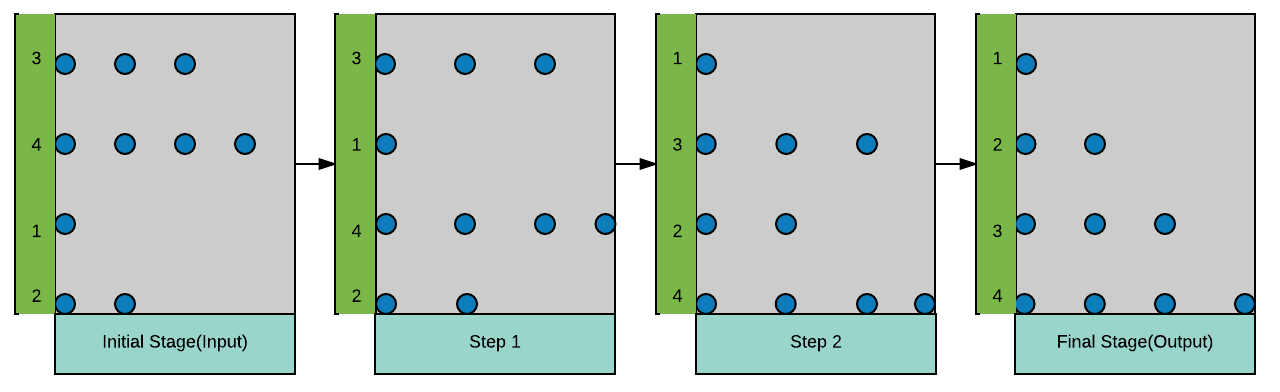
Sorting of `{3, 4, 1, 2}` using Bead Sort. Beads fall down one by one if there is space below.
## Algorithm
1. Find size, **n** and maximum element, **m** of the given array `A[]`.
2. Allocate memory and mark the beads such that there are n levels/rows and m rods/columns.
3. For all n in `A[]`, drop **n** beads(one bead per rod) along the rods, such that no bead is already present below it.
4. Repeat step 3 till a sorted sequence of numbers is obtained from top to bottom.
5. Put sorted values in array using beads.
## Complexity
**Time complexity**
- **O(1)**: All beads are dropped simultaneously in a single operation. It cannot be implemented in practice.
- **O(n<sup>0.5</sup>)**: It’s the estimation for the physical model, in which beads slide down along the greased spokes. The time of free fall is proportional to the square root of the maximum height, which is proportional to n.
- **O(n)**: The beads are moved one row at a time.
- **O(S)**: where S is the sum of the integers in the input set: Each bead is moved individually.
**Space complexity**: **O(n<sup>2</sup>)**
---
<p align="center">
A massive collaborative effort by <a href="https://github.com/OpenGenus/cosmos">OpenGenus Foundation</a>
</p>
---
|
code/sorting/src/bead_sort/bead_sort.c
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
void bead_sort(int *a, int len)
{
int i, j, max, sum;
unsigned char *beads;
# define BEAD(i, j) beads[i * max + j]
for (i = 1, max = a[0]; i < len; i++)
if (a[i] > max) max = a[i];
beads = calloc(1, max * len);
/* mark the beads */
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
for (j = 0; j < a[i]; j++)
BEAD(i, j) = 1;
for (j = 0; j < max; j++) {
/* count how many beads are on each post */
for (sum = i = 0; i < len; i++) {
sum += BEAD(i, j);
BEAD(i, j) = 0;
}
/* mark bottom sum beads */
for (i = len - sum; i < len; i++) BEAD(i, j) = 1;
}
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < max && BEAD(i, j); j++);
a[i] = j;
}
free(beads);
}
int main()
{
int i, x[] = {5, 3, 1, 7, 4, 1, 1, 20};
int len = sizeof(x)/sizeof(x[0]);
bead_sort(x, len);
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
printf("%d\n", x[i]);
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/bead_sort/bead_sort.cpp
|
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define BEAD(i, j) beads[i * max + j]
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
// function to perform the above algorithm
void beadSort(vector<int>& a)
{
// Find the maximum element
int max = a[0];
for (size_t i = 1; i < a.size(); ++i)
if (a[i] > max)
max = a[i];
// allocating memory
vector<unsigned char> beads(max * a.size(), 0);
// mark the beads
for (size_t i = 0; i < a.size(); ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < a[i]; ++j)
BEAD(i, j) = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < max; ++j)
{
// count how many beads are on each post
int sum = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < a.size(); ++i)
{
sum += BEAD(i, j);
BEAD(i, j) = 0;
}
// Move beads down
for (size_t i = a.size() - sum; i < a.size(); ++i)
BEAD(i, j) = 1;
}
// Put sorted values in array using beads
for (size_t i = 0; i < a.size(); ++i)
{
int j;
for (j = 0; j < max && BEAD(i, j); ++j)
;
a[i] = j;
}
}
// driver function to test the algorithm
int main()
{
vector<int> a{5, 3, 1, 7, 4, 1, 1, 20};
beadSort(a);
cout << "After Sorting.. " << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < a.size(); ++i)
cout << a[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/bead_sort/bead_sort.cs
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
using System;
using System.Linq;
namespace CS
{
public class BeadSort
{
public BeadSort()
{
}
static int[] Sort(int[] arr) {
int max = arr.Max();
var grid = new bool[arr.Length, max];
int[] levelCount = new int[max];
for(int i = 0; i < max; i++) {
levelCount[i] = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < arr.Length; j++) {
grid[j, i] = false;
}
}
foreach (var num in arr)
{
var tmpNum = num;
for (int j = 0; tmpNum > 0; j++, tmpNum--)
{
grid[levelCount[j]++, j] = true;
}
}
var sorted = new int[arr.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
int putt = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < max && grid[arr.Length - 1 - i, j] == true; j++)
{
putt++;
}
sorted[i] = putt;
}
return sorted;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
const int numbers = 25;
int[] arr = new int[numbers];
var rand = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < numbers; i++)
{
arr[i] = rand.Next(99);
}
Console.WriteLine("Before Sorting");
foreach (var num in arr)
{
Console.Write(num + " ");
}
var sorted = Sort(arr);
Console.WriteLine("\nSorted:");
foreach (var num in sorted)
{
Console.Write(num + " ");
}
}
}
}
|
code/sorting/src/bead_sort/bead_sort.java
|
import java.util.Arrays;
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
public class BeadSort {
private enum BeadSortStatus {
MARKED,
NOT_MARKED,
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrayToSort = new int[]{4, 1, 6, 2, 40, 5, 3, 8, 7};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(beadSort(arrayToSort)));
}
public static int[] beadSort(int[] arr) {
int max = 0;
for (int anArr : arr) {
if (anArr > max) {
max = anArr;
}
}
//Set up abacus
BeadSortStatus[][] grid = new BeadSortStatus[arr.length][max];
int[] levelcount = new int[max];
for(int i = 0; i < max; i++) {
levelcount[i] = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
grid[j][i] = BeadSortStatus.NOT_MARKED;
}
}
//Drop the beads
for (int anArr : arr) {
int num = anArr;
for (int j = 0; num > 0; j++, num--) {
grid[levelcount[j]++][j] = BeadSortStatus.MARKED;
}
}
//Count the beads
int[] sorted=new int[arr.length];
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int putt = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < max && grid[arr.length - 1 - i][j] == BeadSortStatus.MARKED; j++) {
putt++;
}
sorted[i] = putt;
}
return sorted;
}
}
|
code/sorting/src/bead_sort/bead_sort.js
|
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
function range(x) {
var res = [];
for (var i = 0; i < x; i++) {
res.push(i);
}
return res;
}
function determinePrev(arr, idx) {
return arr
.filter(function(x) {
return x.length > idx;
})
.map(function() {
return 1;
})
.reduce(function(p1, p2) {
return p1 + p2;
}, 0);
}
function beadsort(arr) {
var ref = arr.map(function(x) {
return range(x);
});
var inter = [];
var idx = 0;
var prev = determinePrev(ref, idx);
while (prev) {
inter.push(range(prev));
idx++;
prev = determinePrev(ref, idx);
}
idx = 0;
prev = determinePrev(inter, idx);
var out = [];
while (prev) {
out.push(prev);
idx++;
prev = determinePrev(inter, idx);
}
return out.reverse();
}
console.log(beadsort([4, 1, 6, 2, 40, 5, 3, 8, 7]));
|
code/sorting/src/bead_sort/bead_sort.m
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
//
// bead_sort.m
// Created by DaiPei on 2017/10/12.
//
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface BeadSort : NSObject
- (void)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array;
@end
@implementation BeadSort
- (void)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array {
NSNumber *max = @(INTMAX_MIN);
int n = (int)array.count;
// find the max value
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if ([max compare:array[i]] == NSOrderedAscending) {
max = array[i];
}
}
int m = max.intValue;
int8_t *beads = calloc(m * n, sizeof(int8_t));
// put beads
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (j < array[i].intValue) {
beads[i * m + j] = 1;
}
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// count beads
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum += beads[i * m + j];
beads[i * m + j] = 0;
}
// move down beads
for (int i = n - sum; i < n; i++) {
beads[i * m + j] = 1;
}
}
// put sorted value in array using beads
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int j;
for (j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (beads[i * m + j] == 0) {
break;
}
}
array[i] = @(j);
}
}
@end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
NSMutableArray *array = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:3];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
uint32_t ran = arc4random() % 10;
[array addObject:@(ran)];
}
NSLog(@"before: %@", array);
BeadSort *bs = [[BeadSort alloc] init];
[bs sort:array];
NSLog(@"after: %@", array);
}
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/bead_sort/bead_sort.php
|
<?php
function columns($arr) {
if (count($arr)==0)
return array();
else if (count($arr)==1)
return array_chunk($arr[0],1);
array_unshift($arr,NULL);
$transpose=call_user_func_array('array_map', $arr);
return array_map('array_filter',$transpose);
}
function beadsort($arr) {
foreach ($arr as $e)
$poles []=array_fill(0, $e, 1);
return array_map('count',columns(columns($poles)));
}
$a=(beadsort(array(15,23,5,14,13,2,1)));
print_r(array_reverse($a));
|
code/sorting/src/bead_sort/bead_sort.py
|
# Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
def bead_sort(obj):
if all([type(x) == int and x >= 0 for x in obj]):
ref = [range(x) for x in obj] # for reference
else:
raise ValueError("All elements must be positive integers")
inter = [] # for intermediate
ind = 0 # for index
prev = sum([1 for x in ref if len(x) > ind]) # prev for previous
while prev:
inter.append(range(prev))
ind += 1
prev = sum([1 for x in ref if len(x) > ind])
ind = 0
prev = sum([1 for x in inter if len(x) > ind])
out = []
while prev:
out.append(prev)
ind += 1
prev = sum([1 for x in inter if len(x) > ind])
out = out[::-1]
return out
|
code/sorting/src/bead_sort/bead_sort.swift
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
//
// bead_sort.swift
// Created by DaiPei on 2017/10/12.
