licenses
listlengths 1
3
| version
stringclasses 677
values | tree_hash
stringlengths 40
40
| path
stringclasses 1
value | type
stringclasses 2
values | size
stringlengths 2
8
| text
stringlengths 25
67.1M
| package_name
stringlengths 2
41
| repo
stringlengths 33
86
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.1.1 | 92573689d59edeb259f16715a716e7932f94c261 | code | 1072 | module SparseExtra
using SparseArrays
using SparseArrays: AbstractSparseMatrixCSC, AbstractSparseVector
using SparseArrays: getcolptr, getrowval, getnzval, nonzeroinds
using SparseArrays: rowvals, nonzeros
using SparseArrays: sparse_check_Ti, _goodbuffers
if isdefined(SparseArrays, :UMFPACK)
using SparseArrays.UMFPACK: UmfpackLU
using SparseArrays: UMFPACK
else
using SuiteSparse.UMFPACK: UmfpackLU
using SuiteSparse: UMFPACK
end
using VectorizationBase
using VectorizationBase: vsum, vprod, vmaximum, vminimum, bitselect
using LinearAlgebra, StaticArrays
using DataStructures
using DataStructures: FasterForward
using FLoops
include("iternz.jl")
export iternz
include("sparse_helpers.jl")
export unsafe_sum, colnorm!, colsum, sparse_like, getindex_
include("solve.jl")
export par_solve!, par_solve, par_inv!, par_inv
include("graph.jl")
export dijkstra, DijkstraState, sparse_feature_vec, sparse_feature, Path2Edge, path_cost, path_cost_nt, MkPair
include("genericmatrix.jl")
export GenericSparseMatrixCSC
include("simd.jl")
end # module SparseExtra
| SparseExtra | https://github.com/SobhanMP/SparseExtra.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.1.1 | 92573689d59edeb259f16715a716e7932f94c261 | code | 1528 | """
Like `SparseMatrixCSC` but allows any container for the vectors tho they should all be Dense `1-indexed` Vectors
"""
struct GenericSparseMatrixCSC{
Tv, Ti,
Av<:AbstractVector{Tv},
Aic<:AbstractVector{Ti},
Air<:AbstractVector{Ti}} <: AbstractSparseMatrixCSC{Tv, Ti}
m::Int
n::Int
colptr::Aic
rowval::Air
nzval::Av
function GenericSparseMatrixCSC(
m::Integer, n::Integer,
colptr::Aic,
rowval::Air,
nzval::Av) where {Av, Aic, Air}
Ti = eltype(Aic)
Ti === eltype(Air) || error("eltype of GSM's col and row must be the same")
sparse_check_Ti(m, n, Ti)
_goodbuffers(Int(m), Int(n), colptr, rowval, nzval) || throw(ArgumentError("Invalid buffer"))
new{eltype(Av), Ti, Av, Aic, Air}(Int(m), Int(n), colptr, rowval, nzval)
end
end
GenericSparseMatrixCSC(a::SparseMatrixCSC) = GenericSparseMatrixCSC(a.m, a.n, a.colptr, a.rowval, a.nzval)
@inline SparseArrays.rowvals(x::GenericSparseMatrixCSC) = x.rowval
@inline SparseArrays.nonzeros(x::GenericSparseMatrixCSC) = x.nzval
@inline SparseArrays.getcolptr(x::GenericSparseMatrixCSC) = x.colptr
@inline SparseArrays.getrowval(x::GenericSparseMatrixCSC) = x.rowval
@inline SparseArrays.getnzval(x::GenericSparseMatrixCSC) = x.nzval
Base.size(S::GenericSparseMatrixCSC) = (getfield(S, :m), getfield(S, :n))
Base.size(S::GenericSparseMatrixCSC, i) = if i <= 0
error()
elseif i == 1
getfield(S, :m)
elseif i == 2
getfield(S, :n)
else
error()
end
| SparseExtra | https://github.com/SobhanMP/SparseExtra.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.1.1 | 92573689d59edeb259f16715a716e7932f94c261 | code | 4514 | """
Work structure for `dijkstra`
"""
struct DijkstraState{T<:Real,U<:Integer}
parent::Vector{U}
distance::Vector{T}
visited::Vector{Bool}
q::PriorityQueue{U,T,FasterForward}
end
function set_src(state::DijkstraState{T, U}, srcs) where {T, U}
for src in srcs
state.distance[src] = zero(T)
state.q[src] = zero(T)
end
end
"""
DijkstraState(nv, T, src::AbstractVector{U}) where U -> DijkstraState
Initialize a `DijkstraState` for a graph of size `nv`, weight of type `T`, and srcs as initiale points
"""
function DijkstraState(nv, T, srcs::AbstractVector{U}) where U
state = DijkstraState{T,U}(
zeros(U, nv),
fill(typemax(T), nv),
zeros(Bool, nv),
PriorityQueue{U,T,FasterForward}(FasterForward()))
set_src(state, srcs)
return state
end
"""
DijkstraState(::DijkstraState{T, U}, src) where {T, U} -> DijkstraState{T, U}
clean up the DijkstraState to reusue the memory and avoid reallocations
"""
function DijkstraState(state::DijkstraState{T, U}, srcs) where {T, U}
fill!(state.parent, zero(U))
fill!(state.distance, typemax(T))
fill!(state.visited, false)
empty!(state.q)
set_src(state, srcs)
return state
end
"""
dijkstra(distmx::AbstractSparseMatrixCSC, state::DijkstraState, [target]) -> Nothing
Given a `distmx` such that `distmx[j, i]` is the distance of the arc i→j and strucutral zeros mean no arc, run the dijkstra algorithm until termination or reaching target (whichever happens first).
"""
function dijkstra(
distmx::SparseArrays.AbstractSparseMatrixCSC{T},
state::DijkstraState{T,U},
target=nothing) where {T<:Real, U<:Integer}
nzval = distmx.nzval
rowval = distmx.rowval
cptr = distmx.colptr
visited, distance, parent, q = state.visited, state.distance, state.parent, state.q
target !== nothing && visited[target] && return
@inbounds while !isempty(state.q)
peek(state.q) == target && break
u = dequeue!(state.q)
d = distance[u]
visited[u] && continue
visited[u] = true
for r in cptr[u]:cptr[u+1]-1
v = rowval[r]
δ = nzval[r]
alt = d + δ
if !visited[v] && alt < distance[v]
parent[v] = u
distance[v] = alt
q[v] = alt
end
end
end
end
"""
extract_path(::DijkstraState{T, U}, d) -> U[]
return the path found to `d`.
"""
function extract_path(state::DijkstraState{T, U}, d) where {T, U}
r = U[]
c = d
while c != 0
push!(r, c)
c = state.parent[c]
end
return r
end
"""
Path2Edge(x, [e=length(x)])
[Unbenchmarked] faster version of `zip(view(x, 1:e), view(x, 2:e))`. Only works on 1-index based arrays with unit strides
"""
struct Path2Edge{T,V<:AbstractVector{T}}
x::V
e::Int
function Path2Edge{T,V}(x::V, e=length(x)) where {T,V<:AbstractVector{T}}
@assert length(x) >= e
new{T,V}(x, e)
end
end
Path2Edge(x::V, e=length(x)) where{T,V<:AbstractVector{T}} = Path2Edge{T,V}(x, e)
Base.length(p::Path2Edge) = p.e - 1
Base.eltype(::Path2Edge{T}) where {T} = NTuple{2,T}
Base.iterate(p::Path2Edge, state=1) =
if p.e <= state
nothing
else
(p.x[state], p.x[state+1]), state + 1
end
"""
path_cost(::AbstractSparseMatrixCSC, r, n)
return the total weight of the path r[1:n]
"""
function path_cost(w::SparseMatrixCSC{T}, r, n=length(r)) where T
cost = zero(T)
for (i, j) in Path2Edge(r, n)
cost += w[i, j]
end
cost
end
"""
path_cost(f::Function, ::AbstractSparseMatrixCSC, r, n)
return the total weight of the path r[1:n], with `f` applied to each weight before summation
"""
function path_cost(f::F, w::SparseMatrixCSC{T}, r, n=length(r)) where {F, T}
cost = zero(f(zero(T)))
for (i, j) in Path2Edge(r, n)
cost += f(w[i, j])
end
cost
end
"""
path_cost_nt(::AbstractSparseMatrixCSC, r, n)
like `path_cost`, but for matrices that are transposed
"""
function path_cost_nt(w::SparseMatrixCSC{T}, r, n=length(r)) where T
cost = zero(T)
for (i, j) in Path2Edge(r, n)
cost += w[j, i]
end
cost
end
"""
path_cost_nt(f::Function, ::AbstractSparseMatrixCSC, r, n)
like `path_cost`, but for matrices that are transposed
"""
function path_cost_nt(f, w::SparseMatrixCSC{T}, r, n=length(r)) where T
cost = zero(T)
for (i, j) in Path2Edge(r, n)
cost += f(w[j, i])
end
cost
end
| SparseExtra | https://github.com/SobhanMP/SparseExtra.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.1.1 | 92573689d59edeb259f16715a716e7932f94c261 | code | 7357 | """
Helper structure for iternz, all methods. `iternz` just returns this wrapper and the `Base.iterate` method is overloaded.
"""
struct IterateNZ{N, T}
m::T
end
"""
`iternz(x)`
shortcut for `IterateNZ`.
"""
iternz(x) = IterateNZ{ndims(x), typeof(x)}(x)
Base.eltype(x::IterateNZ{N}) where N = Tuple{eltype(x.m), Vararg{Int, N}}
# default definition, do nothing
"""
skip_col(::IterateNZ, ::S) -> S
Move the cursor to the bottom of the current column. Does nothing by default and only makes sense for matrices.
"""
@inline skip_col(::IterateNZ, s) = s
"""
skip_row_to(::IterateNZ, ::S, i) -> S
Move the cursor to the bottom of the `i-1`th element. Does nothing by default and only makes sense for matrices.
"""
@inline skip_row_to(::IterateNZ, s, i) = s
Base.length(x::IterateNZ{2, <:AbstractSparseMatrixCSC}) = nnz(x.m)
@inline Base.iterate(x::IterateNZ{2, <:AbstractSparseMatrixCSC}, state=(1, 1)) =
@inbounds let (j, ind) = state
while j < size(x.m, 2) && ind >= getcolptr(x.m)[j + 1] # skip empty cols or one that have been exhusted
j += 1
end
(j > size(x.m, 2) || ind > nnz(x.m)) && return nothing
(getnzval(x.m)[ind], getrowval(x.m)[ind], j), (j, ind + 1)
end
@inline skip_col(x::IterateNZ{2, <:AbstractSparseMatrixCSC}, state) =
@inbounds let (j, ind) = state, m = x.m
j, max(getcolptr(m)[j + 1] - 1, ind)
end
@inline skip_row_to(x::IterateNZ{2, <:AbstractSparseMatrixCSC{Tv, Ti}}, state, i) where {Tv, Ti}=
@inbounds let (j, ind) = state,
r1 = convert(Ti, x.m.colptr[j])
r2 = convert(Ti, x.m.colptr[j + 1] - 1)
iTi = convert(Ti, i)
# skip empty cols
r3 = searchsortedfirst(rowvals(x.m), iTi, r1, r2, Base.Forward)
if r3 > r2
j + 1, getcolptr(x.m)[j + 1]
else
j, max(ind, convert(Int, r3))
end
end
@inline Base.length(x::IterateNZ{1, <:AbstractSparseVector}) = nnz(x.m)
@inline Base.iterate(x::IterateNZ{1, <:AbstractSparseVector}, state=0) = @inbounds let m = x.m
state += 1
if state > nnz(m)
nothing
else
(nonzeros(m)[state], nonzeroinds(m)[state]), state
end
end
Base.length(x::IterateNZ{N, <:AbstractArray}) where N = length(x.m)
@inline Base.iterate(x::IterateNZ{N, <:AbstractArray}) where N = begin
c = CartesianIndices(x.m)
i, s = iterate(c)
mi, ms = iterate(x.m)
(mi, Tuple(i)...), (ms, c, s)
end
@inline Base.iterate(x::IterateNZ{N, <:AbstractArray}, state) where N = @inbounds begin
ms, ii, is = state
res = iterate(ii, is)
res === nothing && return nothing
res1 = iterate(x.m, ms)
res1 === nothing && return nothing # shoud not happen
mi, nms = res1
i, s = res
(mi, Tuple(i)...), (nms, ii, s)
end
@inline function Base.iterate(x::IterateNZ{2, <:StridedMatrix})
ind, i, j = firstindex(x.m), 1, 1
return ((x.m[ind], i, j), (ind, i, j))
end
@inline Base.iterate(x::IterateNZ{2, <:StridedMatrix}, state) = @inbounds begin
ind, i, j = state
i += 1
if i > size(x.m, 1)
ind = ind + stride(x.m, 2) - (size(x.m, 1) - 1) * stride(x.m, 1)
i = 1
j += 1
else
ind += stride(x.m, 1)
end
if j > size(x.m, 2)
return nothing
end
(x.m[ind], i, j), (ind, i, j)
end
@inline skip_col(x::IterateNZ{2, <:StridedMatrix}, state) =
@inbounds begin
ind, i, j = state
i1 = size(x.m, 1)
ind = ind + (i1 - i) * stride(x.m, 1)
(ind, i1, j)
end
@inline skip_row_to(x::IterateNZ{2, <:StridedMatrix}, state, i1) =
@inbounds begin
ind, i, j = state
(ind + (i1 - i - 1) * stride(x.m, 1), i1 - 1, j)
end
Base.IteratorSize(x::IterateNZ{2, <:Transpose}) = Base.IteratorSize(iternz(x.m.parent))
Base.length(x::IterateNZ{2, <:Transpose}) = length(iternz(x.m.parent))
@inline Base.iterate(x::IterateNZ{2, <:Transpose}) =
let state = iternz(x.m.parent),
a = iterate(state)
a === nothing && return nothing
(v, i, j), s = a
(v, j, i), (state, s)
end
@inline Base.iterate(::IterateNZ{2, <:Transpose}, state) =
let a = iterate(state...)
a === nothing && return nothing
(v, i, j), s = a
(v, j, i), (state[1], s)
end
Base.IteratorSize(x::IterateNZ{2, <:Adjoint}) = Base.IteratorSize(iternz(x.m.parent))
Base.length(x::IterateNZ{2, <:Adjoint}) = length(iternz(x.m.parent))
@inline Base.iterate(x::IterateNZ{2, <:Adjoint}) =
let state = iternz(x.m.parent),
a = iterate(state)
a === nothing && return nothing
(v, i, j), s = a
(adjoint(v), j, i), (state, s)
end
@inline Base.iterate(::IterateNZ{2, <:Adjoint}, state) =
let a = iterate(state...)
a === nothing && return nothing
(v, i, j), s = a
(adjoint(v), j, i), (state[1], s)
end
Base.IteratorSize(x::IterateNZ{2, <:Diagonal}) = Base.IteratorSize(iternz(x.m.diag))
Base.length(x::IterateNZ{2, <:Diagonal}) = length(iternz(x.m.diag))
@inline Base.iterate(x::IterateNZ{2, <:Diagonal}) = let state = iternz(x.m.diag),
a = iterate(state)
a === nothing && return nothing
(v, i), s = a
(v, i, i), (state, s)
end
@inline Base.iterate(::IterateNZ{2, <:Diagonal}, state) =
let a = iterate(state...)
a === nothing && return nothing
(v, i), s = a
(v, i, i), (state[1], s)
end
Base.IteratorSize(::IterateNZ{2, <:UpperTriangular}) = Base.SizeUnknown()
@inline Base.iterate(x::IterateNZ{2, <:UpperTriangular}) =
let inner_state = iternz(x.m.data)
iternzut(inner_state, iterate(inner_state))
end
@inline Base.iterate(::IterateNZ{2, <:UpperTriangular}, state) =
let (inner_state, s) = state
iternzut(inner_state, iterate(inner_state, s))
end
@inline iternzut(iterator, a) = @inbounds begin
while a !== nothing
(v, i, j), state = a
i <= j && return (v, i, j), (iterator, state)
state = skip_col(iterator, state)
a = iterate(iterator, state)
end
nothing
end
Base.IteratorSize(::IterateNZ{2, <:LowerTriangular}) = Base.SizeUnknown()
@inline Base.iterate(x::IterateNZ{2, <:LowerTriangular}) =
let inner_state = iternz(x.m.data)
iternzlt(inner_state, iterate(inner_state))
end
@inline Base.iterate(::IterateNZ{2, <:LowerTriangular}, state) =
let (inner_state, s) = state
iternzlt(inner_state, iterate(inner_state, s))
end
@inline iternzlt(iterator, a) = @inbounds begin
while a !== nothing
(v, i, j), state = a
i >= j && return (v, i, j), (iterator, state)
state = skip_row_to(iterator, state, j)
a = iterate(iterator, state)
end
nothing
end
Base.IteratorSize(::IterateNZ{2, <:Symmetric}) = Base.SizeUnknown()
@inline Base.iterate(x::IterateNZ{2, <:Symmetric}) =
let iterator = iternz(x.m.data)
iternzsym(x.m, iterator, iterate(iterator))
end
@inline Base.iterate(x::IterateNZ{2, <:Symmetric}, state) =
let (iterator, (v, i, j), r, s) = state
if r
(v, j, i), (iterator, (v, i, j), false, s)
else
iternzsym(x.m, iterator, iterate(iterator, s))
end
end
@inline iternzsym(m::Symmetric, iterator, a) = @inbounds begin
while a !== nothing
r, state = a
(_, i, j) = r
if m.uplo == 'U'
i <= j && return r, (iterator, r, i != j, state)
state = skip_col(iterator, state)
elseif m.uplo == 'L'
i >= j && return r, (iterator, r, i != j, state)
state = skip_row_to(iterator, state, j)
end
a = iterate(iterator, state)
end
nothing
end
| SparseExtra | https://github.com/SobhanMP/SparseExtra.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.1.1 | 92573689d59edeb259f16715a716e7932f94c261 | code | 116 | Base.argmax(vx::Vec{N}) where N =
let m = vmaximum(vx) == vx,
u = getfield(m, :u)
trailing_zeros(u) + 1
end | SparseExtra | https://github.com/SobhanMP/SparseExtra.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.1.1 | 92573689d59edeb259f16715a716e7932f94c261 | code | 3502 | """
solve lu\\b in parallel
"""
const LU = Union{Transpose{T, <: UmfpackLU{T}}, UmfpackLU{T}} where T
const LU_has_lock = hasfield(UmfpackLU, :lock)
if LU_has_lock
if isdefined(UMFPACK, :duplicate)
@eval begin
using SparseArrays.UMFPACK: duplicate
UMFPACK.duplicate(F::Transpose{T, <:UmfpackLU}) where T = Transpose(duplicate(F.parent))
UMFPACK.duplicate(F::Adjoint{T, <:UmfpackLU}) where T = Adjoint(duplicate(F.parent))
Base.copy(F::LU; copynumeric=false, copysymbolic=false) = duplicate(F)
end
end
else
@eval begin
SparseArrays._goodbuffers(S::AbstractSparseMatrixCSC) = _goodbuffers(size(S)..., getcolptr(S), getrowval(S), nonzeros(S))
SparseArrays._checkbuffers(S::AbstractSparseMatrixCSC) = (@assert _goodbuffers(S); S)
end
end
# Base.copy(F::LU; a...) = copy(F)
@inline pfno(a...) = nothing
"""
ldiv! but in parallel. use `cols`` to skip columns and `f(col, index)` to apply a thread safe function to that column.
"""
function par_solve!(x, lu::LU, b::AbstractMatrix; cols=axes(b, 2), f::F=nothing) where F
if LU_has_lock
@floop for i in cols
@init dlu = copy(lu; copynumeric=false, copysymbolic=false)
v = view(x, :, i)
ldiv!(v, dlu, view(b, :, i))
if f !== nothing f(v, i) end
end
else
@floop for i in cols
v = view(x, :, i)
ldiv!(v, lu, view(b, :, i))
if f !== nothing f(v, i) end
end
end
return x
end
par_solve(lu::LU, b::AbstractMatrix; cols=axes(b, 2)) = par_solve!(similar(b), lu, b; cols)
"""
like par_solve but use `f` and `g` to create the column (and then destroy it).
"""
function par_solve_f!(x, f!::F, g!::G, lu::LU{T}; cols=1:size(lu, 2)) where {T, F, G}
size(x, 1) == size(lu, 1) || error("can't")
if LU_has_lock
@floop for i in cols
@init dlu = copy(lu; copynumeric=false, copysymbolic=false)
@init storage = zeros(T, size(lu, 1))
f!(storage, i)
v = view(x, :, i)
ldiv!(v, dlu, storage)
g!(storage, i)
end
else
@floop for i in cols
@init storage = zeros(T, size(lu, 1))
f!(storage, i)
v = view(x, :, i)
ldiv!(v, lu, storage)
g!(storage, i)
end
end
return x
end
function _par_inv_init(x, i)
x[i] = one(eltype(x))
return
end
function _par_inv_fin(x, i)
x[i] = zero(eltype(x))
return
end
"""
return `lu \\ I`
"""
par_inv!(x, lu::LU; cols=1:size(lu, 2)) = par_solve_f!(x, _par_inv_init, _par_inv_fin, lu; cols)
par_inv(lu::LU{T}; cols=1:size(lu, 2)) where T = par_inv!(Matrix{T}(undef, size(lu)...), lu; cols)
using Base.Threads
using SparseArrays, LinearAlgebra
function par_ldiv!_t_f(lhs, F, rhs; cols)
for i in cols
ldiv!(view(lhs, :, i), F, view(rhs, :, i))
end
return
end
function par_ldiv!_t(lhs::AbstractMatrix{T}, F, rhs::AbstractMatrix{T}; cols=axes(rhs, 2)) where T
size(lhs) == size(rhs) || error("rhs and lhs are not equal sized")
c = ceil(Int, length(cols) / nthreads())
foreach(wait, [
@spawn par_ldiv!_t_f(lhs, copy(F; copynumeric=false, copysymbolic=false), rhs;
cols = view(cols, (i - 1) * c + 1: min(i * c, length(cols))))
for i in 1:nthreads()])
return lhs
end
par_ldiv_t(F, rhs; cols=axes(rhs, 2)) = par_ldiv!(similar(rhs), F, rhs; cols)
export par_ldiv!_t | SparseExtra | https://github.com/SobhanMP/SparseExtra.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.1.1 | 92573689d59edeb259f16715a716e7932f94c261 | code | 2447 | @inline unsafe_sum(a, i0=firstindex(a), i1=lastindex) = unsafe_sum(a, i0:i1)
function unsafe_sum(a::StridedVector{T}, r) where {T}
stride(a, 1) == 1 || error()
s = zero(T)
@inbounds for i in r
s += a[i]
end
s
end
function colnorm!(x::SparseMatrixCSC{Tv, Ti}) where {Tv, Ti}
for i in axes(x, 2)
a, b = getcolptr(x)[i], getcolptr(x)[i + 1] - 1
s = unsafe_sum(getnzval(x), a, b)
@inbounds for j in a:b
getnzval(x)[j] /= s
end
end
end
function colnorm!(x::SparseMatrixCSC{Tv, Ti}, abs, offset) where {Tv, Ti}
abs_ind = 1
for i in axes(x, 2)
of = if abs_ind <= length(abs) && i == abs[abs_ind]
abs_ind += 1
offset
else
zero(offset)
end
r = getcolptr(x)[i]: getcolptr(x)[i + 1] - 1
s = unsafe_sum(nonzeros(x), r) + of
@inbounds for j in r
nonzeros(x)[j] /= s
end
end
end
@inline function colsum(x::SparseMatrixCSC, i)
@boundscheck checkbounds(x, :, i)
return unsafe_sum(getnzval(x), getcolptr(x)[i], getcolptr(x)[i + 1] - 1)
end
sparse_like(t::SparseMatrixCSC, T::Type) =
SparseMatrixCSC(t.m, t.n, t.colptr, t.rowval, Vector{T}(undef, nnz(t)))
sparse_like(t::SparseMatrixCSC, z) =
SparseMatrixCSC(t.m, t.n, t.colptr, t.rowval, fill(z, nnz(t)))
sparse_like(t::SparseMatrixCSC, z::Vector) =
SparseMatrixCSC(t.m, t.n, t.colptr, t.rowval, z)
sparse_like(t::SparseMatrixCSC) =
SparseMatrixCSC(t.m, t.n, t.colptr, t.rowval, copy(t.nzval))
@static if isdefined(SparseArrays, :FixedSparseCSC)
using SparseArrays: FixedSparseCSC
sparse_like(t::FixedSparseCSC, T::Type) =
FixedSparseCSC(t.m, t.n, t.colptr, t.rowval, Vector{T}(undef, nnz(t)))
sparse_like(t::FixedSparseCSC, z) =
FixedSparseCSC(t.m, t.n, t.colptr, t.rowval, fill(z, nnz(t)))
sparse_like(t::FixedSparseCSC, z::Vector) =
FixedSparseCSC(t.m, t.n, t.colptr, t.rowval, z)
sparse_like(t::FixedSparseCSC) =
FixedSparseCSC(t.m, t.n, t.colptr, t.rowval, copy(t.nzval))
end
function getindex_(A::SparseMatrixCSC{Tv, Ti}, i0::T, i1::T)::T where {Tv, Ti, T}
@boundscheck checkbounds(A, i0, i1)
r1 = convert(Ti, A.colptr[i1])
r2 = convert(Ti, A.colptr[i1 + 1] - 1)
(r1 > r2) && return zero(T)
r3 = searchsortedfirst(rowvals(A), i0, r1, r2, Base.Forward)
@boundscheck !((r3 > r2) || (rowvals(A)[r3] != i0))
return r3
end | SparseExtra | https://github.com/SobhanMP/SparseExtra.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.1.1 | 92573689d59edeb259f16715a716e7932f94c261 | code | 5344 | using Test, SparseArrays, SparseExtra, LinearAlgebra
using SparseArrays: getnzval, getcolptr, getrowval
using Graphs
using Graphs.Experimental.ShortestPaths: shortest_paths, dists
using StaticArrays
using VectorizationBase
iternz_naive(x) = let f = findnz(x)
collect(zip(f[end], f[1:end-1]...))
end
test_iternz_arr(_a::AbstractArray{T, N}, it=iternz(_a)) where {T, N} = begin
a = Array(_a)
x = collect(it)
@test length(unique(x)) <= length(a)
@test length(unique(x)) == length(x)
@test all((a[i...] == v for (v, i...) in x))
seen = Set{NTuple{N, Int}}()
for (_, i...) in x
@test i ∉ seen
push!(seen, i)
end
for I in CartesianIndices(a)
@test iszero(a[I]) || Tuple(I) ∈ seen
end
end
@testset "iternz (Symmetric)" begin
for i in 1:20
for uplo in [:U, :L]
A = Symmetric(sprandn(i, i, 1 / i), uplo)
test_iternz_arr(A)
B = Symmetric(rand(i, i), uplo)
test_iternz_arr(B)
end
end
end
@testset "iternz (SparseMatrixCSC)" begin
for i in 1:20
A = sprandn(100, 100, 1 / i)
@test collect(iternz(A)) == iternz_naive(A)
end
end
@testset "iternz (adjoint)" begin
for i in 1:10
test_iternz_arr(adjoint(randn(i, i) + randn(i, i)im))
test_iternz_arr(adjoint(sprandn(i, i, 0.5) + sprandn(i, i, 0.5)im))
end
end
@testset "iternz (SparseVector)" begin
for i in 1:10
A = sprandn(100, i / 100)
@test collect(iternz(A)) == iternz_naive(A)
end
end
@testset "iternz (Vectors)" begin
for i in 1:10
a = randn(100 + i)
@test collect(iternz(a)) == collect(zip(a, eachindex(a)))
end
end
@testset "iternz (Array)" begin
for i in 1:5
a = randn((rand(3:4) for i in 1:i)...)
test_iternz_arr(a)
end
a = randn(10)
test_iternz_arr(a)
test_iternz_arr(view(a, 3:6))
end
@testset "iternz (Diagonal)" begin
for i in 1:10
test_iternz_arr(Diagonal(randn(i)))
test_iternz_arr(Diagonal(sprandn(i, 0.5)))
end
end
@testset "iternz (Upper/Lower Triangular)" begin
for i in 1:10
A = randn(i, i)
B = sprandn(i, i, 0.5)
test_iternz_arr(UpperTriangular(A))
test_iternz_arr(LowerTriangular(A))
test_iternz_arr(UpperTriangular(B))
test_iternz_arr(LowerTriangular(B))
end
end
@testset "iternz (transpose)" begin
for i in 1:10
test_iternz_arr(transpose(randn(i, i)))
test_iternz_arr(transpose(sprandn(i, i, 0.5)))
end
end
@testset "unsafe sum" begin
for s in 1:100
a = randn(s)
for i in 1:s,
j in i:s
@test unsafe_sum(a, i, j) == sum(view(a, i:j))
end
end
end
@testset "unsafe sum" begin
for s in 1:100
a = sprandn(s, s, 0.1)
getnzval(a) .= abs.(getnzval(a))
a = a + I
b = copy(a)
colnorm!(a)
for i in axes(a, 2)
@test sum(a[:, i]) ≈ 1
@test colsum(a, i) ≈ sum(a[:, i])
@test colsum(b, i) ≈ sum(b[:, i])
@test a[:, i] .* sum(b[:, i]) ≈ b[:, i]
end
end
end
# @testset "par solve" begin
# for s in 1:100
# a = sprandn(s, s, 0.1) + I
# b = randn(s, s)
# @test maximum(par_inv(lu(a)) * a - I) <= 1e-5
# @test a \ b ≈ par_solve(lu(a), b)
# end
# end
@testset "Path2Edge" begin
for _ in 1:10
a = rand(1:100, 1000)
for i in [10, 200, 1000]
@test collect(Path2Edge(a, i)) == collect(zip(a, view(a, 2:i)))
end
end
end
@testset "simd argmax" begin
function f(t, i)
tx = ntuple(_ -> rand(t), i)
ax = collect(tx)
vx = Vec{i, t}(tx...)
@test argmax(vx) == argmax(ax)
return
end
for t in [Int8, Int32, Int64, Float64, Float32],
i in 1:100,
j in 1:100
f(Int8, i)
end
end
@testset "dijkstra" begin
graph = Graphs.SimpleGraphs.erdos_renyi(100, 0.4; is_directed=true)
state = DijkstraState(nv(graph), Float64, SVector{0, Int}())
weight = spzeros(nv(graph), nv(graph))
for i in vertices(graph),
j in outneighbors(graph, i)
weight[i, j] = rand() + 1e-3
end
tw = sparse(transpose(weight))
for src in vertices(graph)
state = DijkstraState(state, SVector(src))
dijkstra(tw, state)
odj = shortest_paths(graph, src, transpose(tw))
@test dists(odj) ≈ state.distance
for j in vertices(graph)
i = state.parent[j]
i == 0 && continue
@test has_edge(graph, i, j)
@test state.distance[i] + tw[j, i] ≈ state.distance[j]
end
end
end
@testset "sparse_like" begin
function good_same(t, z, eq=true)
@test size(z) == size(t)
@test getcolptr(z) === getcolptr(t)
@test getrowval(z) === getrowval(t)
eq && @test getnzval(z) == getnzval(t)
@test getnzval(z) !== getnzval(t)
end
t = sprandn(100, 100, 0.1)
good_same(t, sparse_like(t))
good_same(t, sparse_like(t, rand(1:2, nnz(t))), false)
good_same(t, sparse_like(t, 0), false)
all(getnzval(sparse_like(t, 2)) .== 2)
good_same(t, sparse_like(t, Bool), false)
@test isa(getnzval(sparse_like(t, Bool)), Vector{Bool})
end
| SparseExtra | https://github.com/SobhanMP/SparseExtra.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.1.1 | 92573689d59edeb259f16715a716e7932f94c261 | docs | 1054 | [](https://sobhanmp.github.io/SparseExtra.jl/)

[](https://codecov.io/gh/SobhanMP/SparseExtra.jl)
Collections of mostly sparse stuff developed by me. See documentation. But big picture, there is a very fast dijkstra implementation that uses sparse matrices as graph representation, parallel LU solve (i.e., Ax=b), and iternz an API for iterating over sparse structures like SparseMatrixCSC, Diagonal, bidiagonal that is composable meaning that if you have a new vector type, implementing the iternz will make it work with other sparse object that already use it.
Most of this was developed in the context of this [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.14351) which is something to keep in mind when testing dense sparse matrices. Traffic graphs usually have less than 6 neighbors and are very balanced.
| SparseExtra | https://github.com/SobhanMP/SparseExtra.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.1.1 | 92573689d59edeb259f16715a716e7932f94c261 | docs | 749 | # SparseExtra
```@meta
DocTestSetup = :(using SparseArrays, LinearAlgebra, SparseExtra)
```
**SparseExtra.jl** is a a series of helper function useful for dealing with sparse matrix, random walk, and shortest path on sparse graphs and some more. Most of this was developed for an unpublished paper which would help explain some of the design choises.
# [SparseExtra](@id sparse-extra)
```@docs
SparseExtra.par_solve_f!
SparseExtra.skip_row_to
SparseExtra.extract_path
SparseExtra.skip_col
SparseExtra.IterateNZ
SparseExtra.path_cost
SparseExtra.GenericSparseMatrixCSC
SparseExtra.path_cost_nt
SparseExtra.DijkstraState
SparseExtra.Path2Edge
SparseExtra.par_solve!
SparseExtra.dijkstra
SparseExtra.iternz
SparseExtra.par_inv!
```
| SparseExtra | https://github.com/SobhanMP/SparseExtra.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.1.1 | 92573689d59edeb259f16715a716e7932f94c261 | docs | 8252 | ```@meta
EditURL = "../lit/iternz.jl"
```
# The `iternz` API
This returns an iterator over the structural non-zero elements of the array (elements that aren't zero due to the structure not zero elements) i.e.
```julia
all(iternz(x)) do (v, k...)
x[k...] == v
end
```
The big idea is to abstract away all of the speciall loops needed to iterate over sparse containers. These include special Linear Algebra matrices like `Diagonal`, and `UpperTriangular` or `SparseMatrixCSC`. Furethemore it's possible to use this recursively i.e. An iteration over a `Diagonal{SparseVector}` will skip the zero elements (if they are not stored) of the SparseVector.
For an example let's take the sum of the elements in a matrix such that `(i + j) % 7 == 0`. The most general way of writing it is
````julia
using BenchmarkTools, SparseArrays
const n = 10_000
const A = sprandn(n, n, max(1000, 0.1 * n*n) / n / n);
function general(x::AbstractMatrix)
s = zero(eltype(x))
@inbounds for j in axes(x, 2),
i in axes(x, 1)
if (i + j) % 7 == 0
s += x[i, j]
end
end
return s
end
@benchmark general($A)
````
````
BenchmarkTools.Trial: 11 samples with 1 evaluation.
Range (min … max): 461.048 ms … 468.458 ms ┊ GC (min … max): 0.00% … 0.00%
Time (median): 463.496 ms ┊ GC (median): 0.00%
Time (mean ± σ): 463.928 ms ± 2.200 ms ┊ GC (mean ± σ): 0.00% ± 0.00%
█
▇▁▇▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▇▁▁▁▇▇▁▁▁▁▇▁▁▇▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁█▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▇ ▁
461 ms Histogram: frequency by time 468 ms <
Memory estimate: 0 bytes, allocs estimate: 0.
````
Now this is pretty bad, we can improve the performance by using the sparse structure of the problem
````julia
using SparseArrays: getcolptr, nonzeros, rowvals
function sparse_only(x::SparseMatrixCSC)
s = zero(eltype(x))
@inbounds for j in axes(x, 2),
ind in getcolptr(x)[j]:getcolptr(x)[j + 1] - 1
i = rowvals(x)[ind]
if (i + j) % 7 == 0
s += nonzeros(x)[ind]
end
end
return s
end
````
````
sparse_only (generic function with 1 method)
````
We can test for correctness
````julia
sparse_only(A) == general(A)
````
````
true
````
and benchmark the function
````julia
@benchmark sparse_only($A)
````
````
BenchmarkTools.Trial: 301 samples with 1 evaluation.
Range (min … max): 15.765 ms … 19.260 ms ┊ GC (min … max): 0.00% … 0.00%
Time (median): 16.511 ms ┊ GC (median): 0.00%
Time (mean ± σ): 16.646 ms ± 566.611 μs ┊ GC (mean ± σ): 0.00% ± 0.00%
▁▃▅▄█▃▄ ▃ ▁▄ ▁
▃▁▃▃▄█████████▇██▆▅▇██▅▆▅█▇▅▃▆▅▃▆▅▆▄▃▄▁▁▃▁▄▃▅▃▁▃▁▁▃▃▁▁▁▁▁▃▁▃ ▄
15.8 ms Histogram: frequency by time 18.6 ms <
Memory estimate: 0 bytes, allocs estimate: 0.
````
we can see that while writing the function requires understanding how CSC matrices are stored, the code is 600x faster. The thing is that this pattern gets repeated everywhere so we might try and abstract it away. My proposition is the iternz api.
````julia
using SparseExtra
function iternz_only(x::AbstractMatrix)
s = zero(eltype(x))
for (v, i, j) in iternz(x)
if (i + j) % 7 == 0
s += v
end
end
return s
end
iternz_only(A) == general(A)
````
````
true
````
````julia
@benchmark sparse_only($A)
````
````
BenchmarkTools.Trial: 266 samples with 1 evaluation.
Range (min … max): 15.932 ms … 32.230 ms ┊ GC (min … max): 0.00% … 0.00%
Time (median): 17.630 ms ┊ GC (median): 0.00%
Time (mean ± σ): 18.806 ms ± 2.971 ms ┊ GC (mean ± σ): 0.00% ± 0.00%
▄█▅▂█▁▃
▅█████████▄▅▅▆▅▆▆▄▄▄▄▅▃▁▃▄▃▄▃▁▅▄▁▃▃▃▁▁▃▁▃▃▃▁▄▃▃▁▁▃▃▃▁▃▃▁▁▃▃ ▃
15.9 ms Histogram: frequency by time 28.3 ms <
Memory estimate: 0 bytes, allocs estimate: 0.
````
The speed is the same as the specialized version but there is no `@inbounds`, no need for ugly loops etc. As a bonus point it works on all of the specialized matrices
````julia
using LinearAlgebra
all(iternz_only(i(A)) ≈ general(i(A)) for i in [Transpose, UpperTriangular, LowerTriangular, Diagonal, Symmetric]) # symmetric changes the order of exection.
````
````
true
````
Since these interfaces are written using the iternz interface themselves, the codes generalize to the cases where these special matrices are combined, removing the need to do these tedious specialization.
For instance the 3 argument dot can be written as
````julia
function iternz_dot(x::AbstractVector, A::AbstractMatrix, y::AbstractVector)
(length(x), length(y)) == size(A) || throw(ArgumentError("bad shape"))
acc = zero(promote_type(eltype(x), eltype(A), eltype(y)))
@inbounds for (v, i, j) in iternz(A)
acc += x[i] * v * y[j]
end
acc
end
const (x, y) = randn(n), randn(n);
const SA = Symmetric(A);
````
Correctness tests
````julia
dot(x, A, y) ≈ iternz_dot(x, A, y) && dot(x, SA, y) ≈ iternz_dot(x, SA, y)
````
````
true
````
Benchmarks
````julia
@benchmark dot($x, $A, $y)
````
````
BenchmarkTools.Trial: 500 samples with 1 evaluation.
Range (min … max): 9.153 ms … 16.797 ms ┊ GC (min … max): 0.00% … 0.00%
Time (median): 9.794 ms ┊ GC (median): 0.00%
Time (mean ± σ): 9.998 ms ± 744.517 μs ┊ GC (mean ± σ): 0.00% ± 0.00%
▃ ▂▄█▃ ▁
██████▇██████▆█▅▄▄▅▄▄▄▄▄▄▅▄▄▄▃▄▃▄▄▃▃▃▁▃▁▁▂▂▂▁▂▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▂ ▄
9.15 ms Histogram: frequency by time 12.9 ms <
Memory estimate: 0 bytes, allocs estimate: 0.
````
````julia
@benchmark iternz_dot($x, $A, $y)
````
````
BenchmarkTools.Trial: 426 samples with 1 evaluation.
Range (min … max): 10.760 ms … 16.682 ms ┊ GC (min … max): 0.00% … 0.00%
Time (median): 11.519 ms ┊ GC (median): 0.00%
Time (mean ± σ): 11.727 ms ± 741.895 μs ┊ GC (mean ± σ): 0.00% ± 0.00%
▅█▄▁▂▂
▅▇▇▆█▇▇████████▆█▄▆██▆▄▆▄▆▅▆▃▄▄▃▄▂▄▃▃▂▂▁▃▁▁▁▂▃▁▁▃▁▃▁▁▁▃▃▁▁▁▂ ▄
10.8 ms Histogram: frequency by time 14.5 ms <
Memory estimate: 0 bytes, allocs estimate: 0.
````
````julia
@benchmark dot($x, $SA, $y)
````
````
BenchmarkTools.Trial: 9 samples with 1 evaluation.
Range (min … max): 607.881 ms … 623.882 ms ┊ GC (min … max): 0.00% … 0.00%
Time (median): 609.728 ms ┊ GC (median): 0.00%
Time (mean ± σ): 611.193 ms ± 4.900 ms ┊ GC (mean ± σ): 0.00% ± 0.00%
▁ █ ▁ ▁█ ▁ ▁
█▁▁█▁█▁██▁▁▁▁▁▁█▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁▁█ ▁
608 ms Histogram: frequency by time 624 ms <
Memory estimate: 0 bytes, allocs estimate: 0.
````
````julia
@benchmark iternz_dot($x, $SA, $y)
````
````
BenchmarkTools.Trial: 440 samples with 1 evaluation.
Range (min … max): 10.576 ms … 17.101 ms ┊ GC (min … max): 0.00% … 0.00%
Time (median): 11.173 ms ┊ GC (median): 0.00%
Time (mean ± σ): 11.371 ms ± 740.788 μs ┊ GC (mean ± σ): 0.00% ± 0.00%
▂▃ █▆▃▄▃
▆███████████▇▆▇▇▅▆▆▆▅▄▅▅▃▄▃▃▃▃▃▂▁▂▁▁▂▂▃▁▃▁▁▂▂▁▂▁▁▁▂▁▁▁▃▁▁▁▁▂ ▃
10.6 ms Histogram: frequency by time 14.4 ms <
Memory estimate: 0 bytes, allocs estimate: 0.
````
## API:
The Api is pretty simple, the `iternz(A)` should return an iteratable such that
```julia
all(A[ind...] == v for (v, ind...) in iternz(A))
```
If the matrix is a container for a different type, the inner iteration should be done via iternz. This repo provides the `IterateNZ` container whose sole pupose is to hold the array to overload `Base.iterate`. Additionally matrices have the `skip_col` and `skip_row_to` functions defined. The idea that if meaningful, this should return a state such that iterating on that state will give the first element of the next column or in the case of `skip_row_to(cont, state, i)`, iterate should return `(i, j)` where j is the current column.
## TODO
- test with non-one based indexing
---
*This page was generated using [Literate.jl](https://github.com/fredrikekre/Literate.jl).*
| SparseExtra | https://github.com/SobhanMP/SparseExtra.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.1.1 | 92573689d59edeb259f16715a716e7932f94c261 | docs | 1122 | ```@meta
EditURL = "<unknown>/docs/lit/par_ldiv.jl"
```
# parallel ldiv!
````julia
using SparseExtra, LinearAlgebra, SparseArrays, BenchmarkTools
const n = 10_000
const A = sprandn(n, n, 5 / n);
const C = A + I
const B = Matrix(sprandn(n, n, 1 / n));
const F = lu(C);
const X = similar(B);
````
Standard:
````julia
@benchmark ldiv!($X, $F, $B)
````
````
BenchmarkTools.Trial: 1 sample with 1 evaluation.
Single result which took 96.309 s (0.00% GC) to evaluate,
with a memory estimate of 0 bytes, over 0 allocations.
````
With FLoops.jl:
````julia
@benchmark par_solve!($X, $F, $B)
````
````
BenchmarkTools.Trial: 1 sample with 1 evaluation.
Single result which took 25.195 s (0.00% GC) to evaluate,
with a memory estimate of 1.24 MiB, over 163 allocations.