//
import Foundation
func beadSort(_ array: inout [Int]) {
let n = array.count
var m = Int.min
// find the max value
for i in 0..<n {
if array[i] > m {
m = array[i]
}
}
var beads = [Int8](repeatElement(0, count: m * n))
// put beads
for i in 0..<n {
for j in 0..<m {
if j < array[i] {
beads[i * m + j] = 1
}
}
}
for j in 0..<m {
// count beads
var sum = 0
for i in 0..<n {
sum += Int(beads[i * m + j])
beads[i * m + j] = 0
}
// move down beads
for i in n - sum..<n {
beads[i * m + j] = 1
}
}
// put sorted value in array using beads
for i in 0..<n {
var j = 0
while j < m {
if beads[i * m + j] == 0 {
break
}
j += 1
}
array[i] = j
}
}
|
code/sorting/src/bead_sort/bead_sort_numpy.py
|
# Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
import numpy as np
def bead_sort(arr):
"""
>>> bead_sort([5, 3, 1, 7, 4, 1, 1, 20])
[1, 1, 1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 20]
"""
# expand input array to table of beads
beads = np.zeros((len(arr), max(arr)), int)
for i, x in enumerate(arr):
beads[i, :x] = 1
# move beads down
for j, s in enumerate(beads.sum(axis=0)):
beads[:-s, j] = 0
beads[-s:, j] = 1
# reduce table of moved down beads back to array
return list(beads.sum(axis=1))
|
code/sorting/src/bogo_sort/README.md
|
# Bogosort
Bogosort or **permutation sort** is an extremely inefficient sorting algorithm. This is due to it's random nature: it randomly generates permutations of it's input until it finds one that is sorted. It has no use in practical applications.
## Explanation
Consider an array: `[ 2 3 5 0 1 ]`
```
5 3 2 0 1 (1st shuffling)
1 3 2 5 0 (2nd shuffling)
1 0 2 5 3 (2nd shuffling)
.
.
.
0 1 2 3 5 (nth shuffling) - Sorted Array
```
Where, **n** is unknown as this algorithm does not tell, in which step the resultant permutation will be sorted.
## Algorithm
```
while not in_order(list) do
shuffle (list)
done
```
## Complexity
**Time complexity**
- Worst case: **O(∞)**
- Average case: **O(n * n!)**
- Best case: **O(n)**
**Space complexity**: **O(1)** auxillary
---
<p align="center">
A massive collaborative effort by <a href="https://github.com/OpenGenus/cosmos">OpenGenus Foundation</a>
</p>
---
|
code/sorting/src/bogo_sort/bogo_or_permutation_sort.py
|
# Python program for implementation of Bogo Sort or Permutation Sort
import random
# Sorts array a[0..n-1] using Bogo sort
def bogoSort(a):
n = len(a)
while (is_sorted(a)== False):
shuffle(a)
# To check if array is sorted or not
def is_sorted(a):
n = len(a)
for i in range(0, n-1):
if (a[i] > a[i+1] ):
return False
return True
# To generate permutation of the array
def shuffle(a):
n = len(a)
for i in range (0,n):
r = random.randint(0,n-1)
a[i], a[r] = a[r], a[i]
# Driver code to test above
a = [3, 2, 4, 1, 0, 5]
bogoSort(a)
print("Sorted array :")
for i in range(len(a)):
print ("%d" %a[i]),
|
code/sorting/src/bogo_sort/bogo_sort.c
|
/* Part of cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
/*
* bogo_sort.c
* created by Riya
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int
main()
{
int num[10]={1, 4, 7, 5, 9, 2, 6, 3, 8, 0};
int i;
bogosort(num, 10);
printf("The array after sorting is:");
for (i = 0;i < 10;i++) {
printf("%d\n", num[i]);
} printf("\n");
}
int
is_sorted(int *a, int n)
{
while ( --n >= 1 ) {
if ( a[n] < a[n-1] )
return (0);
}
return (1);
}
void
shuffle(int *a, int n)
{
int i, t, temp;
for (i = 0;i < n;i++) {
t = a[i];
temp = rand() % n;
a[i] = a[temp];
a[temp] = t;
}
}
void
bogosort(int *a, int n)
{
while ( !is_sorted(a, n) )
shuffle(a, n);
}
|
code/sorting/src/bogo_sort/bogo_sort.cpp
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
// C++ implementation of BogoSort by ldaw
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
bool isSorted(const std::vector<int> &v)
{
int i = v.size();
while (--i > 0)
if (v[i] < v[i - 1])
return false;
return true;
}
void shuffle(std::vector<int> &v)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
std::swap( v[i], v[ rand() % v.size() ] );
}
void bogoSort(std::vector<int> &v)
{
while (!isSorted(v) )
shuffle(v);
}
int main()
{
std::srand(time(NULL));
std::vector<int> v = {2, 4, 1, 3, 6, 7, 8, 5};
// Please note, initializer lists are a C++11 feature
bogoSort(v);
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
std::cout << v[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/bogo_sort/bogo_sort.fs
|
//Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
open System
let rnd = Random()
//Simple method to shuffle lists, not really random in terms of crypthography
let shuffle (x:IComparable list)=
List.sortBy(fun x -> rnd.Next()) x
let isSorted (sList:IComparable list)=
let folder = fun (a,b) x -> (a && (b<=x),x)
fst << List.fold (folder) (true,sList.[0]) <| sList
let rec bogosort (x: IComparable list)=
let shuffled = shuffle x
if isSorted shuffled then
shuffled
else
bogosort x
[<EntryPoint>]
let main (argv) =
printfn "%A" <| bogosort [14;3;31;4;92;1]
0
|
code/sorting/src/bogo_sort/bogo_sort.go
|
//Part of Cosmos Project by OpenGenus Foundation
//Bogo Sort implementation on golang
//Written by Guilherme Lucas(guilhermeslucas)
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sort"
"math/rand"
)
func shuffle(arr []int) []int {
for i := range arr {
j := rand.Intn(i + 1)
arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
}
return arr
}
func bogoSort (array []int) []int {
for {
if sort.IntsAreSorted(array) {
return array
}
array = shuffle(array[:])
}
}
func main() {
var array = []int{1,5,8,2,6,9}
sorted := bogoSort(array)
fmt.Println("Sorted sequence is:", sorted)
}
|
code/sorting/src/bogo_sort/bogo_sort.java
|
public class Bogosort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args.length == 1) {
String[] arr = args[0].split(",");
Integer[] intArr = new Integer[arr.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
intArr[i] = Integer.parseInt(arr[i]);
}
intArr = sort(intArr);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = intArr[i].toString();
}
System.out.println(String.join(", ", arr));
} else {
System.out.println("An array needs to be passed in!");
}
}
public static boolean isSorted(Integer[] arr) {
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i - 1] > arr[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
};
public static Integer[] shuffle(Integer[] arr) {
String[] strArr = new String[arr.length];
Integer count = arr.length, temp, index;
while (count > 0) {
index = (int)(Math.random() * count);
count--;
temp = arr[count];
arr[count] = arr[index];
arr[index] = temp;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
strArr[i] = arr[i].toString();
}
System.out.println(String.join(", ", strArr));
return arr;
}
public static Integer[] sort(Integer[] arr) {
boolean sorted = false;
while (!sorted) {
arr = shuffle(arr);
sorted = isSorted(arr);
}
return arr;
}
}
|
code/sorting/src/bogo_sort/bogo_sort.js
|
function bogosort(arr) {
var isSorted = function(arr) {
for (var i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i - 1] > arr[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
};
function shuffle(arr) {
var count = arr.length,
temp,
index;
while (count > 0) {
index = Math.floor(Math.random() * count);
count--;
temp = arr[count];
arr[count] = arr[index];
arr[index] = temp;
}
return arr;
}
function sort(arr) {
var sorted = false;
while (!sorted) {
arr = shuffle(arr);
sorted = isSorted(arr);
}
return arr;
}
return sort(arr);
}
console.log(bogosort([-5, 3, 6, 3, 7, 8]));
|
code/sorting/src/bogo_sort/bogo_sort.m
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
//
// bogo_sort.m
// Created by DaiPei on 2017/10/14.
//
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface BogoSort : NSObject
- (void)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array;
@end
@implementation BogoSort
- (void)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array {
while (![self isSorted:array]) {
[self shuffle:array];
}
}
- (BOOL)isSorted:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array {
if (array.count <= 1) {
return YES;
}
for (int i = 1; i < array.count; i++) {
if ([array[i] compare:array[i - 1]] == NSOrderedAscending) {
return NO;
}
}
return YES;
}
- (void)shuffle:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array {
for (int i = 0; i < array.count; i++) {
int j = arc4random() % array.count;
[self swap:array at:i and:j];
}
}
- (void)swap:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array at:(NSUInteger)indexA and:(NSUInteger)indexB {
NSNumber *tmp = array[indexA];
array[indexA] = array[indexB];
array[indexB] = tmp;
}
@end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
int n = 0;
NSLog(@"What is the size of the array?");
scanf("%d", &n);
NSMutableArray *array = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:n];
NSLog(@"Enter elements of the array one by one:");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int tmp;
scanf("%d", &tmp);
[array addObject:@(tmp)];
}
BogoSort *bs = [[BogoSort alloc] init];
[bs sort:array];
NSLog(@"%@", array);
}
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/bogo_sort/bogo_sort.pl
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
/*
* Implementation of bogo_sort in prolog by arvchristos
* using random_permutation predicate
* usage: bogo_sort(List_unsorted, List_sorted).
* true when List_sorted is a sorted permutation of List List_unsorted
*
* Predicate ...
*/
ordered([_]).
ordered([H|[H1|T]]) :-
H =< H1,
ordered([H1|T]).
bogo_sort(X,Y):-
random_permutation(X,Y1),
( ordered(Y1) -> Y = Y1 ; bogo_sort(X,Y) ).
|
code/sorting/src/bogo_sort/bogo_sort.py
|
import random
# Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
def bogo_sort(l):
while not in_order(l):
random.shuffle(l)
return l
def in_order(l):
if not l:
return True
last = l[0]
for x in l[1:]:
if x < last:
return False
last = x
return True
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(bogo_sort([5, 2, 3, 4, 1]))
|
code/sorting/src/bogo_sort/bogo_sort.rb
|
def bogosort(arr)
arr.shuffle! until in_order?(arr)
arr
end
def in_order?(arr)
return true if arr.empty?
last = arr[0]
arr[1...arr.length].each do |x|
return false if x < last
last = x
end
true
end
p bogosort([3, 2, 1])
|
code/sorting/src/bogo_sort/bogo_sort.swift
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
//
// bogo_sort.swift
// Created by DaiPei on 2017/10/14.