````
with manual loops
````julia
@benchmark par_ldiv!_t($X, $F, $B)
````
````
BenchmarkTools.Trial: 1 sample with 1 evaluation.
Single result which took 25.395 s (0.00% GC) to evaluate,
with a memory estimate of 1.24 MiB, over 130 allocations.
````
---
*This page was generated using [Literate.jl](https://github.com/fredrikekre/Literate.jl).*
| SparseExtra | https://github.com/SobhanMP/SparseExtra.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
]
| 0.3.1 | 9d2868bcdf21fecc37c545032ab687af072bb5db | code | 2894 | # ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Licensed under the ISC License. See LICENCE in the project root.
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
module SpectralGaussianSimulation
using GeoStatsBase
using Variography
using Statistics
using FFTW
using CpuId
import GeoStatsBase: preprocess, solvesingle
export SpecGaussSim
"""
SpecGaussSim(var₁=>param₁, var₂=>param₂, ...)
Spectral Gaussian simulation (a.k.a. FFT simulation).
## Parameters
* `variogram` - theoretical variogram (default to `GaussianVariogram()`)
* `mean` - mean of Gaussian field (default to `0`)
## Global parameters
* `threads` - number of threads in FFT (default to all physical cores)
### References
Gutjahr 1997. *General joint conditional simulations using a fast
Fourier transform method.*
"""
@simsolver SpecGaussSim begin
@param variogram = GaussianVariogram()
@param mean = 0.0
@global threads = cpucores()
end
function preprocess(problem::SimulationProblem, solver::SpecGaussSim)
hasdata(problem) && @warn "Conditional spectral Gaussian simulation is not currently supported"
# retrieve problem info
pdomain = domain(problem)
npts = nelms(pdomain)
dims = size(pdomain)
center = CartesianIndex(dims .÷ 2)
c = LinearIndices(dims)[center]
# number of threads in FFTW
FFTW.set_num_threads(solver.threads)
# result of preprocessing
preproc = Dict()
for covars in covariables(problem, solver)
for var in covars.names
# get user parameters
varparams = covars.params[(var,)]
# get variable type
V = variables(problem)[var]
# determine variogram model and mean
γ = varparams.variogram
μ = varparams.mean
# check stationarity
@assert isstationary(γ) "variogram model must be stationary"
# compute covariances between centroid and all locations
covs = sill(γ) .- pairwise(γ, pdomain, [c], 1:npts)
C = reshape(covs, dims)
# move to frequency domain
F = sqrt.(abs.(fft(fftshift(C))))
F[1] = zero(V) # set reference level
# save preprocessed inputs for variable
preproc[var] = (γ=γ, μ=μ, F=F)
end
end
preproc
end
function solvesingle(problem::SimulationProblem, covars::NamedTuple,
solver::SpecGaussSim, preproc)
# retrieve problem info
pdomain = domain(problem)
dims = size(pdomain)
varreal = map(covars.names) do var
# unpack preprocessed parameters
γ, μ, F = preproc[var]
# result type
V = variables(problem)[var]
# perturbation in frequency domain
P = F .* exp.(im .* angle.(fft(rand(V, dims))))
# move back to time domain
Z = real(ifft(P))
# adjust mean and variance
σ² = Statistics.var(Z, mean=zero(V))
Z .= √(sill(γ) / σ²) .* Z .+ μ
# flatten result
var => vec(Z)
end
Dict(varreal)
end
end
| SpectralGaussianSimulation | https://github.com/juliohm/SpectralGaussianSimulation.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
]
| 0.3.1 | 9d2868bcdf21fecc37c545032ab687af072bb5db | code | 1016 | using SpectralGaussianSimulation
using GeoStatsBase
using Variography
using Plots, VisualRegressionTests
using Test, Pkg, Random
# workaround GR warnings
ENV["GKSwstype"] = "100"
# environment settings
islinux = Sys.islinux()
istravis = "TRAVIS" ∈ keys(ENV)
datadir = joinpath(@__DIR__,"data")
visualtests = !istravis || (istravis && islinux)
if !istravis
Pkg.add("Gtk")
using Gtk
end
@testset "SpectralGaussianSimulation.jl" begin
if visualtests
problem = SimulationProblem(RegularGrid(100,100), :z => Float64, 3)
Random.seed!(2019)
solver = SpecGaussSim(:z => (variogram=GaussianVariogram(range=10.),))
solution = solve(problem, solver)
@plottest plot(solution,size=(900,300)) joinpath(datadir,"isotropic.png") !istravis
Random.seed!(2019)
solver = SpecGaussSim(:z => (variogram=GaussianVariogram(distance=Ellipsoidal([20.,5.],[0.])),))
solution = solve(problem, solver)
@plottest plot(solution,size=(900,300)) joinpath(datadir,"anisotropic.png") !istravis
end
end
| SpectralGaussianSimulation | https://github.com/juliohm/SpectralGaussianSimulation.jl.git |
|
[
"ISC"
]
| 0.3.1 | 9d2868bcdf21fecc37c545032ab687af072bb5db | docs | 1706 | # SpectralGaussianSimulation.jl
[![][travis-img]][travis-url] [![][codecov-img]][codecov-url]
This package provides an implementation of spectral Gaussian simulation
as described in [Gutjahr 1997](https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02769641).
In this method, the covariance function is perturbed in the frequency
domain after a fast Fourier transform. White noise is added to the phase
of the spectrum, and a realization is produced by an inverse Fourier transform.
The method is limited to simulations on regular grids, and care must be taken
to make sure that the correlation length is small enough compared to the grid
size. As a general rule of thumb, avoid correlation lengths greater than 1/3
of the grid. The method is extremely fast, and can be used to generate large
3D realizations.
## Installation
Get the latest stable release with Julia's package manager:
```julia
] add SpectralGaussianSimulation
```
## Usage
This package is part of the [GeoStats.jl](https://github.com/JuliaEarth/GeoStats.jl) framework.
For a simple example of usage, please check [this notebook](https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/JuliaEarth/SpectralGaussianSimulation.jl/blob/master/docs/Usage.ipynb).
## Asking for help
If you have any questions, please [open an issue](https://github.com/JuliaEarth/SpectralGaussianSimulation.jl/issues).
[travis-img]: https://travis-ci.org/JuliaEarth/SpectralGaussianSimulation.jl.svg?branch=master
[travis-url]: https://travis-ci.org/JuliaEarth/SpectralGaussianSimulation.jl
[codecov-img]: https://codecov.io/gh/JuliaEarth/SpectralGaussianSimulation.jl/branch/master/graph/badge.svg
[codecov-url]: https://codecov.io/gh/JuliaEarth/SpectralGaussianSimulation.jl
| SpectralGaussianSimulation | https://github.com/juliohm/SpectralGaussianSimulation.jl.git |
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
]
| 0.2.4 | 12c19821099177fad12336af5e3d0ca8f41eb3d3 | code | 253 | struct Lens{T, Fields, Field}
end
@generated function runlens(main :: T, new_field, lens::Type{Lens{T, Fields, Field}}) where {T, Fields, Field}
quote
$T($([field !== Field ? :(main.$field) : :new_field for field in Fields]...))
end
end | RBNF | https://github.com/thautwarm/RBNF.jl.git |
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
]
| 0.2.4 | 12c19821099177fad12336af5e3d0ca8f41eb3d3 | code | 3457 | AsocList{K, V} = AbstractArray{Tuple{K, V}}
function _genlex(argsym, retsym, lexer_table, reserved_words)
gen_many_lexers = map(lexer_table) do (k, v)
lnode = LineNumberNode(1, "lexing rule: $k")
token_type = reserved_words === nothing ? QuoteNode(k) :
:(s in $reserved_words ? :reserved : $(QuoteNode(k)))
quote
$lnode
s = $v($argsym, offset)
if s !== nothing
line_inc = count(x -> x === '\n', s)
n = ncodeunits(s)
push!($retsym, $Token{$token_type}(lineno, colno, offset, s, n))
if line_inc === 0
colno += n
else
lineno += line_inc
colno = n - findlast(x -> x === '\n', s) + 1
end
offset += n
continue
end
end
end
final = :($throw((SubString($argsym, offset), "Token NotFound")))
Expr(:block, gen_many_lexers..., final)
end
rmlines = @λ begin
e :: Expr -> Expr(e.head, filter(x -> x !== nothing, map(rmlines, e.args))...)
:: LineNumberNode -> nothing
a -> a
end
struct LexerSpec{K}
a :: K
end
function genlex(lexer_table, reserved_words)
ex = quote
function (tokens)
lineno :: $Int64 = 1
colno :: $Int32 = 1
offset :: $Int64 = 1
ret = $Token[]
N :: $Int64 = $ncodeunits(tokens)
while offset <= N
$(_genlex(:tokens, :ret, lexer_table, reserved_words))
end
ret
end
end
# println(rmlines(ex))
ex
end
macro genlex(lexer_table)
genlex(lexer_table) |> esc
end
function mklexer(a :: LexerSpec{Char})
quote (chars, i) -> chars[i] === $(a.a) ? String([$(a.a)]) : nothing end
end
function mklexer(a :: LexerSpec{String})
let str = a.a, n = ncodeunits(str)
quote (chars, i) ->
startswith(SubString(chars, i), $str) ? $str : nothing
end
end
end
function mklexer(a :: LexerSpec{Regex})
let regex = a.a
quote
function (chars, i)
v = match($regex, SubString(chars, i))
v === nothing ? nothing : v.match
end
end
end
end
struct Quoted
left :: String
right :: String
escape :: String
end
function mklexer(a :: LexerSpec{Quoted})
let left = a.a.left,
right = a.a.right,
escape = a.a.escape
quote
function (chars, i)
off = i
n = $ncodeunits(chars)
subs = SubString(chars, off)
if $startswith(subs, $left)
off = off + $(ncodeunits(left))
else
return nothing
end
while off <= n
subs = SubString(chars, off)
if $startswith(subs, $right)
off = off + $(ncodeunits(right))
# so tricky here for the impl of Julia string.
return chars[i:prevind(chars, off)]
end
if $startswith(subs, $escape)
off = off + $(ncodeunits(escape))
else
off = nextind(chars, off)
end
end
nothing
end
end
end
end | RBNF | https://github.com/thautwarm/RBNF.jl.git |
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
]
| 0.2.4 | 12c19821099177fad12336af5e3d0ca8f41eb3d3 | code | 5655 | using MLStyle
struct TokenView
current :: Int
length :: Int
source :: Vector{Token}
end
TokenView(src :: Vector{Token}) = TokenView(1, length(src), src)
struct CtxTokens{State}
tokens :: TokenView
maxfetched :: Int
state :: State
end
CtxTokens{A}(tokens :: TokenView) where A = CtxTokens(tokens, 1, crate(A))
function inherit_effect(ctx0 :: CtxTokens{A}, ctx1 :: CtxTokens{B}) where {A, B}
CtxTokens(ctx0.tokens, max(ctx1.maxfetched, ctx0.maxfetched), ctx0.state)
end
orparser(pa, pb) = function (ctx_tokens)
@match pa(ctx_tokens) begin
(nothing, _) => pb(ctx_tokens)
_ && a => a
end
end
tupleparser(pa, pb) = function (ctx_tokens)
@match pa(ctx_tokens) begin
(nothing, _) && a => a
(a, remained) =>
@match pb(remained) begin
(nothing, _) && a => a
(b, remained) => ((a, b), remained)
end
end
end
manyparser(p) = function (ctx_tokens)
res = []
remained = ctx_tokens
while true
(elt, remained) = p(remained)
if elt === nothing
break
end
push!(res, elt)
end
(res, remained)
end
hlistparser(ps) = function (ctx_tokens)
hlist = Vector{Union{T, Nothing} where T}(nothing, length(ps))
done = false
remained = ctx_tokens
for (i, p) in enumerate(ps)
@match p(remained) begin
(nothing, a) =>
begin
hlist = nothing
remained = a
done = true
end
(elt, a) =>
begin
hlist[i] = elt
remained = a
end
end
if done
break
end
end
(hlist, remained)
end
# what is a htuple? ... In fact a tuple with multielements is called a hlist,
# but in dynamic lang things get confusing..
htupleparser(ps) = function (ctx_tokens)
hlist = Vector{Union{T, Nothing} where T}(nothing, length(ps))
done = false
remained = ctx_tokens
for (i, p) in enumerate(ps)
@match p(remained) begin
(nothing, a) =>
begin
hlist = nothing
remained = a
done = true
end
(elt, a) =>
begin
hlist[i] = elt
remained = a
end
end
if done
break
end
end
(hlist !== nothing ? Tuple(hlist) : nothing, remained)
end
trans(f, p) = function (ctx_tokens)
@match p(ctx_tokens) begin
(nothing, _) && a => a
(arg, remained) => (f(arg), remained)
end
end
optparser(p) = function (ctx_tokens)
@match p(ctx_tokens) begin
(nothing, _) => (Some(nothing), ctx_tokens)
(a, remained) => (Some(a), remained)
end
end
"""
State.put
"""
updateparser(p, f) = function (ctx_tokens)
@match p(ctx_tokens) begin
(nothing, _) && a => a
(a, remained) =>
let state = f(remained.state, a)
(a, update_state(remained, state))
end
end
end
"""
State.get
"""
getparser(p, f) = function (ctx_tokens)
@match p(ctx_tokens) begin
(nothing, _) && a => a
(_, remained) => (f(remained.state), remained)
end
end
tokenparser(f) = function (ctx_tokens)
let tokens = ctx_tokens.tokens
if tokens.current <= tokens.length
token = tokens.source[tokens.current]
if f(token)
new_tokens = TokenView(tokens.current + 1, tokens.length, tokens.source)
max_fetched = max(new_tokens.current, ctx_tokens.maxfetched)
new_ctx = CtxTokens(new_tokens, max_fetched, ctx_tokens.state)
return (token, new_ctx)
end
end
(nothing, ctx_tokens)
end
end
function direct_lr(init, trailer, reducer)
function (ctx_tokens)
res = nothing
remained = ctx_tokens
res, remained = init(remained)
if res === nothing
return (nothing, remained)
end
while true
miscellaneous, remained = trailer(remained)
if miscellaneous === nothing
break
end
res = reducer(res, miscellaneous)
end
(res, remained)
end
end
function update_state(ctx:: CtxTokens{A}, state::B) where {A, B}
CtxTokens(ctx.tokens, ctx.maxfetched, state)
end
function crate
end
function crate(::Type{Vector{T}}) where T
T[]
end
function crate(::Type{Vector{T} where T})
[]
end
function crate(::Type{Nothing})
nothing
end
function crate(::Type{Union{T, Nothing}}) where T
nothing
end
function crate(::Type{Bool})
false
end
function crate(::Type{T}) where T <: Number
zero(T)
end
function crate(::Type{String})
""
end
function crate(::Type{Any})
nothing
end
function crate(::Type{LinkedList})
nil(Any)
end
function crate(::Type{LinkedList{T}}) where T
nil(T)
end
# number = mklexer(LexerSpec(r"\G\d+"))
# dio = mklexer(LexerSpec("dio"))
# a = mklexer(LexerSpec('a'))
# tables = [:number => number, :dio => dio, :a => a]
# lexer = @genlex tables
# preda(::Token{:a}) = true
# preda(_) = false
# prednum(::Token{:number}) = true
# prednum(_) = false
# preddio(::Token{:dio}) = true
# preddio(_) = false
# p = hlistparser([tokenparser(preddio), tokenparser(prednum), tokenparser(preda)])
# source = lexer("dio111a")
# println(source)
# tokens = TokenView(source)
# ctx = CtxTokens{Nothing}(tokens)
# println(p(ctx))
| RBNF | https://github.com/thautwarm/RBNF.jl.git |
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
]
| 0.2.4 | 12c19821099177fad12336af5e3d0ca8f41eb3d3 | code | 13512 | AST = Any
function runlexer
end
function runparser
end
struct PContext
reserved_words :: Set{String}
lexer_table :: Vector{Tuple{Symbol, Expr}}
ignores :: Vector{AST}
tokens :: Vector{Tuple{Symbol, AST}}
grammars :: Vector{Tuple{Symbol, Any, AST, Bool}}
end
struct AliasContext
end
typename(lang, name::Symbol) = Symbol("Struct_", name)
typename(name::Symbol, lang) = typename(lang, name)
const r_str_v = Symbol("@r_str")
function collect_lexer!(lexers, name, node)
@switch node begin
@case :(@quote $_ ($(left::String), $(escape::String), $(right::String)))
push!(lexers, (name, LexerSpec(Quoted(left, right, escape))))
return
@case Expr(:macrocall, &r_str_v, ::LineNumberNode, s)
push!(lexers, (name, LexerSpec(Regex(s))))
return
@case c::Union{Char, String, Regex}
push!(lexers, (name, LexerSpec(c)))
return
@case :($subject.$(::Symbol))
return collect_lexer!(lexers, name, subject)
@case Expr(head, tail...)
return foreach(x -> collect_lexer!(lexers, name, x), tail)
@case QuoteNode(c::Symbol)
push!(lexers, (:reserved, LexerSpec(String(c))))
return
@case _
return
end
nothing
end
@active IsMacro{s}(x) begin
@match x begin
Expr(:macrocall, &(Symbol("@", s)), ::LineNumberNode) => true
_ => false
end
end
@active MacroSplit{s}(x) begin
@match x begin
Expr(:macrocall, &(Symbol("@", s)), ::LineNumberNode, arg) => Some(arg)
_ => nothing
end
end
function collect_context(node)
stmts = @match node begin
quote
$(stmts...)
end => stmts
end
reserved_words :: Set{String} = Set(String[])
ignores :: Vector{AST} = []
tokens :: Vector{Tuple{Symbol, AST}} = []
grammars :: Vector{Tuple{Symbol, Any, AST, Bool}} = []
collector = nothing
unnamed_lexers = Vector{Tuple{Symbol, LexerSpec{T}} where T}()
for stmt in stmts
@match stmt begin
::LineNumberNode => ()
IsMacro{:token} =>
begin
collector = @λ begin
:($name := $node) -> push!(tokens, (name, node))
a -> throw(a)
end
end
IsMacro{:grammar} =>
begin
collector = x -> @match x begin
:($name = $node) =>
begin
collect_lexer!(unnamed_lexers, :unnamed, node)
named = (name=name, typ=nothing, def=node, is_grammar_node=true)
push!(grammars, Tuple(named))
end
:($name :: $t := $node) ||
:($name := $node) && Do(t=nothing) =>
begin
collect_lexer!(unnamed_lexers, :unnamed, node)
named = (name=name, typ=t, def=node, is_grammar_node=false)
push!(grammars, Tuple(named))
end
a => throw(a)
end
end
:(ignore{$(ignores_...)}) =>
begin
append!(ignores, ignores_)
end
:(reserved = [$(reserved_words_to_append...)]) =>
begin
union!(reserved_words, map(string, reserved_words_to_append))
end
::String => nothing # document?
a => collector(a)
end
end
lexers = OrderedSet{Tuple{Symbol, LexerSpec{T}} where T}()
for (k, v) in tokens
collect_lexer!(lexers, k, v)
end
union!(reserved_words, Set([v.a for (k, v) in unnamed_lexers if k === :reserved]))
union!(lexers, unnamed_lexers)
lexer_table :: Vector{Tuple{Symbol, Expr}} = [(k, mklexer(v)) for (k, v) in lexers]
PContext(reserved_words, lexer_table, ignores, tokens, grammars)
end
get_lexer_type(::LexerSpec{T}) where T = T
function sort_lexer_spec(lexer_table)
new_lexer_table = []
segs = []
seg = []
t = Nothing
for (k, v) in lexer_table
now = get_lexer_type(v)
if t == now
push!(seg, (k, v))
else
push!(segs, (t, seg))
seg = [(k, v)]
t = now
end
end
if !isempty(seg)
push!(segs, (t, seg))
end
for (t, seg) in segs
if t === String
sort!(seg, by=x->x[2].a, rev=true)
end
append!(new_lexer_table, seg)
end
new_lexer_table
end
function parser_gen(pc :: PContext, lang, mod::Module)
decl_seqs = []
for each in [:reserved, map(x -> x[1], pc.tokens)...]
push!(decl_seqs, quote
$each = let
f(::$Token{$(QuoteNode(each))}) = true
f(_) = false
$tokenparser(f)
end
end)
end
for (each, _, _, _) in pc.grammars
push!(decl_seqs, quote
function $each
end
end)
end
struct_defs = []
parser_defs = []
for (k, t, v, is_grammar_node) in pc.grammars
(struct_def, parser_def) = grammar_gen(k, t, v, is_grammar_node, mod, lang)
push!(struct_defs, struct_def)
push!(parser_defs, parser_def)
end
append!(decl_seqs, struct_defs)
append!(decl_seqs, parser_defs)
# make lexer
lexer_table = pc.lexer_table
reserved_words = pc.reserved_words
runlexer_no_ignored_sym = gensym("lexer")
push!(decl_seqs, :($runlexer_no_ignored_sym = $(genlex(lexer_table, reserved_words))))
names = :($Set([$(map(QuoteNode, pc.ignores)...)]))
push!(decl_seqs, :(
$RBNF.runlexer(::$Type{$lang}, str) =
$filter(
function (:: $Token{k}, ) where k
!(k in $names)
end,
$runlexer_no_ignored_sym(str))
)
)
for (each, struct_name, _, is_grammar_node) in pc.grammars
if struct_name === nothing
struct_name = typename(lang, each)
end
push!(decl_seqs, quote
$RBNF.runparser(::$typeof($each), tokens :: $Vector{$Token}) =
let ctx = $CtxTokens{$struct_name}($TokenView(tokens))
$each(ctx)
end
end)
end
Expr(:block, decl_seqs...)
end
function analyse_closure!(vars, node)
@match node begin
:($a :: $t = $n) || :($a :: $t << $n) =>
begin
vars[a] = t
analyse_closure!(vars, n)
end
:($a = $n) || :($a << $n) =>
begin
get!(vars, a) do
Any
end
end
IsMacro{:direct_recur} => nothing
Expr(head, args...) =>
for each in args
analyse_closure!(vars, each)
end
_ => nothing
end
end
"""
`fill_subject(node, subject_name)`,
converts `_.field` to `subject_name.field`.
"""
function fill_subject(node, subject_name)
let rec(node) =
@match node begin
:(_.$field) => :($subject_name.$field)
Expr(head, args...) => Expr(head, map(rec, args)...)
a => a
end
rec(node)
end
end
function grammar_gen(name::Symbol, struct_name, def_body, is_grammar_node, mod, lang)
vars = OrderedDict{Symbol, Any}()
analyse_closure!(vars, def_body)
struct_def = if struct_name === nothing
struct_name = typename(lang, name)
quote
struct $struct_name
$([Expr(:(::), k, v) for (k, v) in vars]...)
end
$RBNF.crate(::Type{$struct_name}) = $struct_name($([:($crate($v)) for v in values(vars)]...))
end
else
rt_t = mod.eval(struct_name)
ms = methods(RBNF.crate, (Type{rt_t}, ))
if isempty(ms)
rt_t isa UnionAll &&
error("cannot create automatic RBNF.crate for type $struct_name")
field_ts = rt_t.types
quote
$RBNF.crate(::Type{$rt_t}) = $struct_name($([:($crate($v)) for v in field_ts]...))
end
else
nothing
end
end
parser_skeleton_name = gensym()
return_expr = is_grammar_node ? :result : :(returned_ctx.state)
parser_def = quote
$parser_skeleton_name = $(make(def_body, struct_name, mod))
function $name(ctx_in)
cur_state = $crate($struct_name)
old_state = ctx_in.state
inside_ctx = $update_state(ctx_in, cur_state)
(result, returned_ctx) = $parser_skeleton_name(inside_ctx)
resume_ctx = $update_state(returned_ctx, old_state)
(result === nothing ? nothing : $return_expr, resume_ctx)
end
end
(struct_def, parser_def)
end
function make(node, top, mod::Module)
makerec(node) = make(node, top, mod)
@match node begin
MacroSplit{:r_str}(s) =>
let r = Regex(s)
:($tokenparser(x -> $match($r, x.str) !== nothing))
end
(QuoteNode(sym::Symbol)) && Do(s = String(sym)) ||
(c ::Char) && let s = String([c]) end ||
s::String => :($tokenparser(x -> x.str == $s))
:(!$(s :: Char)) && let s=String([s]) end ||
:(!$(QuoteNode(sym::Symbol))) && Do(s=String(sym)) ||
:(!$(s::String)) => :($tokenparser(x -> x.str != $s))
:_ => :($tokenparser(x -> true))
:[$(elts...)] =>
let elt_ps = map(makerec, elts)
:($hlistparser([$(elt_ps...)]))
end
:($(elts...), ) =>
let elt_ps = map(makerec, elts)
:($htupleparser([$(elt_ps...)]))
end
:($a | $b) =>
let pa = makerec(a), pb = makerec(b)
:($orparser($pa, $pb))
end
MacroSplit{:or}(quote $(nodes...) end) =>
foldl(map(makerec, filter(x -> !(x isa LineNumberNode), nodes))) do prev, each
:($orparser($prev, $each))
end
:($a{*}) =>
let pa = makerec(a)
:($manyparser($pa))
end
:($a => $exp) =>
let pa = makerec(a), argname = Symbol(".", top), fn_name = Symbol("fn", ".", top)
quote
let $fn_name($argname, ) = $(fill_subject(exp, argname))
$getparser($pa, $fn_name)
end
end
end
:($a % $f) =>
let pa = makerec(a)
:($trans($f, $pa))
end
:($a.?) =>
let pa = makerec(a)
:($optparser($pa))
end
:($var :: $_ = $a) || :($var = $a) =>
let pa = makerec(a)
quote
$updateparser($pa,
let top_struct = $top, fields = $fieldnames(top_struct)
(old_ctx, new_var) -> $runlens(old_ctx, new_var, $Lens{top_struct, fields, $(QuoteNode(var))})
end)
end
end
:($var :: $_ << $a) || :($var << $a) =>
let pa = makerec(a)
quote
$updateparser($pa,
let top_struct = $top, fields = $fieldnames(top_struct)
(old_ctx, new_var) -> $runlens(old_ctx, $cons(new_var, old_ctx.$var), $Lens{top_struct, fields, $(QuoteNode(var))})
end)
end
end
a :: Symbol => a
MacroSplit{:direct_recur}(quote $(args...) end) =>
begin
init = nothing
prefix = nothing
for each in args
@match each begin
:(init = $init_) => (init = init_)
:(prefix = $prefix_) => (prefix = prefix_)
_ => ()
end
end
reducer, trailer = @match prefix begin
:[recur..., $(trailer...)] => (:((prev, now) -> [prev..., now...]), trailer)
:[recur, $(trailer...)] => (:((prev, now) -> [prev, now...]), trailer)
:(recur, $(trailer...), ) => (:((prev, now) -> (prev, now...)), trailer)
:(recur..., $(trailer...), ) => (:((prev, now) -> (prev..., now...)), trailer)
_ => throw("invalid syntax for direct_recur")
end
if isempty(trailer)
throw("malformed left recursion found: `a := a`")
end
let initp = makerec(init), trailerp = makerec(:[$(trailer...)])
:($direct_lr($initp, $trailerp, $reducer))
end
end
:($f($(args...))) => makerec(getfield(mod, f)(args...))
z => throw(z)
end
end
rmlines = @λ begin
e :: Expr -> Expr(e.head, filter(x -> x !== nothing, map(rmlines, e.args))...)
:: LineNumberNode -> nothing
a -> a
end
macro parser(lang, node)
ex = parser_gen(collect_context(node), __module__.eval(lang), __module__)
esc(ex)
end | RBNF | https://github.com/thautwarm/RBNF.jl.git |
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
]
| 0.2.4 | 12c19821099177fad12336af5e3d0ca8f41eb3d3 | code | 384 | module RBNF
using MLStyle
using DataStructures
using PrettyPrint
include("Token.jl")
include("Lexer.jl")
include("Lens.jl")
include("NaiveParserc.jl")
include("ParserGen.jl")
PrettyPrint.pp_impl(io, tk::Token{T}, indent::Int) where T = begin
s = "Token{$T}(str=$(tk.str), lineno=$(tk.lineno), colno=$(tk.lineno))"
print(io, s)
return length(s) + indent
end
end # module
| RBNF | https://github.com/thautwarm/RBNF.jl.git |
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
]
| 0.2.4 | 12c19821099177fad12336af5e3d0ca8f41eb3d3 | code | 460 | """
T is for dispatch.
"""
struct Token{T}
lineno :: Int64
colno :: Int32
offset :: Int64
str :: String
span :: Int32
end
"""
Token{T}(str::String; lineno::Int=0, colno::Int=0, offset::Int=0, span::Int=0)
Create a Token of type `T` with content of given `str::String`.
"""
Token{T}(str; lineno::Int=0, colno::Int=0, offset::Int=0, span::Int=0) where T =
Token{T}(lineno, colno, offset, String(str), span)
@as_record Token
| RBNF | https://github.com/thautwarm/RBNF.jl.git |
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
]
| 0.2.4 | 12c19821099177fad12336af5e3d0ca8f41eb3d3 | code | 3023 | """ Check https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.03429.pdf for grammar specification
"""
module QASM
using RBNF
using PrettyPrint
struct QASMLang end
second((a, b)) = b
second(vec::V) where V <: AbstractArray = vec[2]
parseReal(x::RBNF.Token) = parse(Float64, x.str)
struct MainProgram
ver :: Real
prog
end
RBNF.typename(::Type{QASMLang}, name::Symbol) = Symbol(:S_, name)
RBNF.@parser QASMLang begin
# define ignorances
ignore{space}
@grammar
# define grammars
mainprogram::MainProgram := ["OPENQASM", ver=nnreal % parseReal, ';', prog=program]
program = statement{*}
statement = (decl | gate | opaque | qop | ifstmt | barrier)
# stmts
ifstmt := ["if", '(', l=id, "==", r=nninteger, ')', body=qop]
opaque := ["opaque", id=id, ['(', [arglist1=idlist].?, ')'].? , arglist2=idlist, ';']
barrier := ["barrier", value=mixedlist]
decl := [regtype="qreg" | "creg", id=id, '[', int=nninteger, ']', ';']
# gate
gate := [decl=gatedecl, [goplist=goplist].?, '}']
gatedecl := ["gate", id=id, ['(', [arglist1=idlist].?, ')'].?, arglist2=idlist, '{']
goplist = (uop |barrier_ids){*}
barrier_ids := ["barrier", ids=idlist, ';']
# qop
qop = (uop | measure | reset)
reset := ["reset", arg=argument, ';']
measure := ["measure", arg1=argument, "->", arg2=argument, ';']
uop = (iduop | u | cx)
iduop := [op=id, ['(', [lst1=explist].?, ')'].?, lst2=mixedlist, ';']
u := ['U', '(', exprs=explist, ')', arg=argument, ';']
cx := ["CX", arg1=argument, ',', arg2=argument, ';']
idlist = @direct_recur begin
init = id
prefix = (recur, (',', id) % second)
end
mixeditem := [id=id, ['[', arg=nninteger, ']'].?]
mixedlist = @direct_recur begin
init = mixeditem
prefix = (recur, (',', mixeditem) % second)
end
argument := [id=id, ['[', (arg=nninteger), ']'].?]
explist = @direct_recur begin
init = nnexp
prefix = (recur, (',', nnexp) % second)
end
atom = (nnreal | nninteger | "pi" | id | fnexp) | (['(', nnexp, ')'] % second) | neg
fnexp := [fn=fn, '(', arg=nnexp, ')']
neg := ['-', value=nnexp]
nnexp = @direct_recur begin
init = [atom]
prefix = [recur..., binop, atom]
end
fn = ("sin" | "cos" | "tan" | "exp" | "ln" | "sqrt")
binop = ('+' | '-' | '*' | '/')
# define tokens
@token
id := r"\G[a-z]{1}[A-Za-z0-9_]*"
nnreal := r"\G([0-9]+\.[0-9]*|[0-9]*\.[0.9]+)([eE][-+]?[0-9]+)?"
nninteger := r"\G([1-9]+[0-9]*|0)"
space := r"\G\s+"
end
src1 = """
OPENQASM 2.0;
gate cu1(lambda) a,b
{
U(0,0,theta/2) a;
CX a,b;
U(0,0,-theta/2) b;
CX a,b;
U(0,0,theta/2) b;
}
qreg q[3];
qreg a[2];
creg c[3];
creg syn[2];
cu1(pi/2) q[0],q[1];
"""
ast, ctx = RBNF.runparser(mainprogram, RBNF.runlexer(QASMLang, src1))
pprint(ast)
end
| RBNF | https://github.com/thautwarm/RBNF.jl.git |
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
]
| 0.2.4 | 12c19821099177fad12336af5e3d0ca8f41eb3d3 | code | 3471 | using RBNF
using MLStyle
using PrettyPrint
using DataStructures
struct ReML
end
second((a, b)) = b
second(vec::V) where V <: AbstractArray = vec[2]
escape(a) = @match a begin
'\\' => '\\'
'"' => '"'
'a' => '\a'
'n' => '\n'
'r' => '\r'
a => throw(a)
end
join_token_as_str = xs -> join(x.value for x in xs)
maybe_to_bool(::Some{Nothing}) = false
maybe_to_bool(::Some{T}) where T = true
"""
nonempty sequence
"""
struct GoodSeq{T}
head :: T
tail :: Vector{T}
end
join_rule(sep, x) = begin
:([$x, ([$sep, $x] % second){*}] % x -> GoodSeq(x[1], x[2]))
end
RBNF.typename(::Type{ReML}, name:: Symbol) = Symbol(:R, name)
RBNF.@parser ReML begin
# define the ignores
ignore{space}
# define keywords
reserved = [true, false]
@grammar
# necessary
Str := value=str
Bind := [name=id, '=', value=Exp]
Let := [hd=:let, rec=:rec.? % maybe_to_bool,
binds=join_rule(',', Bind),
:in, body=Exp]
Fun := [hd=:fn, args=id{*}, "->", body=Exp]
Import := [hd=:import, paths=join_rule(',', id)]
Match := [hd=:match, sc=Exp, :with,
cases=(['|', Comp, "->", Exp] % ((_, case, _, body), ) -> (case, body)){*},
:end.?] # end for nested match
If := [hd=:if, cond=Exp, :then,
br1=Exp,
:else,
br2=Exp]
Num := [[neg="-"].? % maybe_to_bool, (int=integer) | (float=float)]
Boolean := value=("true" | "false")
NestedExpr = ['(', value=Exp, ')'] => _.value
Var := value=id
Block := [hd=:begin, stmts=Stmt{*}, :end]
Atom = NestedExpr | Num | Str | Boolean | Var
Annotate := [value=Atom, [':', Exp].?]
Call := [fn=Annotate, args=Annotate{*}]
Comp := [[forall=Forall, '.'].?, value=(Call | Let | Fun | Match | If | Block)]
Op := ['`', name=_, '`'] | [is_typeop :: Bool = "->" => true]
Exp := [hd=Comp, tl=[Op, Comp]{*}]
Decl := [hd=:val, name=id, ':', typ=Exp]
Define := [hd=:def, name=id, '=', value=Exp]
Stmt = Data | Import | Class | Instance | Decl | Define | Exp
Module := [hd=:module, name=id, :where, stmts=Stmt{*}, :end.?]
# forall
Constaints:= [hd=:that, elts=join_rule(',', Call)]
Forall := [:forall, fresh=id{*}, (constraints=Constaints).?]
# advanced
Data := [hd=:data, name=id, ":", kind=Exp, :where, stmts=Stmt{*}, :end]
Class := [hd=:class, name=id, ids=id{*}, (constrains=Constaints).?, :where,
interfaces=Decl{*},
:end]
Instance := [hd=:instance, name=id, vars=Exp{*}, :where, impls=Stmt{*}, :end]
@token
id := r"\G[A-Za-z_]{1}[A-Za-z0-9_]*"
str := @quote ("\"" ,"\\\"", "\"")
float := r"\G([0-9]+\.[0-9]*|[0-9]*\.[0.9]+)([eE][-+]?[0-9]+)?"
integer := r"\G([1-9]+[0-9]*|0)"
space := r"\G\s+"
end
src1 = """
module Poly where
def a = "12\\"3"
class Monad m that Functor m where
val bind : forall a b . m a -> (a -> b) -> m b
end
val a : Int
def a = "12345"
val f : Int -> Int
def f = fn a -> a `add` 1
val g : Int
def g = match 1 with
| 1 -> 2
| _ -> 0
end
def z = fn x -> if x `equals` 1 then 1 else 2
"""
tokens = RBNF.runlexer(ReML, src1)
ast, ctx = RBNF.runparser(Module, tokens)
pprint(ast) | RBNF | https://github.com/thautwarm/RBNF.jl.git |
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
]
| 0.2.4 | 12c19821099177fad12336af5e3d0ca8f41eb3d3 | code | 1243 | using RBNF
using MLStyle
# rmlines = @λ begin
# e :: Expr -> Expr(e.head, filter(x -> x !== nothing, map(rmlines, e.args))...)
# :: LineNumberNode -> nothing
# a -> a
# end
# node = quote
# RBNF.@parser TestLang begin
# @token
# a := r"\d"
# @grammar
# b := [(k = k.?), (seqa :: Vector = Many(a => parse_int))]
# end
# end
# @info :show rmlines(macroexpand(Main, node))
# struct TestLang end
# parse_int(x :: RBNF.Token) = parse(Int, x.str)
# RBNF.@parser TestLang begin
# @token
# a := r"\G\d"
# k := "kkk"
# @grammar
# b := [(k = k.?), (seqa :: Vector = Many(a => parse_int))]
# end
# res1, _ = RBNF.runparser(b, RBNF.runlexer(TestLang, "123"))
# println(res1)
# res2, _ = RBNF.runparser(b, RBNF.runlexer(TestLang, "kkk123"))
# println(res2)
# struct TestLang2 end
# RBNF.@parser TestLang2 begin
# @token
# num := r"\G\d+"
# space := r"\G\s+"
# @grammar
# manynumbers := @direct_recur begin
# init = num
# prefix = [recur, space, num]
# end
# end
# res3, _ = RBNF.runparser(manynumbers, RBNF.runlexer(TestLang2, "52 123 123 14312 213"))
# println(res3)
include("qasm.jl")
include("reml.jl") | RBNF | https://github.com/thautwarm/RBNF.jl.git |
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
]
| 0.2.4 | 12c19821099177fad12336af5e3d0ca8f41eb3d3 | docs | 6923 | # Restructured BNF
The Restructured BNF(RBNF) aims at the generating parsers without requiring redundant coding from programmers.
RBNF is designed for
- Maintainability: unlike Regex, RBNF's good readability makes more sense in the syntax level.
- Conciseness: avoid self-repeating you did with other parser generators.
- Efficiency: RBNF just specifies the semantics, we could use customizable back ends/parsing algorithms here.
- Extensibility: mix Julia meta-programming with the notations to define parsers/lexers.
Taking advantage of a BNF source block, **lexers** and **parsers** are generated as well as
some data type definitions representing tokenizers and ASTs.
Some modern facilities of parsing are introduced.
The notations of dedicated escaping lexers makes it super convenient to implement lexers for nested comments, string literals and so on.
```julia
str = @quote ("\"" ,"\\\"", "\"")
```
The notations of grammar macros makes it super easy to achieve code reuse for RBNF.
```julia
join(separator, rule) = :[$rule, ($separator, $rule){*}]
# `join(',', 'a')` generates a parser to parse something like "a" or "a,a,a"
```
# About Implementation and Efficiency
The rudimentary implementation(back end) is the Parser Combinator,
thus the direct left recursions are not supported implicitly,
plus the indirect left recursions are not supported.
Note that currently the lack of further analyses and optimizations may lead
to some problems in expressiveness and performance, however it's not that severe
in many use cases not concerned to real time applications.
We're to figure out a solid way to compile the parser definitions to bottom-up parsers
(thus left recursions wouldn't be a problem) with the capability of processing context sensitive cases.
You can check following projects to see
what I've been achieved and, what I'm now researching.
- https://github.com/thautwarm/RBNF
- https://github.com/thautwarm/rbnfrbnf
- https://github.com/thautwarm/RBNF.hs
# Basic Usage
P.S: rules can be mutually referenced by each other.
## Structures of Defining A Language
Firstly we need an immutable object to denote your language.
```julia
using RBNF
struct YourLang end
RBNF.@parser YourLang begin
ignore{#= tokenizer names to be ignored =#}
# e.g., `ignore{mystring, mychar}`
reserved = [#= reserved identifiers =#]
# strings, symbols and even bool literals are allowed here,
# and their strings will be regarded as reserved keywords.
# e.g., reserved = [true, "if", :else]
@grammar
# define grammar rules
# following ':=' statement defines a grammar node.
# note, a structure named "Struct_node" will be defined as well.
node := #= a combination of rules =#
# following '=' statement defines an alias for a combination of rules.
alias = #= a combination of rules =#
@token
# define tokenizers as well as their corresponding lexers
mystring := "abc"
mychar := 'k'
myregex := r"\G\s+"
myquote := @quote ("begin_string" ,"\\end_string", "end_string")
end
tokens = RBNF.runlexer(YourLang, source_code)
ast, ctx = RBNF.runparser(parser_defined_in_grammar_section, tokens)
```
## Tokenizer
Unlike many other parser generators(yes, I'm talking to you, **** of Rust),
RBNF provides rich information with tokenizers.
```julia
struct Token{T}
lineno :: Int64
colno :: Int32
offset :: Int64
str :: String
span :: Int32
end
```
The type parameter `T` is used to denote which class the tokenizer belongs to.
For instance, if some tokenizer denotes the reserved keywords, their type will
be `Token{:reserved}`.
If a tokenizer is handled with such a lexer:
```julia
@token
identifier = r"\G[A-Za-z_]{1}[A-Za-z0-9_]*"
```
It'll then be of type `Token{:identifier}`.
## Sequence
```julia
@grammar
c = ['a', 'b']
```
`c` parses `[Token(str="a", ...), Token(str="b", ...)]`,
and outputs a list `[Token(str="a", ...), Token(str="b", ...)]`.
## Fields
```julia
@grammar
c := [a='a', b='b']
```
`c` parses `[Token(str="a", ...), Token(str="b", ...)]`,
and outputs `Struct_c(a=Token(str="a", ...), b=Token(str="b", ...))`.
P.S: rule `c` will produce instances of automatically generated data types `Struct_c`. You can specify the names of generated structs by
```julia
RBNF.typename(your_language, name::Symbol) = ...
# transform name.
# e.g., "c" -> "Struct_c":
#
RBNF.typename(your_language, name::Symbol) = Symbol(:Struct_, name)
```
## Custom Data Types
Firstly you just define your own data type in the global scope of current module.
```julia
struct C
a :: Token
b :: Token
end
...
@grammar
c :: C := [a='a', b='b']
...
```
`c` parses `[Token(str="a", ...), Token(str="b", ...)]`,
and outputs `C(a=Token(str="a", ...), b=Token(str="b", ...))`.
## Tuple
```julia
@grammar
c = ('a', 'b')
```
`c` parses `[Token(str="a", ...), Token(str="b", ...)]`,
and outputs a tuple `(Token(str="a", ...), Token(str="b", ...))`.
## Not
Currently **Not** parser is only allowed on literals.
```julia
@grammar
A = !'a'
```
`A` can parse `[Token(str=not_a)]` for all `not_a != "a"`.
## Optional
```julia
...
@grammar
a = "a"
b = "b"
c = [a.?, b]
...
```
`c` can parse tokenizers `[Token(str="a", ...), Token(str="b", ...)]` or
`[Token(str="a", ...)]`,
and outputs `[Token(str="a", ...), Token(str="b", ...)]` or
`[Some(nothing), Token(str="b", ...)]`, respectively.
## Repeat
```julia
@grammar
a = b{*}
```
`a` can parse one or more `b`.
## Or(Alternative)
```julia
@grammar
a = b | c
```
`a` can parse `b` or `c`.
## Keyword
```julia
@grammar
If := [hd=:if, cond=Exp, :then,
br1=Exp,
:else,
br2=Exp]
```
Note that `:if`, `:then` and `:else` should parse
`Token{:reserved}(str=...)`. **Their type should be
`Token{:reserved}`!**
However you always don't have to aware of this.
Further, you just should aware that any other lexer(hereafter `L`)
matching `"if", "then", "else"` won't produce a tokenizer typed `Token{L}`,
but that typed `Token{:reserved}`.