//
import Foundation
func bogoSort(_ array: inout [Int]) {
while !isSorted(array) {
shuffle(&array)
}
}
private func shuffle(_ array: inout [Int]) {
for i in 0..<array.count {
let j = Int(arc4random()) % array.count
swap(&array, at: i, and: j)
}
}
private func isSorted(_ array: [Int]) -> Bool {
if array.count <= 1 {
return true
}
for i in 1..<array.count {
if array[i] < array[i - 1] {
return false
}
}
return true
}
private func swap(_ array: inout [Int], at indexA: Int, and indexB: Int) {
let tmp = array[indexA]
array[indexA] = array[indexB]
array[indexB] = tmp
}
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/BubbleSort.asm
|
; Author: SYEED MOHD AMEEN
; Email: [email protected]
;----------------------------------------------------------------;
; BUBBLESORT SORT SUBROUTINE ;
;----------------------------------------------------------------;
;----------------------------------------------------------------;
; FUNCTION PARAMETERS ;
;----------------------------------------------------------------;
; 1. push number of element in array ;
; 2. push base address of Array ;
;----------------------------------------------------------------;
BUBBLESORT:
POP AX ;RET ADDRESS OF SUBROUTINE
POP SI ;BASE ADDRESS OF ARRAY
POP CX ;COUNTER REGISTER
PUSH AX ;RET ADDRESS PUSH INTO STACK
COUNTER_BUBBLESORT: EQU 0X4000 ;CREATE UPTO EIGHT 16-BIT COUNTER VARIABLE
DPTR_BUBBLESORT: EQU 0X4010 ;DATA POINTER
MOV DS:[COUNTER_BUBBLESORT],CX ;TEMP STORE UPPER COUNTER
MOV DS:[COUNTER_BUBBLESORT+2],CX ;TEMP STORE LOWER COUNTER
MOV DS:[DPTR_BUBBLESORT],SI ;TEMP STORE BASE ADDRESS OF ARRAY
REPEAT_BUBBLESORT:
MOV AH,[SI] ;MOV A[I] INTO AH REG.
CMP AH,[SI+1] ;COMPARE AH WITH A[I+1]
JC NOSWAP_BUBBLESORT ;JUMP IF A[I] < A[I+1]
XCHG AH,[SI+1] ;SWAP ELEMENTS
NOSWAP_BUBBLESORT:
INC SI ;INC ARRAY INDEX REG. (SOURCE INDEX)
LOOP REPEAT_BUBBLESORT
MOV CX,DS:[COUNTER_BUBBLESORT+2] ;FETCH COUNTER INTO CX REG.
MOV SI,DS:[DPTR_BUBBLESORT] ;MOVE STARTING INDEX INTO SI REG.
DEC [COUNTER_BUBBLESORT] ;DEC UPPER COUNTER
JNZ REPEAT_BUBBLESORT ;REPEAT UNTIL COUNTER != 0
RET ;RET SUBROUTINE
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/README.md
|
# Bubble Sort
**Bubble Sort** is the simplest sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly swapping the adjacent elements if they are in wrong order.
In computer graphics it is popular for its capability to detect a very small error (like swap of just two elements) in almost-sorted arrays and fix it with just linear complexity (2n). For example, it is used in a polygon filling algorithm, where bounding lines are sorted by their x coordinate at a specific scan line (a line parallel to x axis) and with incrementing y their order changes (two elements are swapped) only at intersections of two lines. Bubble sort is stable and adaptive in nature.
**Stable :** If any sorting algorithm preserving the order of duplicate elements in the sorted list then that algorithm is called stable.
## Explanation : Why bubble sort algorithm is stable by nature
**Case 1: Sorted by name**
**Name :** A B C D E F G
**Marks:** 5 8 6 4 6 7 10
**Case 2: Sorted by marks**
**Name :** D A C E F B G
**Marks:** 4 5 6 6 7 8 10
In both the cases we have duplicate elements and i.e C and E, but in Case 1 we sort by name and in Case 2 we sort by marks but in both the cases we observe that C comes first and then E. So if duplicate elements exist in the list their order should preserved. Here don't relate order with the index.
**Adaptive :** If any sorting method is taking less time or minimum time over already sorted list then we call that algorithm as adaptive.
## Explanation : Why bubble sort algorithm is adaptive by nature
**Elements :** 2 3 5 7 8
**Bubble sort algorithm** is comparison based algorithm and right now we have sorted list of elements so if you compare the elements you find that
<br>
2 is less than 3
<br>
3 is less than 5
<br>
5 is less than 7
<br>
7 is less than 8
<br>
so we observe n is less than n+1, so no swaping will take place and if no swaping that means list is already sorted and that's why minimum time complexity of bubble sort algorithm is O(n).
## Explanation
**First Pass:**
( 5 1 4 2 8 ) –> ( 1 5 4 2 8 ), Here, algorithm compares the first two elements, and swaps since 5 > 1.
<br>
( 1 5 4 2 8 ) –> ( 1 4 5 2 8 ), Swap since 5 > 4.
<br>
( 1 4 5 2 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 ), Swap since 5 > 2.
<br>
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 ), Now, since these elements are already in order (8 > 5), algorithm does not swap them.
<br>
**Second Pass:**
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 )
<br>
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 ), Swap since 4 > 2
<br>
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
<br>
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
Now, the array is already sorted, but our algorithm does not know if it is completed. The algorithm needs one whole pass without any swap to know it is sorted.
<br>
**Third Pass:**
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
<br>
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
<br>
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
<br>
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
## Algorithm
```
begin BubbleSort(list)
for unsorted_end in list[n...1]
for unsorted_beg of list[1...unsorted_end-1]
if list[unsorted_beg] > list[unsorted_beg+1]
swap(list[unsorted_beg], list[unsorted_beg+1])
end if
end for
end for
return list
end BubbleSort
```
## Implementation in c++
```
void Bubble_Sort(int A[], int n)
{
int i, j, flag=0;
for(i=0;i<n-i;i++)
{
flag=0;
for(j=0;j<n-i-1;j++)
{
if(A[j]>A[j+1])
{
swap(A[j], A[j+1]);
flag=1;
}
}
if(flag==0)
break;
}
}
```
## Complexity
**Time complexity**
- Average and worst case: **O(n<sup>2</sup>)**
- Best case: **O(n)**
**Space complexity**: : **O(1)** auxillary
---
<p align="center">
A massive collaborative effort by <a href="https://github.com/OpenGenus/cosmos">OpenGenus Foundation</a>
</p>
---
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.c
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
#include <stdio.h>
typedef int bool;
/* Swap two elements */
void
swap(int *p, int *q)
{
int temp = *p;
*p = *q;
*q = temp;
}
/* Sort array using bubble sort */
void
bubbleSort(int arr[], int n, bool order)
{
/* Order 1 corresponds to ascending sort */
if (order == 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
swap(&arr[j], &arr[j + 1]);
}
}
}
}
/* Order 0 corresponds to ascending sort */
else if (order == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[j + 1]) {
swap(&arr[j], &arr[j + 1]);
}
}
}
}
/* If any other value of order is passed */
else {
printf("Undefined Sorting Order");
}
}
/* Print sorted array */
void
print(int a[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int
main()
{
int n;
/* Input array size */
printf("What is the size of the array?\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
int arr[n];
/* Input elements of array */
printf("Enter elements of the array one by one\n");
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("\n%d",&arr[i]);
}
bool order;
/* Input order of sorting. 1 for Ascending, 0 for Descending */
printf("Enter order of sorting (1: Ascending; 0: Descending)\n");
scanf("%d", &order);
/* If user inputs order besides 1 or 0 */
if (order != 0 && order != 1) {
printf("Undefined sorting order.\n");
return 1;
}
bubbleSort(arr, n, order);
printf("Sorted array: ");
print(arr, n);
return (0);
}
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.cpp
|
/*
* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
*
* bubble sort synopsis
*
* template<typename _Bidirectional_Iter, typename _Compare>
* void
* bubbleSort(_Bidirectional_Iter begin, _Bidirectional_Iter end, _Compare compare);
*
* template<typename _Bidirectional_Iter>
* void
* bubbleSort(_Bidirectional_Iter begin, _Bidirectional_Iter end);
*/
#include <functional>
template<typename _Bidirectional_Iter, typename _Compare>
void
bubbleSort(_Bidirectional_Iter begin, _Bidirectional_Iter end, _Compare compare)
{
if (begin != end)
{
auto frontOfSorted = end;
for (--frontOfSorted; frontOfSorted != begin; --frontOfSorted)
{
bool swapped{};
for (auto j = begin; j != frontOfSorted; ++j)
{
auto nextOfJ = j;
if (compare(*++nextOfJ, *j))
{
std::iter_swap(nextOfJ, j);
swapped = true;
}
}
if (swapped == false)
break;
}
}
}
template<typename _Bidirectional_Iter>
void
bubbleSort(_Bidirectional_Iter begin, _Bidirectional_Iter end)
{
using value_type = typename std::iterator_traits<_Bidirectional_Iter>::value_type;
bubbleSort(begin, end, std::less<value_type>());
}
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.cs
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
using System;
using System.Linq;
namespace BubbleSortCSharp
{
class BubbleSort
{
static void sort(int[] a){
for (int i = a.Length - 1; i > 0; i--)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= i - 1; j++)
{
if (a[j] > a[j + 1])
{
int temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter values to sort separated by space");
var a = Console.ReadLine().Split(' ')
.Select(i => int.Parse(i))
.ToArray();
sort(a);
Console.WriteLine("Sorted Array: ");
foreach(int item in a)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
}
}
}
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.dart
|
void main() {
List<int> array = [5, 1, 4, 2, 8];
List<int> sortedarray = bubbleSort(array);
print(sortedarray);
}
bubbleSort(List<int> array) {
int lengthOfArray = array.length;
for (int i = 0; i < lengthOfArray - 1; i++) {
print('Index i at pos: ${i}');
for (int j = 0; j < lengthOfArray - i - 1; j++) {
print('loop:${i}');
print('index i and j at pos: ${i} & ${j}');
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return (array);
}
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.elm
|
module BubbleSort exposing (sort)
import Tuple
sort : List a -> (a -> a -> Order) -> List a
sort list order =
let
( swapped, listResult ) =
swapPass ( False, list ) order
in
if swapped then
sort listResult order
else
listResult
swapPass : ( Bool, List a ) -> (a -> a -> Order) -> ( Bool, List a )
swapPass ( swapped, list ) order =
case list of
x0 :: x1 :: xs ->
case order x0 x1 of
LT ->
let
( swapped_, result ) =
swapPass ( swapped, x1 :: xs ) order
in
( swapped_, x0 :: result )
EQ ->
let
( swapped_, result ) =
swapPass ( swapped, x1 :: xs ) order
in
( swapped_, x0 :: result )
GT ->
let
( swapped_, result ) =
swapPass ( swapped, x0 :: xs ) order
in
( True, x1 :: result )
x1 :: [] ->
( swapped, [ x1 ] )
[] ->
( swapped, [] )
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.exs
|
"""
Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
"""
defmodule Sort do
def bubble_sort(list) when length(list)<=1, do: list
def bubble_sort(list) when is_list(list), do: bubble_sort(list, [])
def bubble_sort([x], sorted), do: [x | sorted]
def bubble_sort(list, sorted) do
{rest, [max]} = Enum.split(bubble_move(list), -1)
bubble_sort(rest, [max | sorted])
end
def bubble_move([x]), do: [x]
def bubble_move([x, y | t]) when x > y, do: [y | bubble_move([x | t])]
def bubble_move([x, y | t]) , do: [x | bubble_move([y | t])]
end
IO.inspect Sort.bubble_sort([3,2,1,4,5,2])
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.f
|
!/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
!Fortran implementation of bubble sorting algorithm
program bubblesort
parameter (nkt = 8)
real unsorted(nkt)
real sorted(nkt)
data unsorted/144, 89, 4, 9, 95, 12, 86, 25/
REAL :: temp
INTEGER :: i, j
LOGICAL :: swap
DO j = SIZE(unsorted)-1, 1, -1
swap = .FALSE.
DO i = 1, j
IF (unsorted(i) > unsorted(i+1)) THEN
temp = unsorted(i)
unsorted(i) = unsorted(i+1)
unsorted(i+1) = temp
swap = .TRUE.
END IF
END DO
IF (.NOT. swap) EXIT
sorted(j) = unsorted(j)
END DO
write(*,10) unsorted
10 FORMAT( F6.2 )
end program bubblesort
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.go
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
package main
import "fmt"
func bubbleSort(arrayzor []int) {
swapped := true
for swapped {
swapped = false
for i := 0; i < len(arrayzor)-1; i++ {
if arrayzor[i+1] < arrayzor[i] {
arrayzor[i], arrayzor[i+1] = arrayzor[i+1], arrayzor[i]
swapped = true
}
}
}
}
func main() {
arrayzor := []int{1, 6, 2, 4, 9, 0, 5, 3, 7, 8}
fmt.Println("Unsorted array: ", arrayzor)
bubbleSort(arrayzor)
fmt.Println("Sorted array: ", arrayzor)
}
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.hs
|
-- Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
bubblesort :: (Ord a) => [a] -> [a]
bubblesort [] = []
bubblesort [x] = [x]
bubblesort (x:y:ys) = let (z:zs) = bubblesort (y:ys) in
if x < z then x:z:zs else bubblesort (z:x:zs)
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.java
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Implements the bubble sort sorting algorithm
*/
public class BubbleSort {
static void bubbleSort(int[] array) {
int flag = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
flag = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - 1; j++) {
//check if current element is greater than the next element
if(array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
//if condition is satisfied, swap the elements
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
//set flag to 0
flag = 0;
}
}
//if the flag is still 1, it means the array is sorted
//and we exit from the loop.
if (flag == 1) {
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int array[] = { 4, 2, 3, 1 };
//calls the bubblesort function with parameter array
bubbleSort(array);
System.out.println("Sorted array: ");
//Prints the sorted array
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.jl
|
### /* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
### Julia 0.6 Implementation of bubble sorting algorithm
function bubblesort(arr)
n = length(arr)
for i=1:n, j=1:n-i
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1])
arr[j], arr[j+1] = arr[j+1], arr[j]
end
end
end
v = [144 89 4 9 95 12 86 25]
print("unbubble sorted array = ",v)
bubblesort(v)
print("\nbubble sorted array = ",v)
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.js
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
function bubbleSort(items) {
var length = items.length;
for (var i = length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
//Number of passes
for (var j = length - i; j > 0; j--) {
//Compare the adjacent positions
if (items[j] < items[j - 1]) {
//Swap the numbers
var tmp = items[j];
items[j] = items[j - 1];
items[j - 1] = tmp;
}
}
}
return items;
}
// var collections = [9, 4, 5, 2, 1, 6, 7, 0, 3];
// bubbleSort(collections);
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.kt
|
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
fun <T : Comparable<T>> bubbleSort(array: Array<T>) {
var flag : Boolean
for (i in array.indices) {
flag = true
for (j in 0 until (array.size - i - 1)) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
array[j] = array[j + 1].also { array[j+1] = array[j] }
flag = false
}
}
if (flag) break
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val sample: Array<Int> = arrayOf(0, 10, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 4, 9, 7, 8)
bubbleSort(sample)
println("Sorted: "+sample.joinToString())
}
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.m
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
//
// BubbleSort.m
// Created by DaiPei on 2017/10/9.
//
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface BubbleSort : NSObject
- (void)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array;
@end
@implementation BubbleSort
- (void)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array {
for (int i = 0; i + 1 < array.count; i++) {
BOOL swapped = NO;
for (int j = 0; j < array.count-1-i; j++) {
if ([array[j] compare:array[j + 1]] == NSOrderedDescending) {
[self swap:array at:j and:j + 1];
swapped = YES;
}
}
if (!swapped) {
break;
}
}
}
- (void)swap:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array at:(NSUInteger)indexA and:(NSUInteger)indexB {
NSNumber *tmp = array[indexA];
array[indexA] = array[indexB];
array[indexB] = tmp;
}
@end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
int n = 0;
NSLog(@"What is the size of the array?");
scanf("%d", &n);
NSMutableArray *array = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:n];
NSLog(@"Enter elements of the array one by one:");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int tmp;
scanf("%d", &tmp);
[array addObject:@(tmp)];
}
BubbleSort *bs = [[BubbleSort alloc] init];
[bs sort:array];
NSLog(@"%@", array);
}
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.php
|
<?php
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
$array = [0,1,6,7,6,3,4,2];
function bubble_sort(array $array)
{
do {
$swapped = false;
for( $i = 0, $c = count($array) - 1; $i < $c; $i++) {
if($array[$i] > $array[$i + 1]) {
list($array[$i + 1], $array[$i]) = array($array[$i], $array[$i + 1]);
$swapped = true;
}
}
} while($swapped);
return $array;
}
print 'unsorted array';
echo "\n";
print_r($array);
print 'sorted array';
echo "\n";
print_r(bubble_sort($array));
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.py
|
# Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
def bubble_sort(arr):
"""
>>> arr = [5, 1, 3, 9, 2]
>>> bubble_sort(arr)
>>> arr
[1, 2, 3, 5, 9]
"""
for i in range(len(arr)):
# Terminate algorithm if no more swaps are to be carried out
is_sorted = True
for j in range(i + 1, len(arr)):
# If current(ith) element is greater than the next((i+1)th) element swap them
if arr[i] > arr[j]:
arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
is_sorted = False
if is_sorted:
break
# Less elegant solution, but easier to follow along:
def bubble_sort(alist):
# flag to keep track of whether the list is sorted or not, initially it is set as false
is_sorted = False
# keep comparing till the list is sorted
while not is_sorted:
num_swaps = 0
# iterate through all the elements(except the last) in the list
for i in range(len(alist) - 1):
# if the current element is greater than the next element, pop it out of the list
if alist[i] > alist[i + 1]:
a = alist.pop(i + 1)
# insert the popped element to its right position in the list
alist.insert(i, a)
num_swaps += 1
# if the list is sorted, no more swaps are carried out
if num_swaps == 0:
is_sorted = True
return alist
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.rb
|
# Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
def bubble_sort(array)
n = array.length
loop do
swapped = false
(n - 1).times do |i|
if array[i] > array[i + 1]
array[i], array[i + 1] = array[i + 1], array[i]
swapped = true
end
end
break unless swapped
end
array
end
an_array = [5, 1, 3, 9, 2]
puts bubble_sort an_array
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.rs
|
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
fn bubble_sort(mut arr: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
for _ in 0..arr.len() {
let mut flag = false;
for j in 0..arr.len() - 1 {
if arr[j] > arr[j + 1] {
let temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
flag = true
}
}
if !flag {
break;
}
}
arr
}
fn main() {
let arr = vec![4, 5, 9, 1, 3, 0, 7, 2, 8];
let arr = bubble_sort(arr);
println!("Sorted array: {:?}", arr)
}
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.sh
|
#!/bin/bash
# Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
declare -a array
ARRAYSZ=10
create_array() {
i=0
while [ $i -lt $ARRAYSZ ]; do
array[${i}]=${RANDOM}
i=$((i+1))
done
}
print_array() {
i=0
while [ $i -lt $ARRAYSZ ]; do
echo ${array[${i}]}
i=$((i+1))
done
}
verify_sort() {
i=1
while [ $i -lt $ARRAYSZ ]; do
if [ ${array[$i]} -lt ${array[$((i-1))]} ]; then
echo "Array did not sort, see elements $((i-1)) and $i."
exit 1
fi
i=$((i+1))
done
echo "Array sorted correctly."
}
bubble_sort() {
while true; do
did_swap=0
i=1
while [ $i -lt $ARRAYSZ ]; do
if [ ${array[$((i-1))]} -gt ${array[$i]} ]; then
tmp=${array[$((i-1))]}
array[$((i-1))]=${array[$i]}
array[$i]=$tmp;
did_swap=1
fi
i=$((i+1))
done
if [ $did_swap -eq 0 ]; then
break
fi
done
}
create_array
print_array
bubble_sort
echo
print_array
verify_sort
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.sml
|
(* Bubblesort
* Time complexity: O( n^2 )
*)
fun bubblesort [] = []
| bubblesort (x::xs) =
let
val (y, ys, s) = foldl ( fn (c, (p, ps, s)) =>
if c < p then (p, c::ps, true) else (c, p::ps, s)
) (x, [], false) xs;
val xs' = foldl op:: [] (y::ys)
in
if s then bubblesort xs' else xs'
end
val test_0 = bubblesort [] = []
val test_1 = bubblesort [1,2,3] = [1, 2, 3]
val test_2 = bubblesort [1,3,2] = [1, 2, 3]
val test_3 = bubblesort [6,2,7,5,8,1,3,4] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.swift
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
//
// bubble_sort.swift
// Created by DaiPei on 2017/10/10.