## Rewrite
```julia
@grammar
ab_no_a = ['a', 'b'] % (x -> x[1])
```
`ab_no_a` produces `Token(str="b")` if it gets parsed successfully.
## Parameterised Polymorphisms
Firstly define such a function in the global scope:
```julia
join(separator, rule) = :[$rule, ($separator, $rule){*}]
```
Then, inside `RBNF.@parser Lang begin ... end`, we write down
```julia
@grammar
list = ['[', [join(',', expression)].?, ']']
```
`list` can parse a list of expressions separated by ',',
but you should define the `expression` yourself.
## @direct_recur
Provided for supporting direct left recursions.
```julia
a = @direct_recur begin
init = ['a']
prefix = [recur..., 'a']
end
# parse aaa to [Token_a, Token_a, Token_a]
a = @direct_recur begin
init = ['a']
prefix = [recur, 'a']
end
# parse aaa to [[[Token_a], Token_a], Token_a]
``` | RBNF | https://github.com/thautwarm/RBNF.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 309 | using Documenter, Umbrella
makedocs(
sitename = "Umbrella.jl",
format = Documenter.HTML(),
modules = [Umbrella],
pages = [
"Overview" => "index.md",
"API Reference" => "reference.md",
"Examples" => "examples.md",
]
)
deploydocs(
repo = "github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git"
) | Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 2488 | using Genie, Genie.Router, Genie.Renderer
using Umbrella, Umbrella.Google
const options = Configuration.Options(;
client_id="",
client_secret="",
redirect_uri="http://localhost:3000/oauth2/google/callback",
success_redirect="/yes",
failure_redirect="/no",
scopes=["profile", "openid", "email"],
providerOptions=GoogleOptions(access_type="online")
)
const githubOptions = Configuration.Options(;
client_id="",
client_secret="",
redirect_uri="http://localhost:3000/oauth2/github/callback",
success_redirect="/yes",
failure_redirect="/no",
scopes=["user", "email", "profile"]
)
const facebookOptions = Configuration.Options(;
client_id="",
client_secret="",
redirect_uri="http://localhost:3000/oauth2/facebook/callback",
success_redirect="/yes",
failure_redirect="/no",
scopes=["user", "email", "profile"]
)
google_oauth2 = init(:google, options, Genie.Renderer.redirect)
github_oauth2 = init(:github, githubOptions, Genie.Renderer.redirect)
facebook_oauth2 = init(:facebook, facebookOptions, Genie.Renderer.redirect)
route("/") do
return """
<a href="/oauth2/google">Authenticate with Google</a>
<br/>
<a href="/oauth2/github">Authenticate with GitHub</a>
<br/>
<a href="/oauth2/facebook">Authenticate with Facebook</a>
"""
end
route("/oauth2/google") do
google_oauth2.redirect()
end
route("/oauth2/github") do
github_oauth2.redirect()
end
route("/oauth2/facebook") do
facebook_oauth2.redirect()
end
route("/oauth2/google/callback") do
code = Genie.params(:code, nothing)
function verify(tokens::Google.Tokens, user::Google.User)
println(tokens.access_token)
println(user.email)
end
google_oauth2.token_exchange(code, verify)
end
route("/oauth2/github/callback") do
code = Genie.params(:code, nothing)
function verify(tokens::GitHub.Tokens, user::GitHub.User)
println(tokens.access_token)
println(user.name)
println(user)
end
github_oauth2.token_exchange(code, verify)
end
route("/oauth2/facebook/callback") do
code = Genie.params(:code, nothing)
function verify(tokens::Facebook.Tokens, user::Facebook.User)
println(tokens.access_token)
println(user.first_name)
println(user)
end
facebook_oauth2.token_exchange(code, verify)
end
route("/yes") do
return "234"
end
route("/no") do
return "no"
end
up(3000, async=false) | Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 1272 | using Mux, Umbrella, HTTP
const oauth_path = "/oauth2/google"
const oauth_callback = "/oauth2/google/callback"
const options = Configuration.Options(;
client_id="", # client id from Google API Console
client_secret="", # secret from Google API Console
redirect_uri="http://127.0.0.1:3000$(oauth_callback)",
success_redirect="/protected",
failure_redirect="/no",
scopes=["profile", "openid", "email"]
)
function mux_redirect(url::String, status::Int = 302)
headers = Dict{String, String}(
"Location" => url
)
Dict(
:status => status,
:headers => headers,
:body => ""
)
end
const oauth2 = Umbrella.init(:google, options, mux_redirect)
function callback(req)
params = HTTP.queryparams(req[:uri])
code = params["code"]
oauth2.token_exchange(code,
function (tokens::Google.Tokens, user::Google.User)
println(tokens.access_token)
println(tokens.refresh_token)
println(user.email)
end
)
end
@app http = (
Mux.defaults,
page("/", respond("<a href='$(oauth_path)'>Authenticate with Google</a>")),
page(oauth_path, req -> oauth2.redirect()),
page(oauth_callback, callback),
page("/protected", respond("Congrets, You signed in Successfully!")),
Mux.notfound()
)
serve(http, 3000) | Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 1158 | using Oxygen
using Umbrella
using HTTP
const oauth_path = "/oauth2/google"
const oauth_callback = "/oauth2/google/callback"
const options = Configuration.Options(;
client_id="", # client id from Google API Console
client_secret="", # secret from Google API Console
redirect_uri="http://127.0.0.1:8080$(oauth_callback)",
success_redirect="/protected",
failure_redirect="/no",
scopes=["profile", "openid", "email"]
)
const google_oauth2 = Umbrella.init(:google, options)
@get "/" function ()
return "<a href='$(oauth_path)'>Authenticate with Google</a>"
end
@get oauth_path function ()
# this handles the Google oauth2 redirect in the background
google_oauth2.redirect()
end
@get oauth_callback function (req)
query_params = queryparams(req)
code = query_params["code"]
# handle tokens and user details
google_oauth2.token_exchange(code,
function (tokens::Google.Tokens, user::Google.User)
println(tokens.access_token)
println(tokens.refresh_token)
println(user.email)
end
)
end
@get "/protected" function()
"Congrets, You signed in Successfully!"
end
# start the web server
serve() | Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 1684 | import ArgParse: ArgParseSettings, parse_args, @add_arg_table!
import Mustache
include("templates.jl")
function parse_commandline()
s = ArgParseSettings(description = "Generate code stub for an OAuth2 provider.")
@add_arg_table! s begin
"--provider", "-p" # another option, with short form
help = "the name of the new provider"
arg_type = String
"action" # a positional argument
help = "'init' to initialize the configuration file, 'run' to generate the new provider"
required = true
end
return parse_args(s)
end
parsed_args = parse_commandline()
action = parsed_args["action"]
const ROOT = dirname(@__DIR__)
const HELPER_DIR = @__DIR__
const PROVIDER_DIR = joinpath(ROOT, "src", "providers")
const CONFIG_FILE = "config_generated.jl"
const CONFIG_FILE_DIR = joinpath(HELPER_DIR, CONFIG_FILE)
if action == "init"
provider = uppercasefirst(parsed_args["provider"])
config_f = Mustache.render(
config_tpl,
Dict("provider" => provider, "provider_symbol" => lowercase(provider))
)
open(CONFIG_FILE_DIR, "w") do f
write(f, config_f)
end
elseif action == "run"
if !isfile(CONFIG_FILE_DIR)
@error "$(CONFIG_FILE) is not found, run command with 'init' first"
exit(1)
end
include(CONFIG_FILE_DIR)
file = "$(config["provider"]).jl"
path = joinpath(PROVIDER_DIR, file)
if isfile(path)
@warn "$file exists, provider is not generated"
exit(1)
end
open(path, "w") do f
write(f, Mustache.render(provider_tpl, config))
end
rm(CONFIG_FILE_DIR, force=true)
else
"$(action) is not an option, use 'init' or 'run', see more using --help" |> println
end
| Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 2875 | import Mustache
provider_tpl = Mustache.mt"""
module {{provider}}
using StructTypes
using Umbrella
import HTTP, JSON3, URIs
const AUTH_URL = "{{{provider_auth_url}}}"
const TOKEN_URL = "{{{provider_token_url}}}"
const USER_URL = "{{{provider_user_url}}}"
export {{provider}}Options
Base.@kwdef struct {{provider}}Options <: Umbrella.Configuration.ProviderOptions
{{#provider_opts_fields}}
{{name}}::{{type}}={{#default}}{{default}}{{/default}}{{^default}}""{{/default}}
{{/provider_opts_fields}}
end
Base.@kwdef mutable struct Tokens
{{#token_fields}}
{{name}}::{{type}}={{#default}}{{default}}{{/default}}{{^default}}""{{/default}}
{{/token_fields}}
end
StructTypes.StructType(::Type{Tokens}) = StructTypes.Mutable()
Base.@kwdef mutable struct User
{{#user_fields}}
{{name}}::{{type}}={{#default}}{{default}}{{/default}}{{^default}}""{{/default}}
{{/user_fields}}
end
StructTypes.StructType(::Type{User}) = StructTypes.Mutable()
function redirect_url(config::Umbrella.Configuration.Options)
if config.providerOptions === nothing
options = {{provider}}Options()
else
options = config.providerOptions
end
# TODO: implement building {{provider}} redirect url
end
function token_exchange(code::String, config::Umbrella.Configuration.Options)
try
tokens = _exchange_token(TOKEN_URL, code, config)
profile = _get_user(USER_URL, tokens.access_token)
return tokens, profile
catch e
@error "Unable to complete token exchange" exception=(e, catch_backtrace())
return nothing, nothing
end
end
function _get_user(url::String, access_token::String)
# TODO: implement {{provider}} get user
end
function _exchange_token(url::String, code::String, config::Umbrella.Configuration.Options)
# TODO: implement {{provider}} token exchange
end
Umbrella.register(:{{provider_symbol}}, Umbrella.OAuth2Actions(redirect_url, token_exchange))
end
"""
config_tpl = Mustache.mt"""
config = Dict(
"provider" => "{{provider}}",
"provider_symbol" => "{{provider_symbol}}",
"provider_auth_url" => "",
"provider_token_url" => "",
"provider_user_url" => "",
"token_fields" => [
# TODO: model the token fields required by the oauth2 provider, example below
Dict("name" => "access_token", "type" => "String", "default" => ""),
Dict("name" => "refresh_token", "type" => "String", "default" => ""),
Dict("name" => "expires_in", "type" => "Int64", "default" => 0),
],
"user_fields" => [
# TODO: model the user fields required by the oauth2 provider, example below
Dict("name" => "first_name", "type" => "String", "default" => ""),
Dict("name" => "last_name", "type" => "String", "default" => ""),
Dict("name" => "email", "type" => "String", "default" => ""),
],
)
"""
| Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 1498 | module Configuration
abstract type ProviderOptions end
"""
Options(client_id, client_secret, redirect_uri, success_redirect, failure_redirect, scopes, state, providerOptions)
Represents an Configuration Options with fields:
- `client_id::String` Client id from an OAuth 2 provider
- `client_secret::String` Secret from an OAuth 2 provider
- `redirect_uri::String` Determines where the API server redirects the user after the user completes the authorization flow
- `success_redirect::String` URL path when OAuth 2 successed
- `failure_redirect::String` URL path when OAuth 2 failed
- `scope::String` OAuth 2 scopes
- `state::String` Specifies any string value that your application uses to maintain state between your authorization request and the authorization server's response
"""
mutable struct Options
client_id::String
client_secret::String
redirect_uri::String
success_redirect::String
failure_redirect::String
scope::String
state::Union{String, Nothing}
providerOptions::Union{ProviderOptions, Nothing}
function Options(;
client_id::String="",
client_secret::String="",
redirect_uri::String="",
success_redirect::String="",
failure_redirect::String="",
scopes::Vector{String}=[],
state=nothing,
providerOptions=nothing)
return new(client_id, client_secret, redirect_uri, success_redirect, failure_redirect, join(scopes, "%20"), state, providerOptions)
end
end
end | Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 404 | module Umbrella
include("utils.jl")
include("Configuration.jl")
include("initiator.jl")
const PROVIDER_DIR = joinpath(@__DIR__, "providers")
for file in readdir(PROVIDER_DIR)
name, ext = splitext(file)
if ext == ".jl"
include(joinpath(PROVIDER_DIR, "$(name).jl"))
eval(Expr(:export, Symbol(name)))
end
end
export Configuration, OAuth2Actions, OAuth2
export init, register
end # module
| Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 2113 |
"""
OAuth2(type, redirect, token_exchange)
Represents an OAuth2 with fields:
- `type::Symbol` OAuth 2 provider
- `redirect::Function` Generates the redirect URL and redirects users to provider's OAuth 2 server to initiate the authentication and authorization process.
- `token_exchange::Function` Use `code` responded by the OAuth 2 server to exchange an access token, and get user profile using the access token.
`redirect` and `token_exchange` functions are produced by `init` function, they are configured for a specific OAuth 2 provider, example usage:
```julia
const options = Configuration.Options(
# fill in the values
)
const oauth2 = Umbrella.init(:google, options)
# perform redirect
oauth2.redirect()
# handle token exchange
oauth2.token_exchange(code, verify)
```
"""
mutable struct OAuth2
type::Symbol
redirect::Function
token_exchange::Function
end
mutable struct OAuth2Actions
redirect::Function
token_exchange::Function
end
const oauth2_typed_actions = Dict()
"""
register(type::Symbol, oauth2_actions::OAuth2Actions)
Register a newly implemented OAuth 2 provider.
"""
function register(type::Symbol, oauth2_actions::OAuth2Actions)
oauth2_typed_actions[type] = Dict(
:redirect => oauth2_actions.redirect,
:token_exchange => oauth2_actions.token_exchange
)
end
"""
init(type::Symbol, config::Configuration.Options)
Initiate an OAuth 2 instance for the given provider.
"""
function init(type::Symbol, config::Configuration.Options, redirect_hanlder::Function = redirect)
actions = oauth2_typed_actions[type]
return OAuth2(
type,
function ()
url = actions[:redirect](config)
redirect_hanlder(url)
end,
function (code::String, verify::Function)
tokens, profile = actions[:token_exchange](code, config)
if tokens === nothing || profile === nothing
return redirect_hanlder(config.failure_redirect)
end
verify(tokens, profile)
redirect_hanlder(config.success_redirect)
end
)
end
| Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 173 | import HTTP
function redirect(url::String, status::Int = 302)
headers = Dict{String, String}(
"Location" => url
)
HTTP.Response(status, [h for h in headers])
end | Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 3337 | module Facebook
using StructTypes
using Umbrella
import HTTP, JSON3, URIs
const AUTH_URL = "https://www.facebook.com/v14.0/dialog/oauth"
const TOKEN_URL = "https://graph.facebook.com/v14.0/oauth/access_token"
const USER_URL = "https://graph.facebook.com/me"
export FacebookOptions
Base.@kwdef struct FacebookOptions <: Umbrella.Configuration.ProviderOptions
response_type::String = "code" # code, token, code%20token, granted_scopes
end
Base.@kwdef mutable struct Tokens
access_token::String=""
refresh_token::String=""
token_type::String=""
expires_in::Int64=0
end
StructTypes.StructType(::Type{Tokens}) = StructTypes.Mutable()
Base.@kwdef mutable struct User
id::String=""
first_name::String=""
last_name::String=""
gender::String=""
email::String=""
picture_url::String=""
end
StructTypes.StructType(::Type{User}) = StructTypes.Mutable()
function redirect_url(config::Umbrella.Configuration.Options)
if config.providerOptions === nothing
options = FacebookOptions()
else
options = config.providerOptions
end
state = config.state
params = [
"client_id=$(config.client_id)",
"redirect_uri=$(config.redirect_uri)",
"scope=$(config.scope)",
"response_type=$(options.response_type)",
]
if state !== nothing
push!(params, "state=$(state)")
end
query = join(params, "&")
# query = "client_id=$(config.client_id)&redirect_uri=$(config.redirect_uri)&state=$(state)"
return "$(AUTH_URL)?$(query)"
end
function token_exchange(code::String, config::Umbrella.Configuration.Options)
try
tokens = _exchange_token(TOKEN_URL, code, config)
profile = _get_user(USER_URL, tokens.access_token)
return tokens, profile
catch e
@error "Unable to complete token exchange" exception=(e, catch_backtrace())
return nothing, nothing
end
end
function _get_user(url::String, access_token::String)
query = Dict(
"access_token" => access_token,
"fields" => join(["id", "first_name", "last_name", "picture", "gender", "email"], ",")
)
response = HTTP.get(url, query=query)
body = String(response.body)
user_dict = JSON3.read(body)
user = User()
haskey(user_dict, :id) && (user.id = user_dict[:id])
haskey(user_dict, :first_name) && (user.first_name = user_dict[:first_name])
haskey(user_dict, :last_name) && (user.last_name = user_dict[:last_name])
haskey(user_dict, :gender) && (user.gender = user_dict[:gender])
haskey(user_dict, :email) && (user.email = user_dict[:email])
haskey(user_dict, :picture) && haskey(user_dict[:picture], :data) &&
haskey(user_dict[:picture][:data], :url) && (user.picture_url = user_dict[:picture][:data][:url])
return user
end
function _exchange_token(url::String, code::String, config::Umbrella.Configuration.Options)
query = Dict(
"client_id" => config.client_id,
"redirect_uri" => config.redirect_uri,
"client_secret" => config.client_secret,
"code" => code
)
response = HTTP.get(url, query=query)
body = String(response.body)
tokens = JSON3.read(body, Tokens)
return tokens
end
Umbrella.register(:facebook, Umbrella.OAuth2Actions(redirect_url, token_exchange))
end
| Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 5604 | module GitHub
using StructTypes
using Umbrella
import HTTP, JSON3, URIs
const AUTH_URL = "https://github.com/login/oauth/authorize"
const TOKEN_URL = "https://github.com/login/oauth/access_token"
const USER_URL = "https://api.github.com/user"
export GitHubOptions
Base.@kwdef struct GitHubOptions <: Umbrella.Configuration.ProviderOptions
login::Union{String,Nothing} = nothing
allow_signup::Bool = true
end
mutable struct Tokens
access_token::String
scope::String
token_type::String
function Tokens(; access_token::String="", scope::String="", token_type::String="")
return new(access_token, scope, token_type)
end
end
StructTypes.StructType(::Type{Tokens}) = StructTypes.Mutable()
mutable struct User
login::String
id::Int64
node_id::String
avatar_url::String
gravatar_id::String
url::String
html_url::String
followers_url::String
following_url::String
gists_url::String
starred_url::String
subscriptions_url::String
organizations_url::String
repos_url::String
events_url::String
received_events_url::String
type::String
site_admin::Bool
name::String
company::String
blog::String
location::String
email::String
hireable::Bool
bio::String
twitter_username::String
public_repos::Int64
public_gists::Int64
followers::Int64
following::Int64
created_at::String
updated_at::String
function User(;
login::String="",
id::Int64=0,
node_id::String="",
avatar_url::String="",
gravatar_id::String="",
url::String="",
html_url::String="",
followers_url::String="",
following_url::String="",
gists_url::String="",
starred_url::String="",
subscriptions_url::String="",
organizations_url::String="",
repos_url::String="",
events_url::String="",
received_events_url::String="",
type::String="",
site_admin::Bool=false,
name::String="",
company::String="",
blog::String="",
location::String="",
email::String="",
hireable::Bool=false,
bio::String="",
twitter_username::String="",
public_repos::Int64=0,
public_gists::Int64=0,
followers::Int64=0,
following::Int64=0,
created_at::String="",
updated_at::String=""
)
return new(
login,
id,
node_id,
avatar_url,
gravatar_id,
url,
html_url,
followers_url,
following_url,
gists_url,
starred_url,
subscriptions_url,
organizations_url,
repos_url,
events_url,
received_events_url,
type,
site_admin,
name,
company,
blog,
location,
email,
hireable,
bio,
twitter_username,
public_repos,
public_gists,
followers,
following,
created_at,
updated_at
)
end
end
StructTypes.StructType(::Type{User}) = StructTypes.Mutable()
function redirect_url(config::Umbrella.Configuration.Options)
if config.providerOptions === nothing
options = GitHubOptions()
else
options = config.providerOptions
end
state = config.state
login = options.login
allow_signup = options.allow_signup
params = [
"client_id=$(config.client_id)",
"redirect_uri=$(config.redirect_uri)",
"scope=$(config.scope)",
"allow_signup=$(allow_signup)",
]
if state !== nothing
push!(params, "state=$(state)")
end
if login !== nothing
push!(params, "login=$(login)")
end
# query = "client_id=$(config.client_id)&
# redirect_uri=$(config.redirect_uri)&
# scope=$(config.scope)&
# login=$(login)&
# state=$(state)&
# allow_signup=$(allow_signup)"
query = join(params, "&")
return "$(AUTH_URL)?$(query)"
end
function token_exchange(code::String, config::Umbrella.Configuration.Options)
headers = ["Content-Type" => "application/json"]
body = Dict(
"code" => code,
"client_id" => config.client_id,
"client_secret" => config.client_secret,
"redirect_uri" => config.redirect_uri,
)
try
tokens = _token_exchange(TOKEN_URL, headers, JSON3.write(body))
profile = _get_user(USER_URL, tokens.access_token)
return tokens, profile
catch e
@error "Unable to complete token exchange" exception=(e, catch_backtrace())
return nothing, nothing
end
end
function _get_user(url::String, access_token::String)
headers = ["Authorization" => """Bearer $(access_token)"""]
response = HTTP.get(url, headers)
body = String(response.body)
return JSON3.read(remove_json_null(body), User)
end
function _token_exchange(url::String, headers::Vector{Pair{String,String}}, body::String)
response = HTTP.post(url, headers, body)
tokens = dict_to_struct(URIs.queryparams(String(response.body)), Tokens)
return tokens
end
function remove_json_null(json::String)
return replace(json, "null" => "\"\"")
end
function dict_to_struct(dict::Dict{String, String}, type)
d = Dict(Symbol(k) => v for (k, v) in dict)
type(;d...)
end
Umbrella.register(:github, Umbrella.OAuth2Actions(redirect_url, token_exchange))
end | Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 3934 | module Google
using StructTypes
using Umbrella
import HTTP, JSON3, URIs
const AUTH_URL = "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/v2/auth"
const TOKEN_URL = "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token"
const USER_URL = "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v3/userinfo"
export GoogleOptions
Base.@kwdef struct GoogleOptions <: Umbrella.Configuration.ProviderOptions
response_type::String = "code"
access_type::String = "offline" # online or offline
include_granted_scopes::Union{Bool,Nothing} = nothing
login_hint::Union{String,Nothing} = nothing
prompt::Union{String,Nothing} = nothing # none, consent, select_account
end
mutable struct Tokens
access_token::String
refresh_token::String
scope::String
expires_in::Int64
function Tokens(; access_token::String="", refresh_token::String="", scope::String="", expires_in::Int64=0)
return new(access_token, refresh_token, scope, expires_in)
end
end
StructTypes.StructType(::Type{Tokens}) = StructTypes.Mutable()
mutable struct User
sub::String
given_name::String
family_name::String
picture::String
email::String
email_verified::Bool
locale::String
function User(;
sub::String="",
given_name::String="",
family_name::String="",
picture::String="",
email::String="",
email_verified::Bool=false,
locale::String=""
)
return new(sub, given_name, family_name, picture, email, email_verified, locale)
end
end
StructTypes.StructType(::Type{User}) = StructTypes.Mutable()
function redirect_url(config::Umbrella.Configuration.Options)
if config.providerOptions === nothing
googleOptions = GoogleOptions()
else
googleOptions = config.providerOptions
end
state = config.state
include_granted_scopes = googleOptions.include_granted_scopes
access_type = googleOptions.access_type
response_type = googleOptions.response_type
prompt = googleOptions.prompt
login_hint = googleOptions.login_hint
params = [
"client_id=$(config.client_id)",
"redirect_uri=$(config.redirect_uri)",
"scope=$(config.scope)",
"access_type=$(access_type)",
"response_type=$(response_type)",
]
if state !== nothing
push!(params, "state=$(state)")
end
if include_granted_scopes !== nothing
push!(params, "include_granted_scopes=$(String(include_granted_scopes))")
end
if prompt !== nothing
push!(params, "prompt=$(prompt)")
end
if login_hint !== nothing
push!(params, "login_hint=$(login_hint)")
end
query = join(params, "&")
println(query)
return "$(AUTH_URL)?$(query)"
end
function token_exchange(code::String, config::Umbrella.Configuration.Options)
try
tokens = _exchange_token(TOKEN_URL, code, config)
profile = _get_user(USER_URL, tokens.access_token)
return tokens, profile
catch e
@error "Unable to complete token exchange" exception=(e, catch_backtrace())
return nothing, nothing
end
end
function _get_user(url::String, access_token::String)
headers = ["Authorization" => """Bearer $(access_token)"""]
response = HTTP.get(url, headers)
body = String(response.body)
return JSON3.read(body, User)
end
function _exchange_token(url::String, code::String, config::Umbrella.Configuration.Options)
headers = ["Content-Type" => "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"]
grand_type = "authorization_code"
body = """code=$(code)&client_id=$(config.client_id)&client_secret=$(config.client_secret)&redirect_uri=$(replace(config.redirect_uri, ":" => "%3A"))&grant_type=$(grand_type)"""
response = HTTP.post(url, headers, body)
body = String(response.body)
tokens = JSON3.read(body, Tokens)
return tokens
end
Umbrella.register(:google, Umbrella.OAuth2Actions(redirect_url, token_exchange))
end | Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 1179 |
const MOCK_AUTH_URL = "https://mock.com/oauth2/"
function mock_redirect(url::String) url end
function mock_redirect_url(config::Configuration.Options)
"$(MOCK_AUTH_URL)?client_id=$(config.client_id)&redirect_uri=$(config.redirect_uri)&scope=$(config.scope)"
end
function mock_token_exchange(code::String, config::Configuration.Options)
code, config
end
function mock_verify(tokens, user)
tokens, user
end
register(:mock, OAuth2Actions(mock_redirect_url, mock_token_exchange))
@testset "Init Mock Instance" begin
redirect_uri = "http://localhost:3000/oauth2/callback"
success_redirect = "/yes"
failure_redirect = "/no"
options = Configuration.Options(;
client_id="mock_id",
client_secret="mock_secret",
redirect_uri=redirect_uri,
success_redirect=success_redirect,
failure_redirect=failure_redirect,
scopes=["profile", "openid", "email"]
)
instance = init(:mock, options, mock_redirect)
@test instance.redirect() == "https://mock.com/oauth2/?client_id=mock_id&redirect_uri=http://localhost:3000/oauth2/callback&scope=profile%20openid%20email"
@test instance.token_exchange("test_code", mock_verify) == success_redirect
end | Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | code | 44 | using Umbrella
using Test
include("app.jl") | Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | docs | 3798 | # Umbrella
Umbrella is a simple Julia authentication plugin, it supports Google and GitHub OAuth2 with more to come. Umbrella integrates with Julia web framework such as [Genie.jl](https://github.com/GenieFramework/Genie.jl), [Oxygen.jl](https://github.com/ndortega/Oxygen.jl) or [Mux.jl](https://github.com/JuliaWeb/Mux.jl) effortlessly.
## Prerequisite
Before using the plugin, you need to obtain OAuth 2 credentials, see [Google Identity Step 1](https://developers.google.com/identity/protocols/oauth2#1.-obtain-oauth-2.0-credentials-from-the-dynamic_data.setvar.console_name-.), [GitHub: Creating an OAuth App](https://docs.github.com/en/developers/apps/building-oauth-apps/creating-an-oauth-app) for details.
## Installation
```julia
pkg> add Umbrella
```
## Basic Usage
Many resources are available describing how OAuth 2 works, please advice [OAuth 2.0](https://oauth.net/2/), [Google Identity](https://developers.google.com/identity/protocols/oauth2/web-server#obtainingaccesstokens), or [GitHub OAuth 2](https://docs.github.com/en/developers/apps/building-oauth-apps/creating-an-oauth-app) for details
Follow the steps below to enable OAuth 2 in your application.
### 1. Configuration
OAuth 2 required parameters such as `client_id`, `client_secret` and `redirect_uri` need to be configured through `Configuration.Options`.
`scopes` is a list of resources the application will access on user's behalf, it is vary from one provider to another.
`providerOptions` configures the additional parameters at the redirection step, it is dependent on the provider.
```julia
const options = Configuration.Options(;
client_id = "", # client id from an OAuth 2 provider
client_secret = "", # secret from an OAuth 2 provider
redirect_uri = "http://localhost:3000/oauth2/google/callback",
success_redirect = "/protected",
failure_redirect = "/error",
scopes = ["profile", "openid", "email"],
providerOptions = GoogleOptions(access_type="online")
)
```
`init` function takes the provider and options, then returns an OAuth 2 instance. Available provider values are `:google`, `:github` and `facebook`. This list is growing as more providers are supported.
```julia
oauth2_instance = init(:google, options)
```
The examples will use [Oxygen.jl](https://github.com/ndortega/Oxygen.jl) as the web framework, but the concept is the same for other web frameworks.
### 2. Handle provider redirection
Create two endpoints,
- `/` serve the login page which, in this case, is a Google OAuth 2 link.
- `/oauth2/google` handles redirections to an OAuth 2 server.
```julia
@get "/" function ()
return "<a href='/oauth2/google'>Authenticate with Google</a>"
end
@get "/oauth2/google" function ()
oauth2_instance.redirect()
end
```
`redirect` function generates the URL using the parameters in step 1, and redirects users to provider's OAuth 2 server to initiate the authentication and authorization process.
Once the users consent to grant access to one or more scopes requested by the application, OAuth 2 server responds the `code` for retrieving access token to a callback endpoint.
### 3. Retrieves tokens
Finally, create the endpoint handling callback from the OAuth 2 server. The path must be identical to the path in `redirect_uri` from `Configuration.Options`.
`token_exchange` function performs two actions,
1. Use `code` responded by the OAuth 2 server to exchange an access token.
2. Get user profile using the access token.
A handler is required for access/refresh tokens and user profile handling.
```julia
@get "/oauth2/google/callback" function (req)
query_params = queryparams(req)
code = query_params["code"]
oauth2_instance.token_exchange(code, function (tokens, user)
# handle tokens and user profile here
end
)
end
``` | Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | docs | 3976 | # Examples
Umbrella.jl supports different OAuth 2 providers, and it integrates with Julia web framework such as [Genie.jl](https://github.com/GenieFramework/Genie.jl), [Oxygen.jl](https://github.com/ndortega/Oxygen.jl) or [Mux.jl](https://github.com/JuliaWeb/Mux.jl) effortlessly, some examples to demo how it works.
## Integrate with Genie.jl
Great work [Genie.jl](https://github.com/GenieFramework/Genie.jl)
```julia
using Genie, Genie.Router
using Umbrella, Umbrella.Google
const options = Configuration.Options(;
client_id="", # client id from Google API Console
client_secret="", # secret from Google API Console
redirect_uri = "http://localhost:3000/oauth2/google/callback",
success_redirect="/protected",
failure_redirect="/failed",
scopes = ["profile", "openid", "email"],
providerOptions = GoogleOptions(access_type="online")
)
google_oauth2 = init(:google, options)
route("/") do
return "<a href='/oauth2/google'>Authenticate with Google</a>"
end
route("/oauth2/google") do
google_oauth2.redirect()
end
route("/oauth2/google/callback") do
code = Genie.params(:code, nothing)
function verify(tokens::Google.Tokens, user::Google.User)
# handle access and refresh tokens and user profile here
end
google_oauth2.token_exchange(code, verify)
end
route("/protected") do
"Congrets, You signed in Successfully!"
end
up(3000, async=false)
```
## Integrate with Oxygen.jl
Shout out to [Oxygen.jl](https://github.com/ndortega/Oxygen.jl)
```julia
using Oxygen, Umbrella, HTTP
const oauth_path = "/oauth2/google"
const oauth_callback = "/oauth2/google/callback"
const options = Configuration.Options(;
client_id="", # client id from Google API Console
client_secret="", # secret from Google API Console
redirect_uri="http://127.0.0.1:8080$(oauth_callback)",
success_redirect="/protected",
failure_redirect="/failed",
scopes=["profile", "openid", "email"]
)
const google_oauth2 = Umbrella.init(:google, options)
@get "/" function ()
return "<a href='$(oauth_path)'>Authenticate with Google</a>"
end
@get oauth_path function ()
# this handles the Google oauth2 redirect in the background
google_oauth2.redirect()
end
@get oauth_callback function (req)
query_params = queryparams(req)
code = query_params["code"]
function verify(tokens::Google.Tokens, user::Google.User)
# handle access and refresh tokens and user profile here
end
google_oauth2.token_exchange(code, verify)
end
@get "/protected" function()
"Congrets, You signed in Successfully!"
end
# start the web server
serve()
```
## Integrate with Mux.jl
Well done [Mux.jl](https://github.com/JuliaWeb/Mux.jl)
```julia
using Mux, Umbrella, HTTP
const oauth_path = "/oauth2/google"
const oauth_callback = "/oauth2/google/callback"
const options = Configuration.Options(;
client_id="", # client id from Google API Console
client_secret="", # secret from Google API Console
redirect_uri="http://127.0.0.1:3000$(oauth_callback)",
success_redirect="/protected",
failure_redirect="/no",
scopes=["profile", "openid", "email"]
)
function mux_redirect(url::String, status::Int = 302)
headers = Dict{String, String}(
"Location" => url
)
Dict(
:status => status,
:headers => headers,
:body => ""
)
end
const oauth2 = Umbrella.init(:google, options, mux_redirect)
function callback(req)
params = HTTP.queryparams(req[:uri])
code = params["code"]
oauth2.token_exchange(code,
function (tokens::Google.Tokens, user::Google.User)
println(tokens.access_token)
println(tokens.refresh_token)
println(user.email)
end
)
end
@app http = (
Mux.defaults,
page("/", respond("<a href='$(oauth_path)'>Authenticate with Google</a>")),
page(oauth_path, req -> oauth2.redirect()),
page(oauth_callback, callback),
page("/protected", respond("Congrets, You signed in Successfully!")),
Mux.notfound()
)
serve(http, 3000)
```
| Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | docs | 3798 | # Umbrella
Umbrella is a simple Julia authentication plugin, it supports Google and GitHub OAuth2 with more to come. Umbrella integrates with Julia web framework such as [Genie.jl](https://github.com/GenieFramework/Genie.jl), [Oxygen.jl](https://github.com/ndortega/Oxygen.jl) or [Mux.jl](https://github.com/JuliaWeb/Mux.jl) effortlessly.
## Prerequisite
Before using the plugin, you need to obtain OAuth 2 credentials, see [Google Identity Step 1](https://developers.google.com/identity/protocols/oauth2#1.-obtain-oauth-2.0-credentials-from-the-dynamic_data.setvar.console_name-.), [GitHub: Creating an OAuth App](https://docs.github.com/en/developers/apps/building-oauth-apps/creating-an-oauth-app) for details.
## Installation
```julia
pkg> add Umbrella
```
## Basic Usage
Many resources are available describing how OAuth 2 works, please advice [OAuth 2.0](https://oauth.net/2/), [Google Identity](https://developers.google.com/identity/protocols/oauth2/web-server#obtainingaccesstokens), or [GitHub OAuth 2](https://docs.github.com/en/developers/apps/building-oauth-apps/creating-an-oauth-app) for details
Follow the steps below to enable OAuth 2 in your application.
### 1. Configuration
OAuth 2 required parameters such as `client_id`, `client_secret` and `redirect_uri` need to be configured through `Configuration.Options`.
`scopes` is a list of resources the application will access on user's behalf, it is vary from one provider to another.
`providerOptions` configures the additional parameters at the redirection step, it is dependent on the provider.
```julia
const options = Configuration.Options(;
client_id = "", # client id from an OAuth 2 provider
client_secret = "", # secret from an OAuth 2 provider
redirect_uri = "http://localhost:3000/oauth2/google/callback",
success_redirect = "/protected",
failure_redirect = "/error",
scopes = ["profile", "openid", "email"],
providerOptions = GoogleOptions(access_type="online")
)
```
`init` function takes the provider and options, then returns an OAuth 2 instance. Available provider values are `:google`, `:github` and `facebook`. This list is growing as more providers are supported.
```julia
oauth2_instance = init(:google, options)
```
The examples will use [Oxygen.jl](https://github.com/ndortega/Oxygen.jl) as the web framework, but the concept is the same for other web frameworks.
### 2. Handle provider redirection
Create two endpoints,
- `/` serve the login page which, in this case, is a Google OAuth 2 link.
- `/oauth2/google` handles redirections to an OAuth 2 server.
```julia
@get "/" function ()
return "<a href='/oauth2/google'>Authenticate with Google</a>"
end
@get "/oauth2/google" function ()
oauth2_instance.redirect()
end
```
`redirect` function generates the URL using the parameters in step 1, and redirects users to provider's OAuth 2 server to initiate the authentication and authorization process.
Once the users consent to grant access to one or more scopes requested by the application, OAuth 2 server responds the `code` for retrieving access token to a callback endpoint.
### 3. Retrieves tokens
Finally, create the endpoint handling callback from the OAuth 2 server. The path must be identical to the path in `redirect_uri` from `Configuration.Options`.
`token_exchange` function performs two actions,
1. Use `code` responded by the OAuth 2 server to exchange an access token.
2. Get user profile using the access token.
A handler is required for access/refresh tokens and user profile handling.
```julia
@get "/oauth2/google/callback" function (req)
query_params = queryparams(req)
code = query_params["code"]
oauth2_instance.token_exchange(code, function (tokens, user)
# handle tokens and user profile here
end
)
end
``` | Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.0 | 51e04d71b6631148d0664ba5fb1033c16b0fe2f9 | docs | 139 | # API Reference
## Configuration
```@docs
Configuration.Options
init
register
```
## Handlers
```@docs
OAuth2
```
## OAuth 2 Providers | Umbrella | https://github.com/jiachengzhang1/Umbrella.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 619 | using Yields
using Documenter
makedocs(;
modules=[Yields],
authors="Alec Loudenback <[email protected]> and contributors",
repo="https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl/blob/{commit}{path}#L{line}",
sitename="Yields.jl",
format=Documenter.HTML(;
prettyurls=get(ENV, "CI", "false") == "true",
canonical="https://JuliaActuary.github.io/Yields.jl",
assets=String[],
),
pages=[
"Home" => "index.md",
"API Reference" => "api.md",
"Developer Notes" => "developer.md",
],
)
deploydocs(;
repo="github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl",
)
| Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 755 | abstract type AbstractYieldCurve <: FinanceCore.AbstractYield end
"""
A `YieldCurveFitParameters` is a structure which contains associated parameters for a yield curve fitting procedure. The type of the object determines the method, and the values of the object determine the parameters.
If the fitting data and the rates are passed as `<:Real` numbers instead of a type of `Rate`s, the default interpretation may vary depending on the fitting type/parameter. See the individual docstrings of the types for more information.
Available types are:
- [`Bootstrap`](@ref)
- [`NelsonSiegel`](@ref)
- [`NelsonSiegelSvensson`](@ref)
"""
abstract type YieldCurveFitParameters end
Base.Broadcast.broadcastable(x::T) where {T<:YieldCurveFitParameters} = Ref(x) | Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 8289 | abstract type ParametricModel <: AbstractYieldCurve end
Base.Broadcast.broadcastable(x::T) where {T<:ParametricModel} = Ref(x)
"""
NelsonSiegel(rates::AbstractVector, maturities::AbstractVector; τ_initial=1.0)
Return the NelsonSiegel fitted parameters. The rates should be zero spot rates. If `rates` are not `Rate`s, then they will be interpreted as `Continuous` `Rate`s.
NelsonSiegel(β₀, β₁, β₂, τ₁)
Parameters of Nelson and Siegel (1987) parametric model:
- β₀ represents a long-term interest rate
- β₁ represents a time-decay component
- β₂ represents a hump
- τ₁ controls the location of the hump
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> β₀, β₁, β₂, τ₁ = 0.6, -1.2, -1.9, 3.0
julia> nsm = Yields.NelsonSiegel.(β₀, β₁, β₂, τ₁)
# Extend Help
## References
- https://onriskandreturn.com/2019/12/01/nelson-siegel-yield-curve-model/
- https://www.bis.org/publ/bppdf/bispap25.pdf
```
"""
struct NelsonSiegelCurve{T} <: ParametricModel
β₀::T
β₁::T
β₂::T
τ₁::T
function NelsonSiegelCurve(β₀::T, β₁::T, β₂::T, τ₁::T) where {T<:Real}
(τ₁ <= 0) && throw(DomainError("Wrong parameter ranges"))
return new{T}(β₀, β₁, β₂, τ₁)
end
end
__ratetype(::Type{NelsonSiegelCurve{T}}) where {T}= Yields.Rate{T, typeof(DEFAULT_COMPOUNDING)}
"""
NelsonSiegel(τ_initial)
NelsonSiegel() # defaults to τ_initial=1.0
This parameter set is used to fit the Nelson-Siegel parametric model to given rates. `τ_initial` should be a scalar and is used as the starting τ value in the optimization. The default value for `τ_initial` is 1.0.
When fitting rates using this `YieldCurveFitParameters` object, the Nelson-Siegel model is used. If constructing curves and the rates are not `Rate`s (ie you pass a `Vector{Float64}`), then they will be interpreted as `Continuous` `Rate`s.
See for more:
- [`Zero`](@ref)
- [`Forward`](@ref)
- [`Par`](@ref)
- [`CMT`](@ref)
- [`OIS`](@ref)
"""
struct NelsonSiegel{T} <: YieldCurveFitParameters
τ_initial::T
end
NelsonSiegel() = NelsonSiegel(1.0)
function Base.zero(ns::NelsonSiegelCurve, t)
if iszero(t)
# zero rate is undefined for t = 0
t += eps()
end
Continuous.(ns.β₀ .+ ns.β₁ .* (1.0 .- exp.(-t ./ ns.τ₁)) ./ (t ./ ns.τ₁) .+ ns.β₂ .* ((1.0 .- exp.(-t ./ ns.τ₁)) ./ (t ./ ns.τ₁) .- exp.(-t ./ ns.τ₁)))
end
FinanceCore.discount(ns::NelsonSiegelCurve, t) = discount.(zero.(ns,t),t)
function fit_β(ns::NelsonSiegel,func,yields,maturities,τ)
Δₘ = vcat([maturities[1]], diff(maturities))
param₀ = [1.0, 0.0, 0.0]
_rate(m, p) = rate.(func.(NelsonSiegelCurve(p[1], p[2], p[3],only(τ)), m))
return LsqFit.curve_fit(_rate, maturities, yields, Δₘ,param₀)
end
function __fit_NS(ns::NelsonSiegel,func,yields,maturities,τ)
f(τ) = β_sum_sq_resid(ns,func,yields,maturities,τ)
r = Optim.optimize(f, [ns.τ_initial])
τ = only(Optim.minimizer(r))
return τ, fit_β(ns,func,yields,maturities,τ)
end
function β_sum_sq_resid(ns,func,yields,maturities,τ)
result = fit_β(ns,func,yields,maturities,τ)
return sum(r^2 for r in result.resid)
end
function Zero(ns::NelsonSiegel,yields, maturities=eachindex(yields))
yields = rate.(Continuous().(yields))
func = zero
τ, result = __fit_NS(ns,func,yields,maturities,ns.τ_initial)
return NelsonSiegelCurve(result.param[1], result.param[2], result.param[3], τ)
end
function Par(ns::NelsonSiegel,yields, maturities=eachindex(yields))
yields = rate.(Continuous().(yields))
func = par
τ, result = __fit_NS(ns,func,yields,maturities,ns.τ_initial)
return NelsonSiegelCurve(result.param[1], result.param[2], result.param[3], τ)
end
function Forward(ns::NelsonSiegel,yields, maturities=eachindex(yields))
yields = rate.(Continuous().(yields))
func = forward
τ, result = __fit_NS(ns,func,yields,maturities,ns.τ_initial)
return NelsonSiegelCurve(result.param[1], result.param[2], result.param[3], τ)
end
"""
NelsonSiegelSvensson(yields::AbstractVector, maturities::AbstractVector; τ_initial=[1.0,1.0])
Return the NelsonSiegelSvensson fitted parameters. The rates should be continuous zero spot rates. If `rates` are not `Rate`s, then they will be interpreted as `Continuous` `Rate`s.