//
import Foundation
func bubbleSort(_ array: inout [Int]) {
let n: Int = array.count
for i in stride(from: 0, to: n - 1, by: 1) {
var swapped = false
for j in stride(from: 0, to: n - i - 1, by: 1) {
if array[j] > array[j+1] {
swapped = true
swap(&array, at: j, and: j+1)
}
}
if !swapped {
break
}
}
}
private func swap(_ array: inout [Int], at indexA: Int, and indexB: Int) {
let tmp = array[indexA]
array[indexA] = array[indexB]
array[indexB] = tmp
}
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort.ts
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
export function bubbleSort(items: Array<number>): Array<number> {
let swapped: boolean = false;
do {
swapped = false;
// 1. Run through the list.
items.forEach((item: number, index: number, items: Array<number>) => {
// 2. Compare each adjacent pair of element
if (item > items[index + 1]) {
// 3. Swap elements if not in correct order
const tmp = item;
items[index] = items[index + 1];
items[index + 1] = tmp;
swapped = true;
}
});
// 4. Repeat until no swap is needed
} while(swapped)
return items;
}
// console.log(bubbleSort([5,7,3,1,-7,6,2]));
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort_efficient.cpp
|
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void bubbleSort(vector<int> &v)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size() - 1; i++)
{
bool isSorted = 1;
for (size_t j = 0; j < v.size() - 1 - i; j++)
if (v[j] > v[j + 1])
{
swap(v[j], v[j + 1]);
isSorted = 0;
}
for (size_t j = v.size() - 2; j >= i; j--)
if (v[j] > v[j + 1])
{
swap(v[j], v[j + 1]);
isSorted = 0;
}
if (isSorted)
break;
}
/*
* In this implementation,
* Modification From Normal Bubble Sort:
* 1) Sorting From Both the Sides Simultaneously
* 2) A variable isSorted which automatically breaks out of loop when elements get sorted reducing the total number of iterations.
*/
}
int main()
{
int n;
cout << "Enter the number of elements you want to enter: " << endl;
cin >> n;
vector<int> v(n);
cout << "Enter the elements: " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> v[i];
bubbleSort(v);
cout << "Sorted Elements: " << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
cout << v[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort_extension.swift
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
import Foundation
private func swap<T>(_ array: inout [T], at indexA: Int, and indexB: Int) {
let tmp = array[indexA]
array[indexA] = array[indexB]
array[indexB] = tmp
}
extension Array {
mutating func bubbleSort(compareWith less: (Element, Element) -> Bool) {
let n: Int = self.count
for i in stride(from: 0, to: n - 1, by: 1) {
var swapped = false
for j in stride(from: 0, to: n - i - 1, by: 1) {
if less(self[j + 1], self[j]) {
swapped = true
swap(&self, at: j, and: j + 1)
}
}
if !swapped {
break
}
}
}
}
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort_linked_list.cpp
|
//bubble sort iterative
#include <iostream>
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
this->next = NULL;
}
};
using namespace std;
int len(Node *head)
{
Node *temp = head;
int i = 0;
while (temp != NULL)
{
i++;
temp = temp->next;
}
return i;
}
Node *bubbleSort(Node *head)
{
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return head;
int n = len(head) - 1;
while (n--)
{
Node *prev = NULL;
Node *cur = head;
while (cur->next != NULL)
{
if (cur->data >= cur->next->data)
{
if (prev == NULL)
{
Node *nxt = cur->next;
cur->next = nxt->next;
nxt->next = cur;
prev = nxt;
head = prev;
}
else
{
Node *nxt = cur->next;
prev->next = nxt;
cur->next = nxt->next;
nxt->next = cur;
prev = nxt;
}
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
}
return head;
}
Node *takeinput()
{
int data;
cin >> data;
Node *head = NULL, *tail = NULL;
while (data != -1)
{
Node *newnode = new Node(data);
if (head == NULL)
{
head = newnode;
tail = newnode;
}
else
{
tail->next = newnode;
tail = newnode;
}
cin >> data;
}
return head;
}
void print(Node *head)
{
Node *temp = head;
while (temp != NULL)
{
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
Node *head = takeinput();
head = bubbleSort(head);
print(head);
}
|
code/sorting/src/bubble_sort/bubble_sort_recursive.cpp
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
// using namespace std;
/* This program is the bubble sort implementation
in C++ using recursion*/
void bubbleSort(std::vector<int>& v, int n)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 1)
return;
// sorting in a pass
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){
//comparing the elements and swapping accordingly
if (v[i] > v[i + 1]){
std::swap(v[i], v[i + 1]);
}
}
// recursive call for the next pass
bubbleSort(v, n - 1);
}
int main()
{
int n; // number of elements to be sorted
std::cout << "Enter the number of element:" << '\n';
std::cin >> n;
std::vector<int> v; // vector of all the elements to be sorted
std::cout << "Enter elements:" << '\n';
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{ // input all the elements
int x;
std::cin >> x;
v.push_back(x);
}
bubbleSort(v, n); // calling the sort function
std::cout << "Sorted Elements:" << '\n'; // showing output of the sorted vector
for (int element : v){
std::cout << element << " ";
}
std::cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/bucket_sort/README.md
|
# Bucket Sort
Bucket sort is a sorting algorithm that works by distributing the elements of an array into a number of buckets. Then, we apply a sorting algorithm, **insertion sort** for best optimisation to sort elements in each bucket, and finally, take the elements out of buckets in order and put them back to original array to get the sorted result.
## Explanation

Elements are first distributed among bins/buckets

Then, elements are sorted within each bucket.
## Algorithm
Bucket sort is mainly useful when input is uniformly distributed over a range.
If input is an n element array arr[i] with all elements lying in the range: [0.0, 1.0], and uniformly distributed in the same range, the algorithm is:
**bucket_sort(arr[ ], n)**
1. Create n empty buckets/lists.
2. Do for every array element arr[i]
Insert arr[i] into bucket[n * array[i]]
3. Sort individual buckets by insertion sort
4. Concatenate all sorted buckets in their order, into one sorted list.
## Complexity
The complexity of bucket sort isn’t constant depending on the input.
However, in **average case**, bucket sort has time complexity of **O(n)**, while it's **worst case time complexity is: O(n^2)**.
---
<p align="center">
A massive collaborative effort by <a href="https://github.com/OpenGenus/cosmos">OpenGenus Foundation</a>
</p>
---
|
code/sorting/src/bucket_sort/bucket_sort.c
|
#include<stdio.h>
#define SIZE 10 //number of buckets
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
void bucketSort(int a[], int n) {
int i, j, k, buckets[SIZE];
for(i = 0; i < SIZE; ++i)
buckets[i] = 0;
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i)
++buckets[a[i]];
for(i = 0, j = 0; j < SIZE; ++j)
for(k = buckets[j]; k > 0; --k)
a[i++] = j;
}
int main() {
int i, a[] = {3, 6, 5, 1, 8, 4, 3, 1}, n = sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]); //array to sort, length of array
printf("Before sorting:\n");
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i){
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
bucketSort(a, n);
printf("\n\nAfter sorting:\n");
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i){
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/bucket_sort/bucket_sort.cpp
|
// C++ program to sort an array using bucket sort
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
// Function to sort arr[] of size n using bucket sort
void bucketSort(vector<float>& arr)
{
// 1) Create n empty buckets
vector<float> b[arr.size()];
// 2) Put array elements in different buckets
for (size_t i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
{
int bi = arr.size() * arr[i]; // Index in bucket
b[bi].push_back(arr[i]);
}
// 3) Sort individual buckets
for (size_t i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
sort(b[i].begin(), b[i].end());
// 4) Concatenate all buckets into arr[]
int index = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
for (size_t j = 0; j < b[i].size(); j++)
arr[index++] = b[i][j];
}
/* Driver program to test above funtion */
int main()
{
vector<float> arr{0.897, 0.565, 0.656, 0.1234, 0.665, 0.3434};
bucketSort(arr);
cout << "Sorted array is \n";
for (size_t i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/bucket_sort/bucket_sort.cs
|
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
namespace OpenGenus
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var random = new Random();
// generate randomly sized array (length 1-100) with random values
var inputSize = random.Next(1, 100);
var unsorted = Enumerable.Range(1, inputSize).Select(x => random.Next()).ToArray();
Console.WriteLine("Unsorted");
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", unsorted));
Console.WriteLine("\nSorted");
var sorted = BucketSort(unsorted, 10);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", sorted));
Console.ReadLine();
}
private static int[] BucketSort(int[] unsorted, int bucketCount)
{
// create bucket list
var buckets = new List<List<int>>();
// find min/max values
var max = unsorted.Max();
var min = unsorted.Min();
// determine bucket size (max + 1 used to ensure bucketIndex stays in range)
var bucketSize = (int)Math.Ceiling(( (max + 1) - min ) / (decimal)bucketCount);
// add empty buckets
for (var i = 0; i < bucketCount; i++)
buckets.Add(new List<int>());
// distribute numbers to buckets
for (var i = 0; i < unsorted.Length; i++)
{
var number = unsorted[i];
var bucketIndex = (number - min) / bucketSize;
buckets[bucketIndex].Add(number);
}
// sort each bucket
foreach (var bucket in buckets)
{
// use sort method of choice here
bucket.Sort();
}
// return concatenated buckets as sorted array
return buckets.SelectMany(x => x).ToArray();
}
}
}
|
code/sorting/src/bucket_sort/bucket_sort.go
|
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"strconv"
)
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
func insertionSort(array []float64) {
for i := 0; i < len(array); i++ {
temp := array[i]
j := i - 1
for ; j >= 0 && array[j] > temp; j-- {
array[j+1] = array[j]
}
array[j+1] = temp
}
}
func bucketSort(array []float64, bucketSize int) []float64 {
var max, min float64
for _, n := range array {
if n < min {
min = n
}
if n > max {
max = n
}
}
nBuckets := int(max-min)/bucketSize + 1
buckets := make([][]float64, nBuckets)
for i := 0; i < nBuckets; i++ {
buckets[i] = make([]float64, 0)
}
for _, n := range array {
idx := int(n-min) / bucketSize
buckets[idx] = append(buckets[idx], n)
}
sorted := make([]float64, 0)
for _, bucket := range buckets {
if len(bucket) > 0 {
insertionSort(bucket)
sorted = append(sorted, bucket...)
}
}
return sorted
}
func main() {
array := make([]float64, 0)
for _, arg := range os.Args[1:] {
if n, err := strconv.ParseFloat(arg, 64); err == nil {
array = append(array, n)
}
}
fmt.Printf("%v\n", array)
array = bucketSort(array, 5)
fmt.Printf("%v\n", array)
}
|
code/sorting/src/bucket_sort/bucket_sort.hs
|
-- Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
import System.Environment
import Data.List (sort) -- using sort as the internal bucket sorting algorithm
flatten :: [[a]] -> [a]
flatten xs = (\z n -> foldr (\x y -> foldr z y x) n xs) (:) []
bucketSort :: (RealFrac a, Ord a) => [a] -> Integer -> [a]
bucketSort [] _ = []
bucketSort array bucketSize = flatten $ map sort buckets
where
buckets = [filter (\x -> (getBucketIdx x arMin bucketSize) == i) array | i <- [0..nBuckets]]
nBuckets = (floor (arMax - arMin)) `div` bucketSize + 1
arMax = maximum array
arMin = minimum array
getBucketIdx :: (RealFrac a) => a -> a -> Integer -> Integer
getBucketIdx _ _ 0 = error "num buckets is 0?!"
getBucketIdx num min bucketSize = (floor (num - min)) `div` bucketSize
main :: IO ()
main = getArgs >>= \args -> print $ bucketSort (map (\x-> read x :: Float) (tail args)) (read (head args) :: Integer)
|
code/sorting/src/bucket_sort/bucket_sort.java
|
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class BucketSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//float[] arr={1,9,4,7,2,8};
double arr[] = {0.89, 0.565, 0.656, 0.1234, 0.665, 0.3434};
bucketSort(arr,arr.length);
}
public static void bucketSort(double arr[], int n)
{
// 1) Create n empty buckets
ArrayList<ArrayList<Double>> b=new ArrayList<ArrayList<Double>>();
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
{
b.add(new ArrayList<Double>());
}
// 2) Put array elements in different buckets
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
int bi = (int) (n*arr[i]); // Index in bucket
b.get(bi).add(arr[i]);
}
// 3) Sort individual buckets
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
Collections.sort(b.get(i));
// 4) Concatenate all buckets into arr[]
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < b.get(i).size(); j++)
arr[index++] = b.get(i).get(j);
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;++i)
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
|
code/sorting/src/bucket_sort/bucket_sort.js
|
// InsertionSort to be used within bucket sort
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
function insertionSort(array) {
var length = array.length;
for (var i = 1; i < length; i++) {
var temp = array[i];
for (var j = i - 1; j >= 0 && array[j] > temp; j--) {
array[j + 1] = array[j];
}
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
return array;
}
// Implement bucket sort
function bucketSort(array, bucketSize) {
if (array.length === 0) {
return array;
}
// Declaring vars
var i,
minValue = array[0],
maxValue = array[0],
bucketSize = bucketSize || 5;
// Setting min and max values
array.forEach(function(currentVal) {
if (currentVal < minValue) {
minValue = currentVal;
} else if (currentVal > maxValue) {
maxValue = currentVal;
}
});
// Initializing buckets
var bucketCount = Math.floor((maxValue - minValue) / bucketSize) + 1;
var allBuckets = new Array(bucketCount);
for (i = 0; i < allBuckets.length; i++) {
allBuckets[i] = [];
}
// Pushing values to buckets
array.forEach(function(currentVal) {
allBuckets[Math.floor((currentVal - minValue) / bucketSize)].push(
currentVal
);
});
// Sorting buckets
array.length = 0;
allBuckets.forEach(function(bucket) {
insertionSort(bucket);
bucket.forEach(function(element) {
array.push(element);
});
});
return array;
}
// bucketSort([8,34,1,23,9,0])
|
code/sorting/src/bucket_sort/bucket_sort.m
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
//
// bucket_sort.m
// Created by DaiPei on 2017/10/14.
//
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#define DEFAULT_STEP 5
@interface BucketSort : NSObject
- (void)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array;
- (void)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array withStep:(NSUInteger)step;
@end
@implementation BucketSort
- (void)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array {
[self sort:array withStep:DEFAULT_STEP];
}
- (void)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array withStep:(NSUInteger)step {
// find the max value
NSNumber *max = @(INTMAX_MIN);
NSNumber *min = @(INTMAX_MAX);
for (int i = 0; i < array.count; i++) {
if ([array[i] compare:max] == NSOrderedDescending) {
max = array[i];
}
if ([array[i] compare:min] == NSOrderedAscending) {
min = array[i];
}
}
// calculate buckets count
NSUInteger n = (max.integerValue - min.integerValue) / step + 1;
NSMutableArray<NSMutableArray *> *buckets = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
[buckets addObject:[NSMutableArray array]];
}
// put value to buckets
for (int i = 0; i < array.count; i++) {
NSUInteger j = (array[i].integerValue - min.integerValue) / step;
[buckets[j] addObject:array[i]];
}
// sort value in each bucket
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
[self sortCore:buckets[i]];
}
// put sorted value back to origin array
NSUInteger index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
NSMutableArray *bucket = buckets[i];
for (int j = 0; j < bucket.count; j++) {
array[index++] = bucket[j];
}
}
}
- (void)sortCore:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array {
for (int i = 0; i + 1 < array.count; i++) {
int p = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < array.count; j++) {
if ([array[j] compare:array[p]] == NSOrderedAscending) {
p = j;
}
}
[self swap:array at:i and:p];
}
}
- (void)swap:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array at:(NSUInteger)indexA and:(NSUInteger)indexB {
NSNumber *tmp = array[indexA];
array[indexA] = array[indexB];
array[indexB] = tmp;
}
@end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
NSMutableArray *array = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:10];
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
int ran = arc4random() % 100 - 50;
[array addObject:@(ran)];
}
NSLog(@"before: %@", array);
BucketSort *bs = [[BucketSort alloc] init];
[bs sort:array withStep:10];
NSLog(@"after: %@", array);
}
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/bucket_sort/bucket_sort.php
|
<?php
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
function bucket_sort($my_array) {
$n = sizeof($my_array);
$buckets = array();
// Initialize the buckets.
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) {
$buckets[$i] = array();
}
// Put each element into matched bucket.
foreach ($my_array as $i) {
array_push($buckets[ceil($i)], $i);
}
// Sort elements in each bucket using insertion sort.
$j = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
{
// sort only non-empty bucket
if (!empty($buckets[$i])) {
insertion_sort($buckets[$i]);
// Move sorted elements in the bucket into original array.
foreach ($buckets[$i] as $el) {
$my_array[$j++] = $el;
}
}
}
return $my_array;
}
function insertion_sort($my_array, $fn = 'comparison_function') {
if (!is_array($my_array) || !is_callable($fn)) return;
for ($i = 1; $i < sizeof($my_array); $i++) {
$key = $my_array[$i];
$j = $i - 1; // this will be in $b in comparison function
while ( $j >= 0 && $fn($key, $my_array[$j]) ) {
$my_array[$j + 1] = $my_array[$j];
$j = $j - 1; // shift right
}
$my_array[$j + 1] = $key;
}
}
//Following function used to compare each element.
function comparison_function($a, $b) {
return $a < $b;
}
$array = array(7,6,0,1,5,3,4,2);
print 'unsorted array';
echo "\n";
print_r($array);
print 'sorted array';
echo "\n";
print_r(bucket_sort($array));
?>
|
code/sorting/src/bucket_sort/bucket_sort.py
|
# Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
def bucket_sort(A):
buckets = [[] for x in range(10)]
for i, x in enumerate(A):
buckets[int(x * len(buckets))].append(x)
out = []
for buck in buckets:
out += isort(buck)
return out
def isort(A):
if len(A) <= 1:
return A
i = 1
while i < len(A):
k = A[i]
j = i - 1
while j >= 0 and A[j] > k:
A[j + 1] = A[j]
A[j] = k
j -= 1
i += 1
return A
|
code/sorting/src/bucket_sort/bucket_sort.rb
|
# Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
DEFAULT_BUCKET_SIZE = 5
def bucket_sort(input, bucket_size = DEFAULT_BUCKET_SIZE)
print 'Array is empty' if input.empty?
array = input.split(' ').map(&:to_i)
bucket_count = ((array.max - array.min) / bucket_size).floor + 1
# create buckets
buckets = []
bucket_count.times { buckets.push [] }
# fill buckets
array.each do |item|
buckets[((item - array.min) / bucket_size).floor].push(item)
end
# sort buckets
buckets.each(&:sort!)
buckets.flatten.join(' ')
end
puts 'Enter a list of numbers seprated by space'
list = gets
print bucket_sort(list)
|
code/sorting/src/bucket_sort/bucket_sort.swift
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
//
// bucket_sort.swift
// Created by DaiPei on 2017/10/14.
//
import Foundation
private let defaultStep = 5
func bucketSort(_ array: inout [Int]) {
bucketSort(&array, withStep: defaultStep)
}
func bucketSort(_ array: inout [Int], withStep step: Int) {
// find the max and min value in array
var max = Int.min
var min = Int.max
for val in array {
if val > max {
max = val
}
if val < min {
min = val
}
}
// calculate the buckets count
let n = (max - min) / step + 1
var buckets = [[Int]](repeatElement([Int](), count: n))
// put value to buckets
for val in array {
let j = (val - min) / step
buckets[j].append(val)
}
// sort value in buckets
for i in 0..<buckets.count {
sortCore(&buckets[i])
}
// put value back to origin array
var index = 0
for i in 0..<buckets.count {
var bucket = buckets[i]
for j in 0..<bucket.count {
array[index] = bucket[j]
index += 1
}
}
}
private func sortCore(_ array: inout [Int]) {
for i in stride(from: 0, to: array.count - 1, by: 1) {
var min = i
for j in i+1..<array.count {
if array[j] < array[min] {
min = j
}
}
swap(&array, at: min, and: i)
}
}
private func swap(_ array: inout [Int], at indexA: Int, and indexB: Int) {
let tmp = array[indexA]
array[indexA] = array[indexB]
array[indexB] = tmp
}
|
code/sorting/src/bucket_sort/bucket_sorting.cpp
|
// Implementation of Bucket/Bin Sort Algorithm in C++
// Best Time Complexity O(n+k)
// Worst Time Complexity O(n^2)
// Space Complexity O(n)
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Function to sort arr[] of
// size n using bucket sort
void bucketSort(float arr[], int n)
{
// Create n empty buckets
vector<float> b[n];
// Put array elements in different buckets
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Index in bucket
int bi = n * arr[i];
b[bi].push_back(arr[i]);
}
// Sort individual buckets
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sort(b[i].begin(), b[i].end());
// Concatenate all buckets into arr[]
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < b[i].size(); j++)
arr[index++] = b[i][j];
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
float arr[]
= { 0.89, 0.65, 0.56, 0.1, 0.51, 0.434 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
bucketSort(arr, n);
cout << "Sorted array is \n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/circle_sort/README.md
|
# Circle Sort
Circle sort algorithm is an **inplace sorting algorithm** in which we compare the first element to the last element of the given array, the second element to the second last element, and so on and then split the array in two and recurse until we get pairs of sorted elements, which are then put together to get a sorted array.
## Explanation
Circle sort is best explained by drawing concentric circles on an array of integers.
Now, the elements lying on the same circle (i.e., they are diametrically opposite) are compared and swapped. Then the array is split into two and recurse until there are no more swaps.
> Image credits: geeksforgeeks
## Algorithm
```
function inner_circle (index a, index b)
{
start := a
end := b
swap := 0
if (start == end)
return (swap)
while (start< end)
if (value at start > value at end)
swap.values(start , end)
swap++
(end if)
start++
end--
(end while)
swap += inner_circle (a, end)
swap += inner_circle (start, b)
return(swap)
}
function circle_sort (index a, n)
{
while inner_circle (a, a + n - 1)
}
```
## Complexity
The **best case time complexity** of circle sort is:**O(nlogn)**, while in **worst case**, it becomes: **O(nlogn logn)**.