When fitting rates using this `YieldCurveFitParameters` object, the Nelson-Siegel model is used. If constructing curves and the rates are not `Rate`s (ie you pass a `Vector{Float64}`), then they will be interpreted as `Continuous` `Rate`s.
See for more:
- [`Zero`](@ref)
- [`Forward`](@ref)
- [`Par`](@ref)
- [`CMT`](@ref)
- [`OIS`](@ref)
NelsonSiegelSvensson(β₀, β₁, β₂, β₃, τ₁, τ₂)
Parameters of Svensson (1994) parametric model:
- β₀ represents a long-term interest rate
- β₁ represents a time-decay component
- β₂ represents a hump
- β₃ represents a second hum
- τ₁ controls the location of the hump
- τ₁ controls the location of the second hump
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> β₀, β₁, β₂, β₃, τ₁, τ₂ = 0.6, -1.2, -2.1, 3.0, 1.5
julia> nssm = NelsonSiegelSvensson.NelsonSiegelSvensson.(β₀, β₁, β₂, β₃, τ₁, τ₂)
## References
- https://onriskandreturn.com/2019/12/01/nelson-siegel-yield-curve-model/
- https://www.bis.org/publ/bppdf/bispap25.pdf
```
"""
struct NelsonSiegelSvenssonCurve{T} <: ParametricModel
β₀::T
β₁::T
β₂::T
β₃::T
τ₁::T
τ₂::T
function NelsonSiegelSvenssonCurve(β₀::T, β₁::T, β₂::T, β₃::T, τ₁::T, τ₂::T) where {T<:Real}
(τ₁ <= 0 || τ₂ <= 0) && throw(DomainError("Wrong parameter ranges"))
return new{T}(β₀, β₁, β₂, β₃, τ₁, τ₂)
end
end
__ratetype(::Type{NelsonSiegelSvenssonCurve{T}}) where {T}= Yields.Rate{T, typeof(DEFAULT_COMPOUNDING)}
"""
NelsonSiegelSvensson(τ_initial)
NelsonSiegelSvensson() # defaults to τ_initial=[1.0,1.0]
This parameter set is used to fit the Nelson-Siegel parametric model to given rates. `τ_initial` should be a two element vector and is used as the starting τ value in the optimization. The default value for `τ_initial` is [1.0,1.0].
See for more:
- [`Zero`](@ref)
- [`Forward`](@ref)
- [`Par`](@ref)
- [`CMT`](@ref)
- [`OIS`](@ref)
"""
struct NelsonSiegelSvensson{T} <: YieldCurveFitParameters
τ_initial::T
end
NelsonSiegelSvensson() = NelsonSiegelSvensson([1.0,1.0])
function fit_β(ns::NelsonSiegelSvensson,func,yields,maturities,τ)
Δₘ = vcat([maturities[1]], diff(maturities))
param₀ = [1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
_rate(m, p) = rate.(func.(NelsonSiegelSvenssonCurve(p[1], p[2], p[3],p[4],first(τ),last(τ)), m))
return LsqFit.curve_fit(_rate, maturities, yields, Δₘ,param₀)
end
function __fit_NS(ns::NelsonSiegelSvensson,func,yields,maturities,τ)
f(τ) = β_sum_sq_resid(ns,func,yields,maturities,τ)
r = Optim.optimize(f, ns.τ_initial)
τ = Optim.minimizer(r)[[1,2]]
return τ, fit_β(ns,func,yields,maturities,τ)
end
function Zero(ns::NelsonSiegelSvensson,yields, maturities=eachindex(yields))
yields = rate.(Continuous().(yields))
func = zero
τ, result = __fit_NS(ns,func,yields,maturities,ns.τ_initial)
return NelsonSiegelSvenssonCurve(result.param[1], result.param[2], result.param[3],result.param[4], first(τ), last(τ))
end
function Par(ns::NelsonSiegelSvensson,yields, maturities=eachindex(yields))
yields = rate.(Continuous().(yields))
func = par
τ, result = __fit_NS(ns,func,yields,maturities,ns.τ_initial)
return NelsonSiegelSvenssonCurve(result.param[1], result.param[2], result.param[3],result.param[4], first(τ), last(τ))
end
function Forward(ns::NelsonSiegelSvensson,yields, maturities=eachindex(yields))
yields = rate.(Continuous().(yields))
func = forward
τ, result = __fit_NS(ns,func,yields,maturities,ns.τ_initial)
return NelsonSiegelSvenssonCurve(result.param[1], result.param[2], result.param[3],result.param[4], first(τ), last(τ))
end
function Base.zero(nss::NelsonSiegelSvenssonCurve, t)
if iszero(t)
# zero rate is undefined for t = 0
t += eps()
end
Continuous.(nss.β₀ .+ nss.β₁ .* (1.0 .- exp.(-t ./ nss.τ₁)) ./ (t ./ nss.τ₁) .+ nss.β₂ .* ((1.0 .- exp.(-t ./ nss.τ₁)) ./ (t ./ nss.τ₁) .- exp.(-t ./ nss.τ₁)) .+ nss.β₃ .* ((1.0 .- exp.(-t ./ nss.τ₂)) ./ (t ./ nss.τ₂) .- exp.(-t ./ nss.τ₂)))
end
FinanceCore.discount(nss::NelsonSiegelSvenssonCurve, t) = discount.(zero.(nss,t),t)
| Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 4914 | ## Curve Manipulations
"""
RateCombination(curve1,curve2,operation)
Creates a datastructure that will perform the given `operation` after independently calculating the effects of the two curves.
Can only be created via the public API by using the `+`, `-`, `*`, and `/` operatations on `AbstractYield` objects.
As this is double the normal operations when performing calculations, if you are using the curve in performance critical locations, you should consider transforming the inputs and
constructing a single curve object ahead of time.
"""
struct RateCombination{T,U,V} <: AbstractYieldCurve
r1::T
r2::U
op::V
end
__ratetype(::Type{RateCombination{T,U,V}}) where {T,U,V}= __ratetype(T)
FinanceCore.rate(rc::RateCombination, time) = rc.op(rate(rc.r1, time), rate(rc.r2, time))
function FinanceCore.discount(rc::RateCombination, time)
a1 = discount(rc.r1, time)^(-1 / time) - 1
a2 = discount(rc.r2, time)^(-1 / time) - 1
return 1 / (1 + rc.op(a1, a2))^time
end
Base.zero(rc::RateCombination, time) = zero(rc,time,Periodic(1))
function Base.zero(rc::RateCombination, time, cf::C) where {C<:FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency}
d = discount(rc,time)
i = Periodic(1/d^(1/time)-1,1)
return convert(cf, i) # c.zero is a curve of continuous rates represented as floats. explicitly wrap in continuous before converting
end
"""
Yields.AbstractYieldCurve + Yields.AbstractYieldCurve
The addition of two yields will create a `RateCombination`. For `rate`, `discount`, and `accumulation` purposes the spot rates of the two curves will be added together.
"""
function Base.:+(a::AbstractYieldCurve, b::AbstractYieldCurve)
return RateCombination(a, b, +)
end
function Base.:+(a::Constant, b::Constant)
a_kind = rate(a).compounding
rate_new_basis = rate(convert(a_kind, rate(b)))
return Constant(
Rate(
rate(a.rate) + rate_new_basis,
a_kind
)
)
end
function Base.:+(a::T, b) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve}
return a + Constant(b)
end
function Base.:+(a, b::T) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve}
return Constant(a) + b
end
"""
Yields.AbstractYieldCurve * Yields.AbstractYieldCurve
The multiplication of two yields will create a `RateCombination`. For `rate`, `discount`, and `accumulation` purposes the spot rates of the two curves will be added together. This can be useful, for example, if you wanted to after-tax a yield.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> m = Yields.Constant(0.01) * 0.79;
julia> accumulation(m,1)
1.0079
julia> accumulation(.01*.79,1)
1.0079
```
"""
function Base.:*(a::AbstractYieldCurve, b::AbstractYieldCurve)
return RateCombination(a, b, *)
end
function Base.:*(a::Constant, b::Constant)
a_kind = rate(a).compounding
rate_new_basis = rate(convert(a_kind, rate(b)))
return Constant(
Rate(
rate(a.rate) * rate_new_basis,
a_kind
)
)
end
function Base.:*(a::T, b) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve}
return a * Constant(b)
end
function Base.:*(a, b::T) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve}
return Constant(a) * b
end
"""
Yields.AbstractYieldCurve - Yields.AbstractYieldCurve
The subtraction of two yields will create a `RateCombination`. For `rate`, `discount`, and `accumulation` purposes the spot rates of the second curves will be subtracted from the first.
"""
function Base.:-(a::AbstractYieldCurve, b::AbstractYieldCurve)
return RateCombination(a, b, -)
end
function Base.:-(a::Constant, b::Constant)
a_kind = rate(a).compounding
rate_new_basis = rate(convert(a_kind, rate(b)))
return Constant(
Rate(
rate(a.rate) - rate_new_basis,
a_kind
)
)
end
function Base.:-(a::T, b) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve}
return a - Constant(b)
end
function Base.:-(a, b::T) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve}
return Constant(a) - b
end
"""
Yields.AbstractYieldCurve / Yields.AbstractYieldCurve
The division of two yields will create a `RateCombination`. For `rate`, `discount`, and `accumulation` purposes the spot rates of the two curves will have the first divided by the second. This can be useful, for example, if you wanted to gross-up a yield to be pre-tax.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> m = Yields.Constant(0.01) / 0.79;
julia> accumulation(d,1)
1.0126582278481013
julia> accumulation(.01/.79,1)
1.0126582278481013
```
"""
function Base.:/(a::AbstractYieldCurve, b::AbstractYieldCurve)
return RateCombination(a, b, /)
end
function Base.:/(a::Constant, b::Constant)
a_kind = rate(a).compounding
rate_new_basis = rate(convert(a_kind, rate(b)))
return Constant(
Rate(
rate(a.rate) / rate_new_basis,
a_kind
)
)
end
function Base.:/(a::T, b) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve}
return a / Constant(b)
end
function Base.:/(a, b::T) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve}
return Constant(a) / b
end | Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 7783 | abstract type ObservableQuote end
"""
ZeroCouponQuote(price, maturity)
Quote for a set of zero coupon bonds with given `price` and `maturity`.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> prices = [1.3, 0.1, 4.5]
julia> maturities = [1.2, 2.5, 3.6]
julia> swq = Yields.ZeroCouponQuote.(prices, maturities)
```
"""
struct ZeroCouponQuote <: ObservableQuote
price
maturity
end
"""
SwapQuote(yield, maturity, frequency)
Quote for a set of interest rate swaps with the given `yield` and `maturity` and a given payment `frequency`.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> maturities = [1.2, 2.5, 3.6]
julia> interests = [-0.02, 0.3, 0.04]
julia> prices = [1.3, 0.1, 4.5]
julia> frequencies = [2,1,2]
julia> swq = Yields.SwapQuote.(interests, maturities, frequencies)
```
"""
struct SwapQuote <: ObservableQuote
yield
maturity
frequency
function SwapQuote(yield, maturity, frequency)
frequency <= 0 && throw(DomainError("Payment frequency must be positive"))
return new(yield, maturity, frequency)
end
end
"""
BulletBondQuote(yield, price, maturity, frequency)
Quote for a set of fixed interest bullet bonds with given `yield`, `price`, `maturity` and a given payment frequency `frequency`.
Construct a vector of quotes for use with SmithWilson methods, e.g. by broadcasting over an array of inputs.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> maturities = [1.2, 2.5, 3.6]
julia> interests = [-0.02, 0.3, 0.04]
julia> prices = [1.3, 0.1, 4.5]
julia> frequencies = [2,1,2]
julia> bbq = Yields.BulletBondQuote.(interests, maturities, prices, frequencies)
```
"""
struct BulletBondQuote <: ObservableQuote
yield
price
maturity
frequency
function BulletBondQuote(yield, maturity, price, frequency)
frequency <= 0 && throw(DomainError("Payment frequency must be positive"))
return new(yield, maturity, price, frequency)
end
end
"""
SmithWilson(zcq::Vector{ZeroCouponQuote}; ufr, α)
SmithWilson(swq::Vector{SwapQuote}; ufr, α)
SmithWilson(bbq::Vector{BulletBondQuote}; ufr, α)
SmithWilson(times<:AbstractVector, cashflows<:AbstractMatrix, prices<:AbstractVector; ufr, α)
SmithWilson(u, qb; ufr, α)
Create a yield curve object that implements the Smith-Wilson interpolation/extrapolation scheme.
Positional arguments to construct a curve:
- Quoted instrument as the first argument: either a `Vector` of `ZeroCouponQuote`s, `SwapQuote`s, or `BulletBondQuote`s, or
- A set of `times`, `cashflows`, and `prices`, or
- A curve can be with `u` is the timepoints coming from the calibration, and `qb` is the internal parameterization of the curve that ensures that the calibration is correct. Users may prefer the other constructors but this mathematical constructor is also available.
Required keyword arguments:
- `ufr` is the Ultimate Forward Rate, the forward interest rate to which the yield curve tends, in continuous compounding convention.
- `α` is the parameter that governs the speed of convergence towards the Ultimate Forward Rate. It can be typed with `\\alpha[TAB]`
"""
struct SmithWilson{TU<:AbstractVector,TQb<:AbstractVector} <: AbstractYieldCurve
u::TU
qb::TQb
ufr
α
# Inner constructor ensures that vector lengths match
function SmithWilson{TU,TQb}(u, qb; ufr, α) where {TU<:AbstractVector,TQb<:AbstractVector}
if length(u) != length(qb)
throw(DomainError("Vectors u and qb in SmithWilson must have equal length"))
end
return new(u, qb, ufr, α)
end
end
SmithWilson(u::TU, qb::TQb; ufr, α) where {TU<:AbstractVector,TQb<:AbstractVector} = SmithWilson{TU,TQb}(u, qb; ufr = ufr, α = α)
__ratetype(::Type{SmithWilson{TU,TQb}}) where {TU,TQb}= Yields.Rate{Float64, Yields.Continuous}
"""
H_ordered(α, t_min, t_max)
The Smith-Wilson H function with ordered arguments (for better performance than using min and max).
"""
function H_ordered(α, t_min, t_max)
return α * t_min + exp(-α * t_max) * sinh(-α * t_min)
end
"""
H(α, t1, t2)
The Smith-Wilson H function implemented in a faster way.
"""
function H(α, t1::T, t2::T) where {T}
return t1 < t2 ? H_ordered(α, t1, t2) : H_ordered(α, t2, t1)
end
H(α, t1, t2) = H(α, promote(t1, t2)...)
H(α, t1vec::AbstractVector, t2) = [H(α, t1, t2) for t1 in t1vec]
H(α, t1vec::AbstractVector, t2vec::AbstractVector) = [H(α, t1, t2) for t1 in t1vec, t2 in t2vec]
# This can be optimized by going to H_ordered directly, but it might be a bit cumbersome
H(α, tvec::AbstractVector) = H(α, tvec, tvec)
FinanceCore.discount(sw::SmithWilson, t) = exp(-sw.ufr * t) * (1.0 + H(sw.α, sw.u, t) ⋅ sw.qb)
Base.zero(sw::SmithWilson, t) = Continuous(sw.ufr - log(1.0 + H(sw.α, sw.u, t) ⋅ sw.qb) / t)
Base.zero(sw::SmithWilson, t, cf::FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency) = convert(cf, zero(sw, t))
function SmithWilson(times::AbstractVector, cashflows::AbstractMatrix, prices::AbstractVector; ufr, α)
Q = Diagonal(exp.(-ufr * times)) * cashflows
q = vec(sum(Q, dims = 1)) # We want q to be a column vector
QHQ = Q' * H(α, times) * Q
b = QHQ \ (prices - q)
Qb = Q * b
return SmithWilson(times, Qb; ufr = ufr, α = α)
end
"""
timepoints(zcq::Vector{ZeroCouponQuote})
timepoints(bbq::Vector{BulletBondQuote})
Return the times associated with the `cashflows` of the instruments.
"""
function timepoints(qs::Vector{Q}) where {Q<:ObservableQuote}
frequency = maximum(q.frequency for q in qs)
timestep = 1 / frequency
maturity = maximum(q.maturity for q in qs)
return [timestep:timestep:maturity...]
end
"""
cashflows(interests, maturities, frequency)
timepoints(zcq::Vector{ZeroCouponQuote})
timepoints(bbq::Vector{BulletBondQuote})
Produce a cash flow matrix for a set of instruments with given `interests` and `maturities`
and a given payment frequency `frequency`. All instruments are assumed to have their first payment at time 1/`frequency`
and have their last payment at the largest multiple of 1/`frequency` less than or equal to the input maturity.
"""
function cashflows(interests, maturities, frequencies)
frequency = lcm(frequencies)
fq = inv.(frequencies)
timestep = 1 / frequency
floored_mats = floor.(maturities ./ timestep) .* timestep
times = timestep:timestep:maximum(floored_mats)
# we need to determine the coupons in relation to the payment date, not time zero
time_adj = floored_mats .% fq
cashflows = [
# if on a coupon date and less than maturity, pay coupon
((((t + time_adj[instrument]) % fq[instrument] ≈ 0) && t <= floored_mats[instrument]) ? interests[instrument] / frequencies[instrument] : 0.0) +
(t ≈ floored_mats[instrument] ? 1.0 : 0.0) # add maturity payment
for t in times, instrument = eachindex(interests)
]
return cashflows
end
function cashflows(qs::Vector{Q}) where {Q<:ObservableQuote}
yield = [q.yield for q in qs]
maturity = [q.maturity for q in qs]
frequency = [q.frequency for q in qs]
return cashflows(yield, maturity, frequency)
end
# Utility methods for calibrating Smith-Wilson directly from quotes
function SmithWilson(zcq::Vector{ZeroCouponQuote}; ufr, α)
n = length(zcq)
maturities = [q.maturity for q in zcq]
prices = [q.price for q in zcq]
return SmithWilson(maturities, Matrix{Float64}(I, n, n), prices; ufr = ufr, α = α)
end
function SmithWilson(swq::Vector{SwapQuote}; ufr, α)
times = timepoints(swq)
cfs = cashflows(swq)
ones(length(swq))
return SmithWilson(times, cfs, ones(length(swq)), ufr = ufr, α = α)
end
function SmithWilson(bbq::Vector{BulletBondQuote}; ufr, α)
times = timepoints(bbq)
cfs = cashflows(bbq)
prices = [q.price for q in bbq]
return SmithWilson(times, cfs, prices, ufr = ufr, α = α)
end | Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 1230 | module Yields
using Reexport
using PrecompileTools
using FinanceCore
using FinanceCore: Rate, rate, discount, accumulation, Periodic, Continuous, forward
@reexport using FinanceCore: Rate, rate, discount, accumulation, Periodic, Continuous, forward
import BSplineKit
import ForwardDiff
using LinearAlgebra
using UnicodePlots
import LsqFit
import Optim
# don't export type, as the API of Yields.Zero is nicer and
# less polluting than Zero and less/equally verbose as ZeroYieldCurve or ZeroCurve
export LinearSpline, QuadraticSpline,
Bootstrap, NelsonSiegel, NelsonSiegelSvensson, SmithWilson
const DEFAULT_COMPOUNDING = Yields.Continuous()
include("AbstractYieldCurve.jl")
include("utils.jl")
include("bootstrap.jl")
include("SmithWilson.jl")
include("generics.jl")
include("RateCombination.jl")
include("NelsonSiegelSvensson.jl")
include("precompiles.jl")
function MethodError_hint(io::IO, ex::InexactError)
hint = "\nA Periodic rate requires also passing a compounding frequency." *
"\nFor example, call Periodic($(ex.val), 2) for a rate compounded twice per period."
print(io, hint)
end
function __init__()
Base.Experimental.register_error_hint(MethodError_hint, MethodError)
nothing
end
end
| Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 8971 | # bootstrapped class of curve methods
"""
Boostrap(interpolation_method=QuadraticSpline)
This `YieldCurveFitParameters` object defines the interpolation method to use when bootstrapping the curve. Provided options are `QuadraticSpline()` (the default) and `LinearSpline()`. You may also pass a custom interpolation method with the function signature of `f(xs, ys) -> f(x) -> y`.
If constructing curves and the rates are not `Rate`s (ie you pass a `Vector{Float64}`), then they will be interpreted as `Periodic(1)` `Rate`s, except the [`Par`](@ref) curve, which is interpreted as `Periodic(2)` `Rate`s. [`CMT`](@ref) and [`OIS`](@ref) FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency assumption depends on the corresponding maturity.
See for more:
- [`Zero`](@ref)
- [`Forward`](@ref)
- [`Par`](@ref)
- [`CMT`](@ref)
- [`OIS`](@ref)
"""
struct Bootstrap{T} <: YieldCurveFitParameters
interpolation::T
end
__default_rate_interpretation(ns,r::T) where {T<:Rate} = r
__default_rate_interpretation(::Type{Bootstrap{T}},r::U) where {T,U<:Real} = Periodic(r,1)
function Bootstrap()
return Bootstrap(QuadraticSpline())
end
struct BootstrapCurve{T,U,V} <: AbstractYieldCurve
rates::T
maturities::U
zero::V # function time -> continuous zero rate
end
FinanceCore.discount(yc::T, time) where {T<:BootstrapCurve} = exp(-yc.zero(time) * time)
__ratetype(::Type{BootstrapCurve{T,U,V}}) where {T,U,V}= Yields.Rate{Float64, typeof(DEFAULT_COMPOUNDING)}
# Forward curves
"""
ForwardStarting(curve,forwardstart)
Rebase a `curve` so that `discount`/`accumulation`/etc. are re-based so that time zero from the new curves perspective is the given `forwardstart` time.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> zero = [5.0, 5.8, 6.4, 6.8] ./ 100
julia> maturity = [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0]
julia> curve = Yields.Zero(zero, maturity)
julia> fwd = Yields.ForwardStarting(curve, 1.0)
julia> FinanceCore.discount(curve,1,2)
0.9275624570410582
julia> FinanceCore.discount(fwd,1) # `curve` has effectively been reindexed to `1.0`
0.9275624570410582
```
# Extended Help
While `ForwardStarting` could be nested so that, e.g. the third period's curve is the one-period forward of the second period's curve, it will be more efficient to reuse the initial curve from a runtime and compiler perspective.
`ForwardStarting` is not used to construct a curve based on forward rates. See [`Forward`](@ref) instead.
"""
struct ForwardStarting{T,U} <: AbstractYieldCurve
curve::U
forwardstart::T
end
__ratetype(::Type{ForwardStarting{T,U}}) where {T,U}= __ratetype(U)
function FinanceCore.discount(c::ForwardStarting, to)
FinanceCore.discount(c.curve, c.forwardstart, to + c.forwardstart)
end
function Base.zero(c::ForwardStarting, to,cf::C) where {C<:FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency}
z = forward(c.curve,c.forwardstart,to+c.forwardstart)
return convert(cf,z)
end
"""
Constant(rate::Real, cf::CompoundingFrequency=Periodic(1))
Constant(r::Rate)
Construct a yield object where the spot rate is constant for all maturities. If `rate` is not a `Rate` type, will assume `Periodic(1)` for the compounding frequency
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> y = Yields.Constant(0.05)
julia> FinanceCore.discount(y,2)
0.9070294784580498 # 1 / (1.05) ^ 2
```
"""
struct Constant{T} <: AbstractYieldCurve
rate::T
Constant(rate::T) where {T<:Rate} = new{T}(rate)
end
__ratetype(::Type{Constant{T}}) where {T} = T
__default_rate_interpretation(::Type{Constant},r) = Periodic(r,1)
FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency(c::Constant{T}) where {T} = c.rate.compounding
function Constant(rate::T) where {T<:Real}
r = __default_rate_interpretation(Constant,rate)
return Constant(r)
end
Base.zero(c::Constant, time) = c.rate
Base.zero(c::Constant, time, cf::FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency) = convert(cf, c.rate)
FinanceCore.rate(c::Constant) = c.rate
FinanceCore.rate(c::Constant, time) = c.rate
FinanceCore.discount(r::Constant, time) = FinanceCore.discount(r.rate, time)
FinanceCore.discount(r::Constant, from, to) = FinanceCore.discount(r.rate, to - from)
FinanceCore.accumulation(r::Constant, time) = accumulation(r.rate, time)
FinanceCore.accumulation(r::Constant, from, to) = accumulation(r.rate, to - from)
"""
Step(rates,times)
Create a yield curve object where the applicable rate is the effective rate of interest applicable until corresponding time. If `rates` is not a `Vector{Rate}`, will assume `Periodic(1)` type.
The last rate will be applied to any time after the last time in `times`.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia>y = Yields.Step([0.02,0.05], [1,2])
julia>rate(y,0.5)
0.02
julia>rate(y,1.5)
0.05
julia>rate(y,2.5)
0.05
```
"""
struct Step{R,T} <: AbstractYieldCurve
rates::R
times::T
function Step(rates,times=eachindex(rates))
r = __default_rate_interpretation.(Step,rates)
new{typeof(r),typeof(times)}(r, times)
end
end
__ratetype(::Type{Step{R,T}}) where {R,T}= eltype(R)
__default_rate_interpretation(::Type{Step},r) = Periodic(r,1)
FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency(c::Step{T}) where {T} = first(c.rates).compounding
function FinanceCore.discount(y::Step, time)
v = 1.0
last_time = 0.0
for (rate,t) in zip(y.rates,y.times)
duration = min(time - last_time,t-last_time)
v *= FinanceCore.discount(rate,duration)
last_time = t
(last_time > time) && return v
end
# if we did not return in the loop, then we extend the last rate
v *= FinanceCore.discount(last(y.rates), time - last_time)
return v
end
function Zero(b::Bootstrap,rates, maturities)
rates = __default_rate_interpretation.(typeof(b),rates)
return _zero_inner(rates,maturities,b.interpolation)
end
# zero is different than the other boostrapped curves in that it doesn't actually need to bootstrap
# because the rate are already zero rates. Instead, we just cut straight to the
# appropriate interpolation function based on the type dispatch.
function _zero_inner(rates, maturities, interp::QuadraticSpline)
continuous_zeros = rate.(Continuous.(rates))
return BootstrapCurve(
rates,
maturities,
cubic_interp([0.0; maturities],[first(continuous_zeros); continuous_zeros])
)
end
function _zero_inner(rates, maturities, interp::LinearSpline)
continuous_zeros = rate.(Continuous.(rates))
return BootstrapCurve(
rates,
maturities,
linear_interp([0.0; maturities],[first(continuous_zeros); continuous_zeros])
)
end
# fallback for user provided interpolation function
function _zero_inner(rates, maturities, interp::T) where {T}
continuous_zeros = rate.(Continuous.(rates))
return BootstrapCurve(
rates,
maturities,
interp([0.0; maturities],[first(continuous_zeros); continuous_zeros])
)
end
function Par(b::Bootstrap,rates, maturities)
rates = __coerce_rate.(rates,Periodic(2))
return BootstrapCurve(
rates,
maturities,
# assume that maturities less than or equal to 12 months are settled once, otherwise semi-annual
# per Hull 4.7
bootstrap(rates, maturities, [m <= 1 ? nothing : 1 / r.compounding.frequency for (r, m) in zip(rates, maturities)], b.interpolation)
)
end
function Forward(b::Bootstrap,rates, maturities)
rates = __default_rate_interpretation.(typeof(b),rates)
# convert to zeros and pass to Zero
disc_v = Vector{Float64}(undef, length(rates))
v = 1.0
for (i,r) = enumerate(rates)
Δt = maturities[i] - (i == 1 ? 0 : maturities[i-1])
v *= FinanceCore.discount(r, Δt)
disc_v[i] = v
end
z = (1.0 ./ disc_v) .^ (1 ./ maturities) .- 1 # convert disc_v to zero
return Zero(b,z, maturities)
end
function CMT(b::Bootstrap,rates, maturities)
rs = map(zip(rates, maturities)) do (r, m)
if m <= 1
Rate(r, Periodic(1 / m))
else
Rate(r, Periodic(2))
end
end
CMT(b,rs, maturities)
end
function CMT(b::Bootstrap,rates::Vector{T}, maturities) where {T<:Rate}
return BootstrapCurve(
rates,
maturities,
# assume that maturities less than or equal to 12 months are settled once, otherwise semi-annual
# per Hull 4.7
bootstrap(rates, maturities, [m <= 1 ? nothing : 0.5 for m in maturities], b.interpolation)
)
end
function OIS(b::Bootstrap,rates, maturities)
rs = map(zip(rates, maturities)) do (r, m)
if m <= 1
Rate(r, Periodic(1 / m))
else
Rate(r, Periodic(4))
end
end
return OIS(b,rs, maturities)
end
function OIS(b::Bootstrap,rates::Vector{<:Rate}, maturities)
return BootstrapCurve(
rates,
maturities,
# assume that maturities less than or equal to 12 months are settled once, otherwise quarterly
# per Hull 4.7
bootstrap(rates, maturities, [m <= 1 ? nothing : 1 / 4 for m in maturities], b.interpolation)
)
end
| Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 11466 |
## Generic and Fallbacks
"""
discount(yc, to)
discount(yc, from,to)
The discount factor for the yield curve `yc` for times `from` through `to`.
"""
FinanceCore.discount(yc::T, from, to) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve}= discount(yc, to) / discount(yc, from)
"""
forward(yc, from, to, CompoundingFrequency=Periodic(1))
The forward `Rate` implied by the yield curve `yc` between times `from` and `to`.
"""
function FinanceCore.forward(yc::T, from, to) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve}
return forward(yc, from, to, DEFAULT_COMPOUNDING)
end
function FinanceCore.forward(yc::T, from, to, cf::FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve}
r = Periodic((accumulation(yc, to) / accumulation(yc, from))^(1 / (to - from)) - 1, 1)
return convert(cf, r)
end
function FinanceCore.forward(yc::T, from) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve}
to = from + 1
return forward(yc, from, to)
end
function FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency(curve::T) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve}
return DEFAULT_COMPOUNDING
end
"""
par(curve,time;frequency=2)
Calculate the par yield for maturity `time` for the given `curve` and `frequency`. Returns a `Rate` object with periodicity corresponding to the `frequency`. The exception to this is if `time` is less than what the payments allowed by frequency (e.g. a time `0.5` but with frequency `1`) will effectively assume frequency equal to 1 over `time`.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> c = Yields.Constant(0.04);
julia> Yields.par(c,4)
Yields.Rate{Float64, Yields.Periodic}(0.03960780543711406, Yields.Periodic(2))
julia> Yields.par(c,4;frequency=1)
Yields.Rate{Float64, Yields.Periodic}(0.040000000000000036, Yields.Periodic(1))
julia> Yields.par(c,0.6;frequency=4)
Yields.Rate{Float64, Yields.Periodic}(0.039413626195875295, Yields.Periodic(4))
julia> Yields.par(c,0.2;frequency=4)
Yields.Rate{Float64, Yields.Periodic}(0.039374942589460726, Yields.Periodic(5))
julia> Yields.par(c,2.5)
Yields.Rate{Float64, Yields.Periodic}(0.03960780543711406, Yields.Periodic(2))
```
"""
function par(curve, time; frequency=2)
mat_disc = discount(curve, time)
coup_times = coupon_times(time,frequency)
coupon_pv = sum(discount(curve,t) for t in coup_times)
Δt = step(coup_times)
r = (1-mat_disc) / coupon_pv
cfs = [t == last(coup_times) ? 1+r : r for t in coup_times]
# `sign(r)`` is used instead of `1` because there are times when the coupons are negative so we want to flip the sign
cfs = [-1;cfs]
r = internal_rate_of_return(cfs,[0;coup_times])
frequency_inner = min(1/Δt,max(1 / Δt, frequency))
r = convert(Periodic(frequency_inner),r)
return r
end
"""
zero(curve,time)
zero(curve,time,CompoundingFrequency)
Return the zero rate for the curve at the given time.
"""
function Base.zero(c::YC, time) where {YC<:AbstractYieldCurve}
zero(c, time, FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency(c))
end
function Base.zero(c::YC, time, cf::C) where {YC<:AbstractYieldCurve,C<:FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency}
df = discount(c, time)
r = -log(df)/time
return convert(cf, Continuous(r)) # c.zero is a curve of continuous rates represented as floats. explicitly wrap in continuous before converting
end
"""
accumulation(yc, from, to)
The accumulation factor for the yield curve `yc` for times `from` through `to`.
"""
function FinanceCore.accumulation(yc::AbstractYieldCurve, time)
return 1 ./ discount(yc, time)
end
function FinanceCore.accumulation(yc::AbstractYieldCurve, from, to)
return 1 ./ discount(yc, from, to)
end
"""
Par(rates, maturities=eachindex(rates)
Par(p::YieldCurveFitParameters, rates, maturities=eachindex(rates)
Construct a curve given a set of bond equivalent yields and the corresponding maturities. Assumes that maturities <= 1 year do not pay coupons and that after one year, pays coupons with frequency equal to the CompoundingFrequency of the corresponding rate (normally the default for a `Rate` is `1`, but when constructed via `Par` the default compounding Frequency is `2`).
See [`bootstrap`](@ref) for more on the `interpolation` parameter, which is set to `QuadraticSpline()` by default.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> par = [6.,8.,9.5,10.5,11.0,11.25,11.38,11.44,11.48,11.5] ./ 100
julia> maturities = [t for t in 1:10]
julia> curve = Par(par,maturities);
julia> zero(curve,1)
Rate(0.06000000000000005, Periodic(1))
```
"""
function Yields.Par(rates,maturities=eachindex(rates))
# bump to a constant yield if only given one rate
length(rates) == 1 && return Constant(first(rates))
return Yields.Par(Bootstrap(),rates,maturities)
end
"""
Forward(rates,maturities=eachindex(rates))
Forward(p::YieldCurveFitParameters, rates,maturities=eachindex(rates))
Takes a vector of 1-period forward rates and constructs a discount curve. The method of fitting the curve to the data is determined by the [`YieldCurveFitParameters`](@ref) object `p`, which is a `Boostrap(QuadraticSpline())` by default.
If `rates` is a vector of floating point number instead of a vector `Rate`s, see the [`YieldCurveFitParameters`](@ref) for how the rate will be interpreted.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> Yields.Forward( [0.01,0.02,0.03] );
julia> Yields.Forward( Yields.Continuous.([0.01,0.02,0.03]) );
```
"""
function Yields.Forward(rates,maturities=eachindex(rates))
# bump to a constant yield if only given one rate
length(rates) == 1 && return Constant(first(rates))
return Yields.Forward(Bootstrap(),rates,maturities)
end
"""
Zero(rates, maturities=eachindex(rates))
Zero(p::YieldCurveFitParameters,rates, maturities=eachindex(rates))
Construct a yield curve with given zero-coupon spot `rates` at the given `maturities`. The method of fitting the curve to the data is determined by the [`YieldCurveFitParameters`](@ref) object `p`, which is a `Boostrap(QuadraticSpline())` by default.
If `rates` is a vector of floating point number instead of a vector `Rate`s, see the [`YieldCurveFitParameters`](@ref) for how the rate will be interpreted.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> Yields.Zero([0.01,0.02,0.04,0.05],[1,2,5,10])
⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀Yield Curve (Yields.BootstrapCurve)⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
0.05 │⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⡠⠤⠒⠒⠒⠒⠒⠤⠤⠤⢄⣀⣀⣀⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│ Zero rates
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣀⠖⠉⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠉⠉⠉⠉⠒⠒⠒⠢⠤⠤⠤⣄⣀⣀⣀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⠖⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠉⠉⠉⠑⠒⠒⠒⠦⠤⠤⠤⣀⣀⣀⡀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⡔⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠈⠉│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢠⠎⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢠⠃⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢠⠃⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
Continuous │⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⠇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⡜⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⡸⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⢠⠇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⡜⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠒⠒⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
0 │⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
⠀0⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀time⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀30⠀
```
"""
function Yields.Zero(rates,maturities=eachindex(rates))
# bump to a constant yield if only given one rate
length(rates) == 1 && return Constant(first(rates))
return Yields.Zero(Bootstrap(),rates,maturities)
end
"""
Yields.CMT(rates, maturities; interpolation=QuadraticSpline())
Yields.CMT(p::YieldCurveFitParameters,rates, maturities)
Takes constant maturity (treasury) yields (bond equivalent), and assumes that instruments <= one year maturity pay no coupons and that the rest pay semi-annual.
The method of fitting the curve to the data is determined by the [`YieldCurveFitParameters`](@ref) object `p`, which is a `Boostrap(QuadraticSpline())` by default.
# Examples
```julia-repl
# 2021-03-31 rates from Treasury.gov
rates =[0.01, 0.01, 0.03, 0.05, 0.07, 0.16, 0.35, 0.92, 1.40, 1.74, 2.31, 2.41] ./ 100
mats = [1/12, 2/12, 3/12, 6/12, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, 30]
Yields.CMT(rates,mats)
```
"""
function Yields.CMT(rates,maturities=eachindex(rates))
# bump to a constant yield if only given one rate
length(rates) == 1 && return Constant(first(rates))
return Yields.CMT(Bootstrap(),rates,maturities)
end
"""
OIS(rates, maturities)
OIS(p::YieldCurveFitParameters, rates, maturities)
Takes Overnight Index Swap rates, and assumes that instruments <= one year maturity are settled once and other agreements are settled quarterly with a corresponding CompoundingFrequency.
The method of fitting the curve to the data is determined by the [`YieldCurveFitParameters`](@ref) object `p`, which is a `Boostrap(QuadraticSpline())` by default.
# Examples
```julia-repl
julia> ois = [1.8, 2.0, 2.2, 2.5, 3.0, 4.0] ./ 100;
julia> mats = [1 / 12, 1 / 4, 1 / 2, 1, 2, 5];
julia> curve = Yields.OIS(ois, mats)
⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀Yield Curve (Yields.BootstrapCurve)⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
0.1 │⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│ Zero rates
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣀⡤│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣀⡤⠔⠒⠋⠁⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣀⡤⠔⠒⠋⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣀⡤⠔⠒⠋⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣀⡤⠔⠒⠋⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣀⡤⠔⠒⠋⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
Continuous │⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣀⡤⠔⠒⠋⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣀⡤⠔⠒⠋⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣀⡤⠔⠒⠋⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⡠⠔⠊⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⠀⠀⣀⠔⠋⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠀⡠⠎⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
│⠜⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
0.01 │⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀│
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
⠀0⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀time⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀30⠀
```
"""
function Yields.OIS(rates,maturities=eachindex(rates))
# bump to a constant yield if only given one rate
length(rates) == 1 && return Constant(first(rates))
return Yields.OIS(Bootstrap(),rates,maturities)
end
| Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 863 |
# created with the help of SnoopCompile.jl
@setup_workload begin
# 2021-03-31 rates from Treasury.gov
rates =[0.01, 0.01, 0.03, 0.05, 0.07, 0.16, 0.35, 0.92, 1.40, 1.74, 2.31, 2.41] ./ 100
tenors = [1/12, 2/12, 3/12, 6/12, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, 30]
@compile_workload begin
# all calls in this block will be precompiled, regardless of whether
# they belong to your package or not (on Julia 1.8 and higher)
Yields.Par(rates,tenors)
Yields.CMT(rates,tenors)
Yields.Forward(rates,tenors)
Yields.OIS(rates,tenors)
Yields.Zero(NelsonSiegel(), rates,tenors)
Yields.Zero(NelsonSiegelSvensson(), rates,tenors)
Yields.Zero(rates,tenors)
c = Yields.Zero(rates,tenors)
Yields.zero(c,10)
Yields.par(c,10)
Yields.forward(c,5,6)
end
end | Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 6787 | # make interest curve broadcastable so that you can broadcast over multiple`time`s in `interest_rate`
Base.Broadcast.broadcastable(ic::T) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve} = Ref(ic)
function coupon_times(time,frequency)
Δt = min(1 / frequency,time)
times = time:-Δt:0
f = last(times)
f += iszero(f) ? Δt : zero(f)
l = first(times)
return f:Δt:l
end
# internal function (will be used in EconomicScenarioGenerators)
# defines the rate output given just the type of curve
__ratetype(::Type{Rate{T,U}}) where {T,U<:Periodic} = Yields.Rate{T, Periodic}
__ratetype(::Type{Rate{T,U}}) where {T,U<:Continuous} = Yields.Rate{T, Continuous}
__ratetype(curve::T) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve} = __ratetype(typeof(curve))
__ratetype(::Type{T}) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve} = Yields.Rate{Float64, typeof(DEFAULT_COMPOUNDING)}
# https://github.com/dpsanders/hands_on_julia/blob/master/during_sessions/Fractale%20de%20Newton.ipynb
newton(f, f′, x) = x - f(x) / f′(x)
function solve(g, g′, x0, max_iterations = 100)
x = x0
tolerance = 2 * eps(x0)
iteration = 0
while (abs(g(x) - 0) > tolerance && iteration < max_iterations)
x = newton(g, g′, x)
iteration += 1
end
return x
end
# convert to a given rate type if not already a rate
__coerce_rate(x::T,cf) where {T<:Rate} = return x
__coerce_rate(x,cf) = return Rate(x,cf)
abstract type InterpolationKind end
struct QuadraticSpline <: InterpolationKind end
struct LinearSpline <: InterpolationKind end
"""
bootstrap(rates, maturities, settlement_frequency, interpolation::QuadraticSpline())
Bootstrap the rates with the given maturities, treating the rates according to the periodic frequencies in settlement_frequency.
`interpolator` is any function that will take two vectors of inputs and output points and return a function that will estimate an output given a scalar input. That is
`interpolator` should be: `interpolator(xs, ys) -> f(x)` where `f(x)` is the interpolated value of `y` at `x`.
Built in `interpolator`s in Yields are:
- `QuadraticSpline()`: Quadratic spline interpolation.
- `LinearSpline()`: Linear spline interpolation.
The default is `QuadraticSpline()`.
"""
function bootstrap(rates, maturities, settlement_frequency, interpolation::InterpolationKind=QuadraticSpline())
return _bootstrap_choose_interp(rates, maturities, settlement_frequency, interpolation)
end
# the fall-back if user provides own interpolation function
function bootstrap(rates, maturities, settlement_frequency, interpolation)
return _bootstrap_inner(rates, maturities, settlement_frequency, interpolation)
end
# dispatch on the user-exposed InterpolationKind to the right
# internally named interpolation function
function _bootstrap_choose_interp(rates, maturities, settlement_frequency, i::QuadraticSpline)
return _bootstrap_inner(rates, maturities, settlement_frequency, cubic_interp)
end
function _bootstrap_choose_interp(rates, maturities, settlement_frequency, i::LinearSpline)
return _bootstrap_inner(rates, maturities, settlement_frequency, linear_interp)
end
function _bootstrap_inner(rates, maturities, settlement_frequency, interpolation_function)
discount_vec = zeros(length(rates)) # construct a placeholder discount vector matching maturities
# we have to take the first rate as the starting point
discount_vec[1] = discount(Constant(rates[1]), maturities[1])
for t = 2:length(maturities)
if isnothing(settlement_frequency[t])
# no settlement before maturity
discount_vec[t] = discount(Constant(rates[t]), maturities[t])
else
# need to account for the interim cashflows settled
times = settlement_frequency[t]:settlement_frequency[t]:maturities[t]
cfs = [rate(rates[t]) * settlement_frequency[t] for s in times]
cfs[end] += 1
function pv(v_guess)
v = interpolation_function([[0.0]; maturities[1:t]], vcat(1.0, discount_vec[1:t-1], v_guess...))
return sum(v.(times) .* cfs)
end
target_pv = sum(map(t2 -> discount(Constant(rates[t]), t2), times) .* cfs)
root_func(v_guess) = pv(v_guess) - target_pv
root_func′(v_guess) = ForwardDiff.derivative(root_func, v_guess)
discount_vec[t] = solve(root_func, root_func′, rate(rates[t]))
end
end
zero_vec = -log.(clamp.(discount_vec,0.00001,1)) ./ maturities
return interpolation_function([0.0; maturities], [first(zero_vec); zero_vec])
end
# the ad-hoc approach to extrapoliatons is based on suggestion by author of
# BSplineKit at https://github.com/jipolanco/BSplineKit.jl/issues/19
# this should not be exposed directly to user
struct _Extrap{I,L,R}
int::I # the BSplineKit interpolation
left::L # a tuple of (boundary, extrapolation function)
right::R # a tuple of (boundary, extrapolation function)
end
function _wrap_spline(itp)
S = BSplineKit.spline(itp) # spline passing through data points
B = BSplineKit.basis(S) # B-spline basis
a, b = BSplineKit.boundaries(B) # left and right boundaries
# For now, we construct the full spline S′(x).
# There are faster ways of doing this that should be implemented...
S′ = diff(S, BSplineKit.Derivative(1))
return _Extrap(itp,
(boundary = a, func = x->S(a) + S′(a)*(x-a)),
(boundary = b, func = x->S(b) + S′(b)*(x-b)),
)
end
function _interp(e::_Extrap,x)
if x <= e.left.boundary
return e.left.func(x)
elseif x >= e.right.boundary
return e.right.func(x)
else
return e.int(x)
end
end
function linear_interp(xs, ys)
int = BSplineKit.interpolate(xs, ys, BSplineKit.BSplineOrder(2))
e = _wrap_spline(int)
return x -> _interp(e, x)
end
function cubic_interp(xs, ys)
order = min(length(xs),3) # in case the length of xs is less than the spline order
int = BSplineKit.interpolate(xs, ys, BSplineKit.BSplineOrder(order))
e = _wrap_spline(int)
return x -> _interp(e, x)
end
# used to display simple type name in show method
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/70043313/get-simple-name-of-type-in-julia?noredirect=1#comment123823820_70043313
name(::Type{T}) where {T} = (isempty(T.parameters) ? T : T.name.wrapper)
function Base.show(io::IO, curve::T) where {T<:AbstractYieldCurve}
println() # blank line for padding
r = zero(curve, 1)
ylabel = isa(r.compounding, Continuous) ? "Continuous" : "Periodic($(r.compounding.frequency))"
kind = name(typeof(curve))
l = lineplot(
t -> rate(zero(curve, t)),
0.0, #from
30.0, # to
xlabel = "time",
ylabel = ylabel,
compact = true,
name = "Zero rates",
width = 60,
title = "Yield Curve ($kind)"
)
show(io, l)
end | Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 542 | using ActuaryUtilities
@testset "ActuaryUtilities.jl integration tests" begin
cfs = [5, 5, 105]
times = [1, 2, 3]
discount_rates = [0.03,Yields.Periodic(0.03,1), Yields.Constant(0.03)]
for d in discount_rates
@test present_value(d, cfs, times) ≈ 105.65722270978935
@test duration(Macaulay(), d, cfs, times) ≈ 2.86350467067113
@test duration(d, cfs, times) ≈ 2.7801016220108057
@test convexity(d, cfs, times) ≈ 10.625805482685939
end
end
| Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 5319 | @testset "NelsonSiegelSvensson" begin
# Per this technical note, the target/source rates should be interpreted as continuous rates:
# https://www.ecb.europa.eu/stats/financial_markets_and_interest_rates/euro_area_yield_curves/html/technical_notes.pdf
# EURAAA_20191111 at https://www.ecb.europa.eu/stats/financial_markets_and_interest_rates/euro_area_yield_curves/html/index.en.html
euraaa_zeros = Continuous.([-0.602009,-0.612954,-0.621543,-0.627864,-0.632655,-0.610565,-0.569424,-0.516078,-0.455969,-0.39315,-0.33047,-0.269814,-0.21234,-0.158674,-0.109075,-0.063552,-0.021963,0.015929,0.050407,0.081771,0.110319,0.136335,0.160083,0.181804,0.201715,0.220009,0.23686,0.252419,0.26682,0.280182,0.292608,0.304191,0.31501] ./ 100)
euraaa_pars = Continuous.([-0.601861,-0.612808,-0.621403,-0.627731,-0.63251,-0.610271,-0.568825,-0.515067,-0.454526,-0.391338,-0.328412,-0.26767,-0.210277,-0.156851,-0.107632,-0.062605,-0.021601,0.015642,0.049427,0.080073,0.107892,0.133178,0.156206,0.17722,0.196444,0.214073,0.230281,0.245221,0.259027,0.271818,0.283696,0.294753,0.305069] ./ 100)
euraaa_maturities = vcat([0.25, 0.5, 0.75], 1:30)
@testset "NelsonSiegel" begin
@testset "EURAAA_20191111" begin
c_param = Yields.NelsonSiegelCurve(0.6202603126029489 /100, -1.1621281759833935 /100, -1.930016080035979 /100, 3.0)
c = Yields.Zero(NelsonSiegel(),euraaa_zeros, euraaa_maturities)
# @testset "parameter: $param" for param in [:β₀, :β₁, :β₂, :τ₁]
# @test getfield(c, param) ≈ getfield(c_param, param)
# end
@testset "zero rates: $t" for (t, r) in zip(euraaa_maturities, euraaa_zeros)
@test Yields.zero(c, t) ≈ r atol = 0.001
end
@testset "par rates: $t" for (t, r) in zip(euraaa_maturities, euraaa_pars)
@test Yields.zero(c, t) ≈ r atol = 0.001
end
@test discount(c,0) == 1.0
@test discount(c,10) ≈ 1 / accumulation(c,10)
@testset "misc constructors" begin
for u in [Yields.Forward, Yields.Zero, Yields.Par]
@test u(NelsonSiegel(), euraaa_zeros) isa Yields.AbstractYieldCurve
end
end
# test that rates as floats work
fzeros = Yields.rate.(euraaa_zeros)
c_fzero = Yields.Zero(NelsonSiegel(),fzeros, euraaa_maturities)
@test c_fzero == c
end
# Nelson-Siegel-Svensson package example at https://nelson-siegel-svensson.readthedocs.io/en/latest/usage.html
@testset "pack" begin
pack_yields = Continuous.([0.01, 0.011, 0.013, 0.016, 0.019, 0.021, 0.026, 0.03, 0.035, 0.037, 0.038, 0.04])
pack_maturities = [10e-5, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 10.0, 15.0, 20.0, 25.0, 30.0]
c_param = Yields.NelsonSiegelCurve(0.04495841387198023, -0.03537510042719209, 0.0031561222355027227, 5.0)
c = Yields.Zero(NelsonSiegel(),pack_yields, pack_maturities)
@testset "zero rates: $t" for (t, r) in zip(pack_maturities, pack_yields)
@test Yields.zero(c, t) ≈ r atol = 0.003
end
end
end
@testset "NelsonSiegelSvensson" begin
@testset "EURAAA_20191111" begin
c_zero = Yields.Zero(NelsonSiegelSvensson(),euraaa_zeros, euraaa_maturities)
c_par = Yields.Par(NelsonSiegelSvensson(),euraaa_pars, euraaa_maturities)
@testset "par and zero constructors" for c in [c_zero,c_par]
@testset "zero rates: $t" for (t, r) in zip(euraaa_maturities, euraaa_zeros)
@test Yields.zero(c, t) ≈ r atol = 0.0001
end
@testset "par rates: $t" for (t, r) in zip(euraaa_maturities, euraaa_pars)
# are the target rates on the ECB site continuous rates or periodic/bond-equivalent?
@test Yields.par(c, t) ≈ r atol = 0.0001
end
end
@testset "misc constructors" begin
for u in [Yields.Forward, Yields.Zero, Yields.Par]
@test u(NelsonSiegelSvensson(), euraaa_zeros) isa Yields.AbstractYieldCurve
end
end
# test that rates as floats work
fzeros = Yields.rate.(euraaa_zeros)
c_fzero = Yields.Zero(NelsonSiegelSvensson(),fzeros, euraaa_maturities)
@test c_fzero == c_zero
end
@testset "EURAAA_20191111 w parms given" begin
c = Yields.NelsonSiegelSvenssonCurve(0.629440 / 100, -1.218082 /100, 12.114098 /100, -14.181117 /100, 2.435976, 2.536963)
@testset "zero rates: $t" for (t, r) in zip(euraaa_maturities, euraaa_zeros)
@test Yields.zero(c, t) ≈ r atol = 0.0001
end
@testset "par rates: $t" for (t, r) in zip(euraaa_maturities, euraaa_pars)
# are the target rates on the ECB site continuous rates or periodic/bond-equivalent?
@test Yields.par(c, t) ≈ r atol = 0.0001
end
@test Yields.zero(c,30) ≈ last(euraaa_zeros) atol = 0.0001
@test discount(c,0) == 1.0
@test discount(c,10) ≈ 1 / accumulation(c,10)
end
end
end
| Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 2120 | @testset "Rate Combinations" begin
riskfree_maturities = [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0]
riskfree = [5.0, 5.8, 6.4, 6.8] ./ 100 # spot rates
rf_curve = Yields.Zero(riskfree, riskfree_maturities)
@testset "base + spread" begin
spread_maturities = [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 3.0] # different maturities
spread = [1.0, 1.8, 1.4, 1.8] ./ 100 # spot spreads
spread_curve = Yields.Zero(spread, spread_maturities)
yield = rf_curve + spread_curve
@test rate(zero(yield, 0.5)) ≈ first(riskfree) + first(spread)
@test discount(yield, 1.0) ≈ 1 / (1 + riskfree[2] + spread[2])^1
@test discount(yield, 1.5) ≈ 1 / (1 + riskfree[3] + spread[3])^1.5
end
@testset "multiplicaiton and division" begin
@testset "multiplication" begin
factor = .79
c = rf_curve * factor
(discount(c,10)-1 * factor) ≈ discount(rf_curve,10)
(accumulation(c,10)-1 * factor) ≈ accumulation(rf_curve,10)
forward(c,5,10) * factor ≈ forward(rf_curve,5,10)
Yields.par(c,10) * factor ≈ Yields.par(rf_curve,10)
c = factor * rf_curve
(discount(c,10)-1 * factor) ≈ discount(rf_curve,10)
(accumulation(c,10)-1 * factor) ≈ accumulation(rf_curve,10)
forward(c,5,10) * factor ≈ forward(rf_curve,5,10)
Yields.par(c,10) * factor ≈ Yields.par(rf_curve,10)
@test discount(Yields.Constant(0.1) * Yields.Constant(0.1),10) ≈ discount(Yields.Constant(0.01),10)
end
@testset "division" begin
factor = .79
c = rf_curve / (factor^-1)
(discount(c,10)-1 * factor) ≈ discount(rf_curve,10)
(accumulation(c,10)-1 * factor) ≈ accumulation(rf_curve,10)
forward(c,5,10) * factor ≈ forward(rf_curve,5,10)
Yields.par(c,10) * factor ≈ Yields.par(rf_curve,10)
@test discount(Yields.Constant(0.1) / Yields.Constant(0.5),10) ≈ discount(Yields.Constant(0.2),10)
@test discount(0.1 / Yields.Constant(0.5),10) ≈ discount(Yields.Constant(0.2),10)
end
end
end | Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 7797 | @testset "SmithWilson" begin
@testset "InstrumentQuotes" begin
maturities = [1.3, 2.7]
prices = [1.1, 0.8]
zcq = Yields.ZeroCouponQuote.(prices, maturities)
@test isa(first(zcq), Yields.ZeroCouponQuote)
@test_throws DimensionMismatch Yields.ZeroCouponQuote.([1.3, 2.4, 0.9], maturities)
rates = [0.4, -0.7]
swq = Yields.SwapQuote.(rates, maturities, 3)
@test first(swq).frequency == 3
@test_throws DimensionMismatch Yields.SwapQuote.([1.3, 2.4, 0.9], maturities, 3)
@test_throws DomainError Yields.SwapQuote.(rates, maturities, 0)
@test_throws DomainError Yields.SwapQuote.(rates, maturities, -2)
rates = [0.4, -0.7]
bbq = Yields.BulletBondQuote.(rates, prices, maturities, 3)
@test first(bbq).frequency == 3
@test first(bbq).yield == first(rates)
@test_throws DimensionMismatch Yields.BulletBondQuote.([1.3, 2.4, 0.9], prices, maturities, 3)
@test_throws DimensionMismatch Yields.BulletBondQuote.(rates, prices, [4.3, 5.6, 4.4, 4.4], 3)
@test first(Yields.BulletBondQuote.(rates, [5.7], maturities, 3)).price == 5.7
@test_throws DomainError Yields.BulletBondQuote.(rates, prices, maturities, 0)
@test_throws DomainError Yields.BulletBondQuote.(rates, prices, maturities, -4)
end
@testset "SmithWilson" begin
ufr = 0.03
α = 0.1
u = [5.0, 7.0]
qb = [2.3, -1.2]
# Basic behaviour
sw = Yields.SmithWilson(u, qb; ufr = ufr, α = α)
@test sw.ufr == ufr
@test sw.α == α
@test sw.u == u
@test sw.qb == qb
@test_throws DomainError Yields.SmithWilson(u, [2.4, -3.4, 8.9], ufr = ufr, α = α)
# Empty u and Qb should result in a flat yield curve
# Use this to test methods expected from <:AbstractYieldCurve
# Only discount and zero are explicitly implemented, so the others should follow automatically
sw_flat = Yields.SmithWilson(Float64[], Float64[], ufr = ufr, α = α)
@test discount(sw_flat, 10.0) == exp(-ufr * 10.0)
@test accumulation(sw_flat, 10.0) ≈ exp(ufr * 10.0)
@test rate(convert(Yields.Continuous(), zero(sw_flat, 8.0))) ≈ ufr
@test discount.(sw_flat, [5.0, 10.0]) ≈ exp.(-ufr .* [5.0, 10.0])
@test rate(convert(Yields.Continuous(), forward(sw_flat, 5.0, 8.0))) ≈ ufr
# A trivial Qb vector (=0) should result in a flat yield curve
ufr_curve = Yields.SmithWilson(u, [0.0, 0.0], ufr = ufr, α = α)
@test discount(ufr_curve, 10.0) == exp(-ufr * 10.0)
# A single payment at time 4, zero interest
curve_with_zero_yield = Yields.SmithWilson([4.0], reshape([1.0], 1, 1), [1.0], ufr = ufr, α = α)
@test discount(curve_with_zero_yield, 4.0) == 1.0
# In the long end it's still just UFR
@test rate(convert(Yields.Continuous(), forward(curve_with_zero_yield, 1000.0, 2000.0))) ≈ ufr
# Three maturities have known discount factors
times = [1.0, 2.5, 5.6]
prices = [0.9, 0.7, 0.5]
cfs = [1 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 1]
curve_three = Yields.SmithWilson(times, cfs, prices, ufr = ufr, α = α)
@test transpose(cfs) * discount.(curve_three, times) ≈ prices
# Two cash flows with payments at three times
prices = [1.0, 0.9]
cfs = [0.1 0.1
1.0 0.1
0.0 1.0]
curve_nondiag = Yields.SmithWilson(times, cfs, prices, ufr = ufr, α = α)
@test transpose(cfs) * discount.(curve_nondiag, times) ≈ prices
# Round-trip zero coupon quotes
zcq_times = [1.2, 4.5, 5.6]
zcq_prices = [1.0, 0.9, 1.2]
zcq = Yields.ZeroCouponQuote.(zcq_prices, zcq_times)
sw_zcq = Yields.SmithWilson(zcq, ufr = ufr, α = α)
@testset "ZeroCouponQuotes round-trip" for idx = 1:length(zcq_times)
@test discount(sw_zcq, zcq_times[idx]) ≈ zcq_prices[idx]
end
# uneven frequencies
swq_maturities = [1.2, 2.5, 3.6]
swq_interests = [-0.02, 0.3, 0.04]
frequency = [2, 1, 2]
swq = Yields.SwapQuote.(swq_interests, swq_maturities, frequency)
swq_times = 0.5:0.5:3.5 # Maturities are rounded down to multiples of 1/frequency, [1.0, 2.5, 3.5]
swq_payments = [
-0.01 0.3 0.02
0.99 0 0.02
0 0.3 0.02
0 0 0.02
0 1.3 0.02
0 0 0.02
0 0 1.02
]
# Round-trip swap quotes
swq_maturities = [1.2, 2.5, 3.6]
swq_interests = [-0.02, 0.3, 0.04]
frequency = 2
swq = Yields.SwapQuote.(swq_interests, swq_maturities, frequency)
swq_times = 0.5:0.5:3.5 # Maturities are rounded down to multiples of 1/frequency, [1.0, 2.5, 3.5]
swq_payments = [-0.01 0.15 0.02
0.99 0.15 0.02
0.0 0.15 0.02
0.0 0.15 0.02
0.0 1.15 0.02
0.0 0.0 0.02
0.0 0.0 1.02]
sw_swq = Yields.SmithWilson(swq, ufr = ufr, α = α)
@testset "SwapQuotes round-trip" for swapIdx = 1:length(swq_interests)
@test sum(discount.(sw_swq, swq_times) .* swq_payments[:, swapIdx]) ≈ 1.0
end
@test Yields.__ratetype(sw_swq) == Yields.Rate{Float64,typeof(Yields.DEFAULT_COMPOUNDING)}
# Round-trip bullet bond quotes (reuse data from swap quotes)
bbq_prices = [1.3, 0.1, 4.5]
bbq = Yields.BulletBondQuote.(swq_interests, bbq_prices, swq_maturities, frequency)
sw_bbq = Yields.SmithWilson(bbq, ufr = ufr, α = α)
@testset "BulletBondQuotes round-trip" for bondIdx = 1:length(swq_interests)
@test sum(discount.(sw_bbq, swq_times) .* swq_payments[:, bondIdx]) ≈ bbq_prices[bondIdx]
end
@testset "SW ForwardStarting" begin
fwd_time = 1.0
fwd = Yields.ForwardStarting(sw_swq, fwd_time)
@test discount(fwd, 3.7) ≈ discount(sw_swq, fwd_time, fwd_time + 3.7)
end
# EIOPA risk free rate (no VA), 31 August 2021.
# https://www.eiopa.europa.eu/sites/default/files/risk_free_interest_rate/eiopa_rfr_20210831.zip
eiopa_output_qb = [-0.59556534586390800
-0.07442224713453920
-0.34193181987682400
1.54054875814153000
-2.15552046042343000
0.73559290752221900
1.89365225129089000
-2.75927773116240000
2.24893737130629000
-1.51625404117395000
0.19284859623817400
1.13410725406271000
0.00153268224642171
0.00147942301778158
-1.85022125156483000
0.00336230229850928
0.00324546553910162
0.00313268874430658
0.00302383083427276
1.36047951448615000]
eiopa_output_u = 1:20
eiopa_ufr = log(1.036)
eiopa_α = 0.133394
sw_eiopa_expected = Yields.SmithWilson(eiopa_output_u, eiopa_output_qb; ufr = eiopa_ufr, α = eiopa_α)
eiopa_eurswap_maturities = [1:12; 15; 20]
eiopa_eurswap_rates = [-0.00615, -0.00575, -0.00535, -0.00485, -0.00425, -0.00375, -0.003145,
-0.00245, -0.00185, -0.00125, -0.000711, -0.00019, 0.00111, 0.00215] # Reverse engineered from output curve. This is the full precision of market quotes.
eiopa_eurswap_quotes = Yields.SwapQuote.(eiopa_eurswap_rates, eiopa_eurswap_maturities, 1)
sw_eiopa_actual = Yields.SmithWilson(eiopa_eurswap_quotes, ufr = eiopa_ufr, α = eiopa_α)
@testset "Match EIOPA calculation" begin
@test sw_eiopa_expected.u ≈ sw_eiopa_actual.u
@test sw_eiopa_expected.qb ≈ sw_eiopa_actual.qb
end
end
end | Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 710 | @testset "SmoothingSpline" begin
@testset "SmoothingSpline" begin
# EURAAA_20191111
@testset "EURAAA_20191111" begin
euraaa_yields = [-0.602, -0.6059, -0.6096, -0.613, -0.6215, -0.6279, -0.6341, -0.6327, -0.6106, -0.5694, -0.5161, -0.456, -0.3932, -0.3305, -0.2698, -0.2123, -0.1091, 0.0159, 0.0818, 0.1601, 0.2524, 0.315]
euraaa_maturities = [0.25, 0.333, 0.417, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.5, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 15, 17, 20, 25, 30]
ss_param = SmoothingSpline(0.6440719852424944, -1.2135915867261, -1.8281745438894712, 0.1)
ss = est_ss_params(euraaa_yields, euraaa_maturities)
@test ss = ss_param
end
end
end
| Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 13594 | @testset "bootstrapped class of curves" begin
@testset "constant curve and rate -> Constant" begin
yield = Yields.Constant(0.05)
rate = Yields.Yields.Rate(0.05, Yields.Periodic(1))
@test Yields.zero(yield, 1) == Yields.Rate(0.05, Yields.Periodic(1))
@test Yields.zero(Yields.Constant(Yields.Periodic(0.05,2)), 10) == Yields.Rate(0.05, Yields.Periodic(2))
@test Yields.zero(yield, 5, Yields.Periodic(2)) == convert(Yields.Periodic(2), Yields.Rate(0.05, Yields.Periodic(1)))
@testset "constant discount time: $time" for time in [0, 0.5, 1, 10]
@test discount(yield, time) ≈ 1 / (1.05)^time
@test discount(yield, 0, time) ≈ 1 / (1.05)^time
@test discount(yield, 3, time + 3) ≈ 1 / (1.05)^time
end
@testset "constant discount scalar time: $time" for time in [0, 0.5, 1, 10]
@test discount(0.05, time) ≈ 1 / (1.05)^time
end
@testset "constant accumulation scalar time: $time" for time in [0, 0.5, 1, 10]
@test accumulation(0.05, time) ≈ 1 * (1.05)^time
end
@testset "broadcasting" begin
@test all(discount.(yield, [1, 2, 3]) .≈ 1 ./ 1.05 .^ (1:3))
@test all(accumulation.(yield, [1, 2, 3]) .≈ 1.05 .^ (1:3))
end
@testset "constant accumulation time: $time" for time in [0, 0.5, 1, 10]
@test accumulation(yield, time) ≈ 1 * 1.05^time
@test accumulation(yield, 0, time) ≈ 1 * 1.05^time
@test accumulation(yield, 3, time + 3) ≈ 1 * 1.05^time
end
yield_2x = yield + yield
yield_add = yield + 0.05
add_yield = 0.05 + yield
@testset "constant discount added" for time in [0, 0.5, 1, 10]
@test discount(yield_2x, time) ≈ 1 / (1.1)^time
@test discount(yield_add, time) ≈ 1 / (1.1)^time
@test discount(add_yield, time) ≈ 1 / (1.1)^time
end
yield_1bps = yield - Yields.Constant(0.04)
yield_minus = yield - 0.01
minus_yield = 0.05 - Yields.Constant(0.01)
@testset "constant discount subtraction" for time in [0, 0.5, 1, 10]
@test discount(yield_1bps, time) ≈ 1 / (1.01)^time
@test discount(yield_minus, time) ≈ 1 / (1.04)^time
@test discount(minus_yield, time) ≈ 1 / (1.04)^time
end
end
@testset "short curve" begin
z = Yields.Zero([0.0, 0.05], [1, 2])
@test zero(z, 1) ≈ Periodic(0.00,1)
@test discount(z, 1) ≈ 1.00
@test zero(z, 2) ≈ Periodic(0.05,1)
# test no times constructor
z = Yields.Zero([0.0, 0.05])
@test zero(z, 1) ≈ Periodic(0.00,1)
@test discount(z, 1) ≈ 1.00
@test zero(z, 2) ≈ Periodic(0.05,1)
end
@testset "Step curve" begin
y = Yields.Step([0.02, 0.05], [1, 2])
@test zero(y, 0.5) ≈ Periodic(0.02,1)
@test discount(y, 0.0) ≈ 1
@test discount(y, 0.5) ≈ 1 / (1.02)^(0.5)
@test discount(y, 1) ≈ 1 / (1.02)^(1)
@test discount(y, 10) ≈ 1 / (1.02)^(1) / (1.05)^(9)
@test zero(y, 1) ≈ Periodic(0.02,1)
@test discount(y, 2) ≈ 1 / (1.02) / 1.05
@test discount(y, 2) ≈ 1 / (1.02) / 1.05
@test discount(y, 1.5) ≈ 1 / (1.02) / 1.05^(0.5)
@testset "broadcasting" begin
@test all(discount.(y, [1, 2]) .== [1 / 1.02, 1 / 1.02 / 1.05])
@test all(accumulation.(y, [1, 2]) .== [1.02, 1.02 * 1.05])
end
y = Yields.Step([0.02, 0.07])
@test zero(y, 0.5) ≈ Periodic(0.02,1)
@test zero(y, 1) ≈ Periodic(0.02,1)
@test zero(y, 1.5) ≈ Periodic(accumulation(y,1.5)^(1/1.5)-1,1)
end
@testset "Salomon Understanding the Yield Curve Pt 1 Figure 9" begin
maturity = collect(1:10)
par = [6.0, 8.0, 9.5, 10.5, 11.0, 11.25, 11.38, 11.44, 11.48, 11.5] ./ 100
spot = [6.0, 8.08, 9.72, 10.86, 11.44, 11.71, 11.83, 11.88, 11.89, 11.89] ./ 100
# the forwards for 7+ have been adjusted from the table - perhaps rounding issues are exacerbated
# in the text? forwards for <= 6 matched so reasonably confident that the algo is correct
# fwd = [6.,10.2,13.07,14.36,13.77,13.1,12.55,12.2,11.97,11.93] ./ 100 # from text
fwd = [6.0, 10.2, 13.07, 14.36, 13.77, 13.1, 12.61, 12.14, 12.05, 11.84] ./ 100 # modified
y = Yields.Par(Periodic(1).(par), maturity)
@testset "quadratic UTYC Figure 9 par -> spot : $mat" for mat in maturity
@test zero(y, mat) ≈ Periodic(spot[mat],1) atol = 0.0001
@test forward(y, mat - 1) ≈ Yields.Periodic(fwd[mat], 1) atol = 0.0001
end
y = Yields.Par(Bootstrap(LinearSpline()),Yields.Rate.(par, Yields.Periodic(1)), maturity)
@testset "linear UTYC Figure 9 par -> spot : $mat" for mat in maturity
@test zero(y, mat) ≈ Periodic(spot[mat],1) atol = 0.0001
@test forward(y, mat - 1) ≈ Yields.Periodic(fwd[mat], 1) atol = 0.0001
end
end
@testset "Hull" begin
# Par Yield, pg 85
c = Yields.Par(Yields.Periodic.([0.0687,0.0687],2), [2,3])
@test Yields.par(c,2) ≈ Yields.Periodic(0.0687,2) atol = 0.00001
end
@testset "simple rate and forward" begin
# Risk Managment and Financial Institutions, 5th ed. Appendix B
maturity = [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0]
zero = [5.0, 5.8, 6.4, 6.8] ./ 100
curve = Yields.Zero(zero, maturity)
for curve in [Yields.Zero(zero, maturity),Yields.Zero(Bootstrap(LinearSpline()),zero, maturity),Yields.Zero(Bootstrap(QuadraticSpline()),zero, maturity)]
@test discount(curve, 0) ≈ 1
@test discount(curve, 1) ≈ 1 / (1 + zero[2])
@test discount(curve, 2) ≈ 1 / (1 + zero[4])^2
@test forward(curve, 0.5, 1.0) ≈ Yields.Periodic(6.6 / 100, 1) atol = 0.001
@test forward(curve, 1.0, 1.5) ≈ Yields.Periodic(7.6 / 100, 1) atol = 0.001
@test forward(curve, 1.5, 2.0) ≈ Yields.Periodic(8.0 / 100, 1) atol = 0.001
end
y = Yields.Zero(zero)
@test discount(y, 1) ≈ 1 / 1.05
@test discount(y, 2) ≈ 1 / 1.058^2
@testset "broadcasting" begin
@test all(discount.(y, [1, 2]) .≈ [1 / 1.05, 1 / 1.058^2])
@test all(accumulation.(y, [1, 2]) .≈ [1.05, 1.058^2])
end
end
@testset "Forward Rates" begin
# Risk Managment and Financial Institutions, 5th ed. Appendix B
forwards = [0.05, 0.04, 0.03, 0.08]
curve = Yields.Forward(forwards, [1, 2, 3, 4])
@testset "discounts: $t" for (t, r) in enumerate(forwards)
@test discount(curve, t) ≈ reduce((v, r) -> v / (1 + r), forwards[1:t]; init = 1.0)
end
# test constructor without times
curve = Yields.Forward(forwards)
@testset "discounts: $t" for (t, r) in enumerate(forwards)
@test discount(curve, t) ≈ reduce((v, r) -> v / (1 + r), forwards[1:t]; init = 1.0)
end
@test accumulation(curve, 0, 1) ≈ 1.05
@test accumulation(curve, 1, 2) ≈ 1.04
@test accumulation(curve, 0, 2) ≈ 1.04 * 1.05
# test construction using vector of reals and of Rates
@test discount(Yields.Forward(forwards), 1) > discount(Yields.Forward(Yields.Continuous.(forwards)), 1)
@testset "broadcasting" begin
@test all(accumulation.(curve, [1, 2]) .≈ [1.05, 1.04 * 1.05])
@test all(discount.(curve, [1, 2]) .≈ 1 ./ [1.05, 1.04 * 1.05])
end
# addition / subtraction
@test discount(curve + 0.1, 1) ≈ 1 / 1.15
@test discount(curve - 0.03, 1) ≈ 1 / 1.02
@testset "with specified timepoints" begin
i = [0.0, 0.05]
times = [0.5, 1.5]
y = Yields.Forward(i, times)
@test discount(y, 0.5) ≈ 1 / 1.0^0.5
@test discount(y, 1.5) ≈ 1 / 1.0^0.5 / 1.05^1
end
end
@testset "forwardcurve" begin
maturity = [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0]
zeros = [5.0, 5.8, 6.4, 6.8] ./ 100
curve = Yields.Zero(zeros, maturity)
fwd = Yields.ForwardStarting(curve, 1.0)
@test discount(fwd, 0) ≈ 1
@test discount(fwd, 0.5) ≈ discount(curve, 1, 1.5)
@test discount(fwd, 1) ≈ discount(curve, 1, 2)
@test accumulation(fwd, 1) ≈ accumulation(curve, 1, 2)
@test zero(fwd,1) ≈ forward(curve,1,2)
@test zero(fwd,1,Yields.Continuous()) ≈ convert(Yields.Continuous(),forward(curve,1,2))
end
@testset "actual cmt treasury" begin
# Fabozzi 5-5,5-6
cmt = [5.25, 5.5, 5.75, 6.0, 6.25, 6.5, 6.75, 6.8, 7.0, 7.1, 7.15, 7.2, 7.3, 7.35, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6, 7.6, 7.7, 7.8] ./ 100
mats = collect(0.5:0.5:10.0)
targets = [5.25, 5.5, 5.76, 6.02, 6.28, 6.55, 6.82, 6.87, 7.09, 7.2, 7.26, 7.31, 7.43, 7.48, 7.54, 7.67, 7.8, 7.79, 7.93, 8.07] ./ 100
target_periodicity = fill(2, length(mats))
target_periodicity[2] = 1 # 1 year is a no-coupon, BEY yield, the rest are semiannual BEY
@testset "curve bootstrapping choices" for curve in [Yields.CMT(cmt, mats), Yields.CMT(Bootstrap(LinearSpline()),cmt, mats), Yields.CMT(Bootstrap(QuadraticSpline()),cmt, mats)]
@testset "Fabozzi bootstrapped rates" for (r, mat, target, tp) in zip(cmt, mats, targets, target_periodicity)
@test rate(zero(curve, mat, Yields.Periodic(tp))) ≈ target atol = 0.0001
end
@testset "Fabozzi bootstrapped rates" for (r, mat, target, tp) in zip(cmt, mats, targets, target_periodicity)
@test rate(zero(curve, mat, Yields.Periodic(tp))) ≈ target atol = 0.0001
end
@testset "Fabozzi bootstrapped rates" for (r, mat, target, tp) in zip(cmt, mats, targets, target_periodicity)
@test rate(zero(curve, mat, Yields.Periodic(tp))) ≈ target atol = 0.0001
end
end
# Hull, problem 4.34
adj = ((1 + 0.051813 / 2)^2 - 1) * 100
cmt = [4.0816, adj, 5.4986, 5.8620] ./ 100
mats = [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0]
curve = Yields.CMT(cmt, mats)
targets = [4.0405, 5.1293, 5.4429, 5.8085] ./ 100
@testset "Hull bootstrapped rates" for (r, mat, target) in zip(cmt, mats, targets)
@test rate(zero(curve, mat, Yields.Continuous())) ≈ target atol = 0.001
end
# test that showing the curve doesn't error
@test length(repr(curve)) > 0
# # https://www.federalreserve.gov/pubs/feds/2006/200628/200628abs.html
# # 2020-04-02 data
# cmt = [0.0945,0.2053,0.4431,0.7139,0.9724,1.2002,1.3925,1.5512,1.6805,1.7853,1.8704,1.9399,1.9972,2.045,2.0855,2.1203,2.1509,2.1783,2.2031,2.2261,2.2477,2.2683,2.2881,2.3074,2.3262,2.3447,2.3629,2.3809,2.3987,2.4164] ./ 100
# mats = collect(1:30)
# curve = Yields.USCMT(cmt,mats)
# target = [0.0945,0.2053,0.444,0.7172,0.9802,1.2142,1.4137,1.5797,1.7161,1.8275,1.9183,1.9928,2.0543,2.1056,2.1492,2.1868,2.2198,2.2495,2.2767,2.302,2.3261,2.3494,2.372,2.3944,2.4167,2.439,2.4614,2.4839,2.5067,2.5297] ./ 100
# @testset "FRB data" for (t,mat,target) in zip(1:length(mats),mats,target)
# @show mat
# if mat >= 1
# @test rate(zero(curve,mat, Yields.Continuous())) ≈ target[mat] atol=0.001
# end
# end
end
@testset "OIS" begin
ois = [1.8, 2.0, 2.2, 2.5, 3.0, 4.0] ./ 100
mats = [1 / 12, 1 / 4, 1 / 2, 1, 2, 5]
targets = [0.017987, 0.019950, 0.021880, 0.024693, 0.029994, 0.040401]
curve = Yields.OIS(ois, mats)
@testset "bootstrapped rates" for (r, mat, target) in zip(ois, mats, targets)
@test rate(zero(curve, mat, Yields.Continuous())) ≈ target atol = 0.001
end
curve = Yields.OIS(Bootstrap(LinearSpline()),ois, mats)
@testset "bootstrapped rates" for (r, mat, target) in zip(ois, mats, targets)
@test rate(zero(curve, mat, Yields.Continuous())) ≈ target atol = 0.001
end
end
@testset "par" begin
@testset "first payment logic" begin
ct = Yields.coupon_times
@test ct(0.5,1) ≈ 0.5:1:0.5
@test ct(1.5,1) ≈ 0.5:1:1.5
@test ct(0.75,1) ≈ 0.75:1:0.75
@test ct(1,1) ≈ 1:1:1
@test ct(1,2) ≈ 0.5:0.5:1.0
@test ct(0.5,2) ≈ 0.5:0.5:0.5
@test ct(1.5,2) ≈ 0.5:0.5:1.5
end
# https://quant.stackexchange.com/questions/57608/how-to-compute-par-yield-from-zero-rate-curve
c = Yields.Zero(Yields.Continuous.([0.02,0.025,0.03,0.035]),0.5:0.5:2)
@test Yields.par(c,2) ≈ Yields.Periodic(0.03508591,2) atol = 0.000001
c = Yields.Constant(0.04)
@testset "misc combinations" for t in 0.5:0.5:5
@test Yields.par(c,t;frequency=1) ≈ Yields.Periodic(0.04,1)
@test Yields.par(c,t) ≈ Yields.Periodic(0.04,1)
@test Yields.par(c,t,frequency=4) ≈ Yields.Periodic(0.04,1)
end
@test Yields.par(c,0.6) ≈ Yields.Periodic(0.04,1)
@testset "round trip" begin
maturity = collect(1:10)
par = [6.0, 8.0, 9.5, 10.5, 11.0, 11.25, 11.38, 11.44, 11.48, 11.5] ./ 100
curve = Yields.Par(par,maturity)
for (p,m) in zip(par,maturity)
@test Yields.par(curve,m) ≈ Yields.Periodic(p,2) atol = 0.001
end
end
end
end
| Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 827 | # test extending type and that various generic methods are defined
# to fulfill the API of AbstractYieldCurve
@testset "generic methods and type extensions" begin
struct MyYield <: Yields.AbstractYieldCurve
rate
end
Yields.discount(c::MyYield,to) = exp(-c.rate * to)
# Base.zero(c::MyYield,to) = Continuous(c.rate)
my = MyYield(0.05)
@test zero(my,1) ≈ Continuous(0.05)
@test Yields.forward(my,1) ≈ Continuous(0.05)
@test Yields.forward(my,1,2) ≈ Continuous(0.05)
@test discount(my,1,2) ≈ exp(-0.05*1)
@test accumulation(my,1,2) ≈ exp(0.05*1)
@test accumulation(my,1) ≈ exp(0.05*1)
@test Yields.__ratetype(my) == Yields.Rate{Float64,Continuous}
@test Yields.FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency(my) == Continuous()
@test Yields.par(my,1) |> Yields.rate > 0
end | Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 1877 | @testset "Rate type" begin
default = Yields.Rate{Float64,typeof(Yields.DEFAULT_COMPOUNDING)}
y = Yields.Constant(0.05)
@test Yields.__ratetype(y) == Yields.Rate{Float64, Periodic}
@test Yields.__ratetype(typeof(Periodic(0.05,2))) == Yields.Rate{Float64, Periodic}
@test Yields.FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency(y) == Periodic(1)
y = Yields.Constant(Continuous(0.05))
@test Yields.__ratetype(y) == Yields.Rate{Float64, Continuous}
@test Yields.__ratetype(typeof(Continuous(0.05))) == Yields.Rate{Float64, Continuous}
@test Yields.FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency(y) == Continuous()
y = Yields.Step([0.02,0.05], [1,2])
@test Yields.__ratetype(y) == Yields.Rate{Float64, Periodic}
@test Yields.FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency(y) == Periodic(1)
y = Yields.Forward( [0.01,0.02,0.03] )
@test Yields.__ratetype(y) == default
rates =[0.01, 0.01, 0.03, 0.05, 0.07, 0.16, 0.35, 0.92, 1.40, 1.74, 2.31, 2.41] ./ 100
mats = [1/12, 2/12, 3/12, 6/12, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, 30]
y = Yields.CMT(rates,mats)
@test Yields.__ratetype(y) == default
@test Yields.FinanceCore.CompoundingFrequency(y) == Continuous()
combination = y + y
@test Yields.__ratetype(combination) == default
end
@testset "type coercion" begin
@test Yields.__coerce_rate(0.05, Periodic(1)) == Periodic(0.05,1)
@test Yields.__coerce_rate(Periodic(0.05,12), Periodic(1)) == Periodic(0.05,12)
end
#Issue #117
@testset "DecFP" begin
import DecFP
@test Yields.Periodic(1/DecFP.Dec64(1/6)) == Yields.Periodic(6)
mats = convert.(DecFP.Dec64,[1/12, 2/12, 3/12, 6/12, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, 30])
rates = convert.(DecFP.Dec64,[0.01, 0.01, 0.03, 0.05, 0.07, 0.16, 0.35, 0.92, 1.40, 1.74, 2.31, 2.41] ./ 100)
y = Yields.CMT(rates,mats)
@test y isa Yields.AbstractYieldCurve
end | Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | code | 268 | using Yields
using Test
include("generic.jl")
include("bootstrap.jl")
include("RateCombination.jl")
include("SmithWilson.jl")
include("ActuaryUtilities.jl")
include("misc.jl")
include("NelsonSiegelSvensson.jl")
#TODO EconomicScenarioGenerators.jl integration tests
| Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | docs | 8942 | # Yields.jl
[](https://JuliaActuary.github.io/Yields.jl/stable)
[](https://JuliaActuary.github.io/Yields.jl/dev)
[](https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl/actions)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl)
**Yields.jl** provides a simple interface for constructing, manipulating, and using yield curves for modeling purposes.
It's intended to provide common functionality around modeling interest rates, spreads, and miscellaneous yields across the JuliaActuary ecosystem (though not limited to use in JuliaActuary packages).
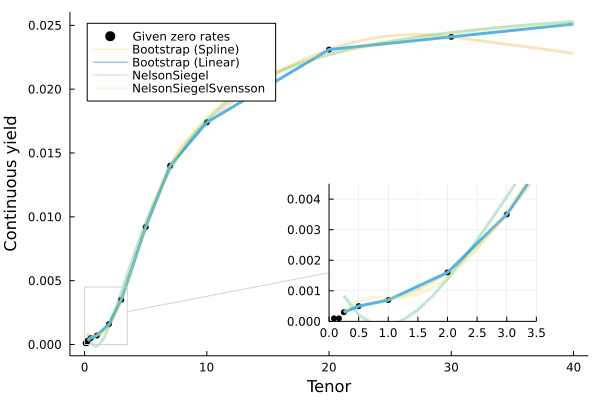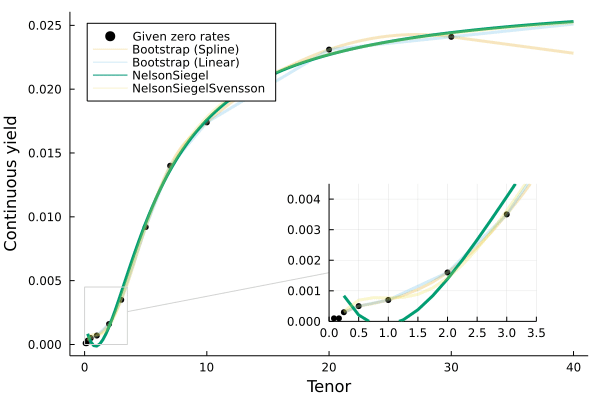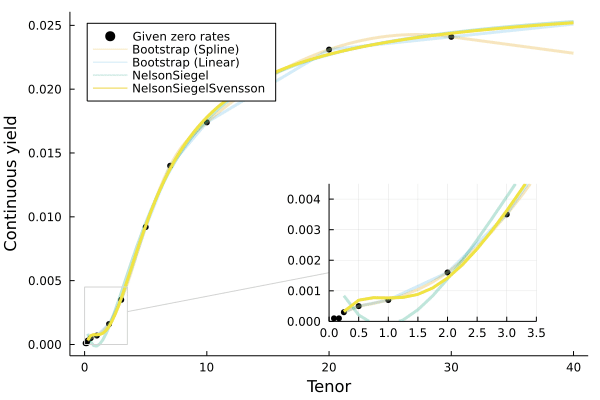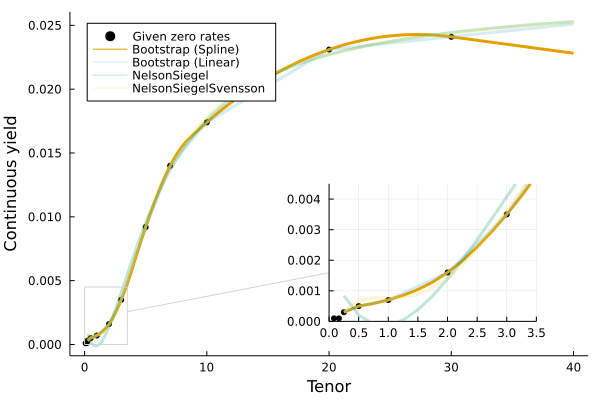
## QuickStart
```julia
using Yields
riskfree_maturities = [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0]
riskfree = [5.0, 5.8, 6.4, 6.8] ./ 100 #spot rates, annual effective if unspecified
spread_maturities = [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 3.0] # different maturities
spread = [1.0, 1.8, 1.4, 1.8] ./ 100 # spot spreads
rf_curve = Yields.Zero(riskfree,riskfree_maturities)
spread_curve = Yields.Zero(spread,spread_maturities)
yield = rf_curve + spread_curve # additive combination of the two curves
discount(yield,1.5) # 1 / (1 + 0.064 + 0.014) ^ 1.5
```
## Usage
### Rates
Rates are types that wrap scalar values to provide information about how to determine `discount` and `accumulation` factors.
There are two `CompoundingFrequency` types:
- `Yields.Periodic(m)` for rates that compound `m` times per period (e.g. `m` times per year if working with annual rates).
- `Yields.Continuous()` for continuously compounding rates.