---
<p align="center">
A massive collaborative effort by <a href="https://github.com/OpenGenus/cosmos">OpenGenus Foundation</a>
</p>
---
|
code/sorting/src/circle_sort/circle_sort.c
|
/*Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void swap(int *p, int *q)
{
int tmp = *p;
*p = *q;
*q = tmp;
}
void print_vector(int *a, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int circle_sort(int *a, int n, int lower, int upper, int swaps)
{
if (lower == upper)
return swaps;
int low = lower;
int high = upper;
int mid = (upper - lower) / 2;
while (lower < upper) {
if (a[lower] > a[upper]) {
swap(&a[lower], &a[upper]);
swaps++;
}
lower++;
upper--;
}
if (lower == upper) {
if(a[lower] > a[upper + 1]) {
swap(&a[lower], &a[upper + 1]);
swaps++;
}
}
circle_sort(a, n, low, low + mid, swaps);
circle_sort(a, n, low + mid + 1, high, swaps);
return swaps;
}
int main()
{
int n;
int *a;
printf("Inform the size of the array:\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
a = (int *) malloc(n * sizeof(int));
printf("Enter elements of the array one by one\n");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
printf("Unsorted List: ");
print_vector(a, n);
circle_sort(a, n, 0, n - 1, 0);
printf("Sorted List: ");
print_vector(a, n);
free(a);
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/circle_sort/circle_sort.cpp
|
/*Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int *p, int *q)
{
int tmp = *p;
*p = *q;
*q = tmp;
}
void print_vector(int *a, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i];
cout << endl;
}
int circle_sort(int *a, int n, int lower, int upper, int swaps)
{
if (lower == upper)
return swaps;
int low = lower;
int high = upper;
int mid = (upper - lower) / 2;
while (lower < upper)
{
if (a[lower] > a[upper])
{
swap(&a[lower], &a[upper]);
swaps++;
}
lower++;
upper--;
}
if (lower == upper)
if (a[lower] > a[upper + 1])
{
swap(&a[lower], &a[upper + 1]);
swaps++;
}
circle_sort(a, n, low, low + mid, swaps);
circle_sort(a, n, low + mid + 1, high, swaps);
return swaps;
}
int main()
{
int n;
int *a;
cout << "Inform the size of the array:" << endl;
scanf("%d", &n);
a = (int *) malloc(n * sizeof(int));
cout << "Enter elements of the array one by one" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
cout << "Unsorted List: " << endl;
print_vector(a, n);
circle_sort(a, n, 0, n - 1, 0);
cout << "Sorted List: " << endl;
print_vector(a, n);
free(a);
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/circle_sort/circle_sort.cs
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
using System;
namespace CircleSort
{
public class CircleSort
{
public static void Main()
{
var sortedArray = Sort(new int[]{2, 14, 4, 6, 8, 1, 5, 3, 7, 11, 0, 13, 20, -1});
Console.WriteLine(String.Join(", ", sortedArray));
}
public static int[] Sort(int[] array)
{
if (array.Length > 0)
{
while (Sort(array, 0, array.Length - 1, 0) != 0);
}
return array;
}
private static int Sort(int[] array, int lo, int hi, int numberOfSwaps)
{
if (lo == hi)
{
return numberOfSwaps;
}
int high = hi;
int low = lo;
int mid = (hi - lo) / 2;
while (lo < hi)
{
if (array[lo] > array[hi])
{
Swap(array, lo, hi);
numberOfSwaps++;
}
lo++;
hi--;
}
if (lo == hi && array[lo] > array[hi + 1])
{
Swap(array, lo, hi + 1);
numberOfSwaps++;
}
numberOfSwaps = Sort(array, low, low + mid, numberOfSwaps);
numberOfSwaps = Sort(array, low + mid + 1, high, numberOfSwaps);
return numberOfSwaps;
}
private static void Swap(int[] array, int index1, int index2)
{
int tmp = array[index1];
array[index1] = array[index2];
array[index2] = tmp;
}
}
}
|
code/sorting/src/circle_sort/circle_sort.java
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CircleSort
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] sortedArray = Sort(new int[]{2, 14, 4, 6, 8, 1, 5, 3, 7, 11, 0, 13, 20, -1});
System.out.println(String.join(", ", Arrays.toString(sortedArray)));
}
public static int[] Sort(int[] array)
{
if (array.length > 0)
{
while (Sort(array, 0, array.length - 1, 0) != 0);
}
return array;
}
private static int Sort(int[] array, int lo, int hi, int numberOfSwaps)
{
if (lo == hi)
{
return numberOfSwaps;
}
int high = hi;
int low = lo;
int mid = (hi - lo) / 2;
while (lo < hi)
{
if (array[lo] > array[hi])
{
Swap(array, lo, hi);
numberOfSwaps++;
}
lo++;
hi--;
}
if (lo == hi && array[lo] > array[hi + 1])
{
Swap(array, lo, hi + 1);
numberOfSwaps++;
}
numberOfSwaps = Sort(array, low, low + mid, numberOfSwaps);
numberOfSwaps = Sort(array, low + mid + 1, high, numberOfSwaps);
return numberOfSwaps;
}
private static void Swap(int[] array, int index1, int index2)
{
int tmp = array[index1];
array[index1] = array[index2];
array[index2] = tmp;
}
}
|
code/sorting/src/circle_sort/circle_sort.js
|
// Reference: https://rosettacode.org/wiki/Sorting_Algorithms/Circle_Sort
const circlesort = (arr, lo, hi, swaps) => {
let high;
let low;
let mid;
let t;
if (lo === hi) {
return swaps;
}
high = hi;
low = lo;
mid = Math.floor((hi - lo) / 2);
while (lo < hi) {
if (arr[lo] > arr[hi]) {
t = arr[lo];
arr[lo] = arr[hi];
arr[hi] = t;
swaps++;
}
lo++;
hi--;
}
if (lo === hi) {
if (arr[lo] > arr[hi + 1]) {
t = arr[lo];
arr[lo] = arr[hi + 1];
arr[hi + 1] = t;
swaps++;
}
}
swaps = circlesort(arr, low, low + mid, swaps);
swaps = circlesort(arr, low + mid + 1, high, swaps);
return swaps;
};
const x = [6, 7, 8, 9, 2, 5, 3, 4, 1];
while (circlesort(x, 0, x.length - 1, 0)) {
console.log(x);
}
|
code/sorting/src/circle_sort/circle_sort.m
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
//
// circle_sort.m
// Created by DaiPei on 2017/10/15.
//
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface CircleSort : NSObject
- (void)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array;
@end
@implementation CircleSort
- (void)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array {
while ([self sort:array low:0 high:(int)array.count - 1]) {}
}
- (BOOL)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array low:(int)low high:(int)high {
BOOL swapped = NO;
if (low == high) {
return swapped;
}
int l = low, h = high;
while (l < h) {
if ([array[l] compare:array[h]] == NSOrderedDescending) {
[self swap:array at:l and:h];
swapped = YES;
}
l++;
h--;
}
if (l == h) {
if ([array[l] compare:array[l + 1]] == NSOrderedDescending) {
[self swap:array at:l and:l + 1];
swapped = YES;
}
}
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
BOOL left = [self sort:array low:low high:mid];
BOOL right = [self sort:array low:mid + 1 high:high];
return swapped || left || right;
}
- (void)swap:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array at:(NSUInteger)indexA and:(NSUInteger)indexB {
NSNumber *tmp = array[indexA];
array[indexA] = array[indexB];
array[indexB] = tmp;
}
@end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
NSMutableArray *array = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:10];
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
int ran = arc4random() % 100 - 50;
[array addObject:@(ran)];
}
NSLog(@"before: %@", array);
CircleSort *cs = [[CircleSort alloc] init];
[cs sort:array];
NSLog(@"after: %@", array);
}
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/circle_sort/circle_sort.py
|
# Python program to implement circle sort
# Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
# function to swap 2 elements of a list
def swap(a, i, j):
temp = a[i]
a[i] = a[j]
a[j] = temp
# recursive function to perfrom circle sort on the given list
def circle_sort(a, lower, upper, swaps):
# base case
if lower == upper:
return swaps
low = lower
high = upper
mid = int((upper - lower) / 2)
while lower < upper:
if a[lower] > a[upper]:
swap(a, lower, upper)
swaps += 1
print(a, swaps)
lower += 1
upper -= 1
if lower == upper:
if a[lower] > a[upper + 1]:
swap(a, lower, upper + 1)
swaps += 1
print(a, swaps)
circle_sort(a, low, low + mid, swaps)
circle_sort(a, low + mid + 1, high, swaps)
return swaps
# hard coded driver function to run the program
if __name__ == "__main__":
a = [6, 5, 3, 1, 8, 7, 2, 4]
print("Unsorted List: ", a)
no_of_swaps = circle_sort(a, 0, len(a) - 1, 0)
print("Sorted List: ", a)
|
code/sorting/src/circle_sort/circle_sort.swift
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
//
// circle_sort.swift
// Created by DaiPei on 2017/10/14.
//
import Foundation
func circleSort(_ array: inout [Int]) {
while circleSort(&array, low: 0, high: array.count - 1) {}
}
private func circleSort(_ array: inout [Int], low: Int, high: Int) -> Bool {
var swaped = false
if low == high {
return swaped
}
var l = low
var h = high
while l < h {
if array[l] > array[h] {
swap(&array, at: l, and: h)
swaped = true
}
l += 1
h -= 1
}
if l == h {
if l + 1 < array.count && array[l] > array[l + 1] {
swap(&array, at: l, and: l + 1)
swaped = true
}
}
let mid = (low + high) / 2
let left = circleSort(&array, low: low, high: mid)
let right = circleSort(&array, low: mid + 1, high: high)
return swaped || left || right
}
private func swap(_ array: inout [Int], at indexA: Int, and indexB: Int) {
let tmp = array[indexA]
array[indexA] = array[indexB]
array[indexB] = tmp
}
|
code/sorting/src/cocktail_sort/cocktail_sort.c
|
#include <stdio.h>
/* CocktailSort function is the function used to sort the array using cocktail algorithm. */
/* Cocktailsort is similar to the bubble sort but the complexity is less comparatively. */
void cocktailsort(int l[], int n)
{
/* argument passed is the list of the array to be sorted and the length of the array */
/* first is used to represent the starting index of the array */
int first = 0;
int temp = 0;
/* last is used to represent the last index of the array */
int last = n - 1;
/* p is the variable used to check if the array contains sorted elements after sorting process */
int p = 1;
while ( p != 0)
{
/* while loop checks the status of the array */
p = 0;
for (int i = first; i < last; ++i)
{
/* for loop is used to do the forward sorting on the array */
if (l[i] > l[i + 1])
{
/* larger element is exchanged with smaller one */
temp = l[i];
l[i] = l[i+1];
l[i+1] = temp;
p = 1;
}
/* after every sorting, largest element is at the last index and value of p is set to 1 */
}
if (! p)
/* if value is not 1, it means the array is sorted already , so the control is sent out of while loop */
break;
else
{
/* value of last is decreased by 1 as largest element need not to be sorted */
p = 0;
last--;
}
for (int i = last; i >= first; --i)
{
/* for loop is used to do backward sort on the array */
if (l[i] > l[i + 1])
{
temp = l[i];
l[i] = l[i+1];
l[i+1] = temp;
p = 1;
}
}
/* the smallest element is placed at the front of the array, so the value of first variable is increased by 1 */
first++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
/* for loop is used to display the sorted array elements */
printf("%d ", l[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{ /* l represents the unsorted array */
int l[] = { 5, 1, 4, 2, 8, 0, 2 };
/* n variable is used to count the length of array */
int n = sizeof(l) / sizeof(l[0]);
/* cocktailsort function is called in order with parameters l and length of array n */
cocktailsort(l,n);
return 0;
}
/* output-> 0 1 2 2 4 5 8 */
|
code/sorting/src/cocktail_sort/cocktail_sort.java
|
class CocktailSort {
/** A method to sort the array. The array will be sorted inplace.