#### Examples
```julia
Continuous(0.05) # 5% continuously compounded
Periodic(0.05,2) # 5% compounded twice per period
```
These are both subtypes of the parent `Rate` type and are instantiated as:
```julia
Rate(0.05,Continuous()) # 5% continuously compounded
Rate(0.05,Periodic(2)) # 5% compounded twice per period
```
Broadcast over a vector to create `Rates` with the given compounding:
```julia
Periodic.([0.02,0.03,0.04],2)
Continuous.([0.02,0.03,0.04])
```
Rates can also be constructed by specifying the `CompoundingFrequency` and then passing a scalar rate:
```julia
Periodic(1)(0.05)
Continuous()(0.05)
```
#### Conversion
Convert rates between different types with `convert`. E.g.:
```julia-repl
r = Rate(Yields.Periodic(12),0.01) # rate that compounds 12 times per rate period (ie monthly)
convert(Yields.Periodic(1),r) # convert monthly rate to annual effective
convert(Yields.Continuous(),r) # convert monthly rate to continuous
```
#### Arithmetic
Adding, substracting, multiplying, dividing, and comparing rates is supported.
### Curves
There are a several ways to construct a yield curve object. If `maturities` is omitted, the method will assume that the timepoints corresponding to each rate are the indices of the `rates` (e.g. generally one to the length of the array for standard, non-offset arrays).
#### Fitting Curves to Rates
There is a set of constructor methods which will return a yield curve calibrated to the given inputs.
- `Yields.Zero(rates,maturities)` using a vector of zero rates (sometimes referred to as "spot" rates)
- `Yields.Forward(rates,maturities)` using a vector of forward rates
- `Yields.Par(rates,maturities)` takes a series of yields for securities priced at par. Assumes that maturities <= 1 year do not pay coupons and that after one year, pays coupons with frequency equal to the CompoundingFrequency of the corresponding rate (2 by default).
- `Yields.CMT(rates,maturities)` takes the most commonly presented rate data (e.g. [Treasury.gov](https://www.treasury.gov/resource-center/data-chart-center/interest-rates/Pages/TextView.aspx?data=yield)) and bootstraps the curve given the combination of bills and bonds.
- `Yields.OIS(rates,maturities)` takes the most commonly presented rate data for overnight swaps and bootstraps the curve. Rates assume a single settlement for <1 year and quarterly settlements for 1 year and above.
##### Fitting techniques
There are multiple curve fitting methods available:
- `Boostrap(interpolation_method)` (the default method)
- where `interpolation` can be one of the built-in `QuadraticSpline()` (the default) or `LinearSpline()`, or a user-supplied function.
- Two methods from the Nelson-Siegel-Svensson family, where τ_initial is the starting τ point for the fitting optimization routine:
- `NelsonSiegel(τ_initial=1.0)`
- `NelsonSiegelSvensson(τ_initial=[1.0,1.0])`
To specify which fitting method to use, pass the object to as the first parameter to the above set of constructors, for example: `Yields.Par(NelsonSiegel(),rates,maturities)`.
#### Kernel Methods
- `Yields.SmithWilson` curve (used for [discounting in the EU Solvency II framework](https://www.eiopa.europa.eu/sites/default/files/risk_free_interest_rate/12092019-technical_documentation.pdf)) can be constructed either directly by specifying its inner representation or by calibrating to a set of cashflows with known prices.
- These cashflows can conveniently be constructed with a Vector of `Yields.ZeroCouponQuote`s, `Yields.SwapQuote`s, or `Yields.BulletBondQuote`s.
#### Other Curves
- `Yields.Constant(rate)` takes a single constant rate for all times
- `Yields.Step(rates,maturities)` doesn't interpolate - the rate is flat up to the corresponding time in `times`
### Functions
Most of the above yields have the following defined (goal is to have them all):
- `discount(curve,from,to)` or `discount(curve,to)` gives the discount factor
- `accumulation(curve,from,to)` or `accumulation(curve,to)` gives the accumulation factor
- `zero(curve,time)` or `zero(curve,time,CompoundingFrequency)` gives the zero-coupon spot rate for the given time.
- `forward(curve,from,to)` gives the zero rate between the two given times
- `par(curve,time)` gives the coupon-paying par equivalent rate for the given time.
### Combinations
Different yield objects can be combined with addition or subtraction. See the [Quickstart](#quickstart) for an example.
When adding a `Yields.AbstractYield` with a scalar or vector, that scalar or vector will be promoted to a yield type via [`Yield()`](#yield). For example:
```julia
y1 = Yields.Constant(0.05)
y2 = y1 + 0.01 # y2 is a yield of 0.06
```
### Forward Starting Curves
Constructed curves can be shifted so that a future timepoint becomes the effective time-zero for a said curve.
```julia-repl
julia> zero = [5.0, 5.8, 6.4, 6.8] ./ 100
julia> maturity = [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0]
julia> curve = Yields.Zero(zero, maturity)
julia> fwd = Yields.ForwardStarting(curve, 1.0)
julia> discount(curve,1,2)
0.9275624570410582
julia> discount(fwd,1) # `curve` has effectively been reindexed to `1.0`
0.9275624570410582
```
## Exported vs Un-exported Functions
Generally, CamelCase methods which construct a datatype are exported as they are unlikely to conflict with other parts of code that may be written. For example, `rate` is un-exported (it must be called with `Yields.rate(...)`) because `rate` is likely a very commonly defined variable within actuarial and financial contexts and there is a high risk of conflicting with defined variables.
Consider using `import Yields` which would require qualifying all methods, but alleviates any namespace conflicts and has the benefit of being explicit about the calls (internally we prefer this in the package design to keep dependencies and their usage clear).
## Internals
For time-variant yields (ie yield *curves*), the inputs are converted to spot rates and interpolated using quadratic B-splines by default (see documentation for alternatives, such as linear interpolations).
### Combination Implementation
[Combinations](#combinations) track two different curve objects and are not combined into a single underlying data structure. This means that you may achieve better performance if you combine the rates before constructing a `Yields` representation. The exception to this is `Constant` curves, which *do* get combined into a single structure that is as performant as pre-combined rate structure.
## Related Packages
- [**`InterestRates.jl`**](https://github.com/felipenoris/InterestRates.jl) specializes in fast rate calculations aimed at valuing fixed income contracts, with business-day-level accuracy.
- Comparative comments: **`Yields.jl`** does not try to provide as precise controls over the timing, structure, and interpolation of the curve. Instead, **`Yields.jl`** provides a minimal, but flexible and intuitive interface for common modeling needs.
| Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | docs | 1358 | # Yields API Reference
Please [open an issue](https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl/issues) if you encounter any issues or confusion with the package.
## Rate Types
When JuliaActuary packages return a rate, they will be of a `Rate` type, such as `Rate(0.05,Periodic(2))` for a 5% rate compounded twice per period. It is recommended to keep rates typed and use them throughout the ecosystem without modifying it.
For example, if we construct a curve like this:
```julia
# 2021-03-31 rates from Treasury.gov
rates =[0.01, 0.01, 0.03, 0.05, 0.07, 0.16, 0.35, 0.92, 1.40, 1.74, 2.31, 2.41] ./ 100
mats = [1/12, 2/12, 3/12, 6/12, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, 30]
curve = Yields.CMT(rates,mats)
```
Then rates from this curve will be typed. For example:
```julia
z = zero(c,10)
```
Now, `z` will be: `Yields.Rate{Float64, Continuous}(0.01779624378877313, Continuous())`
This `Rate` has both the rate an the compounding convention embedded in the datatype.
You can now use that rate throughout the JuliaActuary ecosystem, such as with ActuaryUtilities.jl:
```julia
using ActuaryUtilities
present_values(z,cashflows)
```
If you need to extract the rate for some reason, you can get the rate by calling `Yields.rate(...)`. Using the above example, `Yields.rate(z)` will return `0.01779624378877313`.
```@index
```
```@autodocs
Modules = [Yields]
```
| Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | docs | 3243 | ```@meta
CurrentModule = Yields
```
# Developer Notes
## Custom Curve Types
Types that subtype `Yields.AbstractYieldCurve` should implement a few key methods:
- `discount(curve,to)` should return the discount factor for the given curve through time `to`
For example:
```julia
struct MyYield <: Yields.AbstractYieldCurve
rate
end
Yields.discount(c::MyYield,to) = exp(-c.rate * to)
```
By defining the `discount` method as above and subtyping `Yields.AbstractYieldCurve`, Yields.jl has generic functions that will work:
- `zero(curve,to)` returns the zero rate at time `to`
- `discount(curve,from,to)` is the discount factor between the two timepoints
- `forward(curve,to)` and `forward(curve,from,to)` is the forward zero rate
- `accumulation(curve,to)` and `accumulation(curve,from,to)` is the inverse of the discount factor.
If creating a new type of curve, you may find that it's most natural to define one of the functions versus the other, or that you may define specialized functions which are more performant than the generic implementations.
### `__ratetype`
In some contexts, such as creating performant iteration of curves in [EconomicScenarioGenerators.jl](https://github.com/JuliaActuary/EconomicScenarioGenerators.jl), Julia wants to know what type should be expected given an object type. For this reason, we define an internal, un-exported function which returns the `Rate` type expected given a Yield curve.
Sometimes it is most natural or convenient to expect a certain kind of `Rate` from a given curve. In many advanced use-cases (differentiation, stochastic rates), `Continuous` rates are most natural. For this reason, the `DEFAULT_COMPOUNDING` constant within Yields.jl is $(Yields.DEFAULT_COMPOUNDING). Two comments on this:
1. Becuase Yields.jl returns `Rate` types (e.g. `Rate(0.05,Continuous()`) instead of single scalars (e.g. `0.05`) functions within the `JuliaActuary` universe (e.g. `ActuaryUtilities.present_value) know how to treat rates differently and in general users should not ever need to worry about converting between different compounding conventions.
2. Developers implementing new `AbstractYieldCurve` types can define their own default. For example, using the `MyYield` example above:
- `__ratetype(::Type{MyYield}) = Yields.Rate{Float64, Continuous}`
If the `CompoundingFrequency` is `Continuous`, then it's currently not necessary to define `__ratetype`, as it will fall back onto the generic method defined for `AbstractYieldCurve`s.
If the preferred compounding frequency is `Periodic`, then you must either define the methods (`zero`, `forward`,...) for your type or to use the generic methods then you must define `Yields.CompoundingFrequency(curve::MyCurve)` to return the `Periodic` compounding datatype of the rates to return.
For example, if we wanted `MyCurve` to return `Periodic(1)` rates, then we would define:
`Yields.CompoundingFrequency(curve::MyCurve) = Periodic(1)`
This latter step is necessary and distinct from `__ratetype`. This is due to `__ratetype` relying on type-only information. The `Periodic` type contains as a datafield the compounding frequency. Therefore, the frequency is not known to the type system and is available only at runtime.
| Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 3.5.0 | a421322c1d9539b6d5288ae959e586ed865e0b92 | docs | 8839 | ```@meta
CurrentModule = Yields
```
# Yields.jl
[](https://JuliaActuary.github.io/Yields.jl/stable)
[](https://JuliaActuary.github.io/Yields.jl/dev)
[](https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl/actions)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl)
**Yields.jl** provides a simple interface for constructing, manipulating, and using yield curves for modeling purposes.
It's intended to provide common functionality around modeling interest rates, spreads, and miscellaneous yields across the JuliaActuary ecosystem (though not limited to use in JuliaActuary packages).
## QuickStart
```julia
using Yields
riskfree_maturities = [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0]
riskfree = [5.0, 5.8, 6.4, 6.8] ./ 100 #spot rates, annual effective if unspecified
spread_maturities = [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 3.0] # different maturities
spread = [1.0, 1.8, 1.4, 1.8] ./ 100 # spot spreads
rf_curve = Yields.Zero(riskfree,riskfree_maturities)
spread_curve = Yields.Zero(spread,spread_maturities)
yield = rf_curve + spread_curve # additive combination of the two curves
discount(yield,1.5) # 1 / (1 + 0.064 + 0.014) ^ 1.5
```
## Usage
### Rates
Rates are types that wrap scalar values to provide information about how to determine `discount` and `accumulation` factors.
There are two `CompoundingFrequency` types:
- `Yields.Periodic(m)` for rates that compound `m` times per period (e.g. `m` times per year if working with annual rates).
- `Yields.Continuous()` for continuously compounding rates.
#### Examples
```julia
Continuous(0.05) # 5% continuously compounded
Periodic(0.05,2) # 5% compounded twice per period
```
These are both subtypes of the parent `Rate` type and are instantiated as:
```julia
Rate(0.05,Continuous()) # 5% continuously compounded
Rate(0.05,Periodic(2)) # 5% compounded twice per period
```
Broadcast over a vector to create `Rates` with the given compounding:
```julia
Periodic.([0.02,0.03,0.04],2)
Continuous.([0.02,0.03,0.04])
```
Rates can also be constructed by specifying the `CompoundingFrequency` and then passing a scalar rate:
```julia
Periodic(1)(0.05)
Continuous()(0.05)
```
#### Conversion
Convert rates between different types with `convert`. E.g.:
```julia-repl
r = Rate(Yields.Periodic(12),0.01) # rate that compounds 12 times per rate period (ie monthly)
convert(Yields.Periodic(1),r) # convert monthly rate to annual effective
convert(Yields.Continuous(),r) # convert monthly rate to continuous
```
#### Arithmetic
Adding, substracting, and comparing rates is supported.
### Curves
There are a several ways to construct a yield curve object. If `maturities` is omitted, the method will assume that the timepoints corresponding to each rate are the indices of the `rates` (e.g. generally one to the length of the array for standard, non-offset arrays).
#### Fitting Curves to Rates
There is a set of constructor methods which will return a yield curve calibrated to the given inputs.
- `Yields.Zero(rates,maturities)` using a vector of zero rates (sometimes referred to as "spot" rates)
- `Yields.Forward(rates,maturities)` using a vector of forward rates
- `Yields.Par(rates,maturities)` takes a series of yields for securities priced at par. Assumes that maturities <= 1 year do not pay coupons and that after one year, pays coupons with frequency equal to the CompoundingFrequency of the corresponding rate (2 by default).
- `Yields.CMT(rates,maturities)` takes the most commonly presented rate data (e.g. [Treasury.gov](https://www.treasury.gov/resource-center/data-chart-center/interest-rates/Pages/TextView.aspx?data=yield)) and bootstraps the curve given the combination of bills and bonds.
- `Yields.OIS(rates,maturities)` takes the most commonly presented rate data for overnight swaps and bootstraps the curve. Rates assume a single settlement for <1 year and quarterly settlements for 1 year and above.
##### Fitting techniques
There are multiple curve fitting methods available:
- `Boostrap(interpolation_method)` (the default method)
- where `interpolation` can be one of the built-in `QuadraticSpline()` (the default) or `LinearSpline()`, or a user-supplied function.
- Two methods from the Nelson-Siegel-Svensson family, where τ_initial is the starting τ point for the fitting optimization routine:
- `NelsonSiegel(τ_initial=1.0)`
- `NelsonSiegelSvensson(τ_initial=[1.0,1.0])`
To specify which fitting method to use, pass the object to as the first parameter to the above set of constructors, for example: `Yields.Par(NelsonSiegel(),rates,maturities)`.
#### Kernel Methods
- `Yields.SmithWilson` curve (used for [discounting in the EU Solvency II framework](https://www.eiopa.europa.eu/sites/default/files/risk_free_interest_rate/12092019-technical_documentation.pdf)) can be constructed either directly by specifying its inner representation or by calibrating to a set of cashflows with known prices.
- These cashflows can conveniently be constructed with a Vector of `Yields.ZeroCouponQuote`s, `Yields.SwapQuote`s, or `Yields.BulletBondQuote`s.
#### Other Curves
- `Yields.Constant(rate)` takes a single constant rate for all times
- `Yields.Step(rates,maturities)` doesn't interpolate - the rate is flat up to the corresponding time in `times`
### Functions
Most of the above yields have the following defined (goal is to have them all):
- `discount(curve,from,to)` or `discount(curve,to)` gives the discount factor
- `accumulation(curve,from,to)` or `accumulation(curve,to)` gives the accumulation factor
- `zero(curve,time)` or `zero(curve,time,CompoundingFrequency)` gives the zero-coupon spot rate for the given time.
- `forward(curve,from,to)` gives the zero rate between the two given times
- `par(curve,time)` gives the coupon-paying par equivalent rate for the given time.
### Combinations
Different yield objects can be combined with addition or subtraction. See the [Quickstart](#quickstart) for an example.
When adding a `Yields.AbstractYield` with a scalar or vector, that scalar or vector will be promoted to a yield type via [`Yield()`](#yield). For example:
```julia
y1 = Yields.Constant(0.05)
y2 = y1 + 0.01 # y2 is a yield of 0.06
```
### Forward Starting Curves
Constructed curves can be shifted so that a future timepoint becomes the effective time-zero for a said curve.
```julia-repl
julia> zero = [5.0, 5.8, 6.4, 6.8] ./ 100
julia> maturity = [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0]
julia> curve = Yields.Zero(zero, maturity)
julia> fwd = Yields.ForwardStarting(curve, 1.0)
julia> discount(curve,1,2)
0.9275624570410582
julia> discount(fwd,1) # `curve` has effectively been reindexed to `1.0`
0.9275624570410582
```
## Exported vs Un-exported Functions
Generally, CamelCase methods which construct a datatype are exported as they are unlikely to conflict with other parts of code that may be written. For example, `rate` is un-exported (it must be called with `Yields.rate(...)`) because `rate` is likely a very commonly defined variable within actuarial and financial contexts and there is a high risk of conflicting with defined variables.
Consider using `import Yields` which would require qualifying all methods, but alleviates any namespace conflicts and has the benefit of being explicit about the calls (internally we prefer this in the package design to keep dependencies and their usage clear).
## Internals
For time-variant yields (ie yield *curves*), the inputs are converted to spot rates and interpolated using quadratic B-splines by default (see documentation for alternatives, such as linear interpolations).
### Combination Implementation
[Combinations](#combinations) track two different curve objects and are not combined into a single underlying data structure. This means that you may achieve better performance if you combine the rates before constructing a `Yields` representation. The exception to this is `Constant` curves, which *do* get combined into a single structure that is as performant as pre-combined rate structure.
## Related Packages
- [**`InterestRates.jl`**](https://github.com/felipenoris/InterestRates.jl) specializes in fast rate calculations aimed at valuing fixed income contracts, with business-day-level accuracy.
- Comparative comments: **`Yields.jl`** does not try to provide as precise controls over the timing, structure, and interpolation of the curve. Instead, **`Yields.jl`** provides a minimal, but flexible and intuitive interface for common modeling needs.
| Yields | https://github.com/JuliaActuary/Yields.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.3.1 | dad84aeb9caadb97d2c9cf4d2e994c5d3c8a254a | code | 274 | # This file is a part of JuliaFEM.
# License is MIT: see https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl/blob/master/LICENSE
using Documenter
deploydocs(
repo = "github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git",
target = "build",
deps = nothing,
make = nothing)
| MortarContact2D | https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.3.1 | dad84aeb9caadb97d2c9cf4d2e994c5d3c8a254a | code | 342 | # This file is a part of JuliaFEM.
# License is MIT: see https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl/blob/master/LICENSE
using Documenter, MortarContact2D
makedocs(modules=[MortarContact2D],
format = Documenter.HTML(),
checkdocs = :all,
sitename = "MortarContact2D.jl",
pages = ["index.md"]
)
| MortarContact2D | https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.3.1 | dad84aeb9caadb97d2c9cf4d2e994c5d3c8a254a | code | 464 | # This file is a part of JuliaFEM.
# License is MIT: see https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl/blob/master/LICENSE
"""
2D mortar contact mechanics for JuliaFEM.
# Problem types
- `Mortar2D` to couple non-conforming meshes (mesh tying).
- `MortarContact2D` to add contact constraints.
"""
module MortarContact2D
using FEMBase, SparseArrays, LinearAlgebra, Statistics
include("mortar2d.jl")
include("contact2d.jl")
export Mortar2D, Contact2D
end
| MortarContact2D | https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.3.1 | dad84aeb9caadb97d2c9cf4d2e994c5d3c8a254a | code | 14403 | # This file is a part of JuliaFEM.
# License is MIT: see https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl/blob/master/LICENSE
mutable struct Contact2D <: BoundaryProblem
master_elements :: Vector{Element}
rotate_normals :: Bool
dual_basis :: Bool
max_distance :: Float64
iteration :: Int
contact_state_in_first_iteration :: Symbol
store_fields :: Vector{String}
end
function Contact2D()
return Contact2D([], false, true, Inf, 0, :AUTO, [])
end
function FEMBase.add_elements!(::Problem{Contact2D}, ::Any)
error("use `add_slave_elements!` and `add_master_elements!` to add ",
"elements to the Contact2D problem.")
end
function FEMBase.get_elements(problem::Problem{Contact2D})
return [problem.elements; problem.properties.master_elements]
end
function FEMBase.add_slave_elements!(problem::Problem{Contact2D}, elements)
for element in elements
push!(problem.elements, element)
end
end
function FEMBase.add_master_elements!(problem::Problem{Contact2D}, elements)
for element in elements
push!(problem.properties.master_elements, element)
end
end
function FEMBase.get_slave_elements(problem::Problem{Contact2D})
return problem.elements
end
function FEMBase.get_master_elements(problem::Problem{Contact2D})
return problem.properties.master_elements
end
function get_slave_dofs(problem::Problem{Contact2D})
dofs = Int64[]
for element in get_slave_elements(problem)
append!(dofs, get_gdofs(problem, element))
end
return sort(unique(dofs))
end
function get_master_dofs(problem::Problem{Contact2D})
dofs = Int64[]
for element in get_master_elements(problem)
append!(dofs, get_gdofs(problem, element))
end
return sort(unique(dofs))
end
function create_rotation_matrix(element::Element{Seg2}, time::Float64)
n = element("normal", time)
R = [0.0 -1.0; 1.0 0.0]
t1 = R'*n[1]
t2 = R'*n[2]
Q1 = [n[1] t1]
Q2 = [n[2] t2]
Z = zeros(2, 2)
Q = [Q1 Z; Z Q2]
return Q
end
function create_contact_segmentation(problem::Problem{Contact2D}, slave_element::Element{Seg2}, master_elements::Vector, time::Float64; deformed=false)
result = []
max_distance = problem.properties.max_distance
x1 = slave_element("geometry", time)
if deformed && haskey(slave_element, "displacement")
x1 = map(+, x1, slave_element("displacement", time))
end
slave_midpoint = 1/2*(x1[1] + x1[2])
slave_length = norm(x1[2]-x1[1])
for master_element in master_elements
x2 = master_element("geometry", time)
if deformed && haskey(master_element, "displacement")
x2 = map(+, x2, master_element("displacement", time))
end
master_midpoint = 1/2*(x2[1] + x2[2])
master_length = norm(x2[2]-x2[1])
# charasteristic length
dist = norm(slave_midpoint - master_midpoint)
cl = dist/max(slave_length, master_length)
if cl > max_distance
continue
end
# 3.1 calculate segmentation
x21, x22 = x2
xi1a = project_from_master_to_slave(slave_element, x21, time)
xi1b = project_from_master_to_slave(slave_element, x22, time)
xi1 = clamp.([xi1a; xi1b], -1.0, 1.0)
l = 1/2*abs(xi1[2]-xi1[1])
if isapprox(l, 0.0)
continue # no contribution in this master element
end
push!(result, (master_element, xi1, l))
end
return result
end
function FEMBase.assemble_elements!(problem::Problem{Contact2D}, assembly::Assembly,
elements::Vector{Element{Seg2}}, time::Float64)
props = problem.properties
props.iteration += 1
slave_elements = get_slave_elements(problem)
field_dim = get_unknown_field_dimension(problem)
field_name = get_parent_field_name(problem)
# 1. calculate nodal normals for slave element nodes j ∈ S
normals = calculate_normals([slave_elements...], time; rotate_normals=props.rotate_normals)
tangents = Dict(j => [t2, -t1] for (j, (t1,t2)) in normals)
update!(slave_elements, "normal", time => normals)
update!(slave_elements, "tangent", time => tangents)
Rn = 0.0
# 2. loop all slave elements
for slave_element in slave_elements
nsl = length(slave_element)
X1 = slave_element("geometry", time)
x1 = slave_element("geometry", time)
if haskey(slave_element, "displacement")
u1 = slave_element("displacement", time)
x1 = map(+, x1, u1)
end
la1 = slave_element("lambda", time)
n1 = slave_element("normal", time)
t1 = slave_element("tangent", time)
contact_area = 0.0
contact_error = 0.0
Q2 = create_rotation_matrix(slave_element, time)
master_elements = get_master_elements(problem)
segmentation = create_contact_segmentation(problem, slave_element, master_elements, time)
if length(segmentation) == 0 # no overlapping in master and slave surfaces with this slave element
continue
end
Ae = Matrix(I, nsl, nsl)
if props.dual_basis
De = zeros(nsl, nsl)
Me = zeros(nsl, nsl)
for (master_element, xi1, l) in segmentation
for ip in get_integration_points(slave_element, 3)
detJ = slave_element(ip, time, Val{:detJ})
w = ip.weight*detJ*l
xi = ip.coords[1]
xi_s = dot([1/2*(1-xi); 1/2*(1+xi)], xi1)
N1 = vec(get_basis(slave_element, xi_s, time))
De += w*Matrix(Diagonal(N1))
Me += w*N1*N1'
end
Ae = De*inv(Me)
end
end
# loop all segments
for (master_element, xi1, l) in segmentation
nm = length(master_element)
X2 = master_element("geometry", time)
x2 = master_element("geometry", time)
if haskey(master_element, "displacement")
u2 = master_element("displacement", time)
x2 = map(+, x2, u2)
end
# 3.3. loop integration points of one integration segment and calculate
# local mortar matrices
De = zeros(nsl, nsl)
Me = zeros(nsl, nsl)
Ne = zeros(nsl, 2*nsl)
Te = zeros(nsl, 2*nsl)
He = zeros(nsl, 2*nsl)
ce = zeros(nsl)
ge = zeros(nsl)
for ip in get_integration_points(slave_element, 3)
detJ = slave_element(ip, time, Val{:detJ})
w = ip.weight*detJ*l
xi = ip.coords[1]
xi_s = dot([1/2*(1-xi); 1/2*(1+xi)], xi1)
N1 = vec(get_basis(slave_element, xi_s, time))
Phi = Ae*N1
# project gauss point from slave element to master element in direction n_s
X_s = interpolate(N1, X1) # coordinate in gauss point
n_s = interpolate(N1, n1) # normal direction in gauss point
t_s = interpolate(N1, t1) # tangent condition in gauss point
n_s /= norm(n_s)
t_s /= norm(t_s)
xi_m = project_from_slave_to_master(master_element, X_s, n_s, time)
N2 = vec(get_basis(master_element, xi_m, time))
X_m = interpolate(N2, X2)
u_s = interpolate(N1, u1)
u_m = interpolate(N2, u2)
x_s = map(+, X_s, u_s)
x_m = map(+, X_m, u_m)
la_s = interpolate(Phi, la1)
# contact virtual work
De += w*Phi*N1'
Me += w*Phi*N2'
# contact constraints
Ne += w*reshape(kron(N1, n_s, Phi), 2, 4)
Te += w*reshape(kron(N2, n_s, Phi), 2, 4)
He += w*reshape(kron(N1, t_s, Phi), 2, 4)
ge += w*Phi*dot(n_s, x_m-x_s)
ce += w*N1*dot(n_s, la_s)
Rn += w*dot(n_s, la_s)
contact_area += w
contact_error += 1/2*w*dot(n_s, x_s-x_m)^2
end
sdofs = get_gdofs(problem, slave_element)
mdofs = get_gdofs(problem, master_element)
# add contribution to contact virtual work
for i=1:field_dim
lsdofs = sdofs[i:field_dim:end]
lmdofs = mdofs[i:field_dim:end]
add!(problem.assembly.C1, lsdofs, lsdofs, De)
add!(problem.assembly.C1, lsdofs, lmdofs, -Me)
end
# add contribution to contact constraints
add!(problem.assembly.C2, sdofs[1:field_dim:end], sdofs, Ne)
add!(problem.assembly.C2, sdofs[1:field_dim:end], mdofs, -Te)
add!(problem.assembly.D, sdofs[2:field_dim:end], sdofs, He)
add!(problem.assembly.g, sdofs[1:field_dim:end], ge)
add!(problem.assembly.c, sdofs[1:field_dim:end], ce)
end # master elements done
if "contact area" in props.store_fields
update!(slave_element, "contact area", time => contact_area)
end
if "contact error" in props.store_fields
update!(slave_element, "contact error", time => contact_error)
end
end # slave elements done, contact virtual work ready
S = sort(collect(keys(normals))) # slave element nodes
weighted_gap = Dict{Int64, Vector{Float64}}()
contact_pressure = Dict{Int64, Vector{Float64}}()
complementarity_condition = Dict{Int64, Vector{Float64}}()
is_active = Dict{Int64, Int}()
is_inactive = Dict{Int64, Int}()
is_slip = Dict{Int64, Int}()
is_stick = Dict{Int64, Int}()
la = problem.assembly.la
# FIXME: for matrix operations, we need to know the dimensions of the
# final matrices
ndofs = 2*length(S)
ndofs = max(ndofs, length(la))
ndofs = max(ndofs, size(problem.assembly.K, 2))
ndofs = max(ndofs, size(problem.assembly.C1, 2))
ndofs = max(ndofs, size(problem.assembly.C2, 2))
ndofs = max(ndofs, size(problem.assembly.D, 2))
ndofs = max(ndofs, size(problem.assembly.g, 2))
ndofs = max(ndofs, size(problem.assembly.c, 2))
C1 = sparse(problem.assembly.C1, ndofs, ndofs)
C2 = sparse(problem.assembly.C2, ndofs, ndofs)
D = sparse(problem.assembly.D, ndofs, ndofs)
g = Vector(sparse(problem.assembly.g, ndofs, 1)[:])
c = Vector(sparse(problem.assembly.c, ndofs, 1)[:])
for j in S
dofs = [2*(j-1)+1, 2*(j-1)+2]
weighted_gap[j] = g[dofs]
end
state = problem.properties.contact_state_in_first_iteration
if problem.properties.iteration == 1
@info("First contact iteration, initial contact state = $state")
if state == :AUTO
avg_gap = mean([weighted_gap[j][1] for j in S])
std_gap = std([weighted_gap[j][1] for j in S])
if (avg_gap < 1.0e-12) && (std_gap < 1.0e-12)
state = :ACTIVE
else
state = :UNKNOWN
end
@info("Average weighted gap = $avg_gap, std gap = $std_gap, automatically determined contact state = $state")
end
end
# active / inactive node detection
for j in S
dofs = [2*(j-1)+1, 2*(j-1)+2]
weighted_gap[j] = g[dofs]
if length(la) != 0
p = dot(normals[j], la[dofs])
t = dot(tangents[j], la[dofs])
contact_pressure[j] = [p, t]
else
contact_pressure[j] = [0.0, 0.0]
end
complementarity_condition[j] = contact_pressure[j] - weighted_gap[j]
if complementarity_condition[j][1] < 0
is_inactive[j] = 1
is_active[j] = 0
is_slip[j] = 0
is_stick[j] = 0
else
is_inactive[j] = 0
is_active[j] = 1
is_slip[j] = 1
is_stick[j] = 0
end
end
if (problem.properties.iteration == 1) && (state == :ACTIVE)
for j in S
is_inactive[j] = 0
is_active[j] = 1
is_slip[j] = 1
is_stick[j] = 0
end
end
if (problem.properties.iteration == 1) && (state == :INACTIVE)
for j in S
is_inactive[j] = 1
is_active[j] = 0
is_slip[j] = 0
is_stick[j] = 0
end
end
if "weighted gap" in props.store_fields
update!(slave_elements, "weighted gap", time => weighted_gap)
end
if "contact pressure" in props.store_fields
update!(slave_elements, "contact pressure", time => contact_pressure)
end
if "complementarity condition" in props.store_fields
update!(slave_elements, "complementarity condition", time => complementarity_condition)
end
if "active nodes" in props.store_fields
update!(slave_elements, "active nodes", time => is_active)
end
if "inactive nodes" in props.store_fields
update!(slave_elements, "inactive nodes", time => is_inactive)
end
if "stick nodes" in props.store_fields
update!(slave_elements, "stick nodes", time => is_stick)
end
if "slip nodes" in props.store_fields
update!(slave_elements, "slip nodes", time => is_slip)
end
@info("# | A | I | St | Sl | gap | pres | comp")
for j in S
str1 = "$j | $(is_active[j]) | $(is_inactive[j]) | $(is_stick[j]) | $(is_slip[j]) | "
str2 = "$(round(weighted_gap[j][1]; digits=3)) | $(round(contact_pressure[j][1]; digits=3)) | $(round(complementarity_condition[j][1]; digits=3))"
@info(str1 * str2)
end
# solve variational inequality
# remove inactive nodes from assembly
for j in S
dofs = [2*(j-1)+1, 2*(j-1)+2]
n, t = dofs
if is_inactive[j] == 1
@debug("$j is inactive, removing dofs $dofs")
C1[dofs,:] .= 0.0
C2[dofs,:] .= 0.0
D[dofs,:] .= 0.0
g[dofs,:] .= 0.0
elseif (is_active[j] == 1) && (is_slip[j] == 1)
@debug("$j is in active/slip, removing tangential constraint $t")
C2[t,:] .= 0.0
g[t] = 0.0
D[t, dofs] .= tangents[j]
end
end
problem.assembly.C1 = C1
problem.assembly.C2 = C2
problem.assembly.D = D
problem.assembly.g = sparsevec(g)
end
| MortarContact2D | https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.3.1 | dad84aeb9caadb97d2c9cf4d2e994c5d3c8a254a | code | 8555 | # This file is a part of JuliaFEM.
# License is MIT: see https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl/blob/master/LICENSE
const MortarElements2D = Union{Seg2,Seg3}
mutable struct Mortar2D <: BoundaryProblem
master_elements :: Vector{Element}
end
function Mortar2D()
return Mortar2D([])
end
function FEMBase.add_elements!(::Problem{Mortar2D}, ::Union{Tuple, Vector})
error("use `add_slave_elements!` and `add_master_elements!` to add " *
"elements to the Mortar2D problem.")
end
function FEMBase.add_slave_elements!(problem::Problem{Mortar2D}, elements)
for element in elements
push!(problem.elements, element)
end
end
function FEMBase.add_master_elements!(problem::Problem{Mortar2D}, elements)
for element in elements
push!(problem.properties.master_elements, element)
end
end
function FEMBase.get_slave_elements(problem::Problem{Mortar2D})
return problem.elements
end
function FEMBase.get_master_elements(problem::Problem{Mortar2D})
return problem.properties.master_elements
end
function get_slave_dofs(problem::Problem{Mortar2D})
dofs = Int64[]
for element in get_slave_elements(problem)
append!(dofs, get_gdofs(problem, element))
end
return sort(unique(dofs))
end
function get_master_dofs(problem::Problem{Mortar2D})
dofs = Int64[]
for element in get_master_elements(problem)
append!(dofs, get_gdofs(problem, element))
end
return sort(unique(dofs))
end
function project_from_master_to_slave(slave_element::Element{E}, x2, time;
tol=1.0e-9, max_iterations=5) where {E<:MortarElements2D}
x1_ = slave_element("geometry", time)
n1_ = slave_element("normal", time)
cross2(a, b) = cross([a; 0.0], [b; 0.0])[3]
x1(xi1) = interpolate(vec(get_basis(slave_element, [xi1], time)), x1_)
dx1(xi1) = interpolate(vec(get_dbasis(slave_element, [xi1], time)), x1_)
n1(xi1) = interpolate(vec(get_basis(slave_element, [xi1], time)), n1_)
dn1(xi1) = interpolate(vec(get_dbasis(slave_element, [xi1], time)), n1_)
R(xi1) = cross2(x1(xi1)-x2, n1(xi1))
dR(xi1) = cross2(dx1(xi1), n1(xi1)) + cross2(x1(xi1)-x2, dn1(xi1))
xi1 = 0.0
dxi1 = 0.0
for i=1:max_iterations
dxi1 = -R(xi1)/dR(xi1)
xi1 += dxi1
if norm(dxi1) < tol
return xi1
end
end
len = norm(x1_[2] - x1_[1])
midpnt = mean(x1_)
dist = norm(midpnt - x2)
distval = dist/len
@info("Projection from the master element to the slave failed.")
@info("Arguments:")
@info("Time: $time")
@info("Point to project to the slave element: (x2): $x2")
@info("Slave element geometry (x1): $x1_")
@info("Slave element normal direction (n1): $n1_")
@info("Midpoint of slave element: $midpnt")
@info("Length of slave element: $len")
@info("Distance between midpoint of slave element and x2: $dist")
@info("Distance/Lenght-ratio: $distval")
@info("Number of iterations: $max_iterations")
@info("Wanted convergence tolerance: $tol")
@info("Achieved convergence tolerance: $(norm(dxi1))")
error("Failed to project point to slave surface in $max_iterations.")
end
function project_from_slave_to_master(master_element::Element{E}, x1, n1, time;
max_iterations=5, tol=1.0e-9) where {E<:MortarElements2D}
x2_ = master_element("geometry", time)
x2(xi2) = interpolate(vec(get_basis(master_element, [xi2], time)), x2_)
dx2(xi2) = interpolate(vec(get_dbasis(master_element, [xi2], time)), x2_)
cross2(a, b) = cross([a; 0], [b; 0])[3]
R(xi2) = cross2(x2(xi2)-x1, n1)
dR(xi2) = cross2(dx2(xi2), n1)
xi2 = 0.0
dxi2 = 0.0
for i=1:max_iterations
dxi2 = -R(xi2)/dR(xi2)
xi2 += dxi2
if norm(dxi2) < tol
return xi2
end
end
error("Failed to project point to master surface in $max_iterations iterations.")
end
function calculate_normals(elements::Vector{Element{Seg2}}, time; rotate_normals=false)
normals = Dict{Int64, Vector{Float64}}()
for element in elements
X1, X2 = element("geometry", time)
t1, t2 = (X2-X1)/norm(X2-X1)
normal = [-t2, t1]
for j in get_connectivity(element)
normals[j] = get(normals, j, zeros(2)) + normal
end
end
s = rotate_normals ? -1.0 : 1.0
for j in keys(normals)
normals[j] = s*normals[j]/norm(normals[j])
end
return normals
end
function FEMBase.assemble_elements!(problem::Problem{Mortar2D}, assembly::Assembly,
elements::Vector{Element{Seg2}}, time::Float64)
slave_elements = get_slave_elements(problem)
props = problem.properties
field_dim = get_unknown_field_dimension(problem)
field_name = get_parent_field_name(problem)
# 1. calculate nodal normals for slave element nodes j ∈ S
normals = calculate_normals([slave_elements...], time)
update!(slave_elements, "normal", time => normals)
# 2. loop all slave elements
for slave_element in slave_elements
nsl = length(slave_element)
X1 = slave_element("geometry", time)
n1 = slave_element("normal", time)
# 3. loop all master elements
for master_element in get_master_elements(problem)
nm = length(master_element)
X2 = master_element("geometry", time)
# 3.1 calculate segmentation
xi1a = project_from_master_to_slave(slave_element, X2[1], time)
xi1b = project_from_master_to_slave(slave_element, X2[2], time)
xi1 = clamp.([xi1a; xi1b], -1.0, 1.0)
l = 1/2*abs(xi1[2]-xi1[1])
isapprox(l, 0.0) && continue # no contribution in this master element
# 3.3. loop integration points of one integration segment and calculate
# local mortar matrices
De = zeros(nsl, nsl)
Me = zeros(nsl, nm)
fill!(De, 0.0)
fill!(Me, 0.0)
for ip in get_integration_points(slave_element, 2)
detJ = slave_element(ip, time, Val{:detJ})
w = ip.weight*detJ*l
xi = ip.coords[1]
xi_s = dot([1/2*(1-xi); 1/2*(1+xi)], xi1)
N1 = vec(get_basis(slave_element, xi_s, time))
Phi = N1
# project gauss point from slave element to master element in direction n_s
X_s = interpolate(N1, X1) # coordinate in gauss point
n_s = interpolate(N1, n1) # normal direction in gauss point
xi_m = project_from_slave_to_master(master_element, X_s, n_s, time)
N2 = vec(get_basis(master_element, xi_m, time))
X_m = interpolate(N2, X2)
De += w*Phi*N1'
Me += w*Phi*N2'
end
sdofs = get_gdofs(problem, slave_element)
mdofs = get_gdofs(problem, master_element)
# add contribution to contact virtual work and constraint matrix
for i=1:field_dim
lsdofs = sdofs[i:field_dim:end]
lmdofs = mdofs[i:field_dim:end]
add!(problem.assembly.C1, lsdofs, lsdofs, De)
add!(problem.assembly.C1, lsdofs, lmdofs, -Me)
add!(problem.assembly.C2, lsdofs, lsdofs, De)
add!(problem.assembly.C2, lsdofs, lmdofs, -Me)
end
end # master elements done
end # slave elements done, contact virtual work ready
return nothing
end
function get_mortar_matrix_D(problem::Problem{Mortar2D})
s = get_slave_dofs(problem)
C2 = sparse(problem.assembly.C2)
return sparse(problem.assembly.C2)[s,s]
end
function get_mortar_matrix_M(problem::Problem{Mortar2D})
m = get_master_dofs(problem)
s = get_slave_dofs(problem)
C2 = sparse(problem.assembly.C2)
return -C2[s,m]
end
function get_mortar_matrix_P(problem::Problem{Mortar2D})
m = get_master_dofs(problem)
s = get_slave_dofs(problem)
C2 = sparse(problem.assembly.C2)
D_ = C2[s,s]
M_ = -C2[s,m]
P = cholesky(1/2*(D_ + D_')) \ M_
return P
end
""" Eliminate mesh tie constraints from matrices K, M, f. """
function FEMBase.eliminate_boundary_conditions!(problem::Problem{Mortar2D}, K, M, f)
m = get_master_dofs(problem)
s = get_slave_dofs(problem)
P = get_mortar_matrix_P(problem)
ndim = size(K, 1)
Id = ones(ndim)
Id[s] .= 0.0
Q = sparse(Diagonal(Id))
Q[m,s] .+= P'
K[:,:] .= Q*K*Q'
M[:,:] .= Q*M*Q'
f[:] .= Q*f
return true
end
| MortarContact2D | https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.3.1 | dad84aeb9caadb97d2c9cf4d2e994c5d3c8a254a | code | 756 | # This file is a part of JuliaFEM.
# License is MIT: see https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl/blob/master/LICENSE
using FEMBase, MortarContact2D, Test, SparseArrays, LinearAlgebra, Statistics
@testset "MortarContact2D.jl" begin
@testset "Projecting vertices between surfaces" begin
include("test_mortar2d_calculate_projection.jl")
end
@testset "Mortar coupling, example 1" begin
include("test_mortar2d_ex1.jl")
end
@testset "Mortar coupling, example 2" begin
include("test_mortar2d_ex2.jl")
end
@testset "Contact basic test" begin
include("test_contact2d.jl")
end
@testset "Testing contact segmentation" begin
include("test_contact_segmentation.jl")
end
end
| MortarContact2D | https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.3.1 | dad84aeb9caadb97d2c9cf4d2e994c5d3c8a254a | code | 5706 | # This file is a part of JuliaFEM.
# License is MIT: see https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl/blob/master/LICENSE
using FEMBase, MortarContact2D, Test
using MortarContact2D: get_slave_dofs, get_master_dofs
# Original problem:
#
# using JuliaFEM
# using JuliaFEM.Preprocess
# using JuliaFEM.Testing
#
# mesh = Mesh()
# add_node!(mesh, 1, [0.0, 0.0])
# add_node!(mesh, 2, [1.0, 0.0])
# add_node!(mesh, 3, [1.0, 0.5])
# add_node!(mesh, 4, [0.0, 0.5])
# gap = 0.1
# add_node!(mesh, 5, [0.0, 0.5+gap])
# add_node!(mesh, 6, [1.0, 0.5+gap])
# add_node!(mesh, 7, [1.0, 1.0+gap])
# add_node!(mesh, 8, [0.0, 1.0+gap])
# add_element!(mesh, 1, :Quad4, [1, 2, 3, 4])
# add_element!(mesh, 2, :Quad4, [5, 6, 7, 8])
# add_element!(mesh, 3, :Seg2, [1, 2])
# add_element!(mesh, 4, :Seg2, [7, 8])
# add_element!(mesh, 5, :Seg2, [4, 3])
# add_element!(mesh, 6, :Seg2, [6, 5])
# add_element_to_element_set!(mesh, :LOWER, 1)
# add_element_to_element_set!(mesh, :UPPER, 2)
# add_element_to_element_set!(mesh, :LOWER_BOTTOM, 3)
# add_element_to_element_set!(mesh, :UPPER_TOP, 4)
# add_element_to_element_set!(mesh, :LOWER_TOP, 5)
# add_element_to_element_set!(mesh, :UPPER_BOTTOM, 6)
# upper = Problem(Elasticity, "UPPER", 2)
# upper.properties.formulation = :plane_stress
# upper.elements = create_elements(mesh, "UPPER")
# update!(upper.elements, "youngs modulus", 288.0)
# update!(upper.elements, "poissons ratio", 1/3)
# lower = Problem(Elasticity, "LOWER", 2)
# lower.properties.formulation = :plane_stress
# lower.elements = create_elements(mesh, "LOWER")
# update!(lower.elements, "youngs modulus", 288.0)
# update!(lower.elements, "poissons ratio", 1/3)
# bc_upper = Problem(Dirichlet, "UPPER_TOP", 2, "displacement")
# bc_upper.elements = create_elements(mesh, "UPPER_TOP")
# #update!(bc_upper.elements, "displacement 1", -17/90)
# #update!(bc_upper.elements, "displacement 1", -17/90)
# update!(bc_upper.elements, "displacement 1", -0.2)
# update!(bc_upper.elements, "displacement 2", -0.2)
# bc_lower = Problem(Dirichlet, "LOWER_BOTTOM", 2, "displacement")
# bc_lower.elements = create_elements(mesh, "LOWER_BOTTOM")
# update!(bc_lower.elements, "displacement 1", 0.0)
# update!(bc_lower.elements, "displacement 2", 0.0)
# contact = Problem(Contact2D, "LOWER_TO_UPPER", 2, "displacement")
# contact_slave_elements = create_elements(mesh, "LOWER_TOP")
# contact_master_elements = create_elements(mesh, "UPPER_BOTTOM")
# add_slave_elements!(contact, contact_slave_elements)
# add_master_elements!(contact, contact_master_elements)
# solver = Solver(Nonlinear)
# push!(solver, upper, lower, bc_upper, bc_lower, contact)
# solver()
# master = first(contact_master_elements)
# slave = first(contact_slave_elements)
# um = master("displacement", (0.0,), 0.0)
# us = slave("displacement", (0.0,), 0.0)
# la = slave("lambda", (0.0,), 0.0)
# info("um = $um, us = $us, la = $la")
# @test isapprox(um, [-0.20, -0.15])
# @test isapprox(us, [0.0, -0.05])
# @test isapprox(la, [0.0, 30.375])
# Equivalent test problem
slave = Element(Seg2, [1, 2])
update!(slave, "geometry", ([0.0, 0.5], [1.0, 0.5]))
update!(slave, "displacement", 0.0 => (zeros(2), zeros(2)))
update!(slave, "lambda", 0.0 => (zeros(2), zeros(2)))
update!(slave, "displacement", 1.0 => ([-0.01875, -0.05], [0.01875, -0.05]))
update!(slave, "lambda", 1.0 => ([0.0, 30.375], [0.0, 30.375]))
master = Element(Seg2, [3, 4])
update!(master, "geometry", ([1.0, 0.6], [0.0, 0.6]))
update!(master, "displacement", 0.0 => (zeros(2), zeros(2)))
update!(master, "displacement", 1.0 => ([-0.18125, -0.15], [-0.21875, -0.15]))
problem = Problem(Contact2D, "LOWER_TO_UPPER", 2, "displacement")
push!(problem.properties.store_fields, "complementarity condition")
push!(problem.properties.store_fields, "active nodes")
push!(problem.properties.store_fields, "inactive nodes")
push!(problem.properties.store_fields, "stick nodes")
push!(problem.properties.store_fields, "slip nodes")
add_slave_elements!(problem, [slave])
add_master_elements!(problem, [master])
um = master("displacement", (0.0,), 1.0)
us = slave("displacement", (0.0,), 1.0)
la = slave("lambda", (0.0,), 1.0)
@test isapprox(um, [-0.20, -0.15])
@test isapprox(us, [0.0, -0.05])
@test isapprox(la, [0.0, 30.375])
assemble!(problem, 0.0)
@test iszero(sparse(problem.assembly.K))
@test iszero(sparse(problem.assembly.C1))
@test iszero(sparse(problem.assembly.C2))
@test iszero(sparse(problem.assembly.D))
@test iszero(sparse(problem.assembly.f))
@test iszero(sparse(problem.assembly.g))
empty!(problem.assembly)
assemble!(problem, 1.0)
@test iszero(sparse(problem.assembly.K))
@test iszero(sparse(problem.assembly.f))
C1 = Matrix(sparse(problem.assembly.C1, 4, 8))
C2 = Matrix(sparse(problem.assembly.C2, 4, 8))
D = Matrix(sparse(problem.assembly.D, 4, 8))
g = Vector(sparse(problem.assembly.g, 4, 1)[:])
C1_expected = [
0.5 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 -0.5 0.0
0.0 0.5 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 -0.5
0.0 0.0 0.5 0.0 -0.5 0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 0.5 0.0 -0.5 0.0 0.0]
C2_expected = [
0.0 0.5 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 -0.5
0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 0.5 0.0 -0.5 0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0]
D_expected = [
0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
0.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0]
g_expected = zeros(4)
@test isapprox(C1, C1_expected)
@test isapprox(C2, C2_expected)
@test isapprox(D, D_expected)
@test isapprox(g, g_expected; atol=1.0e-12)
@test_throws Exception add_elements!(problem, [slave])
@test get_slave_dofs(problem) == [1, 2, 3, 4]
@test get_master_dofs(problem) == [5, 6, 7, 8]
| MortarContact2D | https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.3.1 | dad84aeb9caadb97d2c9cf4d2e994c5d3c8a254a | code | 2707 | # This file is a part of JuliaFEM.
# License is MIT: see https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl/blob/master/LICENSE
using FEMBase, MortarContact2D, Test
using MortarContact2D: create_contact_segmentation, calculate_normals
X = Dict(1 => [0.0, 0.0],
2 => [1.0, 0.0],
3 => [0.0, 1.0],
4 => [1.0, 1.0])
slave = Element(Seg2, [1, 2])
master = Element(Seg2, [3, 4])
elements = [slave, master]
update!(elements, "geometry", X)
update!(slave, "displacement", 0.0 => ([0.0,0.0], [0.0,0.0]))
update!(master, "displacement", 0.0 => ([0.0,0.0], [0.0,0.0]))
update!(slave, "displacement", 1.0 => ([0.0,0.0], [0.0,0.0]))
update!(master, "displacement", 1.0 => ([2.0,0.0], [2.0,0.0]))
problem = Problem(Contact2D, "test problem", 2, "displacement")
add_slave_elements!(problem, [slave])
add_master_elements!(problem, [master])
normals = calculate_normals([slave], 0.0)
update!([slave], "normal", 0.0 => normals)
seg1 = create_contact_segmentation(problem, slave, [master], 0.0; deformed=true)
seg2 = create_contact_segmentation(problem, slave, [master], 1.0; deformed=true)
problem.properties.max_distance = 0.0
seg3 = create_contact_segmentation(problem, slave, [master], 0.0; deformed=false)
@test length(seg1) == 1
@test length(seg2) == 0
@test length(seg3) == 0
slave = Element(Seg2, [1, 2])
master = Element(Seg2, [3, 4])
elements = [slave, master]
update!(elements, "geometry", X)
problem = Problem(Contact2D, "test problem", 2, "displacement")
problem.assembly.la = zeros(8)
problem.properties.store_fields = [
"contact area",
"contact error",
"weighted gap",
"contact pressure",
"complementarity condition",
"active nodes",
"inactive nodes",
"stick nodes",
"slip nodes"]
add_slave_elements!(problem, [slave])
add_master_elements!(problem, [master])
assemble!(problem, 0.0)
X[3] += [2.0, 0.0]
X[4] += [2.0, 0.0]
slave = Element(Seg2, [1, 2])
master = Element(Seg2, [3, 4])
elements = [slave, master]
update!(elements, "geometry", X)
problem = Problem(Contact2D, "test problem", 2, "displacement")
add_slave_elements!(problem, [slave])
add_master_elements!(problem, [master])
assemble!(problem, 0.0)
X = Dict(1 => [0.0, 0.0],
2 => [1.0, 0.0],
3 => [0.0, 0.0],
4 => [1.0, 0.0])
slave = Element(Seg2, [1, 2])
master = Element(Seg2, [3, 4])
elements = [slave, master]
update!(elements, "geometry", X)
problem = Problem(Contact2D, "test problem", 2, "displacement")
add_slave_elements!(problem, [slave])
add_master_elements!(problem, [master])
assemble!(problem, 0.0)
empty!(problem.assembly)
problem.properties.iteration = 0
problem.properties.contact_state_in_first_iteration = :INACTIVE
assemble!(problem, 0.0)
| MortarContact2D | https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.3.1 | dad84aeb9caadb97d2c9cf4d2e994c5d3c8a254a | code | 2303 | # This file is a part of JuliaFEM.
# License is MIT: see https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl/blob/master/LICENSE
using FEMBase, MortarContact2D, Test
using MortarContact2D: calculate_normals,
project_from_master_to_slave,
project_from_slave_to_master
X = Dict(
1 => [0.0, 1.0],
2 => [5/4, 1.0],
3 => [2.0, 1.0],
4 => [0.0, 1.0],
5 => [3/4, 1.0],
6 => [2.0, 1.0])
mel1 = Element(Seg2, [1, 2])
mel2 = Element(Seg2, [2, 3])
sel1 = Element(Seg2, [4, 5])
sel2 = Element(Seg2, [5, 6])
update!([mel1, mel2, sel1, sel2], "geometry", X)
master_elements = [mel1, mel2]
slave_elements = [sel1, sel2]
normals = calculate_normals(slave_elements, 0.0)
update!(slave_elements, "normal", 0.0 => normals)
X1 = [0.0, 1.0]
n1 = [0.0, 1.0]
xi2 = project_from_slave_to_master(mel1, X1, n1, 0.0)
@test isapprox(xi2, -1.0)
X1 = [0.75, 1.0]
n1 = [0.00, 1.0]
xi2 = project_from_slave_to_master(mel1, X1, n1, 0.0)
@test isapprox(xi2, 0.2)
X2 = mel1("geometry", xi2, 0.0)
@test isapprox(X2, [3/4, 1.0])
X2 = [0.0, 1.0]
xi1 = project_from_master_to_slave(sel1, X2, 0.0)
@test isapprox(xi1, -1.0)
X2 = [1.25, 1.00]
xi1 = project_from_master_to_slave(sel1, X2, 0.0)
X1 = sel1("geometry", xi1, 0.0)
@test isapprox(X1, [5/4, 1.0])
X = Dict(
1 => [0.0, 0.0],
2 => [0.0, 1.0],
3 => [0.0, 1.0],
4 => [0.0, 0.0])
sel1 = Element(Seg2, [1, 2])
mel1 = Element(Seg2, [3, 4])
update!([sel1, mel1], "geometry", X)
slave_elements = [sel1]
normals = calculate_normals(slave_elements, 0.0)
update!(slave_elements, "normal", 0.0 => normals)
X2 = mel1("geometry", (-1.0, ), 0.0)
xi = project_from_master_to_slave(sel1, X2, 0.0)
@test isapprox(xi, 1.0)
X2 = mel1("geometry", (1.0, ), 0.0)
xi = project_from_master_to_slave(sel1, X2, 0.0)
@test isapprox(xi, -1.0)
X1 = sel1("geometry", (-1.0, ), 0.0)
n1 = sel1("normal", (-1.0, ), 0.0)
xi = project_from_slave_to_master(mel1, X1, n1, 0.0)
@test isapprox(xi, 1.0)
X1 = sel1("geometry", (1.0, ), 0.0)
n1 = sel1("normal", (1.0, ), 0.0)
xi = project_from_slave_to_master(mel1, X1, n1, 0.0)
@test isapprox(xi, -1.0)
@test_throws Exception project_from_master_to_slave(sel1, [0.0, 0.0], 0.0; tol=0.0)
@test_throws Exception project_from_slave_to_master(mel1, [0.0, 1.0], [-1.0, 0.0], 0.0; tol=0.0)
| MortarContact2D | https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.3.1 | dad84aeb9caadb97d2c9cf4d2e994c5d3c8a254a | code | 1615 | # This file is a part of JuliaFEM.
# License is MIT: see https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl/blob/master/LICENSE
# Simple coupling interface of four elements
using FEMBase, MortarContact2D, Test
using MortarContact2D: get_slave_dofs, get_master_dofs,
get_mortar_matrix_D, get_mortar_matrix_M,
get_mortar_matrix_P
# Slave side coordinates:
Xs = Dict(
1 => [0.0, 1.0],
2 => [1.0, 1.0],
3 => [2.0, 1.0])
# Master side coordinates:
Xm = Dict(
4 => [0.0, 1.0],
5 => [5/4, 1.0],
6 => [2.0, 1.0])
# Define elements, update geometry:
X = merge(Xm , Xs)
es1 = Element(Seg2, [1, 2])
es2 = Element(Seg2, [2, 3])
em1 = Element(Seg2, [4, 5])
em2 = Element(Seg2, [5, 6])
elements = [es1, es2, em1, em2]
update!(elements, "geometry", X)
# Define new problem `Mortar2D`, coupling elements using mortar methods
problem = Problem(Mortar2D, "test interface", 1, "u")
@test_throws ErrorException add_elements!(problem, [es1, es2])
add_slave_elements!(problem, [es1, es2])
add_master_elements!(problem, [em1, em2])
# Assemble problem
assemble!(problem, 0.0)
s = get_slave_dofs(problem)
m = get_master_dofs(problem)
@test s == [1, 2, 3]
@test m == [4, 5, 6]
P = get_mortar_matrix_P(problem)
D = get_mortar_matrix_D(problem)
M = get_mortar_matrix_M(problem)
# From my thesis
D_expected = [1/3 1/6 0; 1/6 2/3 1/6; 0 1/6 1/3]
M_expected = [11/30 2/15 0; 41/160 13/20 3/32; 1/480 13/60 9/32]
P_expected = 1/320*[329 -24 15; 46 304 -30; -21 56 285]
# Results:
@test isapprox(D, D_expected)
@test isapprox(M, M_expected)
@test isapprox(P, P_expected)
| MortarContact2D | https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.3.1 | dad84aeb9caadb97d2c9cf4d2e994c5d3c8a254a | code | 1478 | # This file is a part of JuliaFEM.
# License is MIT: see https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl/blob/master/LICENSE
# Construct discrete coupling operator between two elements and eliminate
# boundary conditions from global matrix assembly. Thesis, p. 73.
using FEMBase, MortarContact2D, Test
X = Dict(
1 => [1.0, 2.0],
2 => [3.0, 2.0],
3 => [2.0, 2.0],
4 => [0.0, 2.0],
5 => [3.0, 4.0],
6 => [1.0, 4.0],
7 => [0.0, 0.0],
8 => [2.0, 0.0])
slave = Element(Seg2, [1, 2])
master = Element(Seg2, [3, 4])
elements = [slave, master]
update!(elements, "geometry", X)
problem = Problem(Mortar2D, "test interface", 2, "displacement")
add_slave_elements!(problem, [slave])
add_master_elements!(problem, [master])
assemble!(problem, 0.0)
K_SS = K_MM = [
180.0 81.0 -126.0 27.0
81.0 180.0 -27.0 36.0
-126.0 -27.0 180.0 -81.0
27.0 36.0 -81.0 180.0]
M_SS = M_MM = [
40.0 0.0 20.0 0.0
0.0 40.0 0.0 20.0
20.0 0.0 40.0 0.0
0.0 20.0 0.0 40.0]
f_S = [-27.0, -81.0, 81.0, -135.0]
f_M = [ 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
K = [K_SS zeros(4,4); zeros(4,4) K_MM]
M = [M_SS zeros(4,4); zeros(4,4) M_MM]
f = [f_S; f_M]
eliminate_boundary_conditions!(problem, K, M, f)
K_expected = [
441.0 -81.0 -279.0 81.0
-81.0 684.0 81.0 -36.0
-279.0 81.0 333.0 -81.0
81.0 -36.0 -81.0 252.0]
f_expected = [108.0, -243.0, -54.0, 27.0]
@test isapprox(K[5:8,5:8], K_expected)
@test isapprox(f[5:8], f_expected)
| MortarContact2D | https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.3.1 | dad84aeb9caadb97d2c9cf4d2e994c5d3c8a254a | docs | 836 | [](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/120874712)[](https://travis-ci.org/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl)[](https://coveralls.io/github/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl?branch=master)[](https://juliafem.github.io/MortarContact2D.jl/stable)[](https://juliafem.github.io/MortarContact2D.jl/latest)[](https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl/issues)
This package extends JuliaFEM functionalities for contact mechanics.
| MortarContact2D | https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.3.1 | dad84aeb9caadb97d2c9cf4d2e994c5d3c8a254a | docs | 5859 | # Discretization and numerical integration of projection matrices
[//]: # (This may be the most platform independent comment, and also 80 chars.)
In theoretical studies, we have a continuum setting where we evaluate the
mandatory [line integral](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Line_integral).
When going towards a numerical implementation, this integral must be
calculated in discretized setting, which is arising some practical questions.
For example, displacement is defined using local coordinate system for each
element. Thus, we need to find all master-slave pairs, contact segments, which
are giving contribution to the contact virtual work. Discretization of the
contact interface follows standard isoparametric approach. First we define
finite dimensional subspaces $\boldsymbol{\mathcal{U}}_{h}^{\left(i\right)}$
and $\boldsymbol{\mathcal{V}}_{h}^{\left(i\right)}$,
which are approximations of $\boldsymbol{\mathcal{U}}^{\left(i\right)}$ and
$\boldsymbol{\mathcal{V}}^{\left(i\right)}$. Geometry and displacement
interpolation then goes as a following way:
\begin{align}
\boldsymbol{x}_{h}^{\left(1\right)} &
=\sum_{k=1}^{n^{\left(1\right)}}N_{k}^{\left(1\right)}\boldsymbol{x}_{k}^{\left(1\right)}, & \boldsymbol{x}_{h}^{\left(2\right)} &
=\sum_{l=1}^{n^{\left(2\right)}}N_{l}^{\left(2\right)}\boldsymbol{x}_{l}^{\left(2\right)}, \\\\
\boldsymbol{u}_{h}^{\left(1\right)} &
=\sum_{k=1}^{n^{\left(1\right)}}N_{k}^{\left(1\right)}\boldsymbol{d}_{k}^{\left(1\right)}, & \boldsymbol{u}_{h}^{\left(2\right)} &
=\sum_{l=1}^{n^{\left(2\right)}}N_{l}^{\left(2\right)}\boldsymbol{d}_{l}^{\left(2\right)}.
\end{align}
Moreover, we need also to interpolate Lagrange multipliers in the interface:
\begin{equation}
\boldsymbol{\lambda}_{h}=\sum_{j=1}^{m^{\left(1\right)}}\Phi_{j}\boldsymbol{\lambda}_{j}.
\end{equation}
```julia
function f(x)
return x
end
```
Substituting interpolation polynomials to contact virtual work $\delta\mathcal{W}_{\mathrm{co}}$
yields
\begin{align}
-\delta\mathcal{W}_{\mathrm{co}} & =\int_{\gamma_{\mathrm{c}}^{\left(1\right)}}\boldsymbol{\lambda}\cdot\left(\delta\boldsymbol{u}^{\left(1\right)}-\delta\boldsymbol{u}^{\left(2\right)}\circ\chi\right)\,\mathrm{d}a\nonumber \\
& \approx\int_{\gamma_{\mathrm{c},h}^{\left(1\right)}}\boldsymbol{\lambda}_{h}\cdot\left(\delta\boldsymbol{u}_{h}^{\left(1\right)}-\delta\boldsymbol{u}_{h}^{\left(2\right)}\circ\chi_{h}\right)\,\mathrm{d}a\nonumber \\
& =\int_{\gamma_{\mathrm{c},h}^{\left(1\right)}}\left(\sum_{j=1}^{m^{\left(1\right)}}\Phi_{j}\boldsymbol{\lambda}_{j}\right)\cdot\left(\sum_{k=1}^{n^{\left(1\right)}}N_{k}^{\left(1\right)}\delta\boldsymbol{d}_{k}^{\left(1\right)}-\sum_{l=1}^{n^{\left(2\right)}}\left(N_{l}^{\left(2\right)}\circ\chi_{h}\right)\delta\boldsymbol{d}_{l}^{\left(2\right)}\right)\,\mathrm{d}a\nonumber \\
& =\sum_{j=1}^{m^{\left(1\right)}}\sum_{k=1}^{n^{\left(1\right)}}\boldsymbol{\lambda}_{j}\cdot\int_{\gamma_{\mathrm{c},h}^{\left(1\right)}}\Phi_{j}N_{k}^{\left(1\right)}\delta\boldsymbol{d}_{k}^{\left(1\right)}\,\mathrm{d}a-\sum_{j=1}^{m^{\left(1\right)}}\sum_{l=1}^{n^{\left(2\right)}}\boldsymbol{\lambda}_{j}\cdot\int_{\gamma_{\mathrm{c},h}^{\left(1\right)}}\Phi_{j}\left(N_{l}^{\left(2\right)}\circ\chi_{h}\right)\delta\boldsymbol{d}_{l}^{\left(2\right)}\,\mathrm{d}a\nonumber \\
& =\sum_{j=1}^{m^{\left(1\right)}}\sum_{k=1}^{n^{\left(1\right)}}\boldsymbol{\lambda}_{j}^{\mathrm{T}}\left(\int_{\gamma_{\mathrm{c},h}^{\left(1\right)}}\Phi_{j}N_{k}^{\left(1\right)}\,\mathrm{d}a\right)\delta\boldsymbol{d}_{k}^{\left(1\right)}-\sum_{j=1}^{m^{\left(1\right)}}\sum_{l=1}^{n^{\left(2\right)}}\boldsymbol{\lambda}_{j}^{\mathrm{T}}\left(\int_{\gamma_{\mathrm{c},h}^{\left(1\right)}}\Phi_{j}\left(N_{l}^{\left(2\right)}\circ\chi_{h}\right)\,\mathrm{d}a\right)\delta\boldsymbol{d}_{l}^{\left(2\right)}.\label{2d_projection:eq:discretized_contact_virtual_work}
\end{align}
Here, $\chi_{h}:\gamma_{\mathrm{c},h}^{\left(1\right)}\mapsto\gamma_{\mathrm{c},h}^{\left(2\right)}$
is a discrete mapping from the slave surface to the master surface.
From the equation \ref{2d_projection:eq:discretized_contact_virtual_work},
we find the so called mortar matrices, commonly denoted as $\boldsymbol{D}$
and $\boldsymbol{M}$:
\begin{align}
\boldsymbol{D}\left[j,k\right] & =D_{jk}\boldsymbol{I}_{\mathrm{ndim}}=\int_{\gamma_{\mathrm{c},h}^{\left(1\right)}}\Phi_{j}N_{k}^{\left(1\right)}\,\mathrm{d}a\boldsymbol{I}_{\mathrm{ndim}}, & j=1,\ldots,m^{\left(1\right)}, & k=1,\ldots,n^{\left(1\right)},\\
\boldsymbol{M}\left[j,l\right] & =M_{jl}\boldsymbol{I}_{\mathrm{ndim}}=\int_{\gamma_{\mathrm{c},h}^{\left(1\right)}}\Phi_{j}\left(N_{l}^{\left(2\right)}\circ\chi_{h}\right)\,\mathrm{d}a\boldsymbol{I}_{\mathrm{ndim}}, & j=1,\ldots,m^{\left(1\right)}, & l=1,\ldots,n^{\left(2\right)}.
\end{align}
The process of discretizing mesh tie virtual work
$\delta\mathcal{W}_{\mathrm{mt}}$,
is identical to what is now presented, with a difference that integrals
are evaluated in reference configuration instead of current configuration.
Also, when considering linearized kinematic and small deformations,
integration can be done in reference configuration. For mesh tie contact,
the discretized contact virtual work is
\begin{align}
-\delta\mathcal{W}_{\mathrm{mt},h}= & \sum_{j=1}^{m^{\left(1\right)}}\sum_{k=1}^{n^{\left(1\right)}}\boldsymbol{\lambda}_{j}^{\mathrm{T}}\left(\int_{\Gamma_{\mathrm{c},h}^{\left(1\right)}}\Phi_{j}N_{k}^{\left(1\right)}\,\mathrm{d}A_{0}\right)\delta\boldsymbol{d}_{k}^{\left(1\right)}\nonumber \\
& -\sum_{j=1}^{m^{\left(1\right)}}\sum_{l=1}^{n^{\left(2\right)}}\boldsymbol{\lambda}_{j}^{\mathrm{T}}\left(\int_{\Gamma_{\mathrm{c},h}^{\left(1\right)}}\Phi_{j}\left(N_{l}^{\left(2\right)}\circ\chi_{h}\right)\,\mathrm{d}A_{0}\right)\delta\boldsymbol{d}_{l}^{\left(2\right)}.\label{eq:2d_projection:discretized_virtual_work}
\end{align} | MortarContact2D | https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.3.1 | dad84aeb9caadb97d2c9cf4d2e994c5d3c8a254a | docs | 241 | # MortarContact2D.jl
`MortarContact2D.jl` extends JuliaFEM functionalities to solve plane solid
mechanics problems including contacts. Module is partially build on top of
earlier module `Mortar2D.jl`.
## Theory
## Features
## References
| MortarContact2D | https://github.com/JuliaFEM/MortarContact2D.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 767 | module BenchParticle
using Random
using BenchmarkTools
using HOODESolver
suite = BenchmarkGroup()
function fct(u, p, t)
s1, c1 = sincos(u[1]/2)
s2, c2 = sincos(u[2])
s3, c3 = sincos(u[3])
return [0, 0, u[6], c1*s2*s3/2, s1*c2*s3, s1*s2*c3]
end
Random.seed!(561909)
u0 = 2rand(BigFloat,6)-ones(BigFloat,6)
epsilon=big"1e-7"
ordmax=9
A = [0 0 0 1 0 0;
0 0 0 0 1 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 1 0;
0 0 0 -1 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0]
t_0 = big"0.0"
t_max = big"1.0"
prob = HOODEProblem(fct, u0, (t_0, t_max), missing, A, epsilon)
nb = 10^3
n_tau = 32
suite["solve"] = @benchmarkable solve(prob, nb_t=nb, order=ordmax,
getprecision=false, nb_tau=n_tau, dense=false)
end
BenchParticle.suite
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 231 | using BenchmarkTools
const SUITE = BenchmarkGroup()
for file in readdir(@__DIR__)
if startswith(file, "bench_") && endswith(file, ".jl")
SUITE[file[length("bench_") + 1:end - length(".jl")]] =
include(file)
end
end
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 3702 | using HOODESolver
using DifferentialEquations
using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
using Random
function getmindif(tab::Vector{Vector{BigFloat}})
nmmin = Inf
ret = (0, 0)
for i=1:size(tab,1)
for j=(i+1):size(tab,1)
nm = norm(tab[i]-tab[j], Inf)
if nm < nmmin
nmmin = nm
ret = i, j
end
end
end
return ret, nmmin
end
# henon_heiles
function fct(u, p, t)
return [0, u[4], -2u[1]*u[2], -u[2]-u[1]^2+u[2]^2]
end
function fctmain(n_tau, prec)
Random.seed!(19999909)
setprecision(512)
u0 = 2rand(BigFloat,4)-ones(BigFloat,4)
setprecision(prec)
u0 = BigFloat.(u0)
println("u0=$u0")
t_max = big"1.0"
epsilon=big"1e-7"
println("epsilon=$epsilon")
nbmaxtest=15
ordmax=15
debord=3
pasord=1
y = ones(Float64, nbmaxtest, div(ordmax-debord,pasord)+1 )
res_gen = Array{ Array{BigFloat,1}, 2}(undef, nbmaxtest, div(ordmax-debord,pasord)+1 )
x=zeros(Float64,nbmaxtest)
A = [0 0 1 0; 0 0 0 0;-1 0 0 0; 0 0 0 0]
t_0=big"0.0"
t_max=big"1.0"
prob = HOODEProblem(fct, u0, (t_0, t_max), missing, A, epsilon)
nm = NaN
ordmax += 1
ordprep=undef
nb = 10*2^(nbmaxtest)
solref=undef
while isnan(nm)
ordmax -= 1
@time sol = solve(prob, nb_t=nb, order=ordmax, getprecision=false, nb_tau=n_tau, dense=false)
solref = sol[end]
nm = norm(solref, Inf)
end
tabsol = Array{Array{BigFloat,1},1}(undef,1)
tabsol[1] = solref
println("ordmax=$ordmax")
solref_gen = solref
indref = 1
ind=1
for order=debord:pasord:ordmax
ordprep=order+2
println("eps=$epsilon solRef=$solref order=$order")
nb = 10
indc = 1
labels=Array{String,2}(undef, 1, order-debord+1)
sol =undef
par_u0=missing
println("preparation ordre $order + 2")
while indc <= nbmaxtest
@time solall = solve(prob, nb_t=nb, order=order, getprecision=false, nb_tau=n_tau, par_u0=par_u0, dense=false)
par_u0 = solall.par_u0
sol = solall[end]
push!(tabsol, sol)
res_gen[indc,ind] = sol
(a, b), nm = getmindif(tabsol)
if a != indref
println("New solref !!!! a=$a, b=$b nm=$nm")
indref = a
solref = tabsol[a]
for i=1:ind
borne = (i <ind) ? size(res_gen,1) : indc
for j = 1:borne
nm2 = min( norm(res_gen[j,i] - solref, Inf), 1.1)
y[j,i] = nm2 == 0 ? nm : nm2
end
end
else
diff=solref-sol
y[indc,ind] = min(norm(diff,Inf), 1.1)
end
x[indc] = 1.0/nb
println("result=$y")
println("log2(y)=$(log2.(y))")
nb *= 2
indc += 1
end
for i=debord:pasord:order
labels[1,(i-debord)÷pasord+1] = " eps,order=$(convert(Float32,epsilon)),$i "
end
p=Plots.plot(
x,
view(y,:,1:ind),
xlabel="delta t",
xaxis=:log,
ylabel="error",
yaxis=:log,
legend=:bottomright,
label=labels,
marker=2
)
prec_v = precision(BigFloat)
eps_v = convert(Float32,epsilon)
Plots.savefig(p,"out/r4_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_henon_heiles.pdf")
ind+= 1
end
end
fctmain(32,512)
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 3932 | using HOODESolver
using DifferentialEquations
using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
using Random
function getmindif(tab::Vector{Vector{BigFloat}})
nmmin = Inf
ret = (0, 0)
for i=1:size(tab,1)
for j=(i+1):size(tab,1)
nm = norm(tab[i]-tab[j], Inf)
if nm < nmmin
nmmin = nm
ret = i, j
end
end
end
return ret, nmmin
end
function fct(u, p, t)
s1, c1 = sincos(u[1]/2)
s2, c2 = sincos(u[2])
s3, c3 = sincos(u[3])
return [0, 0, u[6], c1*s2*s3/2, s1*c2*s3, s1*s2*c3]
end
function fctmain(n_tau, prec)
setprecision(512)
Random.seed!(561909)
u0 = 2rand(BigFloat,6)-ones(BigFloat,6)
setprecision(prec)
u0 = BigFloat.(u0)
println("u0=$u0")
t_max = big"1.0"
epsilon=big"1e-7"
println("epsilon=$epsilon")
nbmaxtest=15
ordmax=9
debord=3
pasord=1
y = ones(Float64, nbmaxtest, div(ordmax-debord,pasord)+1 )
res_gen = Array{ Array{BigFloat,1}, 2}(undef, nbmaxtest, div(ordmax-debord,pasord)+1 )
x=zeros(Float64,nbmaxtest)
A = [0 0 0 1 0 0; 0 0 0 0 1 0;0 0 0 0 0 0; 0 0 0 0 1 0; 0 0 0 -1 0 0; 0 0 0 0 0 0]
t_0=big"0.0"
t_max=big"1.0"
prob = HOODEProblem(fct, u0, (t_0, t_max), missing, A, epsilon)
nm = NaN
ordmax += 1
ordprep=undef
nb = 10*2^(nbmaxtest)
solref=undef
while isnan(nm)
ordmax -= 1
@time sol = solve(prob, nb_t=nb, order=ordmax, getprecision=false, nb_tau=n_tau, dense=false)
solref = sol[end]
nm = norm(solref, Inf)
end
tabsol = Array{Array{BigFloat,1},1}(undef,1)
tabsol[1] = solref
println("ordmax=$ordmax")
solref_gen = solref
indref = 1
ind=1
for order=debord:pasord:ordmax
ordprep=order+2
println("eps=$epsilon solRef=$solref order=$order")
nb = 10
indc = 1
labels=Array{String,2}(undef, 1, order-debord+1)
resnorm=0
resnormprec=1
sol =undef
par_u0=missing
println("preparation ordre $order + 2")
while indc <= nbmaxtest
@time solall = solve(prob, nb_t=nb, order=order, getprecision=false, nb_tau=n_tau, par_u0=par_u0, dense=false)
par_u0 = solall.par_u0
sol = solall[end]
push!(tabsol, sol)
res_gen[indc,ind] = sol
(a, b), nm = getmindif(tabsol)
if a != indref
println("New solref !!!! a=$a, b=$b nm=$nm")
indref = a
solref = tabsol[a]
for i=1:ind
borne = (i <ind) ? size(res_gen,1) : indc
for j = 1:borne
nm2 = min( norm(res_gen[j,i] - solref, Inf), 1.1)
y[j,i] = nm2 == 0 ? nm : nm2
end
end
else
diff=solref-sol
y[indc,ind] = min(norm(diff,Inf), 1.1)
end
x[indc] = 1.0/nb
println("result=$y")
println("log2(y)=$(log2.(y))")
nb *= 2
indc += 1
end
for i=debord:pasord:order
labels[1,(i-debord)÷pasord+1] = " eps,order=$(convert(Float32,epsilon)),$i "
end
p=Plots.plot(
x,
view(y,:,1:ind),
xlabel="delta t",
xaxis=:log,
ylabel="error",
yaxis=:log,
legend=:topleft,
label=labels,
marker=2
)
prec_v = precision(BigFloat)
eps_v = convert(Float32,epsilon)
Plots.savefig(p,"out/r4_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_particle.pdf")
if resnorm > resnormprec
break
end
resnormprec = resnorm
ind+= 1
end
end
fctmain(32,512)
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 3399 | using HOODESolver
using DifferentialEquations
using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
using Random
function getmindif(tab::Vector{Vector{BigFloat}})
nmmin = Inf
ret = (0, 0)
for i=1:size(tab,1)
for j=(i+1):size(tab,1)
nm = norm(tab[i]-tab[j], Inf)
if nm < nmmin
nmmin = nm
ret = i, j
end
end
end
return ret, nmmin
end
function fct(u, p, t)
s1, c1 = sincos(u[1]/2)
s2, c2 = sincos(u[2])
s3, c3 = sincos(u[3])
return [0, 0, u[6], c1*s2*s3/2, s1*c2*s3, s1*s2*c3]
end
function fctmain(n_tau, prec)
setprecision(512)
Random.seed!(561909)
u0 = 2rand(BigFloat,6)-ones(BigFloat,6)
setprecision(prec)
u0 = BigFloat.(u0)
println("u0=$u0")
t_max = big"1.0"
epsbase=big"0.1"
nbeps=9
nbmaxtest=14
order=5
A = [0 0 0 1 0 0; 0 0 0 0 1 0;0 0 0 0 0 0; 0 0 0 0 1 0; 0 0 0 -1 0 0; 0 0 0 0 0 0]
t_0=big"0.0"
t_max=big"1.0"
y = ones(Float64, nbmaxtest, nbeps )
for ieps=1:nbeps
epsilon = epsbase^ieps
res_gen = Array{ Array{BigFloat,1}, 1}(undef, nbmaxtest )
x=zeros(Float64,nbmaxtest)
nb = 10*2^(nbmaxtest)
prob = HOODEProblem(fct, u0, (t_0, t_max), missing, A, epsilon)
@time sol = solve(prob, nb_t=nb, order=order, getprecision=false, nb_tau=n_tau, dense=false)
solref = sol[end]
tabsol = Array{Array{BigFloat,1},1}(undef,1)
tabsol[1] = solref
println("eps=$epsilon solRef=$solref order=$order")
nb = 10
indc = 1
labels=Array{String,2}(undef, 1, nbeps)
resnorm=0
resnormprec=1
sol =undef
par_u0=missing
indref = 1
println("preparation ordre $order + 2")
while indc <= nbmaxtest
@time solall = solve(prob, nb_t=nb, order=order, getprecision=false, nb_tau=n_tau, par_u0=par_u0, dense=false)
par_u0 = solall.par_u0
sol = solall[end]
res_gen[indc] = sol
push!(tabsol, sol)
(a, b), nm = getmindif(tabsol)
if a != indref
println("New solref !!!! a=$a, b=$b nm=$nm")
indref = a
solref = tabsol[a]
for j = 1:indc
nm2 = min( norm(res_gen[j] - solref, Inf), 1.1)
y[j,ieps] = nm2 == 0 ? nm : nm2
end
else
diff=solref-sol
y[indc,ieps] = min(norm(diff,Inf), 1.1)
end
x[indc] = 1.0/nb
println("result=$y")
println("log2(y)=$(log2.(y))")
nb *= 2
indc += 1
end
for i=1:ieps
ep=epsbase^i
labels[1,i] = " eps,order=$(convert(Float32,ep)),$order "
end
p=Plots.plot(
x,
view(y,:,1:ieps),
xlabel="delta t",
xaxis=:log,
ylabel="error",
yaxis=:log,
legend=:topleft,
label=labels,
marker=2
)
prec_v = precision(BigFloat)
eps_v = convert(Float32,epsilon)
Plots.savefig(p,"out/r3_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_particle_epsilon.pdf")
end
end
fctmain(32,256)
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 2919 | #=
testODE:
- Julia version:
- Author: ymocquar
- Date: 2019-11-13
=#
using HOODESolver
using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
using Plots.PlotMeasures
function fctMain(n_tau)
# u0 =[big"0.12345678", big"0.1209182736", big"0.1290582671", big"0.1239681094" ]
tab_eps = zeros(BigFloat,7)
epsilon=big"0.15"
for i=1:size(tab_eps,1)
tab_eps[i] = epsilon
epsilon /= 10
end
u0 = BigFloat.([-34//100, 78//100, 67//100, -56//10])
B = BigFloat.([12//100 -78//100 91//100 34//100
-45//100 56//100 3//100 54//100
-67//100 09//100 18//100 89//100
-91//100 -56//100 11//100 -56//100])
alpha = BigFloat.([12//100, -98//100, 45//100, 26//100])
beta = BigFloat.([-4//100, 48//100, 23//100, -87//100])
fct = (u,p,t) -> B*u + t*p[1] +p[2]
t_max = big"1.0"
nbMaxTest=12
order=6
y = ones(Float64, nbMaxTest, size(tab_eps,1) )
x=zeros(Float64,nbMaxTest)
ind=1
A=[0 0 1 0; 0 0 0 0;-1 0 0 0; 0 0 0 0]
for epsilon in tab_eps
prob = HOODEProblem(fct,u0, (big"0.0",t_max), (alpha, beta), A, epsilon, B)
eps_v = convert(Float32,epsilon)
println("epsilon = $eps_v")
nb = 100
indc = 1
labels=Array{String,2}(undef, 1, ind)
while indc <= nbMaxTest
res = solve(prob, nb_tau=n_tau, order=order, nb_t=nb, dense=false)
sol = res[end]
solref = getexactsol(res.par_u0.parphi, u0, t_max)
println("solref=$solref")
println("nb=$nb sol=$sol")
diff=solref-sol
x[indc] = t_max/nb
println("nb=$nb dt=$(1.0/nb) normInf=$(norm(diff,Inf)) norm2=$(norm(diff))")
ni = norm(diff,Inf)
y[indc,ind] = (ni < 1) ? ni : NaN
println("epsilon=$epsilon result=$y")
println("epsilon=$epsilon reslog2=$(log2.(y))")
nb *= 2
indc += 1
end
for i=1:ind
labels[1,i] = " ε = $(convert(Float32,tab_eps[i])) "
end
p=Plots.plot(
x,
view(y,:,1:ind),
xlabel="Δt",
xaxis=:log,
ylabel="error",
yaxis=:log,
legend=:bottomright,
label=labels,
marker=2
)
pp=Plots.plot(
x,
view(y,:,1:ind),
xlabel="Δt",
xaxis=:log,
ylabel="error",
yaxis=:log,
legend=:bottomright,
label=labels,
marker=2,
bottom_margin=30px,
left_margin=60px
)
prec_v = precision(BigFloat)
Plots.savefig(p,"out/r10p_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_epsilon.pdf")
Plots.savefig(p,"out/r10p_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_epsilon.png")
Plots.savefig(pp,"out/r10pp_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_epsilon.pdf")
Plots.savefig(pp,"out/r10pp_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_epsilon.png")
ind+= 1
end
end
# testODESolverEps()
# for i=3:9
# fctMain(2^i)
# end
# setprecision(512)
fctMain(32)
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 2398 | #=
testODE:
- Julia version:
- Author: ymocquar
- Date: 2019-11-13
=#
using HOODESolver
using DifferentialEquations
using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
using Random
function twoscales_solve( par_u0::PrepareU0, order, t, nb)
end
function fctMain(n_tau)
seed=123321
Random.seed!(seed)
u0 = rand(BigFloat, 4)
B = 2rand(BigFloat, 4, 4) - ones(BigFloat, 4, 4)
println("seed = $seed B=$B")
nbeps=48
nbmaxtest=3
paseps = big"10.0"^0.125
ordmin=3
ordmax=14
ordpas = 1
t_max = big"1.0"
A = [0 0 1 0; 0 0 0 0;-1 0 0 0; 0 0 0 0]
for order = ordmin:ordpas:ordmax
y = ones(Float64, nbeps, nbmaxtest)
x=zeros(Float64,nbeps)
for i_eps=1:nbeps
epsilon = big"1.0"/paseps^i_eps
x[i_eps] = epsilon
fct = u -> B*u
parphi = PreparePhi(epsilon, n_tau, A, fct, B)
println("prepareU0 eps=$epsilon n_tau=$n_tau")
@time par_u0 = PrepareU0(parphi, order+2, u0)
solref = getexactsol(parphi, u0, t_max)
eps_v = convert(Float32,epsilon)
println("epsilon = $eps_v solref=$solref")
for indc=1:nbmaxtest
nb = 10*10^indc
@time parGen = PrepareTwoScalePureAB(nb, t_max, order, par_u0)
@time sol = twoscales_pure_ab(parGen, only_end=true)
println("solref=$solref")
println("nb=$nb sol=$sol")
diff=solref-sol
println("nb=$nb dt=$(1.0/nb) normInf=$(norm(diff,Inf)) norm2=$(norm(diff))")
y[i_eps, indc] = norm(diff,Inf)
println("epsilon=$epsilon result=$y")
end
end
labels=Array{String,2}(undef, 1, nbmaxtest)
for i=1:nbmaxtest
nb = 10*10^i
labels[1,i] = " delta t,order=$(1/nb), $order "
mindiff = minimum(y[:,i])
bornediff = min(mindiff*1e20,1)
for j=1:nbeps
if y[j,i] >= bornediff
y[j,i] = NaN
end
end
end
gr()
p=Plots.plot(