* @author KanakalathaVemuru (https://github.com/KanakalathaVemuru)
* @param array an array which has to be sorted
*/
public void sort(int[] array) {
int n = array.length;
int left = 0;
int right = n - 1;
Boolean swapped = true;
while (swapped) {
swapped = false;
for (int i = left; i < right; i++) {
if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) {
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = temp;
swapped = true;
}
}
if (swapped == false) {
break;
}
right = right - 1;
for (int i = right - 1; i >= left; i--) {
if (array[i] > array[i + 1]) {
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = temp;
swapped = true;
}
}
left = left + 1;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int arr[] = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7};
System.out.println("Given Array");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
CocktailSort cs = new CocktailSort();
cs.sort(arr);
System.out.println("\nSorted array");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
|
code/sorting/src/cocktail_sort/cocktail_sort.py
|
# cocktailsort is the function used to sort array
# it is just like bubble sort with less complexity comparatively
def cocktailsort(l):
# first indicates the first index of the array
first = 0
# k is the variable that counts the length of the array
k = len(l)
# last indicates the last index element of the array
last = k - 1
# t variable is used to denote if array is sorted after the sorting process.
# it is initialised 1 to check if array is sorted after every iteration
t = 1
# temp is used as third variable to exchange the values
temp = 0
while t != 0:
# t is set to 0 when loop conditions comes true
# both forward and backward sort runs simultaneously
t = 0
# this for loop will do the forward sort
# the greatest element after each pass will be at the last index
for i in range(first, last, 1):
if l[i] < l[i + 1]:
continue
else:
temp = l[i]
l[i] = l[i + 1]
l[i + 1] = temp
t = 1
# t is initialised to 1 to chech if the loop was sorted or not in the forward sort
# if value of t was not changed the control will jump off the loop
# else the control will move to the backward sort
if t == 0:
break
else:
t = 0
# value of last is decreased everytime that shows the greatest element is found after forward sort
last -= 1
# the next loop will do the backward sort in the array
for i in range(last, first - 1, -1):
if l[i] < l[i + 1]:
continue
else:
temp = l[i]
l[i] = l[i + 1]
l[i + 1] = temp
# t is set to 1 to show array has completed one backward sort pass.
t = 1
# value of first variable is increased everytime as smallest element is found after backward sort
first += 1
# when both the sorting is done the array is returned
return l
# sample array is taken
a = [23, 1, 5, 32, 122, 76, 45]
c = cocktailsort(a)
print("New Array: ")
for i in a:
print(i, end=" ")
# output-> New Array: 1 5 23 32 45 76 122
|
code/sorting/src/comb_sort/README.md
|
# Comb sort
The comb sort is a variant of bubble sort.
In comb sort, gaps (distance of two items from each other) are introduced. The gap in bubble sort is 1. The gap starts out as a large value, and, after each traversal, the gap is lessened, until it becomes 1, where the algorithm basically degrades to a bubble sort. Thus, it removes more than one inversion counts with one swap and performs better than bubble sort.
## Explanation
## Algorithm
```
function combsort(array input)
gap := input.size // Initialize gap size
shrink := 1.3 // Set the gap shrink factor
sorted := false
loop while sorted = false
// Update the gap value for a next comb
gap := floor(gap / shrink)
if gap > 1
sorted := false // We are never sorted as long as gap > 1
else
gap := 1
sorted := true // If there are no swaps this pass, we are done
end if
// A single "comb" over the input list
i := 0
loop while i + gap < input.size // See Shell sort for a similar idea
if input[i] > input[i+gap]
swap(input[i], input[i+gap])
sorted := false
// If this assignment never happens within the loop,
// then there have been no swaps and the list is sorted.
end if
i := i + 1
end loop
end loop
end function
```
## Complexity
**Time complexity**
- Worst case: **O(n<sup>2</sup>)**
- Best case: **O(n)**
**Space complexity**: **O(1)** auxillary
---
<p align="center">
A massive collaborative effort by <a href="https://github.com/OpenGenus/cosmos">OpenGenus Foundation</a>
</p>
---
|
code/sorting/src/comb_sort/comb_sort.c
|
#include <stdio.h>
int
updateGap(int gap)
{
gap = (gap * 10) / 13;
return (gap < 1 ? 1 : gap);
}
void
combSort(int ar[], int n)
{
int gap = n;
int flag = 0;
while (gap > 1 || flag == 1) {
gap = updateGap(gap);
flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (n - gap); i++) {
int x;
if (ar[i] > ar[i + 1]) {
x = ar[i];
ar[i] = ar[i + 1];
ar[i + 1] = x;
flag = 1;
}
}
}
}
int
main()
{
int n;
printf("Enter size of Array \n");
scanf("%d", &n);
int ar[n];
printf("Enter %d Integers \n", n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &ar[i]);
combSort(ar, n);
printf("Sorted Array:- \n");
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d \n", ar[i]);
return (0);
}
|
code/sorting/src/comb_sort/comb_sort.cpp
|
#include <iostream>
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
using namespace std;
int updateGap(int gap)
{
gap = (gap * 10) / 13;
if (gap < 1)
return 1;
else
return gap;
}
void combSort(int ar[], int n)
{
int gap = n;
int flag = 0;
while (gap > 1 || flag == 1)
{
gap = updateGap(gap);
flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (n - gap); i++)
{
int x;
if (ar[i] > ar[i + 1])
{
x = ar[i];
ar[i] = ar[i + 1];
ar[i + 1] = x;
flag = 1;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
cout << "Input number of elements in the array - ";
cin >> n;
int ar[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> ar[i];
combSort(ar, n);
cout << "Array after sorting - ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << ar[i] << endl;
}
|
code/sorting/src/comb_sort/comb_sort.go
|
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func updateGap(gap int) int {
gap = (gap * 10) / 13
if gap < 1 {
return 1
}
return gap
}
func combSort(ar []int, n int) {
gap := n
flag := false
for gap > 1 || flag {
gap = updateGap(gap)
flag = false
for i := 0; i < (n - gap); i++ {
if ar[i] > ar[i+1] {
ar[i], ar[i+1] = ar[i+1], ar[i]
flag = true
}
}
}
}
func main() {
n := 0
fmt.Print("Input number of elements in the array - ")
fmt.Fscan(os.Stdin, &n)
ar := make([]int, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
fmt.Fscan(os.Stdin, &ar[i])
}
combSort(ar, n)
fmt.Print("Array after sorting - ")
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
fmt.Println(ar[i])
}
}
|
code/sorting/src/comb_sort/comb_sort.java
|
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CombSort
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int i;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter no elements you want (Size):");
int size = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[size];
System.out.println("Please enter the " + size + " elements:");
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Sorted array is :");
CombSort cs = new CombSort(a);
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
System.out.printf("%d\t", a[i]);
}
}
private final int[] a;
private CombSort(int[] b)
{
this.a = b;
combSort(a.length);
}
private void combSort(int size)
{
float shrink = 1.3f;
int swap;
int i, gap = size;
boolean swapped = false;
while ((gap > 1) || swapped)
{
if (gap > 1)
{
gap = (int) ((float) gap / shrink);
}
swapped = false;
for (i = 0; gap + i < size; ++i)
{
if (a[i] - a[i + gap] > 0)
{
swap = a[i];
a[i] = a[i + gap];
a[i + gap] = swap;
swapped = true;
}
}
}
}
}
|
code/sorting/src/comb_sort/comb_sort.js
|
// Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation
function is_array_sorted(arr) {
var sorted = true;
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]) {
sorted = false;
break;
}
}
return sorted;
}
// Array to sort
// var arr = [1,1,1,1,5,4,4,2,5,666,3,3,34,4,6,2,5];
var iteration_count = 0;
var gap = arr.length - 2;
var decrease_factor = 1.25;
// Until array is not sorted, repeat iterations
while (!is_array_sorted(arr)) {
// If not first gap
if (iteration_count > 0)
// Calculate gap
gap = gap == 1 ? gap : Math.floor(gap / decrease_factor);
// Set front and back elements and increment to a gap
var front = 0;
var back = gap;
while (back <= arr.length - 1) {
// If elements are not ordered swap them
if (arr[front] > arr[back]) {
var temp = arr[front];
arr[front] = arr[back];
arr[back] = temp;
}
// Increment and re-run swapping
front += 1;
back += 1;
}
iteration_count += 1;
}
// Print the sorted array
//console.log(arr);
|
code/sorting/src/comb_sort/comb_sort.m
|
/* Part of Cosmos by OpenGenus Foundation */
//
// comb_sort.m
// Created by DaiPei on 2017/10/15.
//
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface CombSort : NSObject
- (void)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array;
@end
@implementation CombSort
- (void)sort:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array {
NSUInteger gap = array.count;
BOOL swapped = YES;
double const shrinkFactor = 0.8;
while (gap >= 1 || swapped) {
swapped = NO;
if (gap >= 1) {
gap = (NSUInteger)(gap * shrinkFactor);
}
for (int i = 0; i + gap < array.count; i++) {
if ([array[i] compare:array[i + gap]] == NSOrderedDescending) {
[self swap:array at:i and:i + gap];
swapped = YES;
}
}
}
}
- (void)swap:(NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *)array at:(NSUInteger)indexA and:(NSUInteger)indexB {
NSNumber *tmp = array[indexA];
array[indexA] = array[indexB];
array[indexB] = tmp;
}
@end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
NSMutableArray *array = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:10];
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
int ran = arc4random() % 100 - 50;
[array addObject:@(ran)];
}
NSLog(@"before: %@", array);
CombSort *cs = [[CombSort alloc] init];
[cs sort:array];
NSLog(@"after: %@", array);
}
return 0;
}
|
code/sorting/src/comb_sort/comb_sort.py
|
def combsort(array):
gap = len(array)
swap = True
while gap > 1 or swap:
gap = max(1, int(gap / 1.25))
swap = False
for i in range(len(array) - gap):
j = i + gap
if array[i] > array[j]:
array[i], array[j] = array[j], array[i]
swap = True
numbers = [3, 4, 7, 2, 4, 1, 6, 8, 9, 10]
print(numbers)
combsort(numbers)
print(numbers)
|
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.