x,
y,
xlabel="epsilon",
xaxis=:log,
ylabel="error",
yaxis=:log,
legend=:topleft,
label=labels,
marker=2
)
prec_v = precision(BigFloat)
Plots.savefig(p,"out/r_$(prec_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_epsilon_lgn_2.pdf")
end
end
fctMain(32)
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 5040 | #=
testODE:
- Julia version:
- Author: ymocquar
- Date: 2019-11-13
=#
using HOODESolver
using DifferentialEquations
using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
using Random
function twoscales_solve( par_u0::PrepareU0, order, t, nb)
parGen = PrepareTwoScalePureAB(nb, t, order, par_u0)
return twoscales_pure_ab(parGen, only_end=true)
end
function getmindif(tab::Vector{Vector{BigFloat}})
nmmin = Inf
ret = (1, 2)
for i=1:size(tab,1)
for j=(i+1):size(tab,1)
nm = norm(tab[i]-tab[j], Inf)
if nm < nmmin
nmmin = nm
ret = i, j
end
end
end
return ret, min(nmmin,1.1)
end
function fctMain(n_tau)
# u0 =[big"0.12345678", big"0.1209182736", big"0.1290582671", big"0.1239681094" ]
seed=12996
Random.seed!(seed)
u0=rand(BigFloat,4)
println("seed = $seed")
# tab_eps = zeros(BigFloat,7)
# tab_eps= [big"0.5", big"0.2", big"0.1",big"0.05", big"0.02", big"0.01",big"0.005", big"0.002", big"0.001",big"0.0005", big"0.0002", big"0.0001"]
tab_eps= [big"0.1",big"0.01", big"0.001",big"0.0001", big"0.00001", big"0.000001", big"0.0000001", big"0.00000001", big"0.000000001"]
# epsilon=big"0.1"
# for i=1:7
# tab_eps[i] = epsilon
# epsilon /= 100
# end
nbmaxtest=11
t_max = big"1.0"
A=[0 0 1 0; 0 0 0 0;-1 0 0 0; 0 0 0 0]
tabtabsol = Vector{Vector{Vector{BigFloat}}}()
for order=2:14
ordprep=order+2
y = ones(Float64, nbmaxtest, size(tab_eps,1) )
y_big = ones(BigFloat, nbmaxtest, size(tab_eps,1) )
x=zeros(Float64,nbmaxtest)
ind=1
for epsilon in tab_eps
# fct = u -> [ 1.11u[2]^2+0.8247u[4]^3+0.12647u[3]^4,
# 0.4356789141u[1]-0.87u[3]*u[4],
# 1.9898985/(1+1.1237u[4]^3), 0.97u[1]*u[3]+0.8111u[2]^2 ]
fct = (u,p,t) -> [
u[3]^3 + sin(t^2),
u[4] + u[1]^2 + 1/(1+exp(t))-0.35,
u[1]*u[2]*u[4]*(1+t),
u[2] - u[2]^2 + 1/(1+u[4]^2) + u[1]^2 + cos(exp(t))
]
parphi = PreparePhi(epsilon, n_tau, A, fct)
println("prepareU0 eps=$epsilon n_tau=$n_tau")
nb=10
@time par_u0 = PrepareU0(parphi, ordprep, u0)
@time pargen = PrepareTwoScalesPureAB(nb*2^nbmaxtest, t_max, order, par_u0)
@time solref = twoscales_pure_ab(pargen, only_end=true)
if size(tabtabsol,1) < ind
push!(tabtabsol,Vector{Vector{BigFloat}}())
end
tabsol = tabtabsol[ind]
push!(tabsol, solref)
res_gen = Array{ Array{BigFloat,1}, 1}(undef, nbmaxtest)
indref = 1
eps_v = convert(Float32,epsilon)
println("epsilon = $eps_v solref=$solref")
indc =1
labels=Array{String,2}(undef, 1, ind)
while indc <= nbmaxtest
@time pargen = PrepareTwoScalesPureAB(nb, t_max, order, par_u0)
@time sol= twoscales_pure_ab(pargen, only_end=true)
push!(tabsol, sol)
res_gen[indc] = sol
diff=solref-sol
println("tabsol=$tabsol")
(a, b), nm = getmindif(tabsol)
if a != indref
println("New solref !!!! a=$a, b=$b nm=$nm")
indref = a
solref = tabsol[a]
for i=1:indc
nm2 = min( norm(res_gen[i] - solref, Inf), 1.1)
y[i, ind] = nm2 == 0 ? nm : nm2
y_big[i, ind] = nm2 == 0 ? nm : nm2
end
else
diff=solref-sol
y[indc,ind] = min(norm(diff,Inf), 1.1)
y_big[indc,ind] = min(norm(diff,Inf), 1.1)
end
println("solref=$solref")
println("nb=$nb sol=$sol")
x[indc] = 1.0/nb
println("epsilon=$epsilon result=$y")
println("epsilon=$epsilon reslog2=$(log2.(y))")
println("epsilon=$epsilon result=$y_big")
println("epsilon=$epsilon reslog2=$(log2.(y_big))")
nb *= 2
indc += 1
end
if ind == size(tab_eps,1)
for i=1:ind
labels[1,i] = " epsilon,order=$(convert(Float32,tab_eps[i])),$order "
end
gr()
p=Plots.plot(
x,
view(y,:,1:ind),
xlabel="delta t",
xaxis=:log,
ylabel="error",
yaxis=:log,
legend=:bottomright,
label=labels,
marker=2
)
prec_v = precision(BigFloat)
Plots.savefig(p,"out/r20_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(ordprep)_$(n_tau)_epsilon_fct.pdf")
end
ind+= 1
end
end
end
# testODESolverEps()
# for i=3:9
# fctMain(2^i)
# end
# setprecision(512)
fctMain(32)
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 2396 | #=
testODE:
- Julia version:
- Author: ymocquar
- Date: 2019-11-13
=#
using HOODESolver
using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
using Plots.PlotMeasures
function henon_heiles(u, p, t)
return [0, u[4], -2u[1] * u[2], -u[2] - u[1]^2 + u[2]^2]
end
function fctmain(n_tau, prec)
setprecision(prec)
u0=BigFloat.([90, -44, 83, 13]//100)
tab_eps = zeros(BigFloat,8)
epsilon=big"0.19"
for i=1:size(tab_eps,1)
tab_eps[i] = epsilon
epsilon /= 10
end
nbmaxtest=12
order=6
t_max = big"1.0"
y = ones(Float64, nbmaxtest, size(tab_eps,1) )
x=zeros(Float64,nbmaxtest)
ind=1
A=[0 0 1 0; 0 0 0 0;-1 0 0 0; 0 0 0 0]
for epsilon in tab_eps
prob = HOODEProblem(henon_heiles, u0, (big"0.0",t_max), missing, A, epsilon)
tabsol = Array{Array{BigFloat,1},1}(undef,0)
eps_v = convert(Float32,epsilon)
nb = 60*2^nbmaxtest
res = solve(prob, nb_tau=n_tau, order=order, nb_t=nb, dense=false)
par_u0=res.par_u0
solRef = res[end]
nb = 100
indc =1
labels=Array{String,2}(undef, 1, ind)
while indc <= nbmaxtest
res = solve(prob, nb_tau=n_tau, order=order, nb_t=nb,par_u0=par_u0, dense=false)
sol = res[end]
nm = norm(sol - solRef, Inf)
y[indc,ind] = (nm < 1) ? nm : NaN
x[indc] = 1.0/nb
nb *= 2
indc += 1
end
for i=1:ind
labels[1,i] = " ε = $(convert(Float32,tab_eps[i])) "
end
p=Plots.plot(
x,
view(y,:,1:ind),
xlabel="Δt",
xaxis=:log,
ylabel="error",
yaxis=:log,
legend=:bottomright,
label=labels,
marker=2
)
pp=Plots.plot(
x,
view(y,:,1:ind),
xlabel="Δt",
xaxis=:log,
ylabel="error",
yaxis=:log,
legend=:bottomright,
label=labels,
marker=2,
bottom_margin=30px,
left_margin=60px
)
prec_v = precision(BigFloat)
Plots.savefig(p,"out/r2p_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_epsilon_hh_2.pdf")
Plots.savefig(p,"out/r2p_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_epsilon_hh_2.png")
Plots.savefig(pp,"out/r2pp_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_epsilon_hh_2.pdf")
Plots.savefig(pp,"out/r2pp_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_epsilon_hh_2.png")
ind+= 1
end
end
fctmain(32,256)
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 3187 |
using HOODESolver
using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
using Plots.PlotMeasures
function fctmain(n_tau, prec)
setprecision(prec)
u0 = BigFloat.([-34//100, 78//100, 67//100, -56//10])
B = BigFloat.([12//100 -78//100 91//100 34//100
-45//100 56//100 3//100 54//100
-67//100 09//100 18//100 89//100
-91//100 -56//100 11//100 -56//100])
alpha = BigFloat.([12//100, -98//100, 45//100, 26//100])
beta = BigFloat.([-4//100, 48//100, 23//100, -87//100])
println("u0=$u0")
println("B=$B")
println("alpha=$alpha")
println("beta=$beta")
fct = (u,p,t) -> B*u + t*p[1] +p[2]
t_max = big"1.0"
epsilon=big"0.015"
A = [0 0 1 0; 0 0 0 0;-1 0 0 0; 0 0 0 0]
prob = HOODEProblem(fct,u0, (big"0.0",t_max), (alpha, beta), A, epsilon, B)
# nbmaxtest=6
nbmaxtest=12
ordmax=17
debord=3
pasord=2
y = ones(Float64, nbmaxtest, div(ordmax-debord,pasord)+1 )
x=zeros(Float64,nbmaxtest)
ind=1
for order=debord:pasord:ordmax
nb = 100
indc = 1
labels=Array{String,2}(undef, 1, div(order-debord,pasord)+1)
ordprep = min(order+2,10)
ordprep = order+2
println("preparation ordre $ordprep")
par_u0=missing
while indc <= nbmaxtest
println("u0=$u0")
println("B=$B")
println("alpha=$alpha")
println("beta=$beta")
@time res = solve(prob, nb_tau=n_tau, order=order, order_prep=ordprep, nb_t=nb,par_u0=par_u0, dense=false)
par_u0=res.par_u0
sol = res[end]
solref=getexactsol(res.par_u0.parphi, u0, t_max)
println("solref=$solref")
println("nb=$nb sol=$sol")
diff=solref-sol
x[indc] = 1.0/nb
println("nb=$nb dt=$(1.0/nb) normInf=$(norm(diff,Inf)) norm2=$(norm(diff))")
resnorm = Float64(norm(diff,Inf))
y[indc,ind] = (resnorm < 1) ? resnorm : NaN
println("result=$y")
println("log2(y)=$(log2.(y))")
nb *= 2
indc += 1
end
for i=debord:pasord:order
labels[1,div((i-debord),pasord)+1] = " order=$i "
end
yv = y[:,1:ind]
p=Plots.plot(
x,
yv,
xlabel="Δt",
xaxis=:log,
ylabel="error",
yaxis=:log,
legend=:bottomright,
label=labels,
marker=2,
)
pp=Plots.plot(
x,
yv,
xlabel="Δt",
xaxis=:log,
ylabel="error",
yaxis=:log,
legend=:bottomright,
label=labels,
marker=2,
bottom_margin=30px,
left_margin=60px
)
prec_v = precision(BigFloat)
eps_v = convert(Float32,epsilon)
Plots.savefig(p,"out/res9p_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(ordprep)_$(n_tau)_exact.pdf")
Plots.savefig(p,"out/res9p_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(ordprep)_$(n_tau)_exact.png")
Plots.savefig(pp,"out/res9pp_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(ordprep)_$(n_tau)_exact.pdf")
Plots.savefig(pp,"out/res9pp_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(ordprep)_$(n_tau)_exact.png")
ind+= 1
end
end
# testODESolver()
# for i=3:9
# fctMain(2^i)
# end
fctmain(32, 512)
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 3849 | using HOODESolver
using DifferentialEquations
using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
using Random
function getmindif(tab::Vector{Vector{BigFloat}})
nmmin = Inf
ret = (0, 0)
for i=1:size(tab,1)
for j=(i+1):size(tab,1)
nm = norm(tab[i]-tab[j], Inf)
if nm < nmmin
nmmin = nm
ret = i, j
end
end
end
return ret, nmmin
end
function fctmain(n_tau, prec)
setprecision(prec)
Random.seed!(5612)
u0=rand(BigFloat,4)
t_max = big"1.0"
epsilon=big"1e-3"
println("epsilon=$epsilon")
nbmaxtest=10
ordmax=12
debord=3
pasord=1
y = ones(Float64, nbmaxtest, div(ordmax-debord,pasord)+1 )
fct = u -> [ u[2]^2,1/(1+u[3]^2),0.5-u[4],0.8u[1] ]
res_gen = Array{ Array{BigFloat,1}, 2}(undef, nbmaxtest, div(ordmax-debord,pasord)+1 )
x=zeros(Float64,nbmaxtest)
A = [0 0 1 0; 0 0 0 0;-1 0 0 0; 0 0 0 0]
parphi = PreparePhi(epsilon, n_tau, A, fct)
nm = NaN
ordmax += 1
ordprep=undef
nb = 20*2^(nbmaxtest)
solref=undef
while isnan(nm)
ordmax -= 1
ordprep = ordmax+2
@time par_u0 = PrepareU0(parphi, ordprep, u0)
@time pargen = PrepareTwoScalePureAB(nb, t_max, ordmax, par_u0)
@time solref= twoscales_pure_ab(
pargen,
only_end=true,
diff_fft=false
)
nm = norm(solref, Inf)
end
tabsol = Array{Array{BigFloat,1},1}(undef,1)
tabsol[1] = solref
println("ordmax=$ordmax")
println("solref=$solref")
solref_gen = solref
indref = 1
ind=1
for order=debord:pasord:ordmax
ordprep=order+2
println("eps=$epsilon solRef=$solref order=$order")
nb = 10
indc = 1
labels=Array{String,2}(undef, 1, order-debord+1)
resnorm=0
resnormprec=1
sol =undef
println("preparation ordre $order + 2")
@time par_u0 = PrepareU0(parphi, ordprep, u0)
while indc <= nbmaxtest
@time pargen = PrepareTwoScalePureAB(nb, t_max, order, par_u0)
@time sol = twoscales_pure_ab(
pargen,
only_end=true,
diff_fft=false
)
push!(tabsol, sol)
res_gen[indc,ind] = sol
(a, b), nm = getmindif(tabsol)
if a != indref
println("New solref !!!! a=$a, b=$b nm=$nm")
indref = a
solref = tabsol[a]
for i=1:ind
borne = (i <ind) ? size(res_gen,1) : indc
for j = 1:borne
nm2 = min( norm(res_gen[j,i] - solref, Inf), 1.1)
y[j,i] = nm2 == 0 ? nm : nm2
end
end
else
diff=solref-sol
y[indc,ind] = min(norm(diff,Inf), 1.1)
end
x[indc] = 1.0/nb
println("result=$y")
println("log2(y)=$(log2.(y))")
nb *= 2
indc += 1
end
for i=debord:pasord:order
labels[1,(i-debord)÷pasord+1] = " eps,order=$(convert(Float32,epsilon)),$i "
end
p=Plots.plot(
x,
view(y,:,1:ind),
xlabel="delta t",
xaxis=:log,
ylabel="error",
yaxis=:log,
legend=:topleft,
label=labels,
marker=2
)
prec_v = precision(BigFloat)
eps_v = convert(Float32,epsilon)
Plots.savefig(p,"out/r2_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_fct3.pdf")
if resnorm > resnormprec
break
end
resnormprec = resnorm
ind+= 1
end
end
# testODESolver()
# for i=3:9
# fctMain(2^i)
# end
fctmain(256,512)
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 4033 | using HOODESolver
using LinearAlgebra
using Plots
using Plots.PlotMeasures
function getmindif(tab::Vector{Vector{BigFloat}})
nmmin = Inf
ret = (0, 0)
for i=1:size(tab,1)
for j=(i+1):size(tab,1)
nm = norm(tab[i]-tab[j], Inf)
if nm < nmmin
nmmin = nm
ret = i, j
end
end
end
return ret
end
function fctmain(n_tau, prec)
setprecision(prec)
u0=BigFloat.([90, -44, 83, 13]//100)
t_max = big"1.0"
epsilon=big"0.0017"
println("epsilon=$epsilon")
nbmaxtest=12
ordmax=17
debord=3
pasord=2
y = ones(Float64, nbmaxtest, div(ordmax-debord,pasord)+1 )
res_gen = Array{ Array{BigFloat,1}, 2}(undef, nbmaxtest, div(ordmax-debord,pasord)+1 )
x=zeros(Float64,nbmaxtest)
A = [0 0 1 0; 0 0 0 0;-1 0 0 0; 0 0 0 0]
prob = HOODEProblem(henon_heiles, u0, (big"0.0",t_max), missing, A, epsilon)
tabsol = Array{Array{BigFloat,1},1}(undef,0)
println("ordmax=$ordmax")
indref = 1
ind=1
for order=debord:pasord:ordmax
println("eps=$epsilon order=$order")
nb = 100
indc = 1
labels=Array{String,2}(undef, 1, div(order-debord, pasord)+1)
resnorm=0
resnormprec=1
sol =undef
println("preparation ordre $order + 2")
par_u0 = missing
borindc = (order < ordmax) ? nbmaxtest : nbmaxtest+1
while indc <= borindc
if indc > nbmaxtest
nb = 51*2^nbmaxtest
end
res = solve(prob, nb_tau=n_tau, order=order, nb_t=nb,par_u0=par_u0, dense=false)
par_u0=res.par_u0
sol = res[end]
push!(tabsol, sol)
if indc <= nbmaxtest
res_gen[indc,ind] = sol
x[indc] = 1.0/nb
end
(a, b) = getmindif(tabsol)
if a != 0
indref = a
solref = tabsol[b]
for i=1:ind
borne = (i <ind) ? size(res_gen,1) : min(indc, size(res_gen,1))
for j = 1:borne
nm = norm(res_gen[j,i] - solref, Inf)
if nm == 0
nm = norm(res_gen[j,i] - tabsol[a], Inf)
end
y[j,i] = (nm < 1) ? nm : NaN
end
end
end
println("result=$y")
println("log2(y)=$(log2.(y))")
nb *= 2
indc += 1
end
for i=debord:pasord:order
labels[1,(i-debord)÷pasord+1] = " order = $i "
end
p=Plots.plot(
x,
view(y,:,1:ind),
xlabel="Δt",
xaxis=:log,
ylabel="error",
yaxis=:log,
legend=:bottomright,
label=labels,
marker=2
)
pp=Plots.plot(
x,
view(y,:,1:ind),
xlabel="Δt",
xaxis=:log,
ylabel="error",
yaxis=:log,
legend=:bottomright,
label=labels,
marker=2,
bottom_margin=30px,
left_margin=60px
)
prec_v = precision(BigFloat)
eps_v = convert(Float32,epsilon)
Plots.savefig(p,"out/res4p_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_henon_heiles.pdf")
Plots.savefig(p,"out/res4p_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_henon_heiles.png")
Plots.savefig(pp,"out/res4pp_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_henon_heiles.pdf")
Plots.savefig(pp,"out/res4pp_$(prec_v)_$(eps_v)_$(order)_$(n_tau)_henon_heiles.png")
ind+= 1
end
end
# testODESolver()
# for i=3:9
# fctMain(2^i)
# end
fctmain(32,512)
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 1137 | using Documenter
using DocumenterCitations
using Plots
using HOODESolver
ENV["GKSwstype"] = "100"
bib = CitationBibliography(joinpath(@__DIR__, "references.bib"))
makedocs(
sitename = "HOODESolver.jl",
authors="Yves Mocquard, Nicolas Crouseilles and Pierre Navaro",
format=Documenter.HTML(;
prettyurls=get(ENV, "CI", "false") == "true",
canonical="https://pnavaro.github.io/HOODESolver.jl",
repolink = "https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl/blob/{commit}{path}#{line}",
assets=String[],
),
modules = [HOODESolver],
pages = ["Documentation" => "index.md",
"Numerical Method" => "numerical_method.md",
"DifferentialEquations" => "common_interface.md",
"Quickstart" => "quickstart.md",
"Charged Particle" => "charged_particle.md",
"Future work" => "future_work.md",
"Types" => "types.md",
"Functions" => "functions.md"],
plugins = [bib],
)
deploydocs(;
branch = "gh-pages",
devbranch = "master",
repo="github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl",
)
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 210 | module HOODESolver
include("common_interface.jl")
export HOODEProblem, HOODEInterpolation, AbstractHOODESolution, HOODESolution
export LinearHOODEOperator, isconstant, HOODEAB
export solve, getexactsol
end
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 4333 | #=
polylagrange:
- Julia version:
- Author: ymocquar
- Date: 2019-11-25
=#
include("polyexp.jl")
function getpolylagrange(k::Int64, j::Int64, N::DataType)
@assert k <= j "_getpolylagrange(k=$k,j=$j) k must be less or equal to j"
@assert N <: Signed "the type $N must be an Integer"
result = Polynomial([one(Complex{Rational{N}})])
for l = 0:j
if l != k
result *= Polynomial([l // 1, 1 // 1]) / (l - k)
end
end
return result
end
function interpolate(tab, order, value, N::DataType)
T = (N == BigInt) ? BigFloat : Float64
res = zeros(Complex{T}, size(tab[1]))
for i = 0:order
res .+= getpolylagrange(i, order, N)(-value) * tab[i+1]
end
return res
end
function getpolylagrange(t::Vector{T}, k, j) where {T<:Number}
result = Polynomial([one(T)])
for l = 0:j
if l != k
result *= Polynomial([-t[l+1], one(T)]) / (t[k+1] - t[l+1])
end
end
return result
end
function interpolate(tab_time::Vector{T}, tab, order, value) where {T<:Number}
res = zeros(Complex{T}, size(tab[1]))
for i = 0:order
res .+= getpolylagrange(tab_time, i, order)(value) * tab[i+1]
end
return res
end
interpolate(tab, order, value) = interpolate(tab, order, value, BigInt)
struct CoefExpABRational
tab_coef::Any
function CoefExpABRational(
order::Int64,
epsilon::AbstractFloat,
list_tau,
dt::AbstractFloat,
)
n_tau = size(list_tau, 1)
T = typeof(epsilon)
tab_coef = zeros(Complex{T}, n_tau, order + 1, order + 1)
N = T == BigFloat ? BigInt : Int64
epsilon = rationalize(N, epsilon, tol = epsilon * 10 * Base.eps(T))
dt = rationalize(N, dt, tol = dt * 10 * Base.eps(T))
list_tau = rationalize.(N, list_tau)
pol_x = Polynomial([0 // 1, 1 // dt])
for j = 0:order
for k = 0:j
res = view(tab_coef, :, k + 1, j + 1)
pol = getpolylagrange(k, j, N)
pol2 = pol(pol_x)
for ind = 1:n_tau
ell = list_tau[ind]
pol3 = undef
pol_int = if ell == 0
# in this case the exponentiel value is always 1
Polynomials.integrate(pol2)
else
pol3 = PolyExp(pol2, im * ell / epsilon, -im * ell * dt / epsilon)
Polynomials.integrate(pol3)
end
res[ind] = pol_int(dt) - pol_int(0)
end
end
end
return new(tab_coef)
end
end
struct CoefExpAB
tab_coef::Any
tab_coef_neg::Any
function CoefExpAB(order::Int64, epsilon::AbstractFloat, n_tau, dt)
T = typeof(epsilon)
N = T == BigFloat ? BigInt : Int64
new_prec = precision(BigFloat)
new_prec += T == BigFloat ? order * 16 : 0
setprecision(BigFloat, new_prec) do
list_tau = [collect(0:n_tau/2-1); collect(-n_tau/2:-1)]
T2 = BigFloat
epsilon = T2(epsilon)
dt = T2(dt)
tab_coef = zeros(Complex{T2}, n_tau, order + 1, order + 1)
pol_x = Polynomial([0, 1 / dt])
for j = 0:order
for k = 0:j
res = view(tab_coef, :, k + 1, j + 1)
pol = getpolylagrange(k, j, N)
pol2 = pol(pol_x)
for ind = 1:n_tau
ell = list_tau[ind]
pol_int = if ell == 0
# in this case the exponentiel value is always 1
Polynomials.integrate(pol2)
else
Polynomials.integrate(
PolyExp(pol2, im * ell / epsilon, -im * ell * dt / epsilon),
)
end
res[ind] = pol_int(dt) - pol_int(0)
end
end
end # end of for j=....
end # end of setprecision(...)
# conversion to the new precision
tab_coef = T.(real(tab_coef)) + im * T.(imag(tab_coef))
tab_coef_neg = -conj(tab_coef)
return new(tab_coef, tab_coef_neg)
end
end
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 3934 | using LinearAlgebra
using GenericSchur
include("interface.jl")
struct LinearHOODEOperator{T} <: SciMLBase.AbstractDiffEqLinearOperator{T}
epsilon::T
A::AbstractMatrix
end
SciMLBase.isinplace(linop::LinearHOODEOperator, n::Int) = false
function LinearHOODEOperator(mat::AbstractMatrix{T}) where {T}
P = eigvecs(mat .+ 0im) # ca bug avec les reels
Ad = inv(P) * mat * P
epsilon = 1 / maximum(abs.(Ad))
A = epsilon * mat
Aint = round.(A)
@assert norm(A - Aint, Inf) <= eps(T) "The A matrix must be with integers A=$A"
epsilon = norm(Aint, Inf) / norm(mat, Inf)
LinearHOODEOperator{T}(epsilon, Aint)
end
*(v::T, L::LinearHOODEOperator{T}) where {T<:Number} =
LinearHOODEOperator(L.epsilon / v, L.A)
Base.@propagate_inbounds Base.convert(::Type{AbstractMatrix}, L::LinearHOODEOperator) =
(1 / L.epsilon) * L.A
import SciMLBase: isconstant
isconstant(_::LinearHOODEOperator) = true
function LinearHOODEOperator(linop::DiffEqArrayOperator)
linop.update_func != SciMLBase.DEFAULT_UPDATE_FUNC &&
error("no update operator function for HOODEAB Alg")
LinearHOODEOperator(linop.A)
end
LinearHOODEOperator(linop::LinearHOODEOperator) = linop
function LinearHOODEOperator(odefct::ODEFunction)
return LinearHOODEOperator(odefct.f)
end
isSplitODEProblem(probtype::Any) = false
isSplitODEProblem(probtype::SplitODEProblem) = true
"""
HOODEAB( order=4, ntau=32)
Algorithm for High-Oscillatory equation
"""
struct HOODEAB{order,ntau} <: SciMLBase.AbstractODEAlgorithm
HOODEAB(order::Int = 4; ntau = 32) = new{order,ntau}()
end
export HOODEAB
# OtherHOODE : structure used to store HOODESolution data in the dstats fields
struct OtherHOODE
par_u0::PrepareU0
p_coef::CoefExpAB
absprec::Union{Nothing,Float64}
relprec::Union{Nothing,Float64}
end
"""
solve(prob::ODEProblem, alg::HOODEAB{order, ntau};
dt=nothing,
kwargs...
) where {order,ntau}
common interface solver for Highly oscillatory problems, that an ODE of this form
```math
\\frac{\\delta u(t)}{\\delta t} = \\frac{1}{\\varepsilon} A + F(u(t), t)
```
where ``u \\in \\R^n`` and ``0 < \\varepsilon < 1``
``A`` must be a **periodic matrix** i.e. ``e^{t A} = e^{(t+\\pi) A}`` for any ``t \\in \\R``
## Argument :
- `prob::ODEProblem` : The problem to solve
- `alg::HOODEAB{order, ntau}` : the Adams-Bashforth HOODE algorithm
## Keywords :
- `dt` : duration of a time interval
- `kwargs...` : other keywords
"""
function SciMLBase.solve(
prob::ODEProblem,
alg::HOODEAB{order,ntau};
dt = nothing,
kwargs...,
) where {order,ntau}
isSplitODEProblem(prob.problem_type) || error("HOODEAB alg need SplitODEProblem type")
(!isnothing(dt) && haskey(kwargs, :nb_t)) &&
error("Only one of dt and nb_t must be defined")
haskey(kwargs, :order) &&
error("order must defined as parameter of algorithm : HOODEAB(order)")
linop = LinearHOODEOperator(prob.f.f1)
fct = prob.f.f2.f
p = typeof(prob.p) == SciMLBase.NullParameters ? missing : prob.p
ho_prob = if haskey(prob.kwargs, :B)
HOODEProblem(fct, prob.u0, prob.tspan, p, linop.A, linop.epsilon, prob.kwargs[:B])
else
HOODEProblem(fct, prob.u0, prob.tspan, p, linop.A, linop.epsilon)
end
if !haskey(kwargs, :nb_t) && !isnothing(dt)
kwargs = (kwargs..., nb_t = Int64(round((prob.tspan[2] - prob.tspan[1]) / dt)))
end
sol = SciMLBase.solve(
ho_prob,
HOODETwoScalesAB();
nb_tau = ntau,
order = order,
kwargs...,
)
other = OtherHOODE(sol.par_u0, sol.p_coef, sol.absprec, sol.relprec)
return SciMLBase.build_solution(
prob, # prob::Union{AbstractODEProblem,AbstractDDEProblem},
HOODETwoScalesAB(), # alg,
sol.t, # t,
sol.u, # u,
dense = sol.dense,
interp = sol.interp,
retcode = sol.retcode,
stats = other,
)
end
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 1253 | using Base
using LinearAlgebra
using SparseArrays
function _expmat2(mat)
res = one(mat)
resprec = zero(mat)
mult = one(mat)
i = 1
cpt = 0
while cpt < 4
resprec .= res
mult *= mat
mult /= i
res += mult
i += 1
cpt = resprec == res ? cpt + 1 : 0
end
return res
end
function _expmat1(mat)
valnorm = norm(mat)
if valnorm > 1
b = mat / valnorm
coef_int = Integer(floor(valnorm))
coef_mantissa = valnorm - coef_int
return _expmat2(b)^coef_int * _expmat2(coef_mantissa * b)
else
return _expmat2(mat)
end
end
function _expmat0(mat)
res = setprecision(precision(BigFloat) + 32) do
_expmat1(mat)
end
return BigFloat.(res)
end
Base.exp(mat::Array{Complex{BigFloat},2}) = _expmat0(mat)
Base.exp(mat::Array{BigFloat,2}) = _expmat0(mat)
Base.exp(mat::Array{Integer,2}) = _expmat1(mat)
Base.exp(mat::SparseMatrixCSC{Complex{BigFloat},Int64}) = _expmat0(mat)
Base.exp(mat::SparseMatrixCSC{BigFloat,Int64}) = _expmat0(mat)
Base.exp(mat::SparseMatrixCSC{Float64,Int64}) = _expmat1(mat)
Base.exp(mat::Array{Rational,2}) = Base.exp(float(mat))
Base.exp(mat::SparseMatrixCSC{Rational,Integer}) = Base.exp(float(mat))
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 3995 | #=
fft:
- Julia version:
- Author: ymocquar
- Date: 2019-11-15
=#
# function that reverse the order of the pos lowest bits
using FFTW
function _reverse_num(num, pos)
result = 0
pos_m1 = pos - 1
for i = 0:pos_m1
if (num & (1 << i)) != 0
result |= 1 << (pos_m1 - i)
end
end
return result
end
"""
PrepareFftBig( size_fft::Unsigned, [T=BigFloat])
Immutable structure to operate fft transform,
x is the type of non transformed data also called signal.
# Arguments :
- `size_fft::Integer` : Number of values, must be a power of two
- `[T=BigFloat | x::T ]` : type of the values
# Implementation
- size_fft : size of the signal
- tab_permut : permutation
- root_one : size order roots of one
- root_one_conj : conjugate of root_one
"""
struct PrepareFftBig
size_fft::Any
tab_permut::Any
root_one::Any
root_one_conj::Any
type::DataType
function PrepareFftBig(size_fft::Integer, x::T) where {T<:AbstractFloat}
@assert prevpow(2, size_fft) == size_fft "size_fft=$size_fft is not a power of 2"
power = convert(Int64, log2(size_fft))
tab_permut = zeros(Int64, size_fft)
root_one = zeros(Complex{T}, size_fft)
root_one_conj = zeros(Complex{T}, size_fft)
prec = precision(T)
setprecision(prec + 32) do
for i = 1:size_fft
tab_permut[i] = _reverse_num(i - 1, power) + 1
root_one[i] = round(
exp(one(T) * 2big(pi) * im * (i - 1) / size_fft),
digits = prec + 16,
base = 2,
)
root_one_conj[i] = round(
exp(-one(T) * 2big(pi) * im * (i - 1) / size_fft),
digits = prec + 16,
base = 2,
)
end
end
return new(
size_fft,
tab_permut,
Complex{T}.(root_one),
Complex{T}.(root_one_conj),
typeof(x),
)
end
end
PrepareFftBig(size_fft::Integer, type::DataType) = PrepareFftBig(size_fft, one(type))
PrepareFftBig(size_fft::Integer) = PrepareFftBig(size_fft, one(BigFloat))
function fftbig!(par::PrepareFftBig, signal; flag_inv = false)
s = size(signal, 2)
@assert prevpow(2, s) == s "size_fft(signal)=$s is not a power of 2"
s_div2 = div(s, 2)
len = s
n_len = len >> 1
nb_r = 1
rootO = flag_inv ? par.root_one : par.root_one_conj
# prec= precision(real(rootO[1]))
# setprecision(prec+32) do
while n_len != 0
start = 1
suite = start + n_len
for i = 1:nb_r
deb = 1
for j = deb:nb_r:s_div2
signal[:, start], signal[:, suite] = (signal[:, start] + signal[:, suite]),
(signal[:, start] - signal[:, suite]) * rootO[j]
start += 1
suite += 1
end
start = suite
suite = start + n_len
end
len = n_len
n_len >>= 1
nb_r <<= 1
end
# end
signal .= signal[:, par.tab_permut]
if flag_inv
signal ./= s
end
return signal
end
function fftbig(par::PrepareFftBig, signal; flag_inv = false)
fl = flag_inv
return fftbig!(
par::PrepareFftBig,
copy(convert(Array{Complex{par.type}}, signal)),
flag_inv = fl,
)
end
fftgen(_::Any, t::Array{Complex{Float64}}) = fft(t, (2,))
fftgen(_::Any, t::Array{Float64}) = fft(t, (2,))
fftgen(p::PrepareFftBig, t::Array{T}) where {T<:AbstractFloat} = fftbig(p, t)
fftgen(p::PrepareFftBig, t::Array{Complex{T}}) where {T<:AbstractFloat} = fftbig(p, t)
ifftgen(_::Any, t::Array{Complex{Float64}}) = ifft(t, (2,))
ifftgen(_::Any, t::Array{Float64}) = ifft(t, (2,))
ifftgen(p::PrepareFftBig, t::Array{T}) where {T<:AbstractFloat} =
fftbig(p, t, flag_inv = true)
ifftgen(p::PrepareFftBig, t::Array{Complex{T}}) where {T<:AbstractFloat} =
fftbig(p, t, flag_inv = true)
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
|
[
"MIT"
]
| 0.2.7 | c1f7717862677bc74b0305e0e2d00dc38df2bcf9 | code | 8974 | using SciMLBase
using Reexport
@reexport using SciMLBase
import RecursiveArrayTools
include("twoscales_pure_ab.jl")
struct HOODEFunction{iip,N} <: SciMLBase.AbstractODEFunction{iip}
f::Any
end
(fct::HOODEFunction{false,3})(u, p, t) = fct.f(u, p, t)
(fct::HOODEFunction{false,2})(u, p, t) = fct.f(u, p)
(fct::HOODEFunction{false,1})(u, p, t) = fct.f(u)
function (fct::HOODEFunction{true,4})(u, p, t)
du = zero(u)
fct.f(du, u, p, t)
return du
end
"""
HOODEProblem(f, u0, tspan, p, A, epsilon, B)
The HOODE problem is :
```math
\\frac{du}{dt} = ( \\frac{1}{\\epsilon} A + B) u + f(u,p,t)
```
- The initial condition is ``u(tspan[1]) = u0``.
- The solution ``u(t)`` will be computed for ``tspan[1] ≤ t ≤ tspan[2]``
- Constant parameters to be supplied as the second argument of ``f``.
- Periodic Matrix of the problem.
- epsilon of the problem.
- Matrix of linear problem to get the exact solution
"""
struct HOODEProblem{T} <: SciMLBase.DEProblem
f::HOODEFunction
u0::Vector{T}
tspan::Tuple{T,T}
p::Any
A::AbstractMatrix
epsilon::T
B::Union{Matrix,Missing}
function HOODEProblem(
f,
u0::Vector{T},
tspan::Tuple{T,T},
p,
A::AbstractMatrix,
epsilon::T,
B::Union{Matrix,Missing},
) where {T}
fct = if hasmethod(f, (Vector{T}, Vector{T}, Any, T))
HOODEFunction{true,4}(f)
elseif hasmethod(f, (Vector{T}, Any, T))
HOODEFunction{false,3}(f)
elseif hasmethod(f, (Vector{T}, Any))
HOODEFunction{false,2}(f)
elseif hasmethod(f, (Vector{T},))
HOODEFunction{false,1}(f)
else
println("err !!!!!")
end
return new{T}(fct, u0, tspan, p, A, epsilon, B)
end # end of function
end # end of struct
function HOODEProblem(f, u0, tspan, p, A, epsilon)
return HOODEProblem(f, u0, tspan, p, A, epsilon, missing)
end
struct HOODEInterpolation{T} <: SciMLBase.AbstractDiffEqInterpolation
t::Vector{T}
u_caret::Vector{Array{Complex{T},2}}
parphi::PreparePhi
order::Any
end
(interp::HOODEInterpolation)(t, idxs, deriv, p, continuity) = interp(t)
function (interp::HOODEInterpolation)(t)
return _getresult(
interp.t,
interp.u_caret,
t,
interp.parphi,
interp.t[1],
interp.t[end],
interp.order,
)
# return _getresult(interp.u_caret, t,
# interp.parphi,
# interp.t[1], interp.t[end],
# interp.order)
end
(interp::HOODEInterpolation)(vt::Vector{<:Number}) = RecursiveArrayTools.DiffEqArray(interp.(vt),vt)
if typeof(SciMLBase.AbstractTimeseriesSolution{Float64,Float64,Float64}) == DataType
abstract type AbstractHOODESolution{T,N} <: SciMLBase.AbstractTimeseriesSolution{T,N,N} end
else
abstract type AbstractHOODESolution{T,N} <: SciMLBase.AbstractTimeseriesSolution{T,N} end
end
struct HOODESolution{T} <: AbstractHOODESolution{T,T}
u::Vector{Vector{T}}
u_tr::Union{Vector{Vector{T}},Nothing}
t::Vector{T}
dense::Bool
order::Integer
par_u0::PrepareU0
p_coef::CoefExpAB
prob::HOODEProblem{T}
retcode::Any
interp::Union{HOODEInterpolation,Nothing}
tslocation::Any
absprec::Any
relprec::Any
end
function HOODESolution(retcode::Symbol)
return HOODESolution(
nothing,
nothing,
nothing,
nothing,
nothing,
nothing,
retcode,
nothing,
nothing,
nothing,
)
end
(sol::HOODESolution)(t) = sol.dense ? sol.interp(t) : undef
abstract type AbstractHOODEAlgorithm end
struct HOODETwoScalesAB <: AbstractHOODEAlgorithm end
struct HOODEETDRK2 <: AbstractHOODEAlgorithm end
struct HOODEETDRK3 <: AbstractHOODEAlgorithm end
struct HOODEETDRK4 <: AbstractHOODEAlgorithm end
import SciMLBase:solve
"""
function solve(prob::HOODEProblem{T};
nb_tau::Integer=32,
order::Integer=4,
order_prep::Integer=order+2,
dense::Bool=true,
nb_t::Integer=100,
getprecision::Bool=dense,
verbose=100,
par_u0::Union{PrepareU0,Missing}=missing,
p_coef::Union{CoefExpAB,Missing}=missing
) where T<:AbstractFloat
specific interface solver for Highly oscillatory problems, that an ODE of this form:
```math
\\frac{\\delta u(t)}{\\delta t} = \\frac{1}{\\varepsilon} A + F(u(t), t)
```
where ``u \\in \\R^n`` and ``0 < \\varepsilon < 1``
``A`` must be a **periodic matrix** i.e. ``e^{t A} = e^{(t+\\pi) A}`` for any ``t \\in \\R``
## Argument :
- `prob::HOODEProblem{T}` : The problem to solve
## Keywords :
- `nb_tau::Integer=32` : number of values of FFT transform, must be power of twoscales_pure_ab
- `order::Integer=4` : order of Adams-Bashforth method, and also of the interpolatation
- `order_prep::Integer=order+2` : order of the preparation
- `dense::Bool=true` : if true it is possible to compute solution at any time of the interval
- `nb_t::Integer=100` : number of period slices
- `getprecision::Bool=dense` : compute the absolute and relative precision
- `par_u0::Union{PrepareU0,Missing}=missing` : preparation data for u0
- `p_coef::Union{CoefExpAB,Missing}=missing` : coefficients for Adams-Bashforth method
## Examples :
"""
function SciMLBase.solve(prob::HOODEProblem{T}; kwargs...) where {T<:AbstractFloat}
return SciMLBase.solve(prob, HOODETwoScalesAB(); kwargs...)
end
function SciMLBase.solve(
prob::HOODEProblem{T},
alg::HOODETwoScalesAB;
nb_tau::Integer = 32,
order::Integer = 4,
order_prep::Integer = order + 2,
dense::Bool = true,
nb_t::Integer = 100,
getprecision::Bool = dense,
verbose = 100,
par_u0::Union{PrepareU0,Missing} = missing,
p_coef::Union{CoefExpAB,Missing} = missing,
) where {T<:AbstractFloat}
retcode = SciMLBase.ReturnCode.Success
nb_tau = prevpow(2, nb_tau)
traceln(
100,
"solve function prob=$prob,\n nb_tau=$nb_tau, order=$order, order_prep=$order_prep, dense=$dense,\n nb_t=$nb_t, getprecision=$getprecision, verbose=$verbose";
verbose = verbose,
)
if getprecision
s1 = SciMLBase.solve(
prob;
nb_tau = nb_tau,
order = order,
order_prep = order_prep,
dense = dense,
nb_t = nb_t,
getprecision = false,
verbose = verbose - 10,
par_u0 = par_u0,
)
n_nb_t = Integer(floor(1.1373 * nb_t + 1))
s2 = SciMLBase.solve(
prob;
nb_tau = nb_tau,
order = order,
order_prep = order_prep,
dense = dense,
nb_t = n_nb_t,
getprecision = false,
verbose = verbose - 10,
par_u0 = s1.par_u0,
)
absprec = norm(s1.u[end] - s2.u[end])
relprec = absprec / max(norm(s1.u[end]), norm(s2.u[end]))
# if dense
# for i = 1:10
# t = rand(T) * (prob.tspan[2]-prob.tspan[1])
# + prob.tspan[1]
# a, b = s1(t), s2(t)
# ap = norm(a-b)
# rp = ap/max(norm(a),norm(b))
# absprec = max(absprec,ap)
# relprec = max(relprec,rp)
# end
# end
return HOODESolution(
s1.u,
s1.u_tr,
s1.t,
dense,
order,
s1.par_u0,
s1.p_coef,
prob,
retcode,
s1.interp,
0,
Float64(absprec),
Float64(relprec),
)
end
par_u0 = if ismissing(par_u0)
parphi = PreparePhi(
prob.epsilon,
nb_tau,
prob.A,
prob.f,
prob.B;
t_0 = prob.tspan[1],
paramfct = prob.p,
)
PrepareU0(parphi, order_prep, prob.u0)
else
par_u0
end
pargen = PrepareTwoScalesPureAB(
nb_t,
prob.tspan[2],
order,
par_u0,
p_coef = p_coef,
verbose = verbose,
)
if dense
u_mat, _, u_caret = twoscales_pure_ab(pargen, res_fft = true, verbose = verbose)
t = collect(0:nb_t) * (prob.tspan[2] - prob.tspan[1]) / nb_t .+ prob.tspan[1]
interp = HOODEInterpolation{T}(t, u_caret, par_u0.parphi, order)
u = reshape(mapslices(x -> [x], u_mat, dims = 1), size(u_mat, 2))
u_tr = reshape(mapslices(x -> [x], transpose(u_mat), dims = 1), size(u_mat, 1))
else
u = Array{Array{T,1},1}(undef, 2)
u[1] = copy(prob.u0)
u[end] = twoscales_pure_ab(pargen, verbose = verbose, only_end = true)
t = [prob.tspan[1], prob.tspan[2]]
u_tr = nothing
interp = nothing
end
return HOODESolution(
u,
u_tr,
t,
dense,
order,
par_u0,
pargen.p_coef,
prob,
retcode,
interp,
0,
nothing,
nothing,
)
end
| HOODESolver | https://github.com/pnavaro/HOODESolver.jl.git |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